Abstract
About seven decades ago, it was discovered that special long-chain soluble polymers added to fluid at nanomolar concentrations significantly reduce resistance to turbulent flow (Toms effect). These so-called drag-reducing polymers (DRPs) do not affect resistance to laminar flow. While the flow parameters associated with the Toms effect do not occur in the cardiovascular system, many later studies demonstrated that intravenous injections of DRPs given to experimental animals produced significant hemodynamic effects, such as increasing tissue perfusion, suggesting potential clinical use of these polymers. Moreover, it was found that the specific viscoelastic properties of these polymers make them capable of modifying traffic of blood cells in microvessels and beneficially redistributing them in the blood capillary system—a phenomenon related to rheological properties of DRPs and not related to their specific chemistry. The domain of drag reducing polymers includes many organic and water-soluble, synthetic and natural long-chain molecules. The study presented here employed chemical and rheological methods, as well as macro and microfluidic tests, to characterize the DRP that we discovered in the Aloe vera plant, which was found to be a more powerful drag reducer and less fragile than many synthetic DRPs. The drag-reducing component of aloe gel was purified and chemically identified, which helped to standardize preparation and made this polymer a strong candidate for clinical use. Examples of successful testing of the aloe-derived DRP in animal models are described.
1. Introduction
A remarkable discovery of 20th century, the Toms effect [1], described the ability of soluble, long-chain (molecular weight > 106 Da) polymers to reduce resistance to turbulent flow in pipes. It was demonstrated that the addition of nanomolar concentrations of these polymers, characterized by a relatively linear structure and unique elastic properties, significantly increased flow rates at a constant pressure drop or decreased the pressure gradients at constant flow conditions. The polymers had no effect on flow resistance at a laminar flow, nor did they change the viscosity of fluid at extremely low concentrations, which were effective in reducing resistance to turbulent flow [2,3]. These water-soluble molecules, so called drag reducing polymers (DRPs), have been found to produce beneficial hemodynamic effects in experimental animals [4,5], including an increase in tissue perfusion and tissue oxygenation and a decrease in vascular resistance, when intravenously injected aiming at nanomolar concentrations (0.2–2 nM or 0.001–0.01 mg/mL) [6]. These polymers have been successfully applied in animal models of various pathological conditions, including hemorrhagic shock, atherosclerosis, and diabetes [4,5,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. In in vitro microfluidic studies, it was discovered that, in addition to reducing turbulent flow resistance, DRPs modified dynamics of red blood cell (RBC) distribution in microcirculation, preventing them from moving toward the vessel center. Without DRPs, the near-wall space contains plasma and mostly platelets and leukocytes (so-called Fåhraeus effect), which significantly reduces RBC concentrations in capillaries. Presence of DRPs in vascular system reverses the Fåhraeus effect and significantly increases traffic of RBCs in arterioles and capillaries, thus increasing tissue perfusion and oxygen delivery/gas exchange [5,6,16,17].
Several DRPs have been shown to be effective in vivo including high molecular weight (MW) polyethylene oxide (PEO) [5,7,8,14], polyacrylamide (PAM) [4,9,12,13], and certain polysaccharides [5,11,15]. However, none of the tested DRPs were found, in their present form, to be ideal for biomedical applications. PEO rapidly mechanically degrades when exposed to turbulence and other high stress flow conditions. Although blood flow in small arteries is laminar, turbulent flow is found in the aorta. In addition, blood can be exposed to high stress conditions, such as stenotic arteries, artificial heart valves, blood pumps, and other blood contacting devices, which would break down fragile long chain polymer molecules. The more stable PAM is not a suitable DRP candidate for biomedical applications because of its reported toxicity [13,14]. Some high MW polysaccharides were shown to be very effective in various animal models [5,11,15], resistant to mechanical degradation [18,19,20], and generally non-toxic [21,22]. Therefore, it was essential to find new DRPs for potential clinical use and to develop a set of standard tests to characterize these new DRPs and assess their properties in preclinical models prior to clinical trials for feasibility, safety, and putative benefit.
High MW polysaccharides, such as a polymer extracted from okra and characterized as a rhamnogalactogalacturonan, have been shown to be effective drag reducing polymers, which produced an increase in mean aortic blood flow, measured by an electromagnetic flow probe, and a decrease in peripheral resistance in a rodent model [14]. It was found by Gowda [23] that relatively high MW polysaccharides could be isolated from aloe plants via alcohol extraction. An aloe based polysaccharide is an attractive DRP for biomedical applications since toxicological studies have shown that acetylated mannan (or acemannan), a product extracted from the aloe leaf gel, has minimal systemic toxicity when injected intraperitoneally or intravenously [21,24]. Importantly, it was discovered in our laboratory that a polymer extracted from the Aloe vera plant mucilage was also a very effective drag-reducer [5,25]. The Aloe vera leaf consists of three major components: clear sheets comprised of cell walls and membranes, microparticles comprised of degenerated cellular organelles, and a viscous liquid gel comprised of the liquid components of mesophyll cells [26]. The DRP was extracted from the viscous gel portion of the aloe leaves with ethanol. It is known that the ethanol insoluble portion of the gel is >50% carbohydrate [26]. A mannan component has been identified in this portion of all aloe species studied, although differences in MW, degree of acetylation, and mannose-glucose ratio have been observed [26,27]. In one study, the polysaccharides found in the Aloe vera gel have been characterized as at least four different partially acetylated linear glucomannans, which contain 1–4 glycosidic linkages [28]. In addition, the polysaccharides in Aloe vera were shown to be composed of β-(1,4)-linked acetylated polymannans containing O-acetyl groups with a mannose monomer to acetyl ratio of approximately 1:1 [21]. A structure of the Aloe vera gel’s major component was proposed by Chow et al. [27], based on their data from chromatography, carbohydrate compositional analysis, linkage analysis and NMR. This structure consists of a linear β-1,4-linked mannose backbone with β-1,4-linked glucose substituting for mannose approximately every 30 residues. Mannose residues are acetylated at O2, O3 or O6 and sidechains are single galactose residues α-1,6-linked to the mannoses residues in the backbone. However, the structure of the active drag reducing component of the Aloe vera DRP remained unknown.
