A Model for Fuel Spray Formation with Atomizing Air
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Governing Equations
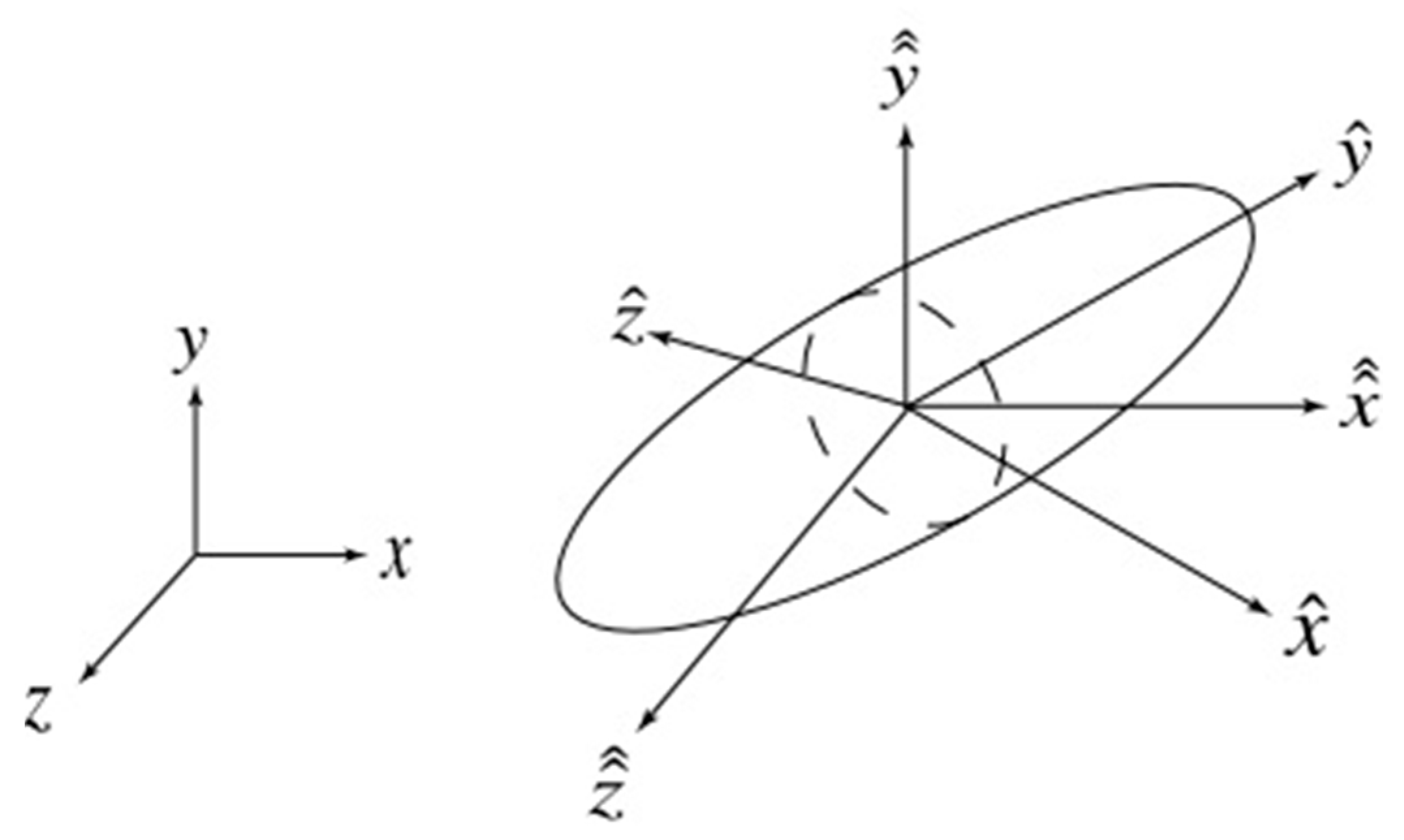
2.1. Equations of Motion for Ellipsoidal Particles
2.1.1. Translational Motion
