Abstract
Foshou yam (Dioscorea esculenta) is a tuber food crop in China. It is a rare species of the yam family and known for its high nutritional value. From 2019 to 2021, tuber rot was observed in Foshou yam in Wuxue, Hubei Province, China. Fungal strains were isolated from diseased tubers, and ten representative strains were identified based on microscopical characterization and multi-locus phylogenetic analysis. A total of five different species were identified, including Curvularia geniculata, Curvularia muehlenbeckiae, Fusarium commune, Penicillium oxalicum, and Penicillium sclerotigenum. Pathogenicity test revealed that these fungi are the pathogens of tuber rot in Foshou yam. Among them, P. oxalicum exhibited the strongest pathogenicity. To our knowledge, this is the first report of tuber rot in D. esculenta caused by these five species worldwide. This study provides important information for the future management of tuber rot in Foshou yam.
1. Introduction
Yam (Dioscorea spp.), a perennial tuberous crop, serves as a staple food source in tropical and subtropical regions [1,2]. It ranks as the fourth most produced root and tuber crop globally, following potatoes, cassava, and sweet potatoes, with annual production reaching approximately 89 million tons (2023, FAO, https://www.fao.org/faostat, accessed on 10 May 2025). As one of the primary centers of origin and domestication for yams, China boasts a cultivation history exceeding two thousand years [3,4]. The two predominant cultivated species, Dioscorea polystachya and Dioscorea alata, are extensively grown throughout China for vegetable crops and traditional medicinal resources [5,6]. Yam tubers contain a diverse range of nutritional ingredients and bioactive compounds, including starch, dietary fiber, proteins, polysaccharides, allantoin, dioscorin, flavonoids, sapogenins, polyphenols, and others [7]. These phytochemicals exhibit pharmacological properties such as spleen and stomach nourishment, immune enhancement, and anti-aging effects [7]. Furthermore, the tuber’s unique flavor and bioactivities have driven substantial consumer demand, positioning yam-derived products as promising candidates for functional food development and nutraceutical applications [7].
Foshou yam (D. esculenta) is a rare variety, mainly grown in Wuxue, Hubei Province, China, and known for its unique taste and high nutritional value [8,9]. It has a low soluble sugar content but is rich in amino acids, making it an ideal functional food. In addition, it is colloquially termed the ‘Dabie Mountain Ginseng’, reflecting its esteemed status in traditional health practices [9].
Fungal diseases pose a significant threat to yam production. Many fungal pathogens have been documented to infect yams. For example, yam anthracnose, caused by Collectotrichum gleosporioides, is one of the most important diseases in global yam production [10,11]. Concentric leaf spot, caused by Sclerotium rolfsii, is considered the second most destructive foliar disease on yam [12]. This pathogen is able to produce extensive hyphae and sclerotia, enhancing its persistence in the field [13]. Many other pathogens, such as Alternaria alternata, Cercospora dioscoreae, Curvularia eragrostidis, Cylindrosporium dioscoreae, Pseudocercospora contraria, and Nigrospora oryzae, have also been reported to cause leaf spot on yam [10,14,15]. Yam tuber rot, caused by various fungal pathogens, is a major postharvest constraint that substantially shortens the storage potential of yam tubers. These pathogens include species belonging to Fusarium, Aspergillus, Macrophomina, Rhizopus, Penicillium, Sclerotium, and Botrydiplodia. Among them, Fusarium tuber rot is especially damaging [10,16]. Other factors, such as the soil nutrient status, as well as the interactions among plants, endophytes, saprophytes, and pathogens, may also have some impact on plant fungal diseases [17].
