Biotechnological Potential of Weizmannia ginsengihumi in the Conversion of Xylose into Lactic Acid: A Sustainable Strategy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Screening of Weizmannia spp. (Bacillus sp.) Strains from Sugarcane Bagasse
2.2. Identification and Molecular Characterization
2.3. Bacterial Growth Curve
2.4. Fermentation
2.5. Central Composite Planning and Response Surface Methodology
2.6. Analytical Methods
2.6.1. Determination of Bacterial Growth
2.6.2. Quantification of Lactic Acid and Residual Sugar
2.6.3. Statistical Analyses
2.6.4. Validation of Optimal Point and Fermentation Kinetics in Shaker
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Isolation and Selection
3.2. Biochemical Characterization and Molecular Identification
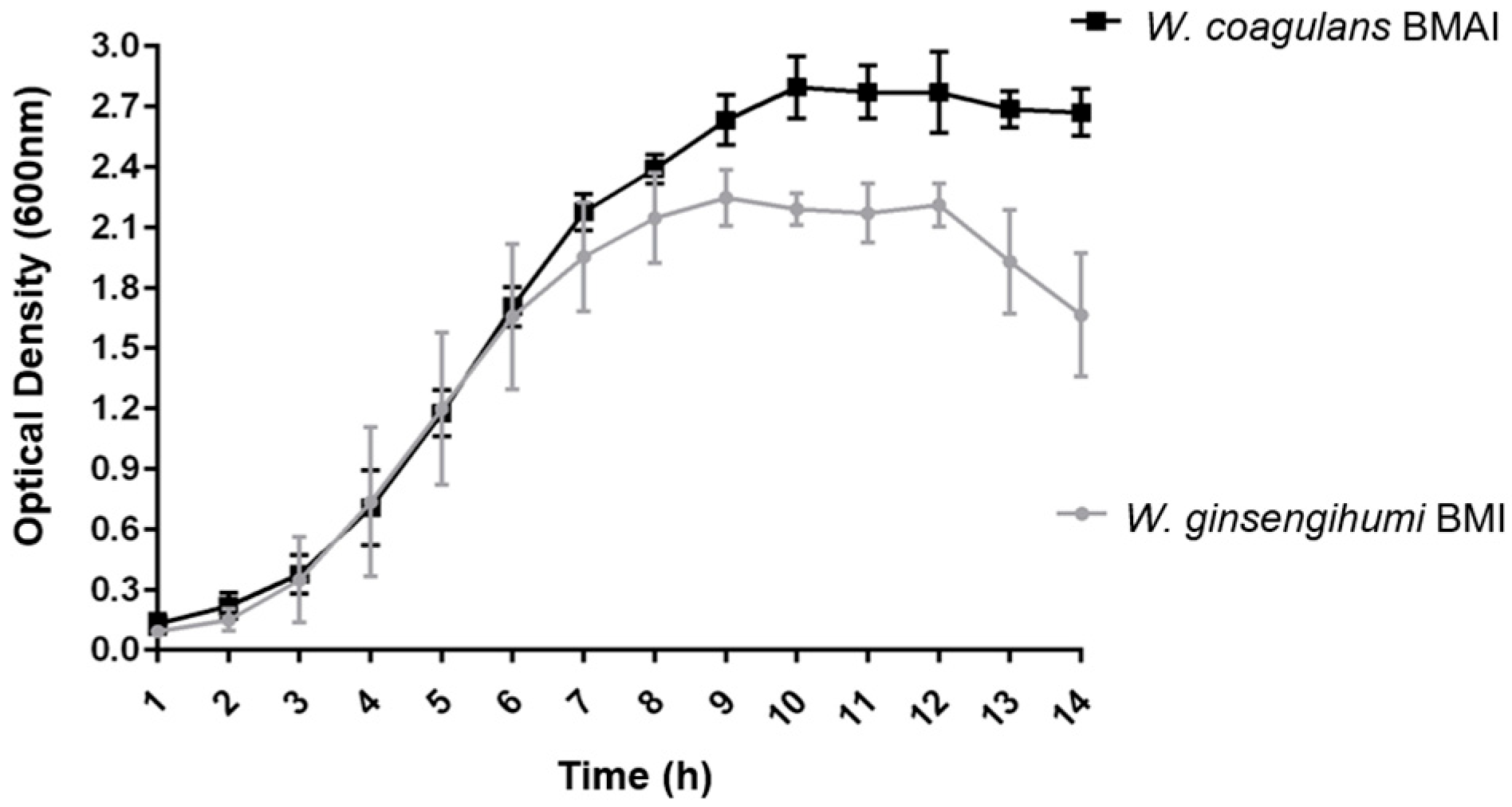
3.3. Growth Curve
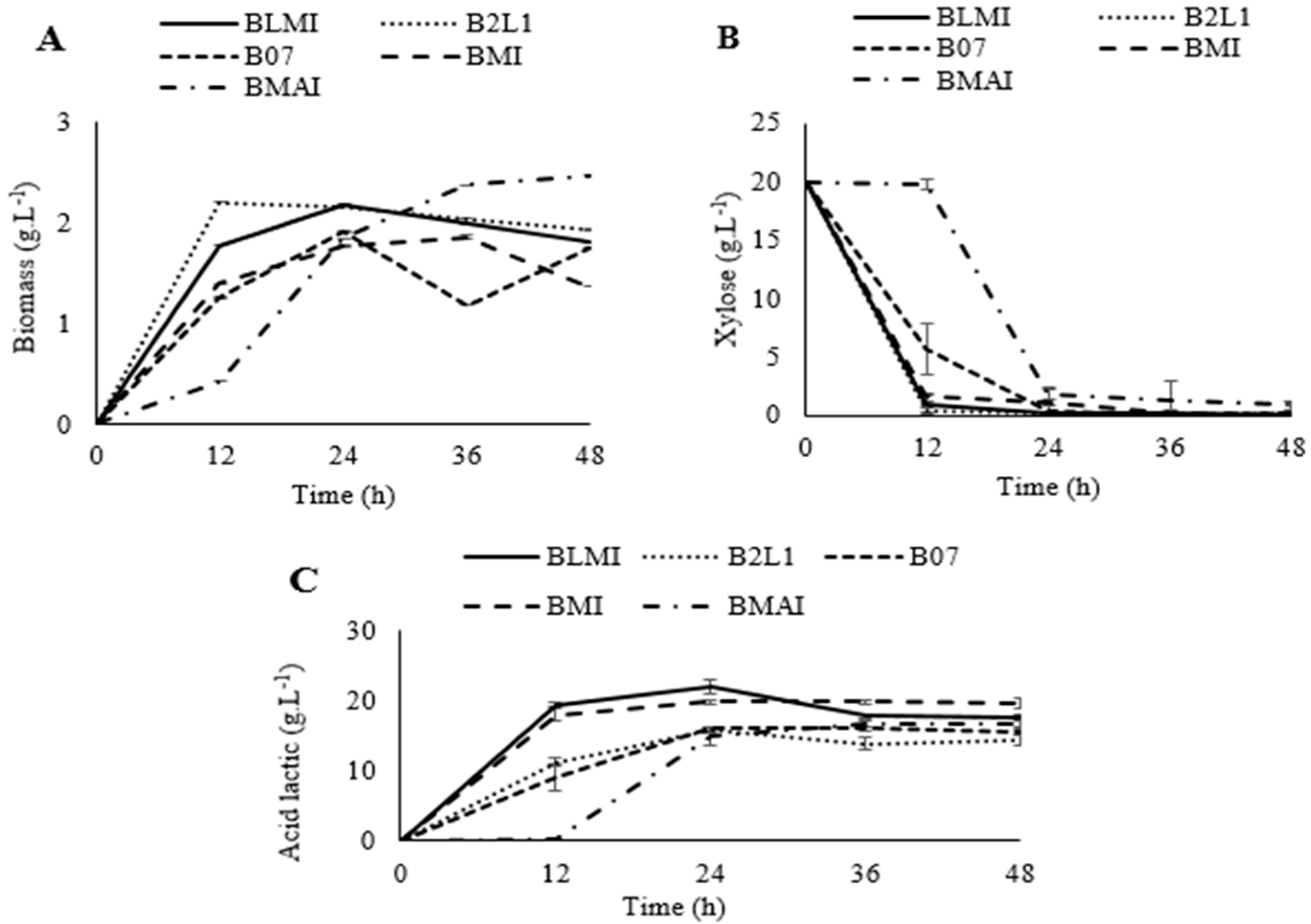
3.4. Fermentation
3.5. Experimental Design
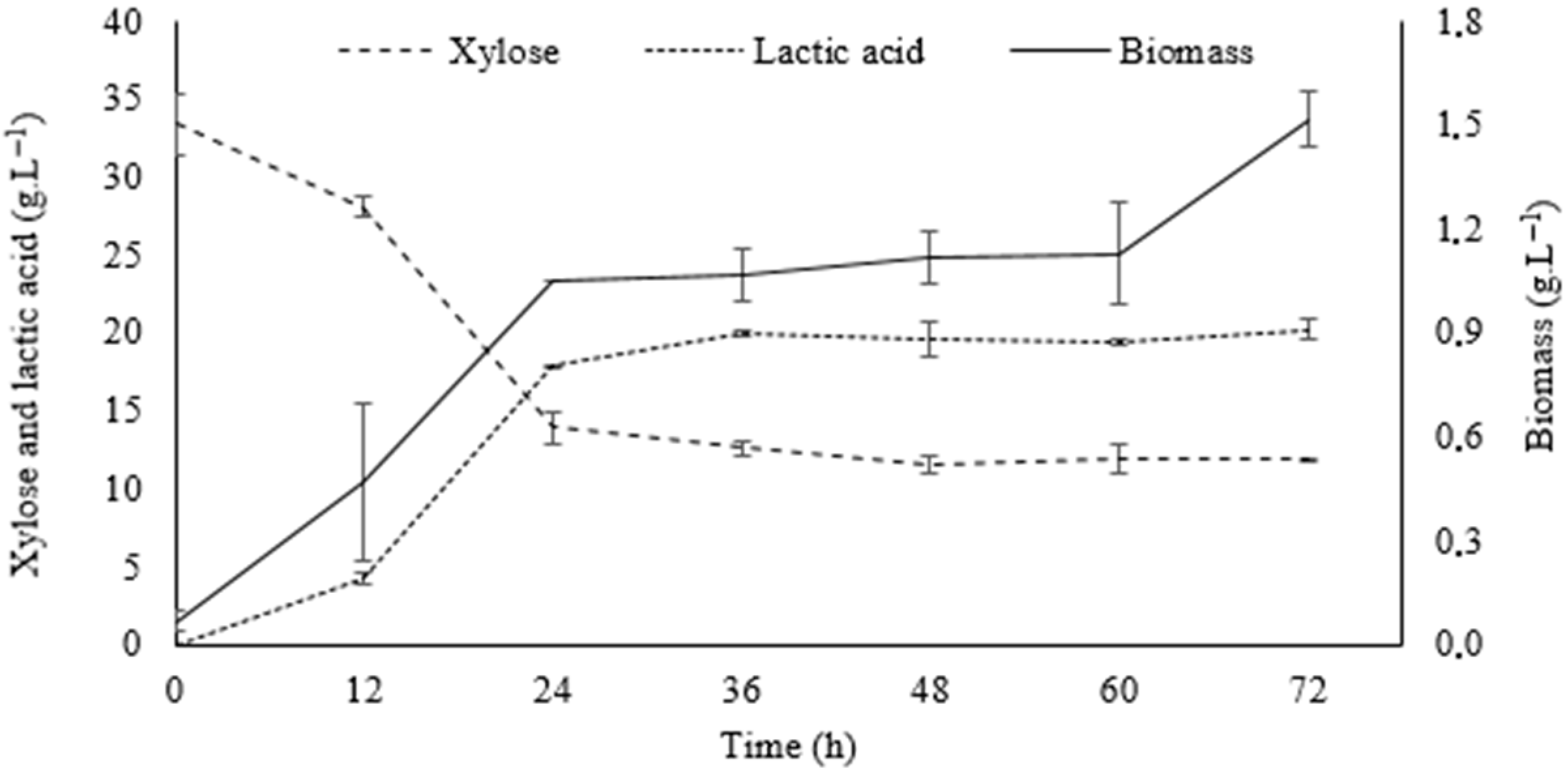
3.6. Validation of Optimal Point and Fermentation Kinetics in Shaker
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Narayanan, N.; Rovychoudhury, P.K.; Srivastava, A. L(+) lactic acid fermentation and its product polymerization. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 7, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, A.; Cirlini, M.; Calani, L.; Bernini, V.; Neviani, E.; Del Rio, D.; Galaverna, G.; Lazzi, C. In vitro metabolism of elderberry juice polyphenols by lactic acid bacteria. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juodeikiene, G.; Vidmantiene, D.; Basinskiene, L.; Cernauskas, D.; Bartkiene, E.; Cizeikiene, D. Green metrics for sustainability of biobased lactic acid from starchy biomass vs chemical synthesis. Catal. Today 2015, 239, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Koubaa, M.; Bals, O.; Vorobiev, E. Recent insights in the impact of emerging technologies on lactic acid bacteria: A review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.; Vandenberghe, L.P.S.; Woiciechowski, A.L.; de Oliveira, J.; Letti, L.A.J.; Soccol, C.R. Production and Application of Lactic Acid. Curr. Dev. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, J.; Aravindan, R.; Viruthagiri, T. Recent Trends in the Production, Purification and Application of Lactic Acid. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q 2008, 22, 245–264. [Google Scholar]
