Removal of Nutrients by Using Green Microalgae from Lab-Scale Treated Palm Oil Mill Effluent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Preparation of Microalgae Growth Media
2.3. Green Microalgae Isolation and Culture
2.4. Morphological Identification
2.5. Molecular Identification
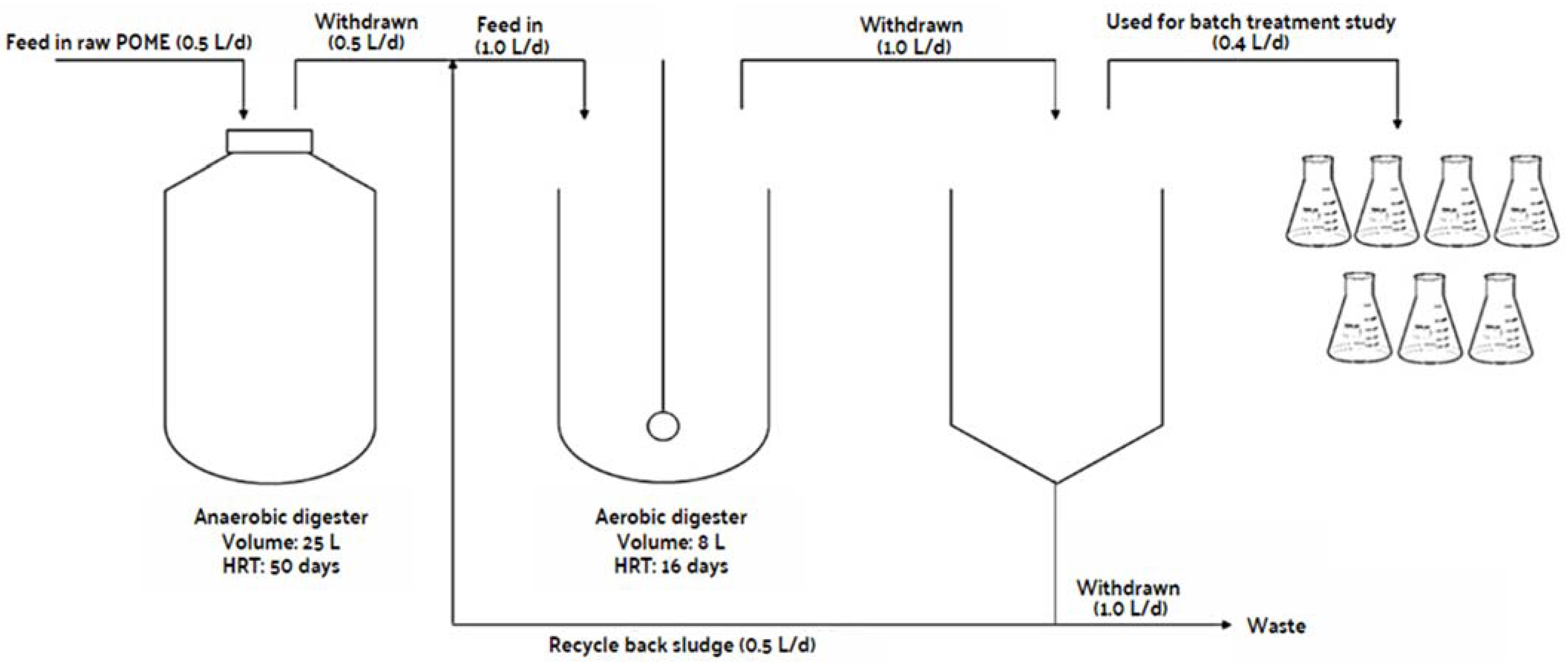
2.6. Experimental Setup
2.7. Analytical Methods
2.7.1. Analysis of Chlorophyll
2.7.2. Nutrients Removal Analysis
2.7.3. Specific Rate of Growth
2.7.4. Kinetic Study
2.8. Quality Control
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological Identification
3.2. Molecular Identification
3.3. Selection of Green Microalgae
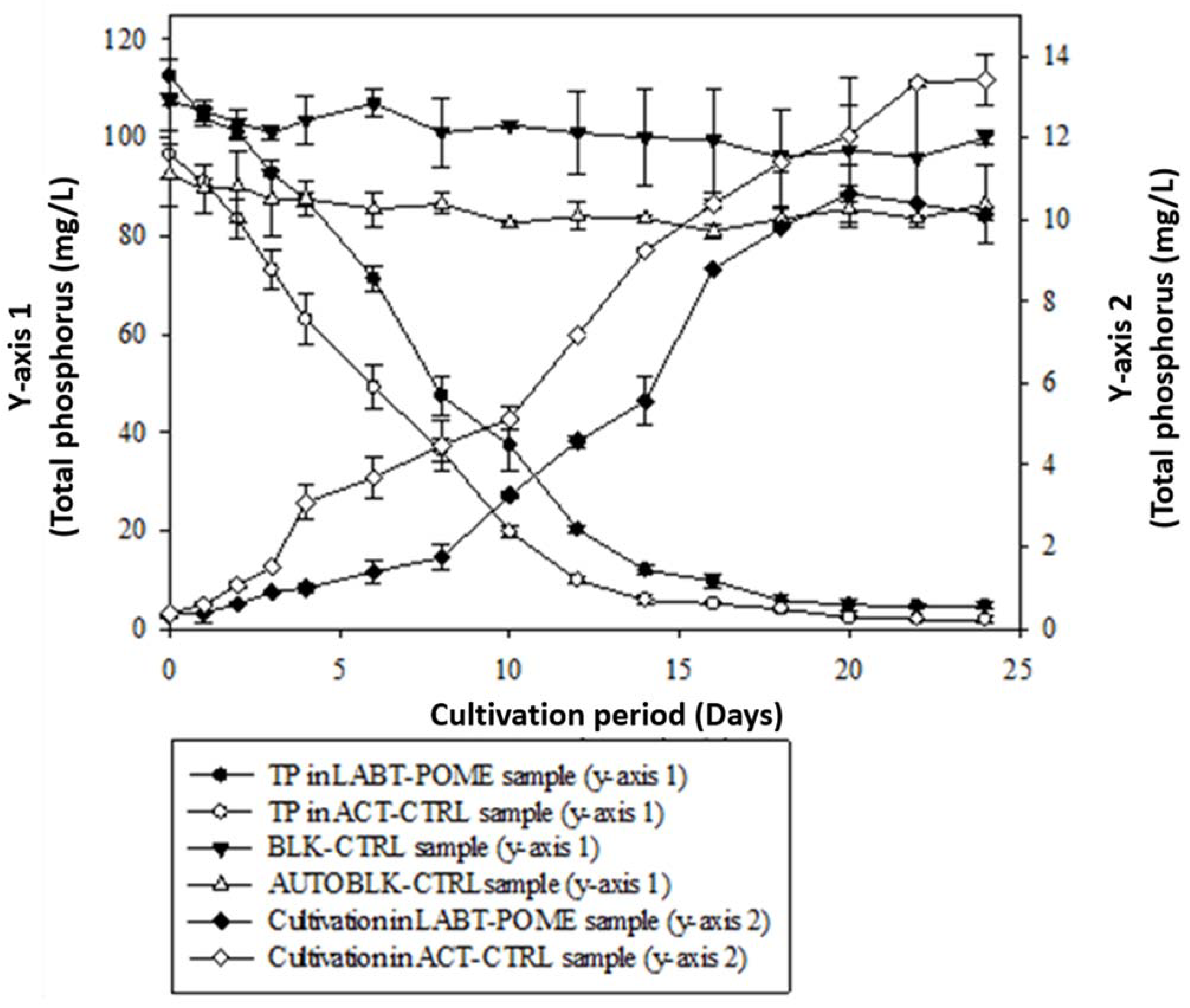
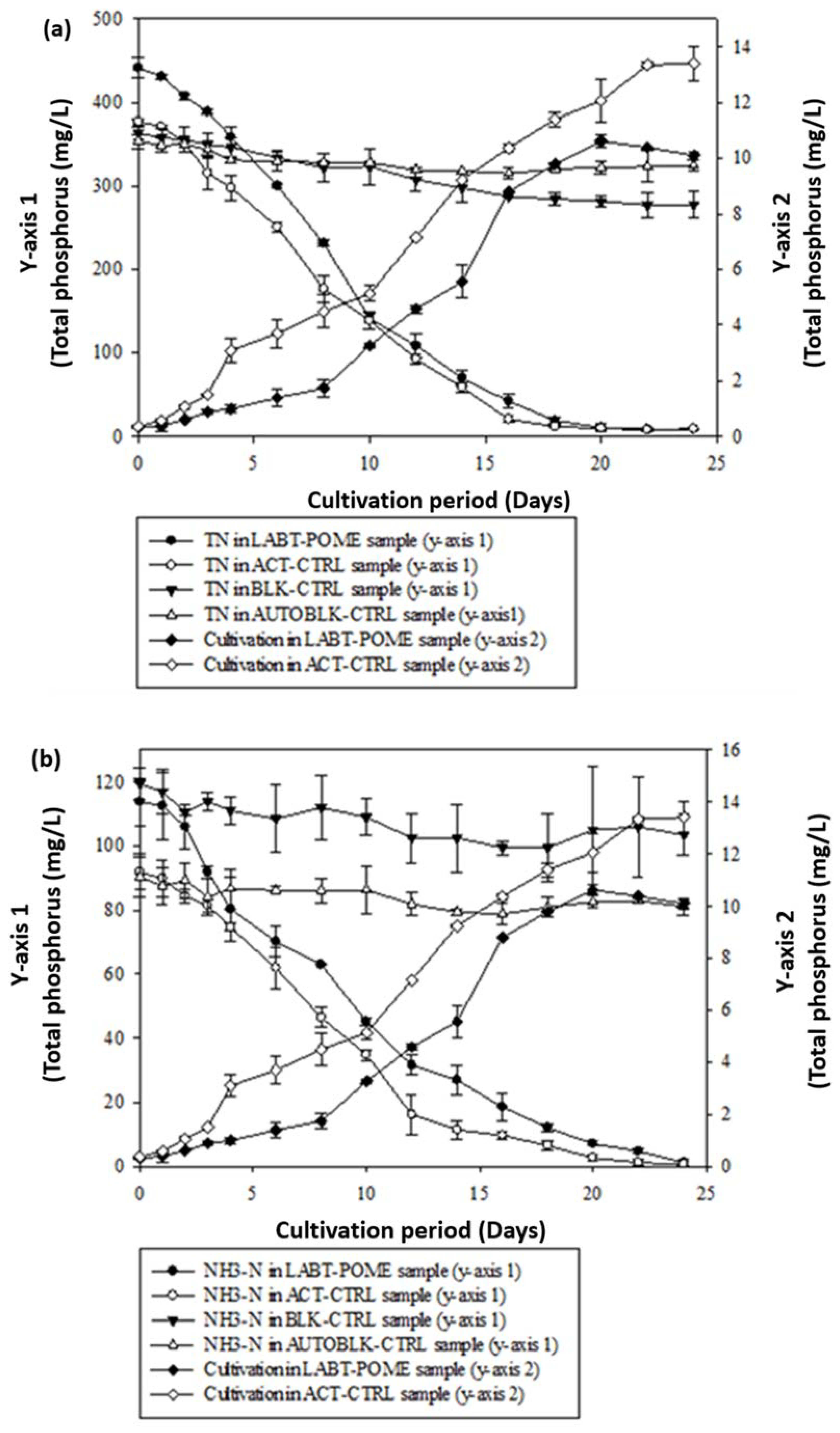
3.4. Total Phosphorus (TP) Removal by Choloroccus oleofaciens from LABT-POME
3.5. Total Nitrogen (TN) Removal by Choloroccus oleofaciens from LABT-POME
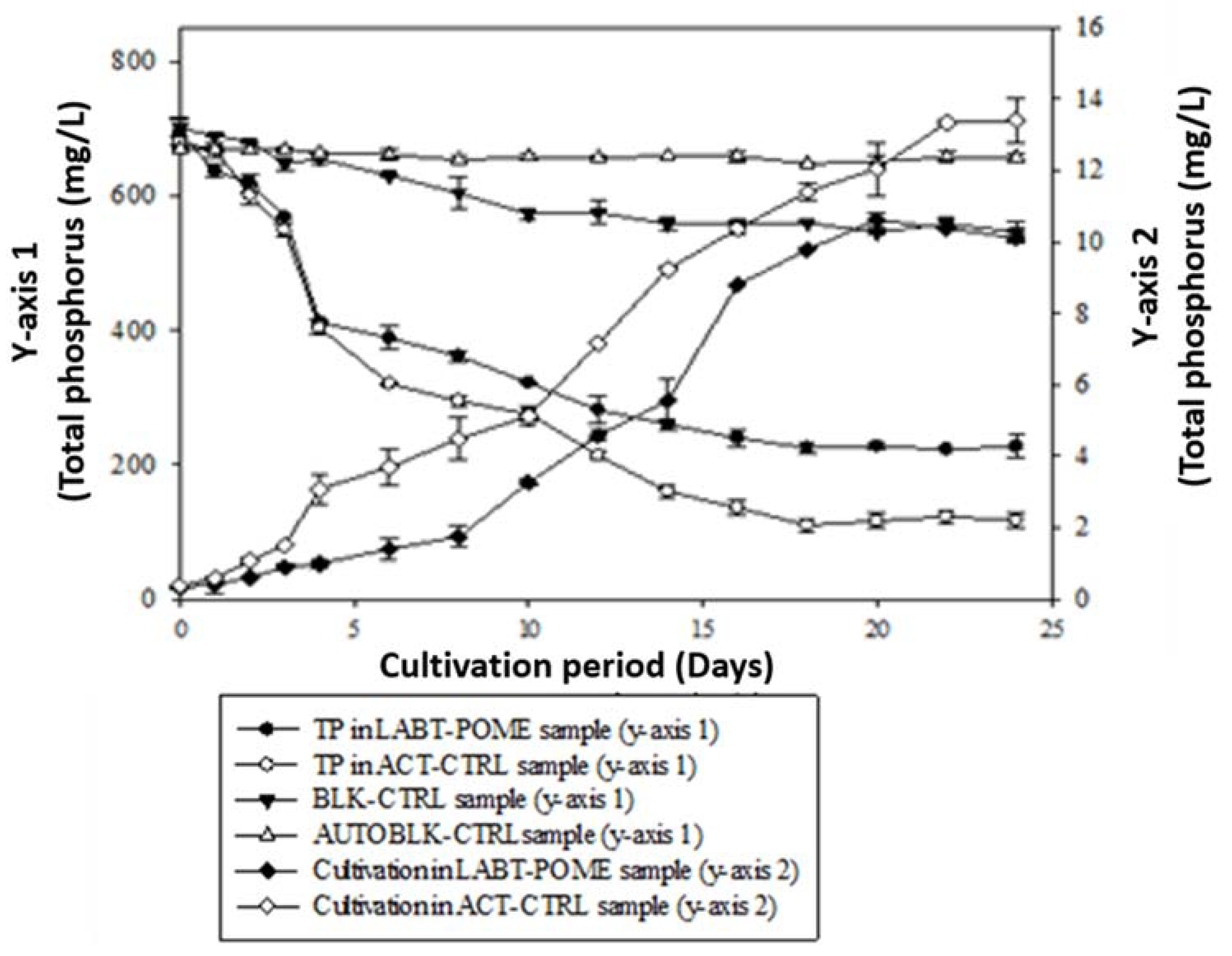
3.6. Soluble Chemical Oxygen Demand (SCOD) Reduction from LABT-POME
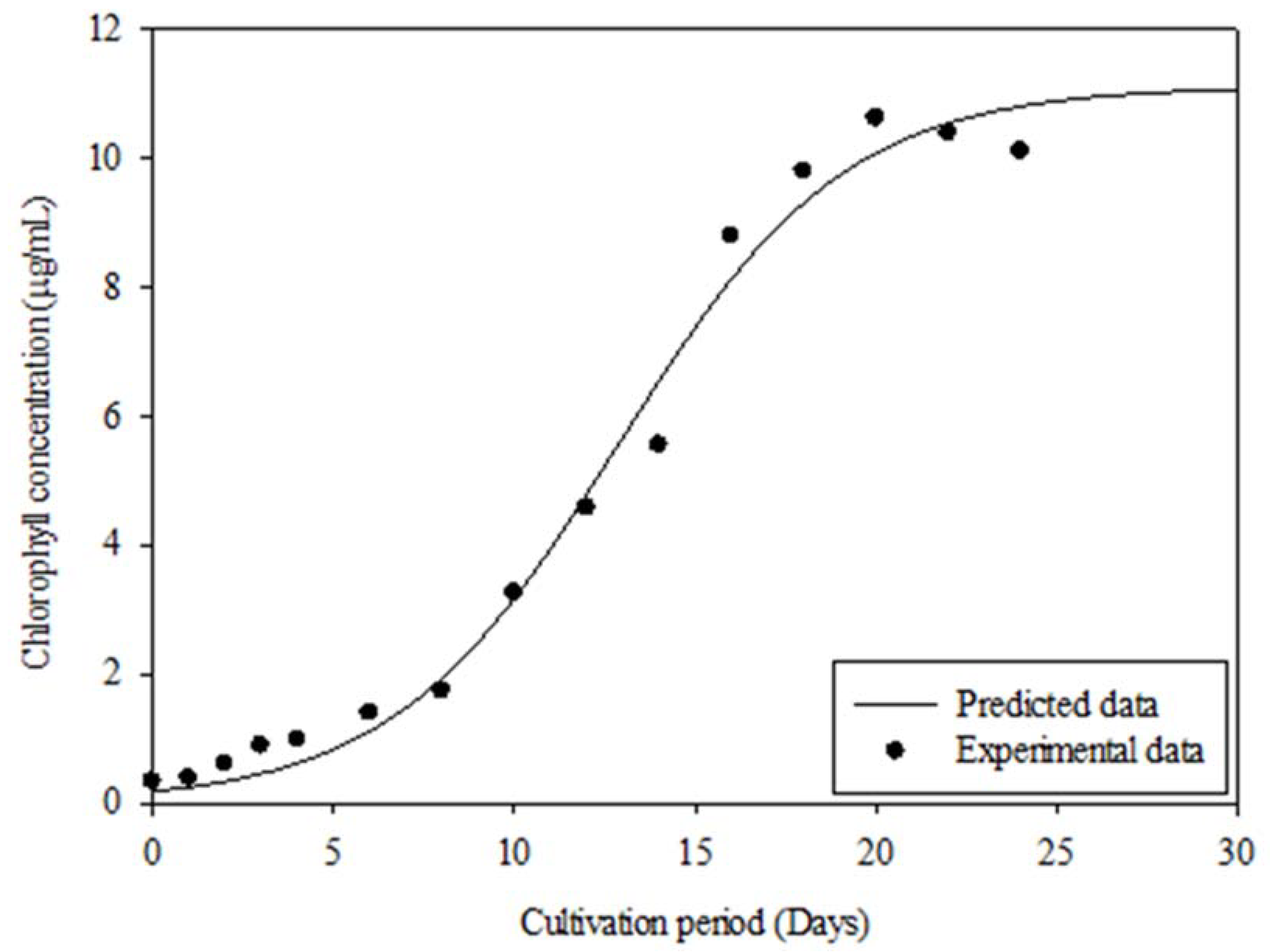
3.7. Microalgae Growth Kinetic Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ng, F.L.; Phang, S.-M.; Thong, C.-H.; Periasamy, V.; Pindah, J.; Yunus, K.; Fisher, A.C. Integration of bioelectricity generation from algal biophotovoltaic (BPV) devices with remediation of palm oil mill effluent (POME) as substrate for algal growth. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariz, H.B.; Takriff, M.S.; Yasin, N.H.M.; Ba-Abbad, M.M.; Hakimi, N.I.N.M. Potential of the microalgae-based integrated wastewater treatment and CO2 fixation system to treat Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME) by indigenous microalgae; Scenedesmus sp. and Chlorella sp. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udaiyappan, A.F.M.; Hasan, H.A.; Takriff, M.S.