Rheological Characterization of a Concentrated Phosphate Slurry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Concentrated Phosphate Slurry Samples
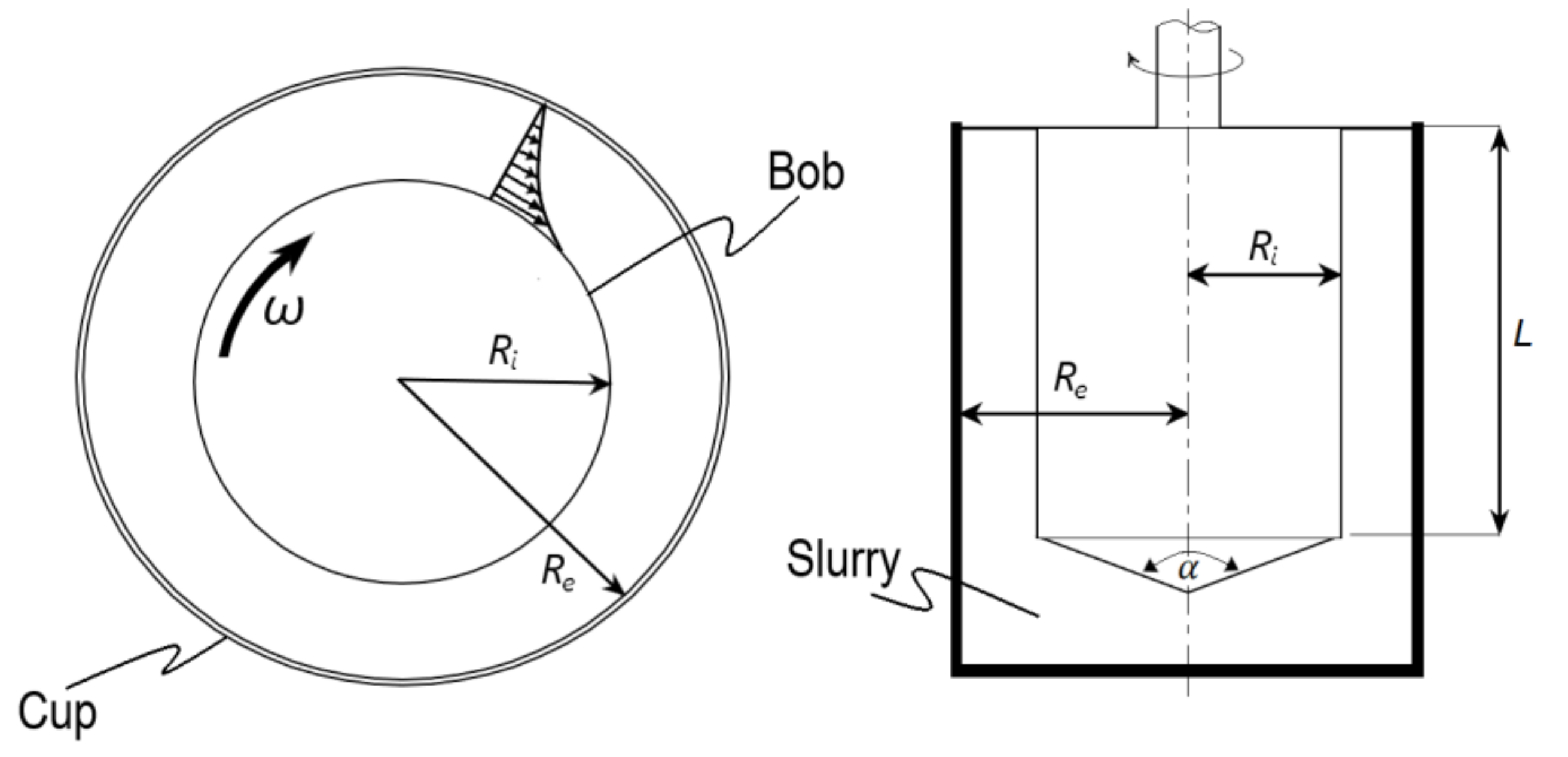
2.2. Suspension Characteristics
2.3. Experimental Data
2.4. Rheological Models
2.5. Determination of Model Parameters
3. Results and Discussions
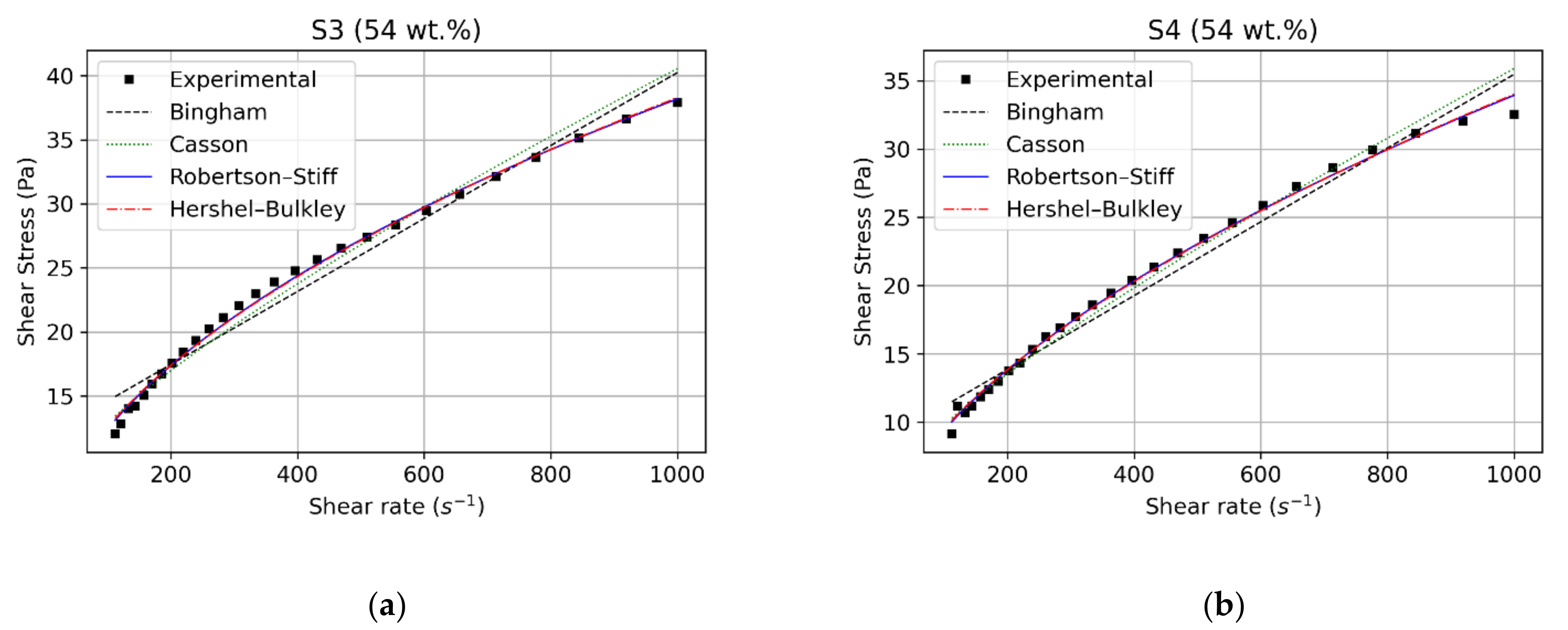
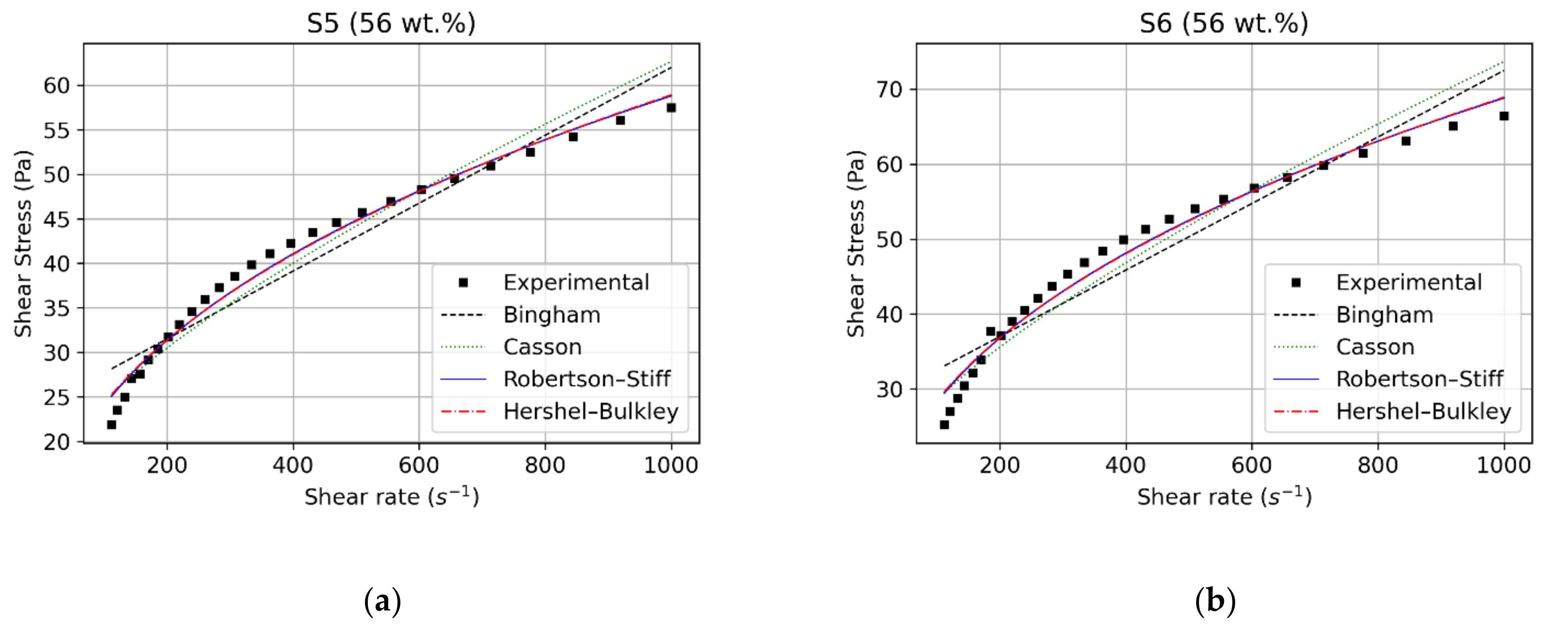
3.1. Rheological and Statistical Evaluation
3.2. Effect of Particles Concentration
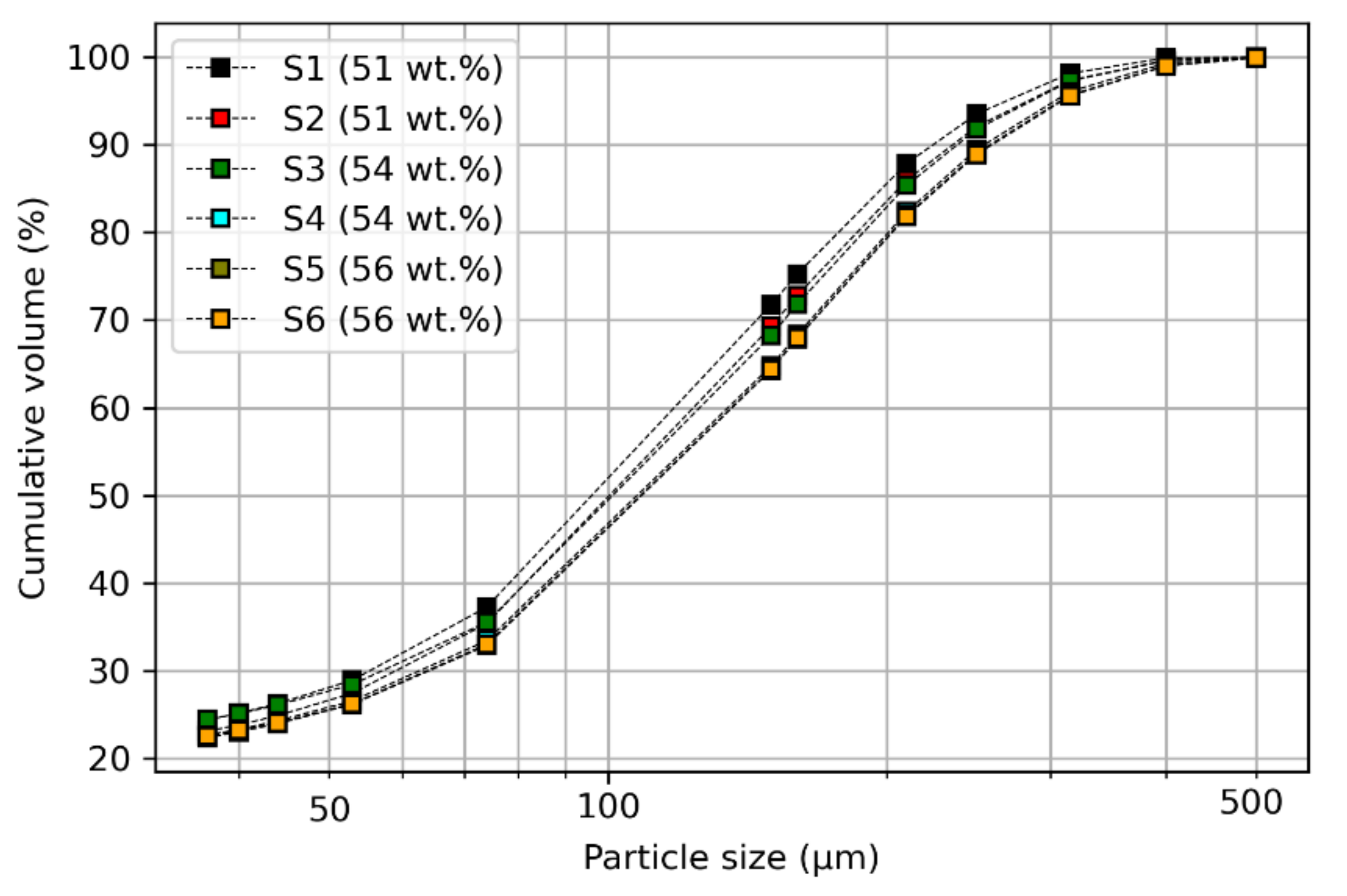
3.3. Effect of Particle Size Distribution
3.4. Laminar Pipe Flow
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Rotational Speed (rpm) | Shear Stress | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| τ (Pa) | ||||||
| Measuring Points | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 |
| 776.5 | 24.47 | 27.66 | 47.42 | 40.55 | 72.63 | 66.39 |
| 713.8 | 23.26 | 26.48 | 46.19 | 39.94 | 70.31 | 65.07 |
| 656.2 | 22.2 | 25.39 | 44.44 | 38.4 | 67.79 | 63.13 |
| 603.2 | 20.47 | 24.58 | 42.74 | 37.07 | 65.63 | 61.48 |
| 554.5 | 19.52 | 23.66 | 41.17 | 35.69 | 63.71 | 59.79 |
| 509.7 | 18.78 | 22.71 | 39.77 | 34.42 | 61.9 | 58.22 |
| 468.5 | 18.01 | 21.79 | 38.54 | 33.25 | 60.09 | 56.79 |
| 430.7 | 17.27 | 20.91 | 37.35 | 32.21 | 58.39 | 55.35 |
| 395.9 | 16.51 | 20.1 | 36.24 | 31.2 | 56.83 | 54.02 |
| 364 | 15.79 | 19.35 | 35.13 | 30.24 | 55.3 | 52.66 |
| 334.6 | 15.09 | 18.65 | 34.03 | 29.32 | 53.73 | 51.27 |
| 307.6 | 14.39 | 18.02 | 32.87 | 28.5 | 52.21 | 49.9 |
| 282.7 | 13.71 | 17.43 | 31.74 | 27.67 | 50.65 | 48.4 |
| 259.9 | 13.09 | 16.89 | 30.54 | 26.84 | 48.95 | 46.86 |
| 238.9 | 12.49 | 16.35 | 29.31 | 26.02 | 47.27 | 45.31 |
| 219.6 | 12.17 | 15.84 | 28.12 | 25.15 | 45.69 | 43.69 |
| 201.9 | 11.55 | 15.32 | 26.92 | 24.28 | 43.89 | 42.08 |
| 185.6 | 11.18 | 14.8 | 25.74 | 23.41 | 42.34 | 40.48 |
| 170.6 | 10.82 | 14.31 | 24.59 | 22.49 | 40.5 | 39.03 |
| 156.8 | 10.39 | 13.83 | 23.5 | 21.63 | 38.56 | 37.13 |
| 144.1 | 9.797 | 13.32 | 22.32 | 20.7 | 36.79 | 36.19 |
| 132.5 | 9.117 | 12.85 | 21.34 | 19.79 | 34.93 | 33.85 |
| 121.8 | 8.646 | 12.29 | 20.27 | 18.92 | 33.16 | 32.14 |
| 112 | 8.036 | 11.84 | 19.12 | 18.09 | 31.42 | 30.41 |
| 102.9 | 7.567 | 11.42 | 17.97 | 17.3 | 29.63 | 28.74 |