Dioscorea esculenta is an important yam species in China; however, research on fungal diseases affecting this crop remains limited. Identifying the fungal pathogens associated with D. esculenta is essential for effective disease management and sustainable production. Between 2019 and 2021, tuber rot was observed in Foshou yam (D. esculenta) in Wuxue, Hubei Province, China. The disease led to significant yield losses, resulting in considerable economic impact. This study aims to isolate and identify the causal pathogens of tuber rot in Foshou yam through morphological and molecular characterization, thereby providing a scientific basis for future disease management strategies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Isolation
Diseased Foshou yam plants were observed in Wuxue, Hubei Province, China, between 2019 and 2021, exhibiting wilting symptoms (Figure 1A). The tubers showed rot and watery necrotic lesions (Figure 1B,C). Infected tubers were collected in sterile plastic bags and transported to the laboratory. For fungal isolation, tubers were rinsed with running water to remove soil and cut into 3–4 mm pieces using a sterilized blade. The tissues were surface-disinfected in 5% sodium hypochlorite for 5 min, rinsed three times with sterile distilled water, and air-dried in a laminar flow cabinet. The samples were then plated onto potato dextrose agar (PDA; Difco™, Detroit, MI, USA) and incubated at 25 °C in the dark for 3–7 days. Hyphal tips from emerging colonies were sub-cultured three times on fresh PDA to obtain pure isolates, which were preserved in the Fungi Herbarium of Yangtze University, Jingzhou, China.
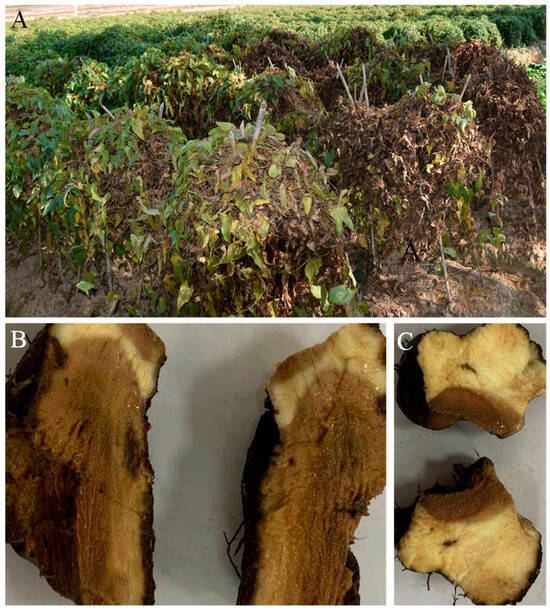

Figure 1.
Photographs of diseased Foshou yam (Dioscorea esculenta) in Wuxue city, China. (A) Diseased Foshou yam plants in the farm; (B,C) typical symptoms of yam tuber rot (cross-section).
2.2. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
To identify the fungi, isolates with distinct colony characteristics were selected as representative strains for genomic DNA extraction and PCR amplification. DNA was extracted from fresh 3-day-old mycelia grown on PDA using a modified CTAB method [18]. Different gene regions, including the internal transcribed spacer (ITS), β-tubulin (TUB2), calmodulin (CAL), elongation factor 1-α (TEF1), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), and second largest subunit of the RNA polymerase (RPB2) were amplified using primer pairs ITS4/ITS5 [19], Bt2a/Bt2b [20], CMD5/CMD6 [21], EF1-728F/EF1-986R [22], gpd1/gpd2 [23], and RPB2-5F/RPB2-7cR [24], respectively. Different gene regions were chosen for PCR amplification based on fungal genera: ITS and GAPDH for Curvularia spp., ITS, TUB2, TEF1, and RPB2 for Fusarium sp., and ITS, TUB2, CAL, and RPB2 for Penicillium spp. The PCR reaction mixture was prepared in a total volume of 25 μL, consisting of 2 μL DNA template, 1.25 μL of each forward and reverse primer, and 20.5 μL of 1.1 × Taq PCR StarMix (TSINGKE, Beijing, China). The PCR amplification was performed using a Bio-Rad T100TM Thermal Cycler (Hercules, CA, USA). Successful PCR products were sent to BGI (Beijing, China) for purification and Sanger sequencing (both directions).
