Abstract
In contact with water, chia seeds release mucilage (MC), which is a source of various health-promoting compounds including dietary fibres. MC has been previously used as a thickening agent in cow milk yoghurt, but there are no available data on its application in goat milk. In this study, three goat milk yoghurts (without—MC0, with 1.5%—MC15 and with 3% mucilage—MC30) were produced. The rheology, texture, microbial counts, syneresis, microstructure and sensory acceptance of the yoghurts were investigated. The MC addition resulted in a reduced hysteresis area, but increased yoghurt viscosity at lower shear rates. It also improved all texture parameters at both concentration levels, while syneresis values were reduced only in sample MC30. The MC addition promoted lactobacilli viability in both supplemented yoghurts. The texture perceived by sensory evaluation was rated the highest for the sample MC30, which was also the most accepted by consumers overall. Critical attributes that reduced the acceptability of all yoghurts were flavour and acidity. In conclusion, chia seed mucilage can be used as a functional ingredient in goat milk yoghurt to produce an innovative dairy product and meet consumer expectations.
1. Introduction
Goat milk is recognised as a nutritious food with positive effects on human health. The demand for this type of milk and its products is constantly increasing, due to the growing interest in artisanal products and the preference of health-conscious consumers. The main components of goat milk are present in a more favourable form and ratio than in cow’s milk. For example, the fat globules in goat milk are smaller and more uniform, which makes this type of milk more digestible; the proportion of caseins and serum proteins is more favourable, the risk of allergies is lower and the content of various nutrients is higher [1,2,3].
Fermented dairy products are excellent carriers of functional ingredients that have a positive effect on human health. However, achieving an acceptable texture and stability of yoghurts made from goat’s milk is often a challenge for manufacturers due to the specific protein profile of goat’s milk, especially the low or absent content of αs1 casein, a protein responsible for the firm texture and favourable consistency of goat yoghurt [3]. Forecasts show that yoghurt is the fastest growing dairy product, both in terms of financial value and volume, underlining the potential of convenience consumption. The market for this dairy product is expected to grow by 6.95% annually (CAGR 2024-2028) [4]. Various plant-based ingredients are used in yoghurts to increase the nutritional value and health benefits. However, these hybrid products are often not accepted from a sensory point of view: fermented sheep milk with collagen exhibited off-taste and odour [5], and 1% spirulina supplementation caused an unacceptable flavour, colour change and graininess of the yoghurt [6]. On the other hand, mucilage from chia seeds (MC) is characterised by a neutral, discrete nutty taste, and has proven to be a food thickener with high nutritional value [7].
Chia seed mucilage, which is obtained from the outer layers of chia seeds, is considered a new functional ingredient with great potential for the food industry [8]. It consists of branched polysaccharides, composed of xylose, mannose, glucose, galactose, arabinose and uronic acids (glucuronic and galacturonic acids) linked by glycosidic bonds. Other components such as proteins, ω-3 fatty acid-rich fats and ash are also found in MC [9]. MC represents a promising source of hydrocolloids, offering diverse and desirable functional characteristics, including water absorption capacity, emulsifying and foaming properties, and high solubility in both cold and hot water [8]. It has been demonstrated that mucilages can be successfully used as thickening agents in foods by increasing the flexibility and viscosity of the continuous phase, while their heteropolysaccharides provide a fermentable carbon source [10].
The seeds’ mucilage has a prebiotic effect, which has been confirmed by several in vitro studies. It was reported that basil seed mucilage exhibits prebiotic properties and stimulates the growth of lactic acid bacteria both in vivo and in vitro [11]. Tamarillo seed mucilage also demonstrated probiotic activity, resistance to digestive enzymes and a stimulatory effect on the growth of beneficial gut microbiota, while showing an inhibitory effect on some pathogenic bacteria [12]. Chia mucilage contains planteose, a health-promoting galactosyl sucrose oligosaccharide (GSO). GSOs, first identified in psyllium, are prebiotics that stimulate the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract [13]. Chia seed mucilage provides dietary fibres as well as macro- and micronutrients, but also highly valuable polysaccharides that can effectively lower the glycemic index of foods and regulate satiety [9].
To date, several studies have confirmed that chia seed mucilage is a suitable stabilizer for cow milk yoghurt as it improves firmness, viscosity and consistency [14,15,16]. However, to our knowledge, there are no published studies investigating the effects of chia seed mucilage on the properties of goat milk yoghurt. Thus, in order to assess the suitability of chia seed mucilage as a stabilizer in goat milk yoghurt, the aim of this study was to examine the impact of MC addition on the texture, syneresis, flow behaviour, starter bacteria count and sensory acceptability of yoghurt.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chia Seed Mucilage Extraction
The mucilage was extracted from chia seeds (Salvia hispanica L.) (purchased at the local market, imported from the Netherlands) using a cold extraction by distilled water (at room temperature; chia seeds: water weight ratio of 1:40) for two hours. Separation of chia mucilage was performed by SJE 741SS juicer (SENCOR, Tokyo, Japan), with two passages of the seeds through the juicer. The extracted chia mucilage was mixed with 5% w/v of inulin, which served as a drying aid (Cosucra, Warcoing, Belgium). This mixture was spread in a 2 cm thick layer and dried in the laboratory oven (UF 55, Memmert, Schwabach, Germany) at 70 °C until it was completely dry. Dried mucilage was collected, vacuum packed and stored at 4 °C until further use. The dried mucilage was ground in a mill to obtain a powdered product that was measured and added to the milk before heat treatment. The yield of chia seed mucilage was calculated following the procedure by Wang et al. [17] with some modifications. Briefly, after the extraction, chia mucilage was dried at 105 °C to the constant weight. The chia seed mucilage yield (%) was calculated as the ratio between the dry weight mucilage and the weight of seed used for mucilage extraction.
Dietary fibre content of mucilage was analysed according to the standard AOAC 985.29:2003 method [18], following a procedure previously described by Cvetkovic et al. [19], using a gravimetric method after enzymatic digestion. First, the sample underwent treatment with α-amylase in a 100 °C water bath to gelatinize, hydrolyze and depolymerize starch. Next, protease was applied in a 60 °C water bath to solubilize and break down proteins, followed by amyloglucosidase treatment at the same temperature to convert starch fragments into glucose. Each sample was analysed in duplicates. Ethyl alcohol was then used to precipitate soluble fibre, removing depolymerized proteins and starch-derived glucose. The resulting residue was washed with ethyl alcohol and acetone, dried and weighed. The residue was further analysed for residual proteins and ashes. Finally, the total fibre content was calculated by subtracting the weight of ash and residual protein from the initial sample weight, standardized to 100 g of sample.
2.2. Preliminary Experiments
Preliminary tests were carried out to determine the lower and higher MC content to be used in the main trial (Tables S1 and S2 in the Supplementary Material). For this purpose, six goat milk yoghurts with different MC concentrations (0.5% w/w, 1% w/w, 1.5% w/w, 2% w/w, 3% and 4% w/w) and a control, without mucilage (MC0), were prepared. One day after production, the texture of the yoghurts was analysed with a texture analyser, and a sensory evaluation of the yoghurts was carried out by panellists experienced in the quality assessment of goat milk products. The results showed that MC concentrations below 1.5% had no effect on the texture parameters and did not result in any sensory-perceptible differences, while 1.5% and 2% resulted in comparable values for the same parameters. In this context, 1.5% w/w MC was chosen as the lower and 3% w/w MC as the higher concentration to further investigate the effects of their application on different properties of goat milk yoghurt. Concentrations higher than 3% w/w MC were not considered due to the occurrence of off-flavour.
2.3. Milk Preparation and Yoghurt Production
Raw goat milk (3.3 ± 0.1% w/w milk fat, 2.41 ± 0.05% w/w protein, 10.83 ± 0.80% w/w dry matter, pH 6.7) was obtained from a local farm of Alpine goats. For each trial, 6 L of raw milk was collected and the experiment was repeated three times in succession. Milk was divided into three batches, the control batch MC0 (without addition) and two batches supplemented with mucilage powder MC15 (with 1.5% w/w) and MC30 (with 3% w/w). After adding the powder, the milk was thoroughly mixed for 2 min and hydrated for 2 h. The control milk and the prepared mixtures were pasteurized at 90 °C/5 min, immediately cooled to 43 °C and inoculated with the starter culture Yoflex L811 (Chr Hansen, Nieuwegein, The Netherlands), containing Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus strains (0.1% w/v). The inoculated milk was incubated in covered glass jars (approx. 2 L each) in a thermostat at 43 °C until a pH value of 4.6 was reached. The yoghurt samples (MC0, MC15 and MC30) were cooled to 28 °C and stirred uniformly. The yoghurts were then filled into glass bottles, sealed with aluminium caps, cooled to 4–7 °C in the refrigerator and stored for 21 days. The yoghurt production was repeated three times.