Our studies [5,11,29] showed aloe derived DRP (AV-DRP) to be effective in vivo, improving perfusion and reducing mortality in animal models of severe hemorrhagic shock and myocardial ischemia. A more recent study demonstrated that AV-DRP reduced foreign body reaction and increased well-structured collagen deposition when injected into animals that had received synthetic biodegradable scaffold implants [30]. In addition, AV-DRP was found to be resistant to mechanical degradation in vitro [31] making it a strong candidate for use in biomedical applications. In the study presented here, we aimed to further characterize AV-DRP by using chemical and rheological methods and then to describe the effects of AV-DRP on blood flow using a microfluidic-based model of the microcirculation. We hope that the results of this study will help this amazing natural DRP to be accepted for preclinical and clinical examination and finally be approved for treatments of various microcirculatory disorders.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Preparation of AV-DRP
A detailed procedure for AV-DRP extraction and purification was developed in our laboratory at the early stage of aloe and other potential natural DRP investigations [25]. The AV-DRP was extracted from freshly cut leaves of Aloe vera plants obtained from Silverthorn Ranch Nursery (Fallbrook, CA, USA). Leaves were removed from the Aloe vera plant and sliced open lengthwise. The exposed gel was scraped from the interior of the leaves and mixed with sterile saline. This mixture was filtered through several layers of cheesecloth, and the resulting filtrate was collected, stirred, and centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for one hour at 4 °C. The DRP was then selectively precipitated from the supernatant using 100% ethanol. The precipitate was collected and dried overnight in a vacuum. The dried precipitate was then dissolved at a concentration of 2.5 mg/mL in sterile saline with 0.1 mg/mL Gentamicin added as an antibacterial agent. Several days of slow stirring at 4 °C were required to dissolve the precipitate. When completely dissolved, the polymer solution was additionally centrifuged, and the supernatant was dialyzed against sterile saline using a Spectra/Por regenerated cellulose membrane (Spectrum Laboratories, Inc., Rancho Dominguez, CA, USA) with a MW cutoff of 50,000 Da. The dialysis procedure aimed to remove all low MW polymer fractions and other potential low MW impurities.
2.2. In Vitro Hydrodynamic Tests Characterizing the Drag Reducing Ability of AV-DRP
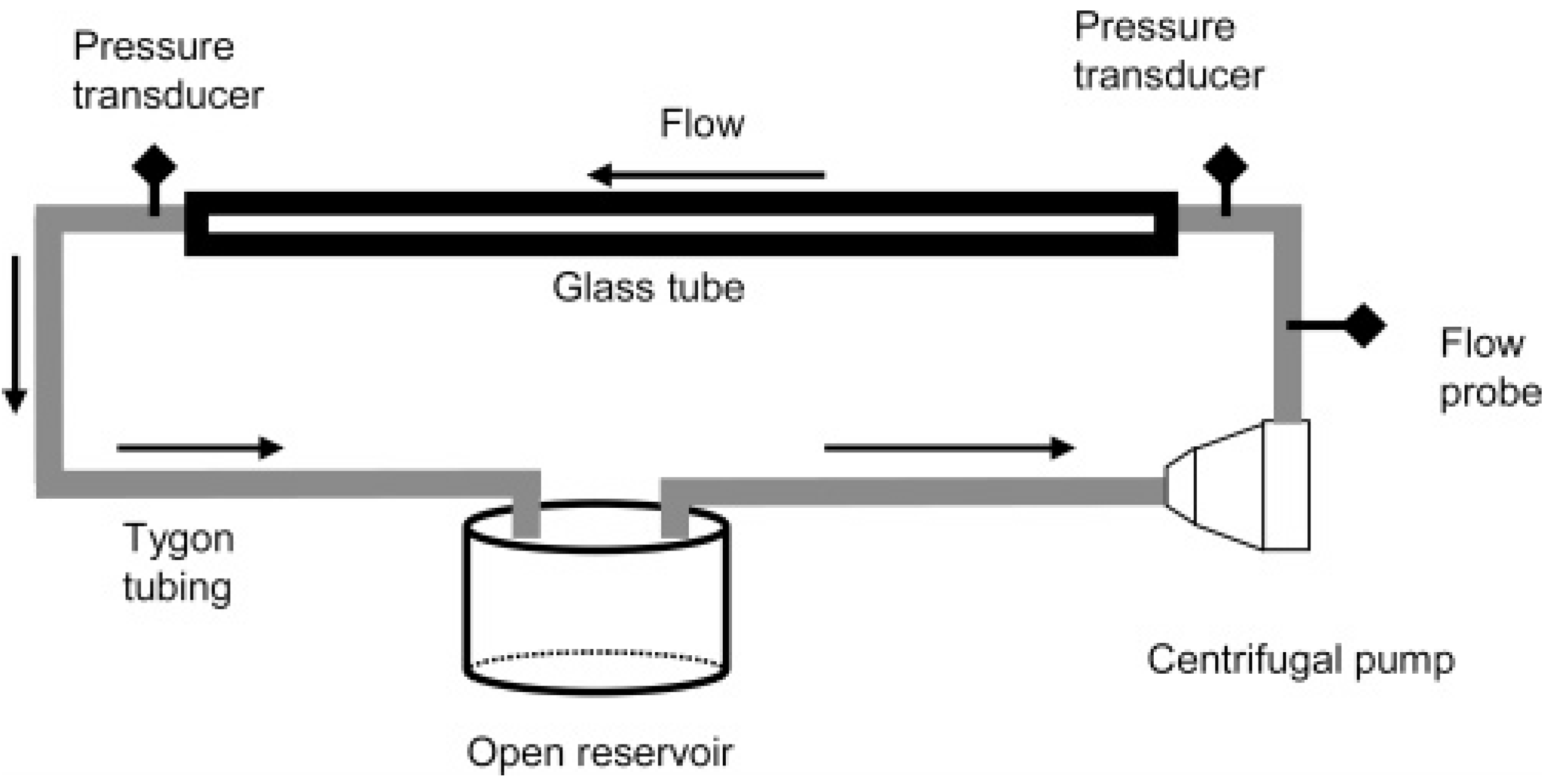
Although flow in the microcirculation is not turbulent, as Reynolds numbers in small arteries and arterioles with diameters of ~0.1–1 mm are much below 100 [32], it has been shown that the same polymers which were found to be effective in turbulent flow also produced beneficial effects in the vascular system. Therefore, the first test to identify candidate polymers evaluated reduction in flow resistance at sufficiently high Reynolds numbers. This recirculating flow system for testing the turbulent flow drag reducing ability of polymers consisted of a centrifugal pump (Medtronic., Minneapolis, MN, USA), a flow meter and clamp-on flow probe (Transonic Systems, Inc., Ithaca, NY, USA), a pressure transducer (PCB Piezotronics, Inc., Depew, NY, USA), a long smooth glass tube and an open fluid reservoir both connected with the pump via tubing (Tygon, Cole-Parmer, Vernon Hills, IL, USA). A schematic of the flow system is shown in Figure 1. Pressures and flow rates were recorded before and after DRP addition. The in vitro flow experiments were performed at room temperature. Drag reduction (percent) at a constant flow rate was calculated using Equation (1):
where DR is drag reduction (%), ΔPP is pressure drop for polymer solution, and ΔP0 is pressure drop for saline alone. Reynolds numbers ranged from 10,000 to 25,000, and length of the tube was at least 10 times the entrance length.