- Ziadi, M.; M’hIr, S.; Aydi, A.; Hamdi, M. Bioreactor Scale-Up and Kinetic Modeling of Lactic Acid and Biomass Production by Enterococcus faecalis SLT13 during Batch Culture on Hydrolyzed Cheese Whey. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grand View Research. Lactic Acid Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report by Raw Material (Sugarcane, Corn, Cassava), by Application (Industrial, F&B, Pharmaceuticals, Personal Care, PLA), and Segment Forecasts, 2018–2025. San Francisco, 2019. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/lactic-acid-and-poly-lactic-acid-market (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Taib, N.-A.A.B.; Rahman, R.; Huda, D.; Kuok, K.K.; Hamdan, S.; Bin Bakri, M.K.; Bin Julaihi, M.R.M.; Khan, A. A review on poly lactic acid (PLA) as a biodegradable polymer. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 1179–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; Tashiro, Y.; Sonomoto, K. Lactic acid production from lignocellulose-derived sugars using lactic acid bacteria: Overview and limits. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 156, 286–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juturu, V.; Wu, J.C. Microbial production of lactic acid: The latest development. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnu, C.; Seenayya, G.; Reddy, G. Direct fermentation of various pure and crude starchy substrates to L(+) lactic acid using Lactobacillus amylophilus GV6. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 18, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandri, M.; Schneider, R.; Mehlmann, K.; Venus, J. Recent Advances in D-Lactic Acid Production from Renewable Resources. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 57, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, L.Y.A. Avaliação Do Potencial Biotecnológico de Linhagens de Lactobacillus spp. Visando a Produção de Ácido D(−) Lático de Segunda Geração. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yankov, D. Fermentative Lactic Acid Production from Lignocellulosic Feedstocks: From Source to Purified Product. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 823005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CONAB. Produção de Cana Chega a 610,1 Milhões de Toneladas Na Safra 2022/23 Com Melhora Na Produtividade Nas Lavouras. Companhia Nacional de Abastecimento. Available online: https://www.conab.gov.br/ultimas-noticias/4977-producao-de-cana-chega-a-610-1-milhoes-de-toneladas-na-safra-2022-23-com-melhora-na-produtividade-nas-lavouras (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Pedreschi, R. Aproveitamento de Bagaço de Cana Da Indústria Sucroalcooleira Na Produção de Painéis de Aglomerados. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal de Lavras, Lavras, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Alokika; Anu; Kumar, A.; Kumar, V.; Singh, B. Cellulosic and hemicellulosic fractions of sugarcane bagasse: Potential, challenges and future perspective. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 169, 564–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U., Jr.; Steele, P.H. Pyrolysis of Wood/Biomass for Bio-oil: A Critical Review. Energy Fuels 2006, 20, 848–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.S.; Patel, S.; Saini, N.; Chen, S. Robust demarcation of 17 distinct Bacillus species clades, proposed as novel Bacillaceae genera, by phylogenomics and comparative genomic analyses: Description of Robertmurraya kyonggiensis sp. nov. and proposal for an emended genus Bacillus limiting it only to the members of the Subtilis and Cereus clades of species. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 5753–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelson, T.; Kask, K.; Jõgi, E.; Talpsep, E.; Suitso, I.; Nurk, A. l(+)-Lactic acid producer Bacillus coagulans SIM-7 DSM 14043 and its comparison with Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. lactis DSM 20073. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2006, 39, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroedter, L.; Streffer, F.; Streffer, K.; Unger, P.; Venus, J. Biorefinery Concept Employing Bacillus coagulans: LX-Lignin and L-(+)-Lactic Acid from Lignocellulose. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; Tashiro, Y.; Sonomoto, K. Recent advances in lactic acid production by microbial fermentation processes. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 877–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Ma, C.; Xu, P. Biotechnological routes based on lactic acid production from biomass. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.Y.; Jin, M.H. Characterization of Weizmannia ginsengihumi LGHNH from Wild-Ginseng and Anti-Aging Effects of Its Cultured Product. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Lett. 2022, 50, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolieng, V.; Tanaka, N.; Shiwa, Y.; Thitiprasert, S.; Kanchanasin, P.; Phongsopitanun, W.; Booncharoen, A.; Thongchul, N.; Tanasupawat, S. Weizmannia acidilactici sp. nov., a lactic acid producing bacterium isolated from soils. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 46, 126389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, P.; Lee, S.; Wang, Y.; Tan, C.; Shang, N. Weizmannia coagulans: An Ideal Probiotic for Gut Health. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Du, L.; Fang, X.; Liao, Z. Application of Weizmannia coagulans in the medical and livestock industry. Ann. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, L.F.; Sass, D.C.; Neto, P.M.A.; Contiero, J. Evaluation of a new method for (L+) lactic acid purification, using ethyl ether. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 26, 101653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitel, S.M.; Coelho, L.F.; Contiero, J. Efficient Conversion of Agroindustrial Waste into D(−) Lactic Acid by Lactobacillus delbrueckii Using Fed-Batch Fermentation. Biomed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 4194052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulitto, M.; Fusco, S.; Bartolucci, S.; Franzén, C.J.; Contursi, P. Bacillus coagulans MA-13: A promising thermophilic and cellulolytic strain for the production of lactic acid from lignocellulosic hydrolysate. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, G.; Patel, M.; Gill, S.R. Draft Genome Sequence of Weizmannia coagulans MB BCM9, a Stable Spore-Forming Probiotic. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2023, 12, e0121222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.P.N.; Banerjee, A.; Liu, G.-H.; Thamchaipenet, A. Genome-based reclassification of Bacillus acidicola, Bacillus pervagus and the genera Heyndrickxia, Margalitia and Weizmannia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2023, 73, 005961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamueangmun, P.; Abdullahi, A.D.; Kabir, H.; Unban, K.; Kanpiengjai, A.; Venus, J.; Shetty, K.; Saenjum, C.; Khanongnuch, C. Lignocellulose Degrading Weizmannia coagulans Capable of Enantiomeric L-Lactic Acid Production via Consolidated Bioprocessing. Fermentation 2023, 9, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tang, Z.; Li, W.; Deng, X.; Yu, L.