Abstract
Ocean waves deliver an immense amount of energy to coasts around the planet, powering high-velocity flows that interact with nearshore marine plants and animals. Although some of these interactions are beneficial, it is often advantageous for subtidal and intertidal ecological communities if wave-induced water velocities can be reduced by safely dissipating wave energy. This function is often fulfilled by seaweeds and marine plants, which thereby act as ecosystem engineers, modifying the environment to the benefit of the community. Recent advances in hydro-mechanical theory help to explain the mechanisms by which vegetation dissipates wave energy, highlighting the role that organisms’ tendency to bend in flow—their structural flexibility—plays in their ability to engineer wave-induced flows. Here, I review these theories and their application to salt marsh plants, seagrasses, mangroves, and seaweeds, focusing on the ways that marine vegetation serves a foundational role in community function.
1. Introduction
As they shoal and break on shores around the planet, ocean waves interact with a rich diversity of marine plants, seaweeds, and invertebrate animals. On the one hand, these interactions can be beneficial. For example, wave-induced water velocities stir kelp fronds and seagrass blades, increasing their access to light for photosynthesis. Turbulence created by breaking waves and bottom friction disperses the gametes broadcast by marine algae and invertebrates, facilitating fertilization and reproduction. On the other hand, the interaction of waves with nearshore biota can be destructive. The same wave-induced velocities that stir fronds and disperse gametes can impose hydrodynamic forces sufficient to shred seaweeds and rip animals from the seafloor. Moreover, the interaction between waves and biology is a two-way street. Just as waves can affect nearshore inhabitants, the hydrodynamic forces imposed on marine vegetation can dissipate wave energy, moderating its biological consequences. In this review, I explore these reciprocal interactions.
2. Ocean Waves
Waves on the ocean’s surface are an effective means of transporting energy. The energy per unit surface area in a wave, W, is proportional to the square of wave height, H (the vertical distance from trough to crest [1,2]):
Here, ρ is seawater’s density (nominally 1025 kg m−3) and g is the acceleration of gravity. With H measured in meters, W has units of J m−2. W is substantial even for small wave heights: for H = 1 m, W = 1257 J m−2. Multiply by the thousands of square km in which waves are aroused by storms at sea, and you can begin to grasp the vast reservoir of energy potentially available to interact with organisms as waves approach a shore.
In deep water, waves with period T travel at phase speed C = gT/(2), and their energy is transported at the group velocity Cg = C/2 [1,2]. Thus, wave-energy flux, the rate at which wave energy is delivered to the nearshore (watts per m of wave crest), is
For a typical wave arriving at an open coast (H = 1 m, T = 10 s), energy flux is 9800 W m−1, enough power in a single meter of wave crest to supply eight typical households. A single meter of storm-wave crest (H = 5 m, T = 15 s) could supply nearly 300 homes.
When waves arrive at a coast, some of their energy is reflected or scattered, but on most shores the bulk of wave energy is ultimately dissipated by friction, either internally in the water column by the viscous processes associated with turbulence (which is greatly amplified when waves break), or by “friction” with solid objects and the seabed. Seaweeds and marine plants contribute to the latter, indeed on some shores their presence controls the rate at which wave energy is dissipated. Therein lies our story.
3. Seaweeds and Marine Plants
For those not familiar with the taxonomy of marine organisms, it may be useful to define a few terms. To a botanist, plants and seaweeds are vastly different types of organism. Most plants are terrestrial, but a few are sufficiently tolerant of salt water to be able to inhabit the interface between land and sea; others have returned to the sea entirely. The marine plants I discuss here are all flowering plants—angiosperms. They have roots, stems, and leaves. Marsh plants typically have a central, upright stem from which leaves emerge. As with terrestrial grasses, seagrasses have a minimal stem and multiple leaves, known as blades. Mangroves—an informal rather than taxonomic term—comprise a variety of salt-tolerant trees, bushes, and palms. By contrast, the term “seaweed” is an informal reference to a wide variety of macroscopic marine algae, including members of the red, green, and brown algae. Many of these are relatively small, a few centimeters to a few tens of centimeters in length, with fronds (the algal analogue of leaves) ranging from simple rope-like structures; to thin, strap-like blades; to bushy branches. A subset of the brown algae—the kelps—are larger. Some have stipes (the algal analogue of stems) that are relatively stiff, elevating fronds a meter or so above the seafloor. Still others—the giant kelps—have flexible, rope-like stipes that can be tens of meters long, buoyed by gas-filled floats (pneumatocysts) that suspend fronds at the water’s surface. None of the marine algae have roots; instead they attach to the seafloor with a holdfast that adheres to the rocky surface.
