Effects of Transglutaminase and Epigallocatechin Gallate on the Structural and Physicochemical Properties of Fish Skin Gelatin from Takifugu rubripes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Yield and Composition of FG
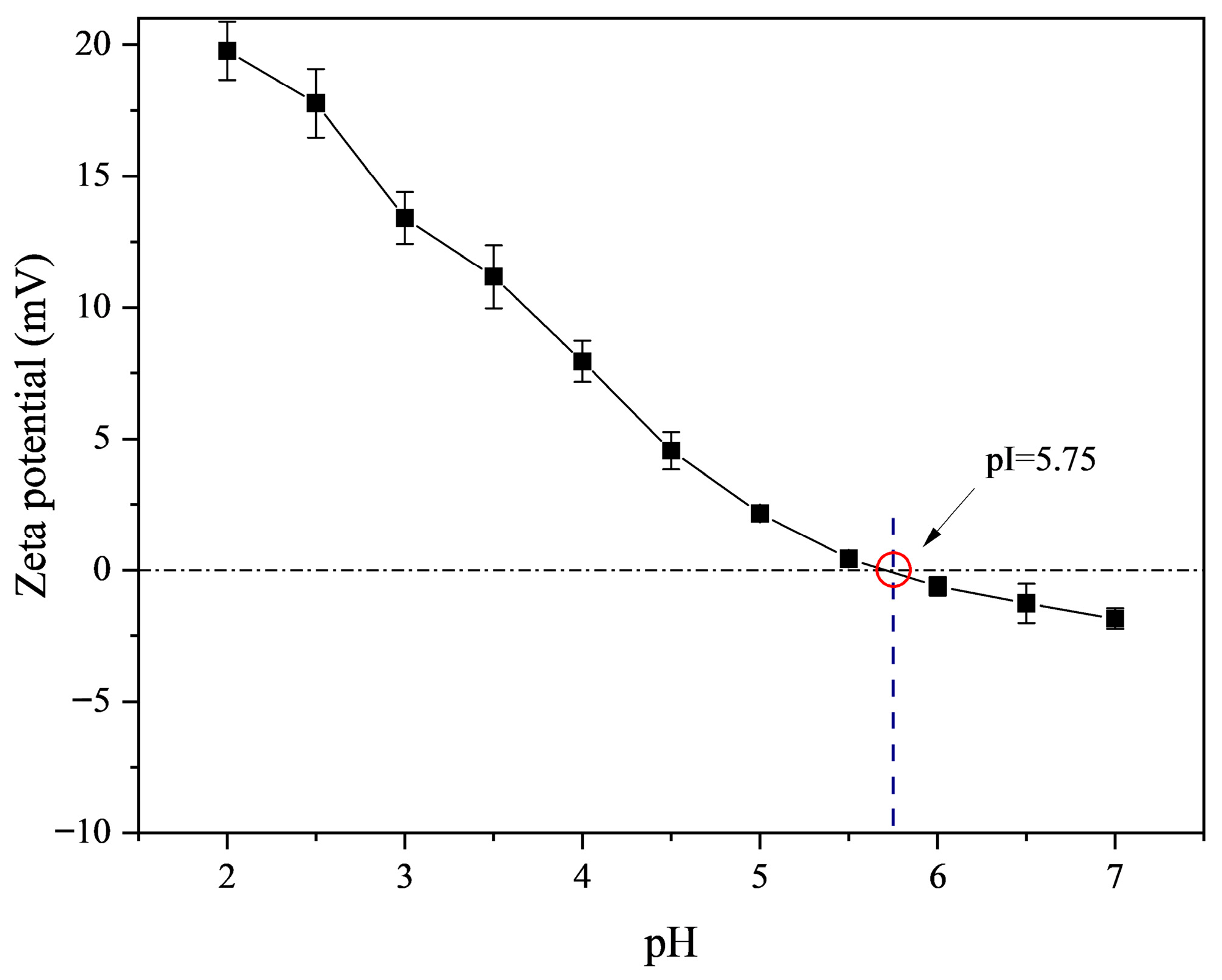
2.2. Zeta Potential of FG
2.3. Structural Properties of TG- and EGCG-Modified Gelatins
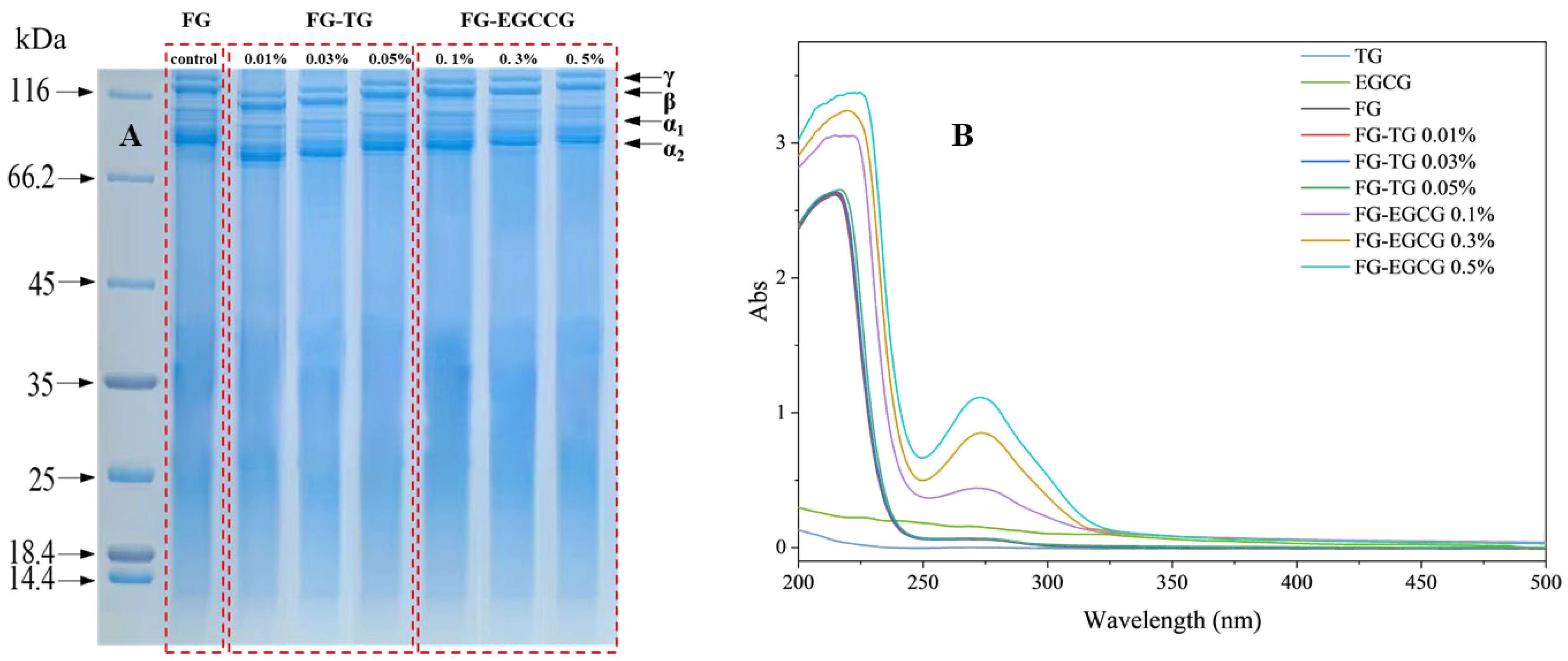
2.3.1. Molecular Weight Distribution
2.3.2. UV Spectral Analysis
2.3.3. Microstructural Analysis
2.4. Physicochemical Properties of TG- and EGCG-Modified Gelatin
2.5. Rheological Property Determination
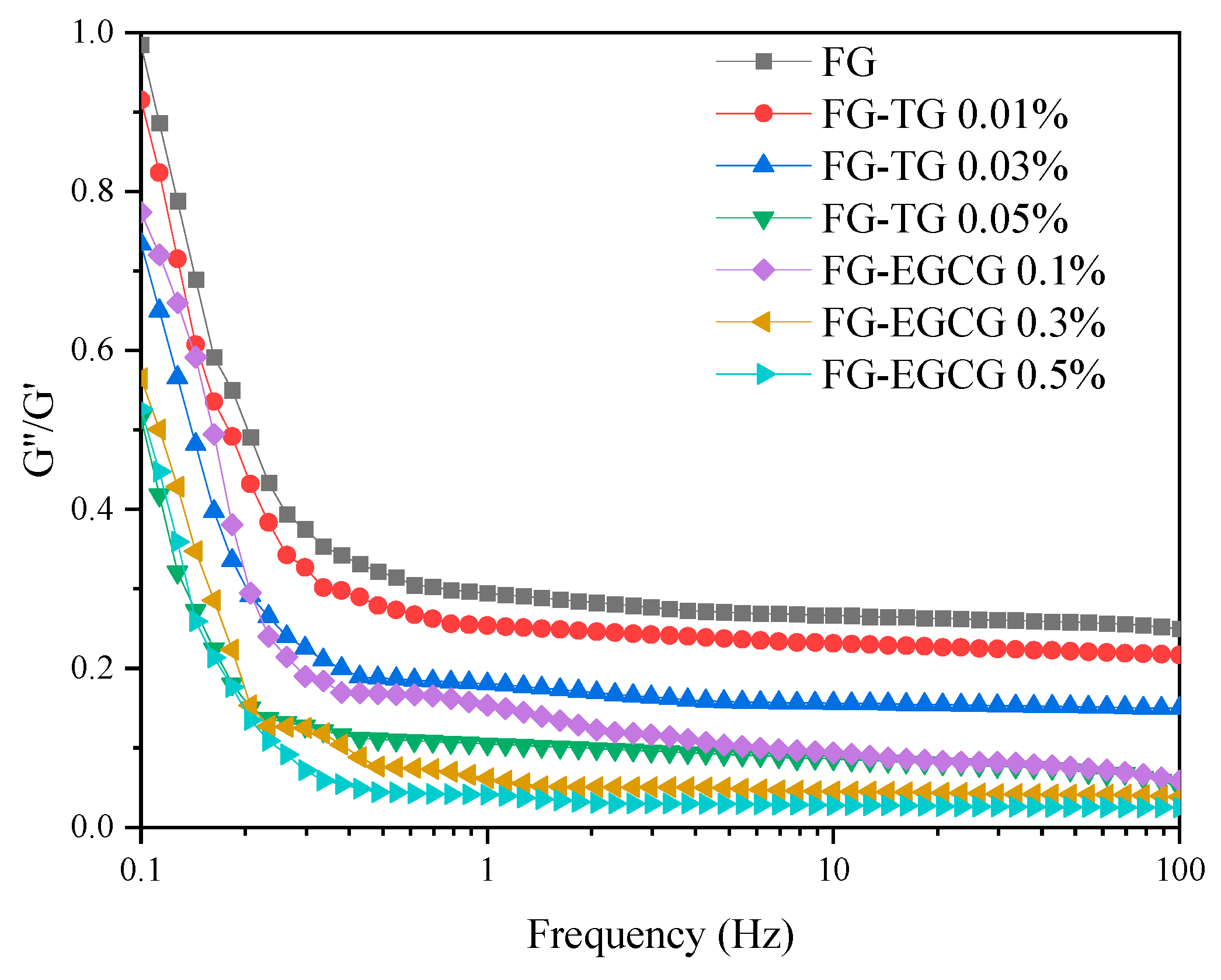
2.5.1. Frequency Sweep Tests
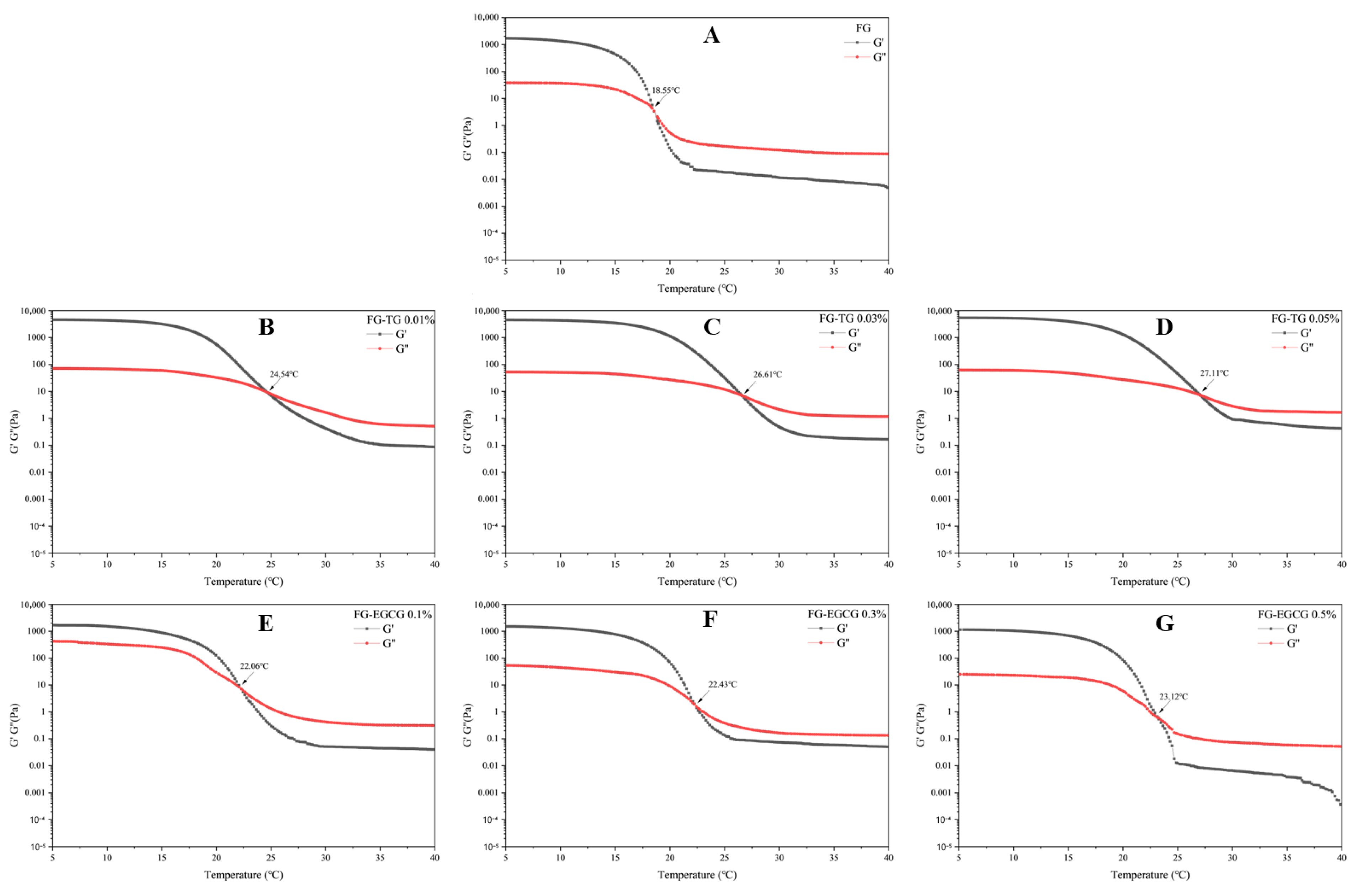
2.5.2. Temperature Sweep Tests
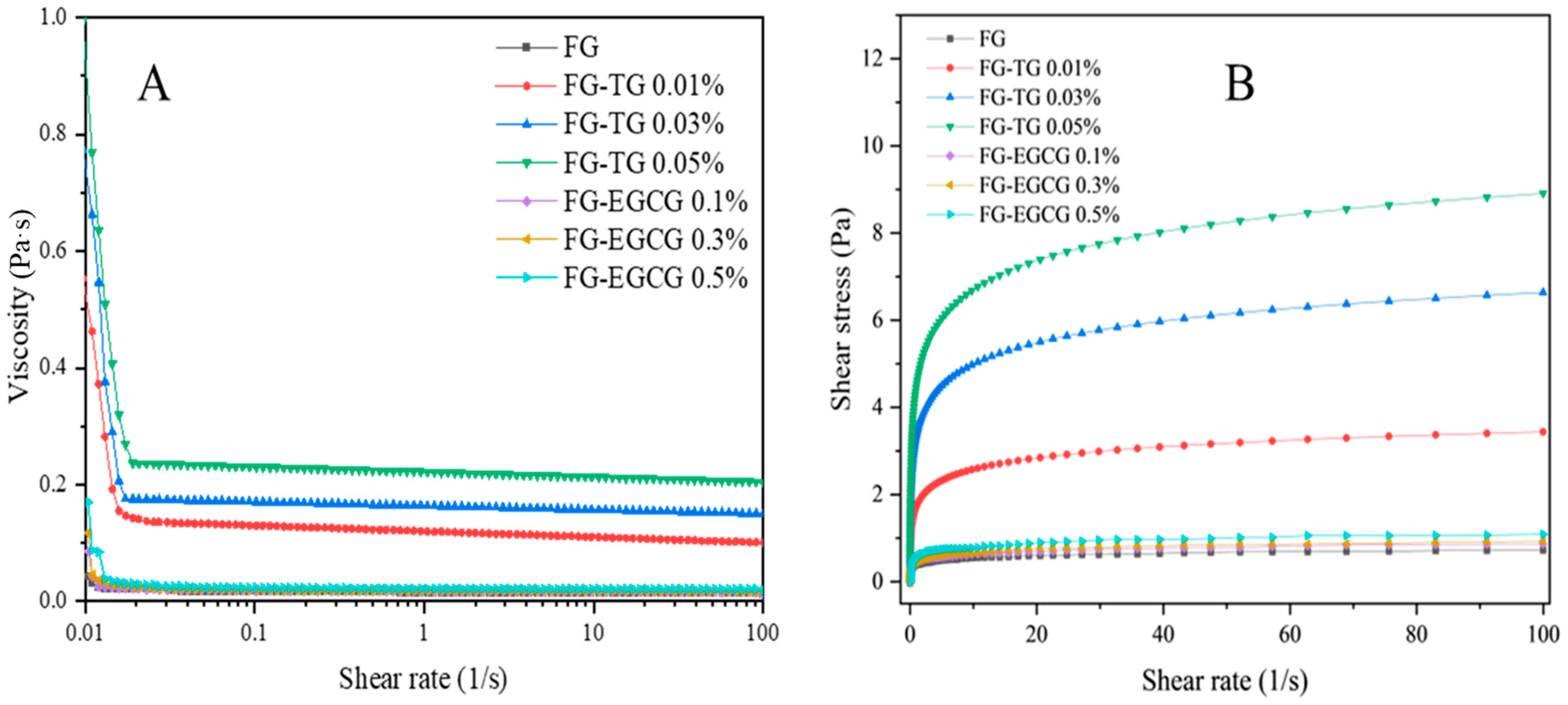
2.5.3. Steady Shear Flow Tests
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Extraction of Takifugu rubripes FG
4.3. Analysis of the Basic Components of Gelatin
4.4. Zeta Potential Measurements
4.5. Preparation of TG- and EGCG-Modified FG Samples
4.6. Gel Permeation Chromatography–Multi-Angle Light Scattering (GPC-MALLS) Analysis
4.7. Physicochemical and Structural Properties of TG- and EGCG-Modified Gelatin
4.7.1. Sodium Dodecyl-Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
4.7.2. Surface Hydrophobicity (H0)
4.7.3. Ultraviolet (UV) Spectral Analysis
4.7.4. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
4.8. Rheological Properties
4.9. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, D.; Nikoo, M.; Boran, G.; Zhou, P.; Regenstein, J.M. Collagen and Gelatin. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 527–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duconseille, A.; Astruc, T.; Quintana, N.; Meersman, F.; Sante-Lhoutellier, V. Gelatin structure and composition linked to hard capsule dissolution: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Gan, J.; Zhou, L.; Chen, H. Physically Crosslinked Hydrogels Based on Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) and Fish Gelatin for Wound Dressing Application: Fabrication and Characterization. Polymers 2020, 12, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao-ya, L.; Ya-xin, S.; Ji-lu, S.; Wei-dong, L.; Ming-zhu, G. Research progress on processing technology of cultured puffer fish and comprehensive utilization of by-products. Food Res. Dev. 2023, 44, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, N.-p.; Wang, L.-y.; Gong, X.; Liu, Y. Comparison of nutritional composition of farmed pufferfish muscles among Fugu obscurus, Fugu flavidus and Fugu rubripes. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2012, 28, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao-ting, C.; Jing-na, W.; Min, X.; Shu-ji, L.; Yong-chang, S.; Kun, Q.; Zhi-yu, L. Analysis and evaluation of the nutritional components in fish skin and fish meat of four species of puffer fish. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 36, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Li, Q.; Jia, H.; Xia, L.; Jin, W.; Shang, M.; Xu, C.; Dong, X. Physiochemical and functional properties of tiger puffer (Takifugu rubripes) skin gelatin as affected by extraction conditions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, H.; Hao, R.; Mráz, J.; Pu, Y.; Li, S.; Dong, X.; Pan, J. Gelling and emulsifying properties of tiger puffer (Takifugu rubripes) skin gelatin as manipulated by pH. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 369, 120886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.d.M.; Assis, C.R.D.; Costa, B.d.A.M.; Neri, R.C.d.A.; Monte, F.T.D.; Freitas, H.M.S.d.C.V.; França, R.C.P.; Santos, J.F.; Bezerra, R.d.S.; Porto, A.L.F. Physical, biochemical, densitometric and spectroscopic techniques for characterization collagen from alternative sources: A review based on the sustainable valorization of aquatic by-products. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1224, 129023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, S.F.; Hong, P.; Ng, K.; Wan mustapha, W.; Babji, A. Physicochemical properties of gelatins extracted from skins of different freshwater fish species. Int. Food Res. J. 2010, 17, 809–816. [Google Scholar]
- de Oliveira, R.; Rigueto, C.V.T.; Rosseto, M.; Krein, D.D.C.; Gomes, K.S.; Loss, R.A.; Dettmer, A. Influence of enzymatic crosslinking on Tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum) skin gelatin film properties. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 4539–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebers, L.; Reichsöllner, R.; Regett, S.; Tovar, G.E.M.; Borchers, K.; Baudis, S.; Southan, A. Differentiation of physical and chemical cross-linking in gelatin methacryloyl hydrogels. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, H.J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, X.; You, X. A Physically Cross-Linked Sodium Alginate–Gelatin Hydrogel with High Mechanical Strength. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 3197–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, Z.; He, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q. Preparation and characterization of gelatin-polysaccharide composite hydrogels for tissue engineering. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Shieh, C.-J.; Dong, C.