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, W.; Guo, X.; et al. Weizmannia coagulans BCF-01: A novel gastrogenic probiotic for Helicobacter pylori infection control. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2313770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewska-Widdrat, A.; Babor, M.; Höhne, M.M.-C.; Alexandri, M.; López-Gómez, J.P.; Venus, J. A mathematical model-based evaluation of yeast extract’s effects on microbial growth and substrate consumption for lactic acid production by Bacillus coagulans. Process Biochem. 2024, 146, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, W.; Luo, J.; Wan, Y. Exploring the potential of lactic acid production from lignocellulosic hydrolysates with various ratios of hexose versus pentose by Bacillus coagulans IPE22. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 261, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Cai, C.; Jiang, T.; Zhao, M.; Ouyang, J. Enhanced l-Lactic Acid Production from Biomass-Derived Xylose by a Mutant Bacillus coagulans. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 173, 1896–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Qiao, H.; Zheng, Z.; Chu, Q.; Li, X.; Yong, Q.; Ouyang, J.; Yang, S. Lactic Acid Production from Pretreated Hydrolysates of Corn Stover by a Newly Developed Bacillus coagulans Strain. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wang, Z.; Miao, H.; Yu, C.; Zheng, Z.; Ouyang, J. Rapid adaptive evolution of Bacillus coagulans to undetoxified corncob hydrolysates for lactic acid production and new insights into its high phenolic degradation. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 383, 129246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Zhou, X.; Bin Hudari, M.S.; Li, Z.; Wu, J.C. Highly efficient production of l-lactic acid from xylose by newly isolated Bacillus coagulans C106. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 132, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Komiyama, A.; Sonomoto, K.; Ishizaki, A.; Hall, S.; Stanbury, P. Two different pathways for D -xylose metabolism and the effect of xylose concentration on the yield coefficient of L -lactate in mixed-acid fermentation by the lactic acid bacterium Lactococcus lactis IO-1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 60, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Ni, Z.; Shao, M.; Han, M.; Huang, D.; Liu, F. Heterologous expression and biochemical characterization of a thermostable xylulose kinase from Bacillus coagulans IPE22. J. Basic Microbiol. 2019, 59, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yang, M.; Qi, B.; Chen, X.; Su, Z.; Wan, Y. Optimizing l-(+)-lactic acid production by thermophile Lactobacillus plantarum As.1.3 using alternative nitrogen sources with response surface method. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 52, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancib, N.; Nancib, A.; Boudjelal, A.; Benslimane, C.; Blanchard, F.; Boudrant, J. The effect of supplementation by different nitrogen sources on the production of lactic acid from date juice by Lactobacillus casei subsp. Rhamnosus. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 78, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madigan, M.T.; Bender, K.S.; Buckley, D.H.; Sattley, W.M.; Stahl, D.A. Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 15th ed.; Pearson Education Limited: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, J.; Ma, R.; Zheng, Z.; Cai, C.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, T. Open fermentative production of l-lactic acid by Bacillus sp. strain NL01 using lignocellulosic hydrolyzates as low-cost raw material. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 135, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, B.; Liu, B.; Yu, B.; Ma, C.; Su, F.; Hua, D.; Li, Q.; Ma, Y.; Xu, P. Efficient production of l-lactic acid from corncob molasses, a waste by-product in xylitol production, by a newly isolated xylose utilizing Bacillus sp. strain. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7908–7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Leonid, N.; Wan-Taek, I.; Sang-Hoon, B.; Lee, J.-S.; Oh, H.-M.; Lee, S.-T. Bacillus ginsengihumi sp. nov., a Novel Species Isolated from Soil of a Ginseng Field in Pocheon Province, South Korea. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 16, 1554–1560. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.; Ten, L.N.; Baek, S.-H.; Im, W.-T.; Aslam, Z.; Lee, S.-T. Paenibacillus ginsengisoli sp. nov., a novel bacterium isolated from soil of a ginseng field in Pocheon province, South Korea. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2007, 91, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