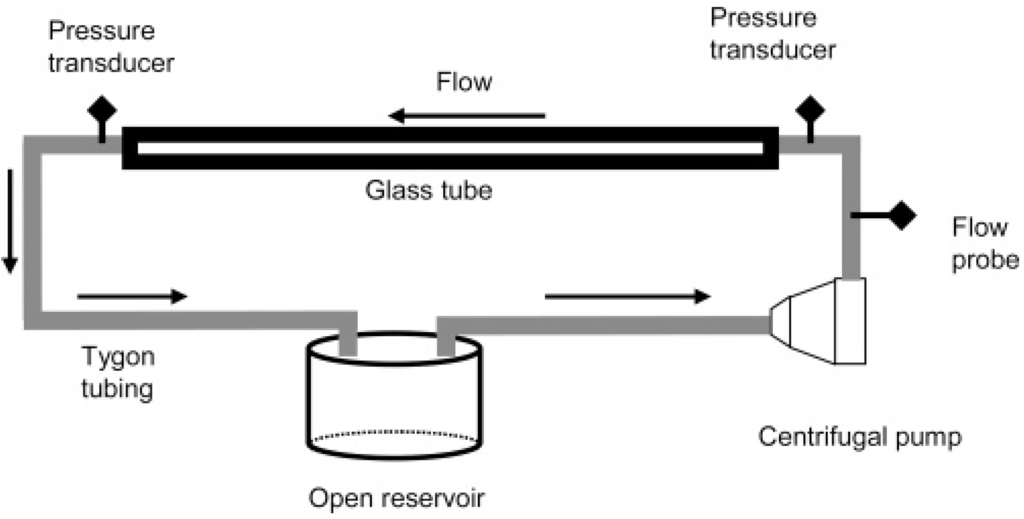
Figure 1.
Schematic of recirculating flow system used for evaluating polymer drag reduction [33].
2.3. Chemical Characterization of AV-DRP
Chemical characterization was performed in an attempt to determine the chemical structure of the active, drag reducing component of AV-DRP. Proteinase K and trypsin assays were used to rule out the presence of polypeptides in the active components of the preparation responsible for the drag-reducing ability of AV-DRP. Since trypsin and proteinase K are both serine proteases, which digest proteins by hydrolyzing peptide bonds [34,35], degradation of the polymer by these enzymes would indicate peptide bonds were present in the active DRP component of aloe. Then, an approach similar to that used in Chow et al. [27], enzymatic digestion with endo-β-D-mannanase, was used to make a preliminary determination of the residues and linkages in the backbone of AV-DRP. After treatment with each enzyme, drag reduction tests of the AV-DRP were used to determine enzymatic cleavage in the polymer backbone. A decrease in drag reducing ability, most likely related to a decrease in MW, was used to indicate cleavage of the polymer.
2.4. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC)
Molecular characteristics, including high MW and relatively linear structure with small or no branches are important in determining a polymer’s potential drag reducing efficiency. Number average and weight average MWs (Mn and Mw), intrinsic viscosity (IV), radius of gyration (Rg), hydrodynamic radius (Rh), and polydispersity index (PDI) were measured using a Viscotek Triple Detector Array gel permeation chromatography (GPC) system (Viscotek, Houston, TX, USA). Separation was performed on a methacrylate-based column with an exclusion limit of 5 × 107 Da. The system combines a refractive index detector, a right angle laser light scattering detector, and a differential viscometer in order to determine average MWs (Mn and Mw), IV, Rg, Rh, and MW distribution in a single experiment. Column and detector temperatures were maintained at 30 °C and the mobile phase was 0.1 M NaNO3 with 0.01% NaN3. The system was calibrated using a PEO standard with a MW of 22 kDa and a narrow MW distribution (PDI ~ 1.0).
2.5. Rheological Characterization
Concentrated DRP solutions are known to exhibit non-Newtonian flow behavior (shear thinning). Rheological parameters such as viscosity, elasticity, and relaxation time of AV-DRP solution vs. shear rates were analyzed in order to fully characterize this polymer, since known effective DRPs have been found to have high viscosity and elasticity when measured at low shear rates in relatively high concentration. The rheological properties were measured over a wide range of shear rates using a Brookfield cone and plate rotational rheometer (Middleboro, MA, USA) as well as a Vilastic 3 viscoelasticity analyzer (Austin, TX, USA). The Vilastic 3 employed controlled oscillatory flow in a cylindrical tube to measure the major rheological parameters including viscosity, elasticity, and relaxation time. These parameters were measured in solutions with a concentration of 2.5 mg/mL in saline. Viscosity of AV-DRP solutions at a concentration of 0.1 mg/mL was measured using a capillary viscometer (Cannon Manning). At this concentration, the DRP solutions behaved as Newtonian fluids, and therefore measurement of asymptotic viscosity was sufficient for rheological characterization.
2.6. Microfluidic Studies
Microfluidic studies were conducted to visualize the effects of AV-DRP on RBC flow in models of the microvessels. As mentioned in Introduction, previous studies showed that the addition of a well-known DRP (high MW PEO) modified traffic of blood cells causing reduction of the near-wall cell free layer by relocation of some RBCs to the near wall space, attenuating the Fåhraeus effect, and delivering more RBCs to capillaries by reduction of the plasma skimming at vessel bifurcations.
Bovine blood was obtained from a local slaughterhouse. The RBCs were washed three times with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and resuspended at a hematocrit of 20% in PBS with 1% bovine serum albumin added to preserve the biconcave shape of the cells. A hematocrit of 20% was chosen since in vivo microcirculatory hematocrit values are 20%–50% lower than the systemic hematocrit [36,37] due to the Fåhraeus effect, which is more pronounced at lower hematocrit for a given vessel diameter [37]. Light microscopy was used to verify normal biconcave shape of the RBCs.
Standard photolithography and replica molding techniques were used to fabricate polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microchannel systems containing a series of bifurcations and expansions [38]. Channel widths ranged from 25 to 200 μm and channel height was 100 μm. A syringe pump (Harvard Apparatus) in infuse mode was used to generate continuous, non-pulsatile flow of the RBC suspensions through the microchannel systems. Although flow in the vascular system is pulsatile, steady flow was chosen because pulsatility is diminished in the microvessels [39]. In order to prevent RBC sedimentation, the suspension in the syringe was kept well mixed by placing a small magnetic stir bar inside the syringe, and manually agitating it using another magnet on the outside. Physiologically relevant flow rates ranging in the parent channel from 0.01 to 0.2 mL/min, depending on channel dimensions, were used for these experiments. Reynolds numbers ranged from 1 to 20, which is within the physiological range for small arteries and arterioles with similar diameters. The RBC suspensions flowing through the microchannels were recorded with a microscopic flow imaging system, which consisted of an inverted research microscope (IX70, Olympus, NJ, USA), a cooled CCD camera (MicroMax DIF, Roper Scientific, NJ, USA), and an associated image acquisition board hosted in a PC. At least twenty images were recorded at each condition. Areas in the main channel and the smaller branch, as well as the bifurcation itself, were imaged.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Drag reduction data are presented as mean percent drag reduction ± standard deviation. Unpaired, two-sample Student’s t-tests assuming unequal variances were used to compare 0.01 mg/mL AV-DPR to saline at each tested Reynolds number. Parameters measured by GPC and viscoelastic properties are presented as mean value ± standard deviation value.
