Comparative Study on the Freeze–Thaw Stability of Sodium Caseinate Emulsion-Filled Konjac Glucomannan/κ-Carrageenan Composite Gels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
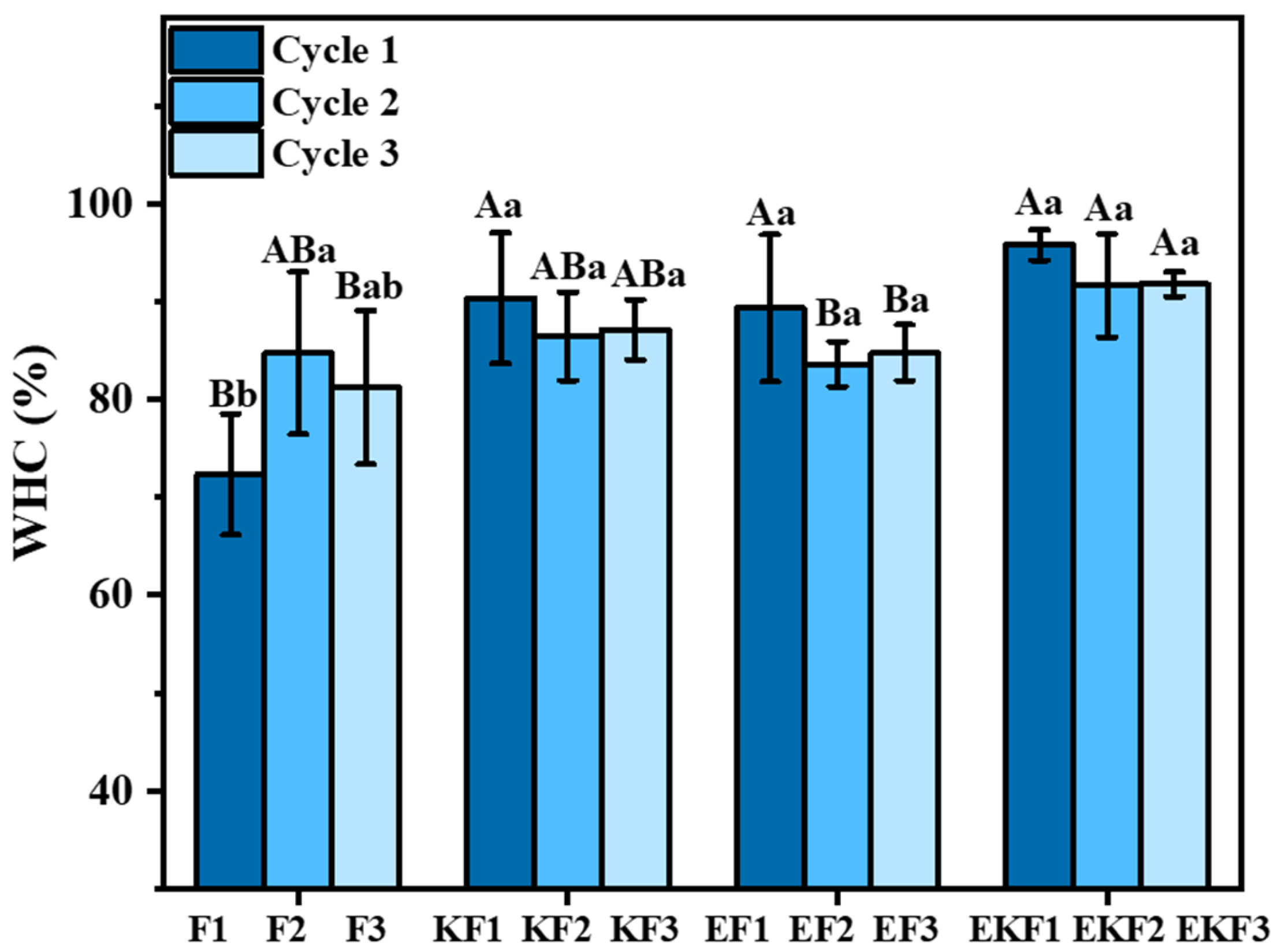
2.1. Water-Holding Capacity of Emulsion Gel with Different Freeze–Thaw Cycles
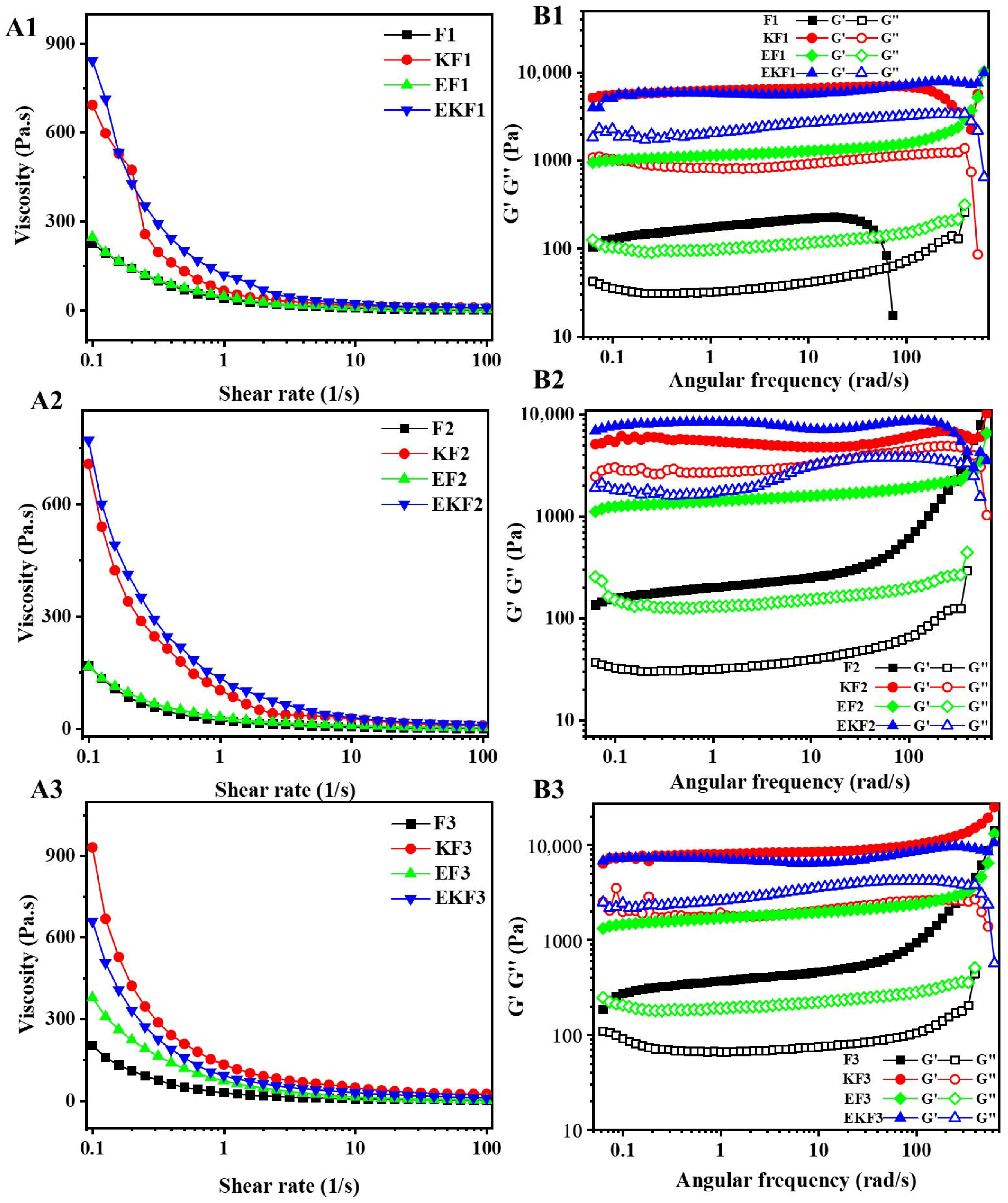
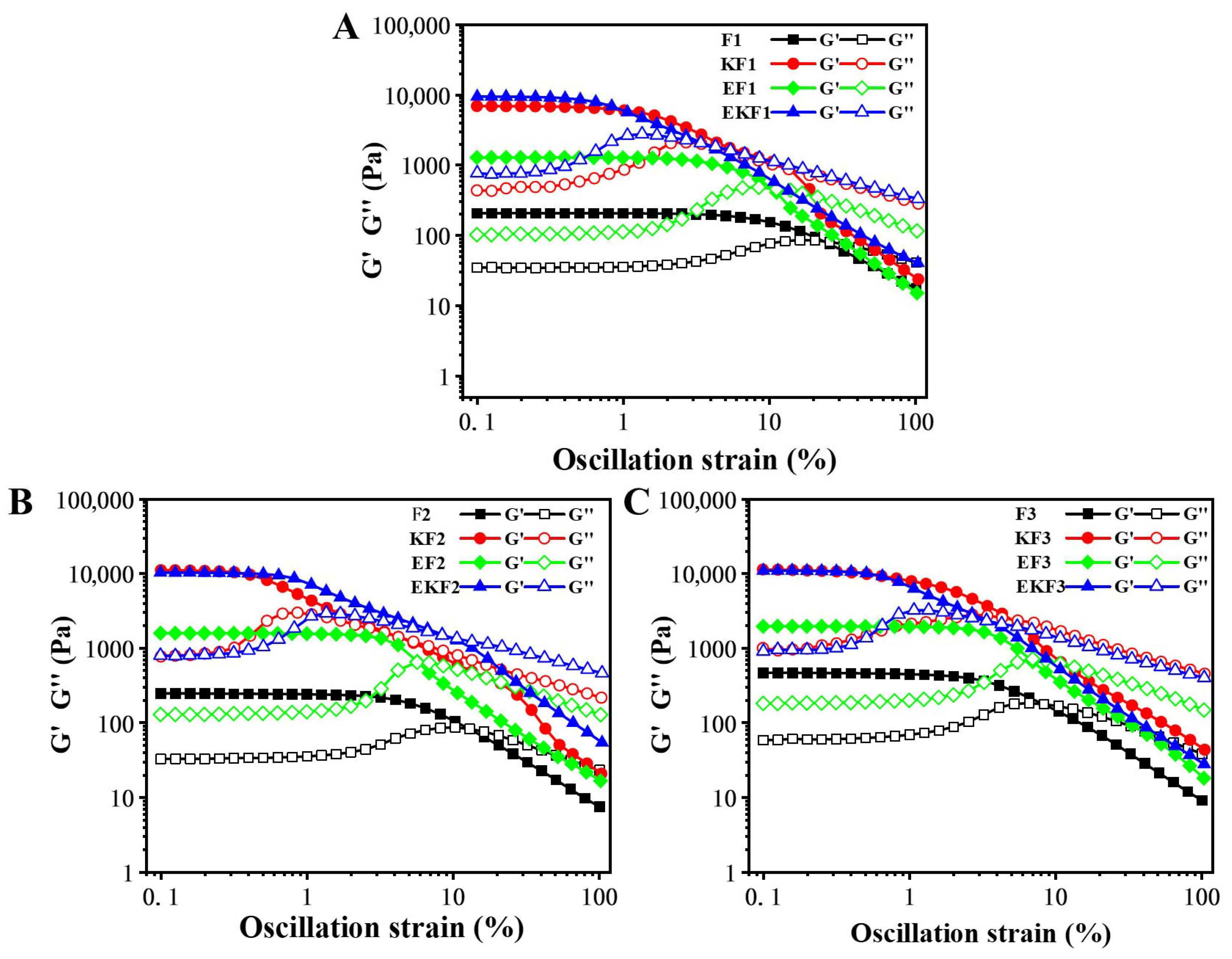
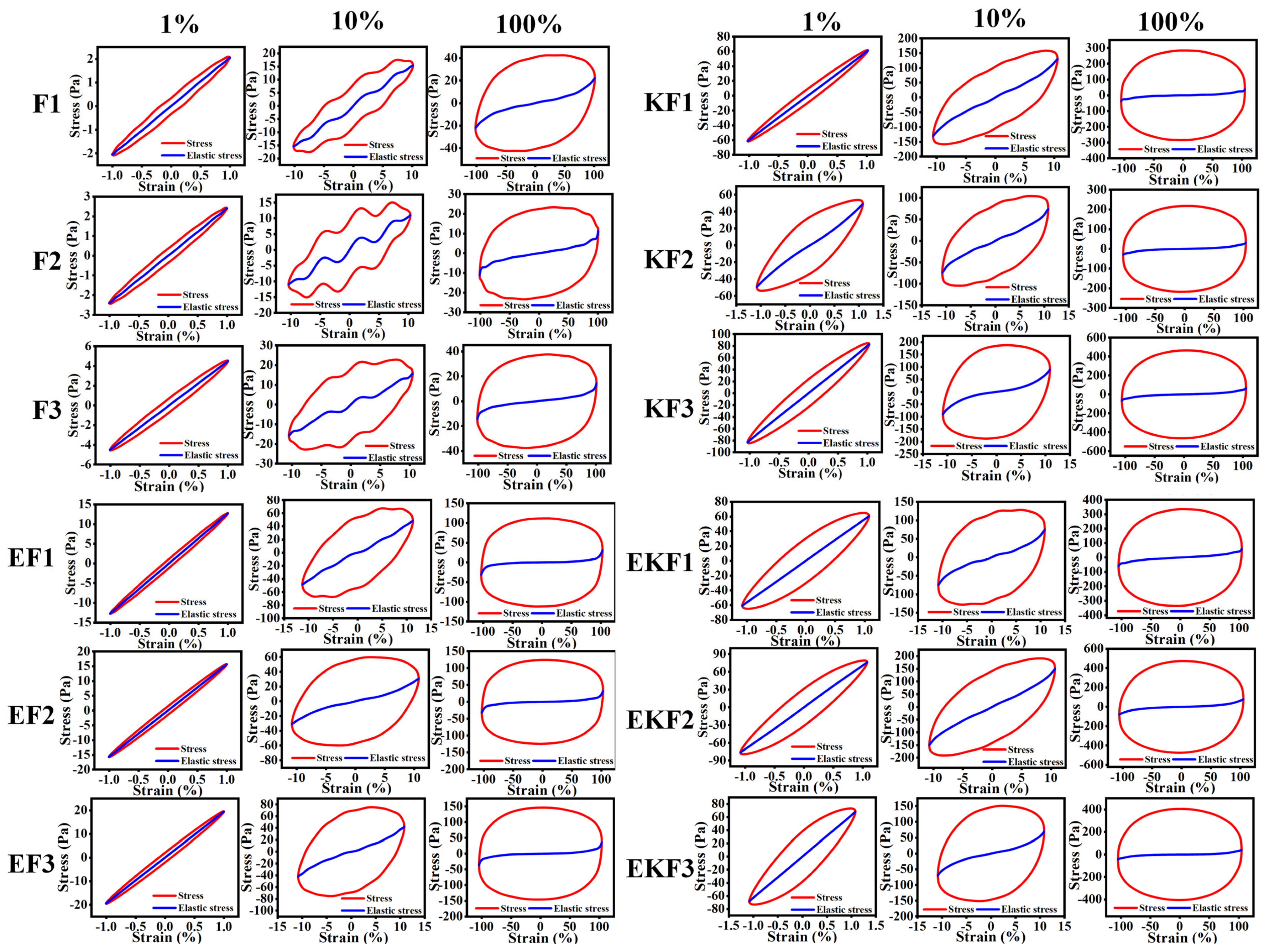
2.2. Rheological Behaviors of Emulsion Gel with Different Freeze–Thaw Cycles
2.3. TPA Analysis of Emulsion Gel with Different Freeze–Thaw Cycles
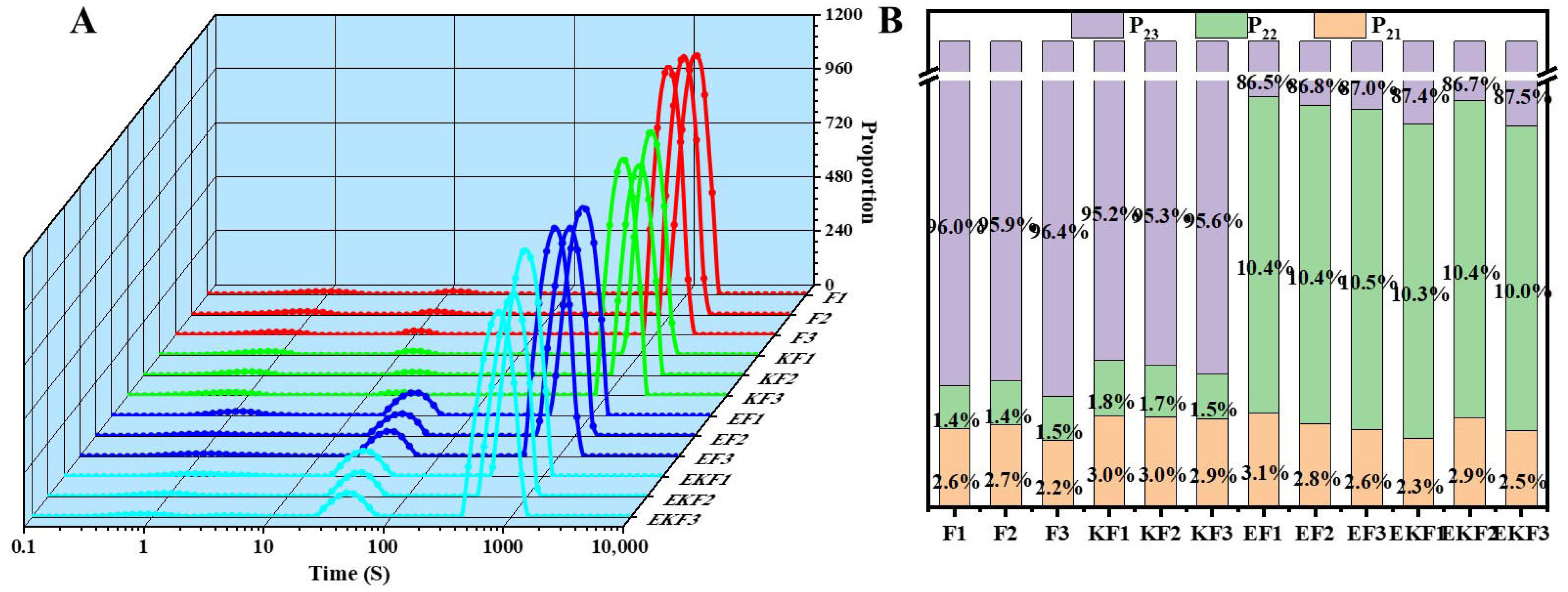
2.4. Water Distribution of Emulsion Gel with Different Freeze–Thaw Cycles
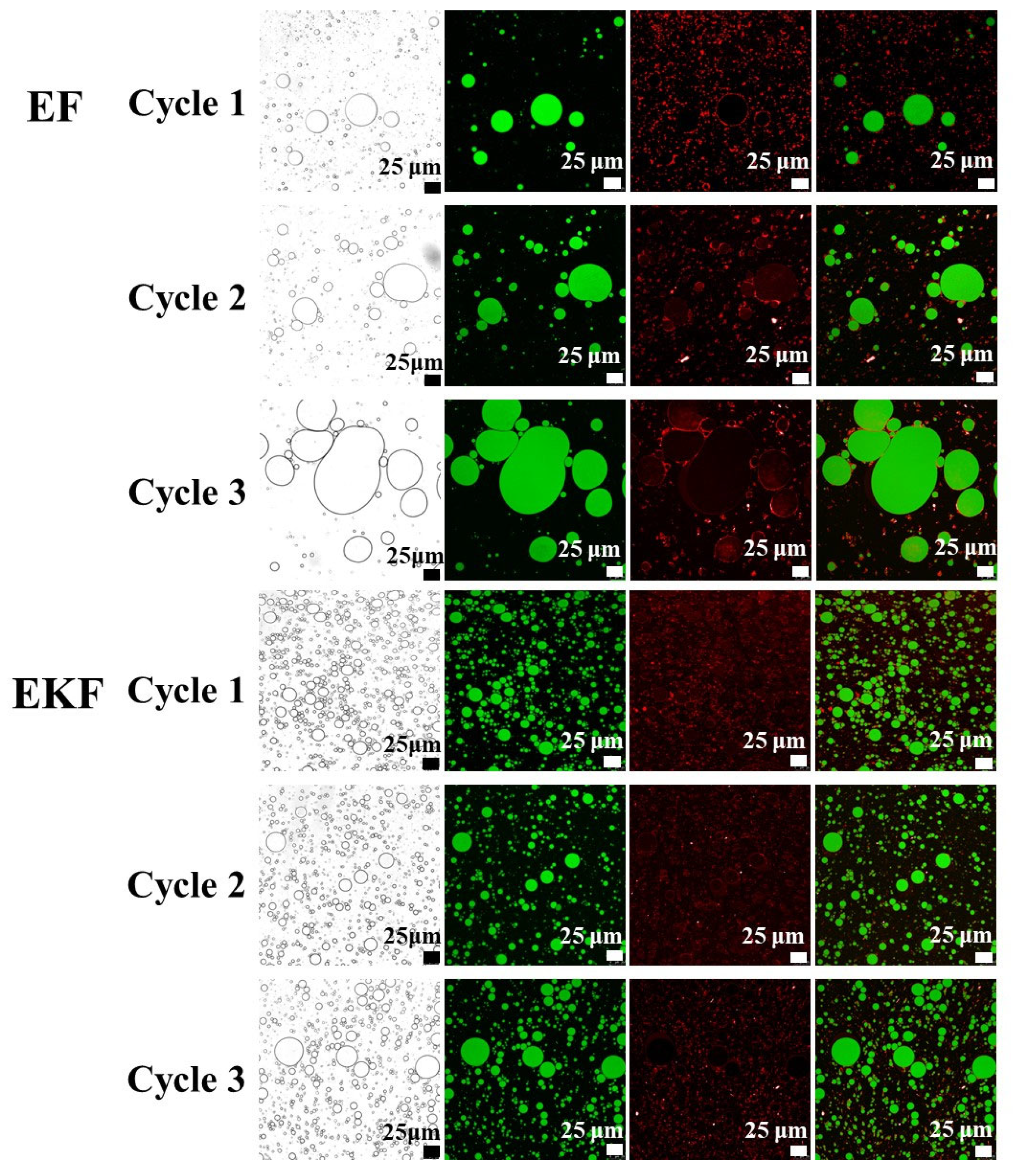
2.5. CLSM Analysis of Emulsion Gel with Different Freeze–Thaw Cycles
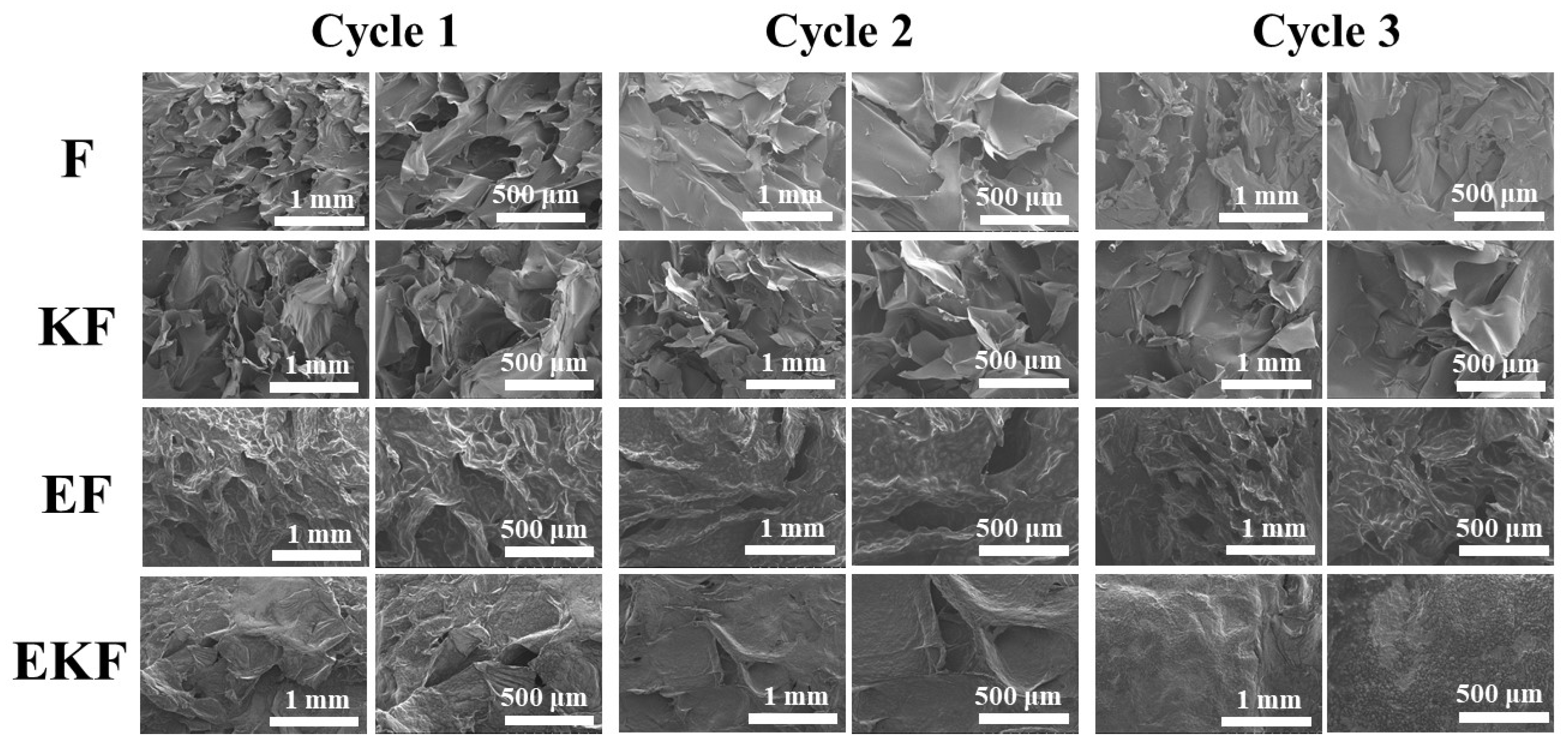
2.6. SEM Analysis of Emulsion Gel with Different Freeze–Thaw Cycles
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation and Freeze–Thaw Treatment of Emulsion-Filled Composite Gel
4.3. Measurement of Water-Holding Capacity
4.4. Measurement of Rheological Behavior
4.5. Textural Properties Measurement
4.6. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Measurement
4.7. Microstructure Observation
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, G.; Wang, B.; Lv, W.; Yang, L.; Xiao, H. Effect of κ-carrageenan on physicochemical and 3D printing properties of walnut protein-stabilized emulsion gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 156, 110288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funami, T.; Ishihara, S.; Maeda, K.; Nakauma, M. Recent development in Pickering emulsion gel technology for food and beverage applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 162, 