Chemical Diversity and Biological Activities of Phaeosphaeria Fungi Genus: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Chemistry and Biology of Microbial Natural Products Isolated from the Genus Phaeosphaeria
2.1. Cyclohexanoids, Naphthoquinones, Anthraquinones, and Phenalenones
2.2. Isocoumarins, Isobenzofuran, and Related Metabolites
2.3. Perylenequinones
2.4. Terpenoide/Steroidal Compounds
2.5. Nitrogen-Containing Compounds
3. Conclusions and Perspective
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IC50 | Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration |
| EC50 | Half Maximal Effective Concentration |
| MIC | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration |
| MIC80 | Minimum Concentration required to Inhibit 80% |
| STAT | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription |
| PKS | Polyketide Synthases |
| NPRS | Non-Ribosomal Peptide Synthetases |
References
- Lam, K.S. New aspects of natural products in drug discovery. Trends Microbiol. 2007, 15, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Glaser, K.B.; Cuevas, C.; Jacobs, R.S.; Kem, W.; Little, R.D.; McIntosh, J.M.; Newman, D.J.; Potts, B.C.; Shuster, D.E. The odyssey of marine pharmaceuticals: A current pipeline perspective. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 31, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Natural products: A continuing source of novel drug leads. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 3670–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B. A new golden age of natural products drug discovery. Cell 2015, 163, 1297–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patridge, E.; Gareiss, P.; Kinch, M.S.; Hoyer, D. An analysis of FAD-approved drugs: Natural products and their derivatives. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, T.; Lin, S. Microbial natural products: A promising source for drug discovery. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biochem. 2017, 1, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, A.L.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Quinn, R.J. The re-emergency of natural products for drug discovery in the genomics era. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2015, 14, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoemaker, R.A.; Babcock, C.E. Phaeosphaeria. Can. J. Bot. 1989, 67, 1500–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hane, J.K.; Lowe, R.G.T.; Solomon, P.S.; Tan, K.C.; Schoch, C.L.; Spatafora, J.W.; Crous, P.W.; Kodira, C.; Birren, B.W.; Galagan, J.E.; et al. Dothideomycete plant interactions illuminated by genome sequencing and EST analysis of the wheat pathogen Stagonospora nodorum. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 3347–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chooi, Y.H.; Muria-Gonzalez, M.J.; Solomon, P.S. A genome wide survey of the secondary metabolite biosynthesis genes in the wheat pathogen Parastagonospora nodorum. Mycology 2014, 5, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chooi, Y.H.; Krill, C.; Barrow, R.A.; Chen, S.; Trengove, R.; Oliver, R.P.; Solomon, P.S. An In planta expressed polyketide synthase produces (R)-mellein in the wheat pathogen Parastagonospora nodorum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chooi, Y.H.; Muria-Gonzalez, M.J.; Mead, O.L.; Solomon, P.S. SnPKS19 encodes the polyketide synthase for alternariol mycotoxin biosynthesis in the wheat pathogen Parastagonospora nodorum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 5309–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mycobank: Phaeosphaeria. Available online: http://www.mycobank.org/Biolomics.aspx?Table=Mycobank&Rec=37177&Fields=All (accessed on 1 November 2018).
- Elsebaia, M.F.; Kehrausa, S.; Guütschowb, M.; Königa, G.M. New polyketides from the marine-derived fungus Phaeosphaeria spartinae. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 1463–1468. [Google Scholar]