| 94.61 | 7.102 | 10.99 | 16.9 | 16.52 | 27.83 | 27.02 |
| 86.97 | 6.586 | 10.51 | 15.87 | 15.63 | 26.04 | 25.2 |
References
- Rusconi, J.; Lakhouaja, A.; Kopuz, M. The Design and Engineering of the 187 Km Khouribga to Jorf Lasfar Phosphate Slurry Pipeline. Procedia Eng. 2016, 138, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hore-Lacy, I. Production of Byproduct Uranium and Uranium from Unconventional Resources. In Uranium for Nuclear Power; Hore-Lacy, I., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2016; pp. 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, A.V. Rare-Earth Geochemistry of ‘old’ Phosphorites and Probability of Syngenetic Precipitation and Accumulation of Phosphate1In Memory of Richard P. Sheldon1. Chem. Geol. 1998, 144, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, S.A.; Khan, K.F.; Birch, W.D. Sedimentary: Phosphates. In Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shall, H.; Zhang, P.; Abdel Khalek, N.; El-Mofty, S. Beneficiation Technology of Phosphates: Challenges and Solutions. Miner. Metall. Process. 2004, 21, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, P. Phosphates and Phosphoric Acid: Raw Materials, Technology, and Economics of the Wet Process. Second Edition, Revised and Expanded; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1989; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Eshtiaghi, N.; Markis, F.; Slatter, P. The Laminar/Turbulent Transition in a Sludge Pipeline. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussot, P. Yield Stress Fluid Flows: A Review of Experimental Data. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2014, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, A. A Review of Technologies for Transporting Heavy Crude Oil and Bitumen via Pipelines. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2014, 4, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stickel, J.J.; Powell, R.L. Fluid Mechanics And Rheology Of Dense Suspensions. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2005, 37, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.; Llewellin, E.W.; Mader, H.M. The Rheology of Suspensions of Solid Particles. Proc. R. Soc. A: Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2010, 466, 1201–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelessidis, V.; Maglione, R.; Tsamantaki, C.; Aspirtakis, Y. Optimal Determination of Rheological Parameters for Herschel-Bulkley Drilling Fluids and Impact on Pressure Drop, Velocity Profiles and Penetration Rates during Drilling. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2006, 53, 203–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshtiaghi, N.; Markis, F.; Yap, S.D.; Baudez, J.-C.; Slatter, P. Rheological Characterisation of Municipal Sludge: A Review. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5493–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Santiago, M.; Santoyo, E.; Bello-Pérez, L.; Santoyo-Gutiérrez, S. Rheological Evaluation of Non-Newtonian Mexican Nixtamalised Maize and Dry Processed Masa Flours. J. Food Eng. 2003, 60, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein, A. Eine Neue Bestimmung Der Moleküldimensionen. Ann. Phys. 1906, 324, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. The Effect of Brownian Motion on the Bulk Stress in a Suspension of Spherical Particles. J. Fluid Mech. 1977, 83, 97–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, I.M.; Dougherty, T.J. A Mechanism for Non-Newtonian Flow in Suspensions of Rigid Spheres. Trans. Soc. Rheol. 1959, 3, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGEARY, R.K. Mechanical Packing of Spherical Particles. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1961, 44, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchiyama, N.; Tanaka, T. Porosity of a Mass of Solid Particles Having a Range of Sizes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fund. 1981, 20, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, M. The Viscosity of a Concentrated Suspension of Spherical Particles. J. Colloid Sci. 1951, 6, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, N.A.; Acrivos, A. On the Viscosity of a Concentrated Suspension of Solid Spheres. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1967, 22, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H.A. Shear-Thickening (“Dilatancy”) in Suspensions of Nonaggregating Solid Particles Dispersed in Newtonian Liquids. J. Rheol. 1989, 33, 329–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, J.; Wagner, N.J. Reversible Shear Thickening in Monodisperse and Bidisperse Colloidal Dispersions. J. Rheol. 