Milk Fermentation by Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG and Streptococcus thermophilus SY-102: Proteolytic Profile and ACE-Inhibitory Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture Preparation
2.2. Fermentation
2.3. Proteolytic Profile Analysis
2.3.1. Free Amino Groups Analysis
2.3.2. Tris-Tricine Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (Tris-Tricine-SDS-PAGE)
2.3.3. Peptides Separation by SEC-HPLC
2.4. ACE-Inhibitory Activity
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. pH Changes during Fermentation
3.2. Proteolytic Profile
3.2.1. Free Amino Groups Determination by TNBS
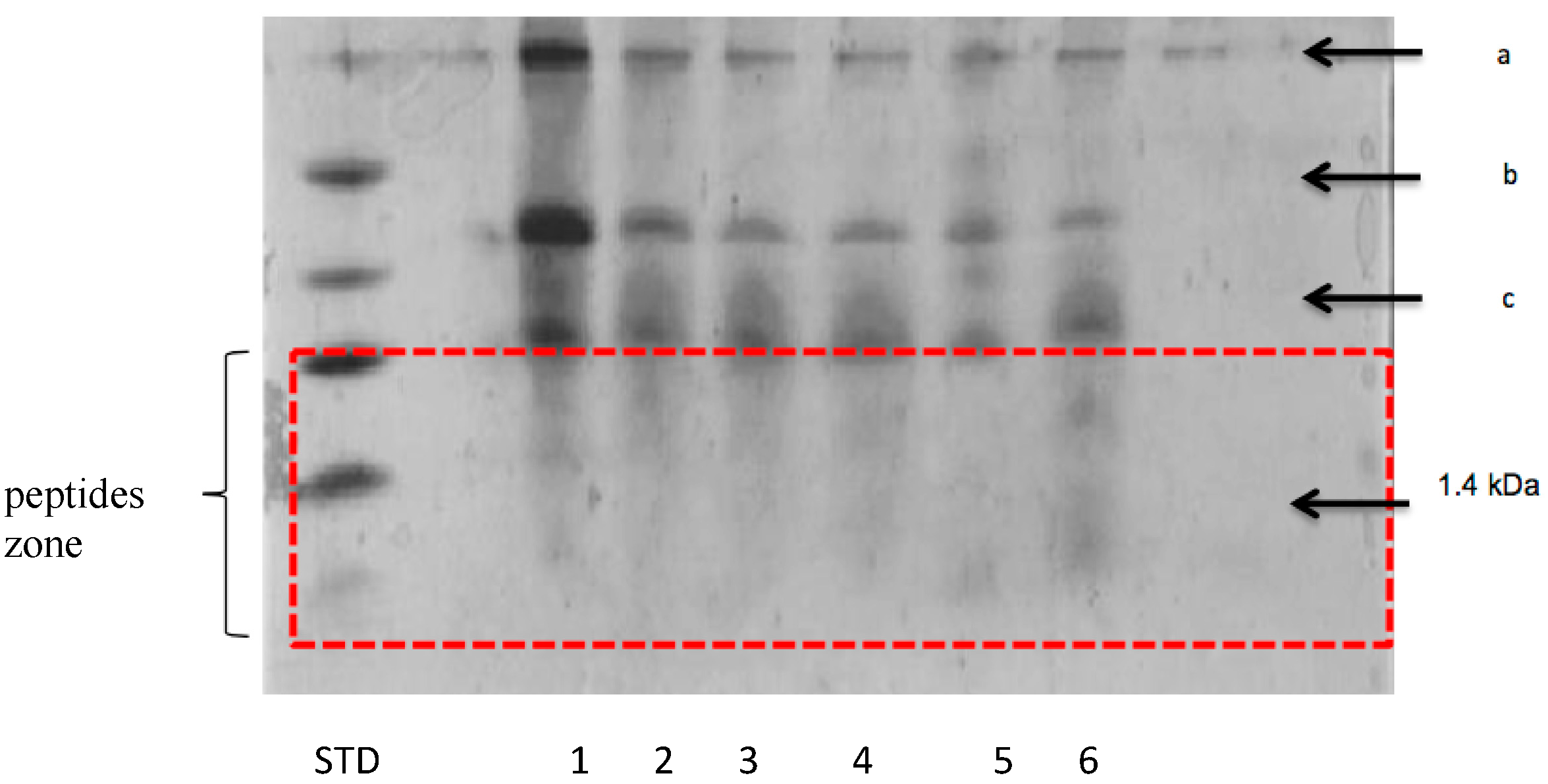
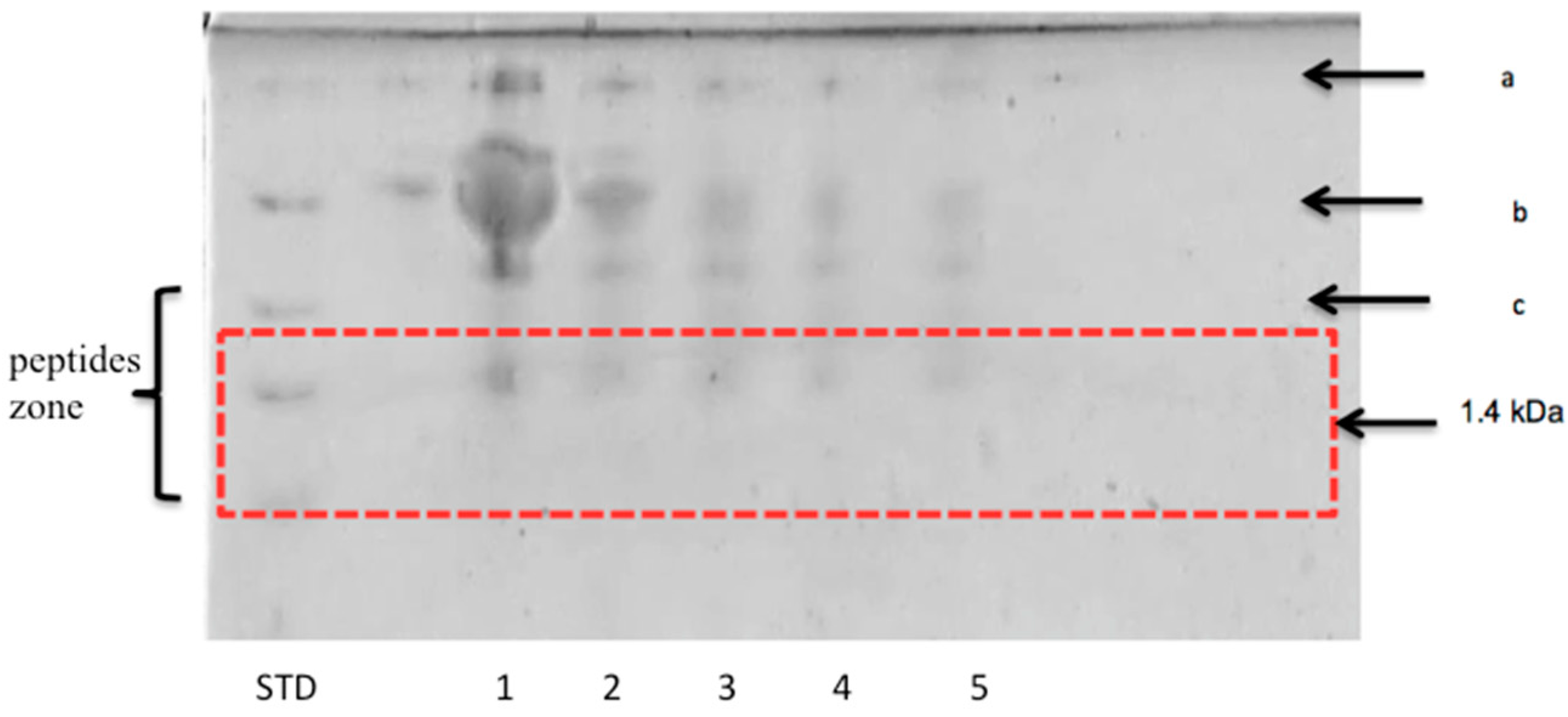
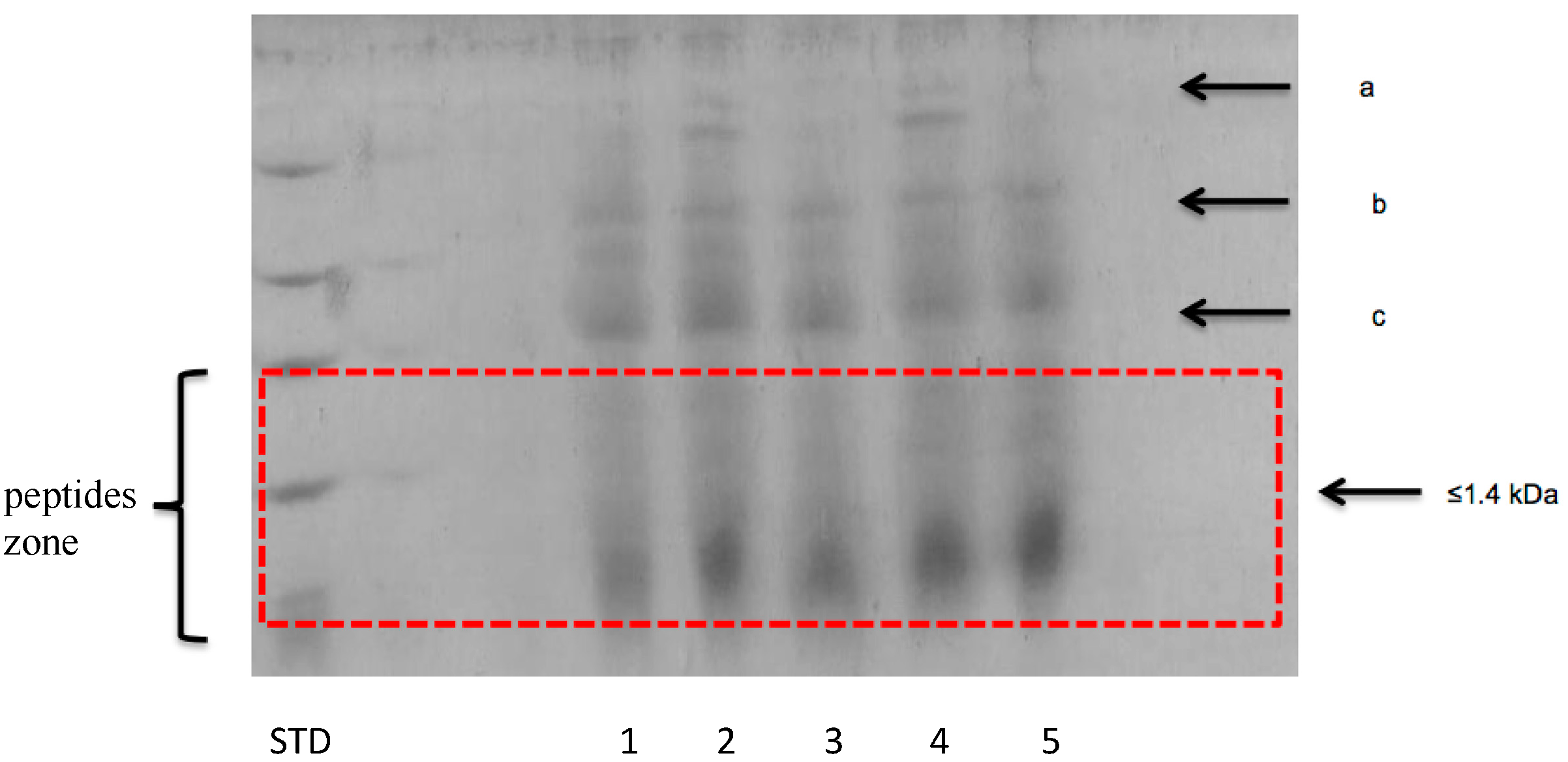
3.2.2. Peptide Separation byTris-Tricine SDS-PAGE
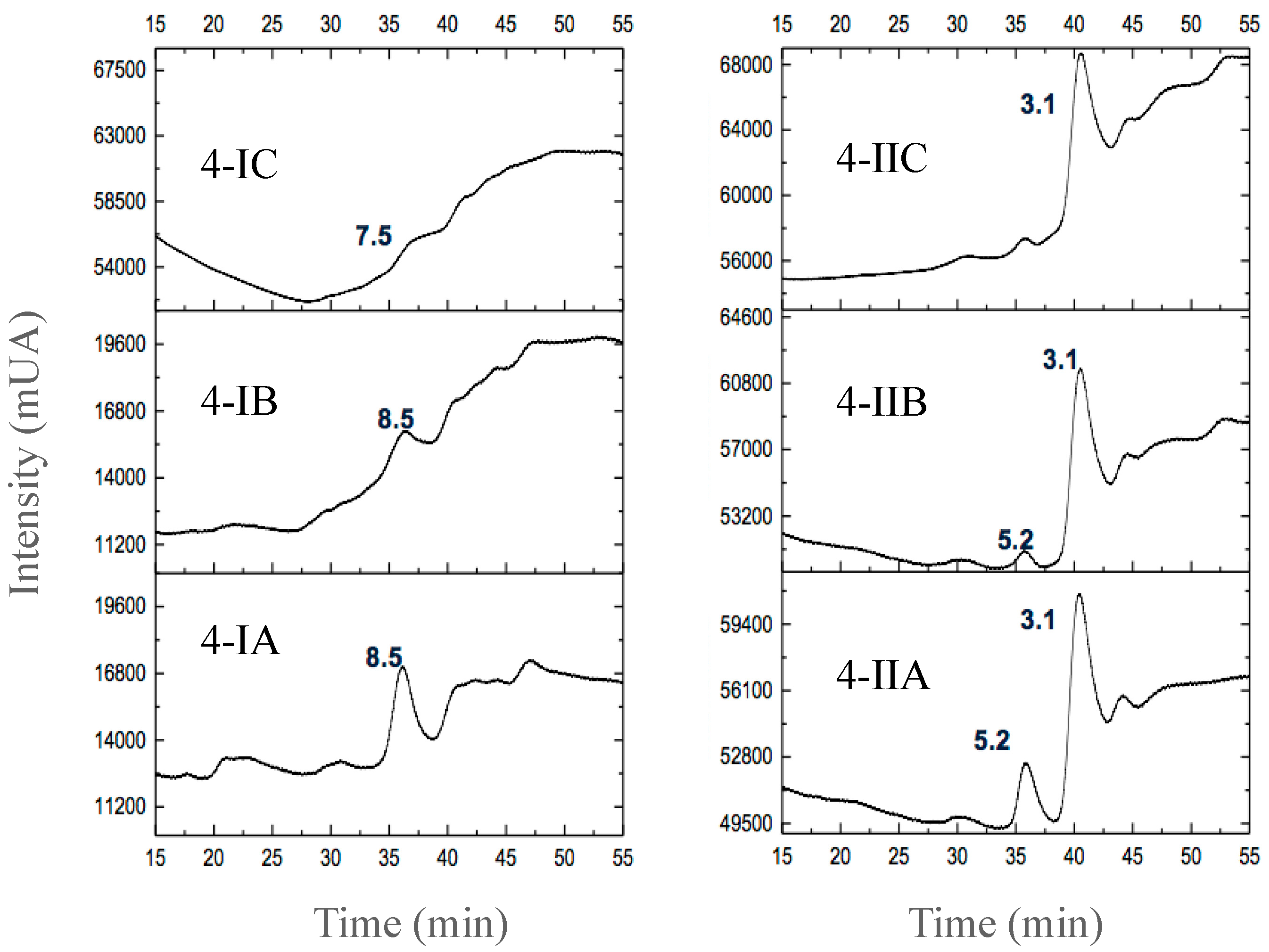
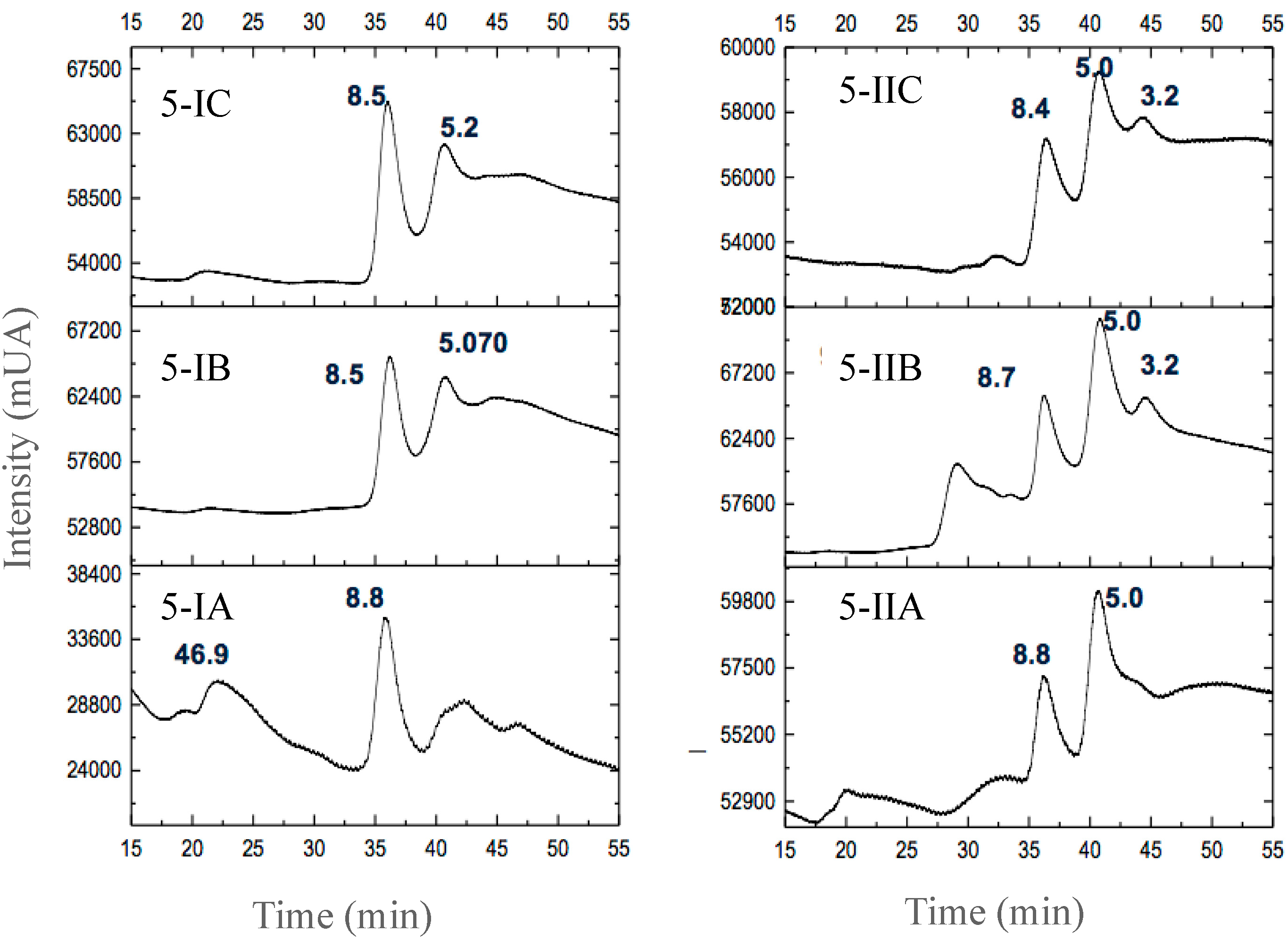
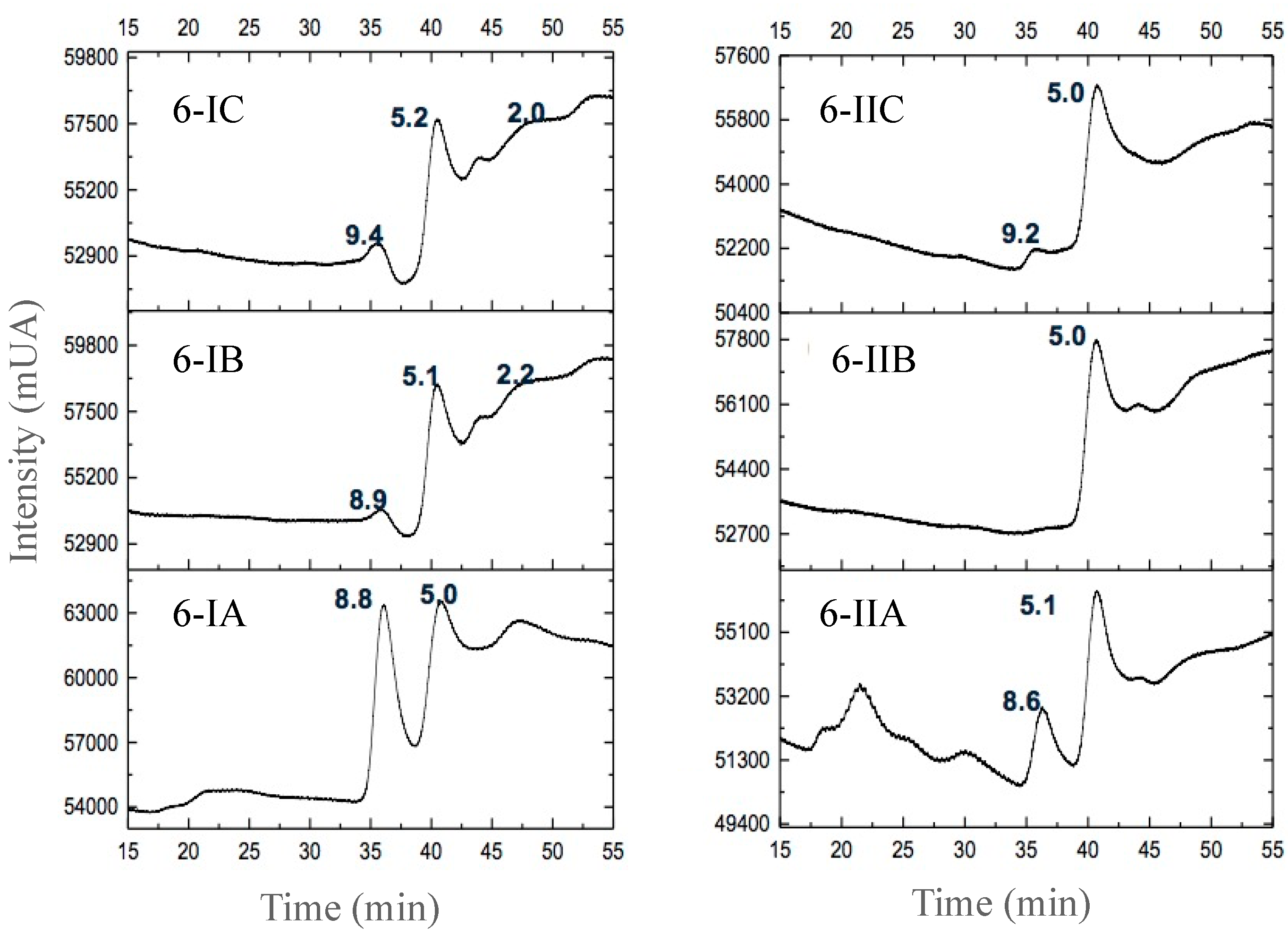
3.2.3. Separation of Peptides with Aromatic Amino Acid Residues
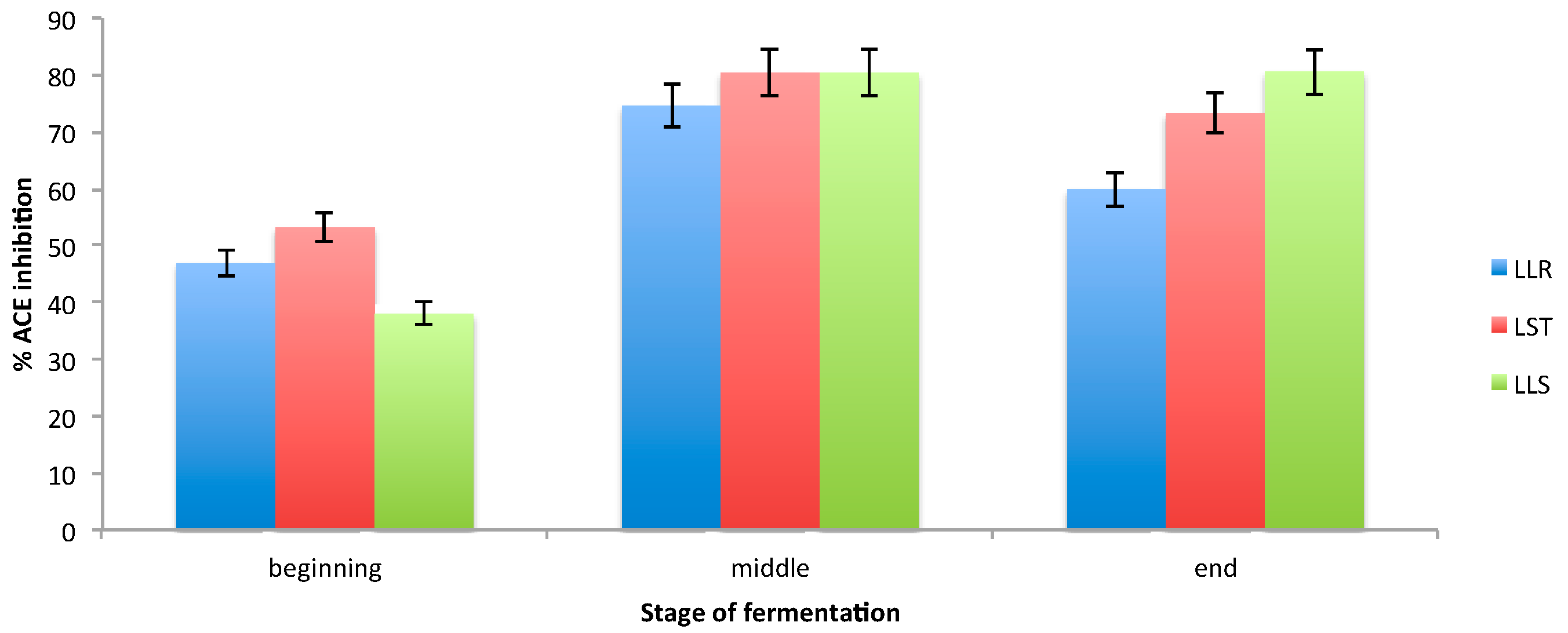
3.3. Determination of ACE Inhibition
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gamechu, T. Review in lactic acid bacteria function in milk fermentation and preservation. Afr. J. Food Sci. 2015, 9, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beltrán-Barrientos, L.M.; Hernández-Mendoza, A.; Torres-Llanez, M.J.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Vallejo-Córdoba, B. Fermented milk as antihypertensive functional food. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4099–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sodini, I.; Lucas, A.; Oliveira, N.M.; Remeuf, F.; Corrieu, G. Effect of mil base and starter culture on acidification, texture and probiotic cell counts in fermented milk processing. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 2479–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nami, Y.; Haghshenas, B.; Vaseghi, R.; Jalaly, H.M.; Lotfi, H.; Eslami, S.; Amin Hejazi, M. Novel autochthonous lactobacilli with probiotic aptitudes as a main starter culture for probiotic fermented milk. LWT 2018, 98, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng-Xin, H.; Ji-Nian, L.; Qian, G.; Ya-Qian, Z.; Hong-Mei, N. Probiotics biofilm-integrated electrospun nanofiber membranes: A new starter culture for fermented milk production. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3198–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, Z.F.; Kumar, S.; Bhat, H.F. Bioactive peptides of animal origin: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 5377–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd El-Fattah, A.M.; Sakr, S.S.; El-Dieb, S.M.; Elkashef, H.A.S. Bioactive peptides with ACE-I and antioxidant activity produced from milk proteolysis. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 20, 3033–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hammami, R.; Fliss, I.; Corsetti, A. Editorial: Application of protective cultures and bacteriocins for food biopreservation. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chai, K.F.; Voo, A.Y.H.; Chen, W.N. Bioactive peptides from food fermentations: A comprehensive review of their sources, bioactivities, applications and future development. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3825–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, B.; Amigo, L.; Recio, I. Critical review and perspectives on food derived antihypertensive peptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9384–9390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Hur, S.J. Antihypertensive peptides from animal products, marine organisms, and plants. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Gonzalez, C.R.; Tuohy, K.M.; Jauregi, P. Production of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity in milk fermented with probiotic strains: Effects of calcium, pH and peptides on the ACE-inhibitory activity. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejati, F.; Rizzello, C.G.; Di Cagno, R.; Sheikh-Zeinoddin, M.; Diviccaro, A.; Minervini, F.; Gobbetti, M. Manufacture of a functional fermented milk enriched of Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides and γ-amino butyric acid (GABA). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 51, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhtab, E.; El-Alfy, M.; Shenana, M.; Mohamed, A.; Yousef, A.E. New potentially antihypertensive peptides liberated in milk during fermentation with selected lactic acid bacteria and kombucha cultures. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 9508–9520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalheiro, F.G.; Baptista, D.P.; Galli, B.D.; Negrão, F.; Eberlin, M.N.; Gigante, M.L. High protein yogurt with addition of Lactobacillus helveticus: Peptide profile and angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE-inhibitory activity. Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begunova, A.V.; Savinova, O.S.; Glazunova, O.A.; Moiseenko, K.V.; Rozhkova, I.V.; Fedorova, T.V. Development of antioxidant and antihypertensive properties during growth of Lactobacillus helveticus, Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus reuteri on cow’s milk: Fermentation and peptidomics study. Foods 2021, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Olivares, L.G.; Añorve-Morga, J.; Castañeda-Ovando, A.; Contreras-López, E.; Jaimez-Ordaz, J. Peptide separation of commercial fermented milk during refrigerated storage. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 34, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daliri, E.B.M.; Lee, B.H.; Park, B.J.; Kim, S.H.; Oh, D.H. Antihypertensive peptides from whey proteins fermented by lactic acid bacteria. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza Pereira, Á.M.; de Farias, D.R.B.; de Queiroz, B.B.; de Caldas Nobre, M.S.; Cavalcanti, M.T.; Salles, H.O.; Dos Santos, K.M.O.; de Medeiros, A.C.D.; Florentino, E.R.; Buriti, F.C.A. Influence of a Co-culture of Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus casei on the Proteolysis and ACE-Inhibitory Activity of a Beverage Based on Reconstituted Goat Whey Powder. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 11, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Serrano, G.M.; García-Garibay, M.; Cruz-Guerrero, A.E.; Gómez-Ruiz, L.; Ayala-Nino, A.; Castaneda-Ovando, A.; Gonzalez-Olivares, L.G. Proteolytic System of Streptococcus thermophilus. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, O.K.; Roux, É.; Awussi, A.A.; Miclo, L.; Jardin, J.; Jameh, N.; Dary, A.; Humbert, G.; Perrin, C. Use of a free form of the Streptococcus thermophilus cell envelope protease PrtS as a tool to produce bioactive peptides. Int. Dairy J. 2014, 38, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buritti, F.; Cardarelli, H.; Filisetti, T.; Saad, S. Synbiotic potential of fresh cream cheese supplemented with inulin and Lactobacillus paracasei in co-culture with Streptococcus thermophilus. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1605–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settachaimongkon, S.; Nout, M.J.R.; Antunes Fernandes, E.C.; Hettinga, K.A.; Vervoort, J.M.; van Hooijdonk, T.C.M.; Zwietering, M.H.; Smid, E.J.; van Valenberg, H.J.F. Influence of different proteolytic strains of Streptococcus thermophilus in co-culture with Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus on the metabolite profile of set-yoghurt. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 177, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, W.M.; de Caldas Nobre, M.S.; Cavalcanti, M.T.; dos Santos, K.M.O.; Salles, H.O.; Alonso Buriti, F.C. Proteolysis of reconstituted goat whey fermented by Streptococcus thermophilus in co-culture with commercial probiotic lactobacillus strains. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2019, 72, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schägger, H.; von Jagow, G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 166, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Olivares, L.G.; Jiménez-Guzmán, J.; Cruz-Guerrero, A.; Rodríguez-Serrano, G.; Gómez-Ruíz, L.; García-Garibay, M. Bioactive peptides released by lactic acid bacteria in comercial fermented milks. Rev. Mex. Ing. Química 2011, 10, 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald, R.J.; Murray, B.A. Bioactive peptides and lactic fermentations. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2006, 59, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Leng, C.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, X.; Chen, H.; Sun, J.; Feng, Z. Transcriptomic and proteomic profiling revealed global changes in Streptococcus thermophilus during pH-controlled batch fermentations. J. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, S.N.; Sandine, W.E. Associative growth and proteolysis of Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus in skim milk. J. Dairy Sci. 1990, 73, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkor, O.N.; Henriksson, A.; Singh, T.K.; Vasiljevic, T.; Shah, N.P. ACE-inhibitory activity of probiotic yoghurt. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirós, A.; Ramos, M.; Muguerza, B.; Delgado, M.A.; Miguel, M.; Aleixandre, A.; Recio, I. Identification of novel antihypertensive peptides in milk fermented with Enterococcus faecalis. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Ronquillo, R.; Cruz-Guerrero, A.; Flores-Nájera, A.; Rodríguez-Serrano, G.; Gómez-Ruiz, L.; Reyes-Grajeda, J.P.; Jiménez-Guzmán, J.; García-Garibay, M. Antithrombotic and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory properties of peptides released from bovine casein by Lactobacillus casei Shirota. Int. Dairy J. 2012, 26, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, E.; Watanabe, R.; Ichimura, T.; Ishida, T.; Kimura, K. Effect of lactose hydrolysis on the milk-fermenting properties of Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus 2038 and Streptococcus thermophilus 1131. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markakiou, S.; Gaspar, P.; Johansen, E.; Zeidan, A.A.; Neves, A.R. Harnessing the metabolic potential of Streptococcus thermophilus for new biotechnological applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 61, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafeez, Z.; Cakir-Kiefer, C.; Lecomte, X.; Miclo, L.; Dary-Mourot, A. The X-prolyl dipeptidyl-peptidase PepX of Streptococcus thermophilus initially described as intracellular is also responsible for peptidase extracellular activity. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 102, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, T.; Cui, Y.; Qu, X. Analysis of the proteolytic system of Streptococcus thermophilus strains CS5, CS9, CS18 and CS20. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 118, 105025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Espla, M.D.; Garault, P.; Monnet, V.; Rul, F. Streptococcus thermophilus cell wall-anchored proteinase: Release, purification, and biochemical and genetic characterization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4772–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ortiz-Chao, P.; Gómez-Ruiz, J.A.; Rastall, R.A.; Mills, D.; Cramer, R.; Pihlanto, A.; Korhonen, H.; Jauregi, P. Production of novel ACE inhibitory peptides from β-lactoglobulin using Protease N Amano. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, F.; De Vuyst, L. Lactic acid bacteria as functional starter cultures for the food fermentation industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, M.C.; Melo, R.L.; Cesari, M.H.; Juliano, L.; Carmona, A.K. Peptidase specificity characterization of C- and N- terminal catalytic sites of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 8519–8525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Guo, T.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Li, F.; Wang, C.; Shi, Y.; Li, D.X.; Zhang, S. Isolation and identification of novel casein-derived bioactive peptides and potential functions in fermented casein with Lactobacillus helveticus. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 156–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocente, N.; Biasutti, M.; Rita, F.; Brichese, R.; Comi, G.; Iacumin, L. Effect of indigenous Lactobacillus rhamnosus isolated from bovine milk on microbiological characteristics and aromatic profile of traditional yogurt. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letort, C.; Juillard, V. Development of a minimal chemically-defined medium for the exponential growth of Streptococcus thermophilus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 91, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garault, P.; Letort, C.; Juillard, V.; Monnet, V. Branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis is essential for optimal growth of Streptococcus thermophilus in milk. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 5128–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Espla, M.D.; Rul, F. PepS from Streptococcus thermophilus. A new member of the aminopeptidase T family of thermophilic bacteria. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 263, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rokka, T.; Syväoja, E.; Tuominen, J. Release of bioactive by enzymatic proteolysis of Lactobacillus GG fermented UHT milk. Milchwiissenschaft 1997, 66, 9. [Google Scholar]
| Fermented Milk | Initial pH | Ending pH | Fermentation Time (h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LLR | 6.73 ± 0.01 | 5.02 ± 0.06 | 56 |
| LST | 6.76 ± 0.01 | 4.51 ± 0.01 | 12 |
| LLS | 6.70 ± 0.01 | 4.56 ± 0.03 | 41 |
| Stage of Fermentation | Time of Fermentation * | Free Amino Groups (mg/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLR | LST | LLS | ||
| Beginning | 1 | 0.544 ± 0.011 | 0.632 ± 0.012 | 0.513 ± 0.00 |
| Middle | 2 | 0.642 ± 0.032 | 0.671 ± 0.036 | 0.526 ± 0.039 |
| 3 | 0.640 ± 0.010 | 0.110 ± 0.047 | 0.593 ± 0.003 | |
| 4 | 0.644 ± 0.00 | 0.236 ± 0.023 | 0.617 ± 0.009 | |
