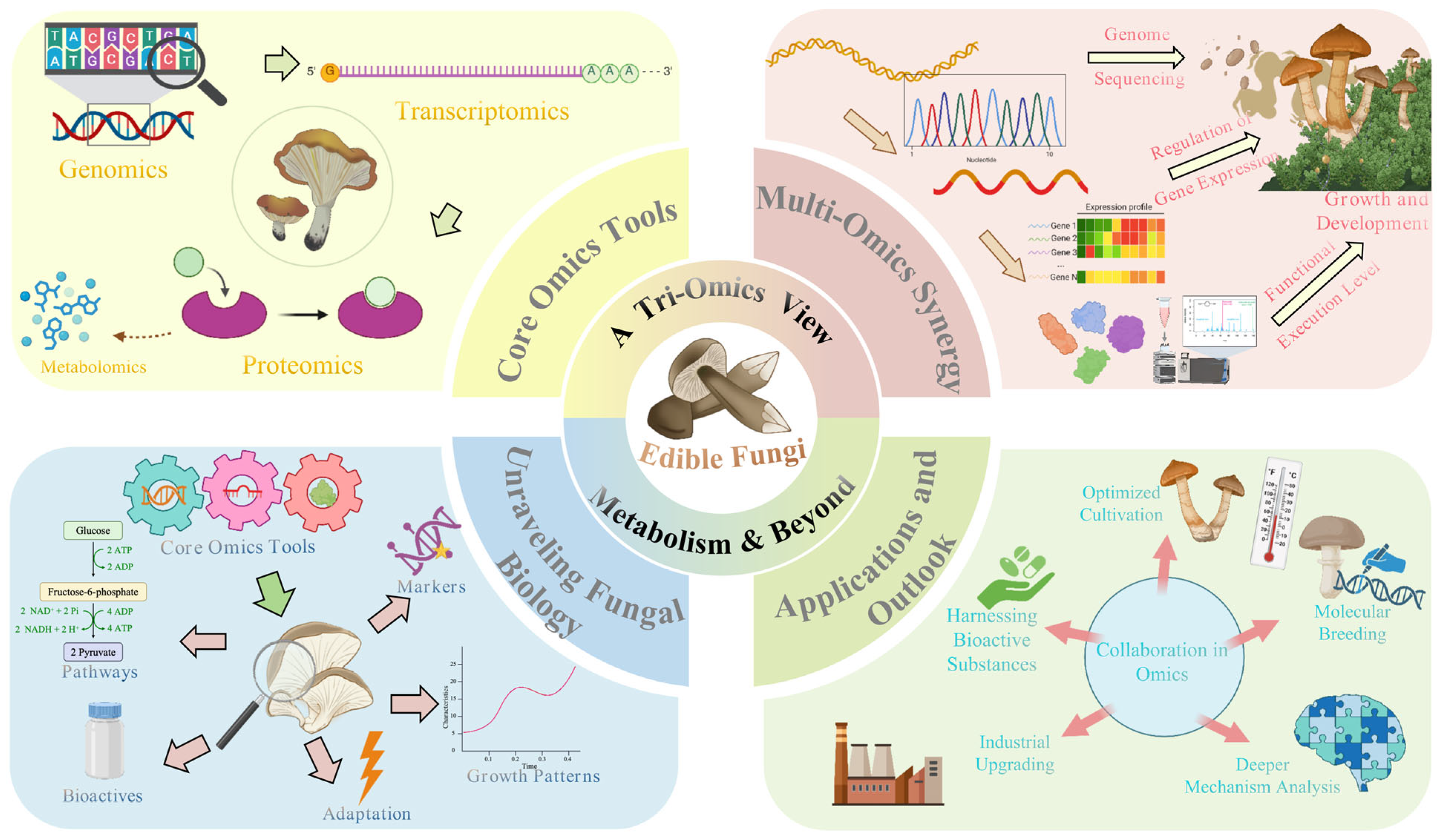
A Review of Genomic, Transcriptomic, and Proteomic Applications in Edible Fungi Biology: Current Status and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
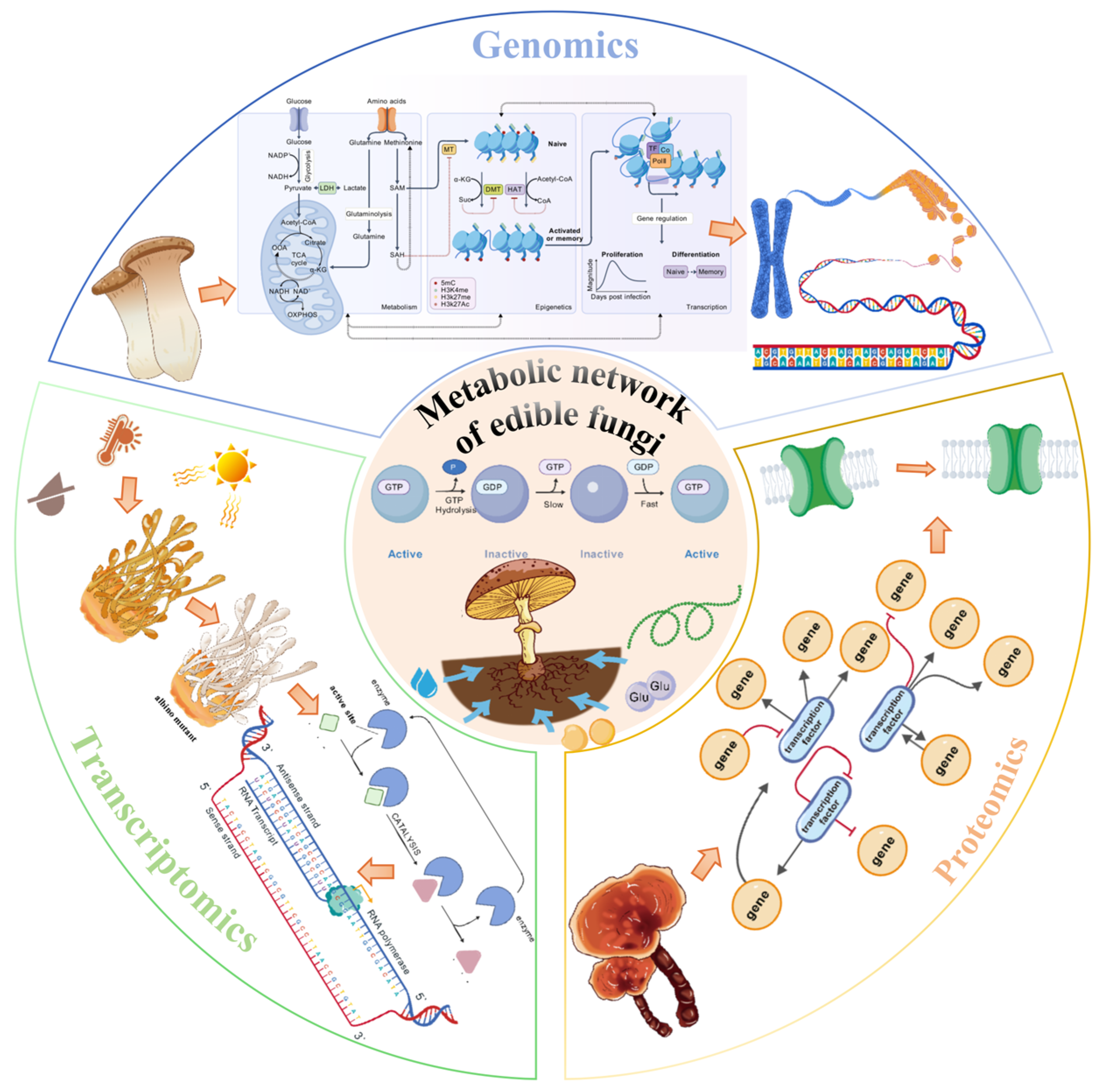
2. Genomics of Edible Fungi: Decoding the Genetic Basis of Metabolic Potential
2.1. Advances in Genome Sequencing Technology and Information Mining
2.2. Functional Annotation of Edible Fungi Genomes
2.2.1. Identification of Carbohydrate-Active enZymes (CAZymes)
2.2.2. Identification of Secondary Metabolism-Related Enzymes
2.2.3. Identification of Metabolic Regulatory Genes
2.2.4. Functional Annotation of the Mitochondrial Genome
2.3. Influence of Edible Fungi Genomic Features and Comparative Genomics on Metabolic Network Construction
2.3.1. Gene Fusion and Metabolic Pathway Evolution
2.3.2. Gene Clusters (SMGCs) and Coordinated Regulation of Secondary Metabolite Synthesis
2.3.3. Gene Family Expansion/Contraction and Metabolic Diversity/Adaptability
2.3.4. Impact of Genetic and Epigenetic Variation on Metabolic Network Regulation
3. Transcriptomic Analysis: Revealing the Dynamic Expression Profile of Metabolic Activities
3.1. Principles, Technologies, and Basic Applications of Transcriptome Sequencing in Edible Fungi Research
3.2. Changes in Gene Expression Profiles Reveal Dynamic Metabolic Regulation
3.2.1. Transcriptional Dynamics and Metabolic Adaptation Across Life Cycles and Tissue Specificity
3.2.2. Environmental Regulation of Transcription and Metabolic Remodeling
3.2.3. Differential Gene Expression Between Strains/Varieties and Comparison of Metabolic Capabilities
4. Proteomic Research: Directly Addressing the Functional Execution Level of Metabolism
4.1. Overview of Proteomic Research Methods
4.2. Protein Expression Abundance and Functional Characterization in Metabolic Analysis
4.2.1. Protein-Level Analysis and Functional Confirmation of Important Enzymes
4.2.2. Global Proteome Responses and Metabolic Correlations Under Different Physiological States
5. Integrative Omics Analysis: Towards a Systems Understanding of Edible Fungi Metabolic Networks
5.1. Examples of Integrated Analysis of Key Metabolic Pathways and Biological Processes
5.1.1. Integrative Analysis of Bioactive Substance Biosynthetic Pathways
5.1.2. Integrated Regulation of Fruiting Body Development and Differentiation
5.1.3. Systematic Analysis of Stress Response Mechanisms
5.1.4. Association Between Optimized Cultivation Conditions and Quality Attributes
5.2. Challenges and Methods of Integrative Analysis
6. Summary
7. Future Directions, Challenges, and Translational Potential
7.1. Translating Omics Discoveries into Applications
7.2. Persistent Challenges and Untapped Potential
7.3. Concluding Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boa, E. Wild Edible Fungi: A Global Overview of Their Use and Importance to People; Non-Wood Forest Products: Rome, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.-C.; Yang, Z.-L.; Cui, B.-K.; Yu, C.-J.; Zhou, L.-W. Species Diversity and Utilization of Medicinal Mushrooms and Fungi in China (Review). Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2009, 11, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-R.; Xiong, H.-K.; Xue, W.T. Research progress on the composition and functional activity of truffles. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2017, 38, 341–345+352. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.W.; Pan, S.-H. Research Advancement of Cordyceps militaris. Asia-Pac. Tradit. Med. 2008, 4, 148–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, Z.; Qian, Z.-M.; Li, W.J.; Yang, F.Q.; Chen, S.L.; Li, E.-W. Recent advances in the analysis of nucleosides in Chinese cordyceps. Mycosystema 2016, 35, 388–403. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.-J.; Lee, T.-H.; Tang, F.-Y.; Zheng, B.-S.; Jiang, Z.-D. Extraction and Contents Determination of Polysaccharide in Cordyceps guangdongensis. J. South China Agric. Univ. 2009, 30, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Z.-M.; Li, W.-Q.; Sun, M.-T.; Liu, X.-Z.; Li, E.-W.; Li, W.-J. Analysis of chemical compounds in Chinese cordyceps. Mycosystema 2016, 35, 476–490. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Hou, C.-L.; Wei, L.; Sun, J.; Fan, L. Antioxidant activities of extracts and sub-fractions from Tuber indicum. Mycosystema 2010, 29, 569–575. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.-M.; Du, X.-F.; Li, X.-J.; Li, S.-Y. Study on inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis in BGC-823 cell by cordycep militaris. Chin. J. Microecol. 2009, 21, 118–121. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.-W.; Wang, Y.-B.; Zhao, X.-F.; Dou, Y.-P. Antibacterial Activity of Fermentation Broth by Cordyceps sinensis and Cordyceps militaris. J. Microbiol. 2008, 28, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.-Y.; Shao, W.-P. Determination of nutritive components of eight edible fungi. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2003, 38, 336–339+345. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G. Nutritional Component of Einght Species of Fungi of Basidiomycetes. J. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2000, 19, 173–176. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.-N.; Yuan, Y.; Liao, X.; Wang, L.-Y.; Shi, F.; Ming, J. Research advance on antioxidant active composition and antioxidant mechanisms of edible fungi. Food Mach. 2016, 32, 207–211. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.-X.; Wang, W.-L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, F.-C.; Zheng, X.-F. Advance in Antitumor Mechanism of Bioactive Compounds in Edible Mushrooms. Biotechnol. Bull. 2015, 31, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, J.; Wang, A.; Shi, C.; Zhuo, L.-J.; Xie, Y.-Z.; Li, W.-Z.; Hu, H.-P. Advance Research on Hypoglycemic Effect of Edible Fungi in China. Edible Fungi China 2020, 39, 1–7+15. [Google Scholar]
- Arshadi, N.; Nouri, H.; Moghimi, H. Increasing the production of the bioactive compounds in medicinal mushrooms: An omics perspective. Microb. Cell Factories 2023, 22, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.-J.; Lyu, J.; Yu, C.-Q.; Sun, D.-J.Y.; Li, L.-M. A multi-omics approach to investigate the etiology of non-communicable diseases:recent advance and applications. Chin. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Zeng, Y.-L.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.-J. Multiomics Studies Facilitate Stroke Drug Development. Chin. J. Stroke 2022, 17, 213–215. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.-Q.; Gao, Q. Multi-omics molecular subgrouping of hepatocellular carcinoma and its application in precision diagnosis and treatment. J. Clin. Hepatol. 2022, 38, 510–514. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Miao, R.; Lin, J.; Feng, R.; Ni, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, D.; Zhao, X. Application of omics technology in the research on edible fungi. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velculescu, V.E.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, W.; Vogelstein, J.; Basrai, M.A.; Bassett, D.E., Jr.; Hieter, P.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. Characterization of the Yeast Transcriptome. Cell 1997, 88, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Dang, Y.; Li, X.-Y.; Wang, X.-L. Proteomics and the development of Proteomics Techniques. Lett. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Obaidi, J.R. Proteomics of edible mushrooms: A mini-review. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.-H.; Fu, Y.-P.; Xiao, S.-J.; Li, C.-T.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Research progress on mushroom phenotyping. Mycosystema 2021, 40, 721–742. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, G.K.; Sarkar, A.; Righetti, P.G.; Pedreschi, R.; Carpentier, S.; Wang, T.; Barkla, B.J.; Kohli, A.; Ndimba, B.K.; Bykova, N.V.; et al. A decade of plant proteomics and mass spectrometry: Translation of technical advancements to food security and safety issues. Mass. Spectrom. Rev. 2013, 32, 335–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, L.; Zhao, R.-H.; Yu, C.-X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.-J.; Chen, M.-J. Proteomics and Its Advance in Edible Fungi. Mol. Plant Breed. 2017, 15, 2656–2661. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.-L. Research progress of omics analysis techniques in edible fungi. China Food Saf. Mag. 2021, 13, 176–177. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.-J.; Hu, B.; Xu, Z.-X.; Zheng, S.-Y.; Wang, C.-X. Research Progress on Transcriptome of Edible Fungi Under Adversity Stress. North. Hortic. 2022, 6, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Li, Y.; Song, X.; Tang, L.; Li, C.; Tan, Q.; Bao, D. The complete mitochondrial genome of the widely cultivated edible fungus Lentinula edodes. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2017, 2, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, N.; Qin, L. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Comparative Genomics Analysis of the Wild Edible Mushroom (Gomphus purpuraceus) Provide Insights into Its Potential Food Application and Artificial Domestication. Genes 2022, 13, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.-W.; Chi, Y.-J. Cloning and Bioinformatics Analysis of Mn P1 cDNA Gene from Hericium erinaceum. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2015, 51, 68–77. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Guo, M.; Yang, H.; Guo, S.; Dong, C. The blue-light receptor CmWC-1 mediates fruit body development and secondary metabolism in Cordyceps militaris. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katrolia, P.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Kopparapu, N.K.; Zheng, X. Gene cloning, expression and homology modeling of first fibrinolytic enzyme from mushroom (Cordyceps militaris). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D.K.; Rühl, M.; Mishra, B.; Kleofas, V.; Hofrichter, M.; Herzog, R.; Pecyna, M.J.; Sharma, R.; Kellner, H.; Hennicke, F.; et al. The genome sequence of the commercially cultivated mushroom Agrocybe aegerita reveals a conserved repertoire of fruiting-related genes and a versatile suite of biopolymer-degrading enzymes. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Deng, W.; Yan, W.; Li, T. Whole Genome Sequence of an Edible and Potential Medicinal Fungus, Cordyceps guangdongensis. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genet. 2018, 8, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vongsangnak, W.; Raethong, N.; Mujchariyakul, W.; Nguyen, N.N.; Leong, H.W.; Laoteng, K. Genome-scale metabolic network of Cordyceps militaris useful for comparative analysis of entomopathogenic fungi. Gene 2017, 626, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, G.J.; Nodwell, J.R. Chromosome level assembly and secondary metabolite potential of the parasitic fungus Cordyceps militaris. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, P.; Xia, Y.; Xiao, G.; Xiong, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Genome sequence of the insect pathogenic fungus Cordyceps militaris, a valued traditional chinese medicine. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Yin, J.; Zhang, B.; Li, Z.; Zhao, S.; Gui, Z. Genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation in subcultured Cordyceps militaris. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 201, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Long, S.; Wu, X.; Feng, B.; Qin, S.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; et al. Genome, transcriptome, and metabolome analyses provide new insights into the resource development in an edible fungus Dictyophora indusiata. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1137159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.W.; Im, J.H.; Kong, W.S.; Park, Y.J. Comparative Analysis of Carbohydrate Active Enzymes in the Flammulina velutipes var. lupinicola Genome. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Gong, J.; Dai, W.; Kang, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, H.-M.; Liu, W.; Liu, L.; Ma, J.; Xia, Z.; et al. The Genome of Ganderma lucidum Provide Insights into Triterpense Biosynthesis and Wood Degradation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36146. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; Hu, H.; Cai, M.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Xiao, C.; Chen, S.; et al. Whole-genome assembly of Ganoderma leucocontextum (Ganodermataceae, Fungi) discovered from the Tibetan Plateau of China. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genet. 2021, 11, jkab337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.-L.; Xu, X.-L.; Chen, T.-Q.; Shi, L.-C.; Miao, X.-Q.; Lan, J. The Analysis of Whole-genome Resequencing of Ganoderma lucidum Originated from South Korea. Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. Mater. Medica-World Sci. Technol. 2019, 21, 764–774. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, W.; Wang, Y.; Xie, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Peng, Y. Whole genome sequence of an edible and medicinal mushroom, Hericium erinaceus (Basidiomycota, Fungi). Genomics 2020, 112, 2393–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Cheng, X.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Nong, W.; Bian, Y.; Cheung, M.K.; Kwan, H.S. Population genomic analysis uncovers environmental stress-driven selection and adaptation of Lentinula edodes population in China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, Y.; Nakade, K.; Yoshida, K.; Natsume, S.; Miyazaki, K.; Sato, S.; van Peer, A.F.; Konno, N. Grouping of multicopper oxidases in Lentinula edodes by sequence similarities and expression patterns. AMB Express 2015, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Yang, W.; Qiu, T.; Gao, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Cui, H.; Guo, L.; Yu, H.; Yu, H. Complete genome sequences and comparative secretomic analysis for the industrially cultivated edible mushroom Lyophyllum decastes reveals insights on evolution and lignocellulose degradation potential. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1137162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, L.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Bian, Y. Opposite Polarity Monospore Genome De Novo Sequencing and Comparative Analysis Reveal the Possible Heterothallic Life Cycle of Morchella importuna. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Qingshan, W.; Baiyintala, W. The whole-genome sequence analysis of Morchella sextelata. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15376. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, R.; Zhang, J.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, G.; Li, M.; Wu, P.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, C.; Qin, Q. A New High-Quality Draft Genome Assembly of the Chinese Cordyceps Ophiocordyceps sinensis. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Gao, X.; Zhang, M.; Hu, C.; Yang, W.; Guo, L.; Yang, S.; Yu, H.; Yu, H. Whole Genome Sequence of an Edible Mushroom Oudemansiella raphanipes (Changgengu). J. Fungi 2023, 9, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, M.; Sun, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Song, C.; Shang, X.; Tan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yu, H. Whole-genome sequence of a high-temperature edible mushroom Pleurotus giganteus (zhudugu). Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 941889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.; Ma, L.; Yang, C.; Ying, Z.; Jiang, X.; Lin, Y.Q. De Novo Sequencing of a Sparassis latifolia Genome and Its Associated Comparative Analyses. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 2018, 1857170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, S.; Hu, C.; Mao, C.; Guo, L.; Yu, H.; Yu, H. Whole Genome Sequence of an Edible Mushroom Stropharia rugosoannulata (Daqiugaigu). J. Fungi 2022, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Bae, E.-K.; Hue, Y.; Choi, B.; Kang, M.-J.; Park, E.-J.; Kim, K.-T. Comparative Genomics Reveals Species-Specific Genes and Symbiotic Adaptations in Tricholoma matsutake. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, D.; Gong, M.; Zheng, H.; Chen, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Jiang, J.; Wu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, G.; et al. Sequencing and Comparative Analysis of the Straw Mushroom (Volvariella volvacea) Genome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Yan, J.; Xie, B.; Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Liu, S.; Li, D.; Yang, Z.; Zeng, X.; Deng, Y.; et al. Genes encoding FAD-binding proteins in Volvariella volvacea exhibit differential expression in homokaryons and heterokaryons. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-Y.; Wang, R.-J.; Zhang, D.; Shang, X.-D.; Tan, Q. Analysis of genes related to lysine biosynthesis based on whole genome of Flammulina velutipes. Microbiol. China 2016, 43, 2225–2233. [Google Scholar]
- Kurata, A.; Fukuta, Y.; Mori, M.; Kishimoto, N.; Shirasaka, N. Draft Genome Sequence of the Basidiomycetous Fungus Flammulina velutipes TR19. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00505-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xu, J.; Liu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Nelson, D.R.; Zhou, S.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Guo, X.; Sun, Y.; et al. Genome sequence of the model medicinal mushroom Ganoderma lucidum. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Lan, J.; Liu, C. Complete Mitochondrial Genome of the Medicinal Mushroom Ganoderma lucidum. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, J.; Bao, D. The complete mitochondrial genome of the Basidiomycete edible fungus Pleurotus eryngii. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2016, 1, 772–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zeng, F.; Hon, C.C.; Zhang, Y.; Leung, F.C.C. The mitochondrial genome of the Basidiomycete fungus Pleurotus ostreatus (oyster mushroom). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 280, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wan, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Tang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhou, C.; Tan, Q.; Bao, D.; Yang, R. Three complete mitochondrial genomes of straw-rotting edible fungus Volvariella volvacea using next generation sequencing. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2018, 3, 1054–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Song, J.; Liang, J. The complete mitochondrial genome of a wild edible mushroom, Russula griseocarnosa. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2019, 4, 3368–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-R.; Zhang, J.-P.; He, Y.-R.; Chang, M.-C.; Meng, J.-L. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Coprinellus micaceus, a wild saprobic mushroom in China. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2021, 6, 1979–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wan, J.; Shang, J.-J.; Feng, Z.; Jin, Y.; Li, H.; Guo, T.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Bao, D.-P.; Zhang, M.; et al. The complete mitochondrial genome of the edible mushroom Grifola frondosa. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2022, 7, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.-N.; Huang, R.-M.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Tong, Z.-J.; Han, X.; Xie, L.-Y.; Xie, B.-G. Genome sequencing and assembly strategy analyses of Flammulina filiformis. Mycosystema 2018, 37, 1578–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.-N.; Huang, R.-M.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Xie, L.-Y.; Jiang, Y.-J.; Xie, B.-G. Sequence analyses of the rDNA structure of Flammulina filiformis. Mycosystema 2018, 37, 1620–1627. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, D.-P.; Zhao, G.-P.; Tan, Q.; Wang, S.-Y.; Chen, M.-J.; Zheng, H.-J.; Zhang, J.-S.; Zhu, Y.-Q.; Wang, H.; Kang, H.; et al. Draft Sequence of the Volvariella volvacea Genome. Acta Edulis Fungi 2010, 17, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, G.-D.; Gao, Q.; Luo, L.-H.; Wang, J.-Y.; Xu, J.-H.; Yin, Y. The Application of High-throughput Sequencing Technology in Plant and Animal Research. Sci. Sin. 2012, 42, 107–124. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Xiao, J. Genome resequencing and transcriptome analysis reveal the molecular mechanism of albinism in Cordyceps militaris. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1153153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhong, H.; Long, X.; Xu, R.; Gong, Y.; Bian, Y.; Zhou, Y. The T-DNA integration characteristics of monokaryotic mutant library in Lentinula edodes. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 314, 111955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Xie, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Y. A Resequencing-Based Ultradense Genetic Map of Hericium erinaceus for Anchoring Genome Sequences and Identifying Genetic Loci Associated with Monokaryon Growth. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, L.; Shang, X.; Peng, B.; Li, Y.; Xiao, S.; Tan, Q.; Fu, Y. Chromosomal genome and population genetic analyses to reveal genetic architecture, breeding history and genes related to cadmium accumulation in Lentinula edodes. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Xie, L.-Y.; Li, Y.-N.; Ma, X.-B.; Yang, H.; Wang, M.; Xie, B.-G. Identification of exogenous DNA insertion site of transformants in Flammulina filiformis using matrix design. Mycosystema 2020, 39, 983–992. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.-L.; Guo, Y.-S.; Yang, D.-G.; Li, L.-W. The Research of Overview in Plant for Functional Genomics Techniques. J. Maize Sci. 2008, 16, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.-X.; Sun, Y.; Xu, P.-L.; Yi, Z.-B.; Du, J.-Z.; Sun, D.-Q. Research Progress in Functional Plant Genomics. Biotechnol. Bull. 2004, 1, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, F.-Y.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Shi, J.-J.; Qian, S.-J. Advances in Cellulase and Its Development Tendency. J. Microbiol. 2008, 28, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Gui, F.; Xie, B.; Deng, Y.; Sun, X.; Lin, M.; Tao, Y.; Li, S. Composition and Expression of Genes Encoding Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes in the Straw-Degrading Mushroom Volvariella volvacea. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58780. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Xu, B.; Li, J.; Huang, Z. Transcriptome analysis of Termitomyces albuminosus reveals the biodegradation of lignocellulose. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2012, 52, 466–477. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.-P.; Liao, J.-H.; Guo, Z.-J.; Cai, Z.-X.; Chen, M.-Y. Genome Survey and Transcriptome Analysis on Mycelia and Primordia of Agaricus blazei. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1824183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsis, T.; Efthimiadou, A.; Bacopoulou, F.; Vlachakis, D.; Eliopoulos, E. Transcription factors and evolution: An integral part of gene expression (Review). World Acad. Sci. J. 2020, 2, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, M.; Huang, C.; Wu, X. Genome-wide characterization of the Zn(II)2Cys6 zinc cluster-encoding gene family in Pleurotus ostreatus and expression analyses of this family during developmental stages and under heat stress. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, I.; Jeandriens, J.; Couvineau, A.; Sanmukh, S.; Latek, D. Signal Transduction by VIP and PACAP Receptors. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, H.; Li, C.; Xu, X.; Sun, C.; Song, J.; Shi, L.; He, L.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of the Ophiocordyceps sinensis fruiting body reveals putative genes involved in fruiting body development and cordycepin biosynthesis. Genomics 2014, 103, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Shi, L.; Yang, R.; Guo, H.; Zhang, S.; Geng, G. Transcriptome analysis of Auricularia fibrillifera fruit-body responses to drought stress and rehydration. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferstl, R.; Akdis, C.A.; O’Mahony, L. Histamine regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. Front. Biosci. 2012, 17, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.-M.; Hinsinger, D.D.; Jiang, G.-F. The complete mitochondrial genome of the Basidiomycete fungus Pleurotus cornucopiae (Paulet) Rolland. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2018, 3, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, K.M.I.; Rheu, K.M.; Kim, M.-S.; Cho, M.-G. The complete mitochondrial genome of an edible mushroom, Sparassis crispa. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2020, 5, 862–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, G.; Li, C.; Ling, J. Cordycepin and pentostatin biosynthesis gene identified through transcriptome and proteomics analysis of Cordyceps kyushuensis Kob. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 218, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.X.; Chen, M.Y.; Lu, Y.P.; Guo, Z.J.; Zeng, Z.H.; Liao, J.H.; Zeng, H. Metabolomics and transcriptomics unravel the mechanism of browning resistance in Agaricus bisporus. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0255765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.-K.; Lu, Y.-P.; Cai, Z.-X.; Guo, Z.-J.; Chen, M.-Y.; Liao, J.-H. Transcriptome Sequencing on SixAgaricus bisporusStrains at Four Developmental Stages. Fujian J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 34, 775–781. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, B.; Li, B.-J.; Guan, W.-Q.; Lin, Q. Transcriptome Sequencing of Agaricus bisporus and Mining of Genes Involved in Browning. Food Sci. 2019, 40, 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.-K.; Cai, Z.-X.; Guo, Z.-J.; Lu, Y.-P.; Chen, M.-Y.; Liao, J.-H.; Wang, Z.-S. Transcriptome Sequencing on Fruiting Body of Agaricus bisporus in Developing Stages. Fujian J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 33, 282–287. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.-P.; Guo, Z.-J.; Cai, Z.-X.; Chen, M.-Y.; Liao, J.-H. Transcriptome analysis of Agaricus blazei fruiting bodies at different developmental stages. Mycosystema 2019, 38, 2161–2173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, D.; Li, R.; Cheng, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wong, G.; Tang, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals relationship of three major domesticated varieties of Auricularia auricula-judae. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, L.; Fan, X.; Bian, Y. De Novo Assembly of Auricularia polytricha Transcriptome Using Illumina Sequencing for Gene Discovery and SSR Marker Identification. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, Z.; Yao, X.; Huang, Y.; Qu, Q.; Shi, X.; Zhang, H.; Shi, X. Identification of cordycepin biosynthesis-related genes through de novo transcriptome assembly and analysis in Cordyceps cicadae. R. Soc. Open. Sci. 2018, 5, 181247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, K.; Ma, B.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, A.; Chen, H. XRN1-associated long non-coding RNAs may contribute to fungal virulence and sexual development in entomopathogenic fungus Cordyceps militaris. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 3302–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.W.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, H.B.; Ye, Z.W.; Wei, T.; Lin, J.F.; Guo, L.Q. Transcriptome Analysis of Cordyceps militaris Reveals Genes Associated With Carotenoid Synthesis and Identification of the Function of the Cmtns Gene. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thananusak, R.; Laoteng, K.; Raethong, N.; Zhang, Y.; Vongsangnak, W. Metabolic Responses of Carotenoid and Cordycepin Biosynthetic Pathways in Cordyceps militaris under Light-Programming Exposure through Genome-Wide Transcriptional Analysis. Biology 2020, 9, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Xin, X.; Weng, Y.; Gui, Z. Transcriptome-wide analysis reveals the progress of Cordyceps militaris subculture degeneration. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, K.; Li, K.; Liu, G.; Dong, C. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Between a Spontaneous Albino Mutant and Its Sibling Strain of Cordyceps militaris in Response to Light Stress. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suparmin, A.; Kato, T.; Dohra, H.; Park, E.Y. Insight into cordycepin biosynthesis of Cordyceps militaris: Comparison between a liquid surface culture and a submerged culture through transcriptomic analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.-W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, J.-F.; Zhao, R.-Y.; Ye, Z.-W.; Guo, L.Q. Transcriptomic Analysis of Cordyceps militaris and Mining of Genes Involved in Carotenoid Biosynthesis. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 150–156. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.X.; Wei, T.; Xue, L.N.; Zheng, Q.W.; Ye, Z.W.; Zou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yun, F.; Guo, L.Q.; Lin, J.F. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Flexibility of Cordycepin Network in Cordyceps militaris Activated by L-Alanine Addition. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raethong, N.; Laoteng, K.; Vongsangnak, W. Uncovering global metabolic response to cordycepin production in Cordyceps militaris through transcriptome and genome-scale network-driven analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsa, B.; Raethong, N.; Chumnanpuen, P.; Wong-Ekkabut, J.; Laoteng, K.; Vongsangnak, W. Alternative metabolic routes in channeling xylose to cordycepin production of Cordyceps militaris identified by comparative transcriptome analysis. Genomics 2020, 112, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-H.; Wu, T.-H.; Ye, Z.-W.; Chen, B.-X.; Guo, L.-Q.; Lin, J.-F. The regulation network of cold-induced primordium formation in Flammulina filiformis based on transcriptome. Mycosystema 2020, 39, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.-B.; Xia, E.-H.; Li, M.; Cui, Y.-Y.; Wang, P.-M.; Zhang, J.-X.; Xie, B.-G.; Xu, J.-P.; Yan, J.-J.; Li, J.; et al. Transcriptome data reveal conserved patterns of fruiting body development and response to heat stress in the mushroom-forming fungus Flammulina filiformis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Chou, T.-S.; Liu, F.; Yan, J.-J.; Wu, T.-J.; Li, S.-J.; Xie, B.-G. Comparison of gene expression patterns between the monokaryotic and dikaryotic mycelia of Flammulina velutipes. Mycosystema 2015, 34, 683–693. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Wang, W.; Xie, B.-G. Comparison of Gene Expression Patterns in the Mycelium and Primordia of Flammulina velutipes, Strain 1123. Acta Edulis Fungi 2014, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, M.; Liang, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, H.; Xie, Y.; Chen, S.; Gao, X.; Li, X.; Xiao, C.; Chen, D.; et al. Transcriptional Dynamics of Genes Purportedly Involved in the Control of Meiosis, Carbohydrate, and Secondary Metabolism during Sporulation in Ganoderma lucidum. Genes 2021, 12, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Xu, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.; Zheng, H.; Gu, Z.; Li, Y.; Shi, G.; Ding, Z. Development of an Efficient Strategy to Improve Extracellular Polysaccharide Production of Ganoderma lucidum Using L-Phenylalanine as an Enhancer. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, B.-J.; Tien, N.; Lee, M.-H.; Bao, B.-Y.; Wu, Y.-S.; Hu, T.-C.; Lee, H.-Z. Induction of apoptosis and ganoderic acid biosynthesis by cAMP signaling in Ganoderma lucidum. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.-J.; Wang, M.; Huang, J.; Yin, Y.-L.; Chen, Y.-J.; Jiang, S.; Jin, Y.-X.; Lan, X.-Q.; Wong, B.H.C.; Liang, Y.; et al. Deep Insight into the Ganoderma lucidum by Comprehensive Analysis of Its Transcriptome. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.-Q.; Wu, T.-X.; Zhong, M.; Lu, H.-Y. Transcriptome Sequencing and Analysis of Grifola frondosa Mycelia. Food Sci. 2017, 38, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.-Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, J.-M. Comparative transcriptome analysis of dikaryotic mycelia and mature fruiting bodies in the edible mushroom Lentinula edodes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Park, Y.-J.; Jang, M.-J. Transcriptome analysis of the edible mushroom Lentinula edodes in response to blue light. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.-E.; Qiao, Y.-N.; Mao, J.-X.; Yang, Z.-S.; Zhang, L.-L.; Li, L.-Y. Comparative analyses of gene expression based on transcriptome data in different laccase activities of monokaryotic mycelia of Lentinula edodes. Mycosystema 2020, 39, 1162–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, R.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, H.; Xiang, Q.; Yu, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Penttinen, P.; et al. RNA-seq Profiling Showed Divergent Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes (CAZymes) Expression Patterns in Lentinula edodes at Brown Film Formation Stage Under Blue Light Induction. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.-i.; Lee, H.-Y.; Markkandan, K.; Moon, S.; Ahn, Y.J.; Ji, S.; Ko, J.; Kim, S.