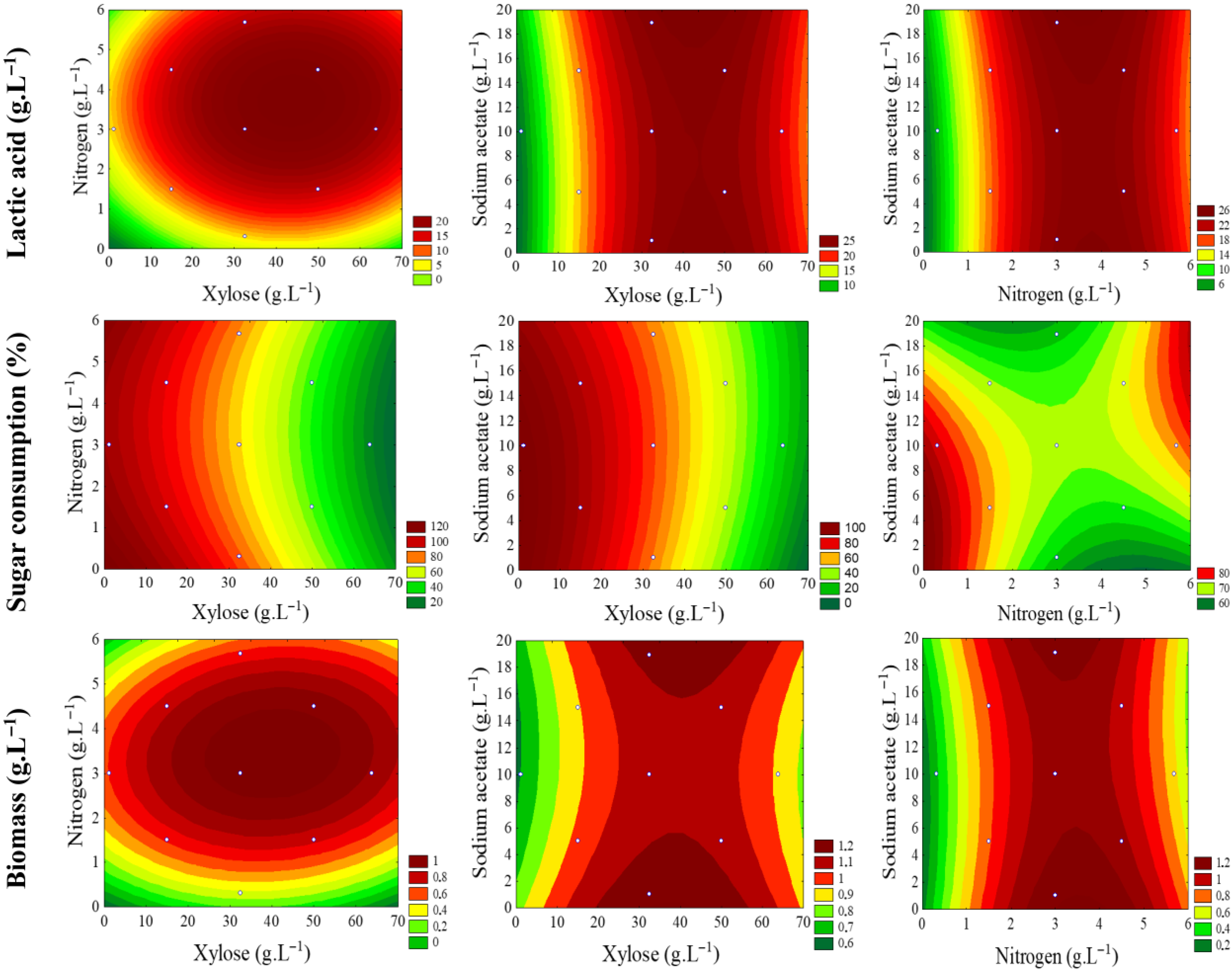
| Trials | Carbon Source (X1) | Nitrogen Source (X2) | Sodium Acetate (X3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coded Level | Real Values (g·L−1) | Coded Level | Real Values (g·L−1) | Coded Level | Real Values g·L−1 | |
| 1 | −1 | 15 | −1 | 1.5 | −1 | 5 |
| 2 | −1 | 15 | −1 | 1.5 | 1 | 15 |
| 3 | −1 | 15 | 1 | 4.5 | −1 | 5 |
| 4 | −1 | 15 | 1 | 4.5 | 1 | 15 |
| 5 | 1 | 50 | −1 | 1.5 | −1 | 5 |
| 6 | 1 | 50 | −1 | 1.5 | 1 | 15 |
| 7 | 1 | 50 | 1 | 4.5 | −1 | 5 |
| 8 | 1 | 50 | 1 | 4.5 | 1 | 15 |
| 9 | 0 | 32.5 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 10 |
| 10 | 0 | 32.5 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 10 |
| 11 | −1.788 | 1.19 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 10 |
| 12 | 1.788 | 63.8 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 10 |
| 13 | 0 | 32.5 | −1.788 | 0.31 | 0 | 10 |
| 14 | 0 | 32.5 | 1.788 | 5.68 | 0 | 10 |
| 15 | 0 | 32.5 | 0 | 3 | −1.788 | 1.05 |
| 16 | 0 | 32.5 | 0 | 3 | 1.788 | 18.94 |
| 17 | 0 | 32.5 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 10 |
| 18 | 0 | 32.5 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 10 |
| Strain | Accession Number | Coverage (%) | Percentage of Similarity (%) | Scientific Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI | KF600778.1 | 95 | 97.46 | Weizmannia ginsengihumi |
| BMAI | CP058594.1 | 99 | 96.81 | Weizmannia coagulans |
| BLMI | AB680332.1 | 96 | 97.49 | Weizmannia coagulans |
| B2L1 | MT538507.1 | 96 | 97.49 | Weizmannia coagulans |
| BUGC | CP058594.1 | 95 | 97.64 | Weizmannia coagulans |
| B07 | CP033687.1 | 98 | 97.27 | Weizmannia coagulans |
| B03 | KF600778.1 | 96 | 97.64 | Weizmannia ginsengihumi |
| BUSI | CP058594.1 | 96 | 97.92 | Weizmannia coagulans |
| Trials | Variables (g·L−1) | Responses (g·L−1) | Productivity (g/L/h) | Product-to-Biomass Conversion (g/g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 | |||
| Xylose | Nitrogen | Sodium Acetate | Lactic Acid | Biomass | Residual Sugar | |||
| 1 | 15.0 | 1.50 | 5.00 | 14.96 | 0.69 | 0.10 | 0.31 | 21.68 |
