Modulating Fermentation in Total Mixed Ration Silages Using Lasalocid Sodium and Essential Oils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Location, Experimental Design, and Treatments
2.2. TMR Composition and Ensiling Methodology
2.3. Laboratory Analyses, Loss Determination, and Aerobic Stability
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilkinson, J.M.; Davies, D.R. The Aerobic Stability of Silage: Key Findings and Recent Developments. Grass Forage Sci. 2013, 68, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanto, I.; Rahmadani, M.; Wiryawan, K.G.; Laconi, E.B.; Jayanegara, A. Evaluation of Essential Oils as Additives during Fermentation of Feed Products: A Meta-Analysis. Fermentation 2023, 9, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Playne, M.J.; Mc Donald, P.T. The Buffering Constituents of Herbage and of Silage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1966, 17, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobim, C.C.; Nussio, L.G.; Reis, R.A.; Schimidt, P. Avanços Metodológicos Na Avaliação Da Qualidade Da Forragem Conservada Methodological Advances in Evaluation. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2007, 36, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y. The Performance of Plant Essential Oils against Lactic Acid Bacteria and Adverse Microorganisms in Silage Production. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1285722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Shao, T. Effects of Storage Temperature and Combined Microbial Inoculants on Fermentation End Products and Microbial Populations of Italian Ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.). Silage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 125, 1682–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Kaka, N.A.; Shao, T. Sequencing and Microbiota Transplantation to Determine the Role of Microbiota on the Fermentation Type of Oat Silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 309, 123371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhao, M.; Yan, Y.; Sun, P.; Yan, X.; Liu, M.; Na, R.; Jia, Y.; Cha, S.; Guo, G. Characteristics of Isolated Lactic Acid Bacteria and Their Effects on the Silage Quality. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 30, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade, R.C.; Orrico Junior, M.A.P.; da Silva, Y.A.; Retore, M.; Fernandes, T.; Orrico, A.C.A.; Junior, F.M.d.V.; Amaral, I.P.d.O. Impact of Monensin Sodium and Essential Limonene Oil on the Fermentation and Chemical Composition of Total Mixed Ration Silages with Moisture Variations. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, G.; Poppi, A.C.O.; Machado, J.; Bueno, A.V.I.; Gomes, A.L.M.; Jobim, C.C.; Daniel, J.L.P. Effects of Protein Source and Lipid Supplementation on Conservation and Feed Value of Total Mixed Ration Silages for Finishing Beef Cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Nutrient Requirements of Dairy Cattle: Eighth Revised Edition; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryce, J.D. A Modification of Barker-Summerson Method for the Determination of Lactic Acid. Analyst 1969, 94, 1151–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L.; Shaver, R.D.; Grant, R.J.; Schmidt, R.J. Silage Review: Interpretation of Chemical, Microbial, and Organoleptic Components of Silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borreani, G.; Tabacco, E.; Schmidt, R.J.; Holmes, B.J.; Muck, R.E. Silage Review: Factors Affecting Dry Matter and Quality Losses in Silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3952–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besharati, M.; Palangi, V.; Ghozalpour, V.; Nemati, Z.; Ayaşan, T. Essential Oil and Apple Pomace Affect Fermentation and Aerobic Stability of Alfalfa Silage. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 51, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, A.V.I.; Lazzari, G.; Jobim, C.C.; Daniel, J.L.P. Ensiling Total Mixed Ration for Ruminants: A Review. Agronomy 2020, 10, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Jeyakumar, E.; Lawrence, R. Journey of Limonene as an Antimicrobial Agent. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 15, 1094–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espina, L.; Gelaw, T.K.; de Lamo-Castellví, S.; Pagán, R.; García-Gonzalo, D. Mechanism of Bacterial Inactivation by (+)-Limonene and Its Potential Use in Food Preservation Combined Processes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, I.P.d.O.; Orrico Junior, M.A.P.; Retore, M.; Fernandes, T.; América, Y.; De Oliveira, M.F.; Orrico, A.C.A. The Fermentative and Nutritional Effects of Limonene and a Cinnamaldehyde–Carvacrol Blend on Total Mixed Ration Silages. Fermentation 2025, 11, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanto, I.; Rahmadani, M.; Wiryawan, K.G.; Jayanegara, A. A Meta-Analysis on the Influence of Essential Oils on Chemical Composition and Fermentative Quality of Silage. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1183, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lana Sousa, B.M.; de Jesus Santos, S.; Backes, A.A.; Silva, C.M.; Fagundes, J.L.; Blank, A.F.; dos Santos Filho, J.R. “Alecrim Pimenta” Nanoformulated Essential oil (Lippia Sidoides) as Additive in Consortium Silages. Cienc. Anim. Bras. 2023, 24, e73623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, V.F.; de Souza, F.J.A.; da Silva, J.R.; Filho, A.S.S.; Miranda, E.S.; de Oliveira, J.C.A.; Mesquita, A.A.; Negrão, F.d.M. Uso de Aditivos Nas. Silagens de Capins Tropicais: Revisão de Literatura. Braz. J. Anim. Environ. Res. 2024, 7, e68716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, A.A.; Stephens, J.C. A Review of Cinnamaldehyde and Its Derivatives as Antibacterial Agents. Fitoterapia 2019, 139, 104405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, L.; Williams, P.; Schmidt, R.J.; Hu, W. A Blend of Essential Plant Oils Used as an Additive to Alter Silage Fermentation or Used as a Feed Additive for Lactating Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 4793–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Zhang, L.; Wei, M.; Wu, B.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, R.; Ju, J.; Dong, C.; Du, L.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum (L) and Molasses (M) on Nutrient Composition, Aerobic Stability, and Microflora of Alfalfa Silage in Sandy Grasslands. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1358085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Nishino, N. Ensiling of Soybean Curd Residue and Wet Brewers Grains with or without Other Feeds as a Total Mixed Ration. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 2380–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantoia Júnior, R.; Capucho, E.; Garcia, T.M.; Del Valle, T.A.; Campana, M.; Zilio, E.M.C.; Azevedo, E.B.; Morais, J.P.G. Lemongrass Essential Oil in Sugarcane Silage: Fermentative Profile, Losses, Chemical Composition, and Aerobic Stability. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2020, 260, 114371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrico, A.C.A.; Lopes, L.S.; Alves, J.P.; Mendes, S.S.; Galeano, E.S.J.; Junior, M.A.P.O.; Fernandes, T.; Retore, M. Yield, Chemical Composition, and Efficiency of Utilization of Applied Nitrogen from BRS Kurumi Pastures. Cienc. Rural 2023, 53, e20210461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.Q.; Hu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.W.; Lü, X.T. Changes of Mineral Nutrition (K, Ca, and Mg) in Soil and Plants Following Historical Nitrogen Inputs in a Temperate Steppe: The Implications for Grass Tetany. Plant Soil 2023, 491, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foskolos, A.; Cavini, S.; Ferret, A.; Calsamiglia, S. Effects of Essential Oil Compounds Addition on Ryegrass Silage Protein Degradation. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 96, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, S.A.; da Silva, T.J.H.; Marques, S.A.J.; Bezerra, F.P.; de Pinho, C.K.A.; Marques, C.C.; Chaves, G.A.L.; Gomes, S.A.C.; Pinho, C.J.V.C. Chemical Composition and Fermentation Characteristics of Maize Silage with Citrus Pulp. Rev. Bras. Saude Prod. Anim. 2022, 23, e21352022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodjatpanah-Montazeri, A.; Danesh Mesgaran, M.; Vakili, A.; Tahmasebi, A.M. Effect of Essential Oils of Various Plants as Microbial Modifier to Alter Corn Silage Fermentation and in Vitro Methane Production. Iran. J. Appl. Anim. Sci. 2016, 6, 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.R.; Long, R.J.; Guo, X.S. Effects of Plant Enzyme Inactivation or Sterilization on Lipolysis and Proteolysis in Alfalfa Silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 2536–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoetis Brazil. Taurotec®–Lasalocida Sódica 15%: Package Insert [Internet]. São Paulo: Zoetis Brazil. 2020. Available online: https://www.zoetis.com.br/especies/bovinos/taurotec/files/bula_bov-alt-40014654-taurotec.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2025).