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
Nucleotide sequences obtained from BGI were manually checked with BioEdit v7.0.9 [25]. The sequences were then analyzed with BLASTn (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed on 5 April 2025) to find similar sequences in the NCBI database. Reliable reference sequences were obtained from recent publications [26,27,28,29,30,31,32]. Phylogenetic analyses were conducted using the OFPT (One-click Fungal Phylogenetic Tool) software v1.9.0 [33]. Specifically, sequences of each genetic region were aligned by MAFFT v7.520 [34] and trimmed by TrimAl v1.2 [35]. Nucleotide substitution models of each dataset were then tested by ModelFinder v1.6.12 [36]. Finally, maximum likelihood (ML) and Bayesian inference (BI) analyses were performed with IQ-TREE v1.6.12 [37] and MrBayes 3.2.7 [38], respectively, using the concatenated datasets with partition information. Sequences generated in this study were deposited in GenBank (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) with accession numbers shown in Table S1.
2.4. Morphology
Colony morphology of the fungal strains was examined on different media after incubation at 25 °C in the dark for 7 days. For the species of Curvularia, PDA and PCA (potato carrot agar) were used. PDA was also used for the species of Fusarium. For the species of Penicillium, three different media were used, including malt extract agar (MEA), Czapek yeast extract agar (CYA), and yeast extract sucrose agar (YES). Conidia morphology of the fungal species was examined under an ECLIPSE Ni-U microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan). Conidial characteristics, such as shape and dimensions, were recorded and compared with the descriptions in previous publications.
2.5. Pathogenicity Test
Pathogenicity of the strains was conducted on healthy Foshou yam tubers. Prior to the assay, the tubers were washed and surface-disinfected as previously described. Each tuber was then bored with a sterile 6 mm cork borer. To perform the assay, fungal strains were cultured on PDA for 5–7 days. Mycelia plugs (5 mm diam) taken from the edge of the colonies were placed in the holes after scooping out the yam tissue. The scooped-out tissue was used to cover the surface of the inoculation points. Tubers in control group were inoculated with pure PDA plugs. The wounds were sealed with petroleum jelly, and the inoculated tubers were placed in a sterile plastic bag. The pathogenicity test was repeated three times. Diseased tubers were used for re-isolation to confirm the causal fungi in accordance with Koch’s postulates.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Diameters of tuber lesions in pathogenicity assays were measured. Statistical significance was determined by the least significant difference (LSD) test (p ≤ 0. 05) in R software (2019, R Core Team, Vienna, Austria).
3. Results
3.1. Fungal Strains
In this study, diseased tubers of Foshou yam collected from Wuxue City were used for fungal isolation. Based on colony morphology, 10 representative fungal strains were selected for further analysis. The strain numbers were YZU 191548, YZU 191566, YZU 201358, YZU 211038, YZU 211044, YZU 201352, YZU 201354, YZU 201362, YZU 211048, and YZU 211050.
3.2. Molecular Phylogeny
Based on BLASTn searches (e-value ≤ 0.05), strains YZU 191548 and YZU 191566 showed 99–100% similarity to Curvularia species. Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Curvularia was conducted using 80 strains (including the two from this study), based on concatenated sequences of ITS and GAPDH. The best-fit substitution models for ITS and GAPDH were TNe+R2 and TNe+I+G4, respectively.
Strain YZU 191548 clustered with the ex-type strain BRIP 57412 and representative strains USJCC-0021 and LC11960 of Curvularia geniculata, with strong support (bootstrap value = 100%, Bayesian posterior probability = 1.00; Figure 2). Curvularia vidyodayana (USJCC-0029) formed a sister clade to Curvularia geniculata. Strain YZU 191566 grouped with the ex-type strain CBS 144.63 and representative strain USJCC-0027 of C. muehlenbeckiae, also supported by a bootstrap value of 100% and a Bayesian posterior probability of 1.00 (Figure 2).