2.4. Rheological Measurements
The rheological properties of stirred yoghurt samples were analysed one day after the yoghurt production using a rheometer (Kinexus Pro+, Malvern, UK) with a four-blade vane as a tool. The amount of yoghurt required to fill the lower geometry was poured into it (approximately 37 mL) and the measurement was carried out at 8 °C.
The thixotropy (shear thinning property) of the yoghurts was investigated by measuring the area between the upward and downward flow curves obtained by linearly increasing and decreasing the shear rate over time (from 0 to 100 s−1 for 5 min) and recording the shear stress. This hysteresis loop area was calculated using software (Origin 8.0, OriginLab Corp., Northampton, MA, USA) as the difference of the area under the increasing and decreasing flow curves [20,21]. The Herschel–Bulkley model (Equation (1)) was used to describe the flow curves. Apparent viscosity was calculated based on the fitted data at shear rates of 10 s−1, 50 s−1 and 100 s−1 from Equation (2). The range of shear rates in this study was chosen according to Conti-Silva et al. [22], who investigated the rheology of liquid and semi-solid materials, including yoghurt. In addition, Ross et al. [23] found strong correlations between the shear rheology at the same shear rates and the sensory properties of fluids thickened with hydrocolloids.
τ0—yield stress, τ—shear stress, K—consistency coefficient, n—flow behaviour index, η—apparent viscosity, γ—shear rate.
τ = τ0 + Kγn,
η = τ0/γ + Kγ(n−1),
2.5. Texture Analysis
The texture of the yoghurts was analysed at 8 °C after 1 and 21 days of storage using a back extrusion test on the TA.XT Plus texture analyser (Stable Micro Systems, Godalming, UK). A 5 kg load cell was used and a probe with a 35 mm diameter cell disk (A/BE) moving at a speed of 0.001 m s−1 was immersed 30 mm into the sample and then returned to its original position. The Exponent program calculated the following parameters from the diagrams obtained: firmness (g), consistency (g·s), cohesiveness (g) and viscosity index (g·s). For each sample, at least five repetitions of the analysis were carried out at each measuring point.
2.6. Microbiological Analysis
For the viable cell count enumeration of commercial starter cultures, 10 mL of yoghurt was diluted in 90 mL of sterile NaCl solution (0.85%) under sterile conditions and homogenized during 2 min in a stomacher (Interlab, BagMixer 400P, San Diego, CA, USA), after which ten-fold dilutions were prepared. For enumeration of lactobacilli, appropriate dilution was pour plated on MRS agar (Merck, Darmastad, Germany), while the M17 agar supplemented with 0.5% of glucose was used for the enumeration of Streptococcus thermophilus. Plates were incubated at 42 °C, whereby the MRS plates were incubated anaerobically (GasPak, BBL, Mesa, AZ, USA). The viable cell count of starter cultures was calculated using formula Colony Forming Units (CFU) = Number of colonies × Dilution factor. Cell count of S. thermophilus and L. bulgaricus was carried out in triplicates after 1, 10 and 21 days of storage at 4 °C [24].
2.7. Induced Syneresis
Induced syneresis was determined after 1 and 21 days of cold storage using the centrifugal method. Then, 20 g of yoghurt was measured in a plastic cuvette and centrifuged at 220× g/10 min, according to Wang et al. [25]. The separated liquid phase representing the expelled whey was decanted and measured, and the syneresis was quantified as weight % using the ratio between the expelled whey and the initial yoghurt mass.
2.8. Microstructure
After 10 days of storage at 7–8 °C, yoghurt samples were collected with a microdispenser and prepared for SEM analysis according to the method of Remeuf et al. [26]. Samples were fixed by immersion in 2.8% w/w glutaraldehyde in phosphate buffer solution (0.05 M, pH 6.0) for 48 h at 7–8 °C. Samples were then dehydrated in 5 steps with increasing ethanol concentrations (30, 50, 70, 90 and 100% w/w, 60 min each), defatted in chloroform for 60 min and stored in 100% w/w ethanol until dried in a critical point carbon dioxide dryer (Critical Point Dryer, K850, Quorum Technologies, Laughton, UK). The dried samples were coated with a thin layer of gold using a sputter coater (SCD 005, BAL-TEC, Los Angeles, CA, USA). Scanning electron microscopy was performed with a JEOL JSM-6390 microscope (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) at 3000× and 15,000× magnification.
2.9. Sensory Evaluation
The sensory properties of the yoghurts were evaluated on the 10th day of storage. The samples were coded and presented to the consumer sensory panel consisting of 20 randomly selected consumers, all employees of the Faculty of Agriculture University of Belgrade and students. A nine-point hedonic scale was used to rate the overall acceptability of the yoghurts (scores ranged from 1—extreme dislike—to 9—extreme like—and 5—neutral attitude). After that, the consumers were interviewed as Miloradovic et al. [27] previously described. For this purpose, a 9-point JAR (Just about right) scale was used to assess the appropriateness of the intensity of acidity, flavour and thickness (1 = not nearly enough acidity/much too weak flavour/not nearly thick enough, 5 = just about right, 9 = much too acidic/much too strong flavour/much too thick). The collected data were scanned in a mean drop analysis (penalty analysis) to identify the critical attributes that had the greatest impact on overall product preference. JAR data were distributed into three groups: 1, 2, 3 and 4 “too little” or “below JAR”, 5 “at JAR”, 6, 7, 8 and 9 “too much” or “above JAR”. The mean drop analysis was carried out using the Jamovi v. 2. 5 statistical platform [28].
2.10. Statistical Analysis
A two-way ANOVA was performed using Statistica 10.0 software (Stat Soft. Inc., Tulsa, OK, USA) to analyse the significant effects of two factors applied (chia mucilage concentration and storage time) and their interactions on yoghurt properties. Significant differences were compared with Fisher’s LSD test at a 95% confidence level.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dietary Fibre Content and Yield of Chia Mucilage
The yield of chia seed mucilage was 5.7 ± 0.07%, which can be considered satisfactory compared to other methods for production of crude chia mucilage [17]. Compositional analysis showed that the dried mucilage contained 11.45 ± 0.8 g/100 g dietary fibre, in agreement with Darwish et al. [15]. Salazar Vega et al. [29] characterised chia mucilage with FT-IR spectroscopy and reported the presence of predominantly hydroxyl groups that form the coarse structure of the carbohydrates, carboxyl groups of uronic acids, carbonyl groups and C–O–C glycosidic bonds, confirming the carbohydrate-based nature of the chia seed extract.
3.2. Rheological Properties
The viscosity of non-Newtonian fluids such as yoghurt cannot be determined by a single value, as the viscosity changes with the applied shear rate. To adequately describe the structure of these materials, it is necessary to investigate their flow behaviour as a function of the applied force, i.e., the rheology of the sample.
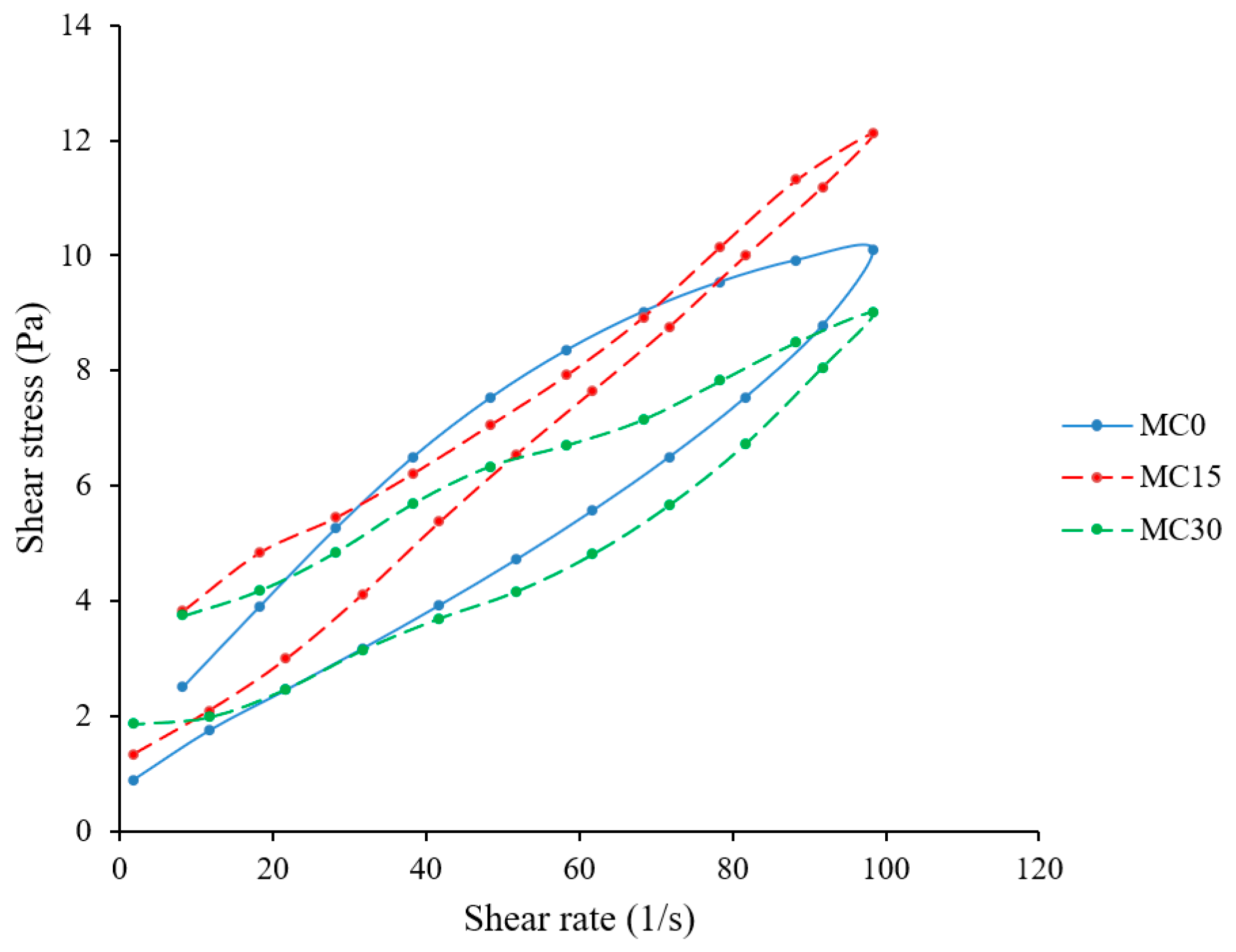
The area of the hysteresis loop represents the energy necessary to destroy the structure of the material [21,30]. In our study, MC addition reduced the hysteresis areas compared to the control sample (Figure 1, Table 1).