4. Ecosystem Services and Ecosystem Engineers
Wave-energy dissipation by marine plants and seaweeds is often considered in the context of ecosystem services, the benefits that they can offer to human society. By benignly dissipating the power of ocean waves, marsh plants, seagrasses, mangroves, and seaweeds can protect shores from erosion and flooding, and provide shelter for economically valuable animals such as fish, shrimp, and crabs ([3,4,5] and references cited therein). In this review, however, I explore marine plants and seaweeds in a different context, that of their role as ecosystem engineers. An ecosystem engineer is a species whose physical presence alters a habitat to the benefit of other species in the local community [6]. Corals are perhaps the most widely recognized marine ecosystem engineers. By precipitating calcium and carbonate ions out of seawater to form solid reefs, corals provide habitat that would otherwise not exist, thereby providing a foundation for an extraordinarily diverse community of seaweeds and animals. Although less renowned, marsh plants, seagrasses, mangroves, and seaweeds are also ecosystem engineers; by altering their habitat in the nearshore they facilitate the development and maintenance of diverse, productive ecological communities.
4.1. Salt Marshes
Salt marshes are found in protected bays and estuaries throughout the temperate seas, occurring relatively high on the shore where they are alternately filled and drained as the tides rise and fall [7]. Dense beds of salt-tolerant marsh plants—such as cord grass (Spartina) and pickleweed (Salicornica)—stifle tidal currents and wave-induced flows to such an extent that sand and mud can settle out of the water column, providing a medium for the plants’ roots. The relatively calm water and unconsolidated sediment in a marsh are the preferred habitat for many invertebrate animals, and act as nursery grounds for fish and shellfish. Salt marshes have been extensively studied by ecologists as a model system in which to quantify the flow of trophic energy (the chemical energy contained in food) from sunlight (via photosynthesis in plants), to the herbivores that eat the plants, and on to the carnivores that prey on the herbivores [7]. Research on wave-energy dissipation by salt-marsh plants has focused on the system’s ability to retain sediments [5].
4.2. Seagrass Beds
Seagrass beds are found in the shallow subtidal waters of shores around the world [8]. Seagrasses can inhabit rocky substrata on moderately protected wave-swept shores, but are more typically found in bays. Common calm-water species include turtle grass (Thallasia) and Neptune grass (Posidonia); common open-coast species include surf grass, eel grass, and wire weed (Phyllospadix, Zostera, and Amphibolus, respectively). Like salt marsh plants, seagrasses act as ecosystem engineers by capturing sediments and providing habitat for diverse species of fish, shrimp, and clams, and they are eaten by a wide variety of animals (e.g., sea turtles and manatees). Seagrass beds have been studied by ecologists primarily for their role in nearshore tropical ecosystems, but owing to the practical difficulties of research in their subtidal habitat they have received less attention than salt marshes. As with salt-marsh plants, study of hydrodynamics of seagrass beds has focused on plants’ interaction with sediments (e.g., [9,10]).
4.3. Mangroves
The term “mangrove” applies to a diverse set of salt-water tolerant trees, bushes, and palms that can form dense assemblages—mangals—in the brackish water of tropical bays where they fill the ecosystem-engineering niche occupied by salt marshes in temperate waters. The aerial roots of these plants form a “virtually impenetrable thicket” [11] capable of effectively dissipating wave-induced flows. They serve as nursery habitat for a variety of fish and shellfish. Unlike salt marshes and seagrass beds, mangals’ extent is limited more by terrestrial factors—lightning strikes, fires, and wind damage from cyclones—than by waves [11].
4.4. Topographic Protection
Salt marshes, mangroves, and many seagrass beds are confined to shores where seafloor topography provides some protection from severe wave exposure. As a rule of thumb, ocean waves approaching a shore break when their height is equal to the water’s depth [12,13], and thereafter rapidly lose energy to turbulence [14]. As a consequence, on gently sloping shores potentially destructive storm waves break far offshore and lose much of their energy before arriving at the shoreline.
4.5. Rocky Shores
By contrast, rocky shores—which form 75% of the planet’s shoreline [15]—are often steep, allowing waves to interact more directly with nearshore species. Despite their potential for extremely energetic interaction with ocean waves, rocky shores support an exceptionally diverse community of seaweeds and invertebrate animals that has served as a model system for ecological study and experimentation (for reviews, see [16,17]). Several species (both seaweeds and invertebrates) act as ecosystem engineers on wave-swept rocky shores. For example, in subtidal temperate waters giant kelps such as Macrocystis, Nereocystis, and Ecklonia form dense forests that provide the physical structure for diverse communities [18]. In the intertidal zone, mussels (e.g., Mytilus and Perna) form tightly packed beds that provide habitat for hundreds of animal species. In contrast to studies of marshes and seagrass beds, where the focus of ecosystem-engineering hydrodynamics has been on sedimentation, studies of wave-induced flows on rocky shores have focused on the potential for hydrodynamic forces to damage or dislodge nearshore seaweeds and animals (e.g., [19,20,21,22,23]).
