Abstract
The structure formation influence on various macroscopic properties of fluid–fluid disperse systems is poorly investigated. The present work deals with the experimental study of the charge transfer in emulsions whose dispersed phase droplets are arranged into chainlike structures under the action of an external force field. The emulsions studied are the fluid system in which water droplets are dispersed in a hydrocarbon-based magnetic fluid. Under the effect of an external uniform magnetic field, anisotropic aggregates form from the emulsion dispersed phase drops. The low-frequency electrical conductivity of emulsions has been measured. It is demonstrated that the emulsions’ conductivity grows several times under the effect of magnetic field parallel to the measuring electrical field. The anisotropic character of the emulsion electrical conductivity in the presence of magnetic field has been demonstrated. It is revealed that the maximal response of conductivity on the magnetic field action takes place at the dispersed phase volume fraction of about 20%. The dynamics of the conductivity variation is analyzed in dependence on the magnetic field strength and the dispersed phase volume fraction. The obtained results may be of interest in the development of potential applications of disperse systems with magnetic-field-controllable properties.
1. Introduction
The physics of colloidal soft-matter systems controlled by external fields presents a very active research area [1,2]. In particular, controlling the properties of colloids by magnetic field has many potential applications including smart optical elements, chip heat dissipation, and intelligent healthcare [3,4]. The essential issue in this context is the determination of the macroscopic properties’ correlation with the microstructure and microgeometry of the disperse system [5,6,7]. This problem is of fundamental importance for the science of disperse systems, and is of applied interest for a number of practical applications of these systems [8,9]. The present work is focused on the electrical conductivity of disperse systems. Targeted regulation of the microstructure by external force fields allows the control and enhancement of the charge transfer processes in such media [10].
It is well established that solid-particle dispersions (magneto- and electrorheological suspensions and magnetic fluids) can change their physical properties by applying an external magnetic (electric) field [11,12,13]. The magnetic (electric) field induces ordering and agglomeration of the dispersed micro- or nanoparticles in the fluid, leading to significant changes in the macroscopic conductivity [14,15,16]. The disadvantage of using an electric field in this case is the inability to independently control the microstructure and the charge transfer process in the system. It should be noted that this requires comparatively high field strengths to achieve a substantial structure formation leading to the conductivity variation in solid particles dispersions.
The use of fluid–fluid dispersed systems (i.e., emulsions) in investigations of such a kind opens up new promising opportunities. Electrical conductivity of the emulsion systems has also been intensively studied [17,18,19]. Emulsions have several advantages over solid-particle suspensions. In particular, they respond more easily to the action of external force fields in the sense of particle mobility. However, the effects of conductivity variation in emulsions appear to be not as drastic as those observed in solid-particle suspensions; the material properties can be adjusted readily in emulsion systems by dissolving additional substances in the both fluids of the system. Thus, the mechanism of the conductivity variation can be examined by varying the material properties carefully in emulsion systems. In addition, the emulsions usually have higher stability with respect to sedimentation/flotation process compared to the solid microparticle suspensions, as the emulsion phase densities can be closer to each other. Furthermore, the emulsions can maintain fluidity even with a high content of the dispersed phase. That said, the abilities to control structural properties and corresponding functional properties of traditional emulsions reported in the existing studies are quite limited. Particularly, the formation of isotropic floccules and fractal aggregates in traditional emulsions were investigated [20,21]. Furthermore, the existing studies of the influence of structure formation processes on the regularities of macroscopic properties of emulsion systems are very limited.
This requires the creation of emulsion systems with effectively regulated microstructure and controlled properties. The magnetic-field-responsive magnetic fluid emulsion is a highly promising model system for studying the influence of the microstructural state on the macroscopic parameters of emulsion systems. Magnetic fluid emulsion is a two-phase mixture consisting of magnetic fluid droplets suspended in a nonmagnetic immiscible liquid [22,23,24] or nonmagnetic droplets suspended in a magnetic fluid [25,26]. In contrast to the electric-field-responsive traditional emulsions, the magnetic fluid emulsions do not demonstrate any additional complicating effects under the action of magnetic fields, such as charge transfer and accumulation, electroconvection, droplets electrorotation, etc. It should be noted that besides the use as model systems, there is a wide range of applications supporting the growing research on the behavior of magnetic fluid emulsions as magnetically controllable media. For instance, their interaction with external magnetic fields has been extensively explored in microfluidics [27,28], sensors [29,30], and biomedical processes, such as targeted drug delivery [31,32] and restorative treatment of retinal detachment [33]. This also motivates the research into macroscopic properties of such systems.
Emulsions containing droplets of a hydrocarbon-based magnetic fluid dispersed in water were mainly investigated. Considerable attention was paid to the study of the microstructure and optical properties of such systems [34,35,36,37]. Inverse systems of nonmagnetic liquid droplets dispersed in magnetic fluid can demonstrate more varied behavior and can gain new applications. Previously we have investigated some aspects of the dielectric behavior of the emulsion of glycerin droplets dispersed in a magnetic fluid [38]. The heat transfer in the emulsion of water droplets dispersed in a hydrocarbon-based magnetic fluid has also been considered [39]. Here, we present the further development of these studies. The electrical conductivity of water in hydrocarbon based magnetic fluid emulsion will be considered. In contrast to the previous results, in this work a much higher response of the emulsion to the action of the magnetic field will be demonstrated. In addition, the temporal evolution of the emulsion electrical properties due the field-induced structuring process will be investigated for the first time; and the anisotropic character of the emulsion will be considered in more detail. In light of the foregoing, the aim of this work is to study the influence of the magnetic field driven structure formation in magnetic fluid emulsion on the peculiarities of its macroscopic electrical conductivity.
2. Materials and Methods
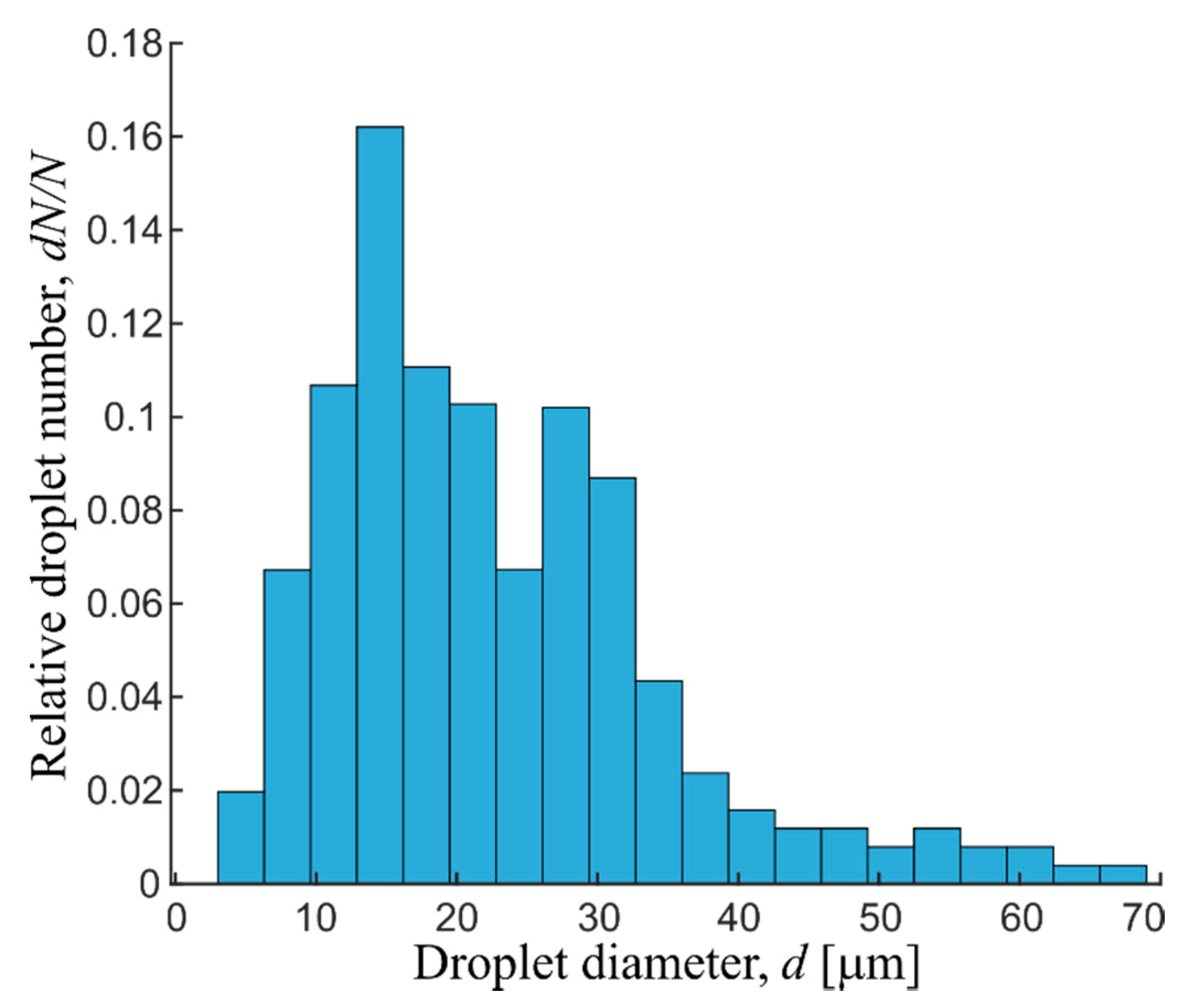
Emulsions forming chain microstructures in magnetic field were obtained by mixing water with a kerosene-based magnetic fluid. To create the emulsions, polyglyceryl-3 polyricinoleate (C27H52O9), a surface-active substance with the low hydrophilic-lipophilic balance equal to 3.5, was used. The surface-active substance was first dissolved in magnetic fluid (~3% vol), and then water was drop-by-drop added at continuous mechanical mixing with a homogenizer. This yielded an average ≈23 µm microdrop emulsion. Figure 1 shows the experimentally determined emulsion drop-size distribution obtained by the optical microscopy image processing using Matlab script. The dispersed phase drop sizes were by several orders of magnitude larger than those of the magnetic fluid magnetic nanoparticles (~10 nm); hence, within the framework of this study, the magnetic fluid can be considered as a continuous magnetizable medium. The obtained emulsions may be classified as water-in-oil.