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Maeda, T.; Mustapha, N.A.; Mohd Yasin, N.; Nazashida Mohd Hakimi, N.I. Microalgae-bacteria interaction in palm oil mill effluent treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 35, 101203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzammil, N.; Loh, S.K. Pilot scale integrated anaerobic-aerobic treatment of palm oil mill effluent. J. Oil Palm Res. 2020, 32, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japar, A.S.; Takriff, M.S.; Yasin, N.H.M. Microalgae acclimatization in industrial wastewater and its effect on growth and primary metabolite composition. Algal Res. 2021, 53, 102163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeesang, C.; Cheirsilp, B. Effect of nitrogen, salt, and iron content in the growth medium and light intensity on lipid production by microalgae isolated from freshwater sources in Thailand. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3034–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Dasgupta, C.N.; Das, D. Cell growth kinetics of Chlorella sorokiniana and nutritional values of its biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 167, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyab, H.; Chelliapan, S.; Lee, C.T.; Khademi, T.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, K.K.; Rezania, S.; Kumar, S.; Ebrahimi, S.S. Improved production of lipid contents by cultivating Chlorella pyrenoidosa in heterogeneous organic substrates. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.A.; González-López, J.; Hontoria-García, E. Influence of carbon source on nitrate removal of contaminated groundwater in a denitrifying submerged filter. J. Hazard. Mater. 2000, 80, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadiran, A.O.; Dlamini, S.C.; Mavuso, A. A comparative study of the phosphate levels in some surface and ground water bodies of Swaziland. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2008, 22, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.K.; Gupta, N.; Kumar, A.; Reece, L.M.; Singh, N.; Rezania, S.; Khan, S.A. Mechanistic understanding and holistic approach of phytoremediation: A review on application and future prospects. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 120, 274–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.T.; Yasin, N.H.M.; Takriff, M.S.; Kamarudin, K.F.; Salihon, J.; Yaakob, Z.; Hakimi, N.I.N.M. Phycoremediation of palm oil mill effluent (POME) and CO2 fixation by locally isolated microalgae: Chlorella sorokiniana UKM2, Coelastrella sp. UKM4 and Chlorella pyrenoidosa UKM7. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 35, 101202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, S.S.; Bong, K.; Mubashir, M.; Cheng, C.; Lam, M.; Lim, J.; Ho, Y.; Lee, K.; Munawaroh, H.; Show, P. Microalgae cultivation in palm oil mill effluent (Pome) treatment and biofuel production. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.W.; Chong, C.C.; Lam, M.K.; Ayoub, M.; Cheng, C.K.; Lim, J.W.; Yusup, S.; Tang, Y.; Bai, J. Holistic process evaluation of non-conventional palm oil mill effluent (POME) treatment technologies: A conceptual and comparative review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidu, H.; Salau, O. Investigating the effect of several Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME) dilutions on biomass and specific growth rate of C. sorokiniana. Int. J. Life Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 4, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, A.; Malik, S.; Zhu, H.; Xu, J.; Nawaz, M.Z.; Nawaz, S.; Alam, A.; Mehmood, M.A. Cultivating microalgae in wastewater for biomass production, pollutant removal, and atmospheric carbon mitigation; a review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zu, Y.; Song, C.; Xie, M.; Qi, Y.; Kansha, Y.; Kitamura, Y. Soybean processing wastewater purification via Chlorella L166 and L38 with potential value-added ingredients production. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 7, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, L.M.M.; Lakmali, W.G.M.; Athukorala, S.N.P.; Jayasundera, K.B. Application of live Chlorococcum aquaticum biomass for the removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 4069–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apandi, N.; Mohamed, R.M.S.R.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Gani, P.; Ibrahim, A.; Kassim, A.H.M. Scenedesmus Biomass Productivity and Nutrient Removal from Wet Market Wastewater, A Bio-kinetic Study. Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 10, 2783–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emparan, Q.; Harun, R.; Kodiappan, J.A. Effect of microalgae-to-palm oil mill effluent (POME) ratio for rapid effective pollutants removal and biomass production. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 198, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.S.; Chin, S.Y.; Lim, J.W.; Witoon, T.; Cheng, C.K. Treatment technologies of palm oil mill effluent (POME)and olive mill wastewater (OMW): A brief review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 15, 100377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidu, H.; Jamaluddin, H.; Mohamad, S.E. Nutrient Removal and Biokinetic Study of Freshwater Microalgae in Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME). Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cheah, W.Y.; Show, P.L.; Juan, J.C.; Chang, J.; Ling, T.C. Microalgae cultivation in palm oil mill effluent (POME) for lipid production and pollutants removal. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 174, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasni, J.; Arisht, S.N.; Yasin, N.H.M.; Abdul, P.M.; Lin, S.