Advancements in Diagnosing Talaromycosis: Exploring Novel Strategies and Emerging Technologies
Abstract
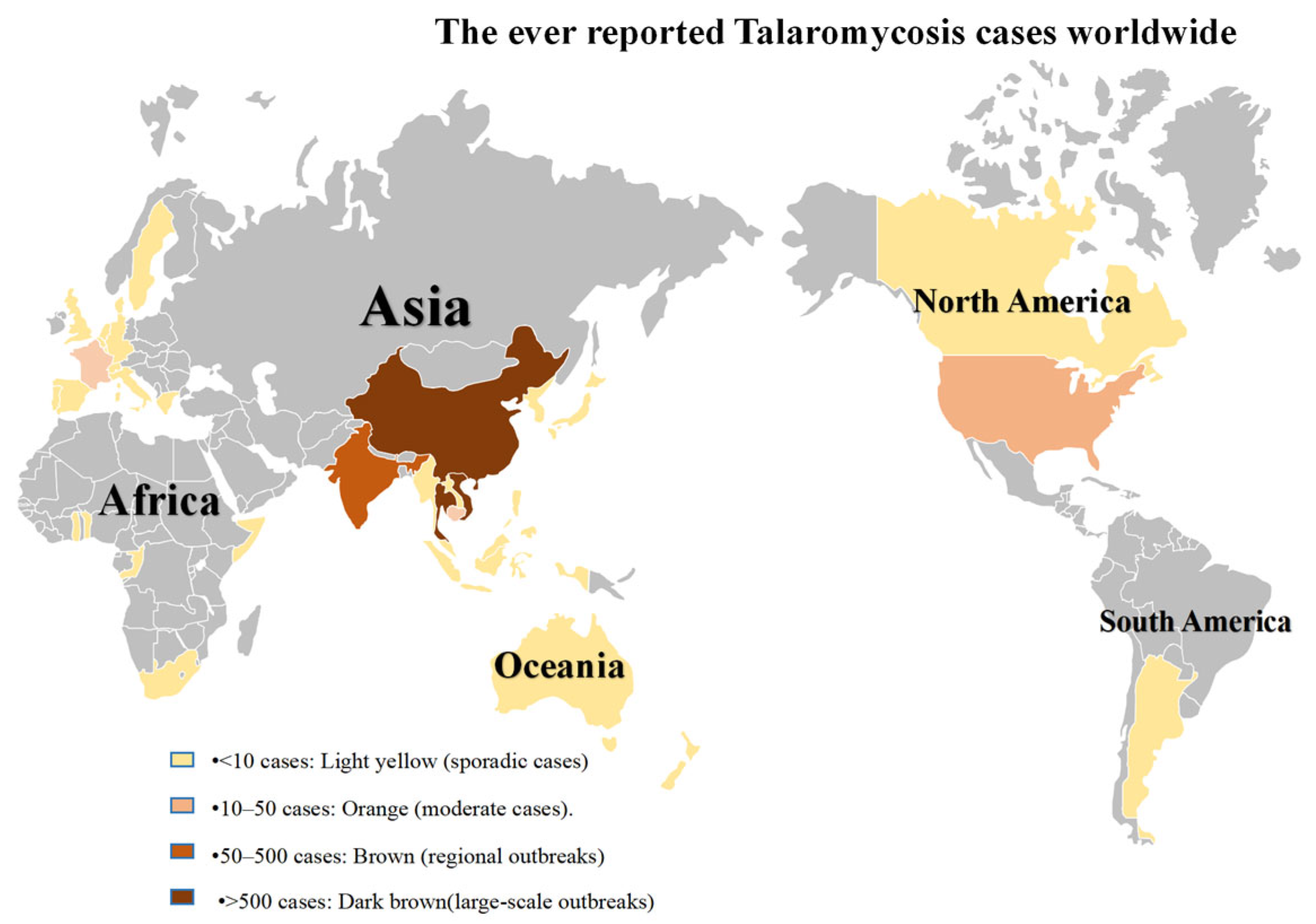
1. Introduction
2. Literature Search and Study-Selection Strategy
3. Current Diagnostic Methods: Strengths and Limitations
3.1. Histopathologic Visualization and Culture (The Gold Standard)
3.2. Serology Test
3.3. Molecular Detection
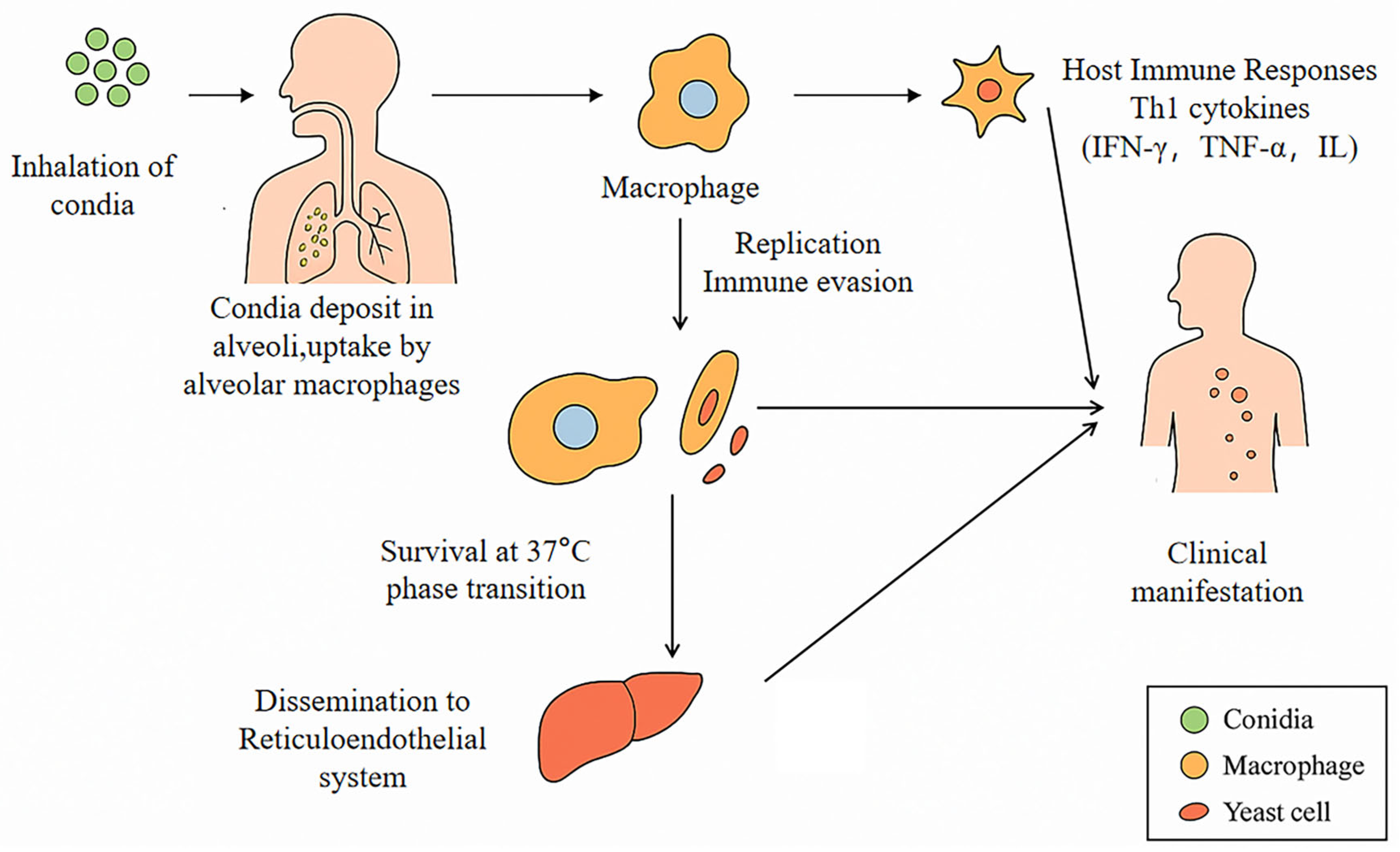
3.4. Immunity-Guided Predictive Diagnosis of T. marneffei
3.5. Emerging Strategies and Technologies
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TM | Talaromycosis |
| IA | Invasive Aspergillosis |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| mAbs | monoclonal antibodie |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| NGS | Next-Generation Sequencing |
| FFPE | Formalin-Fixed and Paraffin-Embedded |
| POCT | Point-of-Care-Testing |
| EIAs | Antigen-Detection Enzyme Immunoassays |
| IFN | Interferon |
| STAT1 | Signal Transducerand Activator of Transcription 1 |
| AARI | ALT/AST Ratio Index |
| POAL | Peripheral Or Abdominal Lymphadenopathy |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| GM | Galactomannan |
| OD | Optical Density |
| ICT | Immunochromatographic Strip Test |
| GNA | Galanthus Nivalis Agglutinin |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| AA | Arachidonic Acid |
References
- Le, T.; Wolbers, M.; Chi, N.H.; Quang, V.M.; Chinh, N.T.; Huong Lan, N.P.; Lam, P.S.; Kozal, M.J.; Shikuma, C.M.; Day, J.N.; et al. Epidemiology, Seasonality, and Predictors of Outcome of AIDS-Associated Penicillium marneffei Infection in Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Meng, S.; Huang, S.; Ruan, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, J.Z.; Wu, N.; Huang, J.; Xie, Z.; Liang, B.; et al. Effects of Talaromyces marneffei infection on mortality of HIV/AIDS patients in southern China: A retrospective cohort study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanasamy, S.; Dat, V.Q.; Thanh, N.T.; Ly, V.T.; Chan, J.F.-W.; Yuen, K.-Y.; Ning, C.; Liang, H.; Li, L.; Chowdhary, A.; et al. A global call for talaromycosis to be recognised as a neglected tropical disease. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e1618–e1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, L.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, J. Efficacy of different antifungal drugs as initial treatment for patients with talaromycosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Med. Mycol. 2021, 31, 101108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Han, R.; Chen, S. An Overlooked and Underrated Endemic Mycosis—Talaromycosis and the Pathogenic Fungus Talaromyces marneffei. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 36, e00051-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanittanakom, N.; Cooper, C.R., Jr.; Fisher, M.C.; Sirisanthana, T. Penicillium marneffei infection and recent advances in the epidemiology and molecular biology aspects. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.R.; Xu, N.L.; Lin, M.; Hu, X.L.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, Y.S.; Cai, S.X. Diffuse interstitial and multiple cavitary lung lesions due to Talaromyces marneffei infection in a non-HIV patient. New Microbes New Infect. 2015, 8, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Liao, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, X.; Tan, C.; Lu, D. Differences in clinical characteristics and prognosis of Penicilliosis among HIV-negative patients with or without underlying disease in Southern China: A retrospective study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Atallah, S.; Al-Shyoukh, A.; DaCunha, M.; Mizusawa, M. Localized Talaromyces marneffei infection presenting as a tonsillar mass mimicking malignancy. IDCases 2020, 21, e00824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ye, J.; Qiu, C.; Wang, L.; Jin, W.; Jiang, C.; Xu, L.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Rapid and precise diagnosis of T. marneffei pulmonary infection in a HIV-negative patient with autosomal-dominant STAT3 mutation: A case report. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2020, 14, 1753466620929225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.M.; Ai, J.W.; Xu, B.; Cui, P.; Cheng, Q.; Wu, H.; Qian, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.C.; Zhou, X.; Xing, L.; et al. Rapid and precise diagnosis of disseminated T. marneffei infection assisted by high-throughput sequencing of multifarious specimens in a HIV-negative patient: A case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supparatpinyo, K.; Khamwan, C.; Baosoung, V.; Sirisanthana, T.; Nelson, K.E. Disseminated Penicillium marneffei infection in Southeast Asia. Lancet 1994, 344, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Xi, L.; Chaturvedi, V. Talaromycosis (Penicilliosis) Due to Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei: Insights into the Clinical Trends of a Major Fungal Disease 60 Years After the Discovery of the Pathogen. Mycopathologia 2019, 184, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Geater, A.F.; Dai, J. Clinical Diagnostic Challenge in a Case of Disseminated Talaromyces marneffei Infection Misdiagnosed Initially as Pulmonary Tuberculosis: A Case Report and Literature Review. Infect. Drug Resist. 