Figure 1.
Droplet size distribution histogram of water in kerosene-based magnetic fluid emulsion.
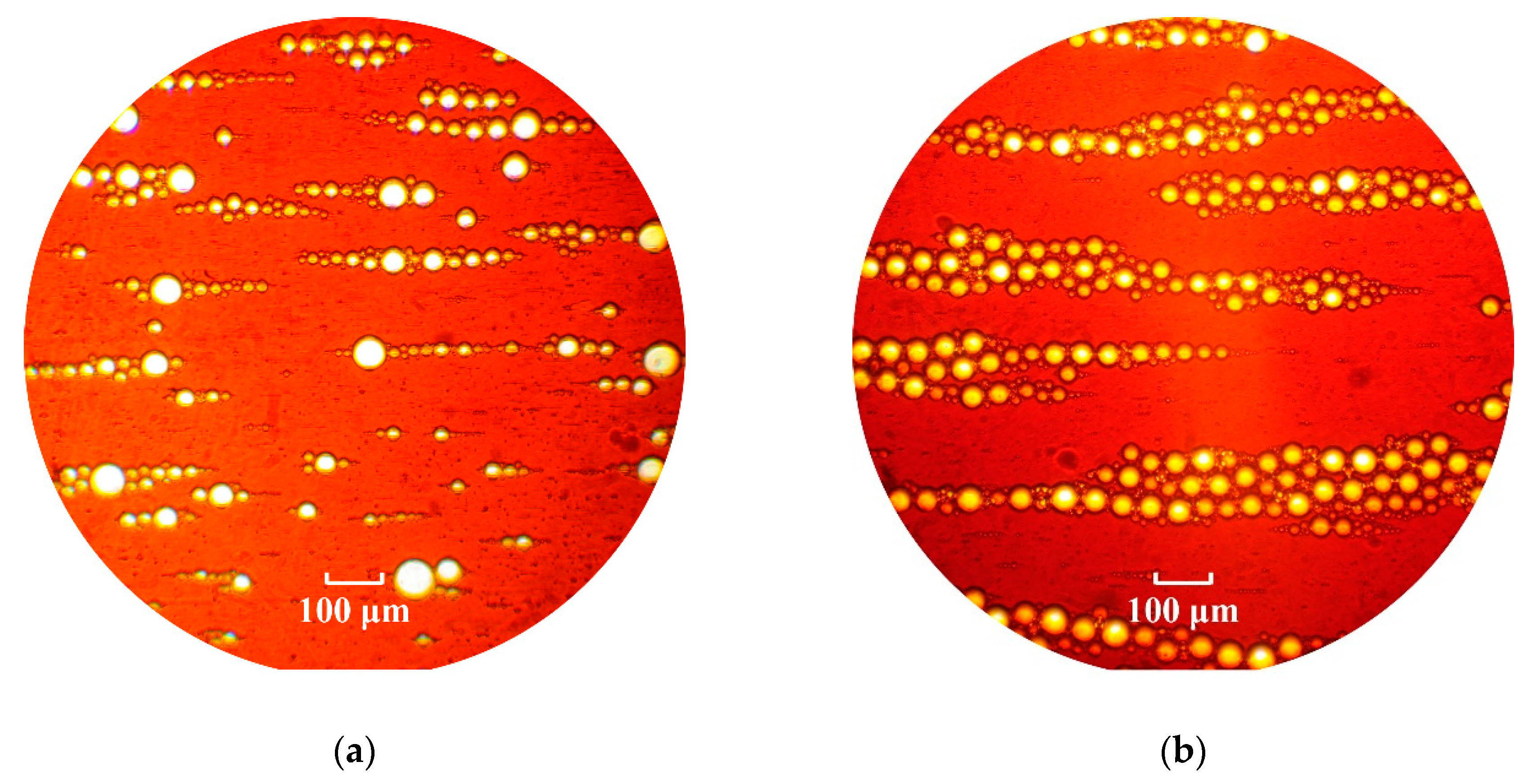
The external stationary magnetic field effect provokes dispersed phase drop aggregation ordered along field direction chain structures. This resulted from the interactions of the field-induced magnetic moments of the emulsion drops. The induced magnetic moments are in opposition to the field in this case, since the nonmagnetic drops immersed in a magnetizable medium may be considered as the diamagnetic particles (“magnetic holes”). The estimated effective interaction parameter (ratio of maximal magnetic interaction energy to thermal energy) for emulsion droplets is in the range 105–107, which indicates the prevalence of magnetic interactions due to the large size of the droplets. At the low (~0.1) dispersed phase volume fractions, the emulsion drops are organized into separate chains, whose image obtained with an optical microscope in transmitted light is shown in Figure 2a. When the emulsion dispersed phase volume fraction grows, the drops arrange into dense column-shape structures instead of separate chains under action of magnetic field, as shown in Figure 2b. The transition from single chains to larger bundles has been previously observed in the suspensions of solid particles in magnetic fields [40,41].

Figure 2.
A horizontal layer of water in magnetic fluid emulsion under action of uniform constant magnetic field, directed horizontally along plane of figure. (a) Dispersed phase volume fraction is φ = 0.1. (b) Dispersed phase volume fraction is φ = 0.3, external magnetic field strength is H = 3.5 kA/m. The layer thickness is about droplets diameter.
The emulsions were prepared from a kerosene-based oleic-acid-stabilized magnetite magnetic fluid. The magnetic fluid used was produced in the Laboratory of Applied Ferrohydrodynamics of the Ivanovo State Power University (Russia). Its density was 1100 kg/m³, magnetite volume fraction was ≈0.07, initial static magnetic permeability was 1.6, dynamic viscosity coefficient was 2 mPa·s, and saturation magnetization was 14.9 kA/m. To increase the electrical conductivity of the water used for the emulsion preparation, some sodium chloride was preadded. The other purpose of the above was to achieve the high initial concentration of the ions dissolved in water, to disregard its change from addition of emulsifier and from contact of water with magnetic fluid. This allows us to consider the characteristics of water determined prior to the emulsion preparation unchanged. Water density was 1100 kg/m³; dynamic viscosity was 1 mPa·s. Density of magnetic fluid close to that of water was selected to slow down the emulsion’s sedimentation-induced stratification processes.