- Elsebaia, M.F.; Kehrausa, S.; Guetschow, M.; Königa, G.M. Spartinoxide, a new enantiomer of A82775C with inhibitory activity toward HLE from the marine-derived fungus Phaeosphaeria spartinae. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Elsebaia, M.F.; El Maddah, F.; Kehrausa, S.; Königa, G.M. New Bicyclo-spartinols from the Marine-derived Fungus Phaeosphaeria spartinae. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 637–639. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Ondeyka, J.G.; Zink, D.L.; Basilio, A.; Vicente, F.; Collado, J.; Platas, G.; Bills, G.; Huber, J.; Dorso, K.; et al. Isolation, structure, and antibacterial activity of Phaeosphenone from a Phaeosphaeria sp. discovered by antisense strategy. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1304–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittayakhajonwut, P.; Sohsomboon, P.; Dramae, A.; Suvannakad, R.; Lapanun, S.; Tantichareon, M. Antimycobacterial substances from Phaeosphaeria sp. BCC8292. Planta Med. 2008, 74, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.Z.; Kumazawa, S.; Tomita, H.; Yoshikawa, N.; Kimura, C.; Mikawa, T.; Rousselianone, A. novel antibiotic related to phenalenone produced by phaeosphaeria rousseliana. J. Antibiot. 1993, 46, 1570–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hu, J.; Wei, H.; Solomon, P.S.; Vuong, D.; Lacey, E.; Stubbs, K.A.; Piggott, A.M.; Chooi, Y.-H. Chemical Ecogenomics-Guided Discovery of Phytotoxic α-Pyrones from the Fungal Wheat Pathogen Parastagonospora nodorum. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 6148–6152. [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet, J.F.; Skajennikoff, M. Isolation and mode of action of a phytotoxin produced by Septoria nodorum. Phytopathol. Z. 1974, 80, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devys, P.M.; Bousquet, J.F.; Skajennikoff, M.; Barbier, M. Ľochracine (meiléine), phytotoxine isolée du milieu de culture de Septoria nodorum Berk. Phytopathol. Z. 1974, 81, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devys, M.; Bousquet, J.F.; Kollmann, A.; Barbier, M. Dihydroisocoumarines et acide mycophénolique du milieu de culture du champignon phytopathogéne Septoria nodorum. Phytochemistry 1980, 19, 2221–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devys, M.; Barbier, M. Isolation of new (−)-(3R,4S)-4-hydroxymellein from the fungus Septoria nodorum Berk. Z. Naturforsch. 1992, 47, 779–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devys, M.; Barbier, M.; Bousquet, J.F.; Kollmann, A. Isolation of the (−)-(3R)-5-hydroxymellein from the fungus Septoria nodorum. Phytochemistry 1994, 35, 825–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, J.F.; Kollmann, A. Variation in metabolite production by Septoria nodorum isolates adapted to wheat or to barley. J. Phytopathol. 1998, 146, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.-C.; Trengove, R.; Maker, G.; Oliver, R.; Solomon, P. Metabolite profiling identifies the mycotoxin alternariol in the pathogen Stagonospora nodorum. Metabolomics 2009, 5, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-L.; Awakawa, T.; Wakimoto, T.; Abe, I. Induced biosyntheses of a novel butyrophenone and two aromatic polyketides in the plant pathogen Stagonospora nodorum. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2013, 3, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerea, A.L.; Branscum, K.M.; King, J.B.; You, J.; Powell, D.R.; Miller, A.N.; Spear, J.R.; Cichewicz, R.H. Secondary metabolites produced by fungi derived from a microbial mat encountered in an iron-rich natural spring. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 4202–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinworrungsee, M.; Kittakoop, P.; Isaka, M.; Chanphen, R.; Tanticharoen, M.; Thebtaranonth, Y. Halorosellins A and B, unique isocoumarin glucosides from the marine fungus Halorosellinia oceanica. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2002, 1, 2473–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayone, W.C.; Honma, M.; Kanamaru, S.; Noguchi, S.; Tanaka, K.; Nehira, T.; Hashimoto, M. Stereochemical investigations of isochromenones and isobenzofuranones isolated from Leptosphaeria sp. KTC 727. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Wang, H.; Zhu, R.; Sun, L.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Lou, H. Phaeosphaerins A-F, cytotoxic perylenequinones from an endolichenic fungus, Phaeosphaeria sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stowe, B.B.; Yamaki, T. the history and physiological action of the gibberellins. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 1957, 8, 181–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassa, T.; Suzuki, K.; Haruki, E. Isolation and identification of gibberellins A4 and A9 from a fungus Phaeosphaeria sp. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1989, 53, 303–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassa, T.; Suzuki, K. Metabolism of gibberellin A9 to gibberellin A4 n a new gibberellin producing fungus Phaeosphaeria sp. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1990, 54, 3373–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaide, H.; Sassa, T. Accumulation of gibberellin A1 and the metabolism of gibberellin A9 to gibberellin A1 in a Phaeosphaeria sp. L487 Culture. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1993, 57, 1403–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassa, T.; Kawaide, H.; Takarada, T. Identification of gibberellins A4, A9, and A24 from Phaeosphaeria sp. L487 cultured in a chemically defined medium. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1994, 58, 438–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaide, H.; Sassa, T.; Kamiya, Y. Plant-like biosynthesis of gibberellin A1 in the fungus Phaeosphaeria sp. L487. Phytochemistry 1995, 39, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, H.; Sassa, T.; Kawaide, H.; Shigihara, T.; Uzawa, J.; Yoshida, S. Isolation and stereo controlled synthesis of a 17-hydroxy-16β,17-dihydrogibberellin, GA82. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 5917–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenmoku, H.; Sugai, T.; Yajima, H.; Sassa, T. Phaeoside, a novel galactoside of hydroxymanoyl oxide from the gibberellin A1-producing Phaeosphaeria sp. L487. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 2418–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsebai, M.F.; Kehraus, S.; König, G.M. Caught between triterpene- and steroid-metabolism: 4α-Carboxylic pregnane-derivative from the marine alga-derived fungus Phaeosphaeria spartinae. Steroids 2013, 78, 880–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devys, M.; Bousquet, J.F.; Kollmann, A.; Barbier, M. La septorine, nouvelle pyrazine substituée du milieu de culture de Septoria nodorum Berk., champignon phytopathogéne. CR Acad. Sci. 1978, 286, 457–458. [Google Scholar]
- Devys, M.; Barbier, M.; Kollmann, A.; Bousquet, J.F. Septorine and N-methoxyseptorine substituted pyrazines from the fungus Septoria nodorum Berk. Tetrahedron Lett. 1982, 23, 5409–5412. [Google Scholar]
- Devys, M.; Barbier, M.; Kollmann, A.; Bousquet, J.F. N-methoxyseptorinol a substituted pyrazine from the fungus Septoria nodorum. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 4393–4394. [Google Scholar]
- Barbier, M.; Devys, M.; Bousquet, J.F.; Kollmann, A. Absoulte stereochemistry of N-methoxyseptorinol isolated from the fungus Septoria nodorum. Phytochemistry 1994, 35, 955–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, J.F.; Belhomme de Franqueville, H.; Kollmann, A.; Fritz, R. Action de la