110901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Mu, Z.; Xu, H.; Bilawal, A.; Jiang, Z.; Hou, J. Seven sour substances enhancing characteristics and stability of whey protein isolate emulsion and its heat-induced emulsion gel under the non-acid condition. Food Res. Int. 2024, 192, 114764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Xu, T.; Zhang, L.; Ma, C. Facile preparation of W/O Pickering emulsion gels stabilized with oleanolic acid for the co-delivery of curcumin and epigallocatechin gallate. Food Chem. 2025, 476, 143436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, H.; Ren, Y.; Sun, M.; Zhang, T.; Li, H.; Liu, X. Functionality and application of emulsion gels in fat replacement strategies for dairy products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 152, 104673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, D.; Cao, J.; Liu, X. Application of emulsion gels as fat substitutes in meat products. Foods 2022, 11, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Li, X.; McClements, D.J.; Ji, H.; Jin, Z.; Qiu, C. Biopolymer-based emulsion gels as fat replacers: A review of their design, fabrication, and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 305, 141297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, S.; Li, S.; Meng, Z. Advances of protein-based emulsion gels as fat analogues: Systematic classification, formation mechanism, and food application. Food Res. Int. 2024, 191, 114703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondineli, A.; Silva, E.K. Pulsed electric field as a pre-treatment in food freezing processes: Fundamentals, mechanisms, applications and impacts on frozen food quality. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, P.; Sun, B.; Yang, W.; Ou, C.; Yuan, C.; Huang, T.; Wei, H. Comparison of freezing and heating treatment sequence on biochemical properties and flavor of swimming crabs (Portunus Trituberculatus) meat during freeze-thaw cycles. Food Res. Int. 2024, 175, 113758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Jiang, F.; Lin, K.; Fang, J.; Chen, F.; Ru, Y.; Weng, H.; Xiao, Q.; Yang, Q.; Xiao, A. Anhydride esterification to regulate water migration and reduce ice crystal formation in κ-carrageenan gel during freezing. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 150, 109726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Huang, K.; Lei, Y.; An, Y.; Xiong, S.; Hu, Y. Effects of freezing on quality attributes of surimi gels with various cross-linking degrees using MTGase: Quantitative analysis based on the ice crystals, network structure, and taste substances. J. Food Eng. 2024, 371, 111975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, K.; Yu, X.; Gao, C.; Yang, Y.; Tang, X.; Feng, X. Effects of quinoa protein Pickering emulsion on the properties, structure and intermolecular interactions of myofibrillar protein gel. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Yu, X.; Yang, Y.; Tang, X. Improving the freeze-thaw stability of fish myofibrils and myofibrillar protein gels: Current methods and future perspectives. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 144, 109041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hei, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Wu, C.; Jiao, B.; Hu, H.; Ma, X.; Zhu, J.; Adhikari, B.; Wang, Q. Freeze-thaw stability of Pickering emulsion stabilized by modified soy protein particles and its application in plant-based ice cream. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naji, S.; Razavi, S.; Karazhiyan, H. Effect of freezing on functional and textural attributes of cress seed gum and xanthan gum. Food and Bioprocess Technology 2013, 6, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tong, C.; Chen, Y.; Xia, X.; Jiang, S.; Qiu, C.; Pang, J. Advances in the construction and application of konjac glucomannan-based delivery systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 129940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yin, Y.; Yue, M.; Sun, H.; Kang, M.; Luo, D.; Shah, B.R.; Ge, Y. Construction of highly stable Pickering emulsion systems based on konjac glucomannan and xanthan gum/lysozyme nanoparticles under pasteurization. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, D.U.; Sharma, H.; Maheshwari, R.; Pareek, A.; Gaur, M.; Prajapati, B.G.; Castro, G.R.; Thanawuth, K.; Suttiruengwong, S.; Sriamornsak, P. Konjac glucomannan: A comprehensive review of its extraction, health benefits, and pharmaceutical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 339, 122266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, N.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, M. Quality characteristics and gastrointestinal fate of low fat emulsified sausage formulated with konjac glucomannan/oat β-glucan composite hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yang, J.; Xia, P.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, K.; Li, B.; Li, J. Effects of konjac glucomannan intake patterns on glucose and lipid metabolism of obese mice induced by a high fat diet. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 9116–9135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ning, Y.; Wu, S.; Wu, G.; Sun, H.; Li, C.; Jia, Y.; Luo, D.; Shah, B.R. Heat stability promoted Pickering emulsions stabilized by glidian/sodium caseinate nanoparticles and konjac glucomannan. LWT 2023, 182, 