1996, 40, 899–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranzano, B.J.; Wagner, N.J. The Effects of Interparticle Interactions and Particle Size on Reversible Shear Thickening: Hard-Sphere Colloidal Dispersions. J. Rheol. 2001, 45, 1205–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.; Jaeger, H.M. The Role of Dilation and Confining Stresses in Shear Thickening of Dense Suspensions. J. Rheol. 2012, 56, 875–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, N.J.; Brady, J.F. Shear Thickening in Colloidal Dispersions. Phys. Today 2009, 62, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.P.; Xu, J.Q.; Feng, C.L.; Yu, A.; Johnston, S.; Standish, N. Packing of Multi-Sized Mixtures of Wet Coarse Spheres. Powder Technol. 2003, 130, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, R.J. Prediction of the Viscosity of Multimodal Suspensions from Unimodal Viscosity Data. Trans. Soc. Rheol. 1968, 12, 281–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Powell, R.L. Effect of Particle Size Distributions on the Rheology of Concentrated Bimodal Suspensions. J. Rheol. 1994, 38, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, L.G.; Klimpel, R.R.; Luckie, P.T. Process Engineering of Size Reduction: Ball Milling; Society for Mining Metallurgy: Englewood, CO, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Mewis, J.; Wagner, N.J. (Eds.) Thixotropy. In Colloidal Suspension Rheology; Cambridge Series in Chemical Engineering; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 228–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denn, M.M.; Morris, J.F. Rheology of Non-Brownian Suspensions. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2014, 5, 203–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujake, J.E., Jr. Rheology of Concentrated Dicalcium Phosphate Suspensions. J. Pharm. Sci. 1965, 54, 1599–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benretem, A.; Benidir, M.; Chaib, R. Factors Influencing Slurry Rheology. World Pumps 2010, 2010, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, B.; El-Hami, K.; Mazouz, H. Study of the Rheological Behavior of Phosphate Slurry and Its Derivatives Products. In International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems for Sustainable Development; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, H.M. Thermal, Rheological, and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene/Phosphate Ore Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 263, 120151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertilizer, M. United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) and International Fertilizer Development Center (IFDC); Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Muscle Shoals, AL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Plastics—Polymers/Resins in the Liquid State or as Emulsions or Dispersions—Determination of Viscosity Using a Rotational Viscometer with Defined Shear Rate; ISO 3219: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993.
- Macosko, C.W. Rheology: Principles, Measurements, and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wazer, J.R. Colwell: Viscosity and Flow Measurement. A Laboratory Handbook of Rheology; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1964; pp. 371–372. Volume 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H. The “yield Stress Myth?” Paper—21 Years On. Appl. Rheol. 2007, 17, 43110–43111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussot, P.; Tocquer, L.; Lanos, C.; Ovarlez, G. Macroscopic vs Local Rheology of Yield Stress Fluids. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2009, 158, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thota Radhakrishnan, A.K.; van Lier, J.B.; Clemens, F.H.L.R. Rheological Characterisation of Concentrated Domestic Slurry. Water Res. 2018, 141, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khataniar, S.; Chukwu, G.A.; Xu, H. Evaluation of Rheological Models and Application to Flow Regime Determination. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 1994, 11, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herschel, W.H. Consistency of Rubber Benzene Solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1924, 16, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turian, R.M.; Ma, T.W.; Hsu, F.L.G.; Sung, D.J. Characterization, Settling, and Rheology of Concentrated Fine Particulate Mineral Slurries. Powder Technol. 