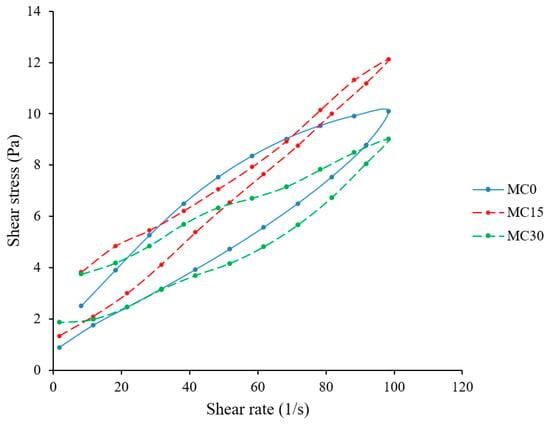
Figure 1.
Flow properties of goat yoghurts as affected by mucilage addition (enclosed areas represent the hysteresis of each sample). The data represent the mean values derived from three separate measurements.

Table 1.
Flow properties of goat milk yoghurts as influenced by mucilage addition.
This could indicate weaker interactions in the protein matrix due to the involvement of mucilage polysaccharide hydrocolloid molecules. However, a low content of mucilage (M15) reduced hysteresis, while a higher content (M30) increased it (hysteresis areas of 158.62 ± 2.00 and 195.57 ± 4.46, respectively). A lower amount of mucilage (MC15) may not be sufficient to significantly strengthen the yoghurt matrix. Instead, its presence may lead to some disruption of the existing protein matrix without significant reinforcement. This disruption may weaken the overall structure, causing it to break apart more easily. Conversely, a higher concentration of hydrocolloid molecules (MC30) can lead to a more structured material that is more difficult to break. Such behaviour could be attributed to an increased number and complexity of interactions occurring within the yoghurt matrix. Furthermore, the swelling of mucilage particles and their function as fillers within the protein matrix, as observed by Ribes et al. [16], contributes to reinforcing the structure of the yoghurt, which in turn leads to a firmer texture and makes it more resistant to breaking apart.
Chia seed mucilage is a heteropolysaccharide hydrocolloid with expressive hydrophilic properties [7]. It consists mainly of carbohydrates and uronic acids with functional anionic carboxyl groups –COO– [7,15,31], making it compatible for interactions with positively charged casein micelles. However, depending on the environmental conditions (pH, ionic strength, other ions), mucilage can also be more neutrally charged (e.g., in yoghurt, where calcium ions can bind to the carboxyl groups). Neutral hydrocolloids act as stabilizers by increasing the viscosity of the continuous phase [32]. In addition, Dickinson [33] described that interfacial complexation between protein and polysaccharide can occur through covalent or electrostatic binding.
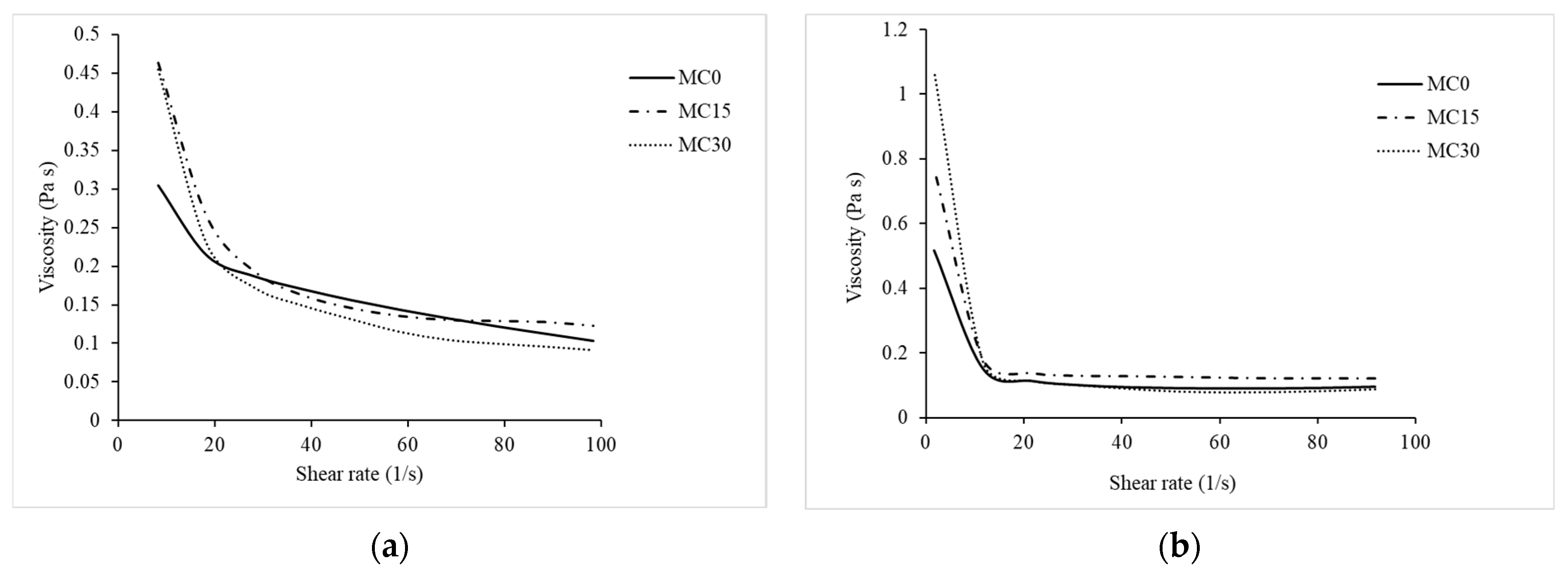
Figure 2a shows three sections that reflect the changes in the structure of the stirred yoghurt with increasing shear rate: (1) the viscosity at steady state resembles the existence of an undisturbed protein network; (2) a marked decrease in viscosity with increasing shear rate indicates the breakup of aggregates in the shear flow and (3) the viscosity tends to constant values typical of Newtonian fluids (higher shear rates would break aggregates into separate colloidal particles with predominantly hydrodynamic forces and the sample would behave like a Newtonian fluid), in agreement with Van Marle et al. [34].
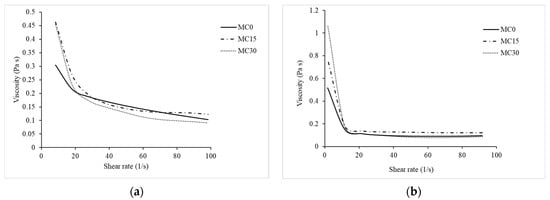
Figure 2.
Apparent viscosity of yoghurts as a function of increasing shear rate from 0 to 100 s−1 (a) and decreasing shear rate from 100 to 0 s−1 (b). The data represent average values from three measurements.
The addition of mucilage improved viscosity compared to the control when looking at the upward shear rate (Figure 2a, Table 1), and at lower shear rates (0.41 ± 0.01 and 0.38 ± 0.04 for MC15 and MC30, respectively, versus 0.30 ± 0.02 for MC0, p < 0.05). As the shear rate approaches zero, the viscosity of the MC supplemented samples tends to increase, indicating that the samples are solid like when stationary.