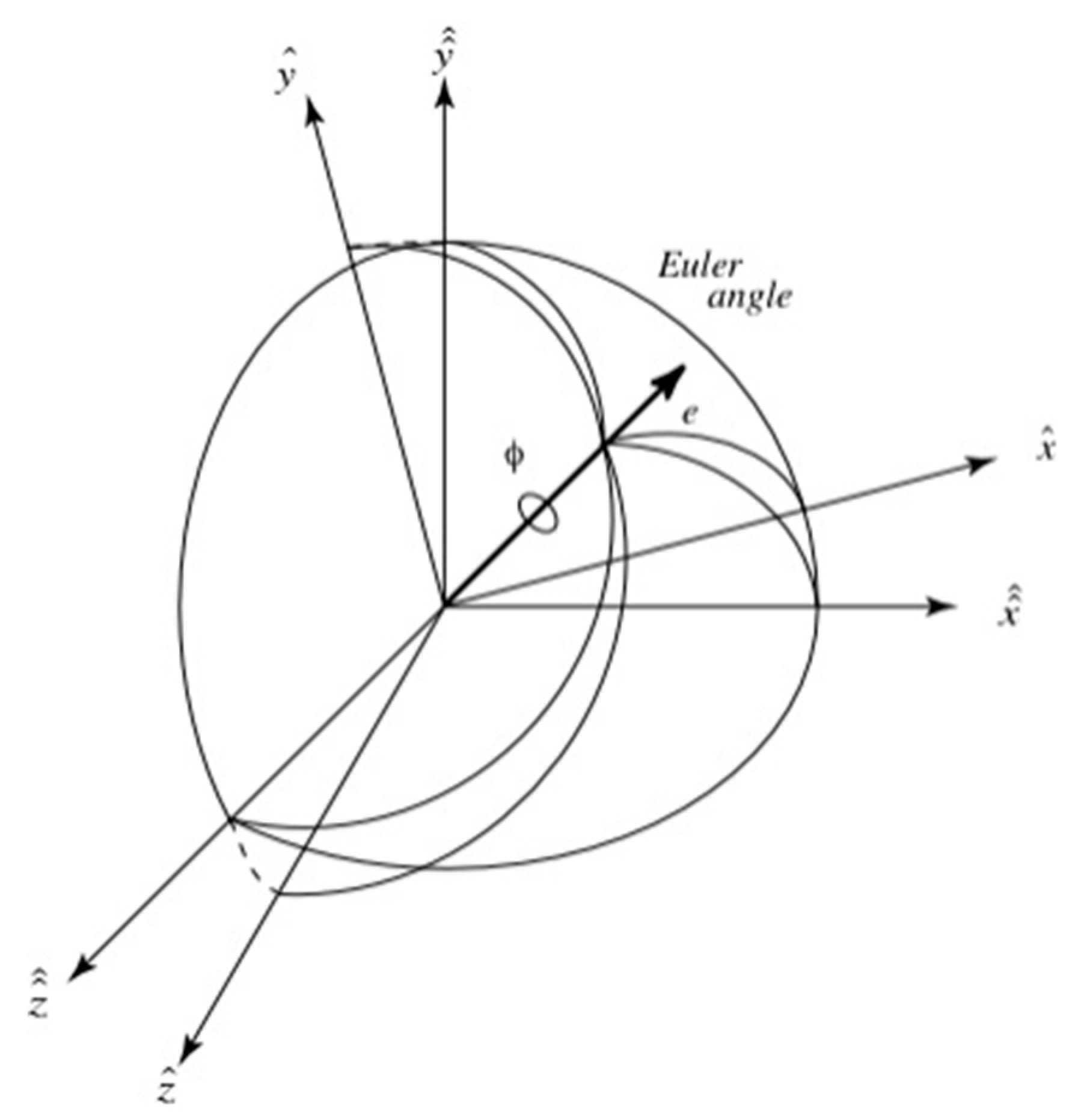
2.1.2. Rotational Motion
2.2. Ellipsoids of Revolution
2.3. Nonlinear Hydrodynamic Drag
2.4. Shear Induced Lift
2.5. Hydrodynamic Torque
2.6. Equations of Droplet Motion