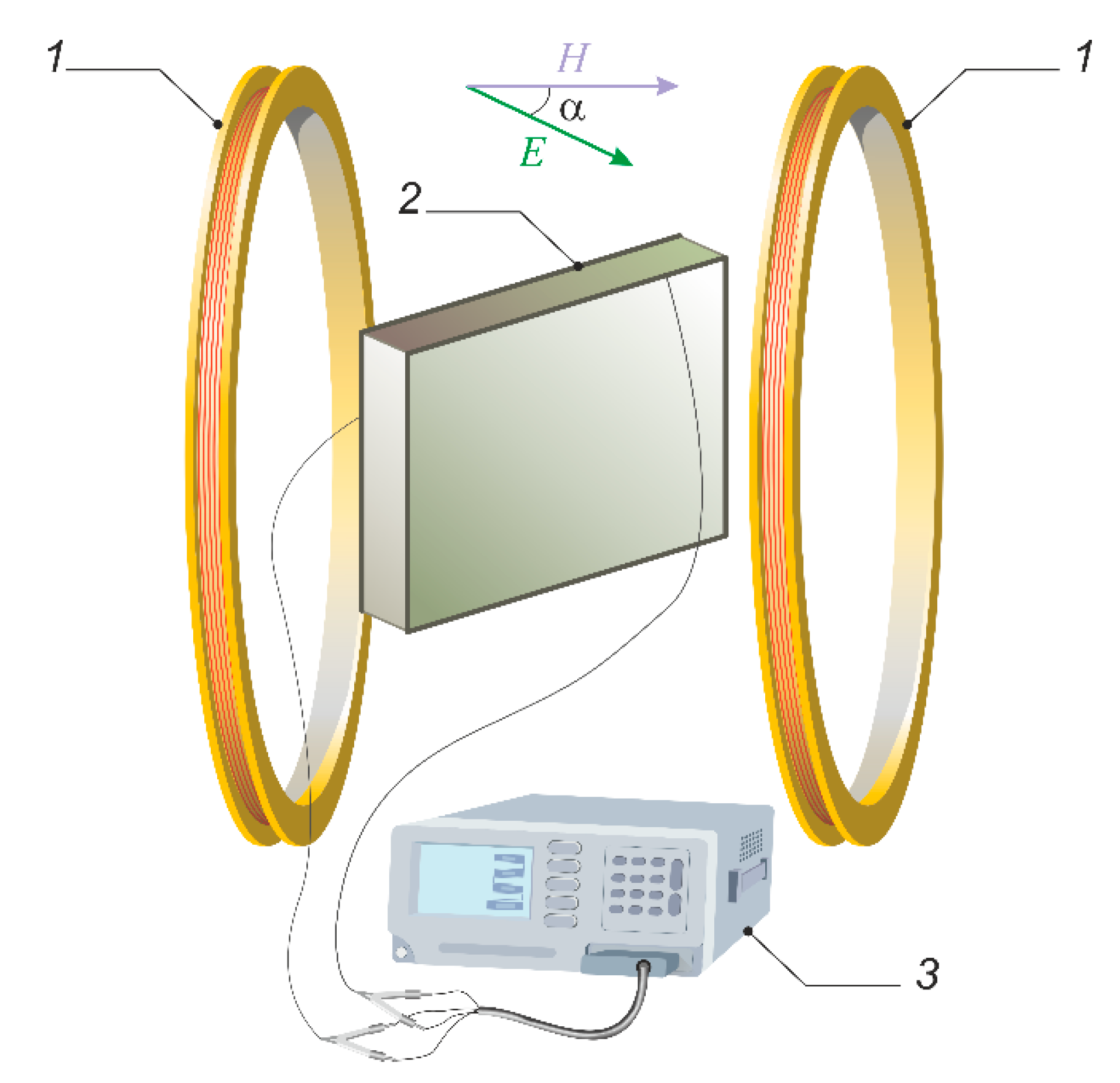
The specific electrical conductivities of the emulsions were investigated using the experimental setup sketched in Figure 3. To determine the electrical conductivity, the emulsion under study was placed into a cell with copper electrodes, i.e., 38 × 44 × 2.5 mm rectangular parallelepiped capacitor. Then the active conductivity was measured using the parallel equivalent circuit. For measurement, the Good Will Instrument LCR-78110G digital alternating current impedance meter was used. The measured active conductivity value G of the cell with the sample inside served to determine the emulsion’s specific electrical conductivity: λ = Gl/S, where l is the distance between electrodes, and S is the electrodes’ area.

Figure 3.
Experimental setup for the electrical conductivity measurement: 1—Helmholtz coils; 2—measuring cell filled with sample under study; 3—alternating current impedance meter.
The measurements used the 10 kHz signal frequency, in order to disregard the electrodes’ polarization effects. The specific electrical conductivities were 2 × 10−6 S/m for the magnetic fluid, 4.4 × 10−2 S/m for the water, and 2.7 × 10−8 S/m for the emulsifier. Due to the great specific conductivity of the dispersed phase compared with the dispersion medium, a significant change of the macroscopic electrical conductivity of such emulsions during structure formation can be expected. The dispersion frequency for the system under study can be assessed from the Wagner formula [17]:
where εi, εe are the dielectric permeabilities of the dispersed phase and dispersion medium correspondingly; λi, λe are the specific electrical conductivities of the dispersed phase and dispersion medium correspondingly; φ is the dispersed phase volume fraction. Substituting corresponding numerical values, one can ascertain that, here, the measuring frequency is much lower than the dispersion frequency for the system under study (7~9 × 106 Hz), hence, this measuring mode can be assumed quasistatic. Note that the physical parameters of a pure magnetic fluid can be considered constant and field-independent in a strength range used in the current experiments.
To study the effect of the magnetic field on the measured values, the sample filled cell was placed into the constant uniform magnetic field created by Helmholtz coils. The cell was able to rotate around a vertical axis, which allows varying and controlling the mutual orientation of the applied magnetic and measuring electric fields. It should be noted that the experimental measuring electric field was weak enough and did not have an effect on the structural state of the emulsion under study, that is, the structure in emulsion formed only under the effect of the applied external magnetic field. The observations have shown that the equilibrium structure establishment time in the studied emulsion usually does not exceed 10–15 s. Note that the time of a single measurement of the sample conductivity is short enough (0.15 s) in comparison with the time of the structure formation processes in medium.
The instrumental error value at the direct measurement of conductivity is quite small, and the resulting experimental error was assessed from the repeatability of results determined mainly by the limited reproducibility of the emulsion properties. It was demonstrated that the magnetic field in the used strength range has no effect on the electrical conductivity of pure magnetic fluid or water. This is consistent with the results of previous studies [42] (pp. 47–52). On the contrary, the application of magnetic field resulted in a notable change in the electrical conductivity of magnetic fluid emulsions.
3. Experimental Results
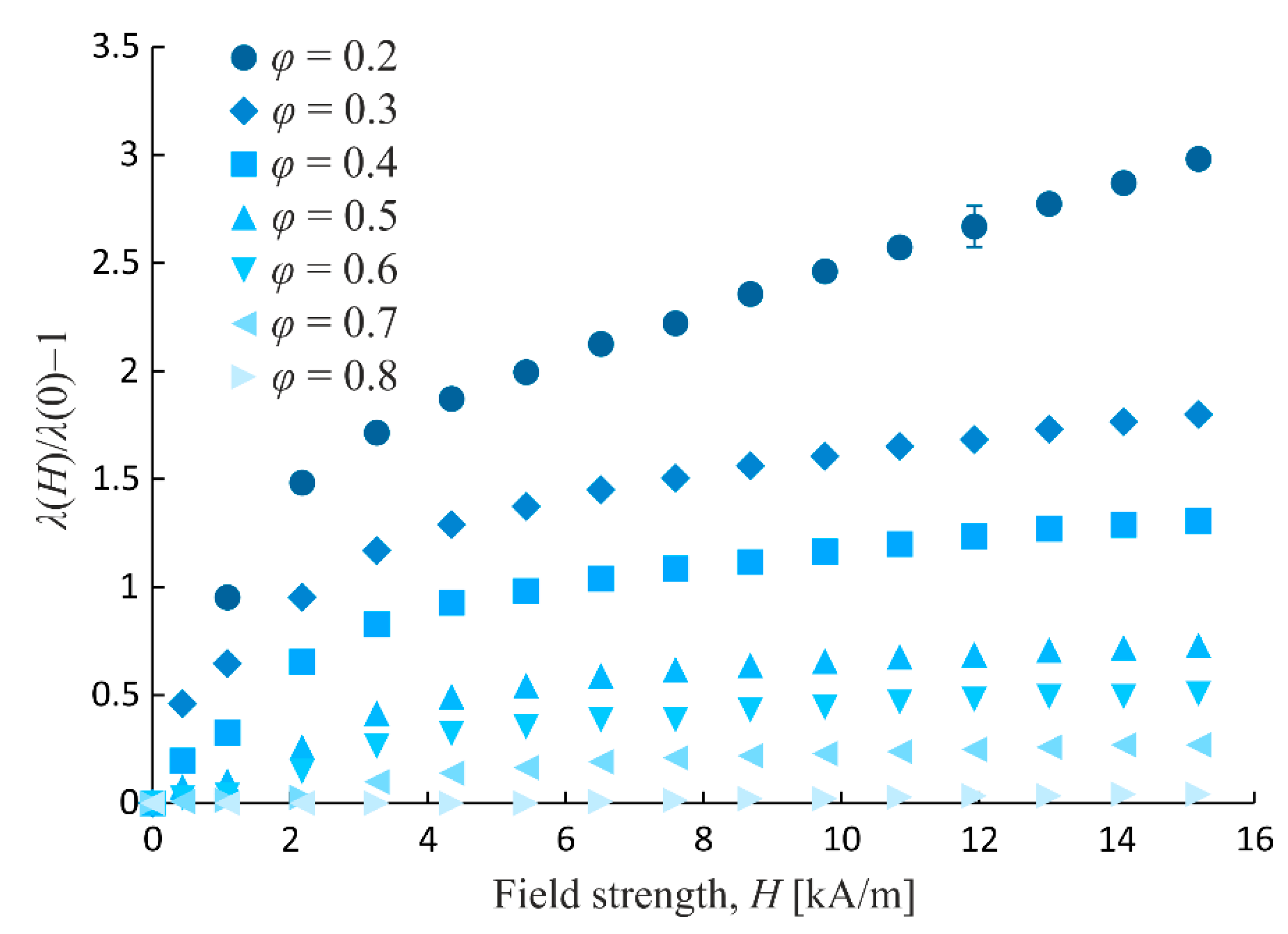
The effect of an external magnetic field codirectional with the electric measuring field was found to increase the emulsion specific electrical conductivity up to fourfold in comparison with the initial value. This is much higher than the thermal conductivity response and the glycerin in magnetic fluid emulsion response observed in previous studies. Thus, Figure 4 shows the experimental dependences of the emulsion specific electrical conductivity relative change on the external magnetic field strength at different volume fractions of dispersed phase, obtained at the parallel orientation of the magnetic and electric fields. Note that the stationary (time-independent) values of the emulsion electrical conductivity are presented in Figure 4. As a rule, the experimental settling times of the stationary electrical conductivity value did not exceed 10~15 s.