5. Wave-Energy Dissipation by Marine Plants and Seaweeds
A general theory has emerged that quantifies the ability of seaweeds and marine plants to dissipate the energy of ocean waves, and thereby predicts their potential to serve as ecosystem engineers. As water moves past an object attached to the seafloor—such as a marsh plant’s stem or a seaweed’s frond—forces are imposed by the water on the object. These forces include drag, a force in the direction of relative flow; lift, a force perpendicular to flow; and the acceleration reaction (an inertial force) acting in the direction of the water’s acceleration [2,24]. Lift is typically negligible for seaweeds and marine plants. The acceleration reaction can play a role in how stems, blades, and fronds bend in flow, but because acceleration is 90° out of phase with velocity in the oscillating flows imposed by waves, the acceleration reaction does not directly contribute to energy dissipation. Thus, in terms of energy dissipation, drag is the pertinent interaction between wave-induced flow and marine vegetation, and here I focus on our current understanding of its mechanics.
The stems, stipes, blades, and fronds of marine plants and seaweeds range in width w from a few mms to a few cm, and length L from a few cm to 10s of meters. Wave-induced water velocities U range from a few cm s−1 to several m s−1. Thus, the Reynolds number of flow past these objects typically exceeds 104 (Re = Uw/ or UL/, where is seawater’s kinematic viscosity, ~10−6 m2 s−1), and the drag on an individual can be appropriately characterized by the standard high-Re quadratic expression [24,25]:
Here is velocity relative to the organism, is a dimensionless drag coefficient, and is a characteristic area over which the flow interacts with the stem, blade, or frond. Traditionally, is taken to be the object’s frontal area, the area projected in the direction of flow [24]. However, when the object is flexible—such as a seagrass blade or algal frond—frontal area typically decreases with increasing as the object reconfigures in flow (e.g., [3,26]). In such cases, it can be more convenient to take as the planform area of the plant or seaweed—the area it subsumes when spread out on a planar surface.
From an organism’s perspective, drag is a force applied to it by moving water. From the water’s perspective, however, drag is a force applied to it by the organism, a force that acts over a distance as the water moves past the stem, blade, or frond. As a result, drag performs work (force distance) on the water, decreasing its kinetic energy. The rate at which energy is dissipated by a stem, blade, or frond is therefore the product of drag (a force) and the velocity of the water relative to the organism (distance per time):
The overbar indicates that is taken as the average over a wave period. With this relationship in hand, models of wave-energy dissipation by marine vegetation proceed by specifying , , and .
To a first approximation, as waves approach shore the velocities they induce can be described by linear wave theory [1,2]. In the shallow water where waves interact with marine plants and seaweeds, vertical velocities are small relative to horizontal velocities, and for purposes of estimating hydrodynamic forces they can be neglected. Maximum horizontal velocity and particle excursion relative to the substratum are
Here, d is water column depth below still water, and z is distance above the sea floor; k is the wave number, , where is wave length [27]:
and are graphed in Figure 1 as functions of d, and for two representative wave heights and periods: H = 1 m and T = 10 s, typical of an average day on many wave-swept shores; and H = 5 m and T = 15 s, conditions representative of a severe storm. Values are plotted for flow at both the water’s surface and the seafloor. and decrease with increasing water column depth, and increase slightly with distance above the seafloor. Note that I have truncated the calculation of and at the depth equal to wave height. At shallower depths, waves have broken, and the flows they induce are better described by solitary, rather than linear, wave theory [2,28]. For rigid objects attached to the seafloor, ; for flexible seaweeds and plants, may differ from U, a complication discussed below.
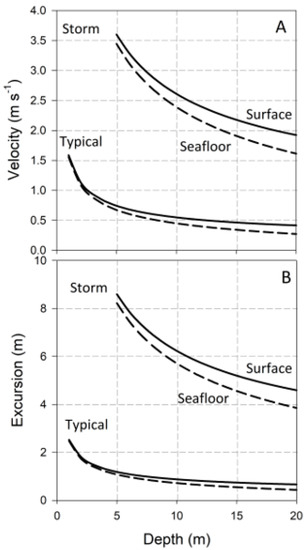
Figure 1.
Velocity and water-particle excursions in ocean waves: (A) Horizontal velocity as a function of water-column depth for two representative wave conditions; (B) Horizontal excursions.
For marine plants and seaweeds, both and are typically functions of water velocity. Even for rigid objects, typically decreases with increasing water velocity [24], a tendency that is amplified for marine plants as stems, blades, and fronds bend and reconfigure to more streamlined shapes under the influence of drag and the acceleration reaction. Similarly, frontal area often decreases as blades and fronds reconfigure. Given the wide variety of shapes among marine plants, an exact accounting for these issues is possible only on an individual-by-individual basis. Nonetheless, general rules have emerged. Recent studies on marsh plants and seagrasses have shown that tends to vary as a function of three dimensionless numbers: , the period parameter; Ca, the Cauchy number; and B, the buoyancy parameter [5,29,30,31,32,33].