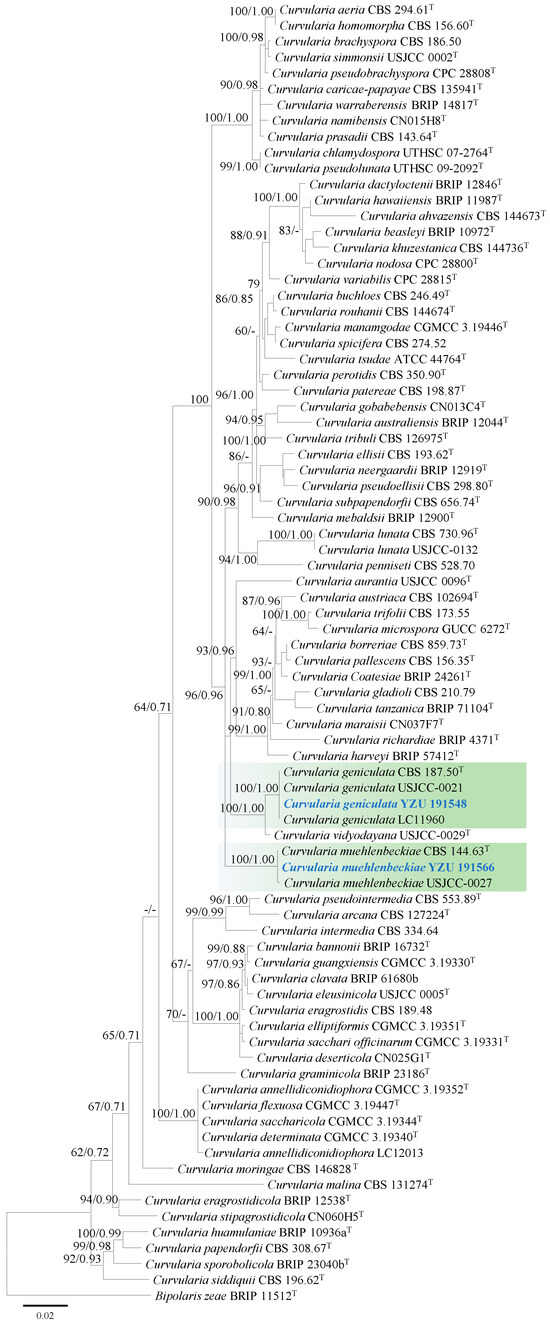
Figure 2.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of Curvularia spp. inferred from the combined datasets of the ITS and GAPDH gene sequences. Bipolaris zeae (BRIP 11512) was used as the outgroup taxon. Bootstrap values and Bayesian posterior probabilities are indicated on the branches. Ex-type strains are indicated with ‘T’. Strains from this study are indicated in blue bold.
Strains YZU 211044, YZU 201358, and YZU 211038 showed high similarity (99–100%) to Fusarium species based on BLASTn searches. Phylogenetic analysis of Fusarium spp. was conducted using concatenated sequences of ITS, TUB2, TEF1, and RPB2. A total of thirty-six strains (including the three from this study) were included in the analysis. The best-fit nucleotide substitution models for each gene were as follows: TIM2e+G4 for ITS and RPB2, TIM2e+I+G4 for TEF1, and TN+F+G4 for TUB2.
The three strains (YZU 211044, YZU 201358, and YZU 211038) clustered with the ex-type strain CBS 110090 and representative strains LC11660, LC13824, and NRRL 28387 of Fusarium commune (F. nisikadoi species complex), with strong support (bootstrap value = 100%, Bayesian posterior probability = 1.00; Figure 3).