septorine, phytotoxine synthetisee par Septoria nodorum, sur la phosphorylation oxydative dans les mitochondries isolees de Coleoptiles de Ble. Can. J. Bat. 1980, 58, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillant, M.L.; Pittet, J.L.; Bernillon, J.; Favre-Bonvin, J.; Arpin, N. Mycosporins from Ascochyta pisi, Cladosporium herbarum and Septoria nodorum. Phytochemistry 1982, 20, 2705–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, K.N.; Hao, W.; Xu, J.; Gibbons, J.; Hucul, J.; Roll, D.; Brady, S.F.; Schroeder, F.C.; Clardy, J. Phaeosphaeride A, an Inhibitor of STAT3-dependent signaling isolated from an endophytic fungus. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 4067–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.B.; Ondeyka, J.; Harris, G.; Herath, K.; Zink, D.; Vicente, F.; Bills, G.; Collado, J.; Platas, G.; Ganzalez del Val, A.; et al. Isolation, Structure, and Biological Activity of Phaeofungin, a cyclic lipodepsipeptide from a Phaeosphaeria sp. using the genome-wide Candida albicans fitness test. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
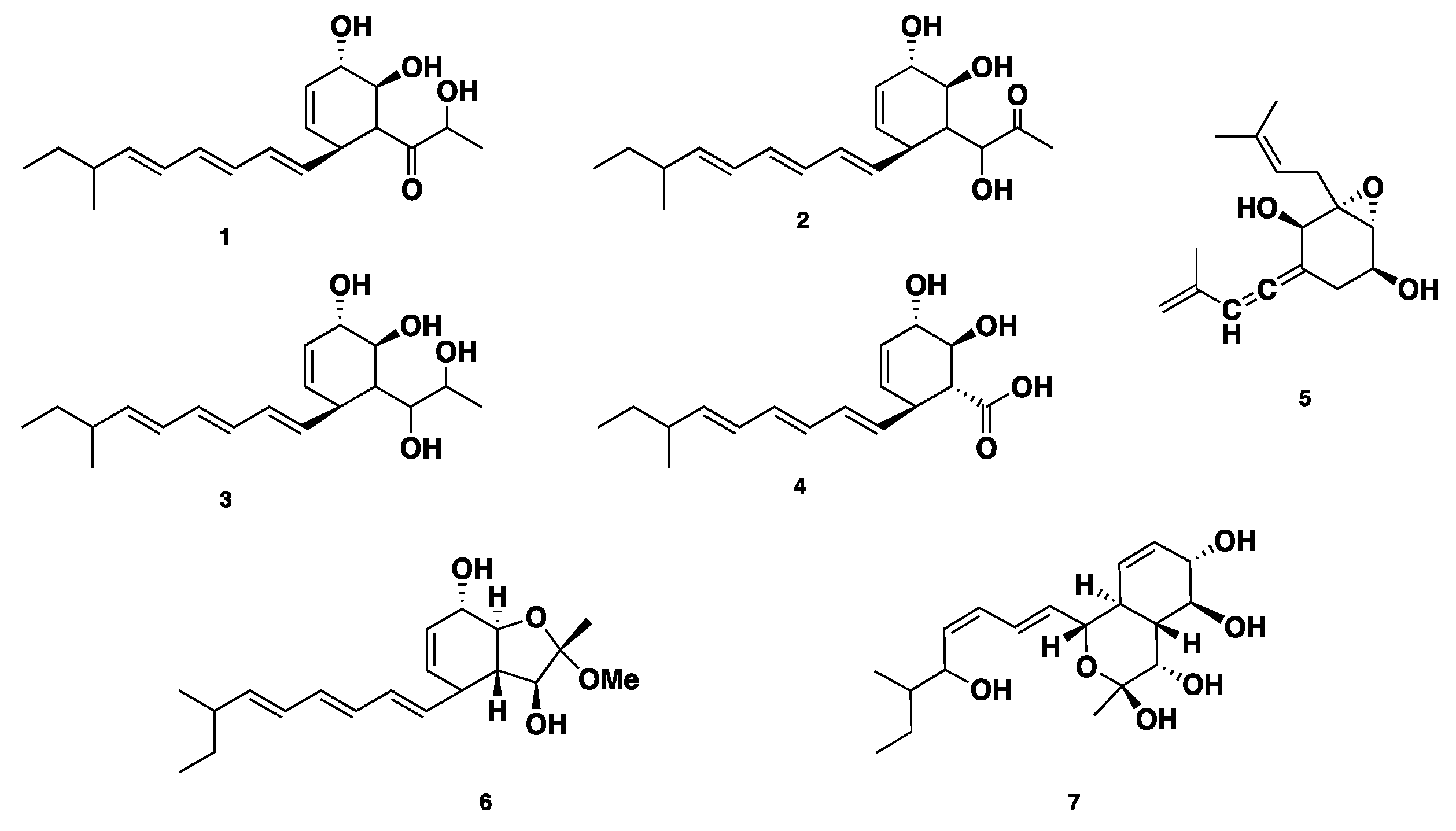
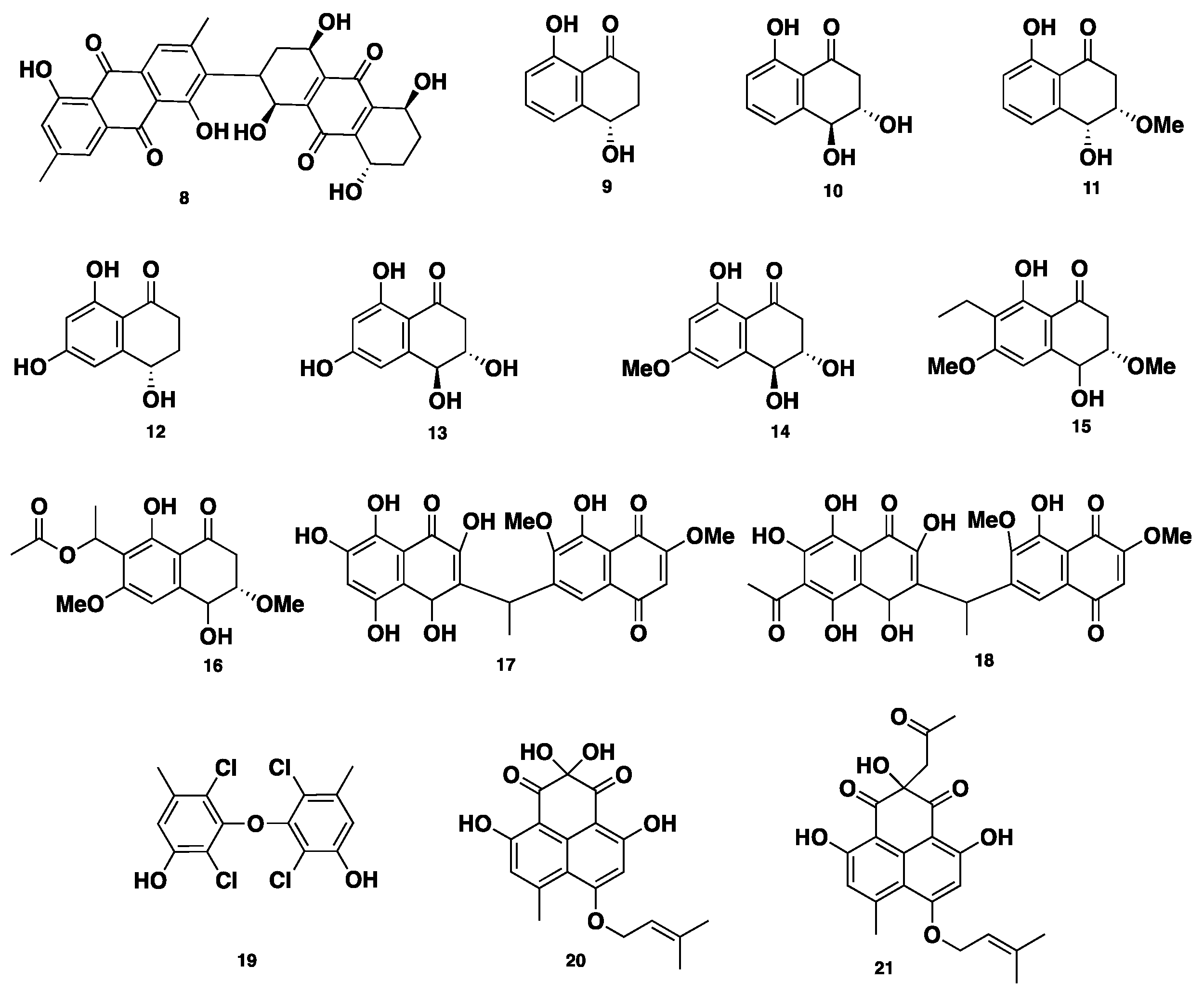
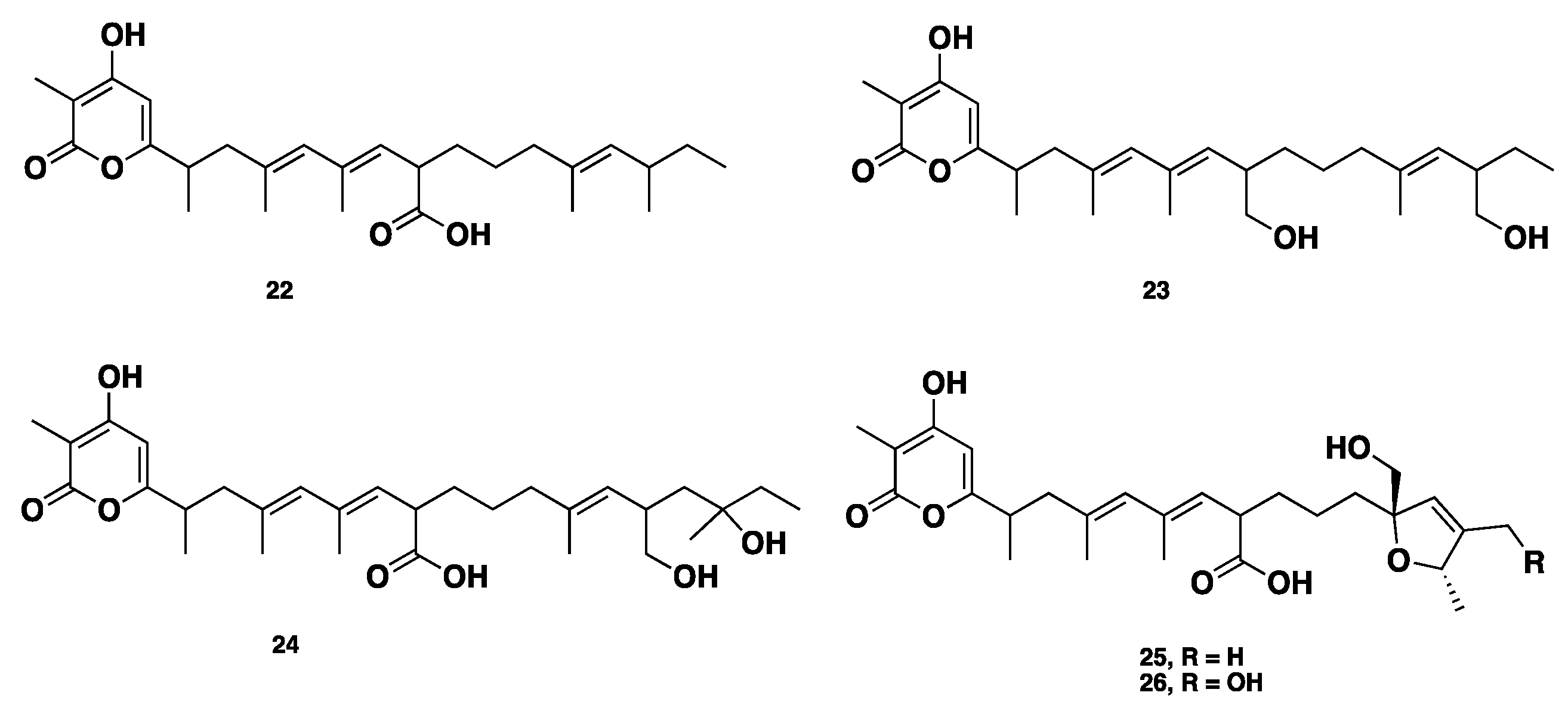
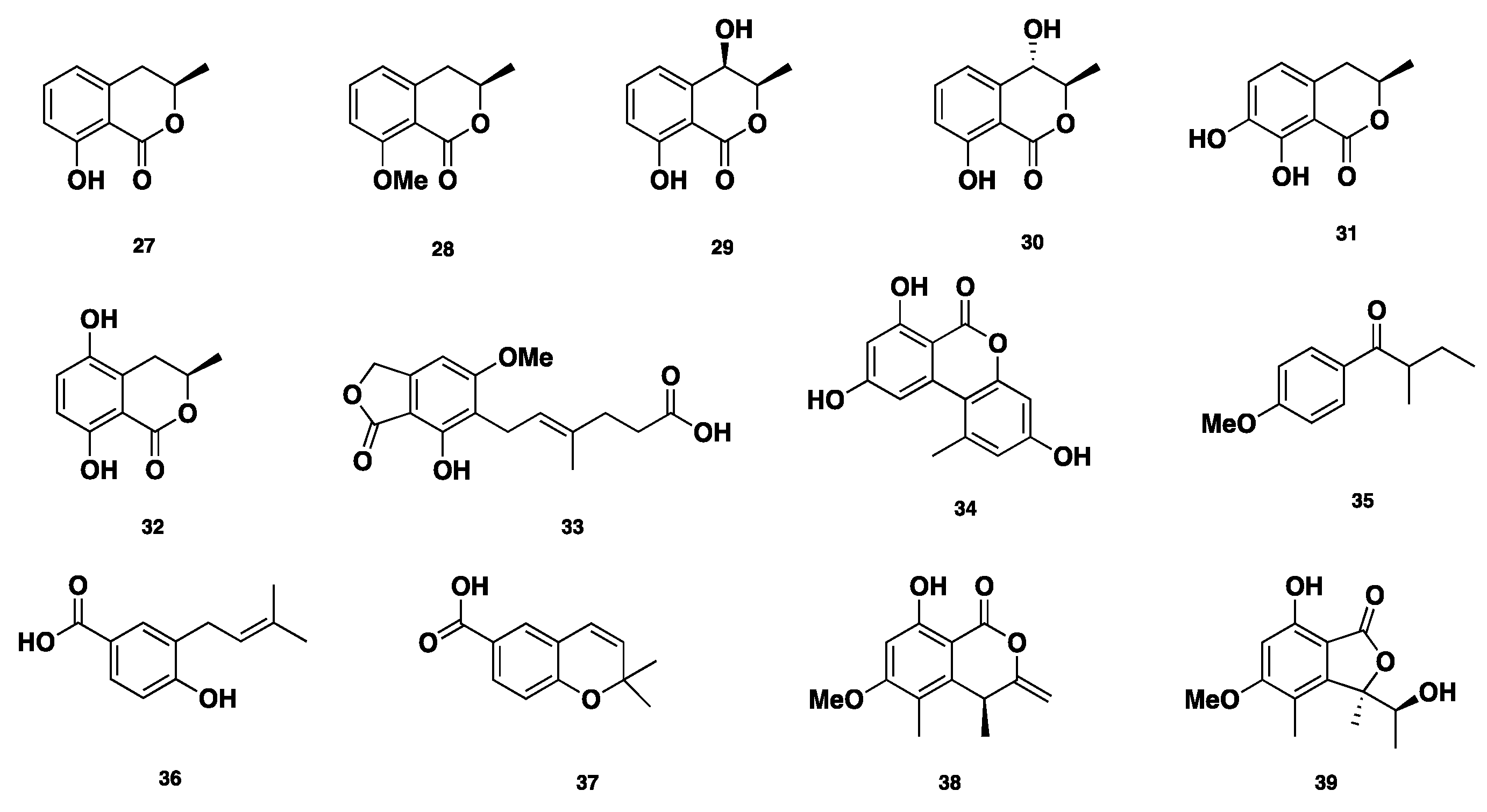
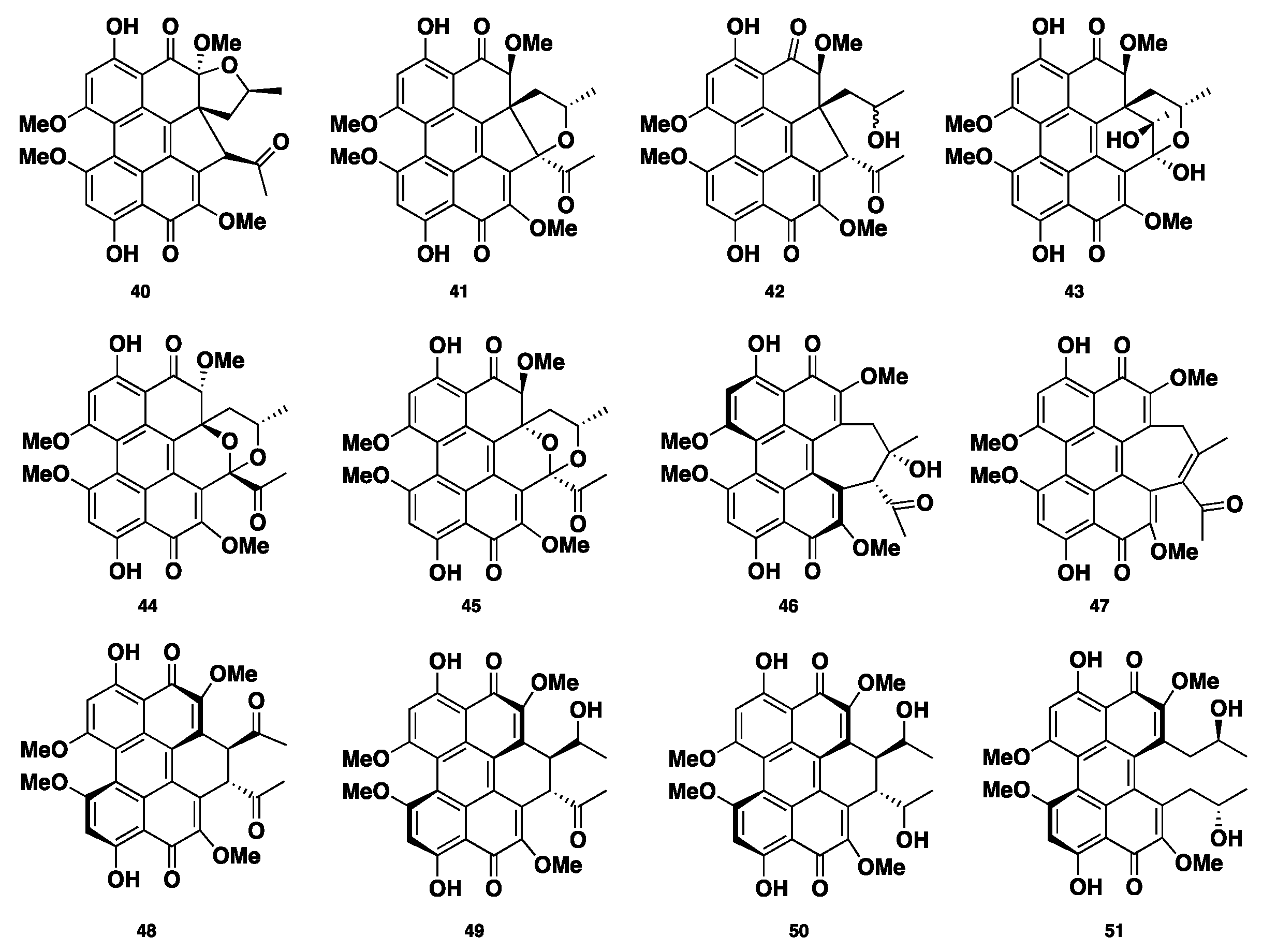
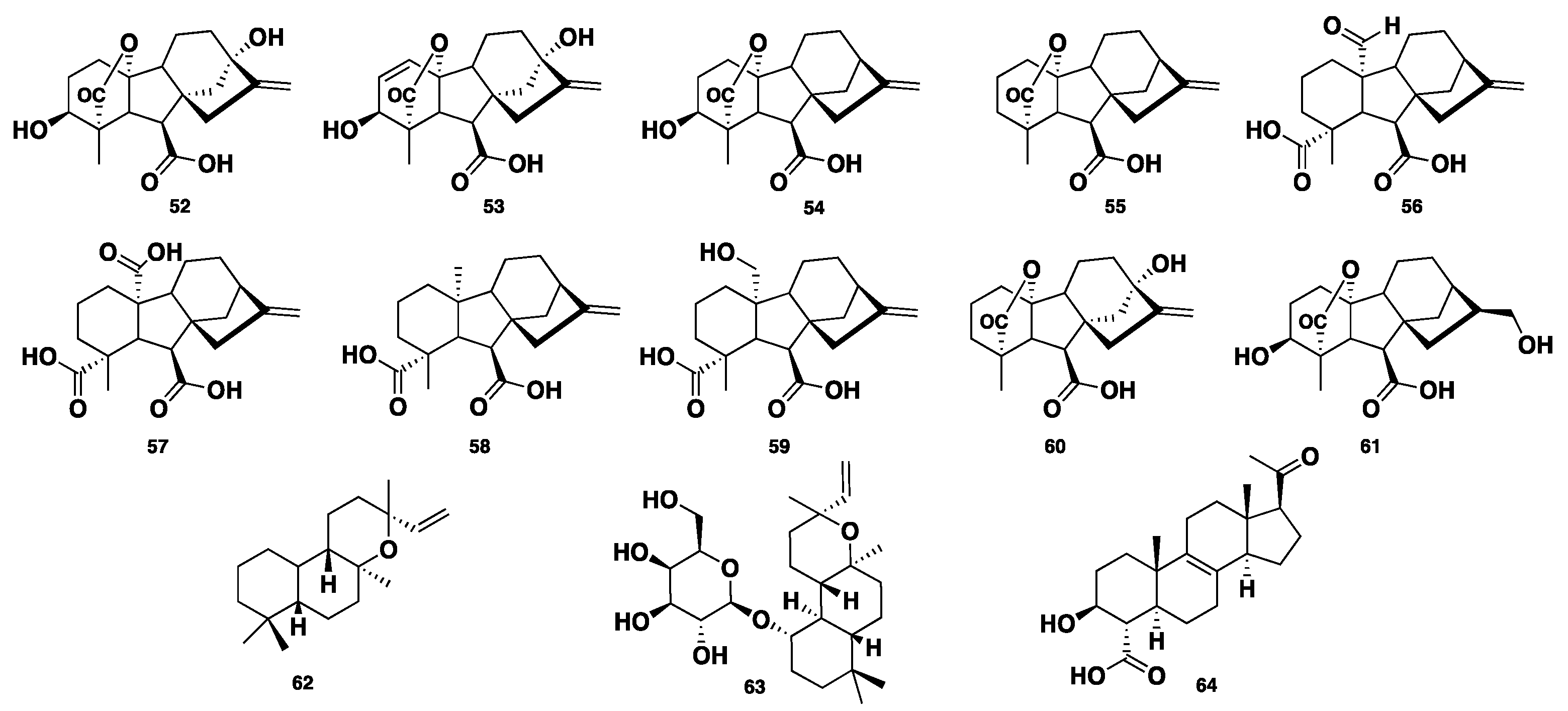
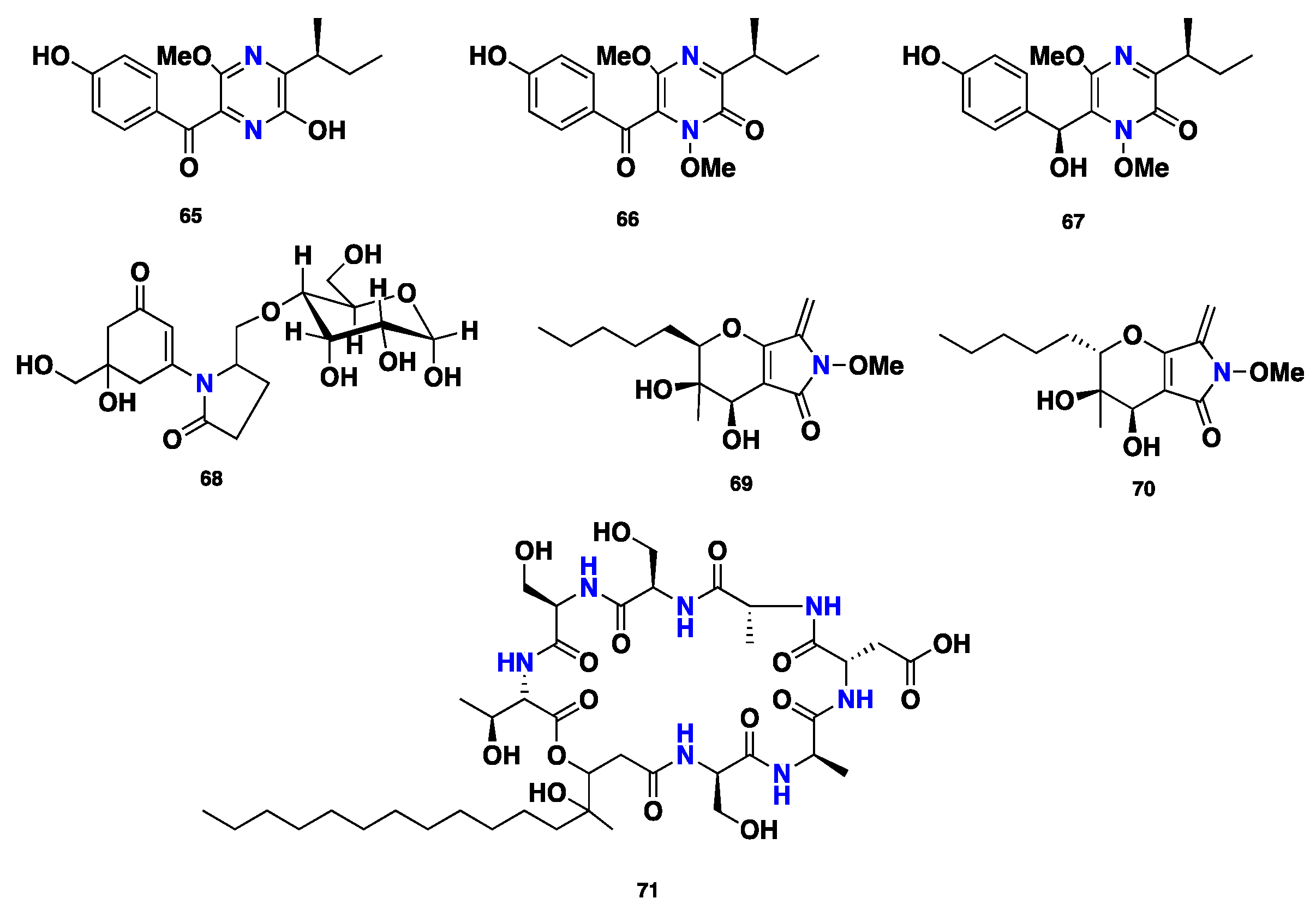
| Name | Class | Species | Biological Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spartinol A–D (1–4) | Polyketide | P. spartinae | Cytotoxic | [15] |
| Spartinoxide (5) | Polyketide | P. spartinae | Cytotoxic | [16] |
| Furanospartinol (6) | Polyketide | P. spartinae | Antimicrobial, cytotoxic | [17] |
| Pyranospartinol (7) | Polyketide | P. spartinae | Antimicrobial, cytotoxic | [17] |
| Phaeosphenone (8) | Polyketide | Phaeosphaeria sp. | Antifungal, antibacterial | [18] |
| 9–19 | Polyketide | Phaeosphaeria sp. | Cytotoxic, anti-tuberculosis | [19] |