| 2 | 15.0 | 1.50 | 15.00 | 16.36 | 0.61 | 2.96 | 0.34 | 26.82 |
| 3 | 15.0 | 4.50 | 5.00 | 17.18 | 0.61 | 0.22 | 0.36 | 28.16 |
| 4 | 15.0 | 4.50 | 15.00 | 16.66 | 0.55 | 0.12 | 0.35 | 30.29 |
| 5 | 50.0 | 1.50 | 5.00 | 19.84 | 0.66 | 34.64 | 0.41 | 30.06 |
| 6 | 50.0 | 1.50 | 15.00 | 19.56 | 0.73 | 37.10 | 0.41 | 26.79 |
| 7 | 50.0 | 4.50 | 5.00 | 21.92 | 0.79 | 30.32 | 0.46 | 27.75 |
| 8 | 50.0 | 4.50 | 15.00 | 21.64 | 0.65 | 30.70 | 0.45 | 33.29 |
| 9 | 32.5 | 3.00 | 10.00 | 23.02 | 0.81 | 11.86 | 0.48 | 28.42 |
| 10 | 32.5 | 3.00 | 10.00 | 22.94 | 0.92 | 13.36 | 0.48 | 24.93 |
| 11 | 1.19 | 3.00 | 10.00 | 2.50 | 0.67 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 3.73 |
| 12 | 63.8 | 3.00 | 10.00 | 23.38 | 1.09 | 37.76 | 0.49 | 21.45 |
| 13 | 32.5 | 0.31 | 10.00 | 0.34 | 0.17 | 32.90 | 0.01 | 2.00 |
| 14 | 32.5 | 5.68 | 10.00 | 22.76 | 1.01 | 11.22 | 0.47 | 22.53 |
| 15 | 32.5 | 3.00 | 1.050 | 22.34 | 1.28 | 12.46 | 0.47 | 17.45 |
| 16 | 32.5 | 3.00 | 18.94 | 25.28 | 1.30 | 8.38 | 0.53 | 19.45 |
| 17 | 32.5 | 3.00 | 10.00 | 24.22 | 1.28 | 9.16 | 0.50 | 18.92 |
| 18 | 32.5 | 3.00 | 10.00 | 25.20 | 1.20 | 6.34 | 0.53 | 21.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, L.P.; Yoshimura, I.; Andrade, F.B.d.; Contiero, J. Biotechnological Potential of Weizmannia ginsengihumi in the Conversion of Xylose into Lactic Acid: A Sustainable Strategy. Fermentation 2025, 11, 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080447
Santos LP, Yoshimura I, Andrade FBd, Contiero J. Biotechnological Potential of Weizmannia ginsengihumi in the Conversion of Xylose into Lactic Acid: A Sustainable Strategy. Fermentation. 2025; 11(8):447. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080447
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Larissa Provasi, Ingrid Yoshimura, Fernanda Batista de Andrade, and Jonas Contiero. 2025. "Biotechnological Potential of Weizmannia ginsengihumi in the Conversion of Xylose into Lactic Acid: A Sustainable Strategy" Fermentation 11, no. 8: 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080447
APA StyleSantos, L. P., Yoshimura, I., Andrade, F. B. d., & Contiero, J. (2025). Biotechnological Potential of Weizmannia ginsengihumi in the Conversion of Xylose into Lactic Acid: A Sustainable Strategy. Fermentation, 11(8), 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080447