Figure 4.
Experimental dependences of magnetic fluid emulsion specific electrical conductivity relative change on external magnetic field strength at different dispersed phase volume fractions. Magnetic and measuring electric fields are parallel-oriented.
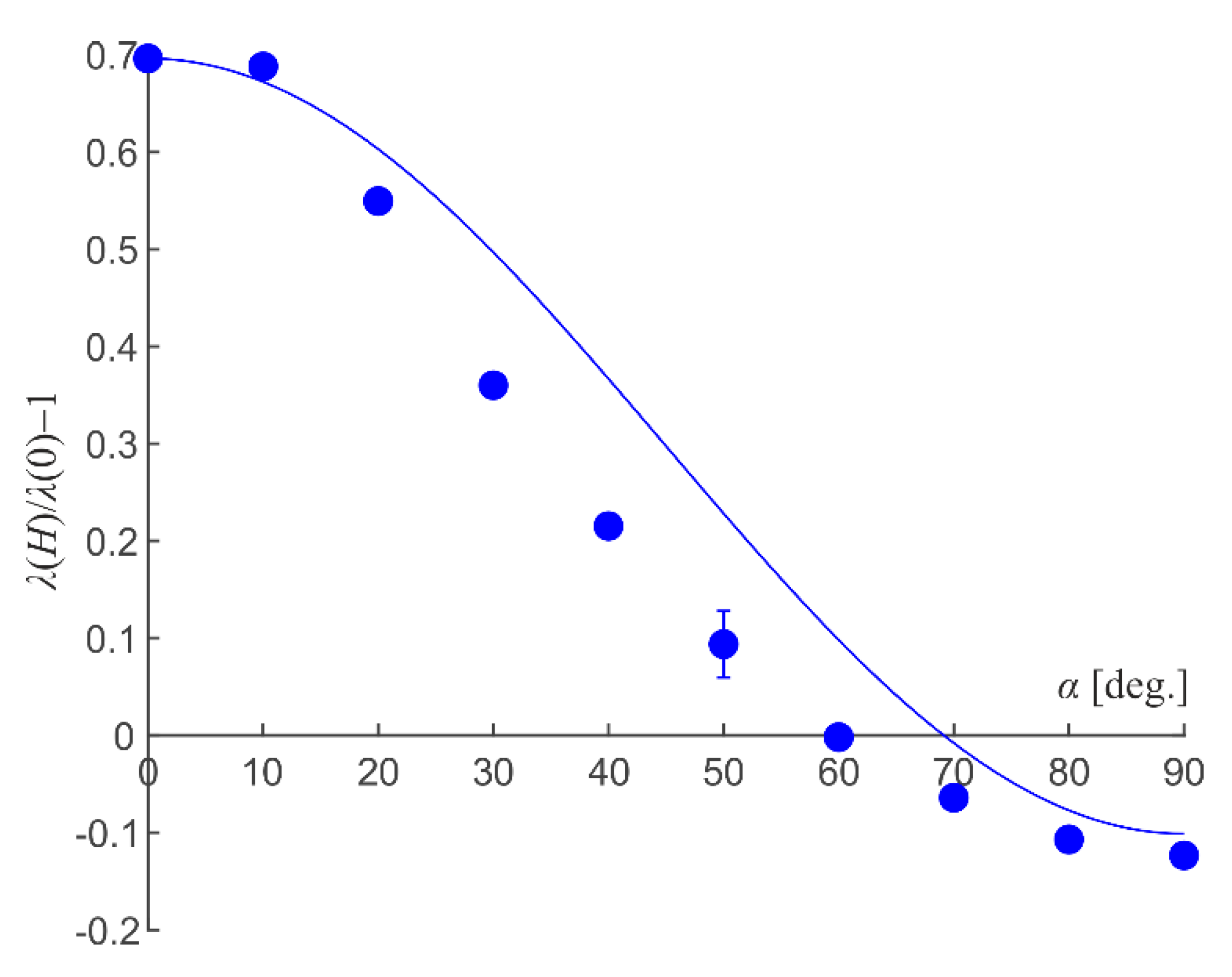
The dependence of the emulsion electrical conductivity on the angle between the magnetic and electric fields directions that can demonstrate the anisotropic character of the electrical conductivity value was investigated, as well. As an example, Figure 5 shows the dependence of the magnetic field-conditioned relative change of emulsion electrical conductivity on the angle between the directions of the external magnetic and measuring electric fields. This figure shows that the electrical conductivity undergoes the greatest change (grows) at the parallel orientation of the magnetic and electric fields. Meanwhile, in the case of a perpendicular orientation of the fields, a much lesser decrease of the medium conductivity is observed: its experimental relative value reaches about −10%. At other angles, the electrical conductivity assumes intermediate values.

Figure 5.
Dependence of magnetic fluid emulsion electrical conductivity relative change on angle between directions of external magnetic and measuring electric fields. Dispersed phase volume fraction is 0.2; magnetic field strength is 1.1 kA/m. Dots are experiments; line is the experimental data approximation by Equation (5).
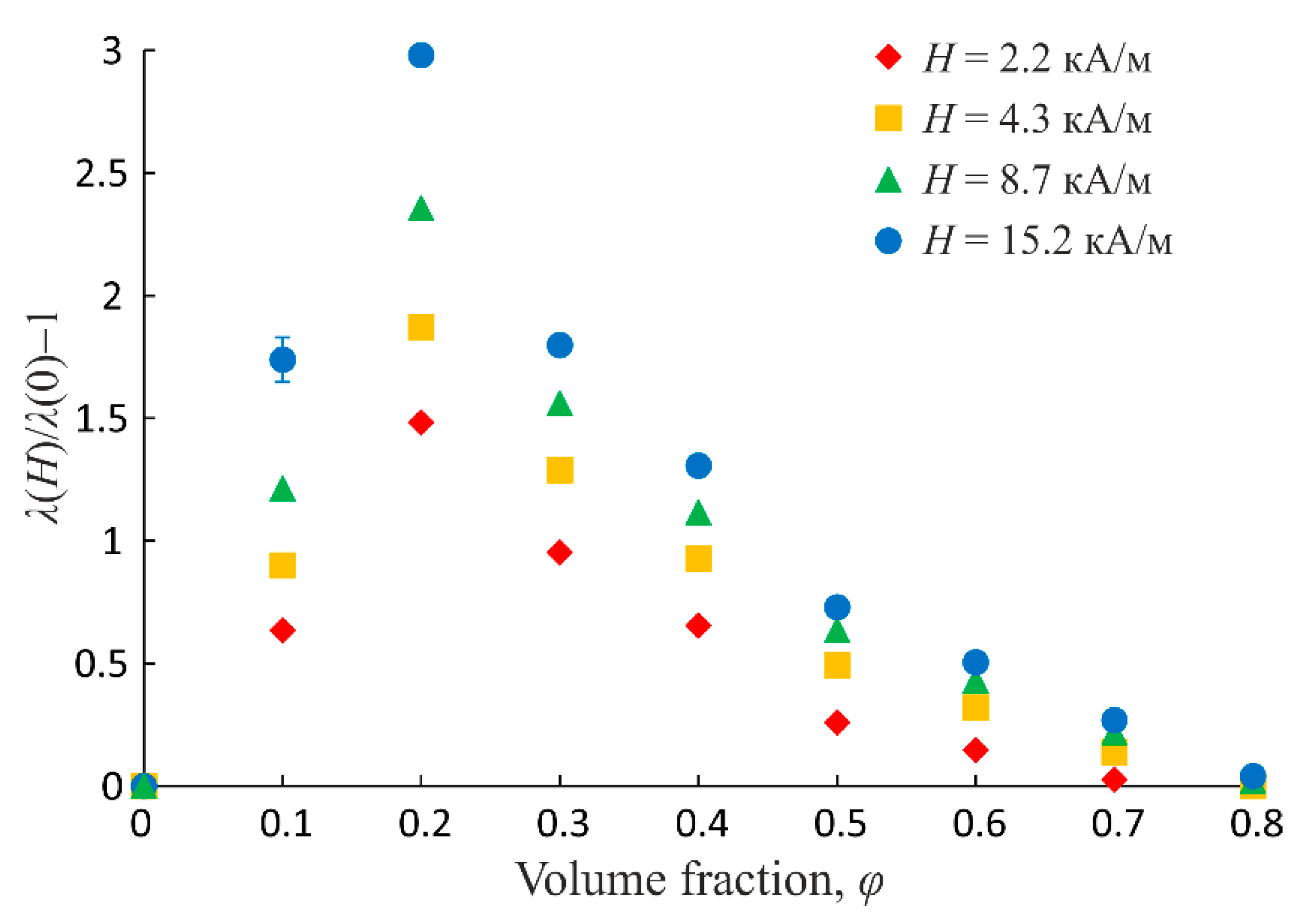
The magnitude of response to the magnetic field action, expressed by the electrical conductivity change, heavily depends on the emulsion dispersed phase volume fraction. Thus, Figure 6 shows the experimental dependences of the electrical conductivity relative change on the emulsion volume fraction obtained at the parallel orientation of the magnetic and electric fields. The dependences relevant to different magnetic field strength values are shown. It is seen that these dependences are of nonmonotonic character, with the maximum at the volume fraction of the dispersed phase φ ≈ 0.2.

