Abstract
The cardiopulmonary system delivers oxygen throughout the body via blood circulation. It is an essential part of the body to sustain the lives of organisms. The integral parts of the cardiopulmonary system—the heart and lungs—are constantly exposed to damaging agents (e.g., dust, viruses), and can be greatly affected by injuries caused by dysfunction in tissues (e.g., myocardial infarction). When damaged, mesenchymal cells, such as fibroblasts, are activated to become myofibroblasts to initiate fibrosis as part of a regenerative mechanism. In diseased states, the excess accumulation of extracellular matrices secreted by myofibroblasts results in further dysfunction in the damaged organs. These fibrotic tissues cannot easily be removed. Thus, there is a growing interest in understanding the fibrotic process, as well as finding biomolecules that can be targets for slowing down or potentially stopping fibrosis. Among these biomolecules, the interest in studying long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs; any non-protein-coding RNAs longer than 200 nucleotides) has intensified in recent years. In this commentary, we summarize the current status of lncRNA research in the cardiopulmonary system by focusing on cardiac and pulmonary fibrosis.
1. Introduction
Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) is a collective term used to describe any non-protein-coding RNAs whose lengths are longer than 200 nucleotides. Compared to protein-coding mRNAs, lncRNAs’ expression is cell-type-specific, although at lower expression levels than mRNAs [1,2]. The exact number of lncRNAs is currently unknown, but it is predicted to be higher than that of mRNAs [3,4]. Given that there are many functions of proteins, the functions of lncRNAs are diverse, ranging from molecular scaffolds for epigenetic and transcription factor complexes, to decoys for other macromolecules (e.g., DNA, RNA, and proteins), signaling molecules, and regulators of mRNA stability and translation [5,6,7].
Fibrosis is a common pathological process in chronic inflammatory diseases, including cardiovascular and lung diseases [8,9]. During fibrosis, fibroblasts are activated to become myofibroblasts to deposit excess extracellular matrices consisting of macromolecules, such as collagens, glycoproteins, and matrix metalloproteinases. As a part of the wound-healing process in some cases (e.g., burns, skin wounds), fibrosis is a necessary process for tissue regeneration [10,11]. However, in other cases, where the complete regeneration of damaged tissue is not possible (e.g., heart, lungs), pathological fibrosis leads to the dysfunction of organs, resulting in various diseases [12,13]. As it is not possible to remove the fibrotic cells without damaging the surrounding tissues, early detection of pathological fibrosis is important to slow down or possibly stop irreversible fibrosis. In this regard, intensive research has been conducted to identify genes, proteins, and signaling pathways activated during fibrosis. Among these macromolecules and signaling pathways, lncRNAs are increasingly being investigated as a missing link to understand fibrosis in various fibrotic diseases [14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. In this commentary, we summarize the current status of lncRNA research in the cardiopulmonary system by focusing on cardiac and pulmonary fibrosis.
2. LncRNAs in Cardiac Fibrosis
Most cardiovascular diseases (e.g., myocardial infarction, cardiac hypertrophy) result in cardiac fibrosis, where cardiac fibroblasts are activated to become myofibroblasts to deposit excess extracellular matrices [21,22]. As it is not currently possible to replace fibrotic scarred tissues in the heart, the research on cardiac fibrosis has intensified in recent years. Through high-throughput screening via microarrays and RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq), a number of lncRNAs have been identified as being involved in cardiac fibrosis [23,24,25] (Figure 1A). Among them, the first functionally and mechanistically characterized cardiac fibrotic lncRNA is Chrf (cardiac hypertrophy-related factor), whose function is discussed below. This previous study was followed by several functional and mechanistic lncRNA studies, including H19 (H19 imprinted maternally expressed transcript) acting to antagonize the suppressor of collagen 1A1, Ybx1 (Y box protein 1), by directly binding it under hypoxia [26]; Meg3 (maternally expressed 3) interacting with P53 to regulate the expression of Mmp2 (matrix metallopeptidase 2) [27]; and Wisper (Wisp2 super-enhancer-associated RNA) interacting with Tial1 (Tia1 cytotoxic granule-associated RNA-binding protein-like 1, also known as TIAR) to regulate alternative splicing of Plod2 (procollagen lysine, 2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 2) to stabilize the extracellular matrix [23]. These lncRNA studies, and more recent ones, are summarized in Table 1.