Conti-Silva et al. [22] found a strong positive correlation between orally perceived viscosity and apparent viscosity measured at 10 s−1. Since lower shear rates are applied in the early stages of food mastication, the apparent viscosity measured at 10 s−1 in the current study may be sufficient to predict the oral thickness of these products; furthermore, typical shear rates during mastication have been reported to be between 10 s−1 and 100 s−1 [35].
At high shear rates (100 s−1), all samples demonstrated similar behaviour (e.g., at mastication or pumping). This indicates that the processing conditions commonly used in yoghurt production do not adversely affect the viscosity and water retention of yoghurt with mucilage compared to the control. However, in future studies, shear rates higher than 100 s−1 should be investigated to confirm this hypothesis, as pumping through the pipes covers the range of shear rates from 100 to 1000 s−1 [35].
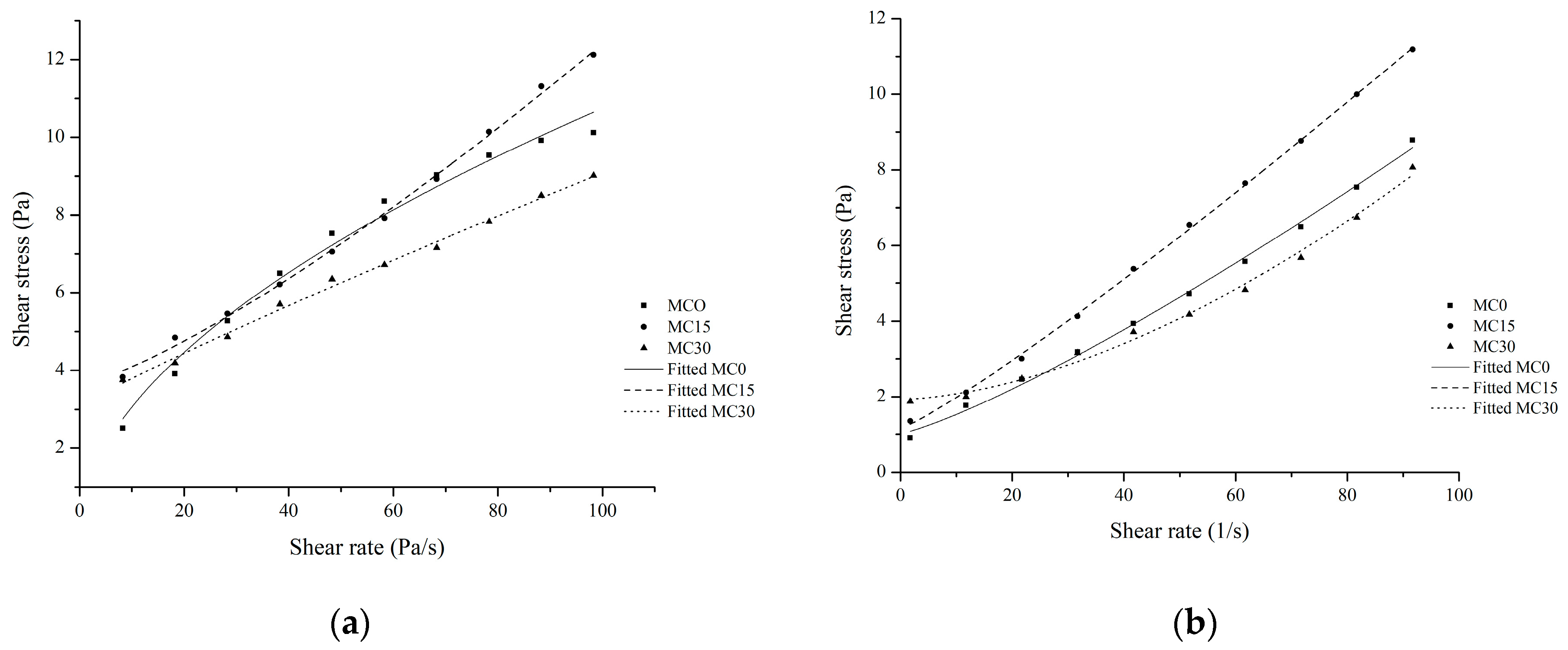
The Herschel–Bulkley model adequately described the flow curves (Figure 3, upward (a) and downward (b)) (r2 > 0.9). All samples exhibited a yield stress, which is the minimum stress that must be overcome for the material to flow. This is to be expected for structured viscoelastic material such as yoghurt [16]. The lowest values for yield stress (results not shown) and η10 were found for the control sample. Similarly, Morell et al. [36] reported that both yield stress and apparent viscosity taken as an indicator of orally perceived thickness of yoghurt with added starch were lowest for control yoghurt.
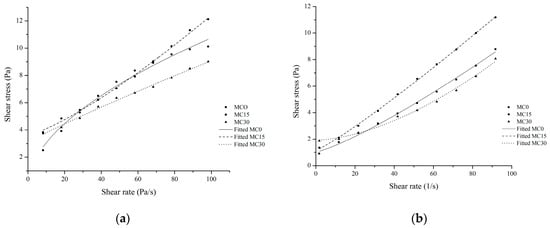
Figure 3.
Upward (a) and downward (b) flow curves fitted to the Herschel–Bulkley model.
3.3. Textural Properties
The results of the viscosity index from the back extrusion partially agreed with the apparent viscosity data measured by shearing the samples at 10 s−1. The results of the texture analysis showed the highest viscosity index for MC30, followed by MC15 and the lowest for the control, with significant differences (p < 0.05) among them (Table 2). On the other hand, the apparent viscosity measured at 10 s−1 could not differentiate the samples containing mucilage. This could be due to the differences between the methods, particularly the type of deformation of the sample during the application of force. Similarly, Conti-Silva et al. [22] concluded that the back extrusion probe, followed by rheology and the sensory panel, had the highest discriminatory ability of samples when testing various foods, including yoghurt.

Table 2.
Textural properties of goat milk yoghurts as affected by mucilage (MC) addition and cold storage for 21 days.
The yoghurt samples differed significantly in all other texture parameters, with MC30 having the highest values for firmness, consistency and cohesiveness measured one day after production. Atik et al. [14] reported that during 28 days of storage, better firmness was achieved with 1 and 2% mucilage than with 3% in yoghurt made from cow milk compared to plain yoghurt. The increased firmness of the experimental yoghurts from our study could be explained by increased dry matter content due to mucilage powder addition, and the greater number of bonds.
After 21 days of storage, MC15 and MC30 showed comparable firmness values, which is probably due to the rebodying of the structure of MC15, which led to a significant increase in firmness and consistency after this period. Lussier et al. [20] defined rebodying of the yoghurt structure as a reorganization of the protein matrix due to various factors such as post-acidification and the weakening of hydrophobic interactions during cold storage. The addition of mucilage significantly influenced the consistency at both time points in proportion to the increase in mucilage concentration. Ribes et al. [16] observed the same trend and explained it by the ability of swollen mucilage particles to act as fillers and reduce the mobility of the protein matrix.
MC30 had the highest viscosity at the end of storage, similar to the results reported by Atik et al. [14] for cow milk yoghurt with 3% chia seed mucilage compared to lower concentrations and plain (not supplemented) yoghurt.