| Ingredients | % of DM |
|---|---|
| BRS Capiaçu grass | 33.21 |
| Ground corn | 43.38 |
| Soybean meal | 19.67 |
| Calcitic limestone | 1.83 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | 1.90 |
| Total | 100.00 |
| DM, % FM | 35.04 |
| Ash, % DM | 6.30 |
| Crude protein, % DM | 18.10 |
| Neutral detergent fiber, % DM | 35.54 |
| Acid detergent fiber, %DM | 23.29 |
| Lignin, % DM | 3.40 |
| Ether extract, % DM | 2.70 |
| Starch, % DM | 22.00 |
| Non-fiber carbohydrates, % DM | 37.01 |
| Buffering capacity, meq NaOH/100 g DM | 13.63 |
| pH | 6.78 |
| Parameters | Season | Control | LASA | LEO | EOB | SEM | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | S | A*S | |||||||
| DMR, % DM | Summer | 94.22 Aa | 97.02 Ab | 96.78 Bb | 96.91 Ab | 0.341 | <0.01 | 0.023 | 0.051 |
| Autumn | 93.95 Aa | 96.30 Ac | 95.18 Ab | 97.24 Ac | |||||
| GLs, % DM | Summer | 1.94 | 1.65 | 2.27 | 2.77 | 0.564 | 0.100 | 0.194 | 0.478 |
| Autumn | 0.54 | 1.43 | 2.59 | 1.98 | |||||
| ELs, kg/ton DM | Summer | 58.51 Ab | 33.07 Aa | 44.17 Ab | 27.39 Aa | 0.664 | 0.049 | <0.01 | 0.166 |
| Autumn | 68.81 Aa | 61.81 Ba | 58.16 Aa | 64.65 Ba | |||||
| pH | Summer | 3.81 Aa | 3.84 Aa | 3.80 Aa | 3.81 Aa | 0.021 | 0.062 | <0.01 | 0.094 |
| Autumn | 3.87 Aa | 3.93 Ba | 3.96 Bb | 3.88 Ba | |||||