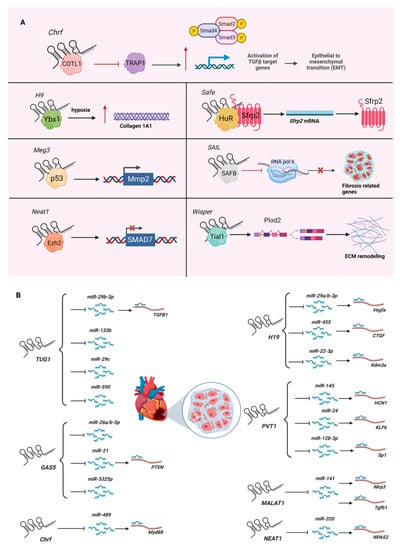
Figure 1.
Role of lncRNAs in cardiac fibrosis: (A) Mechanisms of action of lncRNAs in the pathogenesis of cardiac fibrosis. (B) LncRNAs as miRNA sponges for cardiac fibromiRs. Please see Table 1 for mechanistic descriptions. Figure created with BioRender.com, accessed on 22 June 2022.

Table 1.
List of functionally and mechanistically characterized cardiac fibrotic lncRNAs.
As exemplified by the lncRNA HOTAIR (HOX transcript antisense RNA) [31], it was previously popular to investigate the function of lncRNAs as molecular scaffolds of histone modifiers—especially binding to the core PRC2 (polycomb repressive complex 2) component EZH2 (enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit). However, after the series of studies reporting that EZH2 promiscuously binds any RNAs [32,33,34,35,36], including lncRNAs, many researchers have become more careful about reporting lncRNAs as molecular scaffolds for histone modifiers. Instead, the current trend is to understand the function of lncRNAs as miRNA (microRNA) sponges. MicroRNAs are regulatory RNA species with an average length of 22 nucleotides for their mature forms. The primary function of miRNAs is to bind the 3′-UTR (untranslated region) of mRNAs to negatively regulate their gene expression by degrading their target mRNAs and/or by silencing translation. Partially fueled by the established techniques available to study miRNAs (e.g., gain-of-function via miRNA mimics, loss-of-function via anti-miR (e.g., GapmeRs), and binding assay with the mutation of miRNA-binding sites in the 3′-UTR of the target mRNA and readout by luciferase assay), many lncRNAs are reported to bind miRNAs, including those of cardiac fibrotic lncRNAs. For example, the lncRNA Chrf sequesters miR-489, which targets Myd88 (MYD88 innate immune signal transduction adaptor) in cardiomyocytes to regulate cardiac hypertrophy [37].
Since the discovery of miRNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans in 1993 [38], miRNA research has intensified in recent years. This has led to the usage of miRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets for various diseases, including cardiovascular disease [39,40,41]. In the context of fibrosis, the specific term fibromiR is used to describe the group of miRNAs involved in fibrosis, including miR-1, miR-21, miR-29, and miR-208 [42]. In cardiac fibrosis, several lncRNAs have been reported to function as miRNA sponges to sequester fibromiRs (Figure 1B). For example, the lncRNA H19 sequesters miR-29a/b-3p, which targets Vegfa (vascular endothelial growth factor A) to promote the proliferation of rat cardiac fibroblasts and collagen synthesis via the TGF-β signaling pathway in vitro [43]. Interestingly, the miR-29 family members [44] are also shown to be sequestered by another lncRNA—TUG1 (taurine upregulated 1). In cardiac fibroblasts, TUG1 sequesters miR-29c to promote the activation of murine cardiac fibroblasts to myofibroblasts under hypoxic conditions in vitro [45]. Another study showed that TUG1 sequesters miR-29b-3p, which targets TGFB1 (transforming growth factor beta 1) to regulate the proliferation of human cardiac fibroblasts treated with angiotensin II in vitro [46]. Given that fibrosis is a general disease mechanism for chronic inflammation, more fibromiRs will be shown to be sequestered by lncRNAs in cardiac fibroblasts and fibrosis in the near future.
Although the mechanism of lncRNAs as miRNA sponges is an attractive function, it is not clear how generally lowly expressed lncRNAs (except for those highly expressed lncRNAs, such as MALAT1 (metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1)) sequester much more abundantly expressed miRNAs. Moreover, many miRNAs bind more than one site of the 3′-UTR of protein-coding genes for gene regulation. Given that most mRNAs are much more highly expressed than lncRNAs, it is not clear how efficiently each lncRNA functions as an miRNA sponge in a cell—especially when the copy number of the lncRNA in a cell has not been reported in the original studies, along with the copy number of the miRNA that the target lncRNA sequences. To complicate the matter further, individual lncRNAs have been reported to sponge several miRNAs, as in the case of the lncRNA GAS5 (growth arrest specific 5), for miR-21, miR-26a/b-5p, and miR-5325p in cardiac fibroblasts and fibrosis [47,48,49,50]. Another example is TUG1, which sequesters miR-29b-3p, miR-29c, miR-133b, and miR-590 [45,46,51,52]. As there are more miRNAs being identified to bind these two exemplified lncRNAs in other cell types (e.g., cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells), cellular statuses, and diseases [51,52,53,54,55,56,57], it is important to perform a comparative study of lncRNAs and several miRNAs being reported to be sequestered by the target lncRNAs by measuring the copy numbers of each RNA species. Without such a head-to-head comparative study, more and more miRNAs will be reported to be sequestered by one lncRNA, despite its expression level being far lower than those of the sequestered miRNAs.