3. Results
Previous studies have shown that AV-DRP was a very effective DRP both in vitro and in vivo in animal models [5,25]. However, the drag reducing component of AV-DRP had not been fully characterized, and the polymer preparation methods were not reproducible or suitable for production of large quantities. Therefore, it was important to standardize AV-DRP extraction methods in order to eliminate variability between preparations, as well as to fully characterize this natural DRP. The results of this study show certain progress made toward this standardization and characterization of the aloe-derived DRP.
3.1. In Vitro Testing Drag Reducing Ability of AV-DRP
Drag reducing ability of AV-DRP was assessed at the concentrations of 0.01 to 0.1 mg/mL in turbulent flow. At Reynolds numbers of about 20,000, AV-DRP reduced resistance to flow by 31% ± 6%, and AV-DRP produced a statistically significant drag reduction compared to saline (control) at all tested Reynolds numbers (p < 0.001). At a higher concentration, 0.1 mg/mL, AV-DRP was found to reduce friction by up to 50%. Similar experiments were performed using the same concentration of PEO. PEO WSR-301, a commonly used drag reducing polymer, reduced drag by a maximum 42% at 0.1 mg/mL using the same flow conditions. Comparison of the drag reducing ability demonstrated by these two polymers produced similar results. However, unlike AV-DRP, drag reducing efficiency of the PEO solution started to almost immediately diminish due to repeated exposure to high shear forces in the turbulent flow and especially inside the pump while AV-DRP was practically stable during the entire test. Our experiments confirmed the results of previous studies that have concluded that the DRPs with a linear structure are very efficient but degrade much more rapidly than branched ones [40].
3.2. Chemical Characterization of AV-DRP
Identification of the chemical structure of the active drag reducing component of AV-DRP was necessary before this DRP could be approved for use in the clinical setting. Using a trypsin based assay, as well as a proteinase K based assay, the hypothesis that the active drag reducing component of aloe was a protein was rejected. AV-DRP maintained its drag reducing activity when tested in the turbulent flow system at 0.01 mg/mL following treatment with either trypsin or proteinase K. Since neither enzyme degraded the polymer, it was concluded that the aloe-derived DRP did not contain peptide bonds. Based on these studies and the literature [21,23,27,28,41], it was reasonable to conclude that the drag-reducing component of aloe was a polysaccharide residue. Treatment of AV-DRP with endo-β-D-mannanase, however, did cause degradation of the DRP which resulted in diminishing of the