Liposomes-in-Gel as the Docetaxel Delivery for the Effective Treatment of Psoriasis by Inhibiting the Proliferation of Blood Vessels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
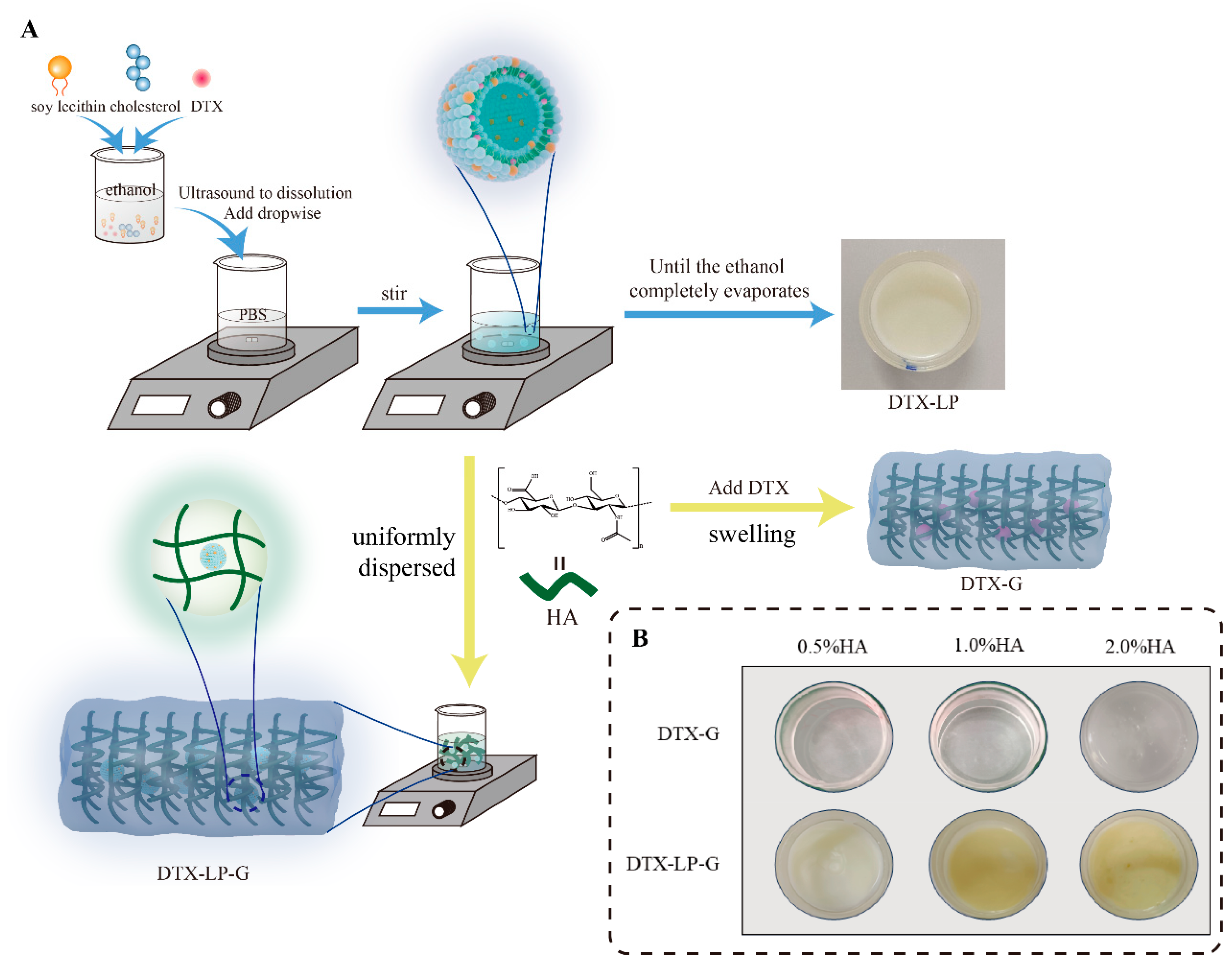
2.1. Prescription and Characterization of DTX-Loaded Formulations
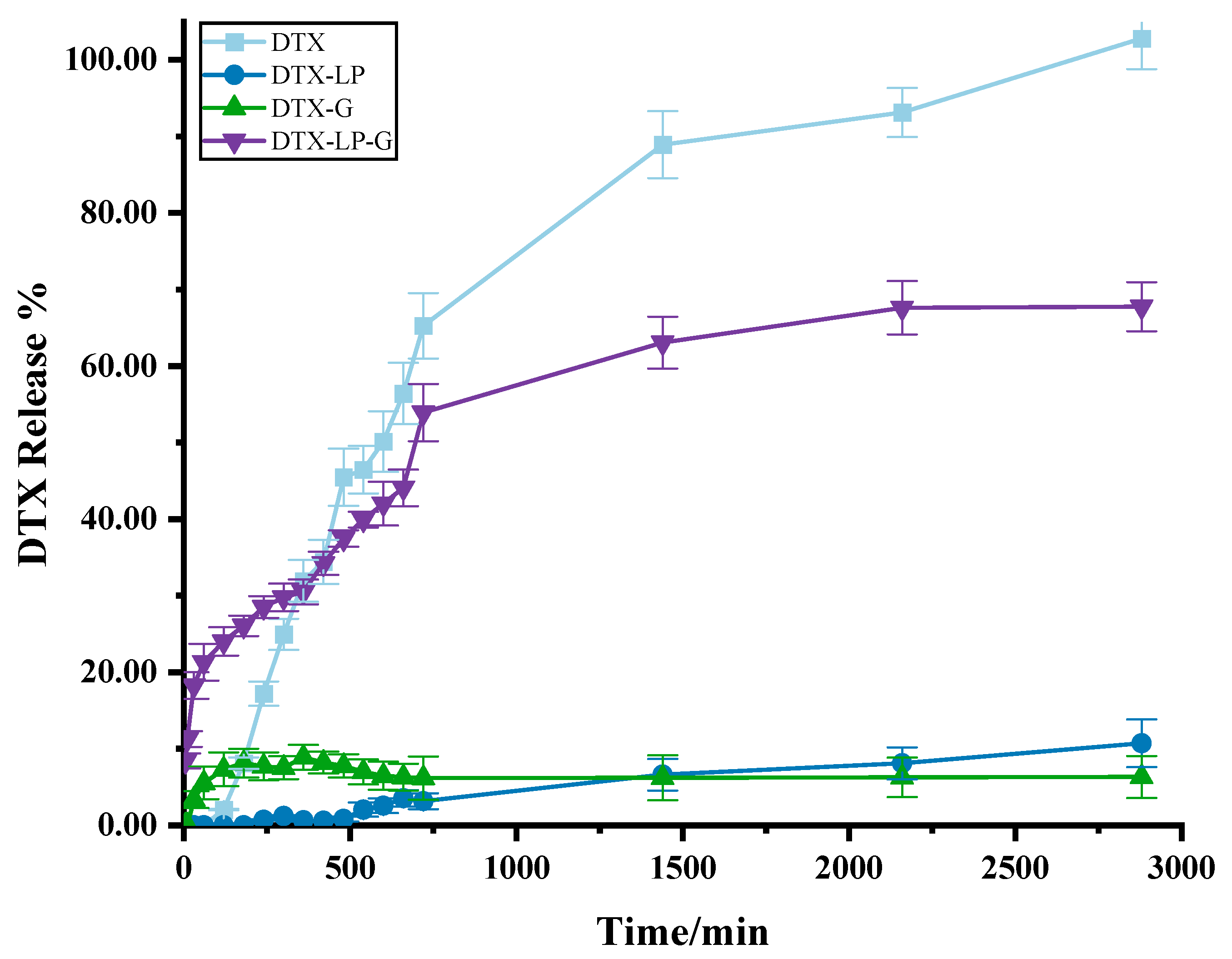
2.2. In Vitro Drug Release of DTX-Loaded Formulations
2.3. Skin Permeation Study of DTX-Loaded Formulations
2.4. Results of Kinetic Studies of DTX-Loaded Formulations
2.5. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity of DTX-Loaded Formulations
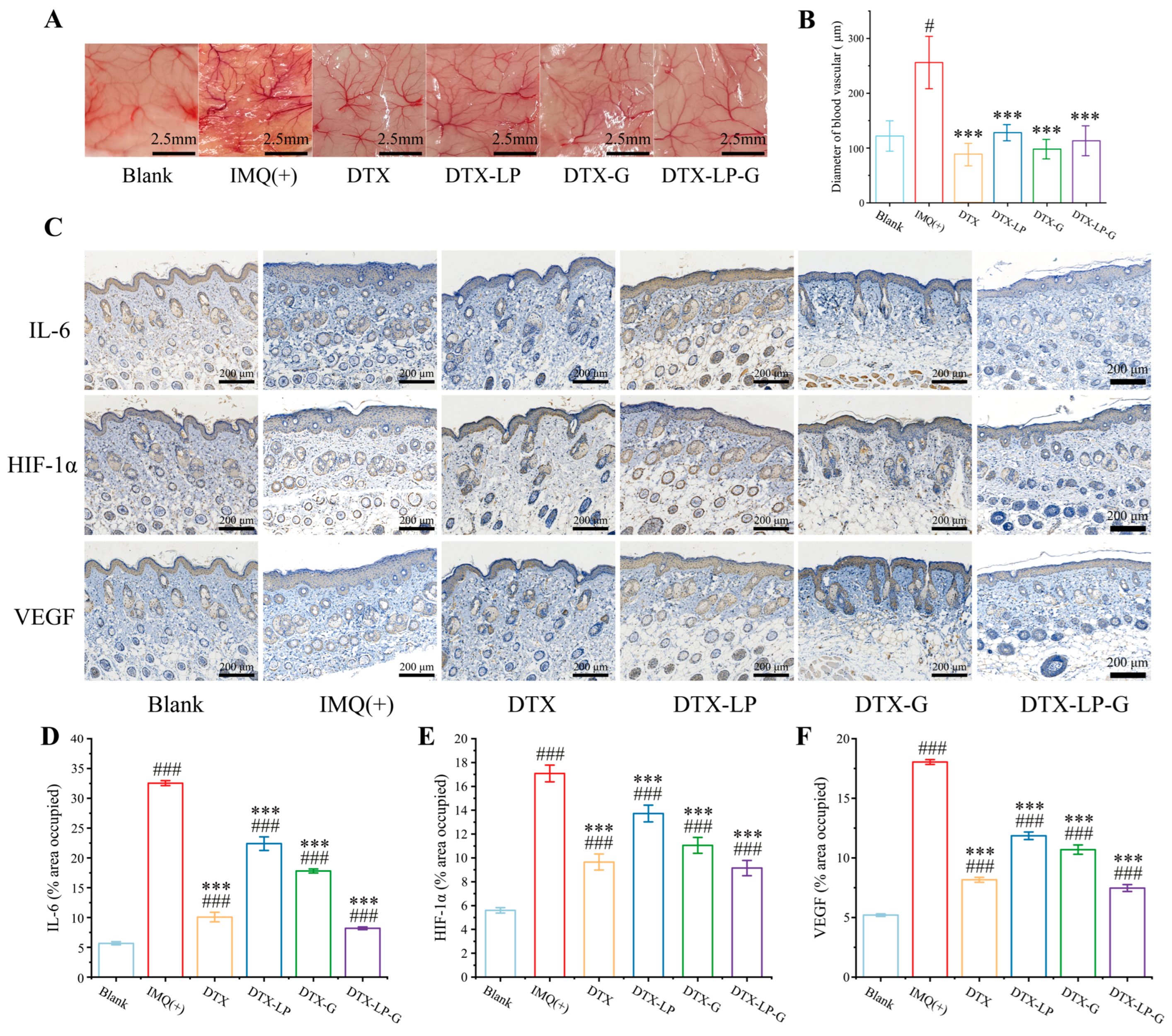
2.6. Alleviation of IMQ-Induced Psoriasis by DTX-Loaded Liposomes-in-Gel
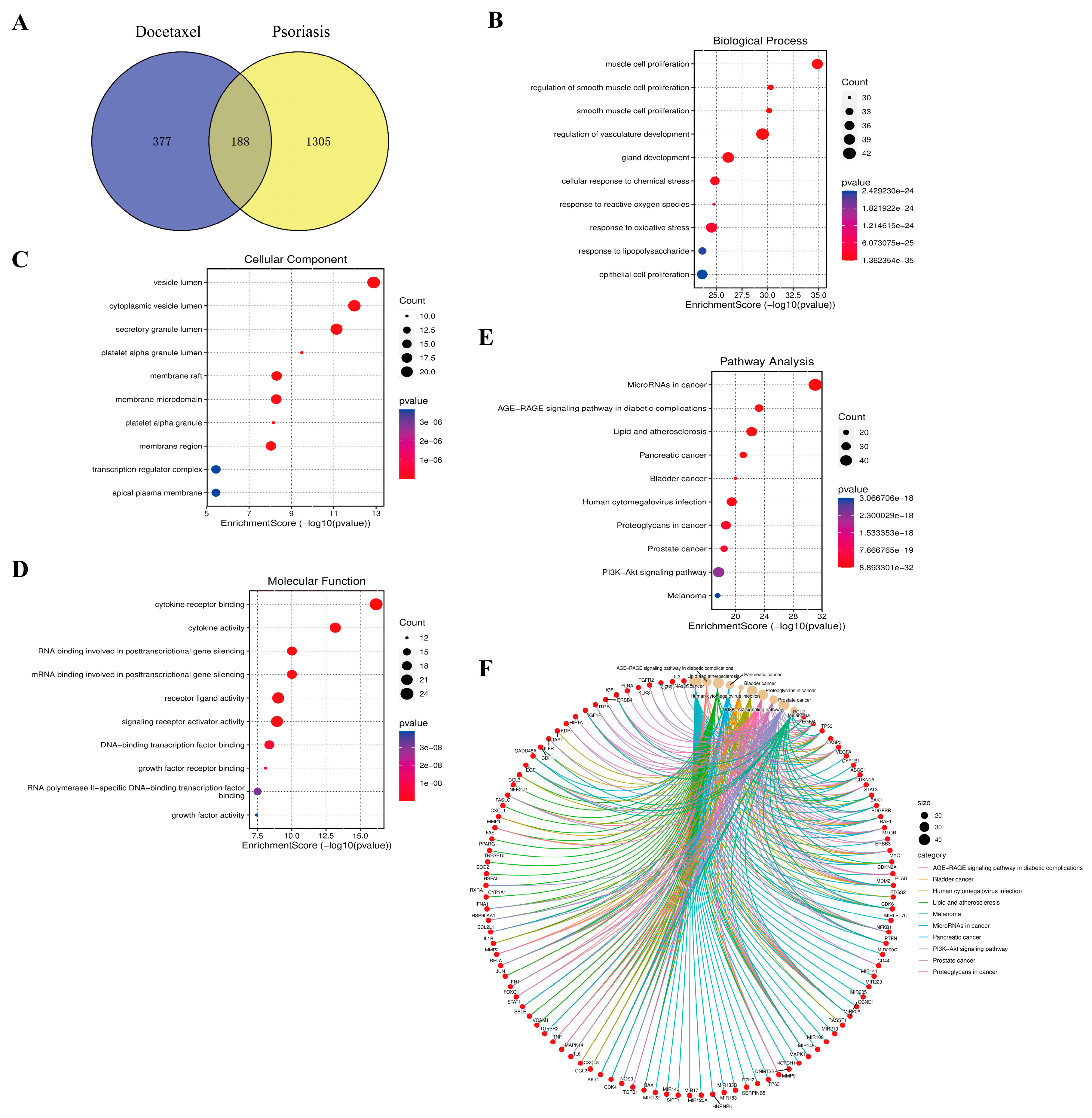
2.7. Results of Enrichment Analysis of Docetaxel and Psoriasis
2.8. DTX-Loaded Liposomes-in-Gel Regulating Immunity and Inhibiting MDA Production
2.9. DTX-Loaded Liposomes-in-Gel Inhibiting Angiogenesis via Regulating IL6-HIF-1α-VEGF Axis
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation and Characterization of DTX-Loaded Liposomes
4.3. Optimization of Hyaluronic Acid Content in DTX-Loaded Gel and DTX-Loaded Liposomes-in-Gel
4.4. In Vitro Drug Release Study
4.5. Skin Permeation Study
4.6. Kinetic Studies
4.7. Extracorporeal Clearance on H2O2
4.8. Establishment of Psoriasis Model
4.9. PASI Score
4.10. Measurement of Ear Swelling and Splenic Index
4.11. Measurement of Blood Vessel Diameter
4.12. Determination of MDA Content in Tissues
4.13. Histological Analysis
4.14. Enrichment Analysis of Docetaxel and Psoriasis
4.15. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bilal, J.; Malik, S.U.; Riaz, I.B.; Kurtzman, D.J. Psoriasis and Psoriatic Spectrum Disease: A Primer for the Primary Care Physician. Am. J. Med. 2018, 131, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Wang, M.; Gao, H.; Zheng, A.; Li, J.; Mu, D.; Tong, J. The Role of Helper T Cells in Psoriasis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 788940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, H.; Lu, C.; Deng, J.; Yan, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Liang, C.L.; Wei, J.; Han, L.; et al. Kaempferol attenuates imiquimod-induced psoriatic skin inflammation in a mouse model. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 198, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C.E. T-cell-targeted biologicals for psoriasis. Curr. Drug Targets-Inflamm. Allergy 2004, 3, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, K.; Berth-Jones, J.; Kragballe, K.; Wozel, G.; de la Brassinne, M. Scalp psoriasis: A review of current topical treatment options. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2007, 21, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas-Melo, F.; Carvalho, A.; Gonçalves, M.B.S.