Figure 6.
Experimental dependences of emulsion electrical conductivity relative change on dispersed phase volume fraction at different magnetic field strength values. External magnetic field is parallel to electric measuring field.
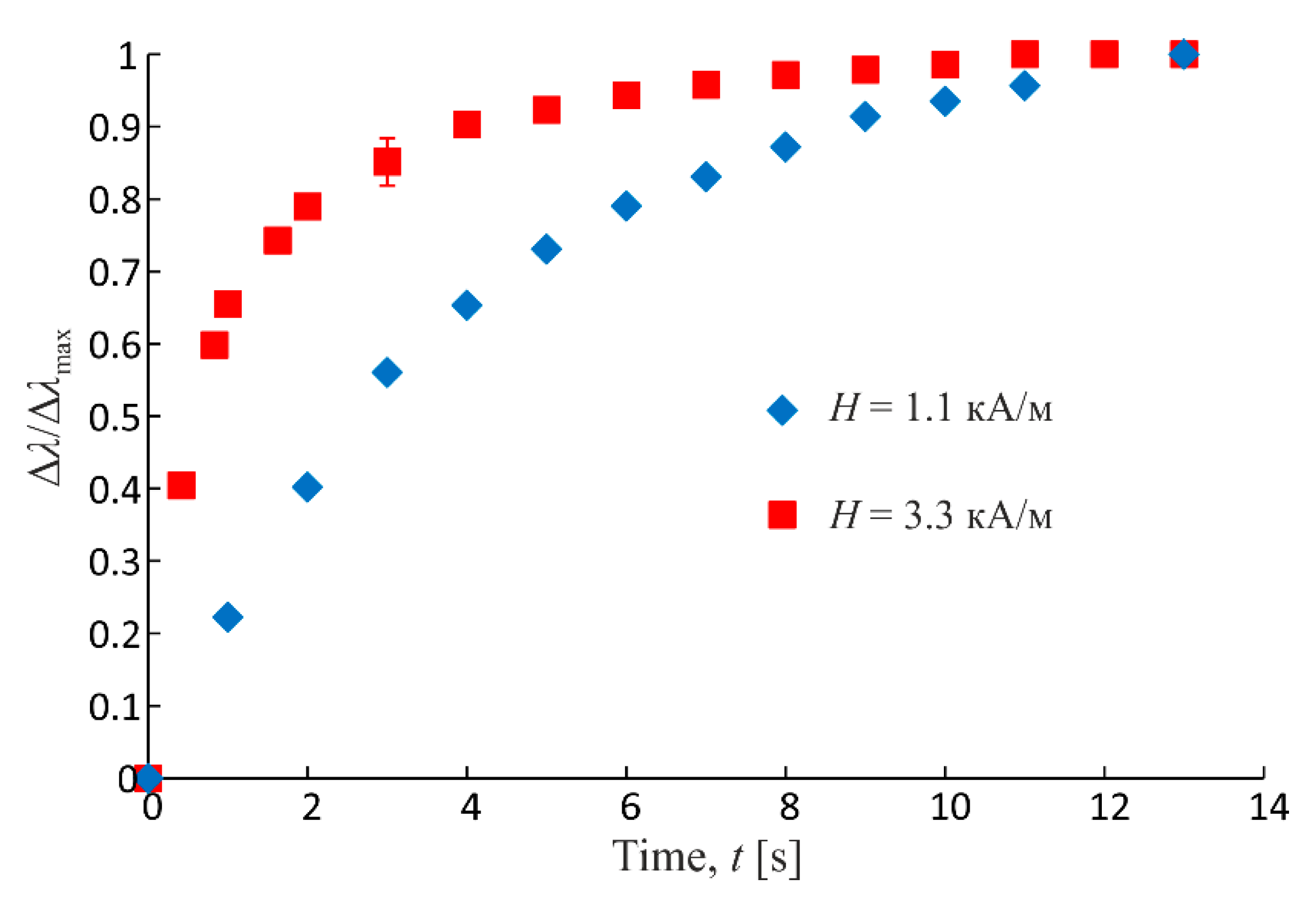
Time evolution of emulsion microstructure within the sample volume under action of magnetic field is evidenced by the character of its macroscopic properties change dynamics, and, in particular, of the parameters characterizing the transfer processes in medium. Thus, Figure 7 shows the measured dependence of the electrical conductivity change on the time of action of the magnetic field codirectional with the electric measuring field. On the ordinate the reduced value is plotted:
where tₘₐₓ is the final value of time of measurements (the end point in Figure 7 and Figure 8). Time zero is the magnetic field switching on moment. Figure 7 shows the dependences of the reduced relative change of conductivity obtained at two different field strength values. It is seen that, at higher values of strength, the change of conductivity and the underlying structure formation process in emulsion are more intensive than at low strengths (the relevant dependence comes to saturation more quickly). This is because the structure-forming magnetic interactions between emulsion dispersed phase drops grow as the external field strength grows.

Figure 7.
Experimental dependences of reduced relative change of emulsion conductivity on time of action of magnetic field (parallel to electric measuring field) at different strength values. Dispersed phase volume fraction is 0.4.

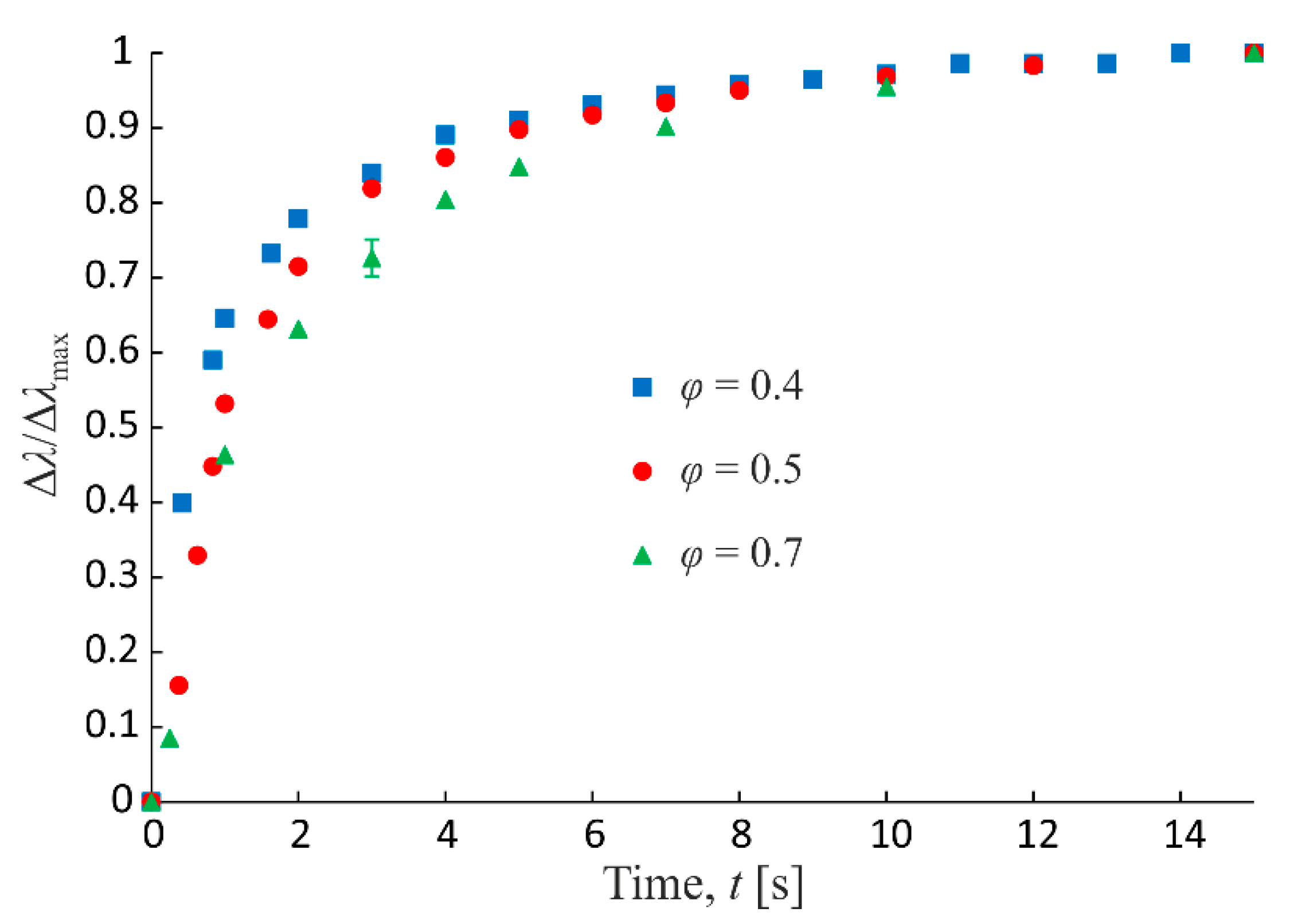
Figure 8.