3. LncRNAs in Pulmonary Fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis is a generalized term used to describe chronic and progressive interstitial lung diseases, including sarcoidosis, Langerhans-cell granulomatosis, eosinophilic pneumonia, lymphangioleiomyomatosis, and pulmonary alveolar proteinosis [58]. Among them, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is the most common form. Unlike cardiac fibrosis, where cardiac fibroblasts are the major source of myofibroblasts, the origin of myofibroblasts in the lungs is still debated, including alveolar epithelial cells, circulating fibrocytes, and lung stromal cell subpopulations (e.g., resident fibroblasts, pericytes, and resident mesenchymal stem cells) [59]. Thus, the lncRNA studies of pulmonary fibrosis extend far beyond those of fibroblasts, complicating the research itself, as many lncRNAs are expressed in a cell-type-specific manner. Generally speaking, not only the activation of fibroblasts, but also epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT)—the process in which differentiated epithelial cells acquire mesenchymal phenotypes [60]—is investigated for pulmonary fibrotic lncRNAs (Figure 2A). Furthermore, unlike cardiac fibrosis, some studies of pulmonary fibrosis involve environmental and occupational agents (e.g., asbestos, cigarette smoke), as these are known causes of pulmonary fibrosis—especially IPF. In addition, the most frequently used murine injury model of IPF is the injection of the chemotherapy agent bleomycin, which has pulmonary toxicity [61,62]. For example, transgenic mice overexpressing the lncRNA PFI (pulmonary fibrosis inhibitor, also known as NONMMUT060091) were challenged with intratracheal injection of bleomycin to induce pulmonary fibrosis. Molecular and histological analyses showed that overexpression of PFI alleviated the negative effects of bleomycin by reducing the deposition of extracellular matrix and differentiation of myofibroblasts [63]. Mechanistically, PFI binds SRSF1 (serine- and arginine-rich splicing factor 1) to inhibit its function on alternative splicing. Other pulmonary fibrotic lncRNAs are summarized in Table 2.
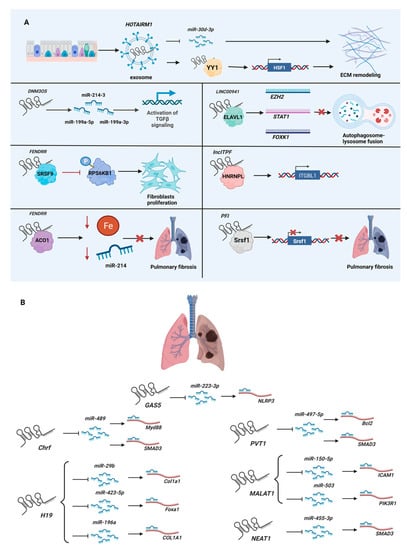
Figure 2.
Role of lncRNAs in pulmonary fibrosis: (A) Mechanisms of action of lncRNAs in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. (B) LncRNAs as miRNA sponges for pulmonary fibromiRs. Please see Table 2 for mechanistic descriptions. Figure created with BioRender.com, accessed on 22 June 2022.

Table 2.
List of functionally and mechanistically characterized pulmonary fibrotic lncRNAs.
As was the case for cardiac fibrotic lncRNAs, the function as miRNA sponges is a popular mechanism investigated for pulmonary fibrotic lncRNAs. Unsurprisingly, many lncRNAs identified as miRNA sponges in cardiac fibrosis are also implicated in pulmonary fibrosis (Figure 2B). Thus, rather than simply listing all lncRNAs functioning as miRNA sponges in pulmonary fibrosis, here, the same lncRNAs identified as miRNA sponges in both cardiac and pulmonary fibrosis are discussed. For example, H19 sequesters miR-455 and miR-22-3p, which target CCN2 (cellular communication network factor 2, also known as CTGF) [70] and Kdm3a (lysine (K)-specific demethylase 3A) mRNAs [71], respectively, in cardiac fibrosis. In pulmonary fibrosis, H19 binds miR-29b, miR-423-5p, and miR-196a to silence the translation of Col1a1 (collagen, type I, alpha 1) [72], Foxa1 (forkhead box A1) [73], and COL1A1 mRNAs [74], respectively. Other lncRNAs functioning as miRNA sponges in both cardiac and pulmonary fibrosis are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
List of cardiac and pulmonary fibrotic lncRNAs functioning as miRNA sponges: In the Cardiac Fibrosis and Pulmonary Fibrosis columns, miRNAs and their target mRNAs are shown, which are separated by a forward slash. When there are multiple entries (i.e., miRNA/target mRNA) for each column, each entry is separated by a semicolon. This applies to the corresponding references as well.