1997, 93, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wang, Y.; Forssberg, E. Slurry Rheology in Wet Ultrafine Grinding of Industrial Minerals: A Review. Powder Technol. 2004, 147, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudez, J.-C.; Coussot, P. Rheology of Aging, Concentrated, Polymeric Suspensions: Application to Pasty Sewage Sludges. J. Rheol. 2001, 45, 1123–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, W.; Weir, I. Investigation of Methods for Direct Rheological Model Parameter Estimation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 1998, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohen, H.A.; Blick, E.F. Golden Section Search Method for Determining Parameters in Robertson-Stiff Non-Newtonian Fluid Model. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 1990, 4, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzner, A.B.; Reed, J.C. Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids—Correlation of the Laminar, Transition, and Turbulent-Flow Regions. Aiche J. 1955, 1, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, W.J.; Peden, J.M. A Generalized and Consistent Pressure Drop and Flow Regime Transition Model for Drilling Hydraulics. Spe Drill. Completion 2000, 15, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixinho, J.; Nouar, C.; Desaubry, C.; Théron, B. Laminar Transitional and Turbulent Flow of Yield Stress Fluid in a Pipe. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2005, 128, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Element | Concentration (wt.%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | |
| Bone phosphate of lime (BPL) | 64.5 | 64.7 | 64.4 | 64.8 | 66.0 | 65.0 |
| CO2 | 7.6 | 7.6 | 7.0 | 7.7 | 7.8 | 7.7 |
| SiO2 | 3.23 | 3.35 | 3.62 | 3.16 | 3.34 | 3.71 |
| MgO | 0.80 | 0.74 | 0.96 | 0.83 | 0.66 | 0.62 |
| Al2O3 | 0.46 | 0.41 | 0.46 | 0.44 | 0.40 | 0.47 |
| Reactive SiO2 | 1.43 | 1.24 | 1.19 | 1.29 | 1.27 | 1.06 |
| Model | Rheological Parameters | Test Samples | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | ||
| Bingham | (Pa) | 5.54 | 3.81 | 6.75 | 4.47 | 16.8 | 18.92 |
| (Pa·s) | 0.024 | 0.02 | 0.037 | 0.03 | 0.051 | 0.061 | |
| Casson | (Pa) | 4.42 | 2.56 | 5.29 | 3.27 | 12.86 | 14.8 |
| (Pa.s) | 0.01 | 0.012 | 0.017 | 0.017 | 0.019 | 0.022 | |
| Herschel–Bulkley | (Pa) | 1.36 | 0.89 | 1.32 | 0.82 | 3.21 | 3.7 |