114847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Sun, H.; Jia, Y.; Jia, Y.; Ning, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Luo, D.; Shah, B.R. Pickering emulsions synergistic stabilized with konjac glucomannan and xanthan gum/lysozyme nanoparticles: Structure, protection and gastrointestinal digestion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 305, 120507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Tian, J.; Janaswamy, S.; Cao, G.; Teng, W.; Song, S.; Wen, C. Role of metal chlorides in the gelation and properties of fucoidan/κ-carrageenan hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, T.; Sun, H.; Niu, Z.; Xu, W.; Li, Z.; He, Y.; Luo, D.; Xi, W.; Wei, J.; Zhang, C. Carrageenan-based Pickering emulsion gels stabilized by xanthan gum/lysozyme nanoparticle: Microstructure, rheological, and texture perspective. Foods 2022, 11, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg-Evron, O.; Davidovich-Pinhas, M.; Bianco-Peled, H. Crosslinking konjac-glucomannan with kappa-carrageenan nanogels: A step toward the design of sacrificial materials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 227, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, K.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, G.; Qiao, D.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, B. Mechanism for the synergistic gelation of konjac glucomannan and κ-carrageenan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Guo, X.; Liu, P.; Li, Y.; Qiu, S.; Wang, Y. Effect of carrageenan on stability and 3D printing performance of high internal phase pickering emulsion stabilized by soy protein isolate aggregates under neutral condition. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 349, 123020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, C.; Gu, L.; Su, Y.; Yang, Y.; Han, Q. The slow release behavior of soy protein isolate/κ-carrageenan composite hydrogel: Effect of konjac glucomannan. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 173, 111242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Cao, S.; Yan, Z.; Liu, X. Tailoring an egg white protein double network emulsion gel as a novel fat substitute for improving freeze-thaw stability of minced meat gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 150, 109763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Katano, T.; Yoshimoto, Y.; Gao, Y.; Nakazawa, N.; Osako, K.; Okazaki, E. Effect of small granules in potato starch and wheat starch on quality changes of direct heated surimi gels after freezing. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 104, 105732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Ma, C.; Yan, X.; Zeng, H.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, X.; Liu, F. Structure, rheology and functionality of whey protein emulsion gels: Effects of double cross-linking with transglutaminase and calcium ions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 102, 105569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyinloye, T.M.; Yoon, W.B. Effect of the Ratio of Protein to Water on the Weak Gel Nonlinear Viscoelastic Behavior of Fish Myofibrillar Protein Paste from Alaska Pollock. Gels 2024, 10, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Thielen, I.; Berton-Carabin, C.C.; van der Linden, E.; Sagis, L.M. Nonlinear interfacial rheology and atomic force microscopy of air-water interfaces stabilized by whey protein beads and their constituents. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, L.-J. Freeze-thaw stability and rheological properties of soy protein isolate emulsion gels induced by NaCl. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Fan, L.; Li, J. Freeze–thaw stability of high-internal-phase emulsion stabilized by chickpea protein microgel particles and its application in surimi. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 8621–8633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, B.-y.; Sun, X.; Liu, Y.-a.; Yu, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, N. Freeze-thaw stability of transglutaminase-induced soy protein-maltose emulsion gel: Focusing on morphology, texture properties, and rheological characteristics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 261, 129716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, K.; Huang, C.; Yu, X.; Gao, C.; Yang, Y.; Tang, X.; Feng, X. Quinoa protein Pickering emulsion: A promising cryoprotectant to enhance the freeze-thaw stability of fish myofibril gels. Food Chem. 2023, 407, 135139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Sun, L.; Xu, Q.; Cao, J.; Pang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Liu, X. Soy protein isolate-sodium alginate emulsion gel co-construction of a dual network system for the development of three-dimensional simulated fats: Effect of sodium alginate concentration and calcium ion addition. Food Chem. 2025, 487, 144652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Li, J. Effect of sodium starch octenyl succinate-based Pickering emulsion on the physicochemical properties of hairtail myofibrillar protein gel subjected to multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Cai, J.; Wang, P.; Zhou, L.; Chai, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, X. Improving the rheological and tribological properties of emulsion-filled gel by ultrasound-assisted cross-linked myofibrillar protein emulsion: Insight into the simulation of oral processing. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2025, 112, 107205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | CAS Emulsion | Composite Gel | Number of Freeze–Thaw Cycles |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | N | 0% KGM 1% KC | 1 |