-J.; Ryu, H.; Hong, C.P. Comparative transcriptome analysis identified candidate genes involved in mycelium browning in Lentinula edodes. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Ding, L.; Niu, X.; Shan, H.; Song, L.; Xi, Y.; Feng, J.; Wei, S.; Liang, Q. Comparative transcriptome analysis on candidate genes associated with fruiting body growth and development in Lyophyllum decastes. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Ren, R.; Tang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, M.; Zhao, W.; He, Y.; Xu, J. Transcriptomics combined with metabolomics unveiled the key genes and metabolites of mycelium growth in Morchella importuna. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, e16288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, M.; Juan, J.; Feng, Z.; Chen, H. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals potential fruiting body formation mechanisms in Morchella importuna. AMB Express 2019, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Cai, Y.; He, P.; Chen, L.; Bian, Y. Comparative transcriptomics reveals potential genes involved in the vegetative growth of Morchella importuna. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-Q.; Ye, H.-L.; Liang, D.-W.; Liu, D.-Y.; Geng, F.; Li, X. De Novo Sequencing and Transcriptome Analysis of Morchella importuna Fruiting Body. Food Sci. 2018, 39, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, G.; Li, M.; Wu, P.; Shu, R.; Gao, X.; Guo, L.; et al. Transcriptomic analysis of the orchestrated molecular mechanisms underlying fruiting body initiation in Chinese cordyceps. Gene 2020, 763, 145061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-Q.; Tong, X.-X.; Tao, X.; Wang, Y.-X.; Peng, C.; Wang, S.-H.; Guo, J.-L. Study on bio-synthesis of cordycepin in Ophiocordyceps sinensis based on RNA-seq. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2017, 48, 4044–4050. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Chen, L.-D.; Ai, L.-Y.; Liu, Y.-C.; Yan, M.; Sun, S.-J. Comparative transcriptomics analyses of Pleurotus eryngii at different developmental stages. Mycosystema 2018, 37, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Sun, M.; Yu, M.; Xu, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Xu, T.; Qian, X.; Sun, S. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Function of a G-Protein α Subunit Gene in the Growth and Development of Pleurotus eryngii. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 69. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.; Gong, W.; Zhu, Z.; Yan, L.; Hu, Z.; Peng, Y. Comparative transcriptomics of Pleurotus eryngii reveals blue-light regulation of carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes) expression at primordium differentiated into fruiting body stage. Genomics 2018, 110, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.-P.; Liang, Y.; Dai, Y.-T.; Yang, C.-T.; Duan, M.-Z.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, S.-N.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Li, Y. De Novo Sequencing and Transcriptome Analysis of Pleurotus eryngii subsp. tuoliensis (Bailinggu) Mycelia in Response to Cold Stimulation. Molecules 2016, 21, 560. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, L.; Yan, K.; Dong, S.; Guo, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Chang, M.; Meng, J. Transcriptome Analysis Revealed That Hydrogen Peroxide-Regulated Oxidative Phosphorylation Plays an Important Role in the Formation of Pleurotus ostreatus Cap Color. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gao, W.; Wu, X.; Zhao, M.; Qu, J.; Huang, C.; Zhang, J. Genome-Wide Characterization and Expression Analyses of Pleurotus ostreatus MYB Transcription Factors during Developmental Stages and under Heat Stress Based on de novo Sequenced Genome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.-K.; Song, J.-L.; Lu, N.; Yuan, W.-D.; Yan, J.; Chen, G.-P. Cloning and expression of thePpFBD1 involved in primordium formation ofPleurotus pulmonarius. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2020, 32, 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Yang, C.; Wei, P.; Song, B.; Yang, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Li, Y. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Identified Candidate Genes Related to Bailinggu Mushroom Formation and Genetic Markers for Genetic Analyses and Breeding. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Ya Li mai mai ti, N.E.z.y.; Hu, Q.; Zou, Y.; Ye, D.; Zhang, H. A Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Physiological Maturation Properties of Mycelia in Pleurotus tuoliensis. Genes 2019, 10, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, C.-B.; Zhao, S.; Song, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y. Identification of Candidate Genes Related to the Development of Pleurotus tuoliensis Fruiting Bodies. Biotechnol. Bull. 2018, 34, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Ma, L.; Xiao, D.; Ying, Z.; Jiang, X.; Lin, Y. Integration of ATAC-Seq and RNA-Seq Identifies Key Genes in Light-Induced Primordia Formation of Sparassis latifolia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.-L.; Zhang, D.; Ma, L.; Wang, H.-Y.; Lin, Y.-S. Preliminary Study on Differentially Expressed Genes of Sparassis latifolia under Light Inducing. Edible Fungi China 2017, 36, 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.; Bai, J.; Zhuo, X.; Zhang, J.; Kuai, B.; Chen, H. Transcriptomic analysis of Stropharia rugosoannulata reveals carbohydrate metabolism and cold resistance mechanisms under low-temperature stress. AMB Express 2022, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Niu, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, S.-H.; Lei, S.-R.; Guo, L.-A.; Zhang, F.-L.; Liu, W.-J.; Chang, L.-J.; Zhao, L.-M. Study on Fructose and Mannose Metabolism Pathway ofTremella fuciformisBased on Transcriptome. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 32, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Yu, T.; Singh, P.K.; Liu, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhu, Q.; Xiao, Z.; Xu, J.; Peng, Y.; Fu, S.; et al. A Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Volvariella volvacea Identified the Candidate Genes Involved in Fast Growth at the Mycelial Growth Stage. Genes 2020, 11, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, S.; Chen, B.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, X.; Xia, H.; Wang, M. De Novo Sequencing and Transcriptome Analysis of Wolfiporia cocos to Reveal Genes Related to Biosynthesis of Triterpenoids. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, B.; Xu, J.; Liu, C. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNAs in Ganoderma lucidum. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Zhao, M.; Hsiang, T.; Feng, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, C. Identification and Characterization of Small Noncoding RNAs in Genome Sequences of the Edible Fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Biomed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2503023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fan, X.-Z.; Chen, L.-F.; Bian, Y.-B. Distribution and sequence characteristics of SSR in the transcriptomes of Auricularia auricula-judae and Auricularia polytricha. Mycosystema 2014, 33, 280–288. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Qu, W.; Chen, C.-Y.; Wang, L.; Ma, W.; Liu, Z.-S.; Ma, J.; Yang, S.; Ding, L.; Gao, Q.; et al. Development of EST-SSR markers based on transcriptome sequencing ofMorchellaspp. and its genetic diversity analysis. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 36, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Mo, M.; Yang, L.; Mi, F.; Cao, Y.; Liu, C.; Tang, X.; Wang, P.; Xu, J. Exploring the Species Diversity of Edible Mushrooms in Yunnan, Southwestern China, by DNA Barcoding. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.-M.; Jayawardena, R.S.; Thongklang, N.; Lv, M.-L.; Zhu, X.-T.; Zhao, Q. Morel Production Associated with Soil Nitrogen-Fixing and Nitrifying Microorganisms. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.-J.; Baek, J.H.; Lee, S.; Kim, C.; Rhee, H.; Kim, H.; Seo, J.-S.; Park, H.-R.; Yoon, D.-E.; Nam, J.-Y.; et al. Whole Genome and Global Gene Expression Analyses of the Model Mushroom Flammulina velutipes Reveal a High Capacity for Lignocellulose Degradation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; Ha, B.; Ro, H.-S. Differential Expression of Laccase Genes in Pleurotus ostreatus and Biochemical Characterization of Laccase Isozymes Produced in Pichia pastoris. Mycobiology 2015, 43, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Ding, X.; Hou, Y.-l. Comparative analysis of transcriptomes revealed the molecular mechanism of development of Tricholoma matsutake at different stages of fruiting bodies. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gu, B.; Huang, J.; Jiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Yin, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yu, G.; Li, Y.; Wong, B.H.C.; et al. Transcriptome and Proteome Exploration to Provide a Resource for the Study of Agrocybe aegerita. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Zhao, T.; Yan, X.; Pang, Q. Proteomic Analysis of Auricularia auricula-judae Under Freezing Treatment Revealed Proteins and Pathways Associated With Melanin Reduction. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 11, 610173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Lin, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Yang, X.; Guo, L.; Yu, H.; Gao, X.; Hu, C. Comparative Proteomic Analyses within Three Developmental Stages of the Mushroom White Hypsizygus marmoreus. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lin, R.; Xu, K.; Guo, L.; Yu, H. Comparative Proteomic Analysis within the Developmental Stages of the Mushroom White Hypsizygus marmoreus. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Guo, L.; Yu, H. Label-Free Comparative Proteomics Analysis Revealed Heat Stress Responsive Mechanism in Hypsizygus marmoreus. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 541967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Yao, Y.; Wei, Q.; Hu, T.; Li, X.; Zhu, B.; Ma, H. Combined analysis of proteomics and metabolism reveals critical roles of oxidoreductase activity in mushrooms stimulated by wolfberry and sea buckthorn substrates. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1543240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, D.; Cai, D.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, X. Label-free based comparative proteomic analysis of Morchella importuna development from the vegetative to the sexual reproductive stages. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 7, 100247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Bai, J.; Dong, Q.; Yue, P.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Guo, J. iTRAQ-based comparative proteome analyses of different growth stages revealing the regulatory role of reactive oxygen species in the fruiting body development of Ophiocordyceps sinensis. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desiderio, A.; Goppa, L.; Santambrogio, C.; Brocca, S.; Buratti, S.; Girometta, C.E.; Sarkar, M.; Venuti, M.T.; Savino, E.; Rossi, P.; et al. Improving the Proteome-Mining of Schizophyllum commune to Enhance Medicinal Mushroom Applications. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tang, H.; Zhao, W.; Yang, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhan, G.; Li, J.; Sun, S. Study of Dimorphism Transition Mechanism of Tremella fuciformis Based on Comparative Proteomics. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, L.; Chen, M.; Guo, Q.; Tong, Z.; Li, Z.; Yu, C.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Y. Comparative Proteomics Study on the Postharvest Senescence of Volvariella volvacea. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Song, F.; Lin, Z.; Chen, L.; Cai, Z. Transcriptome Analysis Explored the Differential Genes’ Expression During the Development of the Stropharia rugosoannulata Fruiting Body. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 924050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, C.; Xia, Y.; Zheng, P.; Shi, S.; Wang, C. Developmental stage-specific gene expression profiling for a medicinal fungus Cordyceps militaris. Mycology 2010, 1, 25–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wan, J.; Shang, J.; Yang, R.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Tan, Q.; et al. Chilling Stress Triggers VvAgo1-Mediated miRNA-Like RNA Biogenesis in Volvariella volvacea. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 523593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Han, J.; Cui, Y.; Shu, X.; Lei, M.; Wang, B.; Jia, D.; Peng, W.; He, X.; Liu, X. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Flammulina filiformis and Multi-Omics Analysis in Response to Low Temperature. J Fungi 2025, 11, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krah, F.-S.; Hess, J.; Hennicke, F.; Kar, R.; Bässler, C. Transcriptional response of mushrooms to artificial sun exposure. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 10538–10546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Mao, C.; Shi, Y.; Fan, X.; Sun, L.; Zhuang, Y. Transcriptome analysis of the response of Hypomyces chrysospermus to cadmium stress. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 990693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Fu, R.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; Lu, D. Genome sequence and transcriptome profiles of pathogenic fungus Paecilomyces penicillatus reveal its interactions with edible fungus Morchella importuna. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 2607–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, J.-Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, R.-J.; Pan, Y.-J.; Tan, Q.; Shang, X.-D. Transcriptome Comparison of Differentially Expressed Genes in the Mycelial Stages of Flammulina velutipes Monokaryon 3_M and the Hybrid Dikaryon G1. Acta Edulis Fungi 2016, 23, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gehrmann, T.; Pelkmans, J.F.; Ohm, R.A.; Vos, A.M.; Sonnenberg, A.S.M.; Baars, J.J.P.; Wösten, H.A.B.; Reinders, M.J.T.; Abeel, T. Nucleus-specific expression in the multinuclear mushroom-forming fungus Agaricus bisporus reveals different nuclear regulatory programs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4429–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, H.; Ding, Y.; Qi, Y.; Gao, Y.; Song, A.; Shen, J.; Qiu, L. Genome-wide gene expression patterns in dikaryon of the basidiomycete fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, M.; Castanera, R.; Lavín, J.L.; Grigoriev, I.V.; Oguiza, J.A.; Ramírez, L.; Pisabarro, A.G. Comparative and transcriptional analysis of the predicted secretome in the lignocellulose-degrading basidiomycete fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 4710–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.-H.; Bao, D.-P.; Wan, J.-N.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Q. Transcriptome analysis of transcription factors activiated at the light-induced brown mycelial film formation stage in Lentinula edodes. Mycosystema 2016, 35, 1106–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, D.; Zheng, Z.; Ma, N.; Yang, W.; Dai, C.; Zhao, M.; Deng, Z.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, L. Label-free proteomic quantification of packaged Flammulina filiformis during commercial storage. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 169, 111312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijoma, G.N.; Heri, S.M.; Matambo, T.S.; Tekere, M. Trends and Applications of Omics Technologies to Functional Characterisation of Enzymes and Protein Metabolites Produced by Fungi. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Zhou, H.; Qu, H.; Gao, H. Proteomics Reveals the Mechanism Underlying the Autolysis of Postharvest Coprinus comatus Fruiting Bodies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 1346–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; Guo, L.; Yu, H.; Yu, H. Responses of the Mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus under Different CO2 Concentration by Comparative Proteomic Analyses. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Jiang, N.; Yan, M.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Song, C.; Yu, H.; et al. Comparative analysis of proteomes and transcriptomes revealed the molecular mechanism of development and nutrition of Pleurotus giganteus at different fruiting body development stages. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1197983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, F.; Giuntoli, B.; Bertolini, E.; Taiti, C.; Marone, E.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Trovato, E.; Sciarrone, D.; Zoccali, M.; Balestrini, R.; et al. Tuberomics: A molecular profiling for the adaption of edible fungi (Tuber magnatum Pico) to different natural environments. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Li, H.; Han, Z.; Ma, X. Integrated transcriptome and metabolism unravel critical roles of carbon metabolism and oxidoreductase in mushroom with Korshinsk peashrub substrates. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, K.; Rakwal, R.; Hirano, M.; Shibato, J.; Nam, H.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Kouzuma, Y.; Agrawal, G.K.; Masuo, Y.; Yonekura, M. Proteomics of two cultivated mushrooms Sparassis crispa and Hericium erinaceum provides insight into their numerous functional protein components and diversity. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 1819–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-X.; Zou, Y.; Yu, Y.-H.; Chen, B.-X.; Zheng, Q.-W.; Ye, Z.-W.; Wei, T.; Ye, S.-Q.; Guo, L.-Q.; Lin, J.-F. Comparative transcriptome and proteome provide new insights into the regulatory mechanisms of the postharvest deterioration of Pleurotus tuoliensis fruitbodies during storage. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Li, T.; Xu, L.; Cheng, Y.; Chang, M.; Meng, J.; Hou, L. Integrated Transcriptomics–Proteomics Analysis Reveals the Response Mechanism of Morchella sextelata to Pseudodiploöspora longispora Infection. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Lu, L.; Yao, F.; Fang, M.; Wang, P.; Meng, J.; Shao, K.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y. High-quality genome assembly and multi-omics analysis of pigment synthesis pathway in Auricularia cornea. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1211795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Luo, F.; Cen, K.; Xiao, G.; Yin, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Zhan, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C. Omics data reveal the unusual asexual-fruiting nature and secondary metabolic potentials of the medicinal fungus Cordyceps cicadae. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Feng, J.; Zhang, T.; Qin, S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, C.; Li, D.; Han, W.; et al. Study of the whole genome, methylome and transcriptome of Cordyceps militaris. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Yu, G.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Wang, M.; Jin, Y.; Lan, X.; Liang, Y.; Sun, H. Genome-wide transcriptome and proteome analysis on different developmental stages of Cordyceps militaris. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, J.-M.; Tang, Y.-J.; Ma, K.; Li, B.; Zeng, X.; Liu, X.-B.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.-L.; Xu, W.-N.; et al. Genome-wide analysis and prediction of genes involved in the biosynthesis of polysaccharides and bioactive secondary metabolites in high-temperature-tolerant wild Flammulina filiformis. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.-Q.; Yan, J.-J.; Li, Y.-N.; Yang, H.; Ma, X.-B.; Wang, M.; Tao, Y.-X.; Xie, B.-G. Cytochrome c peroxidase gene(ffccp) and its differential expression during stipe elongation in Flammulina filiformis. Mycosystema 2020, 39, 993–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qian, J.; Si, W.; Tan, Q.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Y. Melatonin enhances the cadmium tolerance of mushrooms through antioxidant-related metabolites and enzymes. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ma, P.; Li, C.; Xiao, L.; Liang, Z.; Dong, J. Combining transcriptomics and metabolomics to reveal the underlying molecular mechanism of ergosterol biosynthesis during the fruiting process of Flammulina velutipes. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, H.; Zhang, X.; Song, J.; Sun, C.; Ji, A.; Xu, J.; Chen, S. Abundant and Selective RNA-Editing Events in the Medicinal Mushroom Ganoderma lucidum. Genetics 2014, 196, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, J.; Ma, F.; Tang, C.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, X. Investigation of lignocellulolytic enzymes during different growth phases of Ganoderma lucidum strain G0119 using genomic, transcriptomic and secretomic analyses. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Liu, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, C. Integrated Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analyses Reveal Molecular Mechanism of Response to Heat Shock in Morchella sextelata. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, L.; Xun, H.; Li, J.; Qi, B.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, B. Transcriptome Changes during Major Developmental Transitions Accompanied with Little Alteration of DNA Methylome in Two Pleurotus Species. Genes 2019, 10, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.N.; Li, Y.; Guo, T.; Ji, G.Y.; Luo, S.Z.; Ji, K.P.; Cao, Y.; Tan, Q.; Bao, D.P.; Yang, R.H. Whole-Genome and Transcriptome Sequencing of Phlebopus portentosus Reveals Its Associated Ectomycorrhizal Niche and Conserved Pathways Involved in Fruiting Body Development. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 732458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Fueyo, E.; Ruiz-Dueñas, F.J.; López-Lucendo, M.F.; Pérez-Boada, M.; Rencoret, J.; Gutiérrez, A.; Pisabarro, A.G.; Ramírez, L.; Martínez, A.T. A secretomic view of woody and nonwoody lignocellulose degradation by Pleurotus ostreatus. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongbai, B.; Rapior, S.; Hyde, K.D.; Wittstein, K.; Stadler, M. Hericium erinaceus, an amazing medicinal mushroom. Mycol. Prog. 2015, 14, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Guo, Z.; Jin, Q.; Xu, F.; Shen, Y.; Song, T.