-D. Enzymes and Biocatalysis. Catalysts 2022, 12, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricotta, M.; Iannuzzi, M.; Vivo, G.D.; Gentile, V. Physio-pathological roles of transglutaminase-catalyzed reactions. World J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 1, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Tu, Z.-c.; Shangguan, X.; Sha, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Bansal, N. Fish gelatin modifications: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Dai, H.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Fu, Y.; Ma, L.; Peng, L.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.; et al. Preparation of high thermal stability gelatin emulsion and its application in 3D printing. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Du, H.; Roos, Y.; Miao, S. Transglutaminase crosslinked fish gelatins for emulsion stabilization: From conventional to Pickering emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 144, 108979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.-X.; Liang, H.-Y.; Chen, N.; Shi, B.; Zeng, W.-C. Potential of phenolic compounds in Ligustrum robustum (Rxob.) Blume as antioxidant and lipase inhibitors: Multi-spectroscopic methods and molecular docking. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakun, P.; Mlynarczyk, D.T.; Koczorowski, T.; Cerbin-Koczorowska, M.; Piwowarczyk, L.; Kolasiński, E.; Stawny, M.; Kuźmińska, J.; Jelińska, A.; Goslinski, T. Tea-break with epigallocatechin gallate derivatives–Powerful polyphenols of great potential for medicine. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 261, 115820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, B.; Tian, J. Mitochondrial targets exploration of epigallocatechin gallate and theaflavin in regards to differences in stress protection under different temperatures. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2023, 119, 109400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-T.; Zhuang, X.-Y.; Yang, T.-S. Functionalities of Gelatin Modified with 2-Octenyl Succinic Anhydride and Gallic Acid. Foods 2022, 11, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.; Qi, Z.; Jin, J.; Shi, W.; Lu, S.; Dong, J.; Wang, Q. Concentration effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate-bovine bone protein conjugates on emulsion stability. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 675, 132057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Cui, Y.-f.; Liu, Y.-a.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.-c.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, N.; Chen, Q. Mechanism of interaction between astaxanthin and soy protein fibrils: Effects on complexes structure, rheological properties and bioaccessibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 146, 109227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Guan, Q.; Qian, S.