| End | 5 | 0.639 ± 0.006 | 0.240 ± 0.012 | 0.696 ± 0.023 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sebastián-Nicolas, J.L.; Contreras-López, E.; Ramírez-Godínez, J.; Cruz-Guerrero, A.E.; Rodríguez-Serrano, G.M.; Añorve-Morga, J.; Jaimez-Ordaz, J.; Castañeda-Ovando, A.; Pérez-Escalante, E.; Ayala-Niño, A.; et al. Milk Fermentation by Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG and Streptococcus thermophilus SY-102: Proteolytic Profile and ACE-Inhibitory Activity. Fermentation 2021, 7, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7040215
Sebastián-Nicolas JL, Contreras-López E, Ramírez-Godínez J, Cruz-Guerrero AE, Rodríguez-Serrano GM, Añorve-Morga J, Jaimez-Ordaz J, Castañeda-Ovando A, Pérez-Escalante E, Ayala-Niño A, et al. Milk Fermentation by Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG and Streptococcus thermophilus SY-102: Proteolytic Profile and ACE-Inhibitory Activity. Fermentation. 2021; 7(4):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7040215
Chicago/Turabian StyleSebastián-Nicolas, Jessica Lizbeth, Elizabeth Contreras-López, Juan Ramírez-Godínez, Alma Elizabeth Cruz-Guerrero, Gabriela Mariana Rodríguez-Serrano, Javier Añorve-Morga, Judith Jaimez-Ordaz, Araceli Castañeda-Ovando, Emmanuel Pérez-Escalante, Alexis Ayala-Niño, and et al. 2021. "Milk Fermentation by Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG and Streptococcus thermophilus SY-102: Proteolytic Profile and ACE-Inhibitory Activity" Fermentation 7, no. 4: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7040215
APA StyleSebastián-Nicolas, J. L., Contreras-López, E., Ramírez-Godínez, J., Cruz-Guerrero, A. E., Rodríguez-Serrano, G. M., Añorve-Morga, J., Jaimez-Ordaz, J., Castañeda-Ovando, A., Pérez-Escalante, E., Ayala-Niño, A., & González-Olivares, L. G. (2021). Milk Fermentation by Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG and Streptococcus thermophilus SY-102: Proteolytic Profile and ACE-Inhibitory Activity. Fermentation, 7(4), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7040215