2.7. Langevin Model for the Instantaneous Velocity and Velocity Gradient
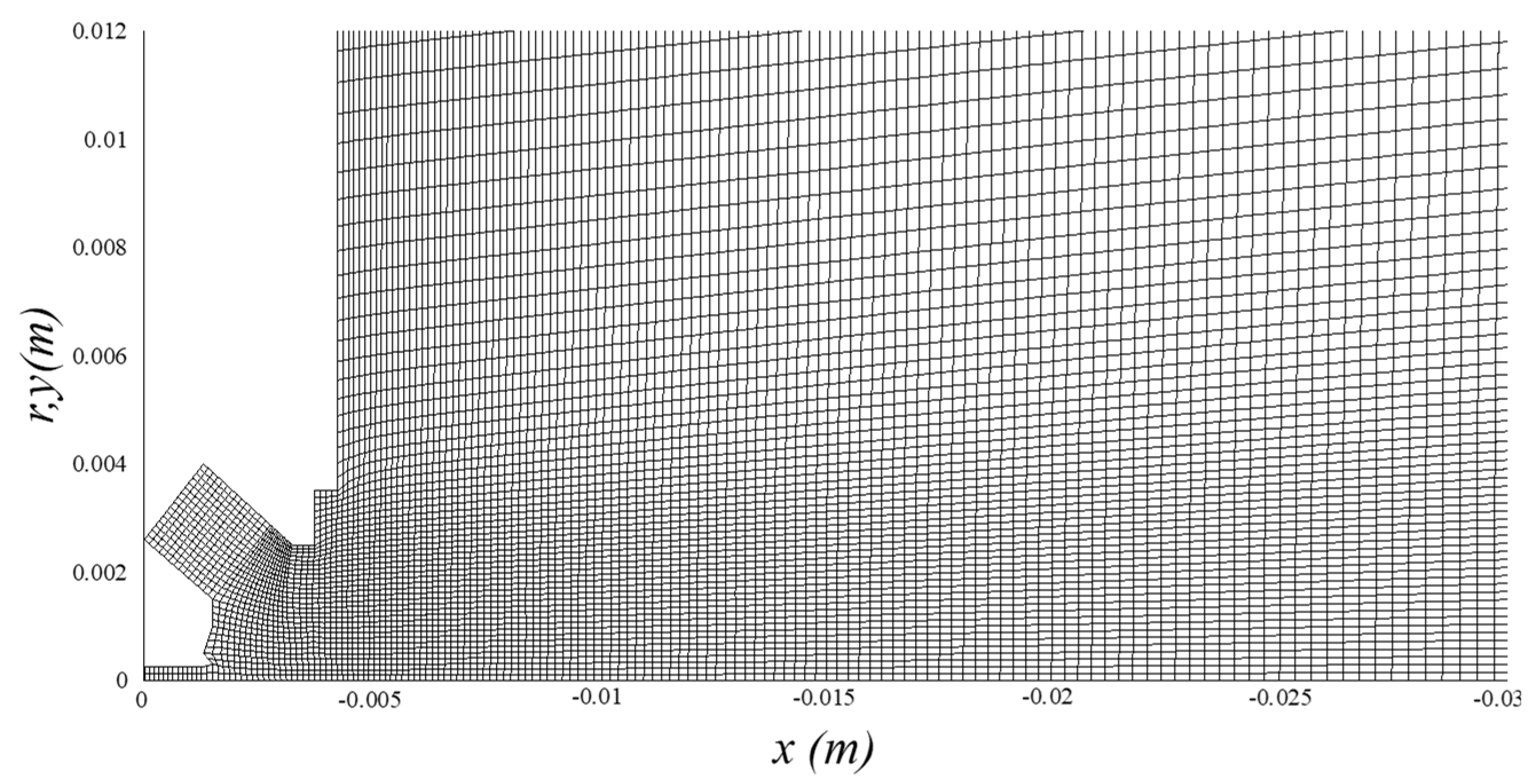
3. Computational Scheme
4. Results
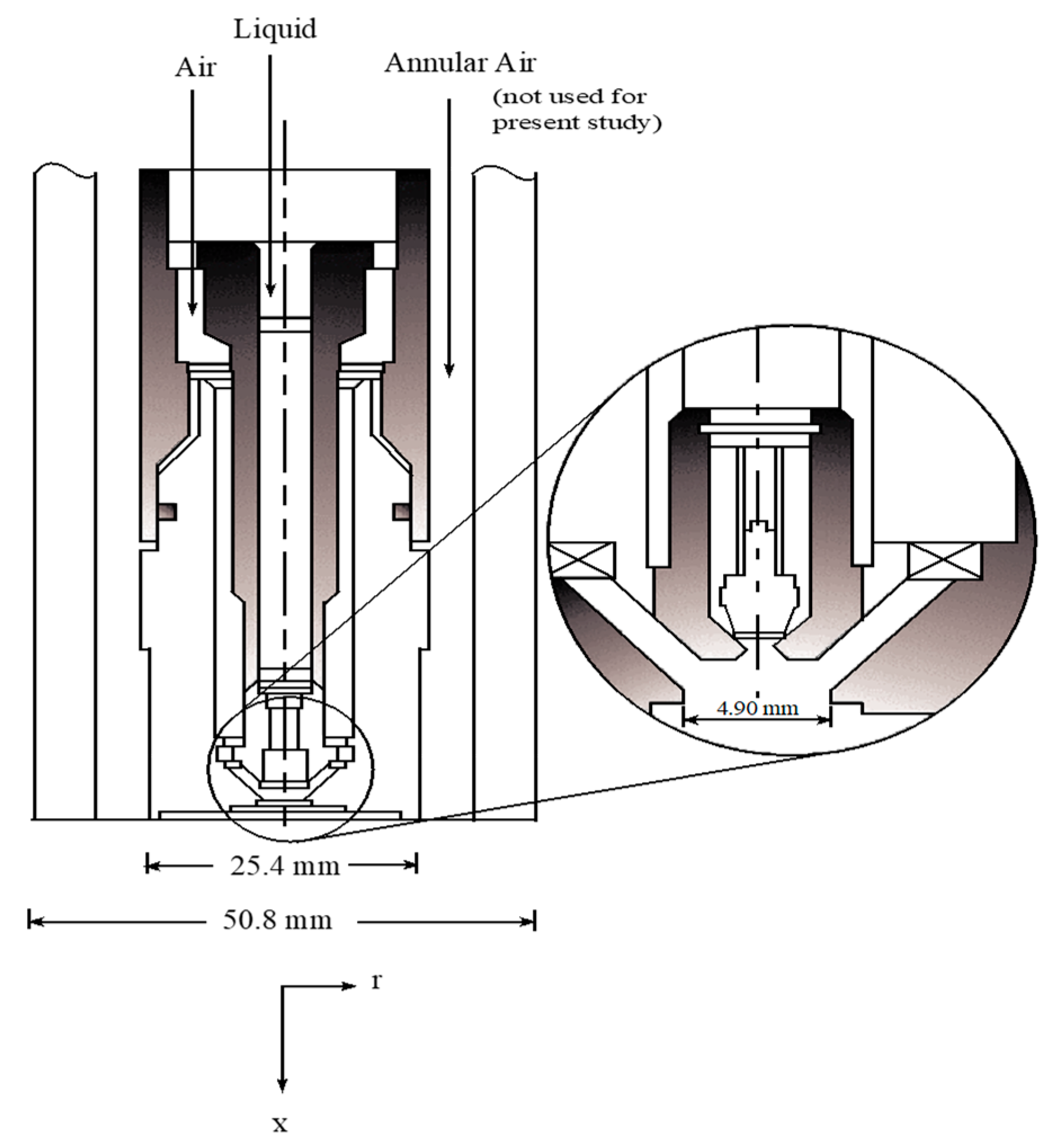
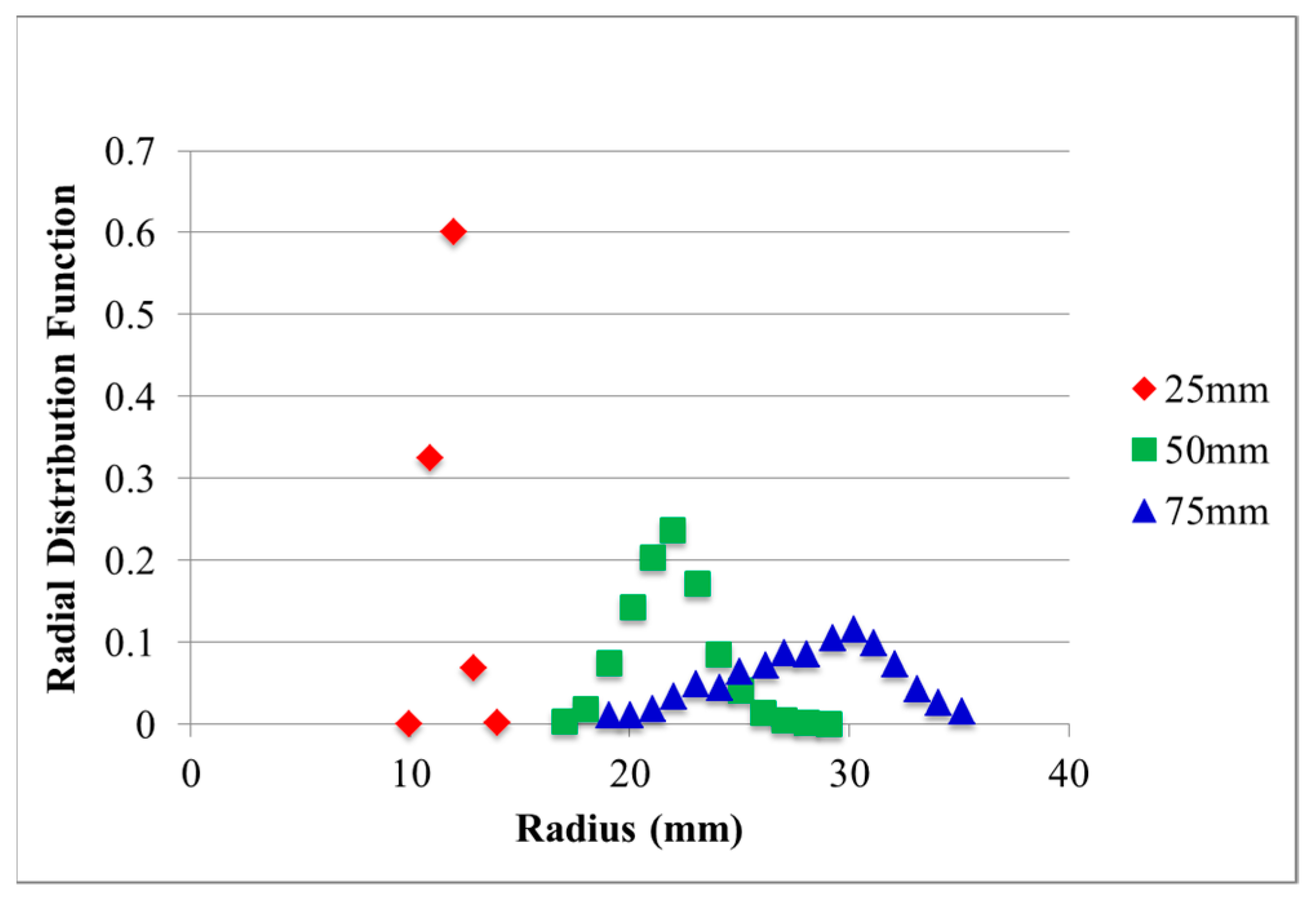
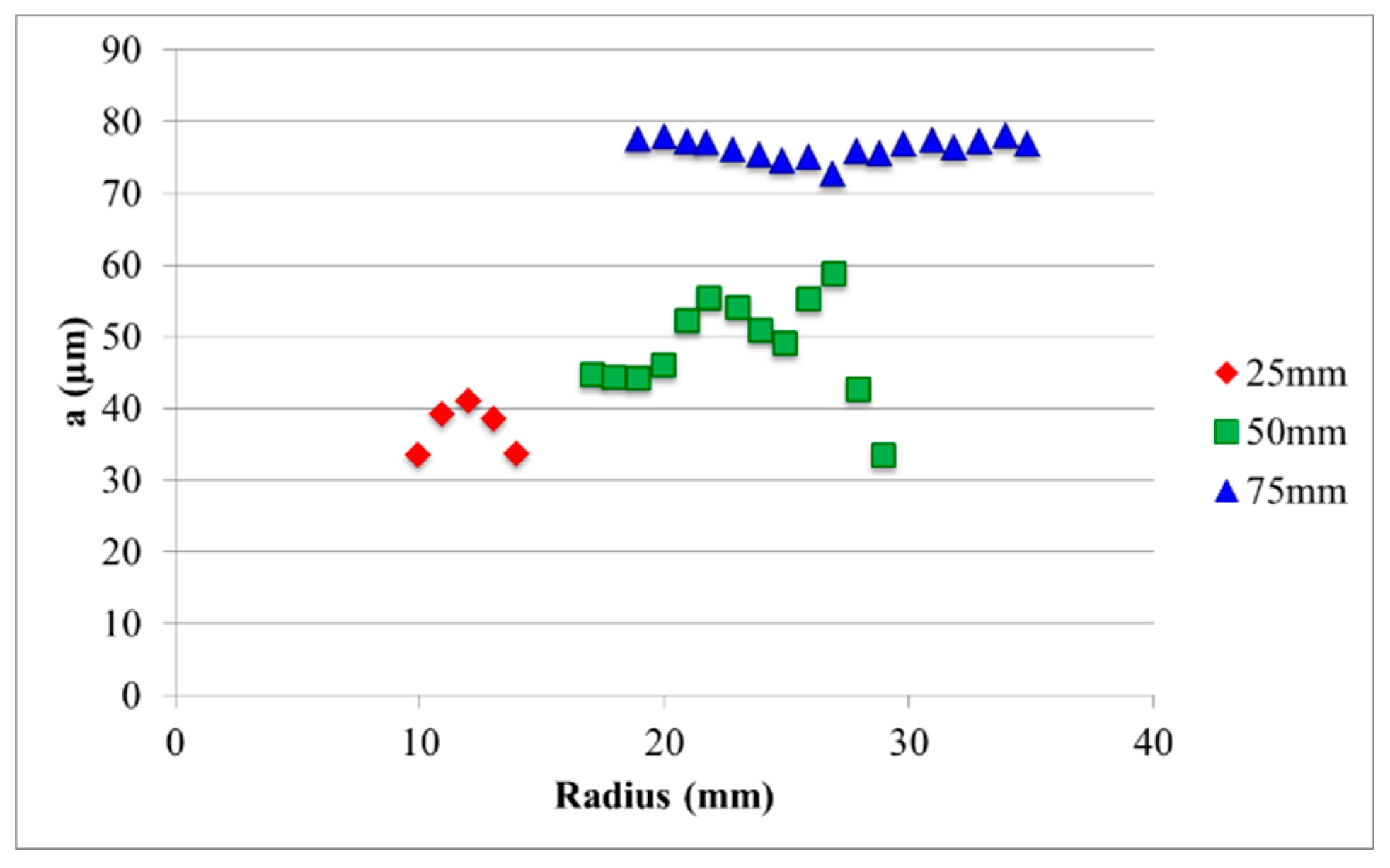