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Ullah, N.; Chen, L. The gelation properties of myofibrillar proteins prepared with malondialdehyde and (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Ma, W.; Liu, R.; Zou, S.; Zhao, Y.; Xiong, S.; Rong, J.; Hu, Y. Insights into the synergistic cross-linking effect of EGCG and TGase on surimi gels. Food Chem. 2025, 491, 145221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhou, W.; Hu, D.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zou, S.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Rong, J.; et al. Effects of EGCG/TGase on the physicochemical properties and in vitro dynamic digestion characteristics of water-saving rinsed surimi gels. Food Chem. 2025, 493, 145668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsuwat, S.; Zhang, P.; Ng, K.; Fang, Z. Fish gelatin as an alternative to mammalian gelatin for food industry: A meta-analysis. LWT 2021, 141, 110899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, C.; Bai, Y.; Lai, K.; Yang, F.; Huang, Y. Characterization of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) skin gelatin extracted with alkaline and different acid pretreatments. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 33, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.M.; Kwak, K.S.; Park, D.C.; Gu, Y.S.; Ji, C.I.; Jang, D.H.; Lee, Y.B.; Kim, S.B. Processing optimization and functional properties of gelatin from shark (Isurus oxyrinchus) cartilage. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xiao, J.; Zhu, M.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y. Study of Physicochemical and Gelation Properties of Fish Gelatin from Different Sources. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Lin, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Yang, W.; Huang, T.; Zhang, Q. Combination Modification of Dynamic High Pressure Microfluidization and Transglutaminase Influence Gel and Structural Properties of Fish Gelatin. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2020, 34, 1990–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wei, Y.; Liu, P.; Deng, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Study of four polyphenol-Coregonus peled (C. peled) myofibrillar protein interactions on protein structure and gel properties. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, A.L.C.; de Góes-Favoni, S.P. Action of microbial transglutaminase (MTGase) in the modification of food proteins: A review. Food Chem. 2015, 171, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Munir, S.; Yu, X.; Yin, T.; You, J.; Liu, R.; Xiong, S.; Hu, Y. Double-crosslinked effect of TGase and EGCG on myofibrillar proteins gel based on physicochemical properties and molecular docking. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, G.; Shi, X.; Ma, C.; Liu, F. Comparative Study of Heat- and Enzyme-Induced Emulsion Gels Formed by Gelatin and Whey Protein Isolate: Physical Properties and Formation Mechanism. Gels 2022, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Weng, R.; Wang, W.; Wei, X.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Lu, F.; Li, Y. Tunable physical and mechanical properties of gelatin hydrogel after transglutaminase crosslinking on two gelatin types. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Wang, Y.; Shang, M.; Pan, J. Impacts of Tannin and Lutein before and after Oxidization on Gelatin Properties of Tiger Puffer (Takifugu rubripes) Skin Gelatin. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 24, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Emara, A.M.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; He, Z. Effect of in vitro oxidation on the water retention mechanism of myofibrillar proteins gel from pork muscles. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsuwan, K.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T. Properties and application of bilayer films based on poly (lactic acid) and fish gelatin containing epigallocatechin gallate fabricated by thermo-compression molding. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Gao, S.; Yang, H. Effects of sucrose addition on the rheology and structure of iota-carrageenan. Food Hydrocolloids 2020, 99, 105317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Liang, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yi, S.; Li, X.; Li, J. Study on the interactions between the screened polyphenols and Penaeus vannamei myosin after freezing treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 217, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Xu, Q.-D.; Chen, N.; He, Q.; Zeng, W.-C. Cross-Linking Modifications of Different Phenolic Compounds on Myofibrillar Protein of Common Carp. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2023, 16, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Li, B.; Zhao, X.; Yi, J. Physicochemical properties of gelatin gels from walleye pollock (Theragra chalcogramma) skin cross-linked by gallic acid and rutin. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, I.J.; Draget, K.I.; Smidsrød, O. Physical and rheological properties of fish gelatin compared to mammalian gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaschar-Ovdat, S.; Davidovich-Pinhas, M.; Fishman, A. Modulating the gel properties of soy glycinin by crosslinking with tyrosinase. Food Res. Int. 2016, 87, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, F.; da Silva, M.A.; Drake, A.F.; Ross-Murphy, S.B.; Dreiss, C.A. Enzymatically Cross-Linked Tilapia Gelatin Hydrogels: Physical, Chemical, and Hybrid Networks. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3741–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Sarabia, A.I.; Solas, M.T.; Montero, P. Effect of microbial transglutaminase on the functional properties of megrim (Lepidorhombus boscii) skin gelatin. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huo, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, C.; Li, M.; Lu, D.; Ren, R.; et al. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure sterilisation and thermal sterilisation combined with glutamine transaminase treatment on the properties of yoghurt. Int. Dairy J. 2024, 149, 105808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yang, L.; Nie, Y.; Yang, M.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Effect of transglutaminase crosslinking on the structural, physicochemical, functional, and emulsion stabilization properties of three types of gelatins. LWT 2022, 163, 113543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Shi, L.; Hao, G.; Chen, J.; Weng, W. Effect of molecular weight on the emulsion properties of microfluidized gelatin hydrolysates. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.-P.; Xiong, Y.L. Microbial transglutaminase-induced structural and rheological changes of cationic and anionic myofibrillar proteins. Meat Sci. 2012, 91, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwate, B.W.; Ballari, R.V.; Kudre, T.G. Influence of spray-drying, freeze-drying and vacuum-drying on physicochemical and functional properties of gelatin from Labeo rohita swim bladder. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zheng, Y.; Xiong, X.; Xue, F. Production of protein-epigallocatechin gallate conjugates using free radicals induced by ultrasound and their gelation behavior. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.-D.; Yu, Z.-L.; Zeng, W.-C. Structural and functional modifications of myofibrillar protein by natural phenolic compounds and their application in pork meatball. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Xu, Q.-D.; Chen, N.; He, Q.; Sun, Q.; Zeng, W.-C. Cross-linking effects of EGCG on myofibrillar protein from common carp (Cyprinus carpio) and the action mechanism. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, Q.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhu, X.; Liu, J.; Granato, D.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J. Effects of different dietary polyphenols on conformational changes and functional properties of protein–polyphenol covalent complexes. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yin, J.; Geng, F.; Nie, S. The synergistic gelation of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide (Dendronans) with xanthan gum and its rheological and texture properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 141, 108674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dong, X.; Xia, G.; Shen, X. Effect of extraction variables on the physical and functional properties of tilapia gelatin. LWT 2021, 146, 111514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.R.; Kolotova, D.S.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Malkin, A.Y. Rheological Properties of Fish Gelatin Modified with Sodium Alginate. Polymers 2021, 13, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Liu, Z.; Yi, J.; Hu, X.; Guo, C. The synergistic effect of κ-carrageenan and l-lysine on the 3D printability of yellow flesh peach gels: The importance of material elasticity in the printing process. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldsine, P.; Abeyta, C.; Andrews, W.H. AOAC International methods committee guidelines for validation of qualitative and quantitative food microbiological official methods of analysis. J. AOAC Int. 2002, 85, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.-c.; McClements, D.J. Microgels formed by electrostatic complexation of gelatin and OSA starch: Potential fat or starch mimetics. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 47, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Han, L.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, K.; Al-Assaf, S.; Nishinari, K.; Phillips, G.O.; Yang, J.; Fang, Y. Effects of temperature and solvent condition on phase separation induced molecular fractionation of gum arabic/hyaluronan aqueous mixtures. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schägger, H.; von Jagow, G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 166, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Tu, Y.; Ren, F.; Zhang, H. Characterization and functional properties of Maillard reaction products of β-lactoglobulin and polydextrose. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 131749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Theng, A.H.P.; Yang, D.; Yang, H. Influence of κ-carrageenan on the rheological behaviour of a model cake flour system. LWT 2021, 136, 110324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Ou, X.; Huang, J.; Luan, G. Structural support of zein network to rice flour gluten-free dough: Rheological, textural and thermal properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 141, 108721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cai, M.; Ma, S.; Lu, H.; Liu, X. Heat-induced gel formation by whey protein isolate-deacetylated konjac glucomannan at varying pH conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Amino Acid | % of Total Protein |