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Veiga, F. Nanocarriers for the topical treatment of psoriasis - pathophysiology, conventional treatments, nanotechnology, regulatory and toxicology. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 176, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Kuai, L.; Huang, F.; Jiang, J.; Song, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Mao, L.; Peng, W.; Luo, Y.; et al. Single-atom catalysts-based catalytic ROS clearance for efficient psoriasis treatment and relapse prevention via restoring ESR1. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleńkowska, J.; Gabig-Cimińska, M.; Mozolewski, P. Oxidative Stress as an Important Contributor to the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagener, F.A.; Carels, C.E.; Lundvig, D.M. Targeting the redox balance in inflammatory skin conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9126–9167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheetham, P.; Petrylak, D.P. Tubulin-targeted agents including docetaxel and cabazitaxel. Cancer J. 2013, 19, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Cao, X.; Li, J.; Cheng, X.; Cheng, G.; Zou, M.; Piao, H. A Novel Surfactant-Free O/O Paclitaxel Ointment for the Topical Treatment of Psoriasis. Aaps. Pharmscitech 2019, 20, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilfoyle, B.E.; Sheihet, L.; Zhang, Z.; Laohoo, M.; Kohn, J.; Michniak-Kohn, B.B. Development of paclitaxel-TyroSpheres for topical skin treatment. J. Control. Release 2012, 163, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Song, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Xie, Y.; Schaefer, H.F., III. Conformers, properties, and docking mechanism of the anticancer drug docetaxel: DFT and molecular dynamics studies. J. Comput. Chem. 2018, 39, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Gong, S.Q.; Liu, L.; Shen, H.; Liu, E.R.; Pan, L.; Gao, N.; Chen, R.L.; Huang, Y.Z. Cyclodextrin-Coordinated Liposome-in-Gel for Transcutaneous Quercetin Delivery for Psoriasis Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 40228–40240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Chen, Z.; Yin, Y.Z.; Tang, C.; Hu, E.; Zheng, S.; Liu, Q.; Xiong, Y. Improving Topical Skin Delivery of Monocrotaline Via Liposome Gel-based Nanosystems. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 940–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holsaeter, A.M.; Wizgird, K.; Karlsen, I.; Hemmingsen, J.F.; Brandl, M.; Skalko-Basnet, N. How docetaxel entrapment, vesicle size, zeta potential and stability change with liposome composition–A formulation screening study. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 177, 106267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahednezhad, F.; Saadat, M.; Valizadeh, H.; Zakeri-Milani, P.; Baradaran, B. Liposome and immune system interplay: Challenges and potentials. J. Control. Release 2019, 305, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Chi, D.; Wang, X.; Lin, G.; He, Z.; Wang, Y. Remote loading paclitaxel–doxorubicin prodrug into liposomes for cancer combination therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 1730–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravar, F.; Saadat, E.; Gholami, M.; Dehghankelishadi, P.; Mahdavi, M.; Azami, S.; Dorkoosh, F.A. Hyaluronic acid-coated liposomes for targeted delivery of paclitaxel, in-vitro characterization and in-vivo evaluation. J. Control. Release 2016, 229, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, M.M.; Alouny, N.N.; Aldosari, B.N.; Alhusaini, A.M.; Abou El Ela, A.E.S. Transdermal Glipizide Delivery System Based on Chitosan-Coated Deformable Liposomes: Development, Ex Vivo, and In Vivo Studies. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Cao, K.; Jia, R.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Xia, H.; Xu, Y.; Xie, Z. Tetramethylpyrazine-loaded liposomes surrounded by hydrogel based on sodium alginate and chitosan as a multifunctional drug delivery System for treatment of atopic dermatitis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 193, 106680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, S.; Hascall, V.C.; Markwald, R.R.; Ghatak, S. Interactions between Hyaluronan and Its Receptors (CD44, RHAMM) Regulate the Activities of Inflammation and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, Q.; Li, Y.; He, Z.; Li, Z.; Guo, T.; Wu, Z.; Feng, N. CD44 Assists the Topical Anti-Psoriatic Efficacy of Curcumin-Loaded Hyaluronan-Modified Ethosomes: A New Strategy for Clustering Drug in Inflammatory Skin. Theranostics 2019, 9, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carita, A.C.; Eloy, J.O.; Chorilli, M.; Lee, R.J.; Leonardi, G.R. Recent Advances and Perspectives in Liposomes for Cutaneous Drug Delivery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 606–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.Y.; Xia, H.M.; Liu, C.; Wu, Y.F.; Liu, X.Y.; Cheng, Y.F.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Yue, Y.; Cheng, X.M.; et al. The novel delivery-exosome application for diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Pathol. Res. Pr. 2023, 242, 154332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathara, M.; Date, T.; Chaudhari, D.; Ghadi, R.; Kuche, K.; Jain, S. Exploring the Promising Potential of High Permeation Vesicle-Mediated Localized Transdermal Delivery of Docetaxel in Breast Cancer to Overcome the Limitations of Systemic Chemotherapy. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 2473–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Zheng, X.X.; Lin, R.Y.; Sun, H.; Wu, H.H.; Zhang, J.S.; Chen, S.H.; Li, Y.S.; Xu, D.H.; Gao, J.Q. Lyophilizable Stem Cell-Hybrid Liposome with Long-Term Stability and High Targeting Capacity. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, e2400704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shu, G.F.; Lu, K.J.; Xu, X.L.; Sun, M.C.; Qi, J.; Huang, Q.L.; Tan, W.Q.; Du, Y.Z. Flexible liposomal gel dual-loaded with all-trans retinoic acid and betamethasone for enhanced therapeutic efficiency of psoriasis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, I.Y.; Bala, S.; Škalko-Basnet, N.; di Cagno, M.P. Interpreting non-linear drug diffusion data: Utilizing Korsmeyer-Peppas model to study drug release from liposomes. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 138, 105026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, M.A.; Madni, A.; Rehman, M.; Rahim, M.A.; Jabar, A. Ionically Cross-Linked Chitosan Nanoparticles for Sustained Delivery of Docetaxel: Fabrication, Post-Formulation and Acute Oral Toxicity Evaluation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 10035–10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miastkowska, M.; Kulawik-Pióro, A.; Lasoń, E.; Śliwa, K.; Malinowska, M.A.; Sikora, E.; Kantyka, T.; Bielecka, E.; Maksylewicz, A.; Klimaszewska, E.; et al. Topical Formulations Based on Ursolic Acid-Loaded Nanoemulgel with Potential Application in Psoriasis Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Siepmann, F. Modeling of diffusion controlled drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam Shibly, S.U.; Ghatak, C.; Sayem Karal, M.A.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Yamazaki, M. Experimental Estimation of Membrane Tension Induced by Osmotic Pressure. Biophys. J. 2016, 111, 2190–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyhani, A.; McKenzie, T.G.; Fu, Q.; Qiao, G.G. Fenton-Chemistry-Mediated Radical Polymerization. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2019, 40, e1900220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Yao, P.; Dai, Q.; Qi, X.; Yang, M.; Zhang, X.; Huang, R.; Yang, J.; et al. Docetaxel-loaded pH/ROS dual-responsive nanoparticles with self-supplied ROS for inhibiting metastasis and enhancing immunotherapy of breast cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsamman, M.; El-Borady, O.M.; Nasr, M.M.; Al-Amgad, Z.; Metwally, A.A. Development of propolis, hyaluronic acid, and vitamin K nano-emulsion for the treatment of second-degree burns in albino rats. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2024, 24, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.M.; Jin, Q.X.; Fujimoto, M.; Li, F.F.; Jin, L.B.; Yu, R.; Yan, G.H.; Zhu, L.H.; Meng, F.P.; Zhang, Q.G.; et al. Dihydroartemisinin Alleviates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Skin Lesion in Mice Involving Modulation of IL-23/Th17 Axis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 704481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karas, A.; Holmannova, D.; Borsky, P.; Fiala, Z.; Andrys, C.; Hamakova, K.; Svadlakova, T.; Palicka, V.; Krejsek, J.; Rehacek, V.; et al. Significantly Altered Serum Levels of NAD, AGE, RAGE, CRP, and Elastin as Potential Biomarkers of Psoriasis and Aging—A Case-Control Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ma, X.; Gao, C.; Luo, Y.; Fei, X.; Zheng, Q.; Ma, X.; Kuai, L.; Li, B.; Wang, R.; et al. Rutin attenuates inflammation by downregulating AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in psoriasis: Network pharmacology analysis and experimental evidence. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 125, 111033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, W.; Xiao, S.; Ji, Y.; Han, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Li, P. Yangxue Jiedu Fang Ameliorates Psoriasis by Regulating Vascular Regression via Survivin/PI3K/Akt Pathway. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 4678087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Guo, J.; Nong, Y.; Mo, W.; Fang, H.; Mi, J.; Qi, Q.; Yang, M. 18β-Glycyrrhetinic acid induces human HaCaT keratinocytes apoptosis through ROS-mediated PI3K-Akt signaling pathway and ameliorates IMQ-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in mice. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 21, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, T.; Boateng, S.T.; Uddin, M.B.; Banang-Mbeumi, S.; Yadav, R.K.; Bock, C.R.; Folahan, J.T.; Siwe-Noundou, X.; Walker, A.L.; King, J.A.; et al. The PI3K-Akt-mTOR and Associated Signaling Pathways as Molecular Drivers of Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Skin Diseases: Update on Therapeutic Strategy Using Natural and Synthetic Compounds. Cells 2023, 12, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Dong, H.; Jin, R.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, X. TRIM22 actives PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway to promote psoriasis through enhancing cell proliferation and inflammation and inhibiting autophagy. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2022, 41, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Guo, J.; Wu, Z. Combinative treatment of Curdione and docetaxel triggers reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated intrinsic apoptosis of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 10037–10048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, K.S.; Nadeem, A.; Ahmad, S.F.; Al-Harbi, N.O.; Ibrahim, K.E.; El-Sherbeeny, A.M.; Alhoshani, A.R.; Alshammari, M.A.; Alotaibi, M.R.; Al-Harbi, M.M. Inhibition of spleen tyrosine kinase attenuates psoriasis-like inflammation