3.4. Microbiological Analysis
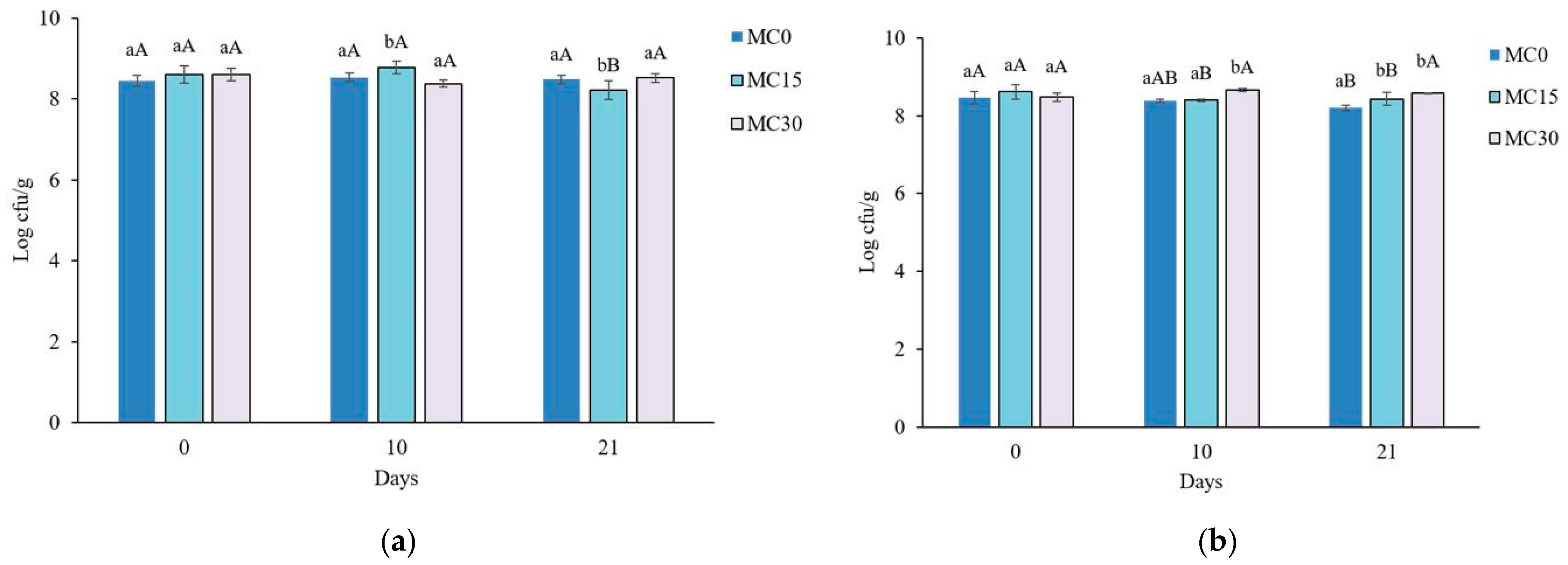
The addition of mucilage did not significantly affect the microbial counts of S. thermophilus and L. bulgaricus at the beginning of the storage period (Figure 4a,b). The growth of L. bulgaricus in MC30 increased after 10 days, while at the end of storage, both yoghurts with mucilage had significantly higher numbers of lactobacilli compared to the control. However, it should be borne in mind that the applied MC supplement also contained a certain amount of inulin as a drying aid, which is well known to act as a prebiotic and increase the viability of some probiotic bacteria such as Bifidobacterium bifidum [37] or L. acidophilus and L. bulgaricus in symbiotic yoghurt with 2% inulin [38]. Although we consider that the impact of inulin (5% w/v added to mucilage wet mass as drying aid before drying) used in our study is negligible, the absence of data on the number of bacteria in another control sample that would have only inulin represents a certain limitation of this study. Future research should include such additional control samples to increase the certainty of the results.
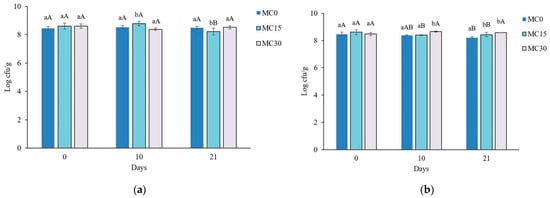
Figure 4.
Viable counts of Streptococcus thermophilus (a) and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus (b) in goat yoghurt during storage. MC0—control yoghurt without mucilage; MC15—yoghurt with 1.5% of mucilage; MC30—yoghurt with 3.0% of mucilage. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between samples in the same storage point. Different uppercase letters indicate statistically significant difference between samples during storage (p < 0.05).
It could be concluded that 3% MC, with the possible synergistic effect of inulin, supported the high viable cell count of both strains of starter bacteria during the storage period, while 1.5% MC had a similar promoting effect on the lactobacilli viable cell count after 21 days of storage. Several studies have found a positive effect of different plant mucilages on the viability of lactic acid bacteria, e.g., 0.4% basil seed mucilage in probiotic yoghurt [39], mucilage from Hyptis suaveolens seeds [40] or flaxseed mucilage [41]. Atik et al. [14] reported that 3% chia seed mucilage in cow milk yoghurt increased the viability of lactic acid bacteria, while Pop et al. [42] observed a similar effect at 1.4%. In addition, chia seed mucilage has proved to be the best encapsulating agent as it maximizes the survival of probiotic bacteria and ensures the thermal stability of the bacteria compared to other polysaccharides (flaxseed mucilage and inulin) [43].
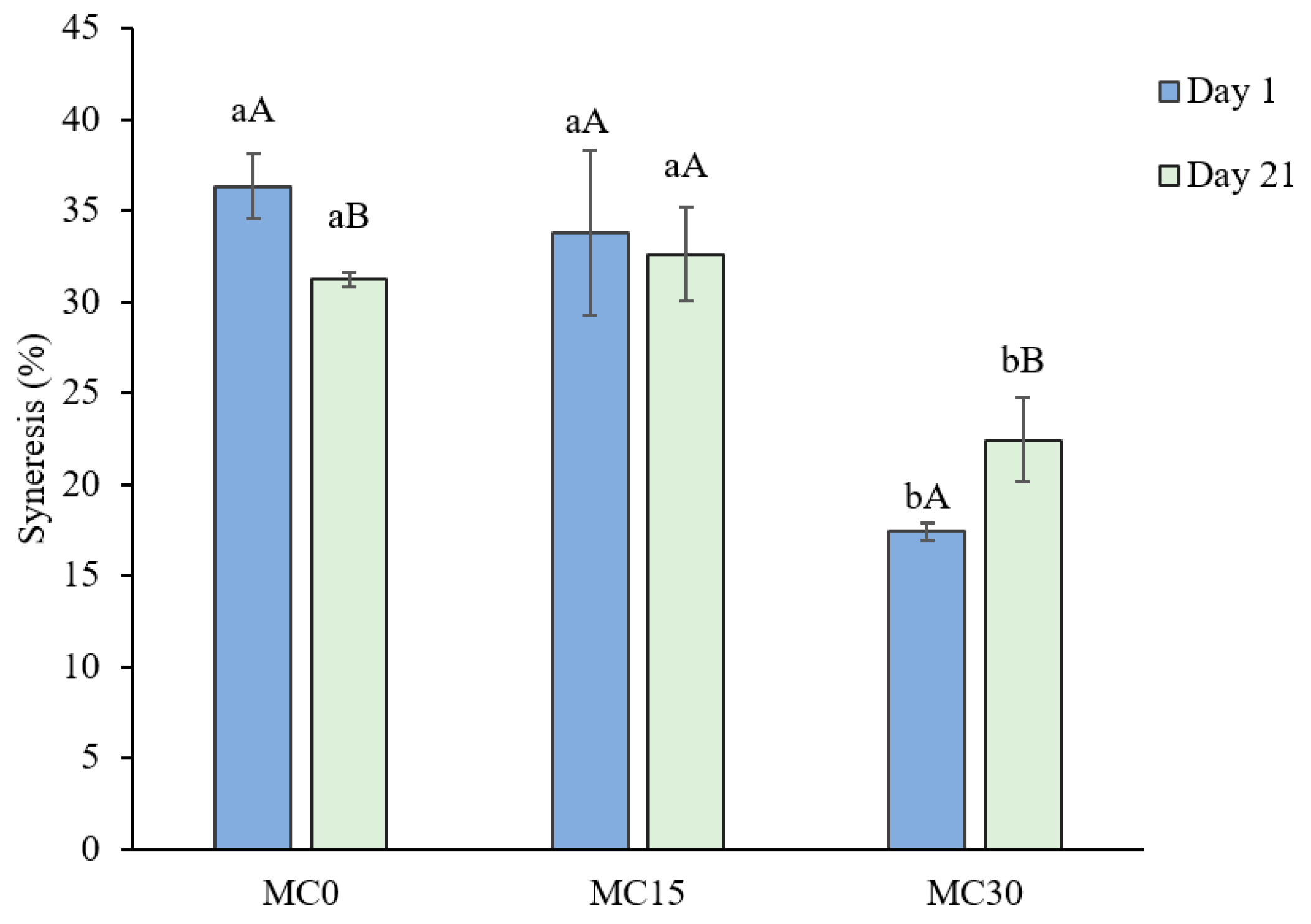
3.5. Induced Syneresis
Supplementation of the goat milk yoghurt with 3% MC resulted in the lowest syneresis values measured at both sampling times, 1 day after production and at the end of storage (Figure 5).
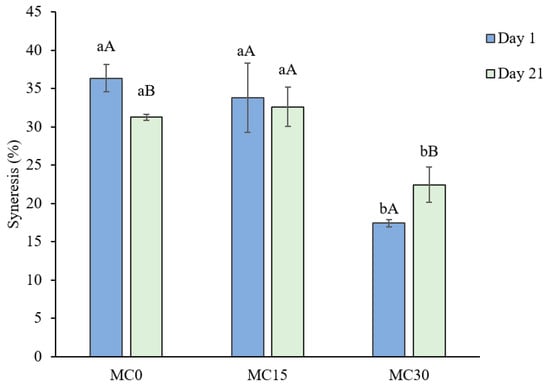
Figure 5.
Induced syneresis (%) of goat milk yoghurt measured after 1 day and 21 days of storage. Yoghurt samples: MC0—control yoghurt without mucilage; MC15—yoghurt with 1.5% mucilage; MC30—yoghurt with 3.0% mucilage. The data are the mean values of three replicate trials ± standard deviation. Different small letters represent significant differences between yoghurts at the same time point; different uppercase letters represent significant differences when comparing one day after production and after 21 days of storage (p < 0.05).