|---|---|
| Aspartic acid | 3.77 ± 0.42 |
| Threonine | 1.63 ± 0.21 |
| Serine | 2.68 ± 0.09 |
| Glutamic acid | 6.40 ± 0.11 |
| Glycine | 15.14 ± 0.67 |
| Alanine | 6.70 ± 0.15 |
| Valine | 1.63 ± 0.08 |
| Methionine | 1.19 ± 0.06 |
| Isoleucine | 0.71 ± 0.02 |
| Leucine | 1.44 ± 0.05 |
| Tyrosine | 0.46 ± 0.03 |
| Phenylalanine | 1.34 ± 0.04 |
| Lysine | 2.48 ± 0.08 |
| Histidine | 0.60 ± 0.01 |
| Arginine | 5.40 ± 0.26 |
| Proline | 8.20 ± 0.35 |
| Total of 16 amino acids | 59.77 ± 0.90 |
| TG/EGCG Concentration (%) | Mn (×105 Da) | Mw (×105 Da) | Polydispersity Index (Mw/Mn) | Rg (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FG 0.00 | 1.410 ± 0.050 c | 3.337 ± 0.026 f | 2.368 ± 0.056 f | 30.100 ± 0.003 d |
| FG-TG 0.01 | 1.293 ± 0.029 d | 3.798 ± 0.019 e | 2.939 ± 0.035 e | 32.600 ± 0.002 c |
| FG-TG 0.03 | 1.780 ± 0.032 b | 5.567 ± 0.021 d | 3.127 ± 0.038 d | 32.500 ± 0.002 c |
| FG-TG 0.05 | 1.861 ± 0.027 a | 6.902 ± 0.015 c | 3.710 ± 0.030 c | 34.600 ± 0.001 b |
| FG-EGCG 0.1 | 1.190 ± 0.031 e | 3.856 ± 0.029 e | 3.240 ± 0.040 d | 32.800 ± 0.072 c |
| FG-EGCG 0.3 | 0.989 ± 0.037 g | 7.834 ± 0.028 b | 7.921 ± 0.051 b | 35.800 ± 0.093 a |
| FG-EGCG 0.5 | 1.038 ± 0.055 f | 15.756 ± 0.031 a | 15.181 ± 0.104 a | 32.268 ± 0.105 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Yang, J.; Al-Assaf, S. Effects of Transglutaminase and Epigallocatechin Gallate on the Structural and Physicochemical Properties of Fish Skin Gelatin from Takifugu rubripes. Gels 2025, 11, 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090725
Han L, Zhang Y, Hu B, Zhang Y, Cao J, Yang J, Al-Assaf S. Effects of Transglutaminase and Epigallocatechin Gallate on the Structural and Physicochemical Properties of Fish Skin Gelatin from Takifugu rubripes. Gels. 2025; 11(9):725. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090725
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Lingyu, Yulong Zhang, Bing Hu, Ying Zhang, Jijuan Cao, Jixin Yang, and Saphwan Al-Assaf. 2025. "Effects of Transglutaminase and Epigallocatechin Gallate on the Structural and Physicochemical Properties of Fish Skin Gelatin from Takifugu rubripes" Gels 11, no. 9: 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090725
APA StyleHan, L., Zhang, Y., Hu, B., Zhang, Y., Cao, J., Yang, J., & Al-Assaf, S. (2025). Effects of Transglutaminase and Epigallocatechin Gallate on the Structural and Physicochemical Properties of Fish Skin Gelatin from Takifugu rubripes. Gels, 11(9), 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090725