in mice through blockade of dendritic cell-Th17 inflammation axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Fleming, C.; Yan, J. New insights of T cells in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2012, 9, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinno-Hashimoto, H.; Eguchi, A.; Sakamoto, A.; Wan, X.; Hashimoto, Y.; Fujita, Y.; Mori, C.; Hatano, M.; Matsue, H.; Hashimoto, K. Effects of splenectomy on skin inflammation and psoriasis-like phenotype of imiquimod-treated mice. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, B.R.; Angeli, J.P.F.; Bayir, H.; Bush, A.I.; Conrad, M.; Dixon, S.J.; Fulda, S.; Gascón, S.; Hatzios, S.K.; Kagan, V.E.; et al. Ferroptosis: A Regulated Cell Death Nexus Linking Metabolism, Redox Biology, and Disease. Cell 2017, 171, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaschler, M.M.; Stockwell, B.R. Lipid peroxidation in cell death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassannia, B.; Vandenabeele, P.; Berghe, T.V. Targeting Ferroptosis to Iron Out Cancer. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 830–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, A.; Muñoz, M.F.; Argüelles, S. Lipid peroxidation: Production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 360438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrică, E.-C.; Cozma, M.-A.; Găman, M.-A.; Voiculescu, V.-M.; Găman, A.M. The Involvement of Oxidative Stress in Psoriasis: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micali, G.; Lacarrubba, F.; Musumeci, M.L.; Massimino, D.; Nasca, M.R. Cutaneous vascular patterns in psoriasis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2010, 49, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, R.; Röcken, M.; Ghoreschi, K. Angiogenesis: Angiogenesis: The new potential target for the therapy of psoriasis? Drug News Perspect. 2008, 21, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zhai, S.; Yuan, J. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) triggers the malignancy of hemangioma cells via activation of HIF-1α/VEGFA signals. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 841, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.-J.; Sah, S.K.; Yang, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, J.; Kim, T.-Y. Rhododendrin inhibits toll-like receptor-7-mediated psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-Z.; Li, J.-Q.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Dong, D.-W.; Qi, X.-R. Tumor-targeting dual peptides-modified cationic liposomes for delivery of siRNA and docetaxel to gliomas. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 5226–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggini, A.; Chimenti, S.; Chiricozzi, A. IL-6 as a druggable target in psoriasis: Focus on pustular variants. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 964069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellor, L.F.; Gago-Lopez, N.; Bakiri, L.; Schmidt, F.N.; Busse, B.; Rauber, S.; Jimenez, M.; Megías, D.; Oterino-Soto, S.; Sanchez-Prieto, R.; et al. Keratinocyte-derived S100A9 modulates neutrophil infiltration and affects psoriasis-like skin and joint disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 1400–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar-Maalej, C.; Diab, R.; Andrieu, V.; Elaissari, A.; Fessi, H. Ethanol injection method for hydrophilic and lipophilic drug-loaded liposome preparation. J. Liposome Res. 2010, 20, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Hu, W.; Yu, X.; Guo, M.; Zhang, X.; Sun, M.; Du, S.; Lu, Y. Combined Thermosensitive Gel Co-Loaded with Dermaseptin-PP and PTX Liposomes for Effective Local Chemotherapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xia, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Xia, H.; Wang, Y.; Yue, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Xu, Y.; et al. Ligustrazine as an Extract from Medicinal and Edible Plant Chuanxiong Encapsulated in Liposome–Hydrogel Exerting Antioxidant Effect on Preventing Skin Photoaging. Polymers 2022, 14, 4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, L.; Sun, R.; Jiang, X.; Lin, X.; Huang, H.; Bao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, R.; Yao, Q. Tumor Microenvironment-Responsive, Multistaged Liposome Induces Apoptosis and Ferroptosis by Amplifying Oxidative Stress for Enhanced Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 30031–30043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Xia, H.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, C.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yue, Y.; Cheng, X.; et al. The Fabrication of Docetaxel-Containing Emulsion for Drug Release Kinetics and Lipid Peroxidation. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, C.; Xia, H.; Cheng, X.; Cheng, Y.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Y. In Vitro Evaluation of Kaempferol-Loaded Hydrogel as pH-Sensitive Drug Delivery Systems. Polymers 2022, 14, 3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, B.; Cui, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lai, L.; Zhang, M.; Xu, X.; Wang, N.; Jiang, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, Q. Exploration of the Components and Pharmacological Mechanisms of Keyin Pill-Induced Liver Injury Based on Network Pharmacology. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 9916949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, N.; Madan, S.; Walia, R.; Tyagi, R.; Fantoukh, O.I.; Hawwal, M.F.; Akhtar, A.; Almarabi, I.; Alam, P.; Saxena, S. Multi-target mechanism of Solanum xanthocarpum for treatment of psoriasis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Saudi Pharm. J. 2023, 31, 101788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Tang, D.; Chen, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y. SRplot: A free online platform for data visualization and graphing. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| CHO:SL | Particle Size (nm) | Zeta (mV) | EE (%) | DLR (%) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:3 | 165.36 ± 2.94 | −35.97 ± 2.19 | 72.59 ± 0.96 | 0.891 ± 0.017 | 7.42 ± 0.02 |
| 1:5 | 143.37 ± 2.04 | −36.08 ± 1.08 | 88.50 ± 1.45 *** | 0.734 ± 0.012 *** | 7.40 ± 0.01 |
| 1:10 | 210.60 ± 3.34 * | −39.00 ± 1.26 | 69.17 ± 1.25 * | 0.312 ± 0.009 *** | 7.43 ± 0.01 |
| HA % | Appearance | DLR (%) | Viscosity (mpa·s) | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DTX-G | 0.5% | white | 0.97 ± 0.03 | 5.57 ± 0.14 | 7.26 ± 0.01 |
| 1.0% | white | 2.21 ± 0.08 *** | 7.41 ± 0.30 * | 7.26 ± 0.02 | |
| 2.0% | white | 1.19 ± 0.10 ** | 11.73 ± 1.56 *** | 7.27 ± 0.02 | |
| DTX-LP-G | 0.5% | milky white | 0.68 ± 0.03 *** | 14.28 ± 1.32 *** | 7.39 ± 0.02 *** |
| 1.0% | light yellow | 0.83 ± 0.01 * | 18.72 ± 0.55 *** | 7.42 ± 0.02 *** | |
| 2.0% | light yellow | 0.73 ± 0.02 ** | 20.22 ± 0.50 *** | 7.43 ± 0.03 *** |
| Mathematical Models | Formulas |
|---|---|
| Zero order | |
| First order | |
| Higuchi | |
| Korsmeyer–Peppas |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, R.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shen, S.; Cao, K.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Shen, W.; Wang, L.; Sun, B.; et al. Liposomes-in-Gel as the Docetaxel Delivery for the Effective Treatment of Psoriasis by Inhibiting the Proliferation of Blood Vessels. Gels 2025, 11, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040228
Jia R, Liu Y, Wu Y, Shen S, Cao K, Chen X, Wu Y, Shen W, Wang L, Sun B, et al. Liposomes-in-Gel as the Docetaxel Delivery for the Effective Treatment of Psoriasis by Inhibiting the Proliferation of Blood Vessels. Gels. 2025; 11(4):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040228
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Ruoyang, Yinyin Liu, Yifang Wu, Si Shen, Keang Cao, Xue Chen, Yang Wu, Wang Shen, Lu Wang, Bin Sun, and et al. 2025. "Liposomes-in-Gel as the Docetaxel Delivery for the Effective Treatment of Psoriasis by Inhibiting the Proliferation of Blood Vessels" Gels 11, no. 4: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040228
APA StyleJia, R., Liu, Y., Wu, Y., Shen, S., Cao, K., Chen, X., Wu, Y., Shen, W., Wang, L., Sun, B., Zhang, Y., & Xia, H. (2025). Liposomes-in-Gel as the Docetaxel Delivery for the Effective Treatment of Psoriasis by Inhibiting the Proliferation of Blood Vessels. Gels, 11(4), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040228