5.1. Period Parameter
Wave-induced flow is oscillatory. As flow reverses direction, the wake that was previously downstream of an object is now upstream, and the structure of the wake’s flow can affect the drag subsequently applied to the object. This effect is most evident when, while flowing in one direction, water has limited distance to come to the sort of steady state it would achieve in unidirectional flow. Thus, if water moves a short distance relative to the flow-wise dimension of an object, can be affected [2,34]. The potential for such an effect is indexed by the period parameter, , (aka the Keulegan–Carpenter number), the ratio of flow excursion to the width of a stiff stem or the length of a flexible leaf or frond [35]:
If KC >> 1, flow can be treated as essentially unidirectional, and flow reversal has little effect on . If is near or less than 1, the effect of oscillatory flow needs to be taken into account. can also be interpreted as the ratio of drag to acceleration reaction [36]. When >> 1, drag is the dominant force acting on a stem, blade, or frond, and acceleration reaction can be neglected.
can also be used to assess the effect of oscillatory flow on the relative velocity experienced by a stem, blade, or frond. If a plant is flexible, it can, within limits, move with the water as the direction of flow reverses. While going with the flow, velocity relative to the organism is near zero, minimal drag is imposed, and little wave energy is dissipated. Only once the structure has reached the limits of its tether to the seafloor does water move relative to it, allowing flow energy to be dissipated. Low implies that an object can go with the flow for most of the water’s excursion, indicating that , and energy dissipation is reduced. Large implies that an object is stationary for most of the water’s excursion, , and energy can be effectively dissipated.
5.2. Cauchy Number
The tendency of a stem, blade, or frond to bend in flow—reconfiguration that, in addition to affecting , can affect both and —depends on the ratio of drag to the object’s resistance to being bent, indexed by the Cauchy number [3]:
Here, is again the length of a stem, blade, or frond (m), E is the elastic modulus of the material from which the object is constructed (Pa; [2,22,37]), and I is the second moment of area of the object’s cross section (m4), an index of how its shape affects its flexibility [2,22]. The term is garnered from engineering beam theory, which notes that —the force required to deflect the tip of a thin, cantilever-like structure (such as a stem, blade, or frond)—increases with the structures’ flexural stiffness, EI, and is inversely proportional to the square of the structures’ length (see [2,22] for a more complete explanation). If Ca << 1, reconfiguration is minimal, frontal area is relatively independent of flow, and varies primarily as a function of Reynolds number and the period parameter. If Ca >> 1, the stem, blade, or frond can substantially bend and reconfigure in flow, affecting both and .
A plant’s interaction with flow can also be affected by its buoyancy, indexed by the buoyancy parameter B [3,5]:
Here, is the density of the stem, blade, or frond, and V is its volume. If , the organism’s buoyancy is positive, tending to counteract drag and hold the stem, blade, or frond upright, thereby maintaining a relatively high and . If buoyancy is negative, the object sinks, which typically acts in concert with drag to bend the structure in the direction of flow, reducing and .
5.3. Models
Models of wave-energy dissipation by marine vegetation have proceeded along two paths. Both agree that Equation (4) governs energy dissipation, and that it is the product that specifies how a particular species interacts with flow. However, they differ on which aspect of that product to focus their attention. One path concentrates on specifying variation in under different flow conditions, the other on specifying as a function of flow. Both characterize the dynamic interaction between flow and vegetation using , Ca, and B.
Early work on the first path [38,39] assumed that vegetation consists of rigid vertical cylinders, in which case . Subsequent work [29,30] used the theory of cantilever bending to account for the fact that reconfiguration of structures in flow affects relative velocity. For simplicity, they assumed a constant , and used Ca and to parameterize empirical models of how varies as a function of flow. These models predict that wave-energy dissipation by flexible vegetation is reduced relative to that of rigid structures.
By contrast, the other path (exemplified by [3,33,36]) assumes that is constant, and instead accounts for the effects of flexibility by adjusting . They assume that stems, blades, and fronds are cantilever-like structures with width w and length L, and that is nominally equal to wL. But if the structure goes with the flow, only a reduced portion, , of the object’s length experiences relative velocity. In that case,
This approach then proceeds by predicting as a function of , Ca, and B [3]. At intermediate values of these parameters, it is difficult to make generalizations. However, at the ends of the spectrum of flexibility, simple rules apply. For minimally flexible and/or highly buoyant stems, blades, and fronds
For highly flexible, minimally buoyant structures,
Thus, like those of the first approach, models following the second approach predict that wave-energy dissipation by flexible vegetation is reduced relative to that of rigid structures.
Regardless of the approach to charactering the product , wave-energy dissipation is scaled up from the individual to the landscape scale by multiplying (Equations (4) and (11)) by N (the number of stems, blades, or fronds per seafloor area) to give an aerial estimate (W m−2):
If N is large, that is if stems, blades, and fronds are densely packed, interaction among structures must be taken into account, but these interactions vary among different morphologies and water-column depths (e.g., [31,40,41,42]).