Experimental dependences of reduced relative change of emulsion conductivity on time of action of magnetic field at different dispersed phase volume fractions. Magnetic field strength is 3.3 kA/m.
The structure formation process dynamics and relevant emulsion macroscopic conductivity change depends on the dispersed phase volume fraction, as well. Thus, Figure 8 shows the experimental time dependences of the reduced relative change of conductivity under action of magnetic field for three volume fractions of the emulsion dispersed phase. The figure shows that, with the growth of volume fraction, the structure formation and conductivity change process slow down. This must be because the growth of intensity of the hydrodynamic interactions of the dispersed phase drops at the growth of volume fraction, which leads to the overall deceleration of the structural processes dynamics.
It should be noted that the time evolution of the structure of solid-particle suspensions under the action of magnetic field has been previously studied in a number of works [43,44,45,46]. It has been shown that the time scale of structure evolution decreases with the field strength, which corresponds to the results of present study. However, in previous studies, the time scale of structure evolution also decreased with the dispersed phase volume fraction, which does not coincide with the results of this study. This contradiction may be due to the fact that previous studies used very low volume fractions (less than 1%), and the effects of hydrodynamic interactions of particles did not play a significant role.
4. Analysis and Discussion
4.1. Conductivity Estimation
Consider the comparison of certain obtained data with the known analytical results for the emulsions conductivity. Consider first the electrical conductivity of an emulsion in the absence of structural order (without an external magnetic field). The effective specific electrical conductivity of the emulsion can be estimated using the Wagner formula [17]:
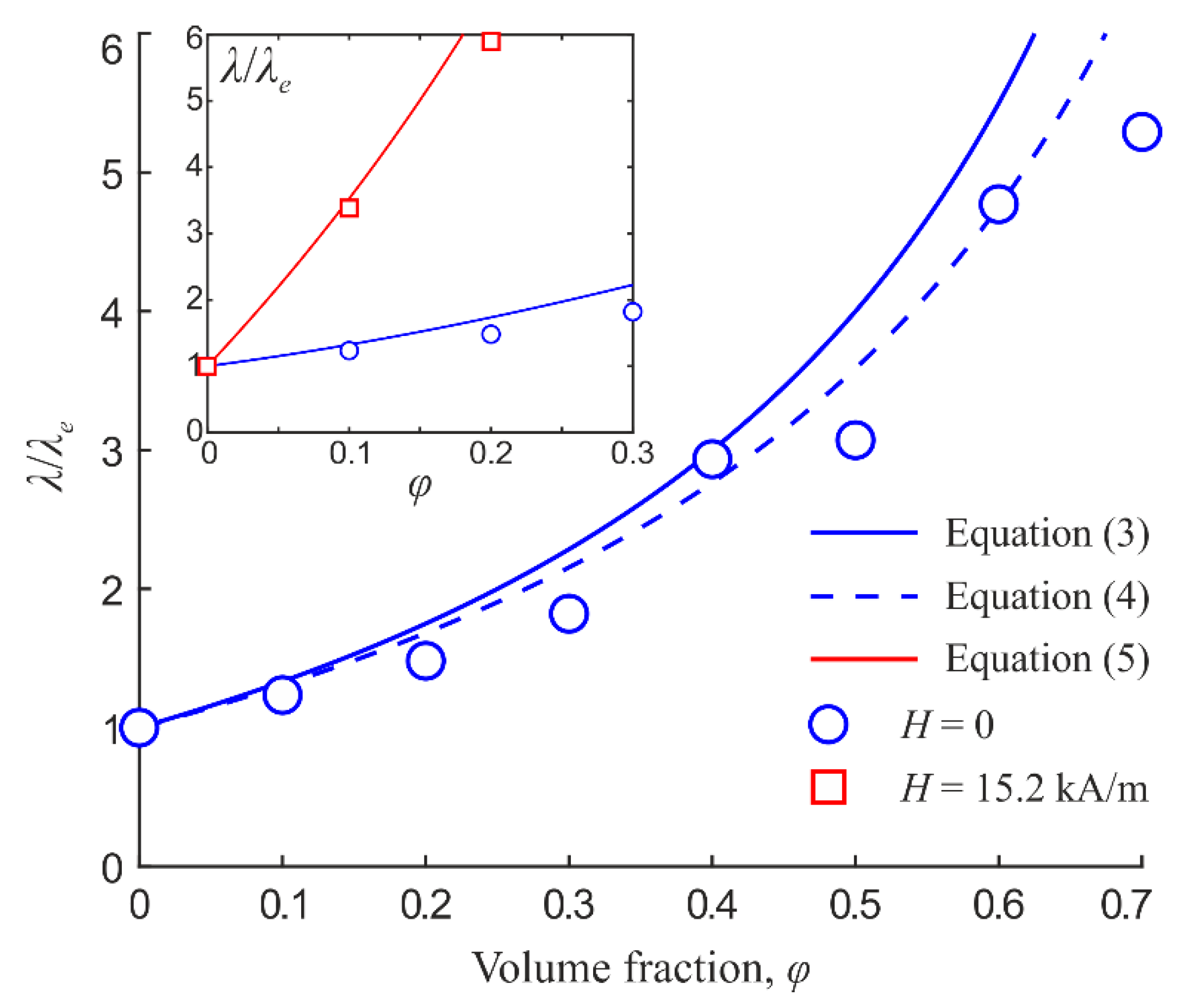
Figure 9 shows the dispersed phase volume fraction dependence of the specific conductivity of the emulsion; the comparison of the experimental data with the corresponding calculation according to Equation (3) is given. As can be seen from the figure, the calculation according to (3) gives higher values of conductivity. This may be due to the presence of a surfactant whose specific conductivity is several orders of magnitude lower than that of the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium. The surfactant forms a concentrated layer on the surface of the droplets, which can create an additional barrier for interphase ion transport. To assess the effect of the adsorbed surfactant layer, we use a model of the system of particles covered with shells. In this case, the effective conductivity of the emulsion can be estimated by the Pauly and Schwan formula [17]:
where λs is the shell specific electrical conductivity; ν = [R/(R + d)]3; R is the dispersed phase droplet radius; d is the shell thickness. The length of a single surfactant molecule (polyglyceryl-3 polyricinoleate) is approximately 3.5 nm. The calculation according to Equation (4) gives a better agreement with the experimental data, as shown in Figure 9.

Figure 9.
Dependences of magnetic fluid emulsion specific electrical conductivity on dispersed phase volume fraction. Magnetic field is parallel to electric field. Dots are experiments; lines are calculations.
The results obtained under the action of magnetic field can be understood considering the emulsion droplets as electric dipoles. If a chain of droplets is aligned with an external electric field then the dipoles enhance each other, leading to an increase in the local electric field strength and effective conductivity. When the chain is perpendicular to the electric field the dipoles reduce each other leading to a decrease in the effective conductivity. The mutual influence of dipoles in the former case is higher than in the latter, therefore the resulting conductivity change in the former case is more pronounced. Some quantitative evaluations of the magnetic field influence on the emulsion’s electrical conductivity are possible if the chain structures appearing in emulsion are approximately replaced with equivalent elongated ellipsoidal particles. The effective conductivity of the suspension of ellipsoidal particles aligned along some direction can be calculated according to the Fricke formula [47]:
where
are the depolarizing factors of the ellipsoidal particle along the major and minor axes correspondingly; e is the ellipsoidal particle eccentricity; α is the angle between the ellipsoid major axis and the electric field direction. As an example, Figure 5 shows the approximation of experimental data by Equation (5); the ellipsoid major to minor axes ratio equal to 1.1 was substituted to obtain a quantitative agreement. The inset in Figure 9 demonstrates the result of conductivity calculation according to Equation (5) when substituting the value 1.4 for the ellipsoid axes ratio. It can be concluded that, even at low volume fractions, the conductivity of chain microstructure emulsion is not equivalent to the conductivity of ellipsoidal particle suspension. First of all, this is due to the fact that the emulsion drops are always separated by a layer of dispersion medium and surfactant, which complicates charge transfer along the droplet chain. Therefore, more advanced models of the structure and properties relationship are needed to describe the systems under study. This is all the more true because the structure in a real emulsion sample is substantially determined by the interaction of droplets with the sample boundaries and can become quite complex.