As stated in the previous section, if indeed lncRNAs primarily function as miRNA sponges, it is a very complicated cascade of events, as the same miRNA is sequestered by several lncRNAs, while one miRNA has several hundred predicted mRNA targets. In this regard, it is interesting to note that the lncRNA FENDRR (FOXF1-adjacent non-coding developmental regulatory RNA) sequesters miR-214 while interacting with ACO1 (aconitase 1, also known as IRP1) to decrease cellular iron concentration and reduce pulmonary fibrosis [66]. Another example is the exosomal lncRNA HOTAIRM1 (HOXA transcript antisense RNA, myeloid-specific 1), which sequesters miR-30d-3p while recruiting YY1 (YY1 transcription factor) to upregulate HSF1 (heat shock transcription factor 1) to promote extracellular matrix remodeling [67]. Although these two studies report lncRNAs as miRNA sponges, other mechanisms of action are proposed to tease out the exact mechanisms of action of lncRNAs.
4. Discussions
For lncRNAs to be recognized further as important molecules for signaling pathways, it is of utmost importance that each lncRNA study carefully characterize expression patterns and functions, including those of isoforms (transcripts of each lncRNA gene). The information about known isoforms can be examined easily from the public databases, such as NCBI’s Entrez Gene and Ensembl. Without such careful studies, it will be a long time before lncRNAs can be considered as potential diagnostic biomarkers of various diseases—especially fibrosis—and possibly as druggable targets. As for fibrotic lncRNAs, especially in the cardiopulmonary system and its associated diseases, the number of functionally characterized fibrotic lncRNAs is scarce. To assist in the identification of lncRNAs expressed in fibroblasts and involved in fibrosis—especially in cardiac and pulmonary fibrosis—we recently released the web application FibroDB [86] (https://rnamedicine.shinyapps.io/FibroDB/, accessed on 12 July 2022).
The identification of lncRNAs involved in cardiac and pulmonary fibrosis is only the first step. The identified lncRNAs must be characterized carefully by performing experiments, including 5/3′-RACE (rapid amplification of cDNA ends) and Northern blotting to identify isoforms of the target lncRNA; in vitro transcription and translation assays to test the coding potential of the target lncRNA; RT-PCR (reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction) using nuclear and cytosol fractions of the target cell separately and FISH (fluorescent in situ hybridization) to identify the subcellular localization of the target lncRNA; gain/loss-of-function experiments to observe phenotypic changes; RNA pull-down followed by mass spectrometry or more advanced methods (e.g., CHART (capture hybridization analysis of RNA targets), ChIRP (chromatin isolation by RNA purification), and RAP (RNA affinity purification), which are comprehensively reviewed in [87]) to identify potential protein binding partners of the target lncRNA; and RIP-PCR (RNA immunoprecipitation followed by RT-PCR) to verify the binding between the target lncRNA and its protein-binding partner(s). It is unfortunate that most lncRNA studies published to date fail to report the presence (or absence) of isoforms, as many isoforms of the target lncRNAs have distinctive tissue/cell-specific expression patterns, as in the case of the paternal imprinting lncRNA gene Airn [88]. On top of this, as more and more lncRNAs are being discovered due to the results of the readily available RNA-Seq method, public databases (e.g., NCBI, Ensembl) have been updating the annotations of human transcriptomes and other model organisms at a rapid pace. This has resulted in significant changes in the numbers of lncRNA genes and their isoforms. Thus, it is highly recommended to check the primer sequences for the target lncRNA regularly (and, of course, before publication) to make sure that the predicted PCR product amplifies the product at the expected product size, and no other products at various sizes. This can be easily performed using the UCSC In-Silico PCR tool (https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgPcr, accessed on 12 July 2022).
5. Conclusions
As summarized in this commentary, a number of lncRNAs involved in cardiac and pulmonary fibrosis have been identified and studied. The most common mechanism to date for these fibrotic lncRNAs is as miRNA sponges, although there remains the question of the amounts of lncRNAs available to sequester much more abundant miRNAs, and why some lncRNAs (e.g., GAS5, H19, MALAT1, MIAT, PVT1) have several miRNAs binding to one lncRNA. These questions should be answered by further experiments, and this mini-review should stimulate such mechanistic studies in cardiac and pulmonary fibrosis.