Equation (14) is analogous to a standard equation in wave theory that describes the effect of bottom friction on wave-energy dissipation per unit seafloor area:
where f is a dimensionless energy friction factor [43,44]. One can reconcile these two perspectives by introducing a new dimensionless coefficient, , equal to NwL (). In that case the friction factor due to vegetation, , is
and energy dissipation per seafloor area owing to vegetation is
6. Theory in Practice
6.1. Salt Marshes, Seagrass Beds, and Mangroves
Theories of wave-energy dissipation have been verified in the field. For example, models applied to the relatively inflexible structure of mangroves successfully predict high rates of energy dissipation [42,45]. Similarly, Riffe et al. [32] found that dissipation by an intermediately flexible salt-marsh sedge (Schoenoplectus americanus) matched that predicted by a model incorporating flexibility, but was 70% less than that predicted for rigid stems. Even at this reduced rate, 56–81% of wave energy was dissipated within 19 m of the marsh’s edge. Research on seagrass beds has followed the same general line of inquiry as that on salt marshes, but has taken note of the greater flexibility of seagrasses, which tends to further reduce their ability to dissipate wave energy. For example, Bradley and Houser [29] found that a seagrass bed dissipated only 30% of wave energy over 39 m.
Energy dissipation by marsh plants, seagrasses, and mangroves reduces the turbulent kinetic energy among plants to such an extent that small particles can effectively settle out of the water column (e.g., [5,10,42]). The resulting “sandification” or “mudification” has beneficial biological effects. It allows sediments to accumulate, providing protection for the plants’ roots; retention of mineral nutrients; burial of organic carbon (amounting to a removal of CO2 from the atmosphere, a benefit in terms of climate change); habitat for infaunal animal species (e.g., clams and mussels); and potential extension of the marsh, bed, or mangal. It also reduces the turbidity of the water column, increasing the light intensity available for photosynthesis, thereby enhancing plants’ growth rates. In short, there is substantial positive internal feedback as a result of the ecosystem engineering provided by marsh plants, seagrasses, and mangroves, benefitting both the engineers themselves and other inhabitants of the community [46,47].
6.2. Rocky Shores
In protected bays and estuaries, wind has a limited distance over which it can raise waves. Consequently, the waves encountered by marshes, seagrass beds, and mangals typically have heights less than 10 cm, whereas on rocky shores waves traveling from distant storms can be nearly 10 m high. The one-hundred-fold difference in wave height implies a hundred-fold difference in horizontal velocity and particle excursions (Equations (5) and (6)), and a ten-thousand-fold difference in wave energy (Equation (1)). Furthermore, the typical elastic modulus, E, of algal stipe material (107 Pa) is a hundred-fold less than that of salt-marsh plants, seagrasses, and mangroves, resulting in Cauchy numbers >> 1 (Equation (9); [5,22]). These substantial differences affect the manner in which seaweeds function as ecosystem engineers.
6.2.1. Giant Kelps
Giant kelps such a Macrocystis and Nereocystis have thin stipes that are extremely flexible (Ca >> 1) and up to 25 m long, longer than the water’s depth (typically 5–15 m). Given the horizontal velocities predicted by Equation (5) and typical wave periods (8–20 s), the period parameter for these kelps is <1 even for storm waves, suggesting that they seldom reach the end of their tethers. Consequently, giant kelps experience minimal relative wave-induced flow and dissipate little wave energy. This simple analysis does not take into account kelp’s buoyancy and the effect of steady currents (e.g., [48]), but nonetheless is borne out by empirical measurements made both in the field and lab [41,49,50,51]. Thus, although giant kelps act as ecosystem engineers by slowing currents [40,41,52] and providing the complex three-dimensional habitat preferred by many species, their engineering effects do not extend to the effective dissipation of wave energy.
6.2.2. Benthic Seaweeds
By contrast, benthic seaweeds can substantially dissipate wave energy. Compared to the efforts required to model marsh plants and seagrasses, modeling wave-energy dissipation by benthic seaweeds is straightforward. As noted previously, the low elastic modulus of algal material ensures that Ca >> 1, and most benthic seaweeds lack pneumatocysts, so their buoyancy number is <1. For typical wave periods (8–20 s), wave heights (1–10 m), and frond lengths (0.1–0.5 m), the period parameters for these benthic seaweeds is substantially > 1, indicating that acceleration reaction is indeed small relative to drag, and flow past the organism can be treated as if it were unidirectional (). These combined effects ensure that these seaweeds are drawn out in the direction of flow by the drag they encounter under nearshore waves. Numerous measurements of algal drag show that (calculated using frond planform area, ) asymptotically decreases with increasing velocity, reaching representative constant values of approximately 0.2–0.4 at velocities above 2–3 m s−1 [26,53]. Seaweeds can densely cover the seafloor. Often the combined planform area of blades exceeds the area of substratum to which they are attached, and factors of = 5–34 have been measured [54]. Thus, for benthic seaweeds on wave-swept shores () ranges from approximately 1 to 14; a value of 2 is probably representative.