| NH3-N, % TN | Summer | 5.10 Ab | 5.40 Ab | 5.24 Ab | 3.06 Aa | 0.467 | 0.046 | 0.086 | 0.063 |
| Autumn | 5.20 Aa | 5.18 Aa | 5.52 Aa | 5.24 Ba | |||||
| LA, % DM | Summer | 3.23 Aa | 4.90 Ab | 6.10 Ab | 5.00 Ab | 0.400 | <0.01 | 0.728 | 0.081 |
| Autumn | 3.33 Aa | 4.50 Aa | 5.40 Ab | 6.40 Bb | |||||
| Ethanol, % DM | Summer | 0.37 Ab | 0.20 Aa | 0.27 Ba | 0.23 Aa | 0.041 | 0.017 | <0.01 | 0.113 |
| Autumn | 0.17 Bb | 0.07 Ba | 0.03 Aa | 0.20 Ab | |||||
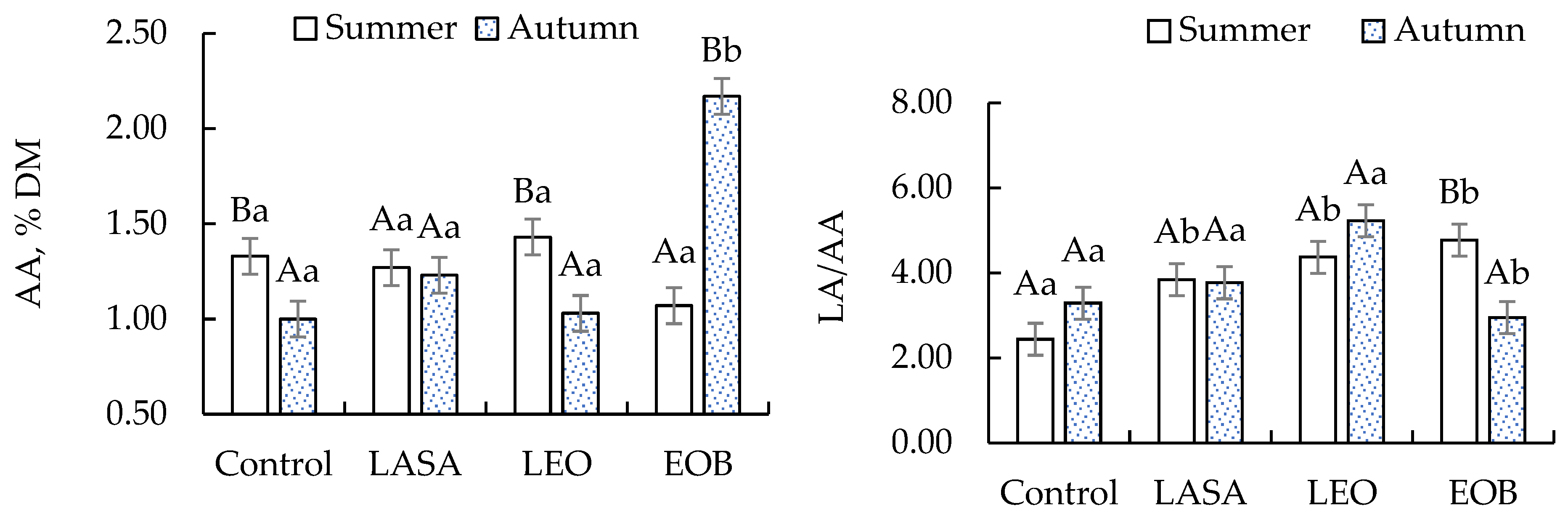
| AA, % DM | Summer | 1.33 Ba | 1.27 Aa | 1.43 Ba | 1.07 Aa | 0.094 | <0.01 | 0.229 | <0.01 |
| Autumn | 1.00 Aa | 1.23 Aa | 1.03 Aa | 2.17 Bb | |||||
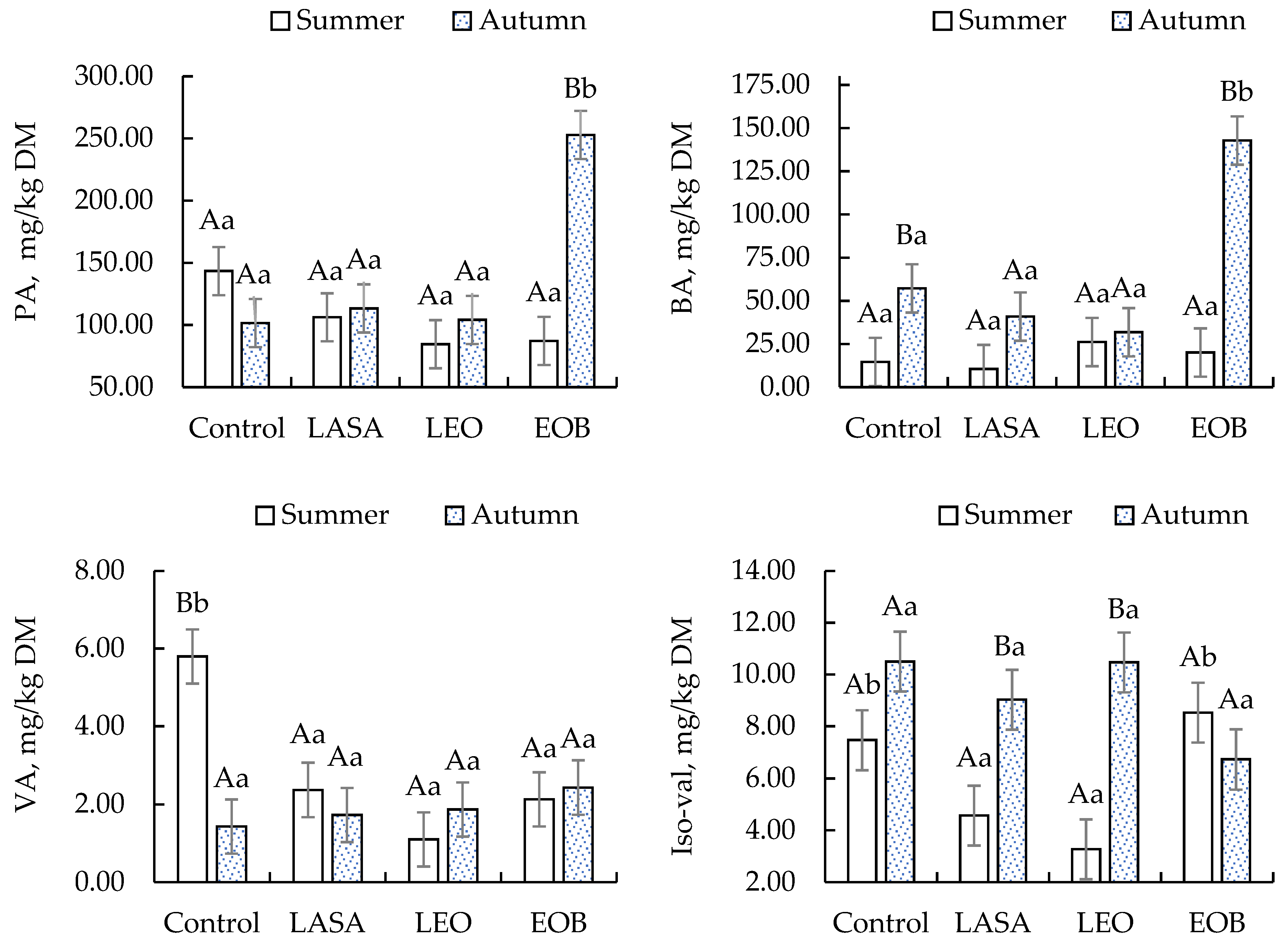
| PA, mg/kg DM | Summer | 143.43 Aa | 106.27 Aa | 84.60 Aa | 87.20 Aa | 0.293 | <0.01 | 0.014 | <0.01 |
| Autumn | 101.63 Aa | 113.37 Aa | 104.17 Aa | 252.83 Bb | |||||
| BA, mg/kg DM | Summer | 14.63 Aa | 10.52 Aa | 26.20 Aa | 20.10 Aa | 0.139 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Autumn | 57.27 Ba | 40.94 Aa | 31.83 Aa | 142.81 Bb | |||||
| Iso-but, mg/kg DM | Summer | 3.37 | 4.07 | 3.17 | 2.63 | 1.380 | 0.990 | 0.379 | 0.797 |
| Autumn | 1.87 | 1.93 | 2.90 | 3.00 | |||||
| VA, mg/kg DM | Summer | 5.80 Bb | 2.37 Aa | 1.10 Aa | 2.13 Aa | 0.697 | 0.045 | 0.063 | <0.01 |