Author Contributions
M.I. and S.U. wrote the manuscript, generated the figures, and approved the final version of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, S.J.; Nowakowski, T.J.; Pollen, A.A.; Lui, J.H.; Horlbeck, M.A.; Attenello, F.J.; He, D.; Weissman, J.S.; Kriegstein, A.R.; Diaz, A.A.; et al. Single-cell analysis of long non-coding RNAs in the developing human neocortex. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, X.; Chen, K.; Cuevas-Diaz Duran, R.; You, Y.; Sloan, S.A.; Zhang, Y.; Zong, S.; Cao, Q.; Barres, B.A.; Wu, J.Q. Comprehensive Identification of Long Non-coding RNAs in Purified Cell Types from the Brain Reveals Functional LncRNA in OPC Fate Determination. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volders, P.J.; Anckaert, J.; Verheggen, K.; Nuytens, J.; Martens, L.; Mestdagh, P.; Vandesompele, J. LNCipedia 5: Towards a reference set of human long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D135–D139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uszczynska-Ratajczak, B.; Lagarde, J.; Frankish, A.; Guigo, R.; Johnson, R. Towards a complete map of the human long non-coding RNA transcriptome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakas, D.; Ozpolat, B. The Role of LncRNAs in Translation. Noncoding RNA 2021, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastian-delaCruz, M.; Gonzalez-Moro, I.; Olazagoitia-Garmendia, A.; Castellanos-Rubio, A.; Santin, I. The Role of lncRNAs in Gene Expression Regulation through mRNA Stabilization. Noncoding RNA 2021, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, J.C.R.; Acuna, S.M.; Aoki, J.I.; Floeter-Winter, L.M.; Muxel, S.M. Long Non-Coding RNAs in the Regulation of Gene Expression: Physiology and Disease. Noncoding RNA 2019, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marzec, J.; Nadadur, S. Inflammation resolution in environmental pulmonary health and morbidity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 449, 116070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtha, L.A.; Schuliga, M.J.; Mabotuwana, N.S.; Hardy, S.A.; Waters, D.W.; Burgess, J.K.; Knight, D.A.; Boyle, A.J. The Processes and Mechanisms of Cardiac and Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Ayadi, A.; Jay, J.W.; Prasai, A. Current Approaches Targeting the Wound Healing Phases to Attenuate Fibrosis and Scarring. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darby, I.A.; Hewitson, T.D. Fibroblast differentiation in wound healing and fibrosis. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2007, 257, 143–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A.; Ramalingam, T.R. Mechanisms of fibrosis: Therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wynn, T.A. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Gui, S.; Yang, F.; Cao, Z.; Cheng, R.; Xia, X.; Li, C. The Roles and Mechanisms of lncRNAs in Liver Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 779606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, W.; Jiang, P.; Yang, L.; Guo, Q.; Xiang, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, R. Long Non-Coding RNAs in Oral Submucous Fibrosis: Their Functional Mechanisms and Recent Research Progress. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 5787–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Abak, A.; Talebi, S.F.; Shoorei, H.; Branicki, W.; Taheri, M.; Akbari Dilmaghani, N. Role of miRNA and lncRNAs in organ fibrosis and aging. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; He, Y.; Gan, Y.; Zhang, B.; Dai, G.; Ru, F.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X. Long Non-coding RNA: An Emerging Contributor and Potential Therapeutic Target in Renal Fibrosis. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 682904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, M.; Guo, J.; Ma, J.; Qiu, M.; Yang, Z. The function of non-coding RNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Open. Med. 2021, 16, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Yue, D.; Blackwell, T.S.; Lv, C.; Song, X. Long non-coding RNAs: Promising new targets in pulmonary fibrosis. J. Gene. Med. 2021, 23, e3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Gou, R.; Tang, L.; Liu, P. Noncoding RNAs in peritoneal fibrosis: Background, Mechanism, and Therapeutic Approach. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangogiannis, N.G. Cardiac fibrosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 1450–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travers, J.G.; Kamal, F.A.; Robbins, J.; Yutzey, K.E.; Blaxall, B.C. Cardiac Fibrosis: The Fibroblast Awakens. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1021–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Micheletti, R.; Plaisance, I.; Abraham, B.J.; Sarre, A.; Ting, C.C.; Alexanian, M.; Maric, D.; Maison, D.; Nemir, M.; Young, R.A.; et al. The long noncoding RNA Wisper controls cardiac fibrosis and remodeling. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaai9118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Fu, X.; Kataoka, M.; Liu, N.; Wang, Y.; Gao, F.; Liang, T.; Dong, X.; Pei, J.; Hu, X.; et al. Long noncoding RNA Cfast regulates cardiac fibrosis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 23, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Nie, X.; Yuan, S.; Li, H.; Fan, J.; Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, H.; Wang, D.W.; et al. Circulating Long Non-coding RNA ENST00000507296 Is a Prognostic Indicator in Patients with Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choong, O.K.; Chen, C.Y.; Zhang, J.; Lin, J.H.; Lin, P.J.; Ruan, S.C.; Kamp, T.J.; Hsieh, P.C.H. Hypoxia-induced H19/YB-1 cascade modulates cardiac remodeling after infarction. Theranostics 2019, 9, 6550–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, M.T.; Gupta, S.K.; Viereck, J.; Foinquinos, A.; Samolovac, S.; Kramer, F.L.; Garg, A.; Remke, J.; Zimmer, K.; Batkai, S.; et al. Inhibition of the Cardiac Fibroblast-Enriched lncRNA Meg3 Prevents Cardiac Fibrosis and Diastolic Dysfunction. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Yin, C.; Li, Y.; Tian, D.; Xiang, Y.; Li, Q.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes cardiac fibrosis in heart failure through increased recruitment of EZH2 to the Smad7 promoter region. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, K.; Lei, W.; Wu, H.; Wu, J.; Yang, Z.; Yan, S.; Lu, X.A.; Li, J.; Xia, X.; Han, X.; et al. LncRNA-Safe contributes to cardiac fibrosis through Safe-Sfrp2-HuR complex in mouse myocardial infarction. Theranostics 2019, 9, 7282–7297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Zhang, M.; Wu, H.; Ding, X.; Li, D.; Dong, X.; Hu, X.; Su, S.; Shang, W.; Wu, J.; et al. SAIL: A new conserved anti-fibrotic lncRNA in the heart. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2021, 116, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.C.; Manor, O.; Wan, Y.; Mosammaparast, N.; Wang, J.K.; Lan, F.; Shi, Y.; Segal, E.; Chang, H.Y. Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science 2010, 329, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cifuentes-Rojas, C.; Hernandez, A.J.; Sarma, K.; Lee, J.T. Regulatory interactions between RNA and polycomb repressive complex 2. Mol. Cell 2014, 55, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davidovich, C.; Wang, X.; Cifuentes-Rojas, C.; Goodrich, K.J.; Gooding, A.R.; Lee, J.T.; Cech, T.R. Toward a consensus on the binding specificity and promiscuity of PRC2 for RNA. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davidovich, C.; Zheng, L.; Goodrich, K.J.; Cech, T.R. Promiscuous RNA binding by Polycomb repressive complex 2. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaneko, S.; Son, J.; Shen, S.S.; Reinberg, D.; Bonasio, R. PRC2 binds active promoters and contacts nascent RNAs in embryonic stem cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 1258–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Goodrich, K.J.; Gooding, A.R.; Naeem, H.; Archer, S.; Paucek, R.D.; Youmans, D.T.; Cech, T.R.; Davidovich, C. Targeting of Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 to RNA by Short Repeats of Consecutive Guanines. Mol. Cell 2017, 65, 1056–1067.e1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Liu, F.; Zhou, L.Y.; Long, B.; Yuan, S.M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.Y.; Sun, T.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, P.F. The long noncoding RNA CHRF regulates cardiac hypertrophy by targeting miR-489. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A.R.; Sharma, G.; Lee, S.S. Therapeutic advances of miRNAs: A preclinical and clinical update. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 28, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotowska-Zimmer, A.; Pewinska, M.; Olejniczak, M. Artificial miRNAs as therapeutic tools: Challenges and opportunities. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2021, 12, e1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Tang, W.; Yang, J.; Peng, J.; Guo, J.; Fan, C. MicroRNA-Related Strategies to Improve Cardiac Function in Heart Failure. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 773083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottier, N.; Cauffiez, C.; Perrais, M.; Barbry, P.; Mari, B. FibromiRs: Translating molecular discoveries into new anti-fibrotic drugs. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Tang, C.; Huang, B.; Gu, L.; Zhou, J.; Mo, Z.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y. LncRNA H19 Drives Proliferation of Cardiac Fibroblasts and Collagen Production via Suppression of the miR-29a-3p/miR-29b-3p-VEGFA/TGF-beta Axis. Mol. Cells 2022, 45, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriegel, A.J.; Liu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Ding, X.; Liang, M. The miR-29 family: Genomics, cell biology, and relevance to renal and cardiovascular injury. Physiol. Genom. 2012, 44, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Jian, Z.; Xiao, Y. Long noncoding RNA TUG1 promotes cardiac fibroblast transformation to myofibroblasts via miR29c in chronic hypoxia. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 3451–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Sun, Z.; Chen, M.; Lun, J. LncRNA TUG1 Regulates Proliferation of Cardiac Fibroblast via the miR-29b-3p/TGF-beta1 Axis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 646806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, H.; Wei, D.; Sun, Z. Silencing lncRNA GAS5 alleviates apoptosis and fibrosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy by targeting miR-26a/b-5p. Acta. Diabetol. 