4.2. Structure Simulation
Consider the structure formation process in a sample of emulsion placed into an electric measuring cell and surrounded by nonmagnetic space in magnetic field. The cell will be simulated by a small volume in the shape of a rectangular parallelepiped restricted with solid impermeable walls. The structure formation process dynamics are largely dependent on the hydrodynamic interactions of the drops with each other and with the bounding walls. Accounting for the hydrodynamic drop-to-wall interactions in the considered geometry is quite complex, hence, this will not be handled here. Hence, the investigation will be limited to the stationary (equilibrium) states. In this case, the structure formation modeling technique is analogous to the one described in Ref. [39]. A distinguishing feature of the considered situation is the possibility of arbitrary orientation of the bounded volume of emulsion relative to the magnetic field, which allows for a more obvious demonstration of the sample shape impact on the structure formation regularities.
The equation of motion of a single droplet at low Reynolds numbers is
where ri is the Cartesian coordinates of ith droplet; ηi, ηe are the dynamic viscosities of the dispersed phased and dispersion medium correspondingly; Fi is the total force acting on a droplet excluding the hydrodynamic force. Equation (7) is the Hadamard–Rybchinsky formula, and it gives an algorithm of emulsion microstructure evolution simulation. The total force comprises the magnetic force and the force of droplets repulsion from each other and from bounding walls:
The repulsive force has been modeled by the dependence of the following form [48]:
where rji = rj − ri; i, j are the droplets numbers; riw is the perpendicular vector dropped from the center of the ith drop to the wall; n = 2; A is the adjusting coefficient. The repulsive force has been attenuated in such a manner that the minimum spacing between the surfaces of the droplets and the surfaces of the droplets and walls was no more than 0.5 μm.
The magnetophoretic force acting on a droplet has been calculated according to the following equation [49]:
where V0 is the droplet volume; H is the magnetic field strength related with the scalar magnetic potential ψ by the equation:
The scalar magnetic potential can be obtained by the solution of Poisson’s equation:
where μ is magnetic permeability. Numerical solution of Equation (12) can be done using the finite-difference method [50]. We will consider the computational domain of rectangular shape. To simulate the uniform magnetic field, we impose the first-type boundary conditions at the bottom and top boundaries:
and the second-type boundary conditions at four side boundaries of the domain:
where r is the coordinates of points at the boundary; n is the outer normal.
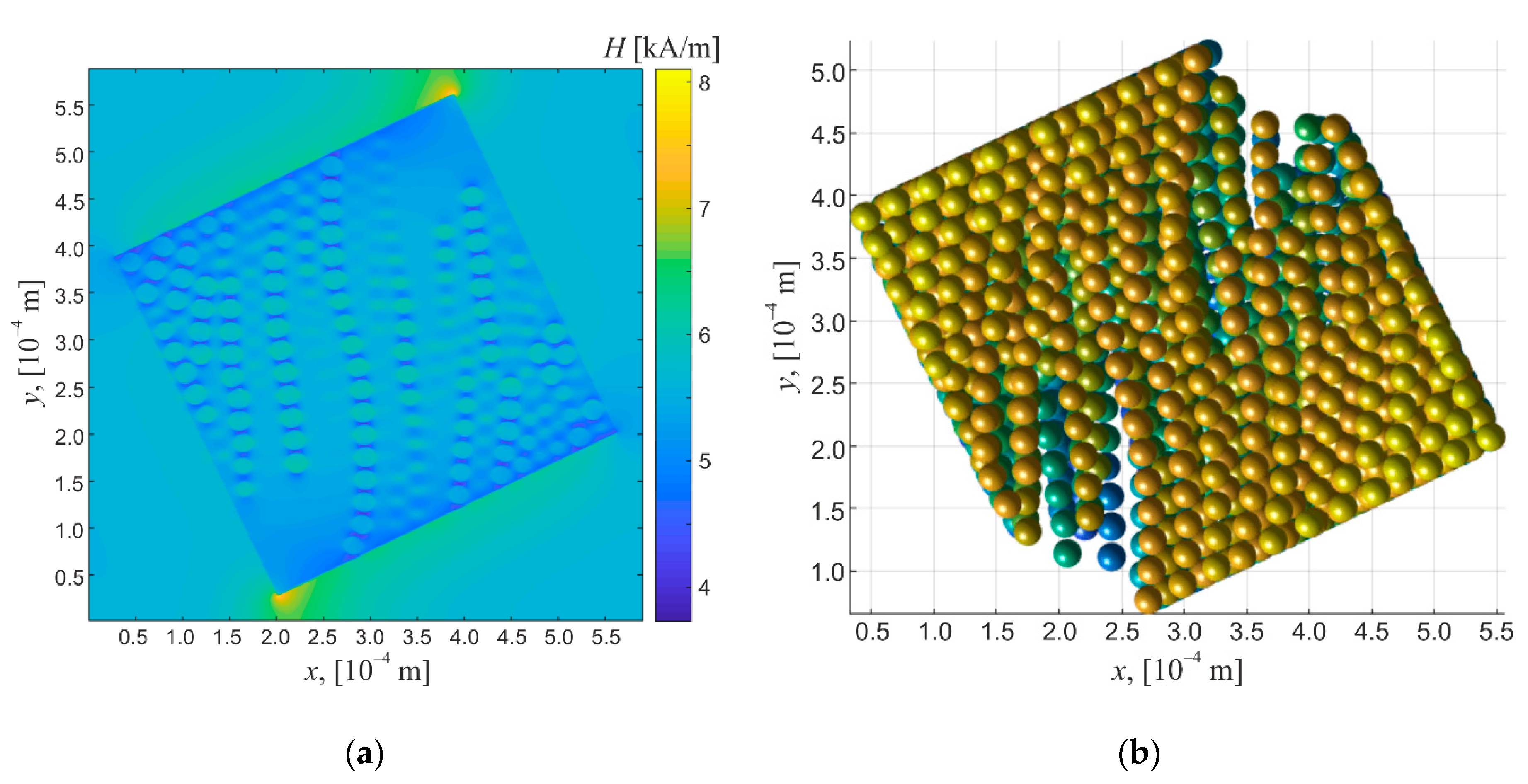
The emulsions of nonmagnetic liquids in magnetic fluid show the magnetic interaction between the dispersed phase drops and the boundaries of the sample whose shape determines the magnetic field distribution. Thus, Figure 10a shows the magnetic field strength distribution in the region of space that contains an emulsion sample whose edges form a certain angle with the direction of the external homogeneous magnetic field. Figure 10b shows the emulsion drops’ microstructure forming in this case. This figure shows that the dispersed phase drops are pushed out of the field strength high values region near the vertices of the rectangular parallelepiped, showing the significant impact of the sample shape on the character of the appearing ordered structural formations. The obtained results substantiate the very limited applicability of the model of ellipsoidal particles suspension to the systems under study.

Figure 10.
(a) Magnetic field distribution in a computational domain containing the magnetic fluid emulsion sample enclosed in rectangular cell. External homogeneous magnetic field is vertical in image plane. (b) Emulsion sample microstructure forming in magnetic field shown in (a). Emulsion volume fraction is 0.2.
Having determined the emulsion sample’s microstructure, the effective electrical conductivity can be calculated by solution of Poisson’s equation for the electric potential. However, additional challenges arise here associated with the calculation of the electric field distribution in the sample under study. Indeed, at a great difference of the electric parameters of the media contained in the computational domain (which takes place in the considered situation), the correct solution of the finite difference equations requires applying direct methods in a high spatial resolution grid. This limits the permissible dimensions of the modeled region as it requires great computational resources. For the above reason, such analysis will not be performed here and will be addressed in further studies.
5. Conclusions
Hence, within the framework of this study, the emulsions formed by water droplets dispersed in a hydrocarbon magnetic fluid were created. It has been shown that under action of a stationary uniform magnetic field, ordered structures of drops in geometries of chains or dense columnlike formations oriented along magnetic field appear in such emulsions. The influence of the emulsion sample shape on the character of the appearing structural formation in magnetic field due to the magnetic interactions of the dispersed drops with the sample boundaries has been demonstrated theoretically. The dependence of the effective electrical conductivity of these emulsions on magnetic fields has been found and investigated. The magnitude of response to magnetic field action depends on the emulsion dispersed phase volume fraction and reaches the greatest value at 20% volume fraction. The anisotropic character of the charge transfer processes in chain microstructure magnetic fluid emulsions in a magnetic field has been demonstrated, evidenced by the dependence of the electrical conductivity value on the magnetic field orientation relative to the electric measuring field. It has been found that the greatest change (growth) of the emulsions’ electrical conductivity values takes place at the parallel magnetic field orientation relative to electric measuring field; at the perpendicular orientation, a much less expressed electrical conductivity reduction is observed. The relative growth of the emulsion electrical conductivity in magnetic field can exceed 300%. It has been shown that structure formation processes, and, associated with them, magnetic fluid emulsion electric conductivity changes in the magnetic field, run more intensively with the field strength growth and slow down when the emulsion dispersed phase volume fraction increases.