| Autumn | 1.43 Aa | 1.73 Aa | 1.87 Aa | 2.43 Aa | |||||
| Iso-val, mg/kg DM | Summer | 7.47 Ab | 4.57 Aa | 3.27 Aa | 8.53 Ab | 0.115 | 0.243 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Autumn | 10.50 Aa | 9.03 Ba | 10.47 Ba | 6.73 Aa | |||||
| LA/AA | Summer | 2.44 Aa | 3.84 Ab | 4.37 Ab | 4.77 Bb | 0.376 | <0.01 | 0.865 | <0.01 |
| Autumn | 3.29 Aa | 3.77 Aa | 5.23 Aa | 2.95 Ab | |||||
| AS, hours | Summer | 102.87 Aa | 114.10 Aa | 110.63 Aa | 125.30 Ab | 3.999 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.266 |
| Autumn | 121.13 Ba | 132.17 Bb | 118.30 Aa | 149.30 Bc | |||||
| Parameters | Season | Control | LASA | LEO | EOB | SEM | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | S | A*S | |||||||
| DM, % FM | Summer | 34.43 | 39.70 | 39.27 | 35.67 | 1.592 | 0.115 | 0.274 | 0.533 |
| Autumn | 35.13 | 35.97 | 37.37 | 35.50 | |||||
| Ash, % DM | Summer | 7.50 Aa | 7.10 Aa | 7.43 Aa | 7.53 Aa | 0.297 | 0.074 | 0.011 | 0.116 |
| Autumn | 8.77 Ba | 7.967 Ab | 7.20 Aa | 8.03 Ab | |||||
| CP, % DM | Summer | 17.45 Aa | 17.77 Aa | 15.02 Aa | 17.46 Aa | 0.112 | 0.857 | 0.045 | 0.213 |
| Autumn | 18.14 Aa | 17.49 Aa | 19.55 Ba | 19.03 Aa | |||||
| NDF, % DM | Summer | 38.57 | 29.93 | 33.23 | 38.00 | 2.558 | 0.165 | 0.601 | 0.090 |