Atik et al. [14] reported that chia seed mucilage as a stabilizer in cow milk yoghurt reduced syneresis levels measured after 28 days of refrigerated storage. However, the reduction in syneresis in their study was dose-dependent up to 2% MC, with no significant change when the dose increased to 3%. The authors linked the reduction in syneresis to the increased fibre content in yoghurts with mucilage, similar to the findings of Chiang et al. [9], who also reported that the fibre fraction of chia mucilage retained water and formed gels. The fibre content has a decisive influence on the water retention capacity of a matrix, and chia mucilage has been found to be superior in this regard compared to other polysaccharide-based supplements [44]. It was found that the isolated chia mucilage has a much higher hydration capacity (27 times its own weight) than the whole seed (12 times) [8].
3.6. Microstructure
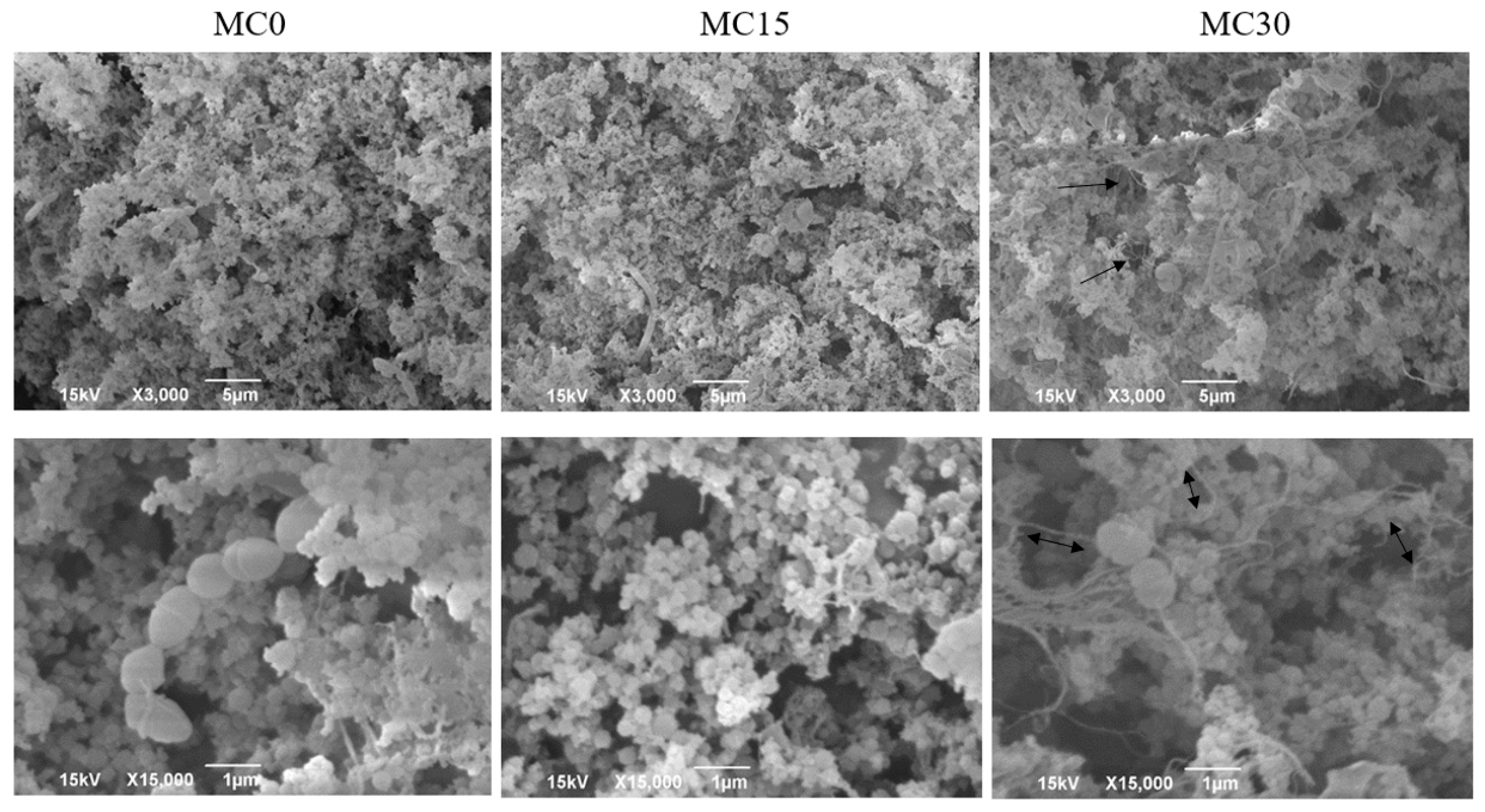
Micrographs of experimental yoghurts are shown in Figure 6. The control yoghurt is characterised by a more open and porous structure with smaller protein aggregates. The addition of mucilage led to the formation of more compact clusters. It was observed that the polysaccharides were able to interact with each other and with the proteins, forming a filamentous network and filling the voids in the matrix (indicated by arrows).

Figure 6.
Scanning electron micrographs of goat milk yoghurts without (MC0) and with added 1.5% mucilage (MC15) or 3.0% mucilage (MC30) at 3000× and 15,000× magnifications. Micrographs were obtained for samples prepared after 10 days of cold storage. Void spaces containing mucilage are marked with arrows, and double arrows mark the effects of mucilage on the yoghurt matrix, pointing to connections between protein aggregates and mucilage filaments.
The filamentous mucilage network in our micrographs closely resembles the images previously published by Semwal et al. [45]. More mucilage material is visible in MC30 yoghurt, which has a dual effect: it binds a larger amount of water (empty spaces with filaments representing polysaccharides) and interacts with proteins, forming more compact aggregates and larger protein clusters (indicated with double arrows). Oliveira et al. [46] discussed that dairy products with plant polyphenolic compounds, which include mucilages, have better physical properties thanks to the connections between polyphenols and proteins, in addition to the electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions between mucilages and caseins. The resulting structural conformation restricts protein rearrangements, which reduces susceptibility to syneresis and increases the stability of mucilage-enriched yoghurt [47], which is consistent with our results on syneresis.
Similar effects on yoghurt structure have been reported for yoghurts supplemented with other polysaccharides such as Tremella fuciformis gum [48] or Psyllium husk mucilage [47]. However, it should be noted that the dehydration method used in mucilage isolation greatly affects the microstructure of chia mucilage, which in turn affects the structure of the food in which it is used [9].
3.7. Sensory Evaluation of Yoghurts
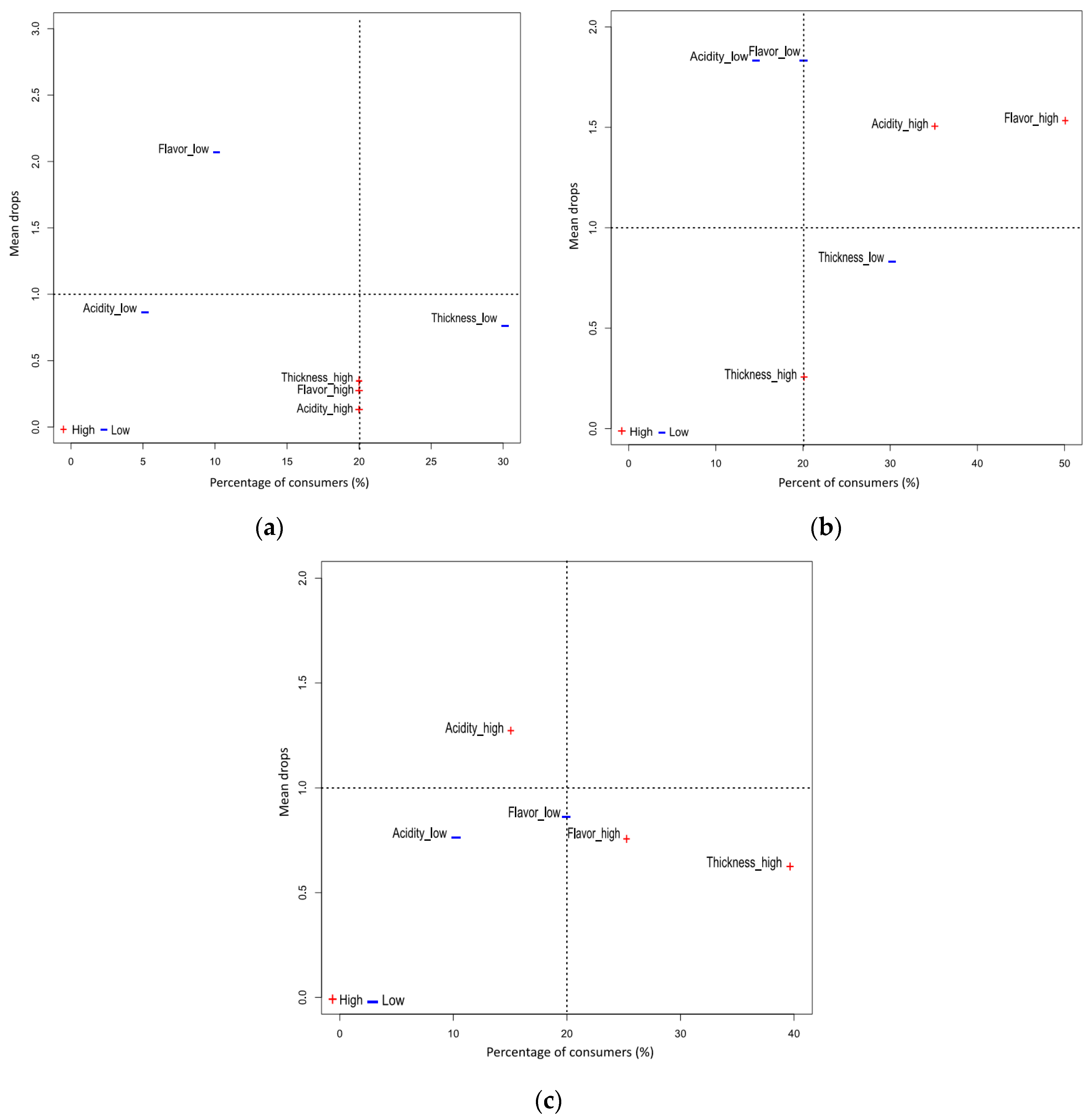
Hedonic scores for overall likability distinguished the yoghurt MC30 as the best accepted by consumers compared to the other two, MC0 and MC15 (8.30 ± 0.50, vs. 8.00 ± 1.00 and 6.80 ± 0.84, respectively). The results of the mean drop analysis from the sensory consumer panel are shown in Figure 7 and Table 3.