| K (Pa·sn) | 0.75 | 0.395 | 1.032 | 0.6 | 2.98 | 3.56 | |
| n | 0.51 | 0.6 | 0.52 | 0.58 | 0.42 | 0.42 | |
| Robertson–Stiff | K (Pa·sn) | 0.99 | 0.5 | 1.28 | 0.72 | 3.87 | 4.56 |
| n | 0.47 | 0.56 | 0.49 | 0.56 | 0.39 | 0.39 | |
| (s−1) | 6.63 | 3.84 | 1.32 | 0.82 | 3.22 | 3.7 | |
| (Pa) | 2.40 | 1.06 | 1.66 | 0.65 | 6.1 | 7.5 | |
| Model | Statistical Indicators | Test Samples | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | ||
| Bingham | R2 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.9 |
| SSE | 12.16 | 9.58 | 51.11 | 36.01 | 210.14 | 356.49 | |
| RMSE | 0.67 | 0.59 | 1.37 | 1.15 | 2.79 | 3.63 | |
| Casson | R2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.93 |
| SSE | 3.94 | 3.87 | 29.94 | 21.22 | 137.33 | 252.25 | |
| RMSE | 0.38 | 0.37 | 1.053 | 0.88 | 2.25 | 3.05 | |
| Herschel–Bulkley | R2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.97 |
| SSE | 0.48 | 0.93 | 6.28 | 5.41 | 44.9 | 93.8 | |
| RMSE | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.48 | 0.44 | 1.28 | 1.86 | |
| Robertson–Stiff | R2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.97 |
| SSE | 0.52 | 0.97 | 5.25 | 4.79 | 40.4 | 86.74 | |
| RMSE | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.44 | 0.42 | 1.22 | 1.79 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maazioui, S.; Maazouz, A.; Benkhaldoun, F.; Ouazar, D.; Lamnawar, K. Rheological Characterization of a Concentrated Phosphate Slurry. Fluids 2021, 6, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids6050178
Maazioui S, Maazouz A, Benkhaldoun F, Ouazar D, Lamnawar K. Rheological Characterization of a Concentrated Phosphate Slurry. Fluids. 2021; 6(5):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids6050178
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaazioui, Souhail, Abderrahim Maazouz, Fayssal Benkhaldoun, Driss Ouazar, and Khalid Lamnawar. 2021. "Rheological Characterization of a Concentrated Phosphate Slurry" Fluids 6, no. 5: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids6050178
APA StyleMaazioui, S., Maazouz, A., Benkhaldoun, F., Ouazar, D., & Lamnawar, K. (2021). Rheological Characterization of a Concentrated Phosphate Slurry. Fluids, 6(5), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids6050178