-K.; Liu, C.-M.; Wu, S.-Y.; Jahim, J.; Takriff, M.S. Comparative toxicity effect of organic and inorganic substances in palm oil mill effluent (POME) using native microalgae species. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 34, 101165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.A.; Lalung, J.; Morad, N.; Ismail, N.; Wan Omar, W.M.; Khan, M.A.; Sillanpää, M.; Rafatullah, M. Post-Treatment of Palm Oil Mill Effluent Using Immobilised Green Microalgae Chlorococcum oleofaciens. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsanti, L.; Gualtieri, P. Algae: Anatomy Biochemistry, and Biotechnology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, H.W.; Bold, H.C. Trichosarcinapolymorpha Gen. et sp. nov. J. Phycol. 1965, 1, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vuuren, S.J.; Taylor, J.; van Ginkel, C.; Gerber, A. A Guide for the Identification of Algae in South African Freshwaters; no. November; North-West University: Potchefstroom, South Africa, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh, M.; Serediak, N. Algae Identification Field Guid; Agriculture and Agri-food: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bellinger, E.G.; Sigee, D.C. Freshwater Algae: Identification, Enumeration and Use as Bioindicators; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fiera, C. Detection of food in the gut content of Heteromurusnitidus (Hexapoda:Collembola) by DNA/PCR-based molecular analysis. North-West. J. Zool. 2014, 10, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, E.; Herrero, A. Nitrogen assimilation and nitrogen control in cyanobacteria. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005, 33, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gour, R.S.; Chawla, A.; Singh, H.; Chauhan, R.S.; Kant, A. Characterisation and Screening of Native Scenedesmus sp. Isolates Suitable for Biofuel Feedstock. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, R.J. Consistent sets of spectrophotometric chlorophyll equations for acetone, methanol and ethanol solvents. Photosynth. Res. 2006, 89, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgadillo-Mirquez, L.; Lopes, F.; Taidi, B.; Pareau, D. Nitrogen and phosphate removal from wastewater with a mixed microalgae and bacteria culture. Biotechnol. Rep. 2016, 11, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermis, H.; Altinbas, M. Determination of biokinetic coefficients for nutrient removal from anaerobic liquid digestate by mixed microalgae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, M.; Corradini, M.G.; Normand, M.D. The logistic (Verhulst) model for sigmoid microbial growth curves revisited. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, S.; Zhou, W.; Dong, R.; Yuan, Z. Cultivation of Chlorella zofingiensis in bench-scale outdoor ponds by regulation of pH using dairy wastewater in winter, South China. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 121, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhao, F.; Cao, Y.; Xing, L.; Liu, W.; Mei, S.; Li, S. Cultivation of Microalgae in Dairy Farm Wastewater without Sterilisation. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2015, 17, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Park, S.Y.; Li, Y. Nutrient recovery from wastewater streams by microalgae: Status and prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 19, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Min, M.; Hu, B.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Li, L.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, P.; Ruan, R. Growing wastewater-born microalga Auxenochlorella protothecoides UMN280 on concentrated municipal wastewater for simultaneous nutrient removal and energy feedstock production. Appl. Energy 2012, 98, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.F.; Lim, B.R.; Lee, K. Influence of nitrate feeding on carbon dioxide fixation by microalgae. J. Environ. Sci. Health-Part A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2006, 41, 2813–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, A.S.; Aziz, N.A.C.; Puad, N.I.M.; Halim, A.A.; Yusof, F.; Yusup, S. Chlorella vulgaris logistic growth kinetics model in high concentrations of aqueous ammonia. IIUM Eng. J. 2018, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Raw POME | a Treatment 1 | b Treatment 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 4–5 | 6–7.5 | 8–9 |
| COD (mg/L) | 70,000–80,000 | 10,000–15,000 | 600–1000 |
| BOD3 (mg/L) | 10,000–20,000 | 1000–2000 | 150–300 |
| TN (mg/L) | 1700–1800 | 800–1000 | 400–500 |
| TP (mg/L) | 820–950 | 500–720 | 80–150 |
| NH3–N (mg/L) | 180–250 | 300–400 | 150–200 |
| Colour | - | - | 3000–3500 |
| Light Microscopy Image (40× Magnification) | SEM Photograph | Cell Dimension (μm) | Characteristics | Genus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
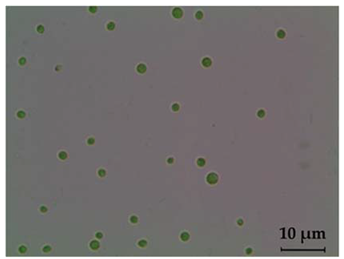 | 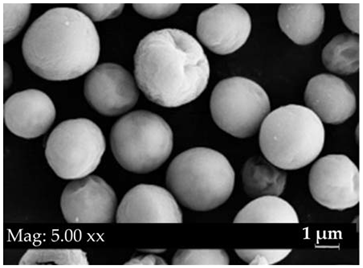 | 0–12 | Chlorococcum sp. | |
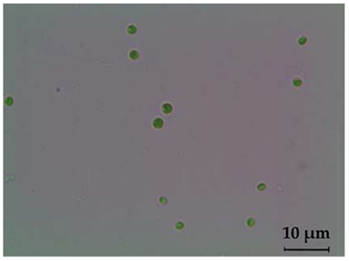 | 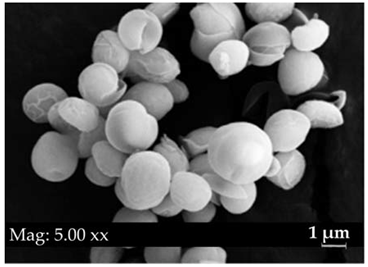 | 2.6–4.5 | green in colour, spherically shaped cells, cup-shaped chloroplasts | Chlorella sp. |
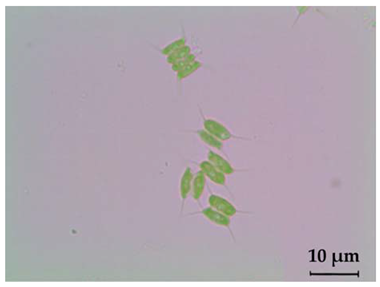 | 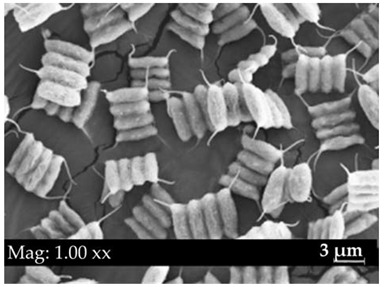 | Long: 11–18 Wide: 3.5–7 | green in colour, 2 or 4 cells attached side by side, two flagella are present, cells arranged in a zigzag or linear pattern | Scenedesmus sp. |
| Microalgae | Dilution of POME (v/v) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 25% | 50% | 75% | |
| Chlorococcum oleofaciens |  |  |  |
| Chlorella sorokiniana |  |  |  |
| 25% | 50% | 75% | |
| Scenedesmus quadricauda |  |  |  |
| Microalgae Species | Before | After |