| F2 | N | 0% KGM 1% KC | 2 |
| F3 | N | 0% KGM 1% KC | 3 |
| KF1 | N | 0.6% KGM 1% KC | 1 |
| KF2 | N | 0.6% KGM 1% KC | 2 |
| KF3 | N | 0.6%KGM 1% KC | 3 |
| EF1 | Y | 0% KGM 1% KC | 1 |
| EF2 | Y | 0% KGM 1% KC | 2 |
| EF3 | Y | 0% KGM 1% KC | 3 |
| EKF1 | Y | 0.6% KGM 1% KC | 1 |
| EKF2 | Y | 0.6% KGM 1% KC | 2 |
| EKF3 | Y | 0.6% KGM 1% KC | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.; Wu, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Shah, B.R.; Xu, W. Comparative Study on the Freeze–Thaw Stability of Sodium Caseinate Emulsion-Filled Konjac Glucomannan/κ-Carrageenan Composite Gels. Gels 2025, 11, 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120961
Chen W, Wu G, Zhang L, Zhang L, Shah BR, Xu W. Comparative Study on the Freeze–Thaw Stability of Sodium Caseinate Emulsion-Filled Konjac Glucomannan/κ-Carrageenan Composite Gels. Gels. 2025; 11(12):961. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120961
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Weifeng, Guanchen Wu, Lanlan Zhang, Lihua Zhang, Bakht Ramin Shah, and Wei Xu. 2025. "Comparative Study on the Freeze–Thaw Stability of Sodium Caseinate Emulsion-Filled Konjac Glucomannan/κ-Carrageenan Composite Gels" Gels 11, no. 12: 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120961
APA StyleChen, W., Wu, G., Zhang, L., Zhang, L., Shah, B. R., & Xu, W. (2025). Comparative Study on the Freeze–Thaw Stability of Sodium Caseinate Emulsion-Filled Konjac Glucomannan/κ-Carrageenan Composite Gels. Gels, 11(12), 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120961