Wave dissipation on a typical rocky shore has been measured [44]. For water excursions of sufficient amplitude to ensure that > 1 ( > 0.3 m), friction-factor values ranged from 4 to 10, well in excess of values found on planar beaches and coral reefs. The authors attribute this high friction factor primarily to notably high variance in benthic topography. But it seems likely that the lush benthic algal cover at their site also contributes substantially to wave-energy dissipation; indeed, given dense algal cover, might account for 20–50% of the shore’s total friction factor. Overall wave-energy flux on the shore was reduced by 28% and 36% over 131 m and 116 m, respectively, so benthic seaweeds may have accounted for a reduction in energy flux of 6–18% on this shore.
The biological consequences of wave-energy dissipation by benthic seaweeds differ from those of salt-marsh plants, seagrasses, and mangroves. For those plants, the effects of ecosystem engineering center on the control of sedimentation and resuspension. By contrast, the engineering effects of benthic seaweeds are due to their ability to reduce disturbance. The structure and functioning of nearshore communities is strongly affected by the rate at which their component species are disturbed—broken or dislodged—by wave-induced hydrodynamic forces (e.g., [19,20,21]). As for other marine vegetation, the candidate forces on seaweeds are drag, lift, and the acceleration reaction. Of these three, the acceleration reaction can be discounted. In habitats outside the surf zone, water accelerations are typically too low to exert substantial forces (<1 m s−2). Accelerations in the surf zone can reach extreme levels (>400 m s−2, [55]), but the spatial extent of these accelerations is too small to exert a threatening acceleration reaction [56]. Thus, drag and lift are the primary hydrodynamic forces available to disturb subtidal and intertidal biota. Unlike seaweeds, some intertidal animals (e.g., mussels) can experience substantial lift [57], which, like drag (Equation (3)), is proportional to the square of . As noted previously, for benthic organisms >> 1, so . The question, then, is how is U affected by the presence of benthic seaweeds?
Energy dissipation accrues as waves approach shore, so it is organisms at the end of the approach—those in the very shallow subtidal and surf zones—that will be most affected by seaweed’s engineering, and it is there that I focus my attention. As noted previously, as waves shoal and break, their behavior departs from that predicted by linear wave theory, and is better predicted by solitary wave theory. Accordingly, the maximum velocity they can impose on benthic organisms is approximately [21,55]:
Drag and lift are both proportional to (Equation (3)), and therefore, for shallow subtidal and intertidal organisms, hydrodynamic force is directly proportional to wave height. Because wave-energy flux is proportional to (Equation (2)), the potential 6–18% seaweed-induced reduction in wave-energy flux at the site observed by Gon et al. [44] would amount to a 3–9% reduction in wave height at breaking, and thereby a 3–9% reduction in lift and drag (e.g., ). Presumably, this reduction in hydrodynamic force would lead to a reduction in the fraction of seaweeds and animals broken or dislodged [21]. If is greater than the 2 assumed in these calculations, hydrodynamic forces might be further decreased. In short, the presence of a lush community of subtidal seaweeds has the potential to decrease the rate of disturbance in very shallow subtidal and intertidal communities, with cascading effects on community ecology. For example, in the absence of wave-induced disturbance, mussels (themselves ecosystem engineers) are the dominant competitor for mid-intertidal space on many shores [16,19,20]. The rate at which mussel beds are disturbed is governed by the maximum lift they encounter [21,57], and therefore by wave height. (As wave-driven flow rushes over a tightly-packed mussel bed, pressure in the high-velocity water above the bed is lower than the slow-moving water in the bed’s intersticies, and the resulting bed-normal pressure gradient imposes a bed-normal—lift—force [57].) Reduced wave height will lead to reduced disturbance, an expansion of the beds, and a shift in community composition and ecological interactions. In summary, energy dissipation afforded by benthic seaweeds offshore provides protection for seaweeds and animals further inshore: ecosystem engineering at a distance.
For several reasons it remains to be seen whether the potential for nearshore vegetation to effectively dissipate wave energy is actually realized, and much work remains to be done. (1) The energetic interaction of waves with nearshore biota applies to humans as well as seaweeds and invertebrates, making it difficult to conduct research on wave-swept shores. Consequently, aerial coverage of seaweeds () has yet to be measured accurately on enough wave-swept rocky shores to be able to ascertain how widespread their ability might be to act as effective ecosystem engineers. (2) As with any general prediction, there are exceptions to the assumptions that underlie the calculations made here for wave dissipation by benthic seaweeds. For example, Durvillea antarctica, which grows in the low to mid intertidal zone on rocky shores in Chile and New Zealand, has fronds that are so exceptionally long (up to 10 m) that it violates the assumption that K >> 1. As a consequence, both direct measurements and modeling [58,59] suggest that this prominent member of the wave-swept community contributes negligibly to wave-energy dissipation. (3) The potential for seaweeds to act as ecosystem engineers may be limited by their ability to resist hydrodynamic forces. On some temperate shores, seaweeds grow large in the calm summer months, but are pruned back or dislodged when drag exceeds their strength in fall and winter storms [21,22,23]. The consequent reduction in would reduce seaweeds’ ability to protect inshore communities just when that protection is most needed. (3) Seasonal variation in —a natural experiment—could be used to directly quantify seaweeds’ contribution to energy dissipation by measuring dissipation in different seasons; that is, at different seaweed densities.