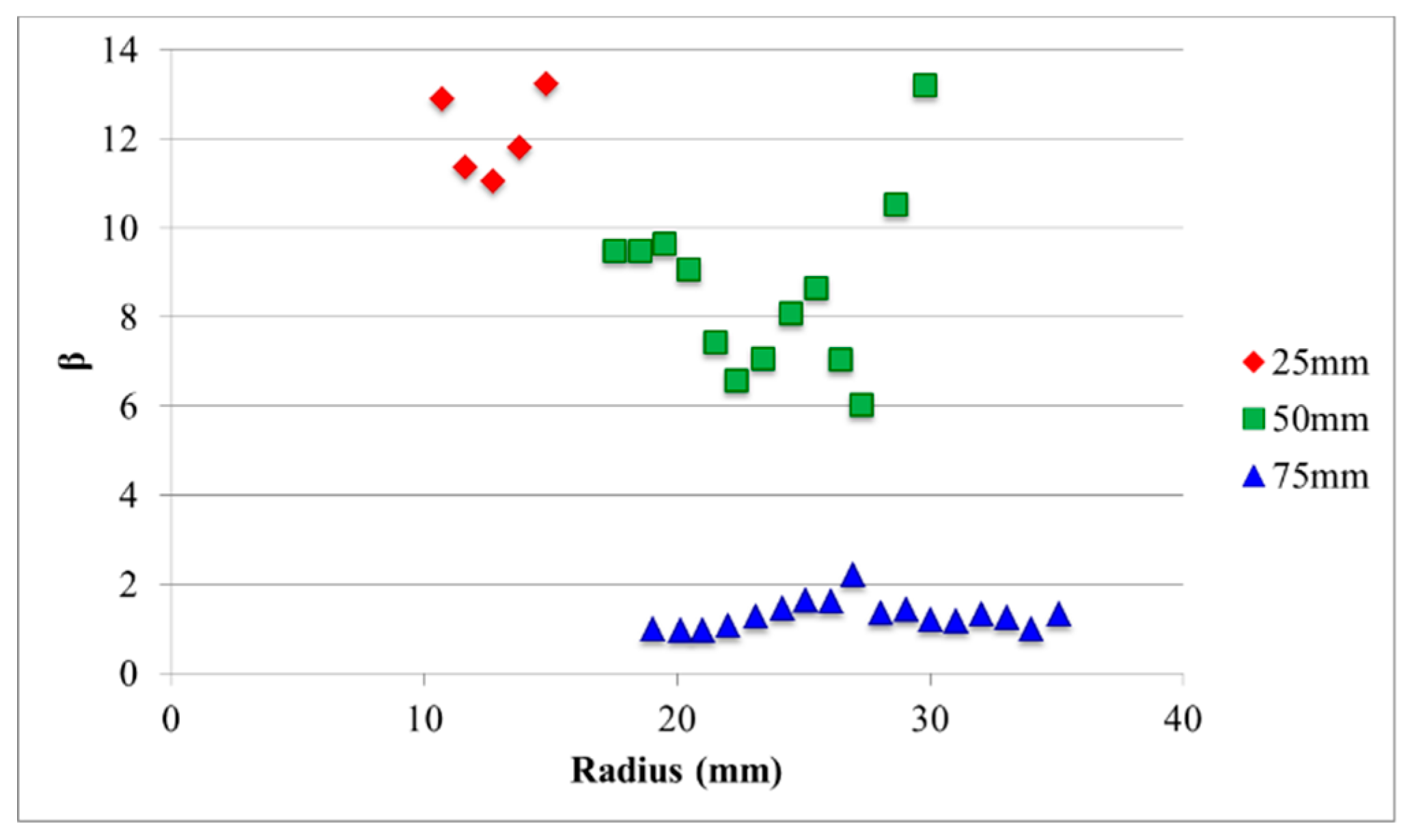
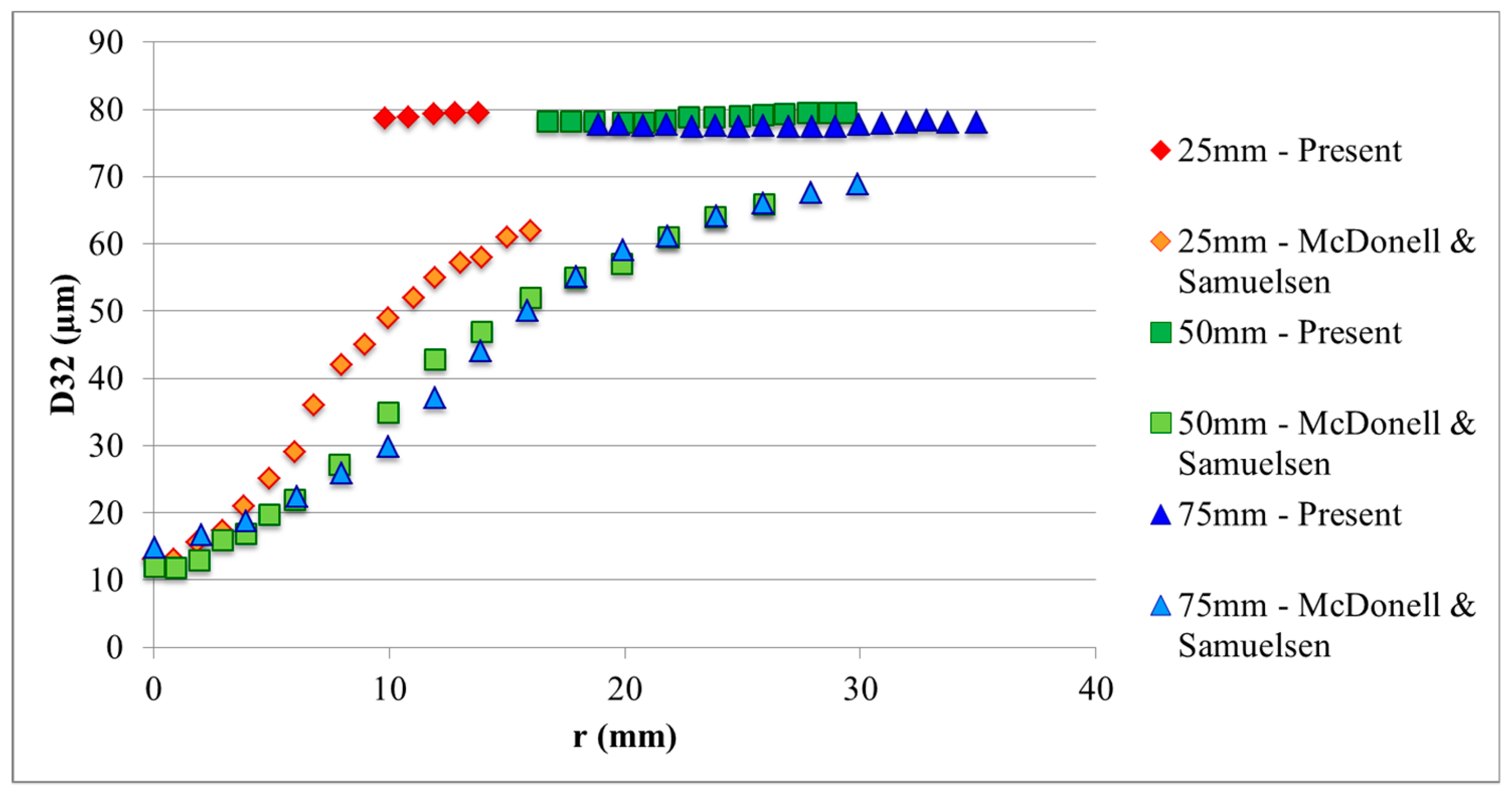
4.1. Simplex Atomizer
4.2. Non-Swirling Atomizing Air
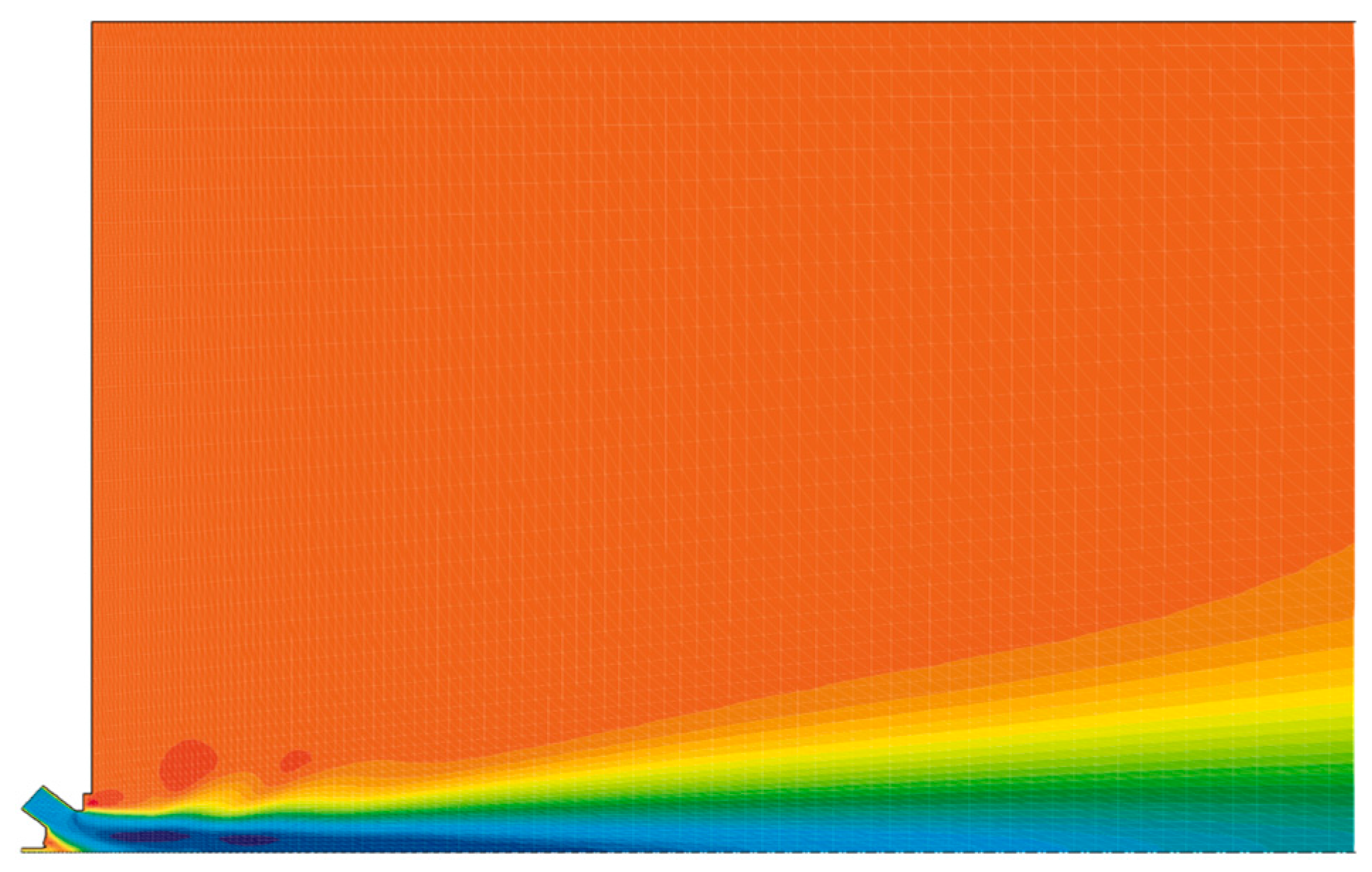
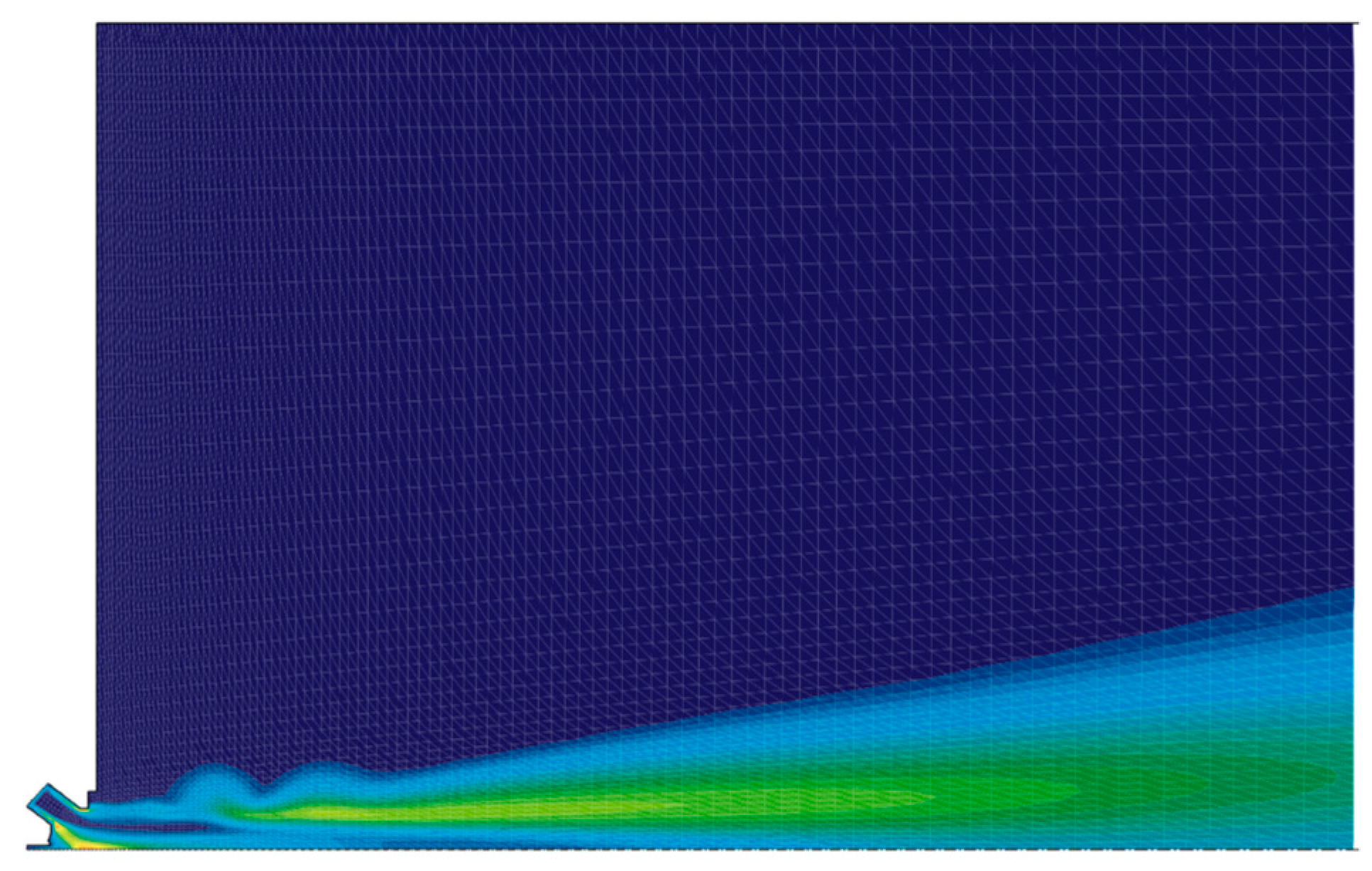
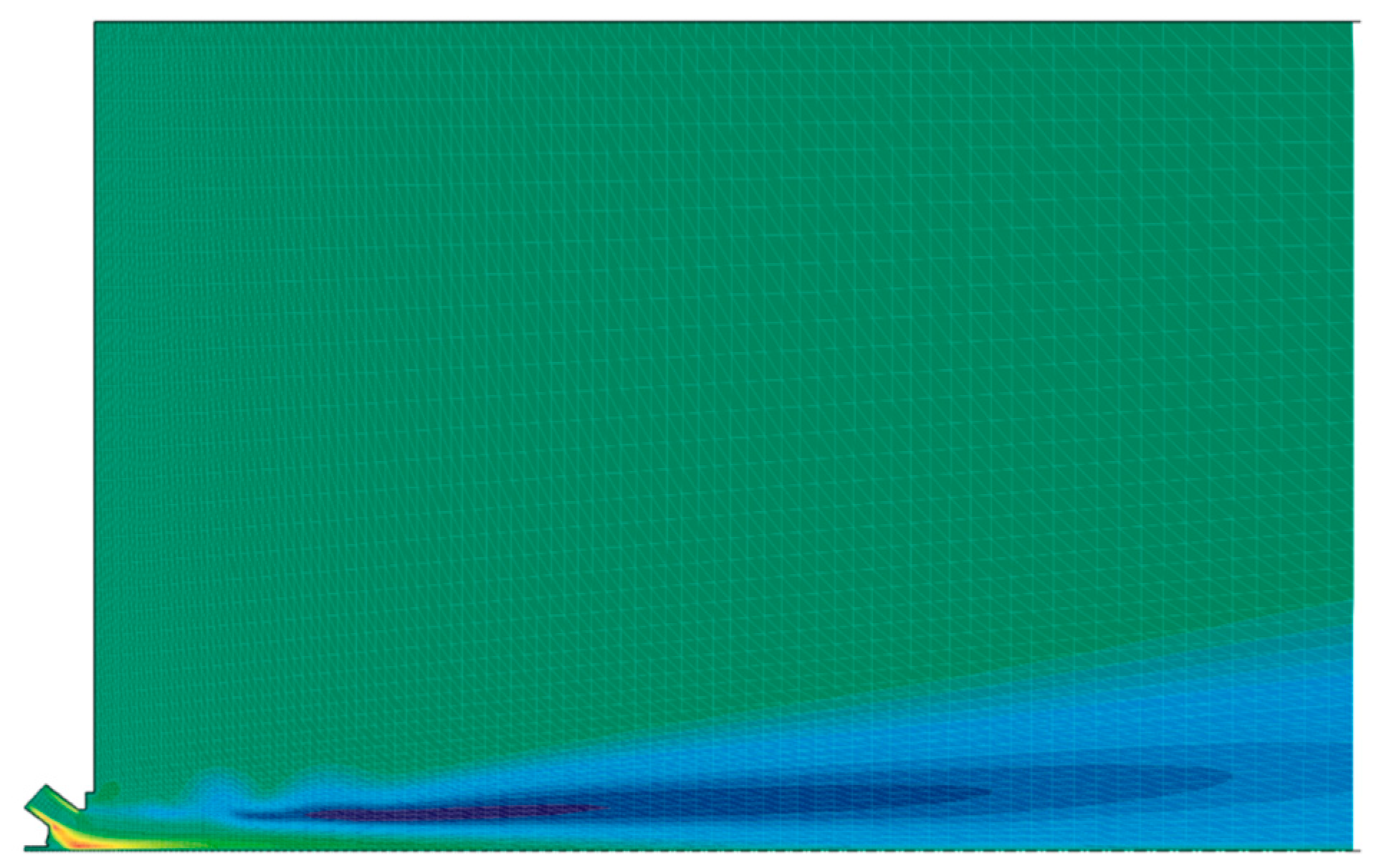