AV-DRP drag reducing efficiency. Before enzyme treatment, the AV-DRP reduced resistance to flow in the pipe by ~40% at a concentration of 0.01 mg/mL; after treatment, the AV-DRP produced no drag reducing effect. Since endo-β-D-mannanase is known to hydrolyze mannans (galactomannans, glucomannans, and galactoglucomannans) containing β-1,4 linkages, it was inferred that the drag reducing element of aloe likely contains a backbone comprised of β-1,4 linked mannose residues.
3.3. GPC
Mean weight average MW of the AV-DRP determined by GPC was 8.4 × 106 ± 3.0 × 106 Da. Intrinsic viscosity was 29.3 ± 3.2 dL/g. Radius of gyration and hydrodynamic radius were 199 ± 26 nm and 153 ± 20 nm respectively. Polydispersity index was calculated to be 1.17 ± 0.17. These molecular characteristics are indicative of effective DRPs, but standard deviations were high. This may be due to the fact that components vary among plants depending on factors such as plant age [41,42], or that slight variations may have still existed in the extraction procedure leading to different actual concentrations of DRP in the final preparation. Tested in parallel, PEO WSR-301, a well-known effective DRP with somewhat lower MW and linear structure, was determined to have a weight average MW of 4.4 × 106 ± 0.2 × 106 Da. Intrinsic viscosity was 13.0 ± 0.5 dL/g. Radius of gyration and hydrodynamic radius were 120 ± 4 nm and 92 ± 3 nm respectively. Polydispersity index was calculated to be 1.4 ± 0.4.
3.4. Viscoelasticity
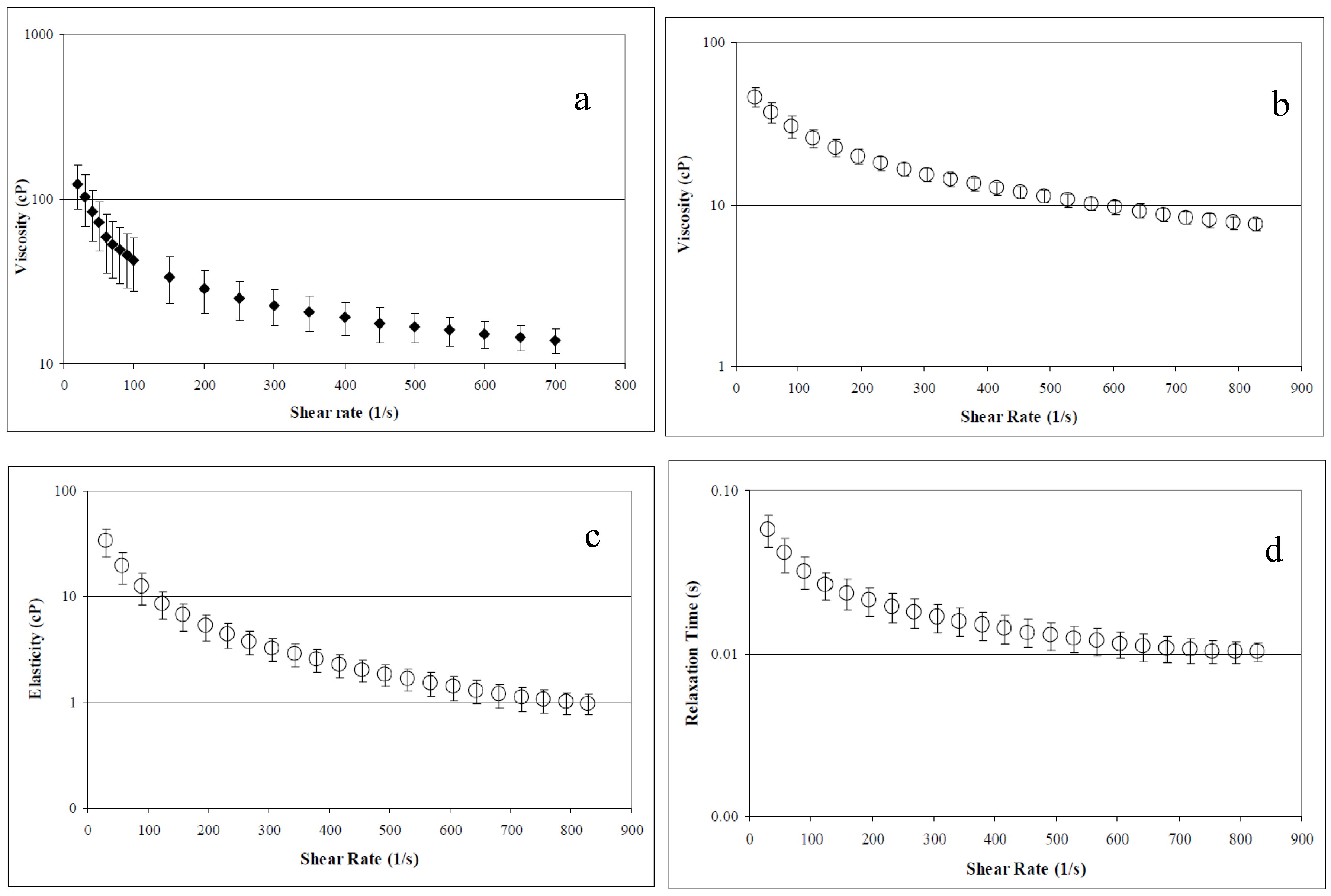
Concentrated AV-DRP solutions demonstrated pronounced non-Newtonian behavior and high viscosity, which are defining characteristics of all effective DRPs. Average viscosity, elasticity, and relaxation time, determined at a concentration of 2.5 mg/mL in saline using the Brookfield cone and plate rheometer and the Vilastic 3 viscoelastometer, are shown in Figure 2. At low concentrations, AV-DRP solutions had Newtonian flow behavior. Average viscosity at a concentration of 0.1 mg/mL was found to be ~1.2 cP. At the concentration applied in the microfluidic studies, 0.01 mg/mL, viscosity of the AV-DRP in buffer alone was ~1.05 cP at room temperature. Asymptotic viscosity of the 20% RBC suspension in PBS was 2.0 cP, and the 20% RBC suspension containing 0.01 mg/mL AV-DRP was ~2.2 cP. At 20% hematocrit and the shear rates applied in this study, the blood behaved as a Newtonian fluid.
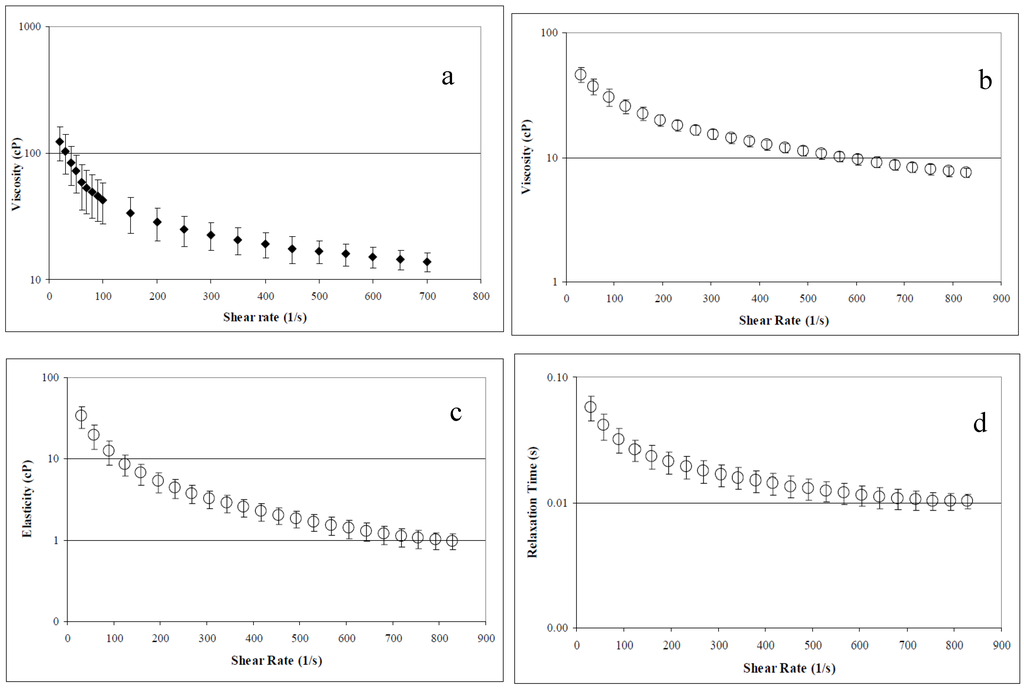
Figure 2.
Aloe derived DRP rheological parameters at 2.5 mg/mL concentration. (a) Viscosity measured in Brookfield cone and plate rheometer. (b) Viscosity measured in a viscoelastometer (Vilastic). (c) Elasticity measured in a viscoelastometer. (d) Relaxation time measured in a viscoelastometer [33].
