Effect of Ohmic Heating Pretreatment on Enzyme Production by Solid-State Fermentation of Brewer’s Spent Grain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganism
2.2. Raw Materials
2.3. Substrate Pretreatment and Inoculation
2.4. Extraction
2.5. Enzymatic Assays
2.5.1. Endo-1,4-β-Glucanase
2.5.2. Xylanase
2.5.3. Amylase
2.5.4. Pectinase
2.5.5. β-Glucosidase
2.5.6. Protease
2.6. Analytical Methods
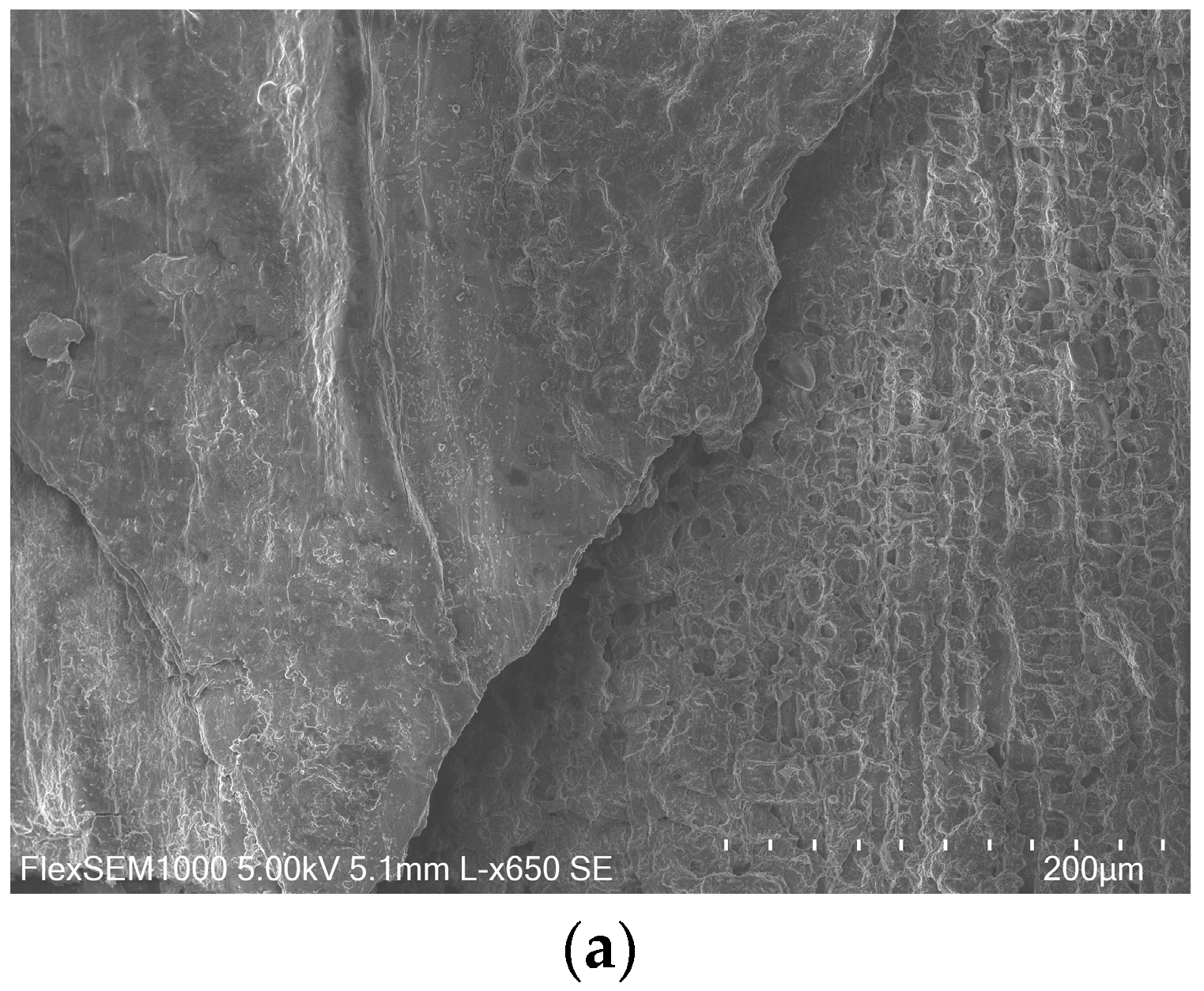
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
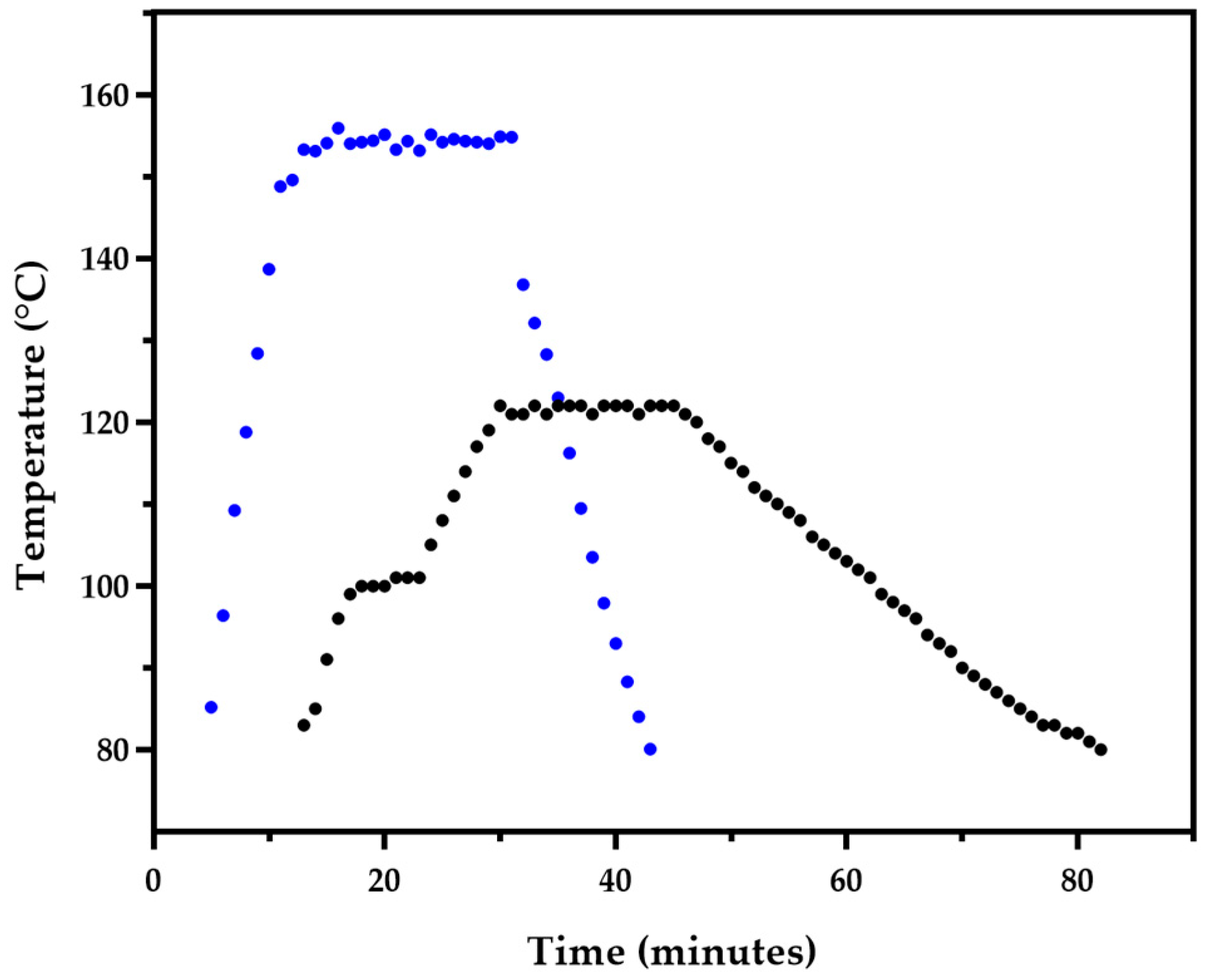
3.1. BSG Pretretatment
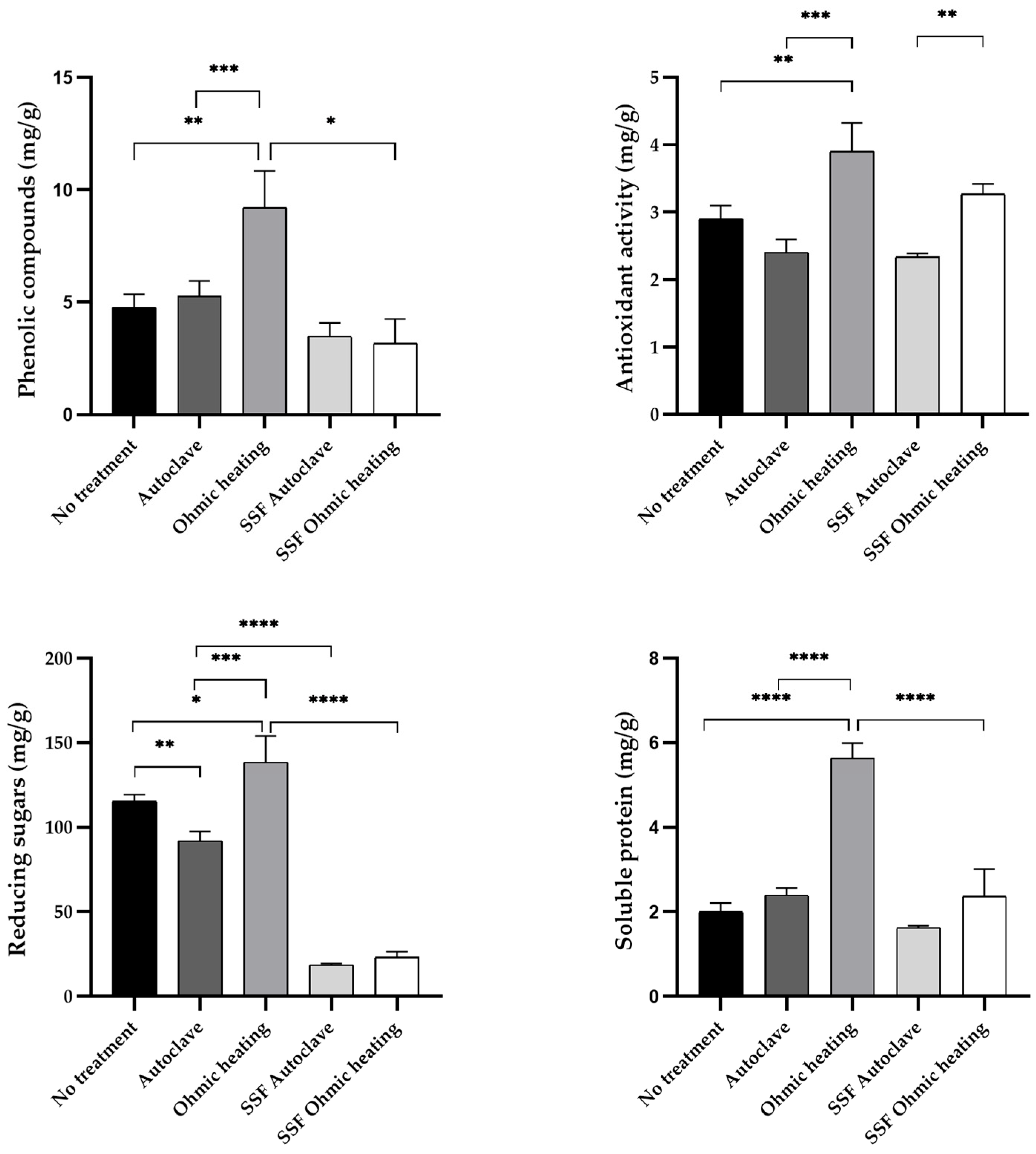
3.2. Substrate Characterization Before and After Fermentation
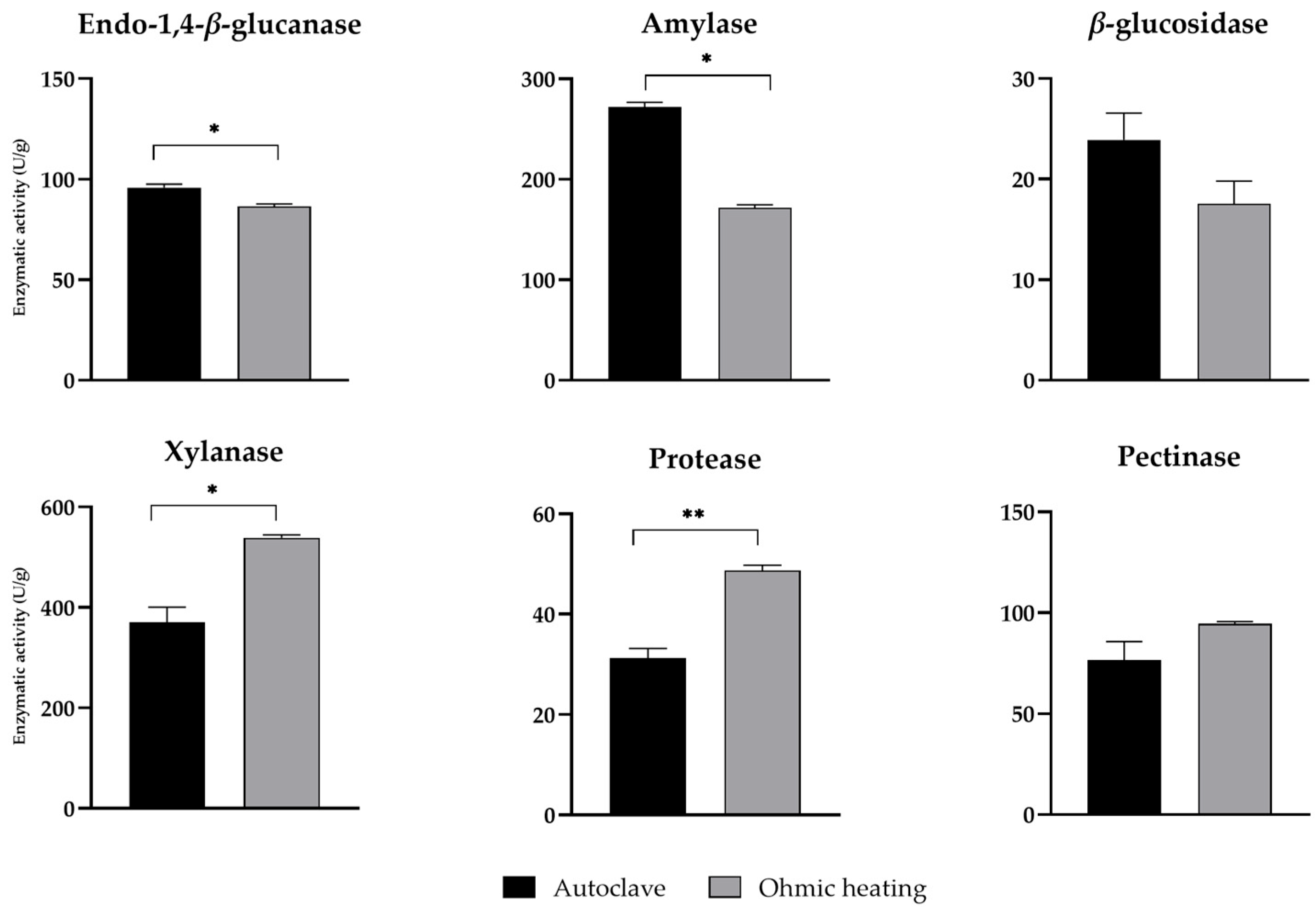
3.3. Enzymatic Activity After Fermentation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SSF | Solid-state fermentation |
| BSG | Brewer’s spent grain |
| OH | Ohmic heating |
| CECT | Coleción Española de Cultivos Tipo |
| CMC | Carboxymethylcellulose |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| DNS | Dinitrosalicylic acid |
| DPPH | 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
References
- Abd El Aty, A.A.; Saleh, S.A.A.; Eid, B.M.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Mostafa, F.A. Thermodynamics Characterization and Potential Textile Applications of Trichoderma Longibrachiatum KT693225 Xylanase. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 14, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegannathan, K.R.; Nielsen, P.H. Environmental Assessment of Enzyme Use in Industrial Production—A Literature Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 42, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Kumar, M.; Mittal, A.; Mehta, P.K. Microbial Enzymes: Industrial Progress in 21st Century. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raveendran, S.; Parameswaran, B.; Ummalyma, S.B.; Abraham, A.; Mathew, A.K.; Madhavan, A.; Rebello, S.; Pandey, A. Applications of Microbial Enzymes in Food Industry. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 56, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, C. Solid-State Fermentation Systems—An Overview. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2005, 25, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intasit, R.; Cheirsilp, B.; Suyotha, W.; Boonsawang, P. Synergistic Production of Highly Active Enzymatic Cocktails from Lignocellulosic Palm Wastes by Sequential Solid State-Submerged Fermentation and Co-Cultivation of Different Filamentous Fungi. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 173, 108086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R. The Outlook for Population Growth. Science (1979) 2011, 333, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussatto, S.I. Brewer’s Spent Grain: A Valuable Feedstock for Industrial Applications. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, A.; Mota, A.C.; Pereira, A.S.; Fernandes, A.M.; Lopes, M.; Belo, I. Rice Husk, Brewer’s Spent Grain, and Vine Shoot Trimmings as Raw Materials for Sustainable Enzyme Production. Materials 2024, 17, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picot-Allain, C.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Ak, G.; Zengin, G. Conventional versus Green Extraction Techniques—A Comparative Perspective. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 40, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavahian, M.; Sastry, S.; Farhoosh, R.; Farahnaky, A. Chapter Six—Ohmic Heating as a Promising Technique for Extraction of Herbal Essential Oils: Understanding Mechanisms, Recent Findings, and Associated Challenges. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Toldrá, F., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 91, pp. 227–273. [Google Scholar]
- Doan, N.K.; Lai, D.Q.; Le, T.K.P. Ohmic Heating: Its Current and Future Application in Juice Processing. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 6908–6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, F.; Machado, L.; Silva, J.; Pereira, R.N.; Vicente, A. Effect of Ohmic Heating on the Extraction of Biocompounds from Aqueous and Ethanolic Suspensions of Pavlova Gyrans. Food Bioprod. Process. 