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Fan, L.; Huang, X.; et al. A Preliminary Exploration of Transcriptome and Proteomic Changes During the Young and Harvest Periods in Morchella sextelata. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, J.L.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Shen, L.; Long, Q. Deep learning-based approaches for multi-omics data integration and analysis. BioData Min. 2024, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheawchanlertfa, P.; Chitcharoen, S.; Raethong, N.; Liu, Q.; Chumnanpuen, P.; Soommat, P.; Song, Y.; Koffas, M.; Laoteng, K.; Vongsangnak, W. Enhancing Genome-Scale Model by Integrative Exometabolome and Transcriptome: Unveiling Carbon Assimilation towards Sphingolipid Biosynthetic Capability of Cordyceps militaris. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soommat, P.; Raethong, N.; Ruengsang, R.; Thananusak, R.; Laomettachit, T.; Laoteng, K.; Saithong, T.; Vongsangnak, W. Light-Exposed Metabolic Responses of Cordyceps militaris through Transcriptome-Integrated Genome-Scale Modeling. Biology 2024, 13, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Li, F.; Han, L.; Wang, J.; Ding, X.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, M.; Li, H. High-Yield-Related Genes Participate in Mushroom Production. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, Y.; Sato, S.; Takizawa, M.; Goto, F.; Eda, K.; Yamauchi, T. Marker-assisted selection of a novel Lentinula edodes cultivation strain with improved post-harvest quality. Mushroom Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 30, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zou, G.; Bao, D.; Wu, Y. Current Advances in the Functional Genes of Edible and Medicinal Fungi: Research Techniques, Functional Analysis, and Prospects. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Saand, M.A.; Huang, L.; Abdelaal, W.B.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Sirohi, M.H.; Wang, F. Applications of Multi-Omics Technologies for Crop Improvement. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 563953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, L.; Xu, M.-H.; Wang, B.; Song, B.; Li, Y. Research progress in comprehensive utilization of spent mushroom substrates. Microbiol. China 2020, 47, 3658–3670. [Google Scholar]
- Zeb, U.; Aziz, T.; Azizullah, A.; Zan, X.Y.; Khan, A.A.; Bacha, S.A.S.; Cui, F.J. Complete mitochondrial genomes of edible mushrooms: Features, evolution, and phylogeny. Physiol. Plant. 2024, 176, e14363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mushroom Species | Genome Research Type | Key Genes | Involved Metabolic Pathways | Significance | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agrocybe aegerita | genome sequencing and hybrid assembly, gene annotation | genes for non-specific peroxidases, dye-decolorizing peroxidases, and Carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes) | lignocellulose degradation | study of fruiting body development, biodegradation potential | [34] |
| Cordyceps guangdongensis | genome sequencing and annotation | CAZymes genes | biosynthesis, transport, and catabolism of secondary metabolites | provides basis for studying genetic and molecular mechanisms of fruiting body development | [35] |
| Cordyceps militaris | construction of genome-scale metabolic network (GSMM) | genes for biosynthesis of cordycepin and hydrolytic enzymes | biosynthesis of cordycepin, central carbon and amino acid metabolism | aids efficient production of high-value bioactive compounds with pharmaceutical potential | [36] |
| Cordyceps militaris | genome sequencing and annotation | genes for non-ribosomal peptide synthetases, type 1 polyketide synthases, and polyketide synthase-non-ribosomal peptide synthetase | biosynthesis of emercellamide and equisetin | further research and characterization of secondary metabolites produced by C. militaris | [37] |
| Cordyceps militaris | genome sequencing and annotation | genes for terpenoid cyclase, terpenoid synthase, fatty-acid synthase, and geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase | biosynthesis of cordycepin | facilitates molecular studies on biology, fungicity, pathogenicity, medicinal compound production | [38] |
| Cordyceps militaris | genome bisulfite sequencing | genes for pyruvate metabolism, glycerophospholipid metabolism, DNA replication, and biosynthesis of N-glycan | pyruvate metabolism, glycerophospholipid metabolism, DNA replication, and N-glycan biosynthesis | helps understand potential mechanisms of strain degeneration in C. militaris | [39] |
| Dictyophora indusiate | secondary metabolite gene cluster analysis | genes for CYP450 family, and biosynthesis of terpene | biosynthesis of terpene | potential for medicinal compound production | [40] |
| Flammulina velutipes var. lupinicola | genome sequencing | lignocellulosic enzyme | lignocellulose degradation | understanding lignocellulose decomposition mechanisms | [41] |
| Ganderma lucidum | genome sequencing and annotation | genes for CAZymes and ligninolytic enzymes | biosynthesis of triterpene, wood degradation | aids bioengineering studies for active ingredient and bioenergy production | [42] |
| Ganoderma leucocontextum | genome sequencing and annotation, genome composition analysis | genes for CAZymes and biosynthesis of ergosterol | biosynthesis of sesquiterpenoid and triterpenoid | preliminary understanding of the biosynthesis of active secondary metabolites | [43] |
| Ganoderma Lucidum | genome resequencing and gene variation detection, annotation | genes for mycelial growth rate and synthesis of triterpene | synthesis of triterpene | reveals genetic mechanisms of G. lucidum mycelial growth and triterpene synthesis | [44] |
| Gomphus purpuraceus | genome sequencing and comparative genomics | genes for CAZymes and α-amylase family | starch/sucrose metabolism | studying biosynthesis of active compounds, understanding survival mechanisms and saprophytic ability | [30] |
| Hericium erinaceus | genome sequencing and annotation, gene identification | CAZymes genes | lignocellulose degradation | characterizes CAZymes and TFs in the genome, expands biological and genetic studies | [45] |
| Lentinula edodes | genome sequencing | genes for kinases and heat shock proteins | stress response | studying domestication process of Chinese L. edodes using population genomics | [46] |
| Lentinula edodes | genome sequence analysis | multicopper oxidase genes | expression of multicopper oxidases in mycelia, growing fruiting bodies, and fruiting bodies after harvest | suggests shared expression patterns and biological functions for laccases within the same group | [47] |
| Lyophyllum decastes | genome sequencing and annotation, CAZyme ID, mating type loci char. | laccase, quinone reductase, and CAZymes genes | lignocellulose degradation | understanding lignin degradation | [48] |
| Morchella importuna | genome sequencing, assembly and annotation, comparative analysis | CAZymes genes | starch degradation | better understanding of Morchella biology and evolution | [49] |
| Morchella sextelata | genome sequencing and annotation, comparative genomics | genes for ER repair protein 1 family, secondary metabolite, and CAZymes | posttranslational modification, protein turnover, amino acid transport and metabolism | discovery of bioactive compounds | [50] |
| Ophiocordyceps sinensis (Medicinal fungi) | genome sequencing and annotation | genes for type I polyketide synthases (PKSs), non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs), and terpene synthase | biosynthesis of cordycepin, carbohydrate, amino acid, and energy metabolism | facilitates discovery and identification of novel secondary metabolite gene clusters, medicinal potential | [51] |
| Oudemansiella raphanipes | genome sequencing | CAZymes genes | biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, wood degradation | wood degradation and bioactive compound synthesis | [52] |
| Pleurotus giganteus | genome sequencing and assembly, comparative genomics | CAZymes genes | lignocellulose degradation, high-temperature adaptation | strong lignocellulolytic ability, development of molecular markers for ID and breeding | [53] |
| Sparassis latifolia | genome sequencing and comparison, SMGC analysis | genes encoding enzymes for carbohydrate and glycoconjugate metabolism, key SM biosynthesis enzymes | indole, terpene, and type I polyketide pathways | elucidates genetic basis of reported medicinal properties | [54] |
| Stropharia rugosoannulata | genome sequencing and comparative genomics | CAZymes genes | lignocellulose degradation | understanding lignocellulolytic ability | [55] |
| Tricholoma matsutake | comparative genomics and symbiotic adaptation | iron homeostasis genes | tryptophan metabolism | adaptation to symbiotic lifestyle and nutrient availability | [56] |
| Volvariella volvacea | genome sequencing and assembly, DEG identification | cellulase, hemicellulase, and pectinase genes | low temperature response, degradation of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin | provides evolutionary model for saprophytic nutrition and specific molecular mechanisms of cold sensitivity | [57] |
| Volvariella volvacea | genome sequencing and phylogenetic analysis | Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)-binding proteins genes | energy transfer and utilization | understanding functional differences between homokaryons and heterokaryons | [58] |
| Flammulina velutipes | genome sequencing and key gene bioinformatics analysis | L-lysine biosynthesis genes | α-aminoadipate pathway | improving varieties for higher lysine content via genetic engineering | [59] |
| Mushroom Species | Samples Collected Condition | Key DEGs | Key Pathways | Significance | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agaricus bisporus | browning susceptible vs. resistant | polyphenol oxidase (PPO) genes | browning-related pathways | reveals browning mechanisms | [93] |
| Agaricus bisporus | six strains at different developmental stages | aminodeoxychorismate synthase, transcriptional enhancer factor genes, among others | fatty acid metabolism, biosynthesis of steroid and folate | reveals important DEGs in fruiting body development from different perspectives | [94] |
| Agaricus bisporus | caps at different post-harvest storage times | PPO genes | browning-related pathways | understanding PPO regulation of browning mechanism in A. bisporus | [95] |
| Agaricus bisporus | four developmental stages of fruiting body | DNA replication, base repair, RNA transport, ribosome etc. | amino acid, carbohydrate, nucleotide, lipid, and energy metabolism | reveals genes related to fruiting body growth and development | [96] |
| Agaricus blazei | different developmental stages of fruiting body | carbohydrate metabolism, fatty acid degradation, amino acid metabolism genes, among others | DNA replication, base excision repair, mismatch repair, RNA transport, and ribosome | understanding gene expression at different fruiting body developmental stages | [97] |