| Autumn | 31.70 | 37.10 | 34.70 | 40.10 | |||||
| ADF, % DM | Summer | 25.10 Aa | 19.43 Aa | 20.97 Aa | 24.63 Aa | 1.744 | 0.045 | 0.164 | 0.097 |
| Autumn | 21.43 Aa | 24.47 Aa | 22.70 Aa | 28.73 Ab | |||||
| LIG, % DM | Summer | 2.77 Aa | 1.93 Aa | 2.20 Aa | 2.40 Aa | 0.355 | 0.114 | <0.01 | 0.251 |
| Autumn | 3.17 Aa | 2.97 Aa | 3.23 Aa | 4.30 Bb | |||||
| Stach, % DM | Summer | 19.13 | 25.97 | 22.50 | 20.97 | 2.389 | 0.472 | 0.188 | 0.335 |
| Autumn | 25.67 | 23.77 | 26.30 | 22.13 | |||||
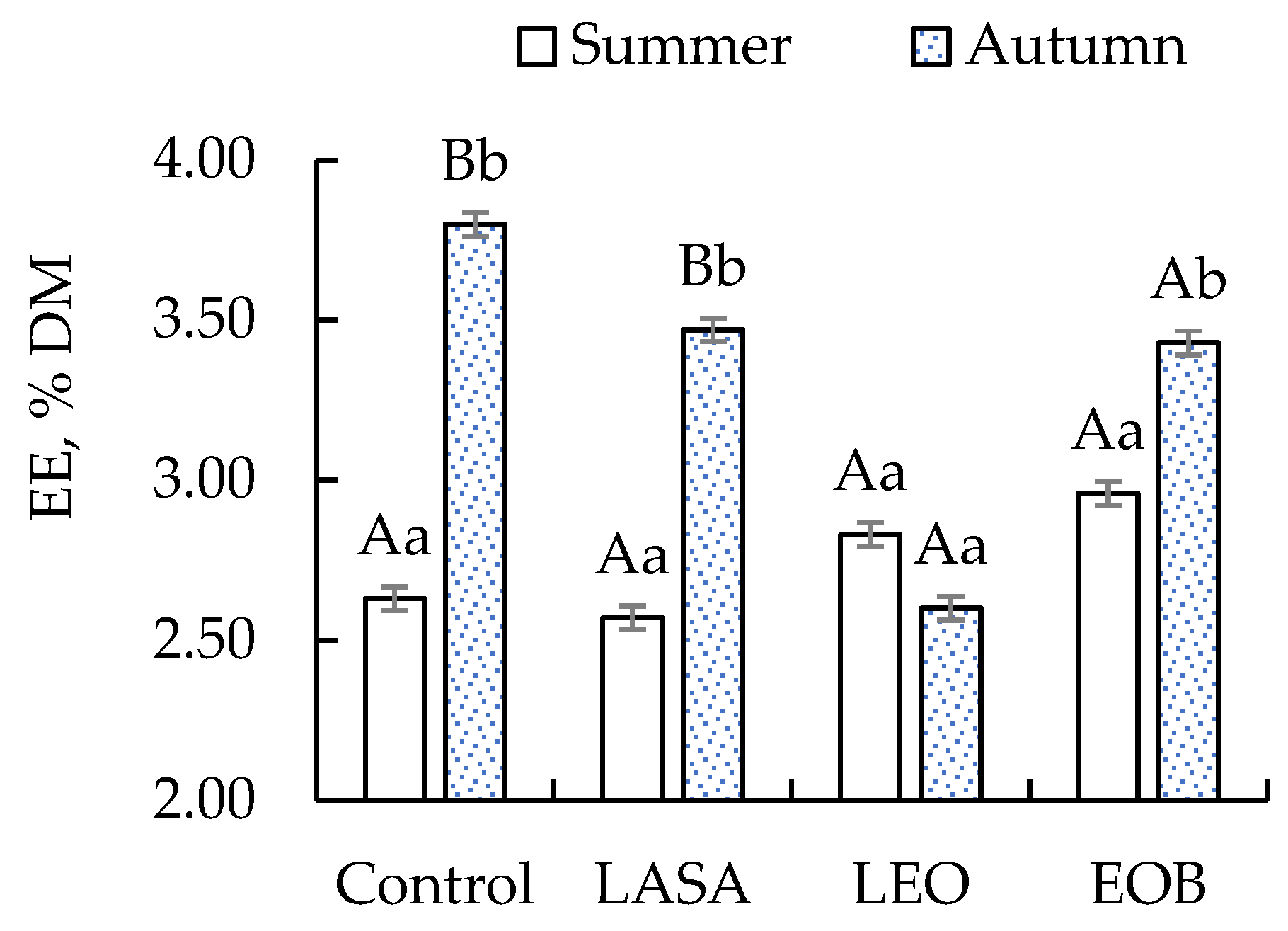
| EE, %DM | Summer | 2.63 Aa | 2.57 Aa | 2.83 Aa | 2.96 Aa | 0.228 | 0.144 | <0.01 | 0.037 |
| Autumn | 3.80 Bb | 3.47 Bb | 2.60 Ab | 3.43 Aa | |||||
| NFCs, % DM | Summer | 35.13 | 42.50 | 38.77 | 35.47 | 2.563 | 0.215 | 0.398 | 0.217 |
| Autumn | 39.10 | 35.47 | 38.67 | 32.33 | |||||
| TDNs, % DM | Summer | 69.33 Aa | 73.33 Bb | 72.00 Ab | 70.00 Ba | 1.041 | 0.040 | 0.012 | 0.141 |
| Autumn | 70.33 Aa | 69.67 Aa | 69.67 Aa | 66.67 Aa | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amaral, I.P.d.O.; de Oliveira, M.F.; Junior, M.A.P.O.; Retore, M.; Fernandes, T.; da Silva, Y.A.; Orrico, A.C.A.; de Andrade, R.C.; Muglia, G.R.P. Modulating Fermentation in Total Mixed Ration Silages Using Lasalocid Sodium and Essential Oils. Fermentation 2025, 11, 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080468
Amaral IPdO, de Oliveira MF, Junior MAPO, Retore M, Fernandes T, da Silva YA, Orrico ACA, de Andrade RC, Muglia GRP. Modulating Fermentation in Total Mixed Ration Silages Using Lasalocid Sodium and Essential Oils. Fermentation. 2025; 11(8):468. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080468
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmaral, Isabele Paola de Oliveira, Mariany Felex de Oliveira, Marco Antonio Previdelli Orrico Junior, Marciana Retore, Tatiane Fernandes, Yara América da Silva, Ana Carolina Amorim Orrico, Ronnie Coêlho de Andrade, and Giuliano Reis Pereira Muglia. 2025. "Modulating Fermentation in Total Mixed Ration Silages Using Lasalocid Sodium and Essential Oils" Fermentation 11, no. 8: 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080468
APA StyleAmaral, I. P. d. O., de Oliveira, M. F., Junior, M. A. P. O., Retore, M., Fernandes, T., da Silva, Y. A., Orrico, A. C. A., de Andrade, R. C., & Muglia, G. R. P. (2025). Modulating Fermentation in Total Mixed Ration Silages Using Lasalocid Sodium and Essential Oils. Fermentation, 11(8), 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080468