3.5. Microfluidic Studies
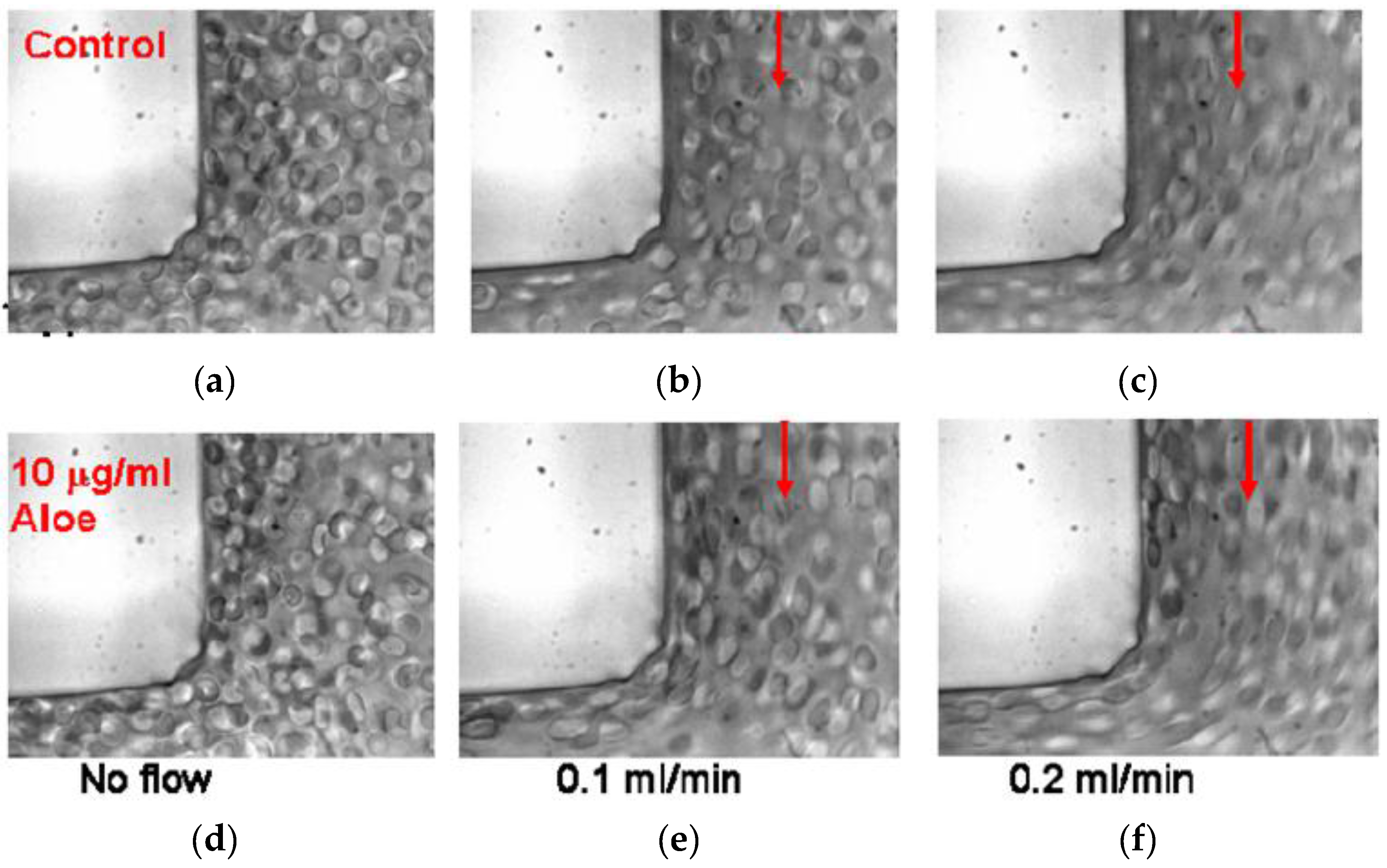
AV-DRPs reduced motion of RBCs from the near wall region toward the channel center, decreasing cell free plasma layer size and the plasma skimming effect in models of microvessels. Upstream of the bifurcation, a developed near wall plasma layer can be seen as control RBCs flow through the bifurcations (Figure 3). Flow direction in each image is indicated by the arrows. When AV-DRP was added to a RBC suspension at a concentration of 0.01 mg/mL, the RBCs were relocated to this near wall region, greatly reducing the plasma layer size. Due to the decrease in the size of the near wall plasma layer more RBCs flowed into the daughter branches, decreasing the plasma skimming effect. As one can see, the RBCs are more elongated because of the closer to the wall location and exposure to the higher near-wall shear stresses due to the elimination of the cell-free layer by the nanomolar concentration of AV-DRP.
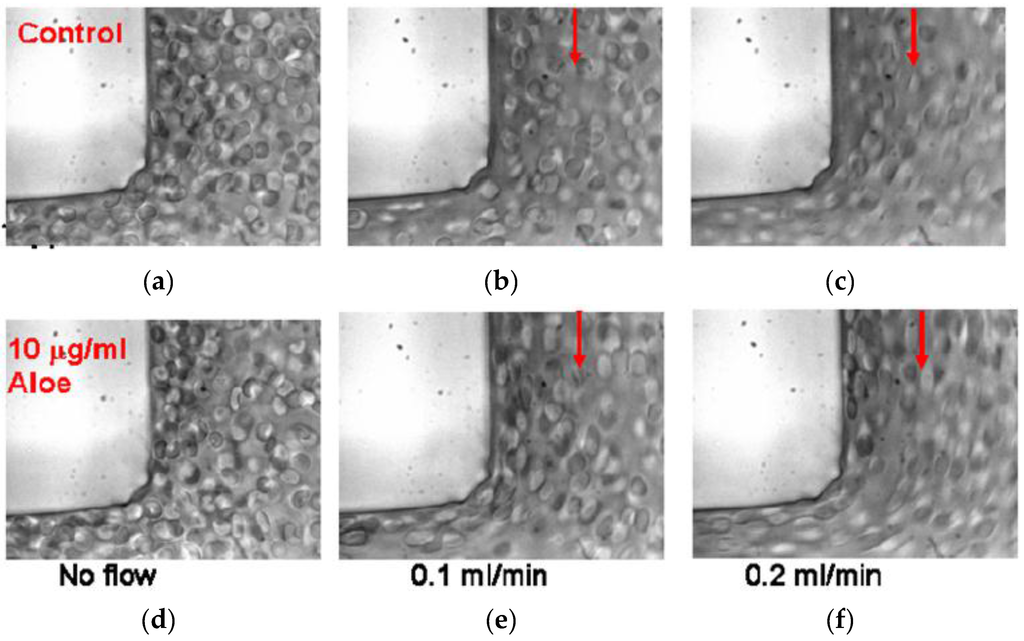
Figure 3.
Red blood cell suspensions in a 100 μm to 100 μm right angle bifurcation with no polymer and no flow (a) and flowing at 0.1 mL/min (b) and 0.2 mL/min (c) and with 0.01 mg/mL AVP and no flow (d) and flowing at 0.1 mL/min (e) and 0.2 mL/min (f) [33].
4. Discussion
DRPs have been shown to improve impaired blood circulation caused by numerous pathologies in animal models [4,5,8,9,10,11,13,14]. Although commonly used DRPs such as PEOs and PAMs were very effective in these models, they are not optimal for potential clinical applications. PEO is degraded quickly by high stresses [43] and PAM presents toxicity issues [13,14,44]. Therefore, other options must be considered for DRP application in vivo. An ideal candidate would include a synthetic or natural DRP, which is well reproducible, resistant to mechanical degradation, biocompatible, and easy to manufacture for potential clinical use.
Since high MW polysaccharides are known to be effective drag reducers [5,11,15] that are resistant to mechanical degradation [18,19,20], and a polysaccharide extracted from the Aloe vera plant was found to have low systemic toxicity when injected either intraperitoneally or intravenously [21], we hypothesized that AV-DRP could be a good candidate DRP for use in the medical field. In the current study, AV-DRP was found to be a promising candidate for the future clinical applications. It reduced resistance by up to 50% at the accessible range of Reynolds numbers in the turbulent flow system used for these studies. The active drag reducing component was determined to be a polysaccharide consisting of β-1,4 linked mannose residues, although additional studies are needed to elucidate the exact chemical structure of this polymer. Molecular and rheological properties of AV-DRP are typical for an effective drag reducer. High standard deviations in molecular and rheological properties observed in our study were likely the result of variations between aloe preparations caused by variations between plants or slight variance in the extraction procedure. The fact that standard deviations in viscoelastic parameters were highest at low shear rates may also indicate the presence of some molecular aggregation, which varied between samples. This aggregation was also likely to be responsible for the higher viscosities measured using the cone and plate rheometer compared to those measured using the Vilastic viscoelastometer. The oscillatory flow in the viscoelastometer could break up these aggregates, significantly reducing the observed viscosity, especially at low shear rates.