|---|---|---|
| Chlorococcum oleofaciens | Light microscope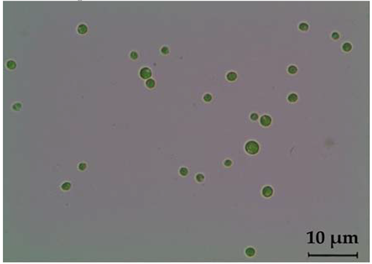 | Light microscope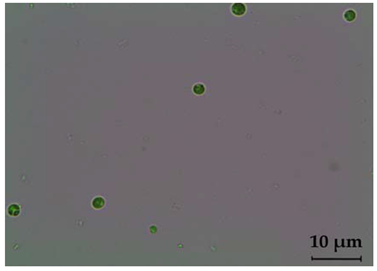 |
SEM | SEM | |
| Chlorella sorokiniana | Light microscope | Light microscope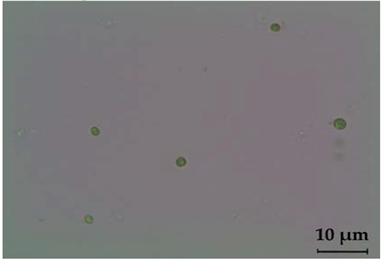 |
SEM | SEM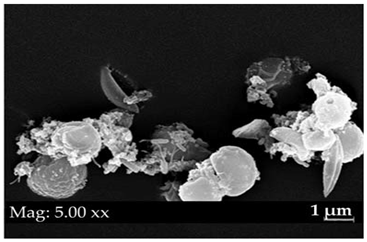 |
| Microalgae | Xo (μg/mL) | Xm (μg/mL) | μ (d−1) | R2 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorococcum oleofaciens | 0.18 | 11.11 | 0.32 | 0.99 | <0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, K.A.; Lalung, J.; Wijaya, D.; Ismail, N.; Wan Omar, W.M.; Wabaidur, S.M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Alam, M.; Rafatullah, M. Removal of Nutrients by Using Green Microalgae from Lab-Scale Treated Palm Oil Mill Effluent. Fermentation 2022, 8, 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110658
Tan KA, Lalung J, Wijaya D, Ismail N, Wan Omar WM, Wabaidur SM, Siddiqui MR, Alam M, Rafatullah M. Removal of Nutrients by Using Green Microalgae from Lab-Scale Treated Palm Oil Mill Effluent. Fermentation. 2022; 8(11):658. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110658
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Kah Aik, Japareng Lalung, Dani Wijaya, Norli Ismail, Wan Maznah Wan Omar, Saikh Mohammad Wabaidur, Masoom Raza Siddiqui, Mahboob Alam, and Mohd Rafatullah. 2022. "Removal of Nutrients by Using Green Microalgae from Lab-Scale Treated Palm Oil Mill Effluent" Fermentation 8, no. 11: 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110658
APA StyleTan, K. A., Lalung, J., Wijaya, D., Ismail, N., Wan Omar, W. M., Wabaidur, S. M., Siddiqui, M. R., Alam, M., & Rafatullah, M. (2022). Removal of Nutrients by Using Green Microalgae from Lab-Scale Treated Palm Oil Mill Effluent. Fermentation, 8(11), 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110658