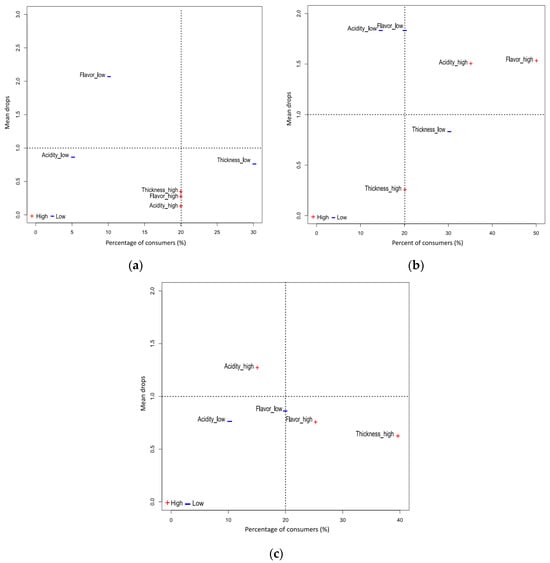
Figure 7.
Mean drop plots of evaluated yoghurts: (a) MC0, (b) MC15 and (c) MC30. The too-low endpoint of the JAR scales is highlighted with blue; the too-high endpoint is highlighted with red. Horizontal axis represents the percentage of consumers who rated the non-JAR attributes, and the vertical dashed line represents the 20% threshold.

Table 3.
Mean drop analysis of yoghurts produced without (MC0) and with 1.5% (MC15) or 3.0% mucilage (MC30).
A weak flavour was cited as the attribute that lowered the overall popularity of MC0, but only by 10% of consumers. Thirty percent of consumers felt that the control yoghurt was not thick enough, but this did not lower the overall rating of the product. For MC15, 50% of consumers perceived the flavour as too intense and 35% as too sour, and both attributes led to a significant reduction in average liking scores, so these attributes are critical points that should be improved to increase the product’s appeal. Yoghurt MC30 received the highest scores for overall acceptability in the JAR groups for all three attributes. However, it was found that 25% of consumers found this sample too acidic and the flavour too intense, which significantly lowered overall acceptability.
Panellists rated the texture of MC30 as the highest in terms of quality. However, a significant number of consumers (40%) perceived it as too thick although it did not have a significant negative impact on the overall liking. It should be emphasized that the preference for yoghurt attributes strongly depends on individual consumer expectations. Therefore, for the marketing of such a product, it would be crucial to identify and target the consumer segment that, due to cultural, traditional or other heritage factors, prefers thicker yoghurt. In this context, Masson et al. [49] identified several groups of French consumers based on similar preferences for various yoghurt attributes, and significant differences in thickness, granularity, texture, stickiness, whey presence and colour were found between the ideal products for different consumer groups. In addition, yoghurt consistency acceptability could also be an ethnicity- and culture-dependent phenomenon [50]. There were no respondents who perceived the consistency of MC30 as too weak. In addition, orally perceived viscosity or thickness of the sample MC30, referred to here as thickness, correlates with the texturizer results and the apparent viscosity measured at 10 s−1. Such results are consistent with Conti-Silva et al. (2018) [22], who previously explained that sensory-perceived thickness corresponds to viscosity at a shear rate of 10 s−1 for different foods. Ross et al. [23] evaluated hydrocolloid-enriched fluids and found a strong positive correlation between apparent viscosity measured at shear rates of 10 s−1 and oral cohesiveness, 50 s−1 and swallowing effort, while viscosity at 100 s−1 correlated well with stickiness and oral residue.
It can be concluded that the attributes that dropped the overall liking scores the most were flavour and acidity when they were not optimal (not JAR), for all yoghurts (positioned the highest on the plots—the highest mean drop values). Furthermore, within the range that includes the instrumentally measured texture parameters for yoghurt MC30 lies the optimal point that panelists evaluated the highest, making it the target to aim for.
4. Conclusions
Consumer preferences are shifting towards foods with more diverse flavours, textures and ingredients, which also have positive effects on health. The chia extract used in this study contained predominantly dietary fibre, which positively influenced the technological properties of yoghurt, e.g., texture (at both MC15 and MC30) and syneresis (at MC30), without adversely affecting the flow properties at the shear rates studied. However, future studies should investigate the effects in a large-scale yoghurt production, as the processing conditions, such as pumping through the pipes, cover a wider range of shear rates (from 100 to 1000 s−1). The mucilage addition exhibited a positive impact on lactobacilli viability during the 21-day storage period.
This study showed that chia mucilage could improve the quality of goat milk yoghurt in terms of both technological and sensory properties, and could be used as a functional, natural ingredient for this dairy product.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation10080382/s1, Table S1: Preliminary results on the textural properties of goat milk yoghurts one day after production as affected by mucilage (MC) addition; Table S2: Sensory scores of yoghurt quality on a five-point scale, obtained during preliminary trial.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.M., M.R. and M.H.; methodology, M.H., M.R., M.M., S.M.L. and I.P.; formal analysis, M.H., M.R., M.M. and I.P.; investigation, M.H., M.R. and S.M.L.; resources, J.M., I.B.J. and S.M.L.; data curation, M.H., M.R., M.M. and S.M.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.H.; writing—review and editing, Z.M., M.R., S.M.L., M.M. and I.B.J.; supervision, J.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation of the Republic of Serbia (grant number 451-03-65/2024-03/200116).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Nayik, G.A.; Jagdale, Y.D.; Gaikwad, S.A.; Devkatte, A.N.; Dar, A.H.; Ansari, M.J. Nutritional profile, processing and potential products: A comparative review of goat milk. Dairy 2022, 3, 622–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.W. Hypo-allergenic and therapeutic significance of goat milk. Small Rumin. Res. 1994, 14, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.W.; Juárez, M.; Ramos, M.; Haenlein, G.F.W. Physico-chemical characteristics of goat and sheep milk. Small Rumin. Res. 2007, 68, 88–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. Dairy Products & Eggs—Worldwide. 2024. Available online: https://www.statista.com/outlook/cmo/food/dairy-products-eggs/yoghurt/worldwide (accessed on 17 June 2024).