7. Conclusions
A general theory has emerged to explain and predict the ability of marine vegetation to dissipate wave energy and thereby to function as an ecosystem engineer. Flexibility, size relative to maximum excursion, and buoyancy play central roles in determining both the velocity relative to the organism and how plants and seaweeds reconfigure. These insights can be applied across the broad spectrum of marine vegetation, making it possible for fluid dynamicists to accurately predict pertinent aspects of flow for virtually any wave-swept ecological community. This ability presents an exceptional opportunity for marine ecologists to collaborate with fluid dynamicists to advance the exploration of nearshore communities.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
I thank J.H. MacMahan and E.B Thornton for stimulating conversations regarding the role of biology in wave mechanics, and D.R. Schiel and two anonymous reviewers for insightful comments on the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Kinsman, B. Wind Waves; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Denny, M.W. Biology and the Mechanics of the Wave-Swept Environment; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1988; pp. 45–71. [Google Scholar]
- Luhar, M.; Nepf, H.M. Flow-induced reconfiguration of buoyant and flexible aquatic vegetation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 2003–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, H.M. Motion of buoyant, flexible aquatic vegetation under waves: Simple theoretical models and parameterization of wave damping. Coast. Eng. 2019, 152, 102497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinoco, R.O.; San Juan, J.E.; Mullarney, J.C. Simplification bias: Lessons from laboratory and field experiments on flow through aquatic vegetation. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2019, 45, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.G.; Lawton, J.H.; Shachak, M. Organisms as ecosystem engineers. Oikos 1994, 69, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennings, S.C.; Bertness, M.D. Salt-marsh communities. In Marine Community Ecology; Bertness, M.D., Gaines, S.D., Hay, M.E., Eds.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 289–316. [Google Scholar]
- Wlliams, S.L.; Heck, K.L. Seagrass community ecology. In Marine Community Ecology; Bertness, M.D., Gaines, S.D., Hay, M.E., Eds.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 339–366. [Google Scholar]
- Van Katwijk, M.M.; Bos, A.R.; Hermus, D.C.R.; Suykerbuyk, M. Sediment modification by seagrass beds: Muddification and sandification induced by plant cover and environmental conditions. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 89, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidenbach, M.A.; Thomas, E.L. Influence of the seagrss, Zostera marina, on wave attenuation and bed shear within a shallow costal bay. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, A.M.; Farnsworth, E.J. Mangrove communities. In Marine Community Ecology; Bertness, M.D., Gaines, S.D., Hay, M.E., Eds.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 423–444. [Google Scholar]
- Galvin, C.J. Wave breaking in shallow water. In Waves on Beaches and Resulting Sediment Transport; Meyer, R.E., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1972; pp. 413–455. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Shore Protection Manual, 4th ed.; U.S Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1984.
- Thornton, E.B.; Guza, R.T. Transformation of wave height distribution. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, E.C.F. Coastal Geomorphology: An Introduction; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Menge, B.A.; Branch, G. Rocky intertidal communities. In Marine Community Ecology; Bertness, M.D., Gaines, S.D., Hay, M.E., Eds.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 221–252. [Google Scholar]
- Witman, J.D.; Dayton, P.K. Rocky subtidal communities. In Marine Community Ecology; Bertness, M.D., Gaines, S.D., Hay, M.E., Eds.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 339–366. [Google Scholar]
- Schiel, D.R.; Foster, M.S. The Biology and Ecology of Giant Kelp Forests; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dayton, P.K. Competition, disturbance, and community organization: The provision and subsequent utilization of space in a rocky intertidal community. Ecol. Monogr. 1971, 41, 351–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paine, R.T.; Levin, S.A. Intertidal landscapes: Disturbance and the dynamics of pattern. Ecol. Monogr. 1981, 51, 145–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny, M.W. Predicting physical disturbance: Mechanistic approaches to the study of survivorship on wave-swept shores. Ecol. Monogr. 1995, 65, 371–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny, M.W. Ecological Mechanics: Principles of Life’s Physical Interactions; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Martone, P.T.; Denny, M.W. To break a coralline: Mechanical constraints on the size and survival of a wave-swept seaweed. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 3433–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, S. Life in Moving Fluids, 2nd ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Schlichting, H.; Gersten, K. Boundary Layer Theory, 8th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Boller, M.L.; Carrington, E. Interspecific comparison of hydrodynamic performance and structural properties among intertidal macroalgae. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 1874–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckart, J.E. The propagation of waves from deep to shallow water. Gravity Waves Natl. Bur. Stand. Circ. 1952, 521, 165–173. [Google Scholar]