2024, 17, 3751–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawila, R.; Chaiwarith, R.; Supparatpinyo, K. Clinical and laboratory characteristics of penicilliosis marneffei among patients with and without HIV infection in Northern Thailand: A retrospective study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Yang, M.L.; Zhong, X.N.; He, Z.Y.; Liu, G.N.; Deng, J.M.; Li, M.H. A comparative analysis of the clinical and laboratory characteristics in disseminated penicilliosis marneffei in patients with and without human immunodeficiency virus infection. Chin. J. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2008, 31, 740–746. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Q.; Sheng, L.; Zhang, J.; Ye, J.; Zhou, J. Analysis of clinical characteristics and prognosis of talaromycosis (with or without human immunodeficiency virus) from a non-endemic area: A retrospective study. Infection 2022, 50, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Zhao, L.; Tan, C.; Chen, X.U.; Yang, Z.; Mo, W. A novel method of combining Periodic Acid Schiff staining with Wright-Giemsa staining to identify the pathogens Penicillium marneffei, Histoplasma capsulatum, Mucor and Leishmania donovani in bone marrow smears. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 1950–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, R.S.; Le, T.; Cai, W.P.; Li, Y.R.; Luo, C.B.; Cao, Y.; Wen, C.Y.; Wang, S.G.; Ou, X.; Chen, W.S.; et al. Clinical epidemiology and outcome of HIV-associated talaromycosis in Guangdong, China, during 2011–2017. HIV Med. 2020, 21, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianopoulos, A. Laboratory Maintenance and Growth of Talaromyces marneffei. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2020, 56, e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Li, L.; Tang, X. Advances in diagnosis and treatment of talaromycosis in patients with AIDS. Chin. Med. J. 2022, 135, 2687–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrese Estrada, J.; Stynen, D.; Van Cutsem, J.; Piérard-Franchimont, C.; Piérard, G.E. Immunohistochemical identification of Penicillium marneffei by monoclonal antibody. Int. J. Dermatol. 1992, 31, 410–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.T.; Hung, C.C.; Liao, C.H.; Sun, H.Y.; Chang, S.C.; Chen, Y.C. Detection of circulating galactomannan in serum samples for diagnosis of Penicillium marneffei infection and cryptococcosis among patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2858–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, F.; Mo, D.; Liang, G.; Yan, R.; Khader, J.A.; Wu, N.; Cao, C. Evaluation of quantitative real-time PCR and Platelia galactomannan assays for the diagnosis of disseminated Talaromyces marneffei infection. Med. Mycol. 2020, 58, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanittanakom, N.; Mekaprateep, M.; Sittisombut, N.; Supparatpinyo, K.; Kanjanasthiti, P.; Nelson, K.E.; Sirisanthana, T. Western immunoblot analysis of protein antigens of Penicillium marneffei. J. Med. Vet. Mycol. 1997, 35, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chongtrakool, P.; Chaiyaroj, S.C.; Vithayasai, V.; Trawatcharegon, S.; Teanpaisan, R.; Kalnawakul, S.; Sirisinha, S. Immunoreactivity of a 38-kilodalton Penicillium marneffei antigen with human immunodeficiency virus-positive sera. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 2220–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeavons, L.; Hamilton, A.J.; Vanittanakom, N.; Ungpakorn, R.; Evans, E.G.; Sirisanthana, T.; Hay, R.J. Identification and purification of specific Penicillium marneffei antigens and their recognition by human immune sera. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruksaphon, K.; Intaramat, A.; Simsiriwong, P.; Mongkolsu, S.; Ratanabanangkoon, K.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Kaltsas, A.; Youngchim, S. An inexpensive point-of-care immunochromatographic test for Talaromyces marneffei infection based on the yeast phase specific monoclonal antibody 4D1 and Galanthus nivalis agglutinin. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Chan, C.M.; Lee, C.; Wong, S.S.; Yuen, K.Y. MP1 encodes an abundant and highly antigenic cell wall mannoprotein in the pathogenic fungus Penicillium marneffei. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ou, X.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Guo, P.; Chen, X.; Cai, W.; Tang, X.; Li, L. Talaromyces marneffei Mp1p Antigen Detection may Play an Important Role in the Early Diagnosis of Talaromycosis in Patients with Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. Mycopathologia 2022, 187, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Xu, H.F.; Han, Z.G.; Zeng, L.; Liang, C.Y.; Chen, X.J.; Chen, Y.J.; Cai, J.P.; Hao, W.; Chan, J.F.; et al. Serological surveillance for Penicillium marneffei infection in HIV-infected patients during 2004–2011 in Guangzhou, China. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.F.; Cai, J.P.; Wang, Y.D.; Dong, H.; Hao, W.; Jiang, L.X.; Long, J.; Chan, C.; Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; et al. Immunoassays based on Penicillium marneffei Mp1p derived from Pichia pastoris expression system for diagnosis of penicilliosis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thu, N.T.M.; Chan, J.F.W.; Ly, V.T.; Ngo, H.T.; Hien, H.T.A.; Lan, N.P.H.; Chau, N.V.V.; Cai, J.-P.; Woo, P.C.Y.; Day, J.N.; et al. Superiority of a Novel Mp1p Antigen Detection Enzyme Immunoassay Compared to Standard BACTEC Blood Culture in the Diagnosis of Talaromycosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 73, e330–e336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Gui, X.; Cao, Q.; Yang, R.; Yan, Y.; Deng, L.; Lio, J. A Clinical Study of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome Associated Penicillium marneffei Infection from a Non-Endemic Area in China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakit, K.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Pruksaphon, K.; Vanittanakom, N.; Youngchim, S. A novel inhibition ELISA for the detection and monitoring of Penicillium marneffei antigen in human serum. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.; Lai, J.; Wei, W.; Zhou, B.; Huang, J.; Jiang, J.; Liang, B.; Liao, Y.; Zang, N.; Cao, C.; et al. Accuracy of rapid diagnosis of Talaromyces marneffei: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Li, X.; Calderone, R.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J.; Cai, W.; Xi, L. Whole blood Nested PCR and Real-time PCR amplification of Talaromyces marneffei specific DNA for diagnosis. Med. Mycol. 2016, 54, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Najafzadeh, M.J.; Zhang, J.; Vicente, V.A.; Xi, L.; de Hoog, G.S. Molecular identification of Penicillium marneffei using rolling circle amplification. Mycoses 2011, 54, e751–e759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongpom, M.; Sirisanthana, T.; Vanittanakom, N. Application of nested PCR to detect Penicillium marneffei in serum samples. Med. Mycol. 2009, 47, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hien, H.T.A.; Thanh, T.T.; Thu, N.T.M.; Nguyen, A.; Thanh, N.T.; Lan, N.P.; Simmons, C.; Shikuma, C.; Van Vinh Chau, N.; Thwaites, G.; et al. Development and evaluation of a real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for the rapid detection of Talaromyces marneffei MP1 gene in human plasma. Mycoses 2016, 59, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornprasert, S.; Praparattanapan, J.; Khamwan, C.; Pawichai, S.; Pimsarn, P.; Samleerat, T.; Leechanachai, P.; Supparatpinyo, K. Development of TaqMan real-time polymerase chain reaction for the detection and identification of Penicillium marneffei. Mycoses 2009, 52, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, C.C.; Teng, J.L.L.; Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y. Rapid Genomic Diagnosis of Fungal Infections in the Age of Next-Generation Sequencing. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wen, Y. Gastrointestinal manifestations of Talaromyces marneffei infection in an HIV-infected patient rapidly verified by metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Chang, Q.; Pan, P.; Zhang, Y. Clinical Characteristics, Laboratory Findings, and Prognosis in Patients with Talaromyces marneffei Infection Across Various Immune Statuses. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 841674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Xu, J. Disseminated Talaromyces marneffei infection after renal transplantation: A case report and literature review. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1115268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.R.; Naccache, S.N.; Samayoa, E.; Biagtan, M.; Bashir, H.; Yu, G.; Salamat, S.M.; Somasekar, S.; Federman, S.; Miller, S.; et al. Actionable diagnosis of neuroleptospirosis by next-generation sequencing. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2408–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Feng, J. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing for mixed pulmonary infection diagnosis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y. Clinical performance of metagenomic next-generation sequencing for diagnosis of invasive fungal disease after hematopoietic cell transplant. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1210857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, P.; Zhang, H.C.; Wu, H.L.; Ye, M.Z.; Zhu, Y.M.; Ai, J.W.; Zhang, W.H. Clinical application and evaluation of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in suspected adult central nervous system infection. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consensus Group of Experts on Application of Metagenomic Next Generation Sequencing in the Pathogen Diagnosis in Clinical Moderate and Severe Infections; Professional Committee of Sepsis and Shock Chinese Research Hospital Association; Professional Committee of Microbial Toxins Chinese Society for Microbiology; Professional Committee of Critical Care Medicine Shenzhen Medical Association. Expert consensus for the application of metagenomic next generation sequencing in the pathogen diagnosis in clinical moderate and severe infections (first edition). Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2020, 32, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Guo, J.; Chen, R.; Hu, L.; Xia, Q.; Wu, W.; Wang, J.; Hu, F. Multicenter evaluation of three different MALDI-TOF MS systems for identification of clinically relevant filamentous fungi. Med. Mycol. 2021, 59, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, P.T.; de Bel, A.; Martiny, D.; Martiny, D.; Ranque, S.; Piarroux, R.; Cassagne, C.; Detandt, M.; Hendrickx, M. Identification of filamentous fungi isolates by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry: Clinical evaluation of an extended reference spectra library. Med. Mycol. 2014, 52, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Liu, M.; Huang, C.; Ma, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, W.; Guo, J.; Huang, J.; Xu, H. MALDI-TOF MS-Based Clustering and Antifungal Susceptibility Tests of Talaromyces marneffei Isolates from Fujian and Guangxi (China). Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 3449–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.K.; Lam, C.S.; Ngan, A.H.; Chow, W.N.; Wu, A.K.; Tsang, D.N.; Tse, C.W.; Que, T.L.; Tang, B.S.; Woo, P.C. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry for rapid identification of mold and yeast cultures of Penicillium marneffei. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.P.; Lao-Araya, M.; Yang, J.; Chan, K.W.; Ma, H.; Pei, L.C.; Kui, L.; Mao, H.; Yang, W.; Zhao, X.; et al. Application of Flow Cytometry in the Diagnostics Pipeline of Primary Immunodeficiencies Underlying Disseminated Talaromyces marneffei Infection in HIV-Negative Children. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Li, X.; Chen, T.; Liang, B.; Wei, W.; Meng, D.; Lin, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, P.; Jing, W.; et al. Predictive models for Talaromyces marneffei infection in HIV-infected patients using routinely collected data. Res. Sq. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, Y.; Chen, H.; Jiang, Z.; He, K.; Tian, Q.; Qin, Y.; Rao, M.; Harypursat, V.; et al. Multicentre derivation and validation of a prognostic scoring system for mortality assessment in HIV-infected patients with talaromycosis. Mycoses 2021, 64, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.K.; Mauger, J.; McGowan, K.L. Immunohistochemical detection of Aspergillus species in pediatric tissue samples. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 121, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piérard, G.E.; Arrese Estrada, J.; Piérard-Franchimont, C.; Thiry, A.; Stynen, D. Immunohistochemical expression of galactomannan in the cytoplasm of phagocytic cells during invasive aspergillosis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1991, 96, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, P.E.; Smedts, F.; Poot, T.; Bult, P.; Hoogkamp-Korstanje, J.A.; Meis, J.F. Immunoperoxidase staining for identification of Aspergillus species in routinely processed tissue sections. J. Clin. Pathol. 1996, 49, 798–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.; Scott-Thomas, A.; Lewis, J.G.; Bhatia, M.; MacPherson, S.A.; Zeng, Y.; Chambers, S.T. Monoclonal Antibodies and Invasive Aspergillosis: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolle, A.M.; Hasenberg, M.; Thornton, C.R.; Solouk-Saran, D.; Männ, L.; Weski, J.; Maurer, A.; Fischer, E.; Spycher, P.R.; Schibli, R.; et al. ImmunoPET/MR imaging allows specific detection of Aspergillus fumigatus lung infection in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1026–E1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, E.A.; Norris, P.C. Eicosanoid storm in infection and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, K.H.; Lam, W.H.; Zhang, H.; Ke, Y.H.; Tse, M.K.; Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Lau, C.C.Y.; Cai, J.P.; Tung, E.T.K.; et al. Talaromyces marneffei Mp1p Is a Virulence Factor that Binds and Sequesters a Key Proinflammatory Lipid to Dampen Host Innate Immune Response. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
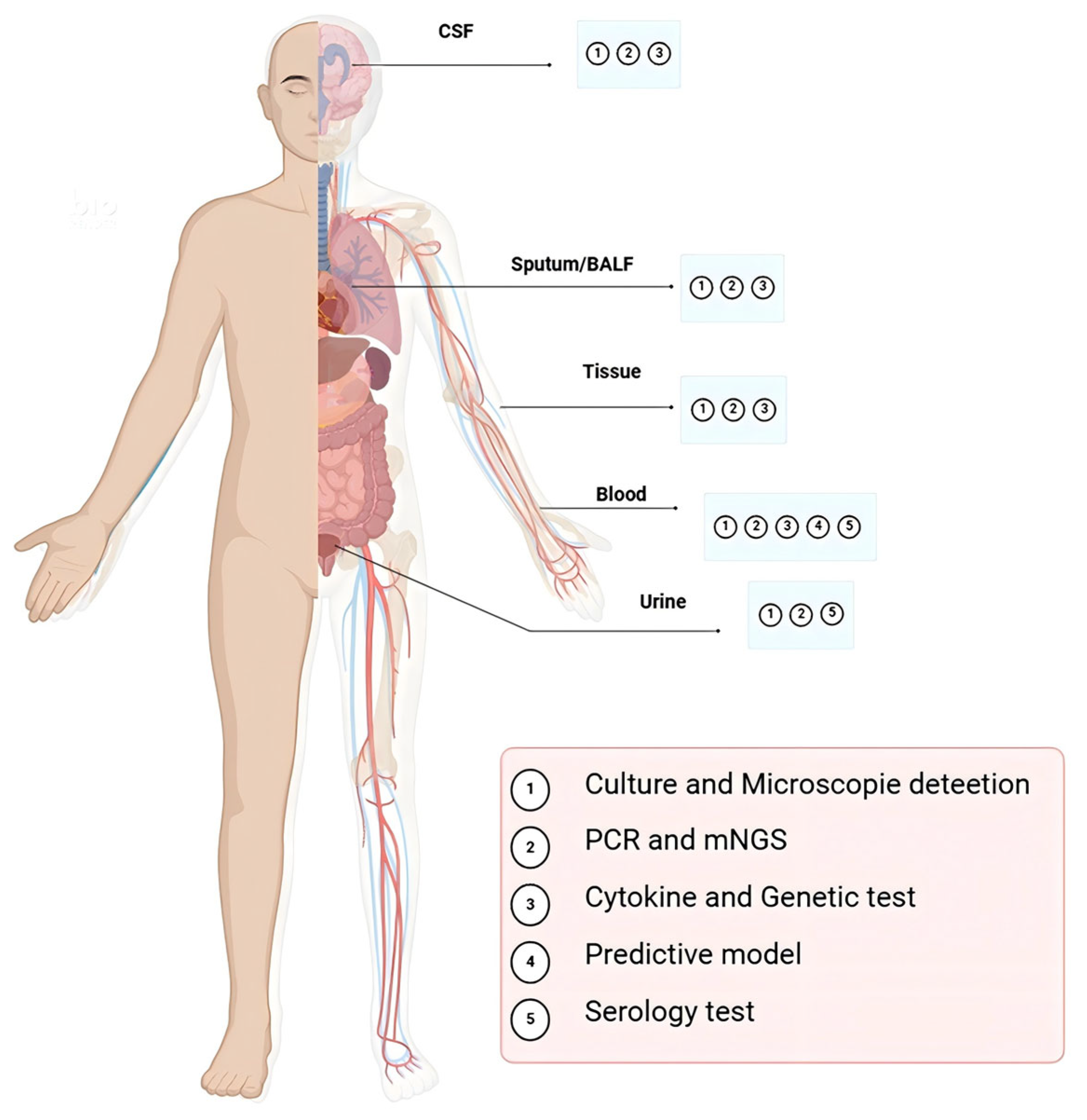
| Diagnosis Approach | Target | Advantage | Disadvantage | Turnaround Time | Approximate Cost | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Culture and microscopic detection | Blood, Skin, Bone marrow, and CSF a | Gold standard; Pathologic changes in the tissue; Morphology of the T. marneffei | Requires pure, uncontaminated fungal isolates for reliable results; Too slow, delays therapeutic intervention, and limited sensitivity(disseminated infection) | 7–14 days (up to 2–4 weeks) | Low | [16,19,20,21,22] |
| Serology test | Blood and Urine | Easily performed on readily accessible samples | False-negative in immunocompromised host | Hours to 1 day | Low | [4,23,24,28,29,30,31,32,33,34] |
| PCR and mNGS | Blood, Skin, Bone marrow, and CSF a | Various sample resources; Platform widely available; Rapid turnaround time | Lack of standardization; Contamination can be problematic | Within 1–2 days | High | [14,17,39,40,41] |
| Cytokine and Genetic test | IgM, IgG, IgA and IgE; IFN-α/γ; CD40L, STAT1/3 | Various sample resources; Rapid turnaround time | Lack of standardization; Unknown pathogen species; Unknown infection site | Within 1–2 days | Moderate | [3,57] |
| Predictive model | Age, AST/ALT ratio, Albumin levels, and BUN b levels | Predict the risk of death in patients with HIV with talaromycosis | Lack of standardization | Immediate (once labs available) | Low | [59] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xi, L.; Lu, S. Advancements in Diagnosing Talaromycosis: Exploring Novel Strategies and Emerging Technologies. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11060434
Wang Y, Wang X, Xi L, Lu S. Advancements in Diagnosing Talaromycosis: Exploring Novel Strategies and Emerging Technologies. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(6):434. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11060434
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yihui, Xiaoyue Wang, Liyan Xi, and Sha Lu. 2025. "Advancements in Diagnosing Talaromycosis: Exploring Novel Strategies and Emerging Technologies" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 6: 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11060434
APA StyleWang, Y., Wang, X., Xi, L., & Lu, S. (2025). Advancements in Diagnosing Talaromycosis: Exploring Novel Strategies and Emerging Technologies. Journal of Fungi, 11(6), 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11060434