| Agaricus blazei | mycelia vs. primordia | response to stress genes | energy production | understanding pathways for polysaccharide and benzaldehyde biosynthesis, and fruiting body formation genes | [83] |
| Auricularia auricula-judae | three morphologically distinct fruiting bodies | peroxidase-like genes | starch and sucrose metabolism, MAPK signaling (yeast), biosynthesis of amino acid, secondary metabolite, and antibiotic | contributes sequence data to public databases, establishes relationships between major varieties | [98] |
| Auricularia fibrillifera | drought stress, rehydration | Tyrosinase and homogenesate1,2-dioxygenase genes, among others | resisting oxidative stress, osmotic adjustment | provides new potential targets for breeding and cultivation of drought-tolerant fungi | [88] |
| Auricularia polytricha | mycelia vs. mature fruiting bodies | tyrosinase genes | metabolism of amino acid, carbohydrate, energy, lipid, nucleotide | reveals candidate genes related to fruiting body formation | [99] |
| Cordyceps cicadae | three developmental stages | 5′-nucleotidase and adenosine deaminase genes | cordycepin biosynthesis | enhancing understanding of biosynthesis of cordycepin and other characteristic secondary metabolites | [100] |
| Cordyceps militari | mycelia vs. fruiting bodies | genes for virulence and sexual development | energy metabolism, signaling pathways | suggests lncRNA expression regulates fungal virulence and sexual development by affecting gene expression | [101] |
| Cordyceps militaris | dark vs. light | Cmtns gene | biosynthesis of carotenoids | reveals carotenoid biosynthesis pathway and improving yield | [102] |
| Cordyceps militaris | dark vs. specific light | glyoxalase system genes | response to light/dark stimulation, biosynthesis of carotenoid and cordycepin | suggests transcriptional co-regulation plays a metabolic control role in light adaptation | [103] |
| Cordyceps militaris | six generations of artificial culture | genes for toxin biosynthesis, DNA methylation and chromatin remodeling, and energy metabolism | strain degeneration | reveals strain degeneration mechanism | [104] |
| Cordyceps militaris | albino mutant vs. normal strain | secondary metabolite backbone genes | response to light | understanding pigment biosynthesis pathway | [105] |
| Cordyceps militaris | submerged vs. liquid surface culture | adenylosuccinate synthetase and phosphoribosylaminoimidazole-succinocarboxamide (SAICAR) synthase genes | purine nucleotide metabolism | reveals cordycepin biosynthesis pathway and improving cordycepin production | [106] |
| Cordyceps militaris | different culture media | cell membrane, catalytic activity | carotenoid biosynthesis | understanding carotenoid biosynthesis pathway in C. militaris | [107] |
| Cordyceps militaris | culture with vs. without L-alanine addition | Zn2Cys6 type TFs | biological of energy production and amino acid transformation | supports improving cordycepin yield and strain breeding | [108] |
| Cordyceps militaris | different carbon sources | cordycepin biosynthesis genes | transcriptional regulation of central carbon metabolism | studying overall metabolic response of C. militaris for cordycepin production | [109] |
| Cordyceps militaris | xylose vs. other carbon sources | pentose and glucuronate interconversions | cordycepin biosynthesis | reveals response mechanism to xylose utilization | [110] |
| Cordyceps militaris | wild-type vs. wc-1 deficient strain | Cmwc-1(a homolog of the blue-light receptor gene white collar-1 (wc-1) in Neurospora crassa) | steroid biosynthesis | investigating role of blue light receptor gene (wc-1) in C. militaris fruiting and secondary metabolism | [32] |
| Flammulina filiformis | mycelia vs. primordia | genes for sugar transporter and unsaturated fatty acid synthesis | glycolysis, phospholipid and sphingolipid metabolism | reveals energy source transition during primordium formation | [111] |
| Flammulina filiformis | four developmental stages | heat stress-induced hsp70, hsp90, fes1 genes | heat stress response | studying gene function and improving mushroom heat tolerance | [112] |
| Flammulina velutipes | monokaryotic vs. dikaryotic mycelia | genes for transcription factors, protein kinases, and WD40 repeat-like proteins | synthesis of fatty acid, amino acid, and most saccharide | screens DEGs before and after mating in F. velutipes | [113] |
| Flammulina velutipes | mycelia vs. primordia | ribosome and DNA replication, among others | glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway | reveals DEGs between F. velutipes dikaryotic mycelia, and primordia | [114] |
| Ganoderma lucidum | three continuous developmental stages | genes for carbohydrate metabolism, triterpenoid and ergosterol biosynthesis | ganoderic acids and ergosterol biosynthesis | reveals genes potentially involved in meiotic transcriptional control, metabolic pathways for energy supply, and biosynthesis of ganoderic acids and ergosterol | [115] |
| Ganoderma lucidum | addition of L-phenylalanine | genes for L-phenylalanine metabolism and cell wall mannoprotein | fungal polysaccharide production | provides effective strategy for high-yield, low-cost fungal polysaccharide production | [116] |
| Ganoderma lucidum | addition of PDE inhibitor or AC activator | genes for squalene synthase and lanosterol synthase | cAMP-induced apoptosis, ganoderic acids (GAs) biosynthesis | reveals cAMP signaling induces fungal apoptosis, and secondary metabolite production | [117] |
| Ganoderma lucidum | mycelia vs. fruiting bodies | FOLymes and CAZymes genes | terpene backbone biosynthesis pathway | provides comprehensive gene expression information | [118] |
| Grifola frondosa | mycelia | polysaccharide synthesis-related genes | polysaccharide synthesis | provides basis for studying polysaccharide metabolic pathways and related functional genes | [119] |
| Lentinula edodes | dikaryotic mycelia vs. mature fruiting bodies | peptidases and phosphotransferases genes | oxidative stress, starvation stress response | elucidating molecular mechanisms of mature fruiting body development and beneficial properties | [120] |
| Lentinula edodes | blue light vs. dark | morphogenesis and photoreception genes | blue light signaling pathway | identification of light-responsive genes | [121] |
| Lentinula edodes | monokaryotic mycelia with different laccase activity | cytochrome P450, glycoside hydrolase, and UDPG dehydrogenase genes | lignin degradation and carbohydrate metabolism | deeper understanding of physiological metabolism in high-laccase-yielding L. edodes strains | [122] |
| Lentinula edodes | dark vs. blue light | CAZymes genes | pentose and glucuronate conversion, starch and sucrose metabolism | aids functional studies of genes involved in developmental control | [123] |
| Lentinula edodes | different vegetative mycelial growth phenotypes (light exposure) | kinases, tyrosinase, glucanase, chitinase, and laccase genes | melanogenesis, cell wall degradation, signaling | analysis of expression patterns of light-induced browning-related genes | [124] |
| Lyophyllum decastes | five developmental stages | extracellular enzymes and TFs genes | signaling pathways | understanding fruiting body development | [125] |
| Morchella importuna | three mycelial growth stages | transketolase (tktA) and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) genes, among others | carbohydrate metabolism | elucidating mechanisms of mycelial growth | [126] |
| Morchella importuna | mycelia vs. young fruiting bodies | CAZymes, mitochondrial proteins, oxidoreductases, and HSPs genes | carbohydrate catabolism and energy metabolism | exploring fruiting body formation mechanisms in M. importuna | [127] |
| Morchella importuna | three mycelial growth stages | CAZymes genes | metabolism of carbohydrates, polysaccharides, hydrolases, caprolactam, β-galactosidase, and disaccharides | reveals carbohydrate catabolism mainly occurs during vegetative mycelial stage | [128] |
| Morchella importuna | mature fruiting bodies | genes for respiration, carbohydrate metabolism, tissue softening, and oxidative browning | molecular mechanism of post-harvest quality changes | provides theoretical basis for post-harvest quality change mechanisms and preservation technology | [129] |
| Chinese cordyceps (Medicinal fungi) | mycelia, sclerotia, and primordia | pheromone receptor and amino acid sensing genes, | DNA synthesis, cell division, MAPK pathway | reveals potential mechanisms of fruiting body initiation | [130] |
| Ophiocordyceps sinensis (Medicinal fungi) | mycelia vs. fruiting bodies | adenosine metabolism enzyme genes | cordycepin biosynthesis | provides data supporting elucidation of cordycepin biosynthesis mechanisms | [131] |
| Ophiocordyceps sinensis (Medicinal fungi) | fruiting bodies | pheromone receptors, G protein γ-subunit, G protein α/β subunits, and cordycepin synthesis enzymes genes | signaling, cordycepin biosynthesis | reveals genes associated with fruiting body development, and cordycepin biosynthesis | [87] |
| Pleurotus eryngii | different developmental stages | genes encoding enzymes involved in carbon and amino acid metabolism | carbon and amino acid metabolism | reveals gene expression changes during fruiting body growth and development | [132] |
| Pleurotus eryngii | transformed vs. wild-type strains | genes for mycelial growth and enzyme activity | MAPK signaling and inositol phosphate metabolism, among others | validates the functional role of GNAI in P. eryngii growth and development | [133] |
| Pleurotus eryngii | dark vs. blue light | CAZymes genes | carbon metabolism, glycolysis and biosynthesis of amino acids | understanding primordia response to blue light at developmental stage | [134] |
| Pleurotus eryngii subsp. Tuoliensis | cold stimulus, mycelia | genes for cell wall and membrane stability, Ca2⁺ signaling, MAPK pathway, and soluble sugar and protein biosynthesis | mycelia response to cold stimulation | understanding molecular mechanisms related to cold stimulus response | [135] |
| Pleurotus ostreatus | H2O2 regulation | genes in the respiratory chain | ATP synthesis | provides basis for breeding dark P. ostreatus strains and understanding pigmentation mechanism | [136] |
| Pleurotus ostreatus | heat stress | MYB gene family | mechanisms of fruiting body development and stress response | promotes further functional analysis of MYB genes | [137] |
| Pleurotus pulmonarius | mycelia vs. fruiting bodies | PpFBD1 (a gene that is highly expressed during the early stages of primordium formation) | synthesis of fungal cell walls | studying DEGs and their functions at different growth stages | [138] |
| Pleurotus tuoliensis | three developmental stages | morphogenesis genes | primary carbohydrate metabolism, cold stimulus and blue light response | indicates vegetative-to-reproductive transition as most active and critical period for gene expression changes | [139] |
| Pleurotus tuoliensis | immature vs. mature mycelia | genes encoding nucleoside diphosphate kinase, GH family proteins, and extracellular polygalacturonase | nucleotide synthesis and energy metabolism | understanding molecular mechanisms of mycelial maturation | [140] |