- Munk, W.H. The solitary wave theory and its application to surf problems. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1949, 51, 376–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, K.; Houser, C. Relative velocity of seagrass blades: Implications for wave attenuation in low-energy environments. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2009, 114, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullarney, J.C.; Henderson, S.M. Wave-forced motion of submerged single-stem vegetation. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, C12061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhar, M.; Nepf, H.M. From the blade scale to the reach scale: A characterization of aquatic vegetative drag. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffe, K.C.; Henderson, S.M.; Mullarney, J.C. Wave dissipation by flexible vegetation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L18607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhar, M.; Infantes, E.; Nepf, H. Seagrass blade motion under waves and its impact on wave decay. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 3736–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarpkaya, T.; Isaacson, M. Wave Forces on Offshore Structures; Van Nostrand-Reinhold Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Keulegan, G.H.; Carpenter, L.H. Forces on cylinders and plates in oscillating fluid. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Std. 1958, 60, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhar, M.; Nepf, H. Wave-induced dynamics of flexible blades. J. Fluids Struture 2016, 61, 20–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosline, J.M. Mechanical Design of Structural Materials in Animals; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple, R.A.; Kirby, J.T.; Hwang, P.A. Wave diffraction due to areas of energy dissipation. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean. Eng. 1984, 110, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Raichle, A.W.; Asano, T. Wave attentuation by vegetation. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean. Eng. 1993, 119, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosman, J.H.; Monismith, S.G.; Denny, M.W.; Koseff, J.R. Currents and turbulence within a kelp forest (Macrocystis pyrifera): Insights from a dynamically scaled laboratory model. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosman, J.H.; Denny, M.W.; Zeller, R.B.; Monismith, S.G.; Koseff, J.R. Interaction of waves and currents with kelp forests (Macrocystis pyrifera): Insights from a dynamically scaled laboratory model. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstman, E.M.; Dohmen-Janssen, M.; Narra, P.; van den Berg, N.J.F.; Siemerink, M.; Balke, T.; Bouma, T.; Hulscher, S. Wave attenuation in mangrove forests: Field data obtained in Trang, Thailand. Coast. Eng. Proc. 2012, 1, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, I.G. Wave boundary layers and friction factors. Coast. Eng. 1966, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gon, C.J.; MacMahan, J.H.; Thornton, E.B.; Denny, M.D. Wave dissipation by bottom friction on the inner shelf of a rocky shore. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2020, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo-Luong, P.; Massel, S. Energy dissipation in non-uniform mangrove forests of arbitrary depth. J. Mar. Sys. 2008, 74, 603–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, L.G. Multiscale flow-vegetation-sediment feedbacks in low-gradient landscapes. Geomorphology 2019, 334, 165–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hare, M.T.; Agular, F.C.; Asaeda, T.; Bakker, E.S.; Chambers, P.A.; Clayton, J.S.; Elger, A.; Ferreira, T.M.; Gross, E.M.; Gunn, D.M.; et al. Plants in aquatic ecosystems: Current models and future directions. Hydrobiologica 2018, 812, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaylord, B.; Denny, M.W.; Koehl, M.A.R. Modulation of wave forces on kelp canopies by alongshore currents. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehl, M.A.R. How do benthic organisms withstand moving water? Amer. Zool. 1984, 24, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwany, M.H.S.; O’Reilly, W.C.; Guza, R.T.; Flick, R.E. Effects of Southern California kelp beds on waves. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1995, 121, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsmore, K.E.; Nickols, K.J.; Miller, L.P.; Denny, M.W.; Gaylord, B. Wave damping by giant kelp, Macrosystis pyrifera. Estuar. Coast. Shelf. Sci. (Submitted).
- Gaylord, B.; Rosman, J.H.; Reed, D.C.; Koseff, J.R.; Fram, J.; McIntyre, S.; Arkema, K.; McDonald, M.A.; Brzezinski, J.L.; Monismith, S.G.; et al. Spatial patterns of flow and their modification within and around a giant kelp forest. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 1838–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martone, P.T.; Kost, L.; Boller, M. Drag reduction in wave-swept macroalgae: Alternative strategies and new predictions. Am. J. Bot. 2012, 99, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, E.G.; Paine, R.T.; Quinn, J.F.; Suchanek, T.H. Wave energy and intertidal productivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 1314–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaylord, B. Detailing agents of physical disturbance: Wave-induced velocities and accelerations on a rocky shore. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1999, 239, 85–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaylord, B. Biological implications of surf-zone complexity. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny, M.W. Lift as a mechanism of patch generation in mussel beds. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1987, 113, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.L.; Hurd, C.L.; Smith, M.J. Field measurement of the dynamics of the bull kelp Durvillea antarctica (Chamiso) Heriot. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2002, 269, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.L.; Hurd, C.L.; Smith, M.J. An idealized model of interactions between fronds of the large seaweed Durvillea antarctica. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 49, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).