2024, 148, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talha, M.; Khalid, S.; Maan, A.A.; Tanveer, N.; Khan, M.K.I.; Asif, M.; Arif, S.; Sarwar, A. Ohmic Assisted Extraction: A Sustainable and Environment Friendly Approach to Substitute Conventional Extraction Methods. Food Rev. Int. 2024, 40, 3508–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavahian, M.; Tiwari, B.K. Moderate Electric Fields and Ohmic Heating as Promising Fermentation Tools. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 64, 102422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, J.; Kupetz, M.; Becker, T. Influence of Hydrothermal Treatment of Brewer’s Spent Grain on the Concentration and Molecular Weight Distribution of 1,3-1,4-β-D-Glucan and Arabinoxylan. Foods 2023, 12, 3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, R.T.; Pereira, R.S.; Rodrigues, R.M.; Pereira, R.N. Characterization and Kinetics of Whey Protein Isolate Amyloid Fibril Aggregates under Moderate Electric Fields. Food Res. Int. 2024, 196, 115033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalheiro, F.; Garrote, G.; Parajó, J.C.; Pereira, H.; Gírio, F.M. Kinetic Modeling of Breweryapos; s Spent Grain Autohydrolysis. Biotechnol. Prog. 2005, 21, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalheiro, F.; Esteves, M.P.; Parajó, J.C.; Pereira, H.; Gırio, F.M. Production of Oligosaccharides by Autohydrolysis of Brewery’s Spent Grain. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 91, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.L. Use of Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent for Determination of Reducing Sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, S.M.; Lopes, M.; Belo, I. Exploring the Use of Hexadecane by Yarrowia Lipolytica: Effect of Dissolved Oxygen and Medium Supplementation. J. Biotechnol. 2024, 380, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulf, F.V.; Vodnar, D.C.; Dulf, E.-H.; Toşa, M.I. Total Phenolic Contents, Antioxidant Activities, and Lipid Fractions from Berry Pomaces Obtained by Solid-State Fermentation of Two Sambucus Species with Aspergillus Niger. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3489–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estevão-Rodrigues, T.; Fernandes, H.; Moutinho, S.; Filipe, D.; Fontinha, F.; Magalhães, R.; Couto, A.; Ferreira, M.; Gamboa, M.; Castro, C.; et al. Effect of Solid-State Fermentation of Brewer’s Spent Grain on Digestibility and Digestive Function of European Seabass (Dicentrarchus Labrax) Juveniles. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2024, 315, 116018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliiski, N.; Niemz, P.; Angelski, D.; Vitchev, P.; Tumbarkova, N. Computing the Thermal Efficiency of Autoclaves during Steaming of Frozen Prisms for Veneer Production at Changing Operational Conditions. Processes 2023, 11, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, P.; Sousa, D.; Fernandes, H.; Ferreira, M.; Costa, A.R.; Filipe, D.; Gonçalves, M.; Peres, H.; Belo, I.; Salgado, J.M. Recent Advances in Production of Lignocellulolytic Enzymes by Solid-State Fermentation of Agro-Industrial Wastes. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 27, 100407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edo, G.I.; Nwachukwu, S.C.; Ali, A.B.M.; Yousif, E.; Jikah, A.N.; Zainulabdeen, K.; Ekokotu, H.A.; Isoje, E.F.; Igbuku, U.A.; Opiti, R.A.; et al. A Review on the Composition, Extraction and Applications of Phenolic Compounds. Ecol. Front. 2025, 45, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdyło, A.; Oszmiański, J.; Czemerys, R. Antioxidant Activity and Phenolic Compounds in 32 Selected Herbs. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, L.T.P.; Choi, Y.-S.; Bae, H.-J. Production of Phenolic Compounds and Biosugars from Flower Resources via Several Extraction Processes. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2018, 125, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Chen, G. Regulation of Phenolic Release in Corn Seeds (Zea Mays, L.) for Improving Their Antioxidant Activity by Mix-Culture Fermentation with Monascus Anka, Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Bacillus Subtilis. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 325, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Ling, T.; Su, X.; Jiang, B.; Nian, B.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Mu, Y.; et al. Integrated Proteomics and Metabolomics Analysis of Tea Leaves Fermented by Aspergillus Niger, Aspergillus Tamarii and Aspergillus Fumigatus. Food Chem. 2021, 334, 127560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, W.; Zhang, P.; Ying, D.; Adhikari, B.; Fang, Z. Fermentation Transforms the Phenolic Profiles and Bioactivities of Plant-Based Foods. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 49, 107763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulf, F.V.; Vodnar, D.C.; Socaciu, C. Effects of Solid-State Fermentation with Two Filamentous Fungi on the Total Phenolic Contents, Flavonoids, Antioxidant Activities and Lipid Fractions of Plum Fruit (Prunus domestica, L.) by-Products. Food Chem. 2016, 209, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Yi, L.; Marek, P.; Iverson, B.L. Commercial Proteases: Present and Future. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.M.; Kumar, R.; Panwar, S.; Kumar, A. Microbial Alkaline Proteases: Optimization of Production Parameters and Their Properties. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2017, 15, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Wu, Q.; Hua, L. 3.01—Industrial Enzymes. In Comprehensive Biotechnology, 3rd ed.; Moo-Young, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos Costa, R.; de Almeida, S.S.; d’Avila Costa Cavalcanti, E.; Freire, D.M.G.; Moura-Nunes, N.; Monteiro, M.; Perrone, D. Enzymes Produced by Solid State Fermentation of Agro-Industrial by-Products Release Ferulic Acid in Bioprocessed Whole-Wheat Breads. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 109843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scapini, T.; dos Santos, M.S.N.; Bonatto, C.; Wancura, J.H.C.; Mulinari, J.; Camargo, A.F.; Klanovicz, N.; Zabot, G.L.; Tres, M.V.; Fongaro, G.; et al. Hydrothermal Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass for Hemicellulose Recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 342, 126033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Enzymes Market in Industrial Applications. Available online: https://www.bccresearch.com/market-research/biotechnology/global-markets-for-enzymes-in-industrial-applications.html (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Saldarriaga-Hernández, S.; Velasco-Ayala, C.; Leal-Isla Flores, P.; de Jesús Rostro-Alanis, M.; Parra-Saldivar, R.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Carrillo-Nieves, D. Biotransformation of Lignocellulosic Biomass into Industrially Relevant Products with the Aid of Fungi-Derived Lignocellulolytic Enzymes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 1099–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, B.F.; Machado, L.; Fernandes, A.M.; Pereira, R.N.; Belo, I. Effect of Ohmic Heating Pretreatment on Enzyme Production by Solid-State Fermentation of Brewer’s Spent Grain. Fermentation 2025, 11, 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080421
Silva BF, Machado L, Fernandes AM, Pereira RN, Belo I. Effect of Ohmic Heating Pretreatment on Enzyme Production by Solid-State Fermentation of Brewer’s Spent Grain. Fermentation. 2025; 11(8):421. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080421
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Bruna F., Luís Machado, Ana M. Fernandes, Ricardo N. Pereira, and Isabel Belo. 2025. "Effect of Ohmic Heating Pretreatment on Enzyme Production by Solid-State Fermentation of Brewer’s Spent Grain" Fermentation 11, no. 8: 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080421
APA StyleSilva, B. F., Machado, L., Fernandes, A. M., Pereira, R. N., & Belo, I. (2025). Effect of Ohmic Heating Pretreatment on Enzyme Production by Solid-State Fermentation of Brewer’s Spent Grain. Fermentation, 11(8), 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080421