2021, 58, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wu, N.; Xia, F.; Liu, S.; Jia, D. Long noncoding RNA GAS5 regulates myocardial ischemiareperfusion injury through the PI3K/AKT apoptosis pathway by sponging miR5325p. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 858–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.C.; Xia, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, D.Q.; Liu, S.C.; Zhou, X.N.; Zhang, F.X. Effect of lncRNA GAS5 on rats with acute myocardial infarction through regulating miR-21. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 8573–8579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Zhang, J.G.; Qin, R.H.; Dai, C.; Shi, P.; Yang, J.J.; Deng, Z.Y.; Shi, K.H. LncRNA GAS5 controls cardiac fibroblast activation and fibrosis by targeting miR-21 via PTEN/MMP-2 signaling pathway. Toxicology 2017, 386, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, S.; Qin, S. Long Noncoding RNA GAS5: A New Factor Involved in Bone Diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 807419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Xia, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Li, Y.; Jia, D.; Gao, Y.; Shi, U.; Zhang, C.; He, Y.; et al. The Role of LncRNA TUG1 in Obesity-Related Diseases. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippova, E.A.; Fridman, M.V.; Burdennyy, A.M.; Loginov, V.I.; Pronina, I.V.; Lukina, S.S.; Dmitriev, A.A.; Braga, E.A. Long Noncoding RNA GAS5 in Breast Cancer: Epigenetic Mechanisms and Biological Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Jiang, H.; Fang, Y.; Han, D.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Gong, X.; Hong, W.; Tu, J.; Wei, W. The essential role of long non-coding RNA GAS5 in glioma: Interaction with microRNAs, chemosensitivity and potential as a biomarker. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrou, G.I.; Hatziagapiou, K.; Zaravinos, A. The Non-Coding RNA GAS5 and Its Role in Tumor Therapy-Induced Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Qi, Y.; Qu, J.; Gai, L.; Shi, Y.; Yuan, C. Pathophysiological Functions of the lncRNA TUG1. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Sun, L.; Wan, F. Molecular mechanisms of TUG1 in the proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion of cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 4393–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wijsenbeek, M.; Cottin, V. Spectrum of Fibrotic Lung Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.F. Origin of Myofibroblasts in Lung Fibrosis. Curr. Tissue Microenviron. Rep. 2020, 1, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Antin, P.; Berx, G.; Blanpain, C.; Brabletz, T.; Bronner, M.; Campbell, K.; Cano, A.; Casanova, J.; Christofori, G.; et al. Guidelines and definitions for research on epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinert, T.; Baldotto, C.S.d.R.; Nunes, F.A.P.; Scheliga, A.A.d.S. Bleomycin-Induced Lung Injury. J. Cancer Res. 2013, 2013, 480608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moeller, A.; Ask, K.; Warburton, D.; Gauldie, J.; Kolb, M. The bleomycin animal model: A useful tool to investigate treatment options for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 362–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Jin, T.; Su, W.; Guo, Y.; Niu, Z.; Guo, J.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Ma, L.; Yu, T.; et al. The long non-coding RNA PFI protects against pulmonary fibrosis by interacting with splicing regulator SRSF1. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 2916–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savary, G.; Dewaeles, E.; Diazzi, S.; Buscot, M.; Nottet, N.; Fassy, J.; Courcot, E.; Henaoui, I.S.; Lemaire, J.; Martis, N.; et al. The Long Noncoding RNA DNM3OS Is a Reservoir of FibromiRs with Major Functions in Lung Fibroblast Response to TGF-beta and Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med 2019, 200, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senavirathna, L.K.; Liang, Y.; Huang, C.; Yang, X.; Bamunuarachchi, G.; Xu, D.; Dang, Q.; Sivasami, P.; Vaddadi, K.; Munteanu, M.C.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA FENDRR Inhibits Lung Fibroblast Proliferation via a Reduction of beta-Catenin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Liang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Yang, X.; Xu, D.; Gou, X.; Sathiaseelan, R.; Senavirathna, L.K.; Wang, P.; Liu, L. Long Noncoding RNA FENDRR Exhibits Antifibrotic Activity in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 62, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Yue, R.; Peng, X.; Yu, H.; Huang, X. Exosomes derived from hypoxia-induced alveolar epithelial cells stimulate interstitial pulmonary fibrosis through a HOTAIRM1-dependent mechanism. Lab. Investig. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Xu, P.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, C.; Song, X. ATF3 -activated accelerating effect of LINC00941/lncIAPF on fibroblast-to-myofibroblast differentiation by blocking autophagy depending on ELAVL1/HuR in pulmonary fibrosis. Autophagy 2022, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Xu, P.; Meng, C.; Song, C.; Blackwell, T.S.; Li, R.