- Szopa, K.; Znamirowska-Piotrowska, A.; Szajnar, K.; Pawlos, M. Effect of Collagen Types, Bacterial Strains and Storage Duration on the Quality of Probiotic Fermented Sheep’s Milk. Molecules 2022, 27, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkallah, M.; Dammak, M.; Louati, I.; Hentati, F.; Hadrich, B.; Mechichi, T.; Ayadi, M.A.; Fendri, I.; Attia, H.; Abdelkafi, S. Effect of Spirulina platensis fortification on physicochemical, textural, antioxidant and sensory properties of yogurt during fermentation and storage. LWT 2017, 84, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybka-Stępień, K.; Otlewska, A.; Góźdź, P.; Piotrowska, M. The renaissance of plant mucilage in health promotion and industrial applications: A review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, L.M. Mucilage from Chia Seeds (Salvia Hispanica): Microestructure, Physico-Chemical Characterization and Applications in Food Industry; Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile: Santiago, Chile, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, J.H.; Ong, D.S.M.; Ng, F.S.K.; Hua, X.Y.; Tay, W.L.W.; Henry, C.J. Application of chia (Salvia hispanica) mucilage as an ingredient replacer in foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 115, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Rubio, J.M.; Mueller, M.; Loeppert, R.; Viernstein, H.; Praznik, W. The Effect of Cladode drying techniques on the prebiotic potential and molecular characteristics of the mucilage extracted from Opuntia ficus-indica and Opuntia joconostle. Sci. Pharm. 2020, 88, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongputtisin, P.; Khanongnuch, C. Prebiotic properties of crude oligosaccharide prepared from enzymatic hydrolysis of basil seed gum. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 1767–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannasin, S.P.; Mustafa, S.; Adzahan, N.M.; Muhammad, K. In vitro prebiotic activities of tamarillo (Solanum betaceum Cav.) hydrocolloids. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Hsieh, Y.S.Y.; Yap, K.; Ang, M.E.; Lahnstein, J.; Tucker, M.R.; Burton, R.A.; Bulone, V. Isolation and structural elucidation by 2D NMR of planteose, a major oligosaccharide in the mucilage of chia (Salvia hispanica L.) seeds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atik, D.S.; Demirci, T.; Öztürk, H.İ.; Demirci, S.; Sert, D.; Akın, N. Chia seed mucilage versus guar gum: Effects on microstructural, textural, and antioxidative properties of set-type yoghurts. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2020, 63, e20190702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, A.M.G.; Khalifa, R.E.; El Sohaimy, S.A. Functional properties of chia seed mucilage supplemented in low fat yoghurt. Alex. Sci. Exch. J. 2018, 39, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribes, S.; Peña, N.; Fuentes, A.; Talens, P.; Barat, J.M. Chia (Salvia hispanica L.) seed mucilage as a fat replacer in yogurts: Effect on their nutritional, technological, and sensory properties. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 2822–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.-H.; Lu, C.-P.; Kuo, M.-I. Combination of ultrasound and heat in the extraction of chia seed (Salvia hispanica L.) mucilage: Impact on yield and technological properties. Processes 2022, 10, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC International. Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cvetković, T.; Ranilović, J.; Gajari, D.; Tomić-Obrdalj, H.; Šubarić, D.; Moslavac, T.; Cikoš, A.-M.; Jokić, S. Podravka and slavonka varieties of pepper seeds (Capsicum annuum L.) as a new source of highly nutritional edible oil. Foods 2020, 9, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lussier, N.; Gilbert, A.; St-Gelais, D.; Turgeon, S.L. Effect of the Heat Exchanger Type on Stirred Yogurt Properties Formulated at Different Total Solids and Fat Contents. Dairy 2023, 4, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miocinovic, J.; Tomic, N.; Dojnov, B.; Tomasevic, I.; Stojanovic, S.; Djekic, I.; Vujcic, Z. Application of new insoluble dietary fibres from triticale as supplement in yoghurt–effects on physico-chemical, rheological and quality properties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti-Silva, A.C.; Ichiba, A.K.T.; da Silveira, A.L.; Albano, K.M.; Nicoletti, V.R. Viscosity of liquid and semisolid materials: Establishing correlations between instrumental analyses and sensory characteristics. J. Texture Stud. 2018, 49, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.I.V.; Tyler, P.; Borgognone, M.G.; Eriksen, B.M. Relationships between shear rheology and sensory attributes of hydrocolloid-thickened fluids designed to compensate for impairments in oral manipulation and swallowing. J. Food Eng. 2019, 263, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschopoulou, E.; Sakkas, L.; Zoidou, E.; Theodorou, G.; Sgouridou, E.; Kalathaki, C.; Liarakou, A.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Politis, I.; Moatsou, G. Effect of milk kind and storage on the biochemical, textural and biofunctional characteristics of set-type yoghurt. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 77, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kristo, E.; LaPointe, G. The effect of apple pomace on the texture, rheology and microstructure of set type yogurt. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 91, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remeuf, F.; Mohammed, S.; Sodini, I.; Tissier, J.P. Preliminary observations on the effects of milk fortification and heating on microstructure and physical properties of stirred yogurt. Int. Dairy J. 2003, 13, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloradovic, Z.; Tomic, N.; Kljajevic, N.; Levic, S.; Pavlovic, V.; Blazic, M.; Miocinovic, J. High heat treatment of goat cheese Milk. The effect on sensory profile, consumer acceptance and microstructure of cheese. Foods 2021, 10, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Jamovi Project. Jamovi (Version 2.5) [Computer Software]. 2024. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- Salazar Vega, I.M.; Quintana Owen, P.; Segura Campos, M.R. Physicochemical, thermal, mechanical, optical, and barrier characterization of chia (Salvia hispanica L.) mucilage-protein concentrate biodegradable films. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Jdayil, B.; Nasser, M.S.; Ghannam, M. Structure breakdown of stirred yoghurt in a circular pipe as affected by casein and fat content. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2013, 19, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kassem, I.A.A.; Ashaolu, T.J.; Kamel, R.; Elkasabgy, N.A.; Afifi, S.M.; Farag, M.A. Mucilage as a functional food hydrocolloid: Ongoing and potential applications in prebiotics and nutraceuticals. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 4738–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basiri, S.; Haidary, N.; Shekarforoush, S.S.; Niakousari, M. Flaxseed mucilage: A natural stabilizer in stirred yogurt. Carbohydr Polym 2018, 187, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, E. Hydrocolloids as emulsifiers and emulsion stabilizers. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Marle, M.E.; Van den Ende, D.; De Kruif, C.G.; Mellema, J. Steady-shear viscosity of stirred yogurts with varying ropiness. J. Rheol. 1999, 43, 1643–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isendahl, H. Rheological Characterization of Typical Food Products; Tetra Pak: Pully, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Morell, P.; Hernando, I.; Llorca, E.; Fiszman, S. Yogurts with an increased protein content and physically modified starch: Rheological, structural, oral digestion and sensory properties related to enhanced satiating capacity. Food Res. Int. 2015, 70, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, D.G.; Hammam, A.R.A.; Alsaleem, K.A.; Osman, D.M. Addition of inulin to probiotic yogurt: Viability of probiotic bacteria (Bifidobacterium bifidum) and sensory characteristics. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazloomi, S.M.; Shekarforoush, S.S.; Ebrahimnejad, H.; Sajedianfard, J. Effect of adding inulin on microbial and physicochemical properties of low fat probiotic yogurt. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2011, 12, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasempour, Z.; Javanmard, N.; Langroodi, A.M.; Alizadeh-Sani, M.; Ehsani, A.; Kia, E.M. Development of probiotic yogurt containing red beet extract and basil seed gum; techno-functional, microbial and sensorial characterization. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 101785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.; Čavarkapa, A.; Unger, F.M.; Viernstein, H.; Praznik, W. Prebiotic potential of neutral oligo-and polysaccharides from seed mucilage of Hyptis suaveolens. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, M.; Villarroel, M.; Rubilar, M.; Shene, C. Lactobacillus acidophilus La-05 encapsulated by spray drying: Effect of mucilage and protein from flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, C.; Vlaic, R.; Fărcaş, A.; Salanță, L.; Ghicăşan, D.; Semeniuc, C.; Rotar, A.M. Influence of pollen, chia seeds and cranberries addition on the physical and probiotics characteristics of yogurt. Bull. UASVM Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 141–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bustamante, M.; Laurie-Martínez, L.; Vergara, D.; Campos-Vega, R.; Rubilar, M.; Shene, C. Effect of three polysaccharides (inulin, and mucilage from chia and flax seeds) on the survival of probiotic bacteria encapsulated by spray drying. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coorey, R.; Tjoe, A.; Jayasena, V. Gelling properties of chia seed and flour. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, E859–E866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semwal, A.; Ambatipudi, K.; Navani, N.K. Development and characterization of sodium caseinate based probiotic edible film with chia mucilage as a protectant for the safe delivery of probiotics in functional bakery. Food Hydrocoll. Health 2022, 2, 100065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.; Alexandre, E.M.C.; Coelho, M.; Lopes, C.; Almeida, D.P.F.; Pintado, M. Incorporation of strawberries preparation in yoghurt: Impact on phytochemicals and milk proteins. Food Chem. 2015, 171, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.N.A.; Salem, A.S.; Hassan, A.A.; Abozied, H.H. Development of functional low-fat yoghurt fortified with psyllium husk mucilage: Quality attributes, microstructure, and antioxidant characteristics. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2024, 23, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Shao, P. Tremella fuciformis polysaccharides as a fat substitute on the rheological, texture and sensory attributes of low-fat yogurt. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, M.; Saint-Eve, A.; Delarue, J.; Blumenthal, D. Identifying the ideal profile of French yogurts for different clusters of consumers. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 3421–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bech, A.C.; Waehrens, S.S.; Bredie, W.L.P. Perception and liking of yogurts with different degrees of granularity in relation to ethnicity, preferred oral processing and lingual tactile acuity. Food Qual. Prefer. 2021, 90, 104158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).