Note that the chain microstructure formation in external fields is characteristic of many functional disperse media. The results obtained in this paper can be useful as models for understanding the influence of structure formation on the transfer processes in suspension and emulsion systems. At the same time, the obtained results open the possibility for the potential applications of the studied emulsions as functional fluid systems with regulated parameters. This motivates further research in such areas as the dielectric spectra of magnetic fluid emulsions and their interactions with electromagnetic waves. The magnitude of the emulsion response to the magnetic field action is expected to be even higher than that demonstrated in the current study, if magnetic fluids of higher concentration are used for the emulsion preparation. In such a case, the flotation processes in emulsions can become quite pronounced. At the same time, our observations have shown the long-term stability of the studied emulsion with respect to coalescence. On the one hand, this indicates the possibility of restoring the properties of emulsions, and on the other hand, it demonstrates the need for further studies of stability problems in relation to potential applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, formal analysis, funding acquisition, investigation, writing—original draft, writing—review & editing, A.R.Z.; validation, L.M.K.; data curation, A.A.Z.; software, visualization, S.D.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Russian Science Foundation, grant number 19-72-00070.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Löwen, H. Colloidal soft matter under external control. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2001, 13, R415–R432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiolerio, A.; Quadrelli, M.B. Smart fluid systems: The advent of autonomous liquid robotics. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1700036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; He, L.; Hu, Y.; Yin, Y. Magnetically induced colloidal assembly into field-responsive photonic structures. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Díaz, I.; Rinaldi, C. Recent progress in ferrofluids research: Novel applications of magnetically controllable and tunable fluids. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 8584–8602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiew, Y.C.; Glandt, E.D. The effect of structure on the conductivity of a dispersion. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1983, 94, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelster, R.; Simon, U. Nanodispersions of conducting particles: Preparation, microstructure and dielectric properties. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1999, 277, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Cho, T.J.; Xu, J.; Lee, D.; Yang, B.; Zachariah, M.R. Effect of nanoparticle clustering on the effective thermal conductivity of concentrated silica colloids. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 011406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar, A.; Chinesta, F.; Heyd, R. Thermal conductivity of suspension of aggregating nanometric rods. Entropy 2017, 19, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeeva, E.V.; Gavrilov, A.N.; McCloskey, J.M.; Tolmachev, Y.V.; Sprunt, S.; Lopatina, L.M.; Selinger, J.V. Thermal conductivity and particle agglomeration in alumina nanofluids: Experiment and theory. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 76, 061203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bica, I.; Choi, H.J. Preparation and electro-thermoconductive characteristics of magnetorheological suspensions. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2008, 22, 5041–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, I.; Liu, Y.D.; Choi, H.J. Physical characteristics of magnetorheological suspensions and their applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heine, M.C.; de Vicente, J.; Klingenberg, D.J. Thermal transport in sheared electro- and magnetorheological fluids. Phys. Fluids 2006, 18, 023301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shima, P.D.; Philip, J. Tuning of thermal conductivity and rheology of nanofluids using an external stimulus. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 20097–20104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, X.; Wang, Y.; Xuan, S.; Gong, X. Magnetic field dependent electric conductivity of the magnetorheological fluids: The influence of oscillatory shear. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 035067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forero-Sandoval, I.Y.; Vega-Flick, A.; Alvarado-Gil, J.J.; Medina-Esquivel, R.A. Study of thermal conductivity of magnetorheological fluids using the thermal-wave resonant cavity and its relationship with the viscosity. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 025010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.-X.; Ma, W.-G.; Zhang, X. Anisotropic thermal conductivity in ferrofluids induced by uniform cluster orientation and anisotropic phonon mean free path. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 138, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T. Electrical properties of emulsions. In Emulsion Science; Sherman, P., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1968; pp. 353–478. [Google Scholar]
- Bumajdad, A.; Eastoe, J. Conductivity of water-in-oil microemulsions stabilized by mixed surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 274, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.-L.; Shan, C.; Wang, Y.; Deng, Q. Effects of oil on aqueous foams: Electrical conductivity of foamed emulsions. ChemPhysChem 2014, 15, 3110–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Calderon, F.; Thivilliers, F.; Schmitt, V. Structured emulsions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 12, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Advances in fabrication of emulsions with enhanced functionality using structural design principles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 17, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lawrence, E.M.; Wu, A.; Ivey, M.L.; Flores, G.A.; Javier, K.; Bibette, J.; Richard, J. Field-induced structures in ferrofluid emulsions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 74, 2828–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivey, M.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Cutillas, S. Magnetic-field-induced structural transitions in a ferrofluid emulsion. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 63, 011403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagne, F.; Braconnot, S.; Mondain-Monval, O.; Pichot, C.; Elaïssari, A. Colloidal and physicochemical characterization of highly magnetic O/W magnetic emulsions. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2003, 24, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakinyan, A.; Dikansky, Y. Drops deformation and magnetic permeability of a ferrofluid emulsion. Colloids Surf. A 2011, 380, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbotin, I.M. Magnetic permeability of inverse ferrofluid emulsion: Nonlinear ferrofluid magnetization law. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 502, 166524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.-T. Micro-magnetofluidics: Interactions between magnetism and fluid flow on the microscale. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2012, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.-J.; Hou, H.-H.; Wang, Y.-N.; Fu, L.-M. Micro-magnetofluidics in microfluidic systems: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 224, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendran, V.; Philip, J. Sensing of biologically important cations such as Na+, K+, Ca2+, Cu2+, and Fe3+ using magnetic nanoemulsions. Langmuir 2013, 29, 4252–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendran, V.; Philip, J. A methanol sensor based on stimulus-responsive magnetic nanoemulsions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 185, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Progress in applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 224001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, J.S.; Erb, R.M.; Denier, C.; Studart, A.R. Magnetic transport, mixing and release of cargo with tailored nanoliter droplets. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2582–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mefford, O.T.; Woodward, R.C.; Goff, J.D.; Vadala, T.P.; Pierre, T.G.S.; Dailey, J.P.; Riffle, J.S. Field-induced motion of ferrofluids through immiscible viscous media: Testbed for restorative treatment of retinal detachment. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 311, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, Q. Magnetically controllable colloidal photonic crystals: Unique features and intriguing applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 6013–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brojabasi, S.; Lahiri, B.B.; Philip, J. External magnetic field dependent light transmission and scattered speckle pattern in a magnetically polarizable oil-in-water nanoemulsion. Phys. B 2014, 454, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belykh, S.S.; Yerin, C.V. Magneto-optic effect in water-based magnetic emulsions. Magnetohydrodynamics 2018, 54, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, D.K.; Laskar, J.M.; Philip, J. Temporal evolution of equilibrium and non-equilibrium magnetic field driven microstructures in a magnetic fluid. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 304, 112737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakinyan, A.; Dikansky, Y.; Bedzhanyan, M. Electrical properties of chain microstructure magnetic emulsions in magnetic field. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2014, 35, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zakinyan, A.; Arefyev, I. Thermal conductivity of emulsion with anisotropic microstructure induced by external field. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darras, A.; Fiscina, J.; Pakpour, M.; Vandewalle, N.; Lumay, G. Ribbons of superparamagnetic colloids in magnetic field. Eur. Phys. J. E 2016, 39, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraudo, J.; Andreu, J.S.; Calero, C.; Camacho, J. Predicting the self-assembly of superparamagnetic colloids under magnetic fields. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 3837–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertman, V.E. Magnetic Fluids Guidebook: Properties and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Promislow, J.H.E.; Gast, A.P.; Fermigier, M. Aggregation kinetics of paramagnetic colloidal particles. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 102, 5492–5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darras, A.; Opsomer, E.; Vandewalle, N.; Lumay, G. Effect of volume fraction on chains of superparamagnetic colloids at equilibrium. Eur. Phys. J. E 2019, 42, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreu, J.S.; Camacho, J.; Faraudo, J. Aggregation of superparamagnetic colloids in magnetic fields: The quest for the equilibrium state. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 2336–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darras, A.; Opsomer, E.; Vandewalle, N.; Lumay, G. Superparamagnetic colloids in viscous fluids. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricke, H. The Maxwell-Wagner dispersion in a suspension of ellipsoids. J. Phys. Chem. 1953, 57, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.E.; Anderson, R.A.; Tigges, C.P. Simulation of the athermal coarsening of composites structured by a uniaxial field. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 108, 3765–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. Electrodynamics of Continuous Media; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Nagel, J.R. Numerical solutions to Poisson equations using the finite-difference method. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2014, 56, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).