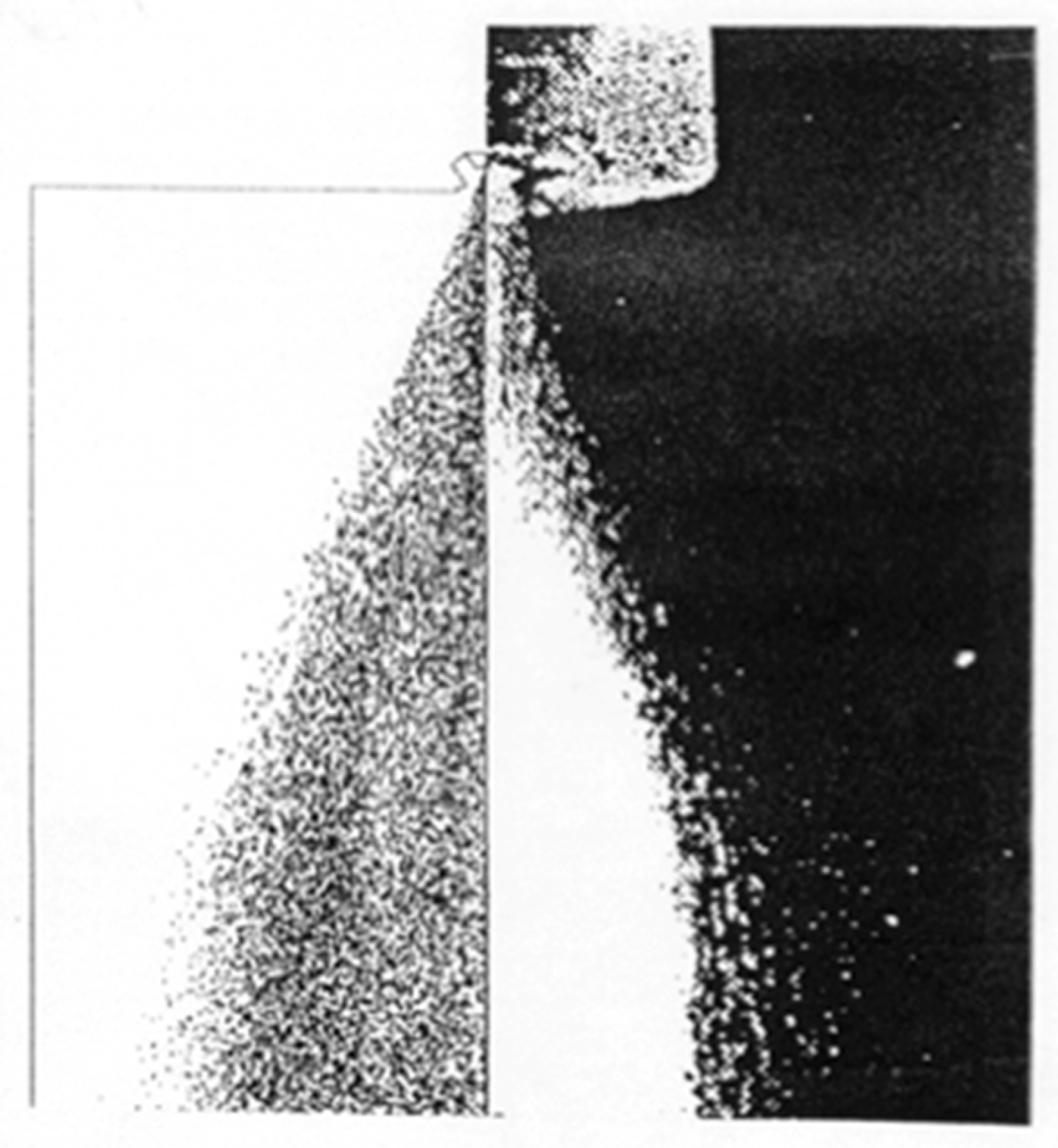
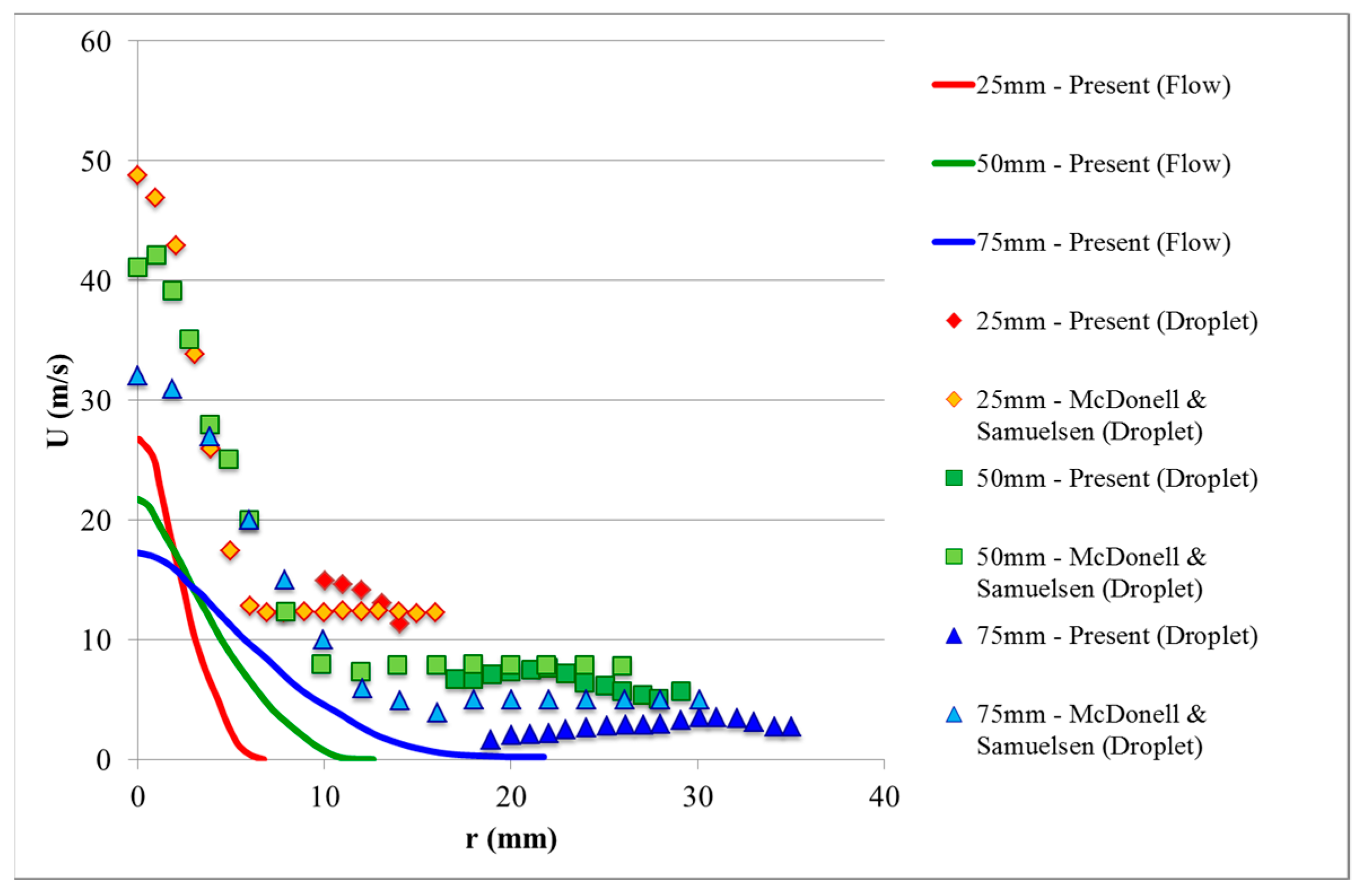
4.3. Spray Simulation
5. Conclusions
- The presented engineering model for simulation of spray leads to results that are in qualitative agreement with the experimental data for the studied cases.
- The average droplet size due to primary breakup mechanisms is in good agreement with the experimental data in regions of the flow where the droplets are nearly spherical.
- In regions of the spray where the droplets are elongated, the predicted droplet diameter overestimates the experimental data.
- The droplet velocity is in reasonable agreement with the experimental data.
- Droplet aspect ratio affects the evaporation rate of droplets.