| Rousselianone A (20) | Polyketide | P. rousseliana | Antibiotic | [20] |
| Rousselianone A’ (21) | Polyketide | P. rousseliana | No activity | [20] |
| Alternapyrones B–F (22–26) | Polyketide | P. nodorum | Cytotoxic, herbicidal | [21] |
| 27–35 | Polyketide | P. nodorum | No activity | [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29] |
| 36–37 | Polyketide | P. nodorum | No activity | [16] |
| 38–39 | Polyketide | Phaeosphaeria sp. | Antifungal | [30,31,32] |
| 40–51 | Polyketide | Phaeosphaeria sp. | Cytotoxic | [33] |
| 52–63 | Diterpene | Phaeosphaeria sp. | Antimicrobial | [34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41] |
| Spartopregnenolone (64) | Steroid | P. spartinae | No activity | [42] |
| 65–67 | Pyrazine alkaloid | P. nodorum | Antimicrobial | [43,44,45,46,47] |
| 68 | Pyrrolidone | P. nodorum | Phytotoxic | [48] |
| 69–70 | Pyrrolidone | P. avenaria | Antifungal, antibacterial | [49] |
| Phaeofungin (71) | Cyclic depsipeptide | Phaeosphaeria sp. | Antifungal, antibacterial | [50] |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Demerdash, A. Chemical Diversity and Biological Activities of Phaeosphaeria Fungi Genus: A Systematic Review. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4040130
El-Demerdash A. Chemical Diversity and Biological Activities of Phaeosphaeria Fungi Genus: A Systematic Review. Journal of Fungi. 2018; 4(4):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4040130
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Demerdash, Amr. 2018. "Chemical Diversity and Biological Activities of Phaeosphaeria Fungi Genus: A Systematic Review" Journal of Fungi 4, no. 4: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4040130
APA StyleEl-Demerdash, A. (2018). Chemical Diversity and Biological Activities of Phaeosphaeria Fungi Genus: A Systematic Review. Journal of Fungi, 4(4), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4040130