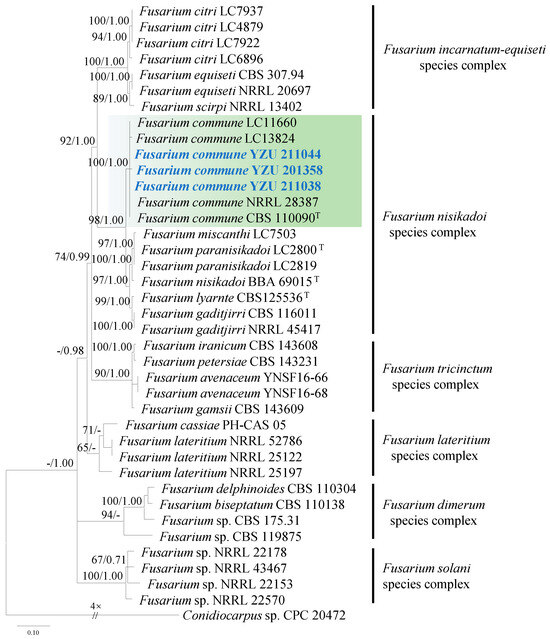
Figure 3.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of Fusarium spp. inferred from the combined datasets of the ITS, TUB2, TEF1, and RPB2 gene sequences. Conidiocarpus sp. (CPC 20472) was used as the outgroup taxon. Bootstrap values and Bayesian posterior probabilities are indicated on the branches. Ex-type strains are indicated with ‘T’. Strains from this study are indicated in blue bold.
For the identification of five strains (YZU 201352, YZU 201354, YZU 201362, YZU 211048, and YZU 211050) of Penicillium species, concatenated sequences of ITS, TUB2, CAL, and RPB2 were used for phylogenetic analysis. The best-fit models for these genes were TIM2e+I+G4, K2P+G4, TNe+I+G4, and TNe+G4, respectively. A total of twenty-nine strains (including five strains from this study) were used for the phylogeny. Based on the generated phylogenetic tree, strains YZU 201354, YZU 201362, and YZU 201,352 were clustered with the ex-type strain (CBS 219.30) and representative strains (SFC20140101-M839, CBS 301.97, and CBS 219.30) of P. oxalicum, supported by a bootstrap value of 99% and a Bayesian posterior probability of 0.89 (Figure 4). Strains YZU 211048 and YZU 211050 were grouped together with ex-type strain (CBS 101033) and representative strains (XG-6 and CNU079938) of P. sclerotigenum, supported by a bootstrap value of 100% and a Bayesian posterior probability of 0.99 (Figure 4).
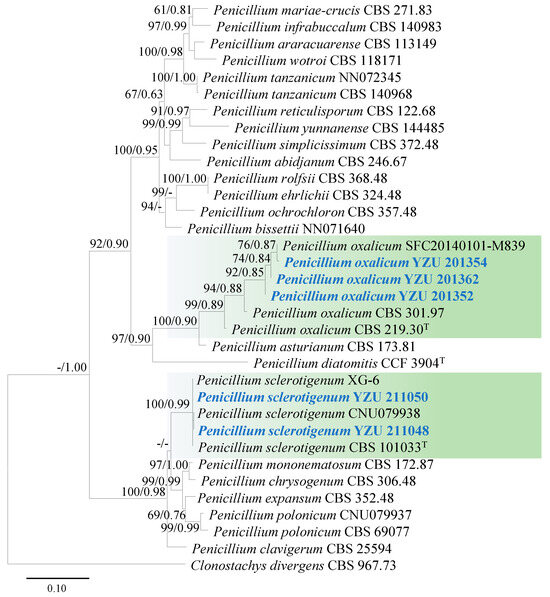
Figure 4.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of Penicillium spp. inferred from the combined datasets of the ITS, TUB2, CAL, and RPB2 gene sequences. Clonostachys divergens (CBS 967.73) was used as the outgroup taxon. Bootstrap values and Bayesian posterior probabilities are indicated on the branches. Ex-type strains are indicated with ‘T’. Strains from this study are indicated in blue bold.
3.3. Taxonomy: Curvularia geniculata YZU 191548
Colony morphology: On PDA, the colony reached approximately 63 mm in diameter after 7 days at 25 °C. It was olivaceous brown with an uneven margin, and the reverse side was dark in the center, surrounded by a yellowish margin (Figure 5A). On PCA, the colony reached 78–79 mm in diameter after 7 days at 25 °C, appeared greyish-green, and had a dark-brown reverse side (Figure 5B).