AV-DRP has previously been shown to be more resistant to mechanical degradation than PEO in both saline and in the presence of RBCs [31] making it a promising candidate for potential use in treatment of chronic circulatory disorders. It has been previously hypothesized that certain polysaccharides may have increased resistance to degradation due to their strong bonds between monomer units as well as intra- and intermolecular interactions lessening the stresses on those bonds [19]. It has also been proven that relatively small branches on a long-chain polymer molecule increase its mechanical stability [20,40]. Although the exact structure of the DRP component of aloe is not yet known, a structure proposed for the main element of the aloe polysaccharide may contain some branches [27] while PEO does not. Finally, since polysaccharides, such as the aloe-based polysaccharide, are comprised of numerous six-carbon rings linked together, the molecules are more rigid, and therefore degradation is not entropically favored [18]. The presence of rings could also allow for some bonds to be broken without breaking up the polymer backbone. Therefore, unlike PEO, the aloe polymer could be expected to withstand some bond breakage without compromising its drag reducing activity. The potential degradation of AV-DRP caused by biologic mechanisms in vivo, however, has not been studied, but must be evaluated before this polymer could be used clinically.
Addition of AV-DRP to blood flowing in models of microvessels caused the RBCs to relocate toward the wall (anti-Fåhraeus effect), reducing the plasma layer size and thus reducing plasma skimming at vessel bifurcations. This effect was previously observed using PEO [5,17]. The prevention of RBC movement toward the center of the vessel by DRPs may improve the transport function of blood in the microcirculation and facilitate gas exchange between RBCs and tissue in vivo by reducing diffusion distance in the smallest arteries and arterioles. The observed increases in the near-wall hematocrit and, thus, in local viscosity with the addition of DRPs produce an increase in wall shear stress in the microchannels. In microvessels, this increase in wall shear stress would cause release of endothelial-derived relaxing factor, nitric oxide [39], promoting vasodilation and thus decreasing overall vascular resistance. In vivo experiments have shown that DRPs cause a decrease in vascular resistance [4,9,14,45,46,47], and local vasodilation caused by RBC redistribution could be one of the mechanisms responsible for this effect. The observed increase in wall shear stress caused by DRPs could also lead to an increase in number of functioning capillaries, which has been seen after the injection of DRPs in previous in vivo studies [8]. In the case of hemorrhagic shock, the reduction in plasma skimming at vessel bifurcations might improve microcirculation, delivering more RBCs to the capillaries and acting as an autotransfusion. This is a very promising DRP phenomenon since the adequate functional capillary density is a major factor of survival in hemorrhagic shock [48].
5. Conclusions
In the study presented here, Aloe vera-based drag reducing polymer (AV-DRP), a blood soluble DRP with great potential for clinical applications, was characterized and evaluated using chemical, rheological and hydrodynamic methods. AV-DRP offered the advantage of biocompatibility and resistance to mechanical stresses which induce degradation to many other tested DRPs. The current work made progress toward standardizing the preparation process and further characterizing this very promising DRP for medical practice. In vivo studies showed that AV-DRP produced strong beneficial effects in various animal models including hemorrhagic shock, myocardial infarction, and inflammatory attack related to biodegradable scaffold implantation [5,11,29,30], which characterized AV-DRP as a superior candidate for clinical use.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Toby Chapman for his advice and assistance related to the chemistry of AV-DRP. This work was supported or partially supported by several grants and contracts from: Department of Health, Commonwealth of Pennsylvania; DARPA; PTEI/NTEC; Pittsburgh Foundation; W81XWH-04-1-0848_USAMRMC; DAMD 17-02-1-0717 USAMRAA.
Author Contributions
Marina Kameneva has discovered the DRP in Aloe vera plants; Joie Marhefka and Marina Kameneva designed experiments, analyzed data, and both contributed to writing the manuscript; Joie Marhefka conducted the experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Toms, B.A. Some observations on the flow of linear polymer solution through straight tubes at large Reynolds numbers. Proc. Int. Congr. Rheol. 1948, 2, 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Lumley, J.L. Drag reduction by additives. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1969, 1, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, A.V. A review on drag reduction with special reference to micellar systems. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1984, 262, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorian, S.S.; Kameneva, M.V.; Shakhnazarov, A.A. Effect of high molecular weight compounds dissolved in blood on hemodynamics. Sov. Phys. Dokl. 1976, 21, 702–703. [Google Scholar]
- Kameneva, M.V.; Wu, Z.J.; Uraysh, A.; Repko, B.; Litwak, K.N.; Billiar, T.R.; Fink, M.P.; Simmons, R.L.; Griffith, B.P.; Borovetz, H.S. Blood soluble drag-reducing polymers prevent lethality from hemorrhagic shock in acute animal experiments. Biorheology 2004, 41, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kameneva, M.V. Microrheological effects of drag-reducing polymers in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2012, 59, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannushkina, I.V.; Grigoryan, S.S.; Kameneva, M.V.; Shakhnazarov, A.A. The possibility that after circulatory ischemia of the brain the blood circulation can be restored by introducing special polymers to the blood. Sov. Phys. Dokl. 1981, 26, 376. [Google Scholar]
- Golub, A.S.; Grigoryan, S.S.; Kameneva, M.V.; Malkina, N.A.; Shoshenko, K.A. Influence of polyethylene oxide on the capillary blood flow of diabetic rats. Sov. Phys. Dokl. 1987, 32, 620–621. [Google Scholar]
- Gannushkina, I.V.; Antelava, A.L.; Baranchikova, M.V. Suppression of Experimental Alimentary Atherosclerosis with Drag Reducing Polymers. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 1993, 116, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannushkina, I.V.; Kameneva, M.V.; Antelava, A.L. Effect of polymers reducing hydrodynamic resistance on systemic hemodynamics. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 1988, 106, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias, C.A.; Kameneva, M.V.; Tenhunen, J.J.; Puyana, J.C.; Fink, M.P. Survival in a rat model of lethal hemorrhagic shock is prolonged following resuscitation with a small volume of a solution containing a drag-reducing polymer derived from aloe vera. Shock 2004, 22, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostardi, R.A.; Greene, H.L.; Nokes, R.F.; Thomas, L.C.; Lue, T. The effect of drag reducing agents on stenotic flow disturbances in dogs. Biorheology 1976, 13, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Faruqui, F.I.; Otten, M.D.; Polimeni, P.I. Protection against atherogenesis with the polymer drag-reducing agent Separan AP-30. Circulation 1987, 75, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polimeni, P.I.; Ottenbreit, B.T. Hemodynamic effects of a poly(ethylene oxide) drag-reducing polymer, Polyox WSR N-60K, in the open-chest rat. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1989, 14, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polimeni, P.I.; Al-Sadir, J.; Cutilletta, A.F. Polysaccharide for enhancement of cardiac output. US Patent 4154822, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Marhefka, J.N.; Antaki, J.F.; Kameneva, M.V. Drag reducing polymers reduce near-wall concentration of platelets in microchannel blood flow. Biorheology 2010, 47, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marhefka, J.N.; Zhao, R.; Wu, Z.; Velankar, S.S.; Antaki, J.F.; Kameneva, M.V. Drag reducing polymers improve tissue perfusion via modification of the RBC traffic in microvessels. Biorheology 2009, 46, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- D’Almeida, A.R.; Dias, M.L. Comparative study of shear degradation of carboxymethylcellulose and poly(ethylene oxide) in aqueous solution. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1997, 56, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenis, P.R. Turbulent Flow Friction Reduction Effectiveness and Hydrodynamic Degradation of Polysaccharides and Synthetic Polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1971, 15, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.A.; Lim, S.T.; Choi, H.J.; Sohn, J.I.; Jhno, M.S. Characterization of drag reducing guar gum in a rotating disk flow. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 83, 2938–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talmadge, J.; Chavez, J.; Jacobs, L.; Munger, C.; Chinnah, T.; Chow, J.T.; Williamson, D.; Yates, K. Fractionation of Aloe vera L. inner gel, purification and molecular profiling of activity. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2004, 4, 1757–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.L.; Sherwood, E.R.; Browder, I.W.; McNamee, R.B.; Jones, E.L.; Di Luzio, N.R. Pre-clinical safety evaluation of soluble glucan. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 1988, 10, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, D.C.; Neelisiddaiah, B.; Anijaneyalu, Y.V. Structural Studies of Polysaccharides from Aloe Vera. Carbohydr. Res. 1979, 72, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamman, J.H. Composition and Applications of Aloe vera Leaf Gel. Molecules 2008, 13, 1599–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameneva, M.V.; Borovetz, H.S.; Griffith, B.P.; Repko, B.M.; Chapman, T. Artificial blood fluids and microflow drag reducing factors for enhanced blood circulation. US Patent 20030026855, 2 January 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Y.; Turner, D.; Yates, K.M.; Tizard, I. Isolation and characterization of structural components of Aloe vera L. leaf pulp. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2004, 4, 1745–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.T.; Williamson, D.A.; Yates, K.M.; Goux, W.J. Chemical characterization of the immunomodulating polysaccharide of Aloe vera L. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshun, K.; He, Q. Aloe vera: A valuable ingredient for the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries—A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 44, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, T.; Repko, B.; Griffith, B.P.; Waters, J.H.; Kameneva, M.V. I.V. infusion of a drag-reducing polymer extracted from aloe vera prolonged survival time in a rat model of acute myocardial ischaemia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2007, 98, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marascalco, P.J.; Blair, H.C.; Nieponice, A.; Robinson, L.J.; Kameneva, M.V. Intravenous injections of soluble drag-reducing polymers reduce foreign body reaction to implants. ASAIO J. 2009, 55, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marhefka, J.N.; Velankar, S.S.; Chapman, T.M.; Kameneva, M.V. Mechanical degradation of drag reducing polymers in suspensions of blood cells and rigid particles. Biorheology 2008, 45, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Whitmore, R.L. Rheology of the Circulation, 1st ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1968; p. 196. [Google Scholar]
- Marhefka, J.N. Study of Drag Reducing Polymers and Mechanisms of Their Intravascular Effect. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ebling, W.; Hennrich, N.; Klockow, M.; Metz, H.; Orth, H.D.; Lang, H. Proteinase K from Tritirachium album Limber. Eur. J. Biochem 1974, 47, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voet, D.; Voet, J.G.; Pratt, C.W. Fundamentals of Biochemistry; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 111–112, 307–309. [Google Scholar]
- Boyle, J. Microcirculatory hematocrit and blood flow. J. Theor. Biol. 1988, 131, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, H.L.; Cokelet, G.R.; Gaehtgens, P. Robin Fahraeus: Evolution of his concepts in cardiovascular physiology. Am. J. Physiol. 1989, 257, H1005–H1015. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McDonald, J.C.; Duffy, D.C.; Anderson, J.R.; Chiu, D.T.; Wu, H.; Schueller, O.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Fabrication of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Elecrophoresis 2000, 21, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyton, A.C.; Hall, J.E. Textbook of Medical Physiology, 9th ed.; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1996; pp. xliii, 1148. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, O.K.; Little, R.C.; Patterson, R.L.; Ting, R.Y. Polymer structures and turbulent shear stability of drag reducing solutions. Nature 1974, 250, 408–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, C.E.; Williamson, D.A.; Stroud, P.A.; Talley, D.J. Evaluation and comparison of commercially available Aloe vera L. products using size exclusion chromatograpy with refractive index and multi-angle laser light scattering detection. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2004, 4, 1727–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dourembos, N.J.; Fetterman, P.S.; Quimby, M.W.; Turner, C.E. Cultivation, extraction and analysis of Cannabis sativa L. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 1971, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, D.H.; Rodriguez, F. Degradation of Drag Reducing Polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1971, 15, 2975–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollister, D.D.; Oyen, F.; Rowe, V.K. Toxicology of acrylamide. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1963, 6, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorian, S.S.; Kameneva, M.V. Resistance-reducing polymers in the blood circulation. In Contemporary Problems of Biomechanics; Chernyi, G.G., Regirer, S.A., Eds.; Mir Publ., CRC Press: Moscow, Russia; Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990; pp. 99–110. [Google Scholar]
- Marhefka, J.N.; Marascalco, P.J.; Chapman, T.M.; Russell, A.J.; Kameneva, M.V. Poly(N-vinylformamide)-A drag-reducing polymer for biomedical applications. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacella, J.J.; Kameneva, M.V.; Brands, J.; Lipowsky, H.H.; Vink, H.; Lavery, L.L.; Villanueva, F.S. Modulation of Pre-capillary Arteriolar Pressure with Drag Reducing Polymers: A Novel Method for Enhancing Microvascular Perfusion. Microcirculation 2012, 19, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, A.G.; Intaglietta, M. High viscosity plasma expanders: Volume resuscitation fluids for lowering the transfusion trigger. Biorheology 2001, 38, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).