| Pleurotus tuoliensis | monokaryotic vs. dikaryotic strains | phenylalanine ammonium lyase and aryl-alcohol oxidase genes | catalytic activity and metabolic process | exploring fruiting body development genes, providing efficient markers for MAS | [141] |
| Sparassis Primordia | dark vs. light | genes associated with metabolism of vitamin B6 and selenocompound metabolism, among others | cysteine synthesis, vitamin B6 metabolism, glycine metabolism | establishes DE map for light-induced primordium formation | [142] |
| Sparassis Primordia | dark vs. light | glutathione S-transferase and HSP 9/12 genes, among others | secondary metabolite synthesis, starch and sucrose metabolism, glutathione metabolism | analysis of molecular mechanisms of light response | [143] |
| Stropharia rugosoannulata | cold stress | carbohydrate enzyme genes | metabolism of carbohydrate, lipid, and xenobiotic | reveals cold resistance mechanisms | [144] |
| Tremella fuciformis | mycelia | L-iditol 2-dehydrogenase and butanol dehydrogenase genes | polysaccharide metabolic pathways | provides data support for studying polysaccharide and other product biosynthesis pathways and mechanisms | [145] |
| Volvariella volvacea | different commercial strains | heat shock proteins genes | stress response | identifying candidate genes involved in rapid growth requirements | [146] |
| Wolfiporia cocos | mycelia vs. sclerotia | diphosphomevalonate decarboxylase and farnesyl diphosphate synthase genes, among others | biosynthesis of triterpenoids | reveals genes related to triterpenoid biosynthesis | [147] |
| Mushroom Species | Proteomic Research | Key Proteins | Key Pathways | Significance | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auricularia auricula-judae | effect of freezing on melanin accumulation mechanism | glycolysis/gluconeogenesis proteins | tyrosine metabolism, ribosome and arginine biosynthesis | provides information on the mechanism of freezing treatment effects on color quality | [158] |
| Hypsizygus marmoreus | protein changes from “scratching” to primordia | oxidoreductases, peptidases, hydrolases | catabolic and carbohydrate-related processes | understanding developmental changes preceding primordia formation | [159] |
| Hypsizygus marmoreus | protein expression during mycelial growth | proteins involved in carbohydrate metabolism, catabolic processes, oxidoreductase activity | carbohydrate metabolism, catabolic processes, oxidoreductase activity | elucidating protein changes during development | [160] |
| Hypsizygus marmoreus | heat stress response | SOD and peroxidase, trehalose synthase, heat shock proteins (HSPs) | expression of catalase | understanding molecular mechanisms of heat stress response | [161] |
| Lentinula edodes | substrate effect on protein expression | proteins involved in carbohydrate and oxidoreductase activity pathways | carbohydrate and oxidoreductase activity pathways | cultivation effects on nutritional quality | [162] |
| Lyophyllum decastes | lignin degradation | laccase, quinone reductase | lignocellulose degradation | confirms lignin degradation mechanism | [48] |
| Morchella importuna | proteome analysis of vegetative vs. sexual stages | lectin proteins | carbohydrate and amino acid metabolic pathways | understanding nutrient metabolism and fruiting body development | [163] |
| Ophiocordyceps sinensis (Medicinal fungi) | Proteome analysis of three key dev. stages | ROS-related proteins, proteins involved in carbon transport and metabolism, response to oxidative stress, antioxidant activity and translation | carbon transport and mechanism, response to oxidative stress, antioxidative activity | understanding biological traits of fruiting body development and high-altitude adaptation | [164] |
| Schizophyllum commun | trehalose biosynthesis pathway | trehalose synthase, trehalose phosphatase, trehalose phosphorylase | growth and development of mycelium, trehalose biosynthesis | potential for industrial trehalose production | [165] |
| Stropharia rugosoannulata | tissue-specific protein expression | proteins for carbon metabolism, energy production, stress response | fatty acid synthesis, mRNA splicing | understanding tissue-specific metabolism | [144] |
| Tremella fuciformis | mechanism and proteomics of conidia–mycelia transition | proteins involved in biosynthesis, DNA replication, and DNA damage repair, among others | MAPK signaling pathway | provides basis for studying dimorphism formation mechanisms | [166] |
| Volvariella volvacea | post-harvest autolysis mechanism | proteins involved in fatty acid metabolism and RNA transport | RNA transport, biosynthesis of fatty acid and amino acid | provides reference for further studies on senescence mechanisms | [167] |
| Mushroom Species | Integrated Omics Technologies | Research Question/Focus | Key Insights Obtained | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agaricus blazei | genomics, transcriptomics | gene function, DEG between mycelia and primordia stages | understanding pathways for polysaccharide and benzaldehyde biosynthesis, fruiting body formation related genes | [83] |
| Agrocybe aegerita | transcriptomics, proteomics | mycelia vs. fruiting bodies | provides clues for nutritional, pharmaceutical, and industrial applications | [157] |
| Auricularia cornea | genomics, transcriptomics, metabolomics | high-quality genome assembly and multi-omics analysis of pigment synthesis pathway | revealed genetic blueprint, evolutionary history, and pigment synthesis mechanism | [190] |
| Cordyceps cicadae | genomics, transcriptomics, metabolomics | asexual fruiting body formation characteristics and secondary metabolism | understanding fungal genetics and promoting medicinal research | [191] |
| Cordyceps kyushuensis | transcriptomics, proteomics | single gene cluster for cordycepin and pentostatin biosynthesis | for improving cordycepin yield and finding more functional proteins | [92] |
| Cordyceps militaris | genomics, transcriptomics | genome, transcriptome, and methylome of a new strain | provides basis for fungal molecular biology | [192] |
| Cordyceps militaris | transcriptomics, proteomics | gene expression differences between mycelia and fruiting bodies | facilitates systematic molecular studies of developmental stages | [193] |
| Dictyophora indusiate | genomics, transcriptomics, metabolomics | fruiting body differentiation | importance of tryptophan metabolism | [40] |
| Flammulina filiformis | genomics, comp. transcriptomics | expression of biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) in wild/cultivated strains and dev. stages | elucidating regulation of secondary metabolites | [194] |
| F. filiformis | genomics, transcriptomics | role of cytochrome c peroxidase gene (FfCcP) in dev. and stress response | upregulation of FfCcP might facilitate stipe elongation | [195] |
| F. velutiper, G. Lucidum, H. erinaceus, H. marmoreus, L. edodes, P. eryngii, P. geesteranus, V. volvacea | comp. metabolomics, proteomics | ameliorative effect of melatonin (MT) on Cd-induced oxidative stress | confirmed widespread presence of MT in edible fungi and its important role in physiological regulation | [196] |
| Flammulina velutipes | transcriptomics, metabolomics | regulation of ergosterol biosynthesis | understanding ergosterol biosynthesis regulation during fruiting and metabolite–gene relationships | [197] |
| Ganoderma lucidum | genomics, transcriptomics | RNA editing | elucidating role of transcriptional plasticity in dev., environmental adaptation, and SM pathway regulation | [198] |
| Ganoderma lucidum | genomics, transcriptomics | lignocellulolytic enzymes | understanding changes in lignocellulose degradation ability during G. lucidum growth | [199] |
| Ganoderma lucidum | genomics, transcriptomics | key genes (Cyt P450s, transporters, regulators), triterpenoid biosynthesis | potential model system for studying SM pathways and regulation in medicinal fungi | [61] |
| Lentinula edodes | proteomics, metabolomics | substrate effect on metabolism and nutrition | linking substrate to protein/metabolite changes | [162] |
| Morchella importuna | genomics, transcriptomics | response mechanisms at different stages post-Paecilomyces infection | fungus–fungus interactions involving edible fungi | [174] |
| Morchella sextelata | transcriptomics, proteomics | heat shock response, development, pathogen infection | heat shock adaptation network; role of sugar metabolism; defense mechanisms against pathogens | [200] |
| P. eryngii var. eryngii, Pleurotus tuoliensis | genomics, transcriptomics | DNA methylation and gene expression during three major developmental transitions | epigenetic and transcriptional regulatory mechanisms supporting gene expression during development | [201] |
| Phlebopus portentosus | genomics, transcriptomics | lignocellulose degradation system and fruiting body development | understanding key pathways and hub genes involved in development | [202] |
| Pleurotus giganteus | transcriptomics, proteomics, nutritional analysis | substrate and mRNA transport within fruiting body | complex interactions between gene expression, protein synthesis, and nutrient allocation | [184] |
| Pleurotus ostreatus | genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics | secreted proteins and environmental interaction | secreted protein transcription depends more on strain genotype than environment | [178] |
| Pleurotus ostreatus | genomics, proteomics, metabolomics | secretome of strains on different substrates | identifying enzymes overproduced in lignocellulose cultures | [203] |
| Volvariella volvacea | genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics | low-temperature autolysis | cold stress might trigger VvAgo1-mediated RNAi to promote low-temperature autolysis | [170] |
| Volvariella volvacea | genomics, transcriptomics | composition and expression of CAZyme-encoding genes | identified CAZymes, showed differential expression between heterokaryon and homokaryon | [81] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; Feng, K.; Chen, B. A Review of Genomic, Transcriptomic, and Proteomic Applications in Edible Fungi Biology: Current Status and Future Directions. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11060422
Xie M, Wang J, Wang F, Wang J, Yan Y, Feng K, Chen B. A Review of Genomic, Transcriptomic, and Proteomic Applications in Edible Fungi Biology: Current Status and Future Directions. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(6):422. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11060422
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Muyun, Jing Wang, Feixiang Wang, Jinfeng Wang, Yunjin Yan, Kun Feng, and Baixiong Chen. 2025. "A Review of Genomic, Transcriptomic, and Proteomic Applications in Edible Fungi Biology: Current Status and Future Directions" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 6: 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11060422
APA StyleXie, M., Wang, J., Wang, F., Wang, J., Yan, Y., Feng, K., & Chen, B. (2025). A Review of Genomic, Transcriptomic, and Proteomic Applications in Edible Fungi Biology: Current Status and Future Directions. Journal of Fungi, 11(6), 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11060422