- Evaporation affects the fluctuation velocity of droplets, but it has little effect on the droplet diffusivity.
- The presented model and simulation algorithm provides a viable tool for the computational prediction of spray simulations.
- Secondary breakup mechanisms may play a major role in the atomization of sprays with complex atomizing airflow patterns and must be included in future studies.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Faeth, G. Evaporation and combustion of sprays. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1983, 9, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, C. Recent advances in droplet vaporization and combustion. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1982, 8, 171–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Siamas, G.; Jagus, K.; Karyiannis, T. Physical modelling and advanced simulations of gas-liquid two-phase jet flows in atomization and sprays. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2010, 36, 131–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutheil, E. Issues in computational studies of turbulent spray combustion. In Experiments and Numerical Simulations of Diluted Spray Turbulent Combustion; Merci, B., Roekaerts, D., Sadiki, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jenny, P.; Roekaerts, D.; Beishuizen, N. Modeling of turbulent dilute spray combustion. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2012, 38, 846–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.M.; Chen, C.P.; Jiang, Y. Turbulence Modulation Effect on Evaporating Spray Characterization. In Proceedings of the 26th Joint Propulsion Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 16–18 July 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Berlemont, A.; Grancher, M.-S.; Gouesbet, G. On the Lagrangian Simulation of Turbulence Influence on Droplet Evaporation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1991, 34, 2805–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvasnak, W.; Ahmadi, G.; Schmidt, D.J. An Engineering Model for the Fuel Spray Formation of Deforming Droplets. At. Sprays 2004, 14, 289–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolakaluri, R.; Li, Y.; Kong, S.-C. A unified spray model for engine spray simulation using dynamic mesh refinement. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2010, 36, 858–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.; Gebretsadik, M.; Habisreuther, P.; Turrini, F.; Zarzalis, N.; Trimis, D. Numerical and experimental investigation on droplet dynamics and dispersion of a jet engine injector. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2015, 75, 144–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doisneau, F.; Arienti, M.; Oefelein, J.C. A semi-Lagrangian transport method for kinetic problems with application to dense-to-dilute polydisperse reacting spray flows. J. Comput. Phys. 2017, 329, 48–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyas, S.; Gil, A.; Margot, X.; Khuong-Anh, D.; Ravet, F. Evaluation of the Eulerian-Lagrangian Spray Atomization (ELSA) model in spray simulations: 2D cases. Math. Comput. Model. 2013, 57, 1686–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, S.V.; Gorokhovski, M.; Moin, P. LES of atomizing spray with stochastic modelling of secondary breakup. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2003, 29, 1503–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, W.P.; Lettieri, C. Large eddy simulation of spray atomization with stochastic modelling of breakup. Phys. Fluids 2010, 22, 115106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irannejad, A.; Banaeizadeh, A.; Jaberi, F. Large eddy simulation of turbulent spray combustion. Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 431–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, W.P.; Marquis, A.J.; Noh, D. An investigation of a turbulent spray flame using Large Eddy Simulation with a stochastic breakup model. Combust. Flame 2017, 186, 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.; Hélie, J.; Gorokhovski, M. Computational methodology for non-evaporating spray in quiescent chamber using Large Eddy Simulation. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2018, 102, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, D.; Gallot-Lavallée, S.; Jones, W.P.; Navarro-Martinez, S. Comparison of droplet evaporation models for a turbulent, non-swirling jet flame with a polydisperse droplet distribution. Combust. Flame 2018, 194, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhou, L.X.; Chan, C.K.; Wang, H.G. Large-eddy simulation of ethanol spray combustion using a SOM combustion model and its experimental validation. Appl. Math. Model. 2015, 39, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senoner, J.M.; Sanjose, M.; Lederlin, T.; Faegle, F.; Garcia, M.; Riber, E.; Cuenot, B.; Gicquel, L.; Pitsch, H.; Poinsot, T. Eulerian and Lagrangian Large-Eddy Simulations of an Evaporating Two-phase Flow. C. R. Mecanique 2009, 337, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, V.N.; Masri, A.R.; Navarro-Martinez, S.; Luo, K.H. Investigation of auto-ignition in turbulent methanol spray flames using Large Eddy Simulation. Combust. Flame 2013, 160, 2941–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonell, V.G.; Samuelsen, G.S. An Experimental Data Base for the Computational Fluid Dynamics of Reacting and Nonreacting Methanol Sprays. J. Fluids Eng. 1995, 117, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, P.J.; Amsden, A.A. The TAB Method for Numerical Computation of Spray Droplet Breakup. SAE Tech. Paper 872089. Available online: https://www.sae.org/publications/technical-papers/content/872089/ (accessed on 20 January 2019).
- Ibrahim, F.A.; Yang, H.Q.; Przekwas, A.J. Modeling of Spray Droplets Deformation and Breakup. AIAA J. Propuls. 1993, 9, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvasnak, W.; Ahmadi, G. Computational Modeling of Dispersion of Deforming Fuel Droplets in a Spray Injector Flow Field. In Proceedings of the 1996 Joint Army-Navy-NASA-Air Force (JANNAF) Propulsion Meeting, JPM and JSM 96, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 9–13 December 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, F.-G.; Ahmadi, G. Dispersion of Ellipsoidal Particles in an Isotropic Pseudo-Turbulent Field. ASME J. Fluids Eng. 1995, 117, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ahmadi, G.; Fan, F.-G.; Mclaughlin, J.B. Ellipsoidal particles transport and deposition in turbulent channel flows. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2001, 27, 971–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, H. Classical Mechanics, 2nd ed.; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Gallily, I.; Cohen, A.H. On the Orderly Nature of the Motion of Nonspherical Large Droplet and Axially Symmetrical Elongated Particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1979, 68, 338–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, P.C. Spacecraft Attitude Dynamics; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Happel, J.; Brenner, H. Low Reynolds Number Hydrodynamics; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Harper, E.Y.; Chang, I.-D. Maximum dissipation resulting from lift in a slow viscous shear flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1968, 33, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, G.B. The Motion of Ellipsoidal Particles Immersed in a Viscous Fluid. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1922, 102, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, H.A. Dynamics of Drop Deformation and Breakup in Viscous Fluids. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1994, 26, 65–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haworth, D.C.; Pope, S.B. A generalized Langevin model for turbulent flows. Phys. Fluids 1986, 29, 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haworth, D.C.; Pope, S.B. A pdf modeling study of self-similar turbulent free shear flows. Phys. Fluids 1987, 30, 1026–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girimaji, S.S.; Pope, S.B. A diffusion model for velocity gradients in turbulence. Phys. Fluids 1990, 2, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schmidt, D.J.; Kvasnak, W.; Ahmadi, G. A Model for Fuel Spray Formation with Atomizing Air. Fluids 2019, 4, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids4010020
Schmidt DJ, Kvasnak W, Ahmadi G. A Model for Fuel Spray Formation with Atomizing Air. Fluids. 2019; 4(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids4010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchmidt, David J., William Kvasnak, and Goodarz Ahmadi. 2019. "A Model for Fuel Spray Formation with Atomizing Air" Fluids 4, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids4010020
APA StyleSchmidt, D. J., Kvasnak, W., & Ahmadi, G. (2019). A Model for Fuel Spray Formation with Atomizing Air. Fluids, 4(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids4010020