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Lv, C. lncITPF Promotes Pulmonary Fibrosis by Targeting hnRNP-L Depending on Its Host Gene ITGBL1. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Z.W.; Tian, L.H.; Yang, B.; Guo, R.M. Long Noncoding RNA H19 Acts as a Competing Endogenous RNA to Mediate CTGF Expression by Sponging miR-455 in Cardiac Fibrosis. DNA Cell Biol. 2017, 36, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.F.; Jiang, H.; Chen, J.; Hu, Q.; Yang, S.; Liu, X.P.; Liu, G. LncRNA H19 ameliorates myocardial infarction-induced myocardial injury and maladaptive cardiac remodelling by regulating KDM3A. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 1099–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; He, R.; An, J.; Deng, P.; Huang, L.; Yang, W. The effect of H19-miR-29b interaction on bleomycin-induced mouse model of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 479, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, X.; Wang, H.; Li, H. Silencing of long noncoding RNA H19 alleviates pulmonary injury, inflammation, and fibrosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome through regulating the microRNA-423-5p/FOXA1 axis. Exp. Lung Res. 2021, 47, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Guo, Z.; Xie, W.; Jin, W.; Zhu, D.; Chen, S.; Ren, T. The lncRNA H19 Mediates Pulmonary Fibrosis by Regulating the miR-196a/COL1A1 Axis. Inflammation 2018, 41, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Han, L.; Yan, W.; Ji, X.; Han, R.; Yang, J.; Yuan, J.; Ni, C. miR-489 inhibits silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by targeting MyD88 and Smad3 and is negatively regulated by lncRNA CHRF. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mo, R.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Ding, Y. lncRNA GAS5 promotes pyroptosis in COPD by functioning as a ceRNA to regulate the miR2233p/NLRP3 axis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 26, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Sahil, A.; Lv, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Dong, R.; Xue, H.; et al. Melatonin alleviates cardiac fibrosis via inhibiting lncRNA MALAT1/miR-141-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome and TGF-beta1/Smads signaling in diabetic cardiomyopathy. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 5282–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.Y.; Zhang, W.H.; Ma, W.T.; Liu, Q.H.; Xing, L.H.; Zhao, G.F. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 exacerbates acute respiratory distress syndrome by upregulating ICAM-1 expression via microRNA-150-5p downregulation. Aging 2020, 12, 6570–6585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Wu, Q.; Yao, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Han, R.; Yang, J.; Ji, X.; Ni, C. MiR-503 modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by targeting PI3K p85 and is sponged by lncRNA MALAT1. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, H.; Zhao, N.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, L. LncRNA Nuclear-Enriched Abundant Transcript 1 Regulates Atrial Fibrosis via the miR-320/NPAS2 Axis in Atrial Fibrillation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 647124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, F.A.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.F.; Wu, C.F. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes pulmonary fibrosis by regulating the microRNA4553p/SMAD3 axis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.; Hu, S.; Yu, J.; Li, W.; Li, P.; Huang, H. CREB1 transcription-activated lncRNA PVT1 promotes cardiac fibrosis via miR-145/HCN1 axis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2022, 353, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.; Hong, Y.; Li, J. PVT1 knockdown inhibited the biological behavior of LPS-induced cardiac fibroblasts by regulating miR-24. Genes. Genom. 2021, 43, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Li, Z.; Ding, W.M.; Yan, L.; Zhao, Q.Y. LncRNA PVT1 regulates atrial fibrosis via miR-128-3p-SP1-TGF-beta1-Smad axis in atrial fibrillation. Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Pan, H.; Yuan, J.; Xu, Q.; Xu, T.; Li, P.; Cheng, D.; Liu, Y.; Ni, C. LncRNA-PVT1 activates lung fibroblasts via miR-497-5p and is facilitated by FOXM1. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 213, 112030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilieva, M.; Miller, H.E.; Agarwal, A.; Paulus, G.K.; Madsen, J.H.; Bishop, A.J.R.; Kauppinen, S.; Uchida, S. FibroDB: Expression Analysis of Protein-Coding and Long Non-Coding RNA Genes in Fibrosis. Noncoding RNA 2022, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, M.; Porter, D.F.; Khavari, P.A. Methods to study RNA-protein interactions. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosen, M.R.; Militello, G.; Weirick, T.; Ponomareva, Y.; Dassanayaka, S.; Moore, J.B.T.; Doring, C.; Wysoczynski, M.; Jones, S.P.; Dimmeler, S.; et al. Airn Regulates Igf2bp2 Translation in Cardiomyocytes. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).