The Fermentative and Nutritional Effects of Limonene and a Cinnamaldehyde–Carvacrol Blend on Total Mixed Ration Silages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. A Description of the Study Site and the Experimental Trials
2.2. TMR Preparation and Filling of Experimental Silos
2.3. Sample Collection, Fermentative Losses, and Analytical Methodologies
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
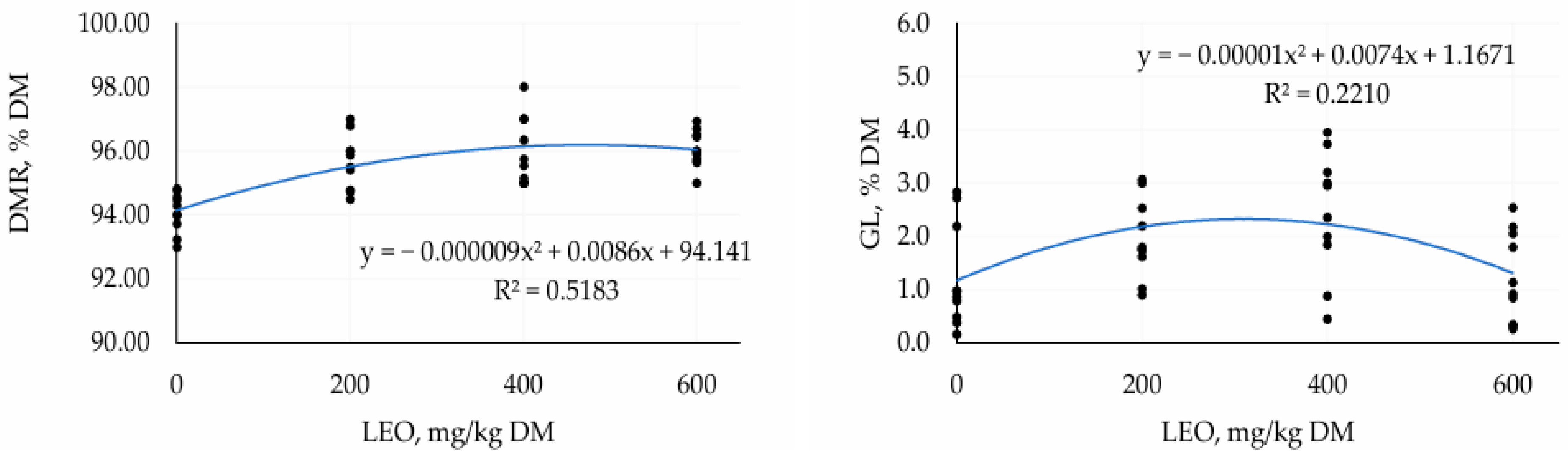
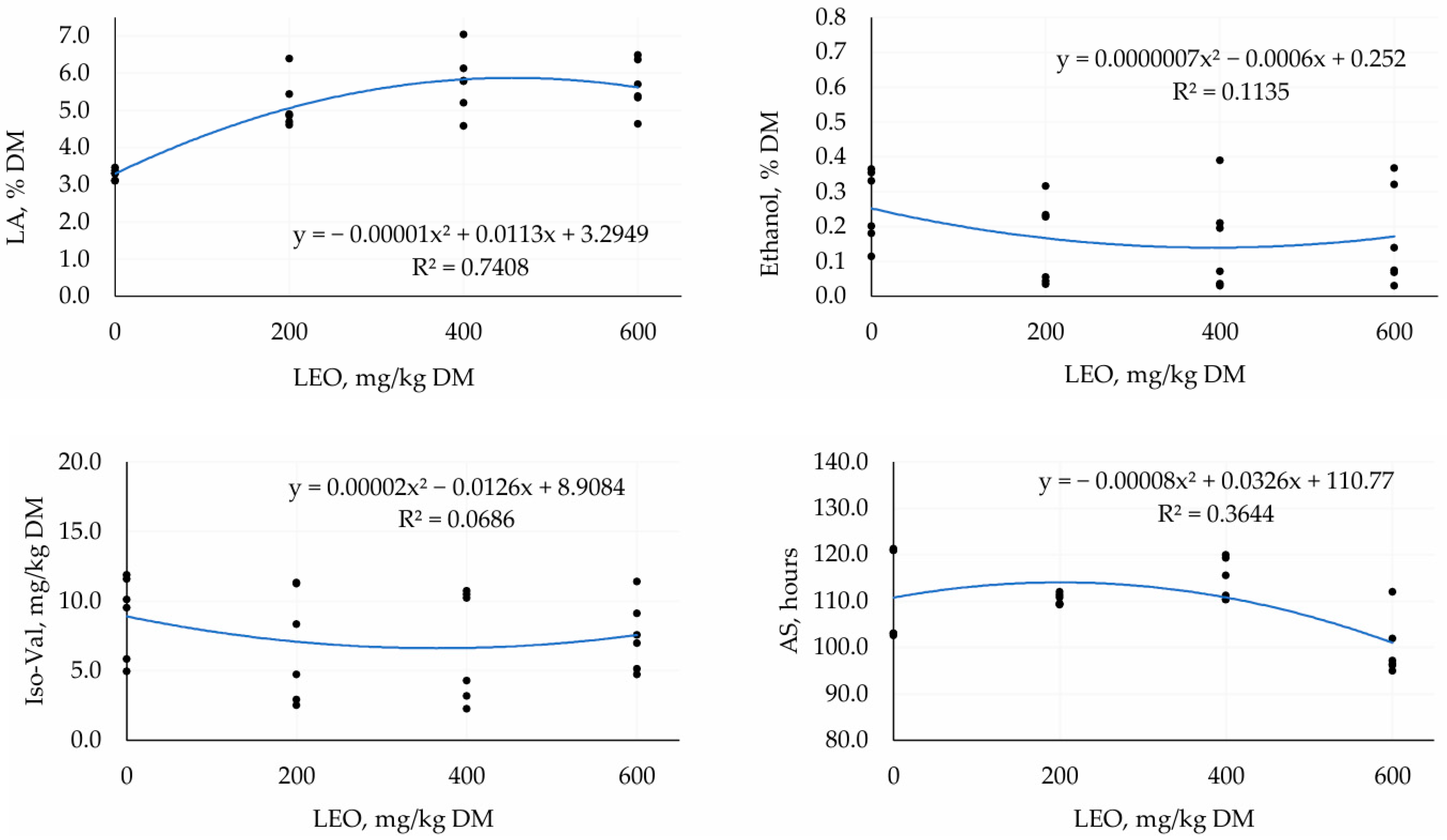
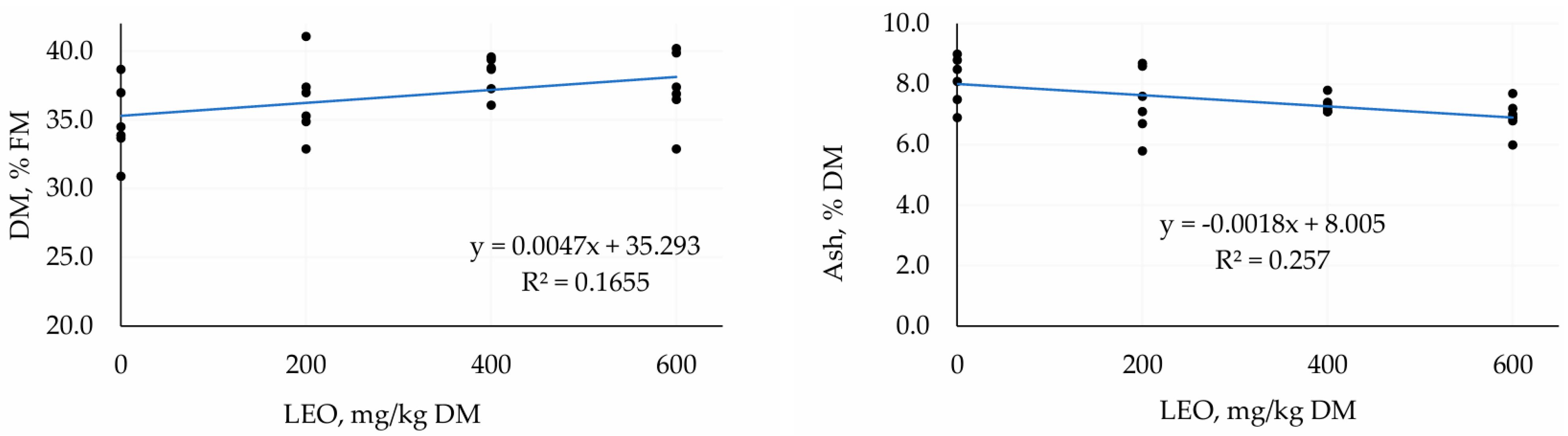
3.1. First Trial—TMR Silage with Different Doses of LEO
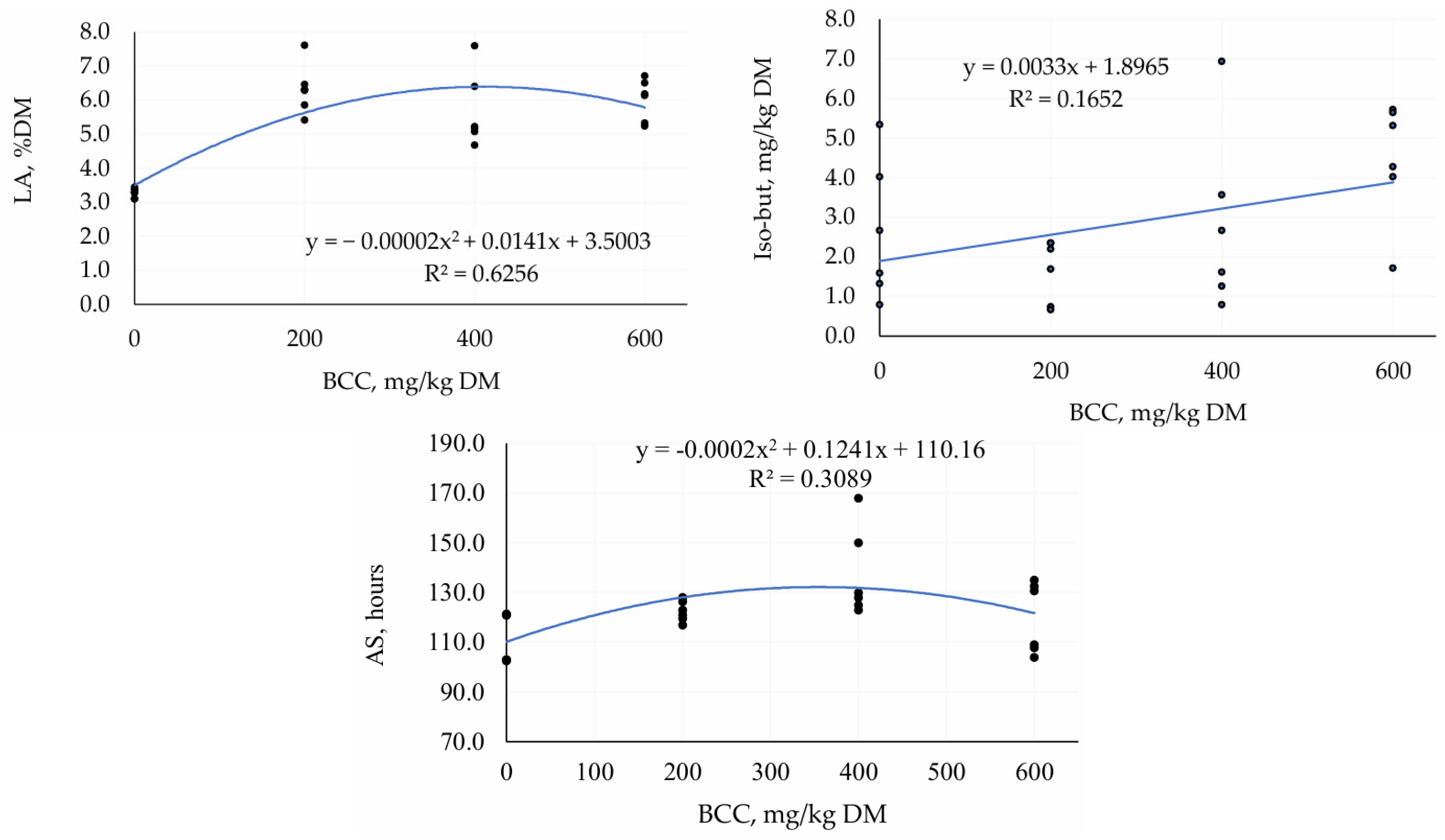
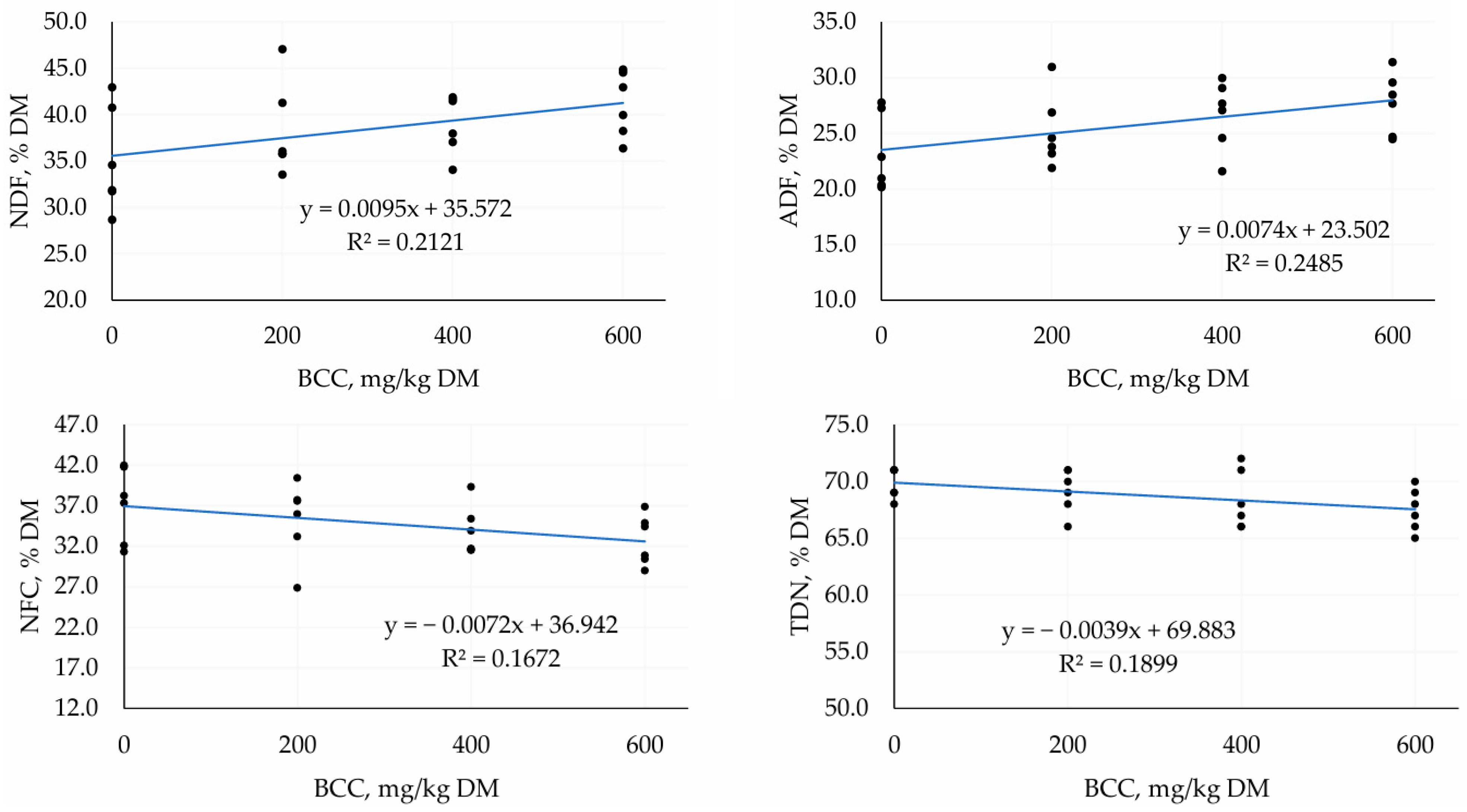
3.2. Second Trial—TMR Silage with Different Doses of BCC
4. Discussion
4.1. First Trial—TMR Silage with Different Doses of LEO
4.2. Second Trial—TMR Silage with Different Doses of BCC
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bueno, A.V.I.; Lazzari, G.; Jobim, C.C.; Daniel, J.L.P. Ensiling Total Mixed Ration for Ruminants: A Review. Agronomy 2020, 10, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L.; Shaver, R.D.; Grant, R.J.; Schmidt, R.J. Silage Review: Interpretation of Chemical, Microbial, and Organoleptic Components of Silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, H.F.C.; Santos, E.M.; de Oliveira, J.S.; de Carvalho, G.G.P.; Cassuce, M.R.; Perazzo, A.F.; Freitas, D.d.S.S.; Santos, V.d.S. Degradabilidade Ruminal in Situ de Silagens de Capim-Elefante Aditivadas Com Farelo de Milho e Inoculante Da Microbiota Autóctone. Rev. Bras. Saúde Produção Anim. 2015, 16, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrico, A.C.A.; Lopes, L.S.; Alves, J.P.; Mendes, S.S.; Galeano, E.S.J.; Junior, M.A.P.O.; Fernandes, T.; Retore, M. Yield, Chemical Composition, and Efficiency of Utilization of Applied Nitrogen from BRS Kurumi Pastures. Cienc. Rural 2023, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade, R.C.; Orrico Junior, M.A.P.; da Silva, Y.A.; Retore, M.; Fernandes, T.; Orrico, A.C.A.; Vargas Junior, F.M.d.; Amaral, I.P.d.O. Impact of Monensin Sodium and Essential Limonene Oil on the Fermentation and Chemical Composition of Total Mixed Ration Silages with Moisture Variations. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantoia Júnior, R.; Capucho, E.; Garcia, T.M.; Del Valle, T.A.; Campana, M.; Zilio, E.M.C.; Azevedo, E.B.; Morais, J.P.G. Lemongrass Essential Oil in Sugarcane Silage: Fermentative Profile, Losses, Chemical Composition, and Aerobic Stability. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2020, 260, 114371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fietz, C.R.; Fisch, G.F. Avaliação de Modelos de Estimativa Do Saldo de Radiação e Do Método de Priestley-Taylor Para a Região de Dourados, MS. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agrícola Ambient. 2009, 13, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRC. Nutrient Requirements of Dairy Cattle, 8th ed.; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jobim, C.C.; Nussio, L.G.; Reis, R.A.; Schimidt, P. Avanços Metodológicos Na Avaliação Da Qualidade Da Forragem Conservada Methodological Advances in Evaluation. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2007, 36, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, L.; Monteagudo, A.B.; Salleres, B.; Castro, P.; Moreno-Gonzalez, J. NIRS Determination of Non-Structural Carbohydrates, Water Soluble Carbohydrates and Other Nutritive Quality Traits in Whole Plant Maize with Wide Range Variability. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 11, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Playne, M.J.; Mc Donald, P.T. The Buffering Constituents of Herbage and of Silage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1966, 17, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryce, J.D. A Modification of Barker-Summerson Method for the Determination of Lactic Acid. Analyst 1969, 94, 1151–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, J.M.; Davies, D.R. The Aerobic Stability of Silage: Key Findings and Recent Developments. Grass Forage Sci. 2013, 68, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.; Cox, D.R. An Analysis of Transformations Revisited, Rebutted. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1982, 77, 209–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borreani, G.; Tabacco, E.; Schmidt, R.J.; Holmes, B.J.; Muck, R.E. Silage Review: Factors Affecting Dry Matter and Quality Losses in Silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3952–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, V.F.; de Souza, F.J.A.; da Silva, J.R.; Silva Filho, A.S.; Miranda, E.S.; de Oliveira, J.C.A.; Mesquita, A.A.; de Mattos Negrão, F. Uso de Aditivos Nas Silagens de Capins Tropicais: Revisão de Literatura. Brazilian J. Anim. Environ. Res. 2024, 7, e68716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Jeyakumar, E.; Lawrence, R. Journey of Limonene as an Antimicrobial Agent. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 15, 1094–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espina, L.; Gelaw, T.K.; de Lamo-Castellví, S.; Pagán, R.; García-Gonzalo, D. Mechanism of Bacterial Inactivation by (+)-Limonene and Its Potential Use in Food Preservation Combined Processes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y. The Performance of Plant Essential Oils against Lactic Acid Bacteria and Adverse Microorganisms in Silage Production. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1285722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susanto, I.; Rahmadani, M.; Wiryawan, K.G.; Jayanegara, A. A Meta-Analysis on the Influence of Essential Oils on Chemical Composition and Fermentative Quality of Silage. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1183, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.; Barry-Ryan, C.; Bourke, P. The Antimicrobial Efficacy of Plant Essential Oil Combinations and Interactions with Food Ingredients. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 124, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damtie, D.; Mekonnen, Y. Antibacterial Activity of Essential Oils from Ethiopian Thyme (Thymus Serrulatus and Thymus Schimperi) against Tooth Decay Bacteria. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, A.V.; Baah, J.; Wang, Y.; Mcallister, T.A.; Benchaar, C. Effects of Cinnamon Leaf, Oregano and Sweet Orange Essential Oils on Fermentation and Aerobic Stability of Barley Silage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soycan Önenç, S.; Korkmaz Turgud, F. Effect of Oregano, Cumin and Cinnamon Essential Oils on Fermentation Quality in Alfalfa Silages. J. Agric. Fac. Ege Univ. 2019, 56, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L.; Williams, P.; Schmidt, R.J.; Hu, W. A Blend of Essential Plant Oils Used as an Additive to Alter Silage Fermentation or Used as a Feed Additive for Lactating Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 4793–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, M.C.; da Silva, D.M.; Dias, D.M.B. Effect of Feed Restriction on Organs and Intestinal Mucosa of Growing Rabbits. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2013, 42, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanto, I.; Rahmadani, M.; Wiryawan, K.G.; Laconi, E.B.; Jayanegara, A. Evaluation of Essential Oils as Additives during Fermentation of Feed Products: A Meta-Analysis. Fermentation 2023, 9, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foskolos, A.; Cavini, S.; Ferret, A.; Calsamiglia, S. Effects of essential oil compounds addition on ryegrass silage protein degradation. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 96, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ingredients | % of DM |
|---|---|
| BRS Capiaçu grass | 33.21 |
| Ground corn | 43.38 |
| Soybean meal | 19.67 |
| Calcitic limestone | 1.83 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | 1.90 |
| Total | 100.00 |
| DM, % FM | 35.04 |
| Ash, % DM | 6.30 |
| Crude protein, % DM | 18.10 |
| Neutral detergent fiber, % DM | 35.54 |
| Acid detergent fiber, %DM | 23.29 |
| Lignin, % DM | 3.40 |
| Ether extract, % DM | 2.70 |
| Starch, % DM | 22.00 |
| Non-fiber carbohydrates, % DM | 37.01 |
| Buffering capacity, meq NaOH/100 g DM | 13.63 |
| pH | 6.78 |
| Parameters | LEO (mg/kg DM) | SEM | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 200 | 400 | 600 | L | Q | ||
| DMR, % of DM | 94.09 | 95.66 | 95.98 | 96.09 | 0.177 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| GLs, % DM | 1.24 | 1.96 | 2.44 | 1.24 | 0.165 | 0.74 | <0.001 |
| ELs, kg/ton DM | 63.66 | 55.15 | 51.17 | 52.49 | 2.557 | 0.07 | 0.28 |
| pH | 3.83 | 3.91 | 3.88 | 3.88 | 0.011 | 0.23 | 0.06 |
| NH3-N, % TN | 5.14 | 5.25 | 5.36 | 5.27 | 1.000 | 0.18 | 0.25 |
| LA, % DM | 3.27 | 5.14 | 5.75 | 5.64 | 0.242 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Ethanol, % DM | 0.24 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 1.092 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| AA, % DM | 1.16 | 1.26 | 1.15 | 1.14 | 0.031 | 0.41 | 0.19 |
| PA, mg/kg DM | 109.53 | 114.36 | 94.38 | 94.36 | 4.656 | 0.11 | 0.79 |
| Iso-but, mg/kg DM | 2.63 | 1.93 | 3.04 | 2.78 | 0.221 | 0.44 | 0.63 |
| BA, mg/kg DM | 23.13 | 19.80 | 29.30 | 31.40 | 2.773 | 0.17 | 0.59 |
| Iso-val, mg/kg DM | 2.79 | 2.49 | 2.49 | 2.67 | 1.074 | 0.45 | 0.02 |
| VA, mg/kg DM | 6.00 | 3.27 | 1.60 | 1.86 | 1.242 | 0.09 | 0.47 |
| AS, hours | 111.99 | 110.36 | 114.47 | 99.81 | 1.684 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Parameters | LEO (mg/kg DM) | SEM | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 200 | 400 | 600 | L | Q | ||
| DM, % FM | 34.78 | 36.43 | 38.32 | 37.30 | 0.541 | 0.04 | 0.18 |
| AS, % DM | 8.13 | 7.42 | 7.32 | 6.93 | 0.170 | 0.01 | 0.59 |
| CP, % DM | 17.63 | 17.74 | 17.29 | 16.07 | 0.504 | 0.20 | 0.46 |
| NDF, % DM | 35.13 | 37.42 | 33.97 | 34.70 | 0.845 | 0.54 | 0.66 |
| ADF, % DM | 23.27 | 24.78 | 21.83 | 23.07 | 0.612 | 0.53 | 0.91 |
| LIG, % DM | 2.97 | 3.33 | 2.72 | 3.15 | 0.169 | 0.95 | 0.89 |
| ST, % DM | 22.40 | 22.40 | 24.02 | 24.15 | 0.723 | 0.23 | 0.96 |
| EE, % DM | 3.22 | 2.97 | 2.72 | 3.18 | 0.110 | 0.72 | 0.10 |
| NFCs, % DM | 37.12 | 34.75 | 38.72 | 39.33 | 0.790 | 0.14 | 0.34 |
| TDN, % DM | 69.83 | 69.00 | 70.83 | 70.67 | 0.417 | 0.21 | 0.67 |
| Parameters | BCC (mg/kg DM) | SEM | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 200 | 400 | 600 | L | Q | ||
| DMR, DM% | 94.09 | 95.73 | 97.08 | 97.06 | 0.230 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| GLs, % DM | 1.07 | 0.99 | 1.91 | 0.72 | 0.008 | 0.85 | 0.18 |
| ELs, kg/ton DM | 63.66 | 51.44 | 46.02 | 44.57 | 3.301 | 0.01 | 0.29 |
| pH | 3.83 | 3.89 | 3.85 | 3.87 | 0.010 | 0.43 | 0.36 |
| NH3-N, % TN | 5.14 | 5.26 | 5.26 | 5.40 | 1.000 | 0.04 | 0.95 |
| LA, % DM | 3.27 | 6.33 | 5.70 | 6.02 | 0.288 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Ethanol, % DM | 0.26 | 0.12 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 0.020 | 0.15 | 0.54 |
| AA, % DM | 1.16 | 1.24 | 1.32 | 1.36 | 0.063 | 0.16 | 0.87 |
| PA, mg/kg DM | 114.29 | 122.07 | 132.60 | 122.19 | 1.004 | 0.66 | 0.62 |
| Iso-but, mg/kg DM | 2.63 | 1.67 | 2.81 | 4.45 | 0.380 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| BA, mg/kg DM | 24.10 | 36.06 | 29.09 | 36.58 | 2.243 | 0.14 | 0.56 |
| Iso-val, mg/kg DM | 8.98 | 9.84 | 7.63 | 8.27 | 0.653 | 0.47 | 0.94 |
| VA, mg/kg DM | 1.43 | 1.47 | 1.85 | 2.04 | 0.143 | 0.09 | 0.85 |
| AS, hours | 111.99 | 122.50 | 131.16 | 119.84 | 2.477 | 0.16 | 0.02 |
| Parameters | BCC (mg/kg DM) | SEM | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 200 | 400 | 600 | L | Q | ||
| DM, % FM | 34.78 | 36.77 | 35.58 | 34.38 | 0.562 | 0.65 | 0.17 |
| AS, % DM | 8.13 | 7.50 | 7.78 | 7.48 | 0.124 | 0.13 | 0.49 |
| CP, % DM | 18.24 | 17.96 | 18.24 | 17.94 | 0.188 | 0.73 | 0.97 |
| NDF, % DM | 35.13 | 38.28 | 39.05 | 41.20 | 0.960 | 0.02 | 0.78 |
| ADF, % DM | 23.27 | 25.23 | 26.68 | 27.73 | 0.695 | 0.01 | 0.70 |
| LIG, % DM | 2.97 | 3.18 | 3.35 | 3.50 | 0.186 | 0.18 | 0.91 |
| ST, % DM | 22.40 | 22.07 | 21.55 | 18.82 | 0.738 | 0.08 | 0.40 |
| EE, % DM | 3.22 | 3.25 | 3.20 | 2.75 | 0.130 | 0.12 | 0.24 |
| NFCs, % DM | 37.12 | 35.30 | 33.90 | 32.75 | 0.827 | 0.04 | 0.83 |
| TDN, % DM | 69.83 | 69.17 | 68.33 | 67.50 | 0.419 | 0.02 | 0.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amaral, I.P.d.O.; Orrico Junior, M.A.P.; Retore, M.; Fernandes, T.; da Silva, Y.A.; de Oliveira, M.F.; Orrico, A.C.A.; de Andrade, R.C.; Muglia, G.R.P. The Fermentative and Nutritional Effects of Limonene and a Cinnamaldehyde–Carvacrol Blend on Total Mixed Ration Silages. Fermentation 2025, 11, 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11070415
Amaral IPdO, Orrico Junior MAP, Retore M, Fernandes T, da Silva YA, de Oliveira MF, Orrico ACA, de Andrade RC, Muglia GRP. The Fermentative and Nutritional Effects of Limonene and a Cinnamaldehyde–Carvacrol Blend on Total Mixed Ration Silages. Fermentation. 2025; 11(7):415. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11070415
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmaral, Isabele Paola de Oliveira, Marco Antonio Previdelli Orrico Junior, Marciana Retore, Tatiane Fernandes, Yara América da Silva, Mariany Felex de Oliveira, Ana Carolina Amorim Orrico, Ronnie Coêlho de Andrade, and Giuliano Reis Pereira Muglia. 2025. "The Fermentative and Nutritional Effects of Limonene and a Cinnamaldehyde–Carvacrol Blend on Total Mixed Ration Silages" Fermentation 11, no. 7: 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11070415
APA StyleAmaral, I. P. d. O., Orrico Junior, M. A. P., Retore, M., Fernandes, T., da Silva, Y. A., de Oliveira, M. F., Orrico, A. C. A., de Andrade, R. C., & Muglia, G. R. P. (2025). The Fermentative and Nutritional Effects of Limonene and a Cinnamaldehyde–Carvacrol Blend on Total Mixed Ration Silages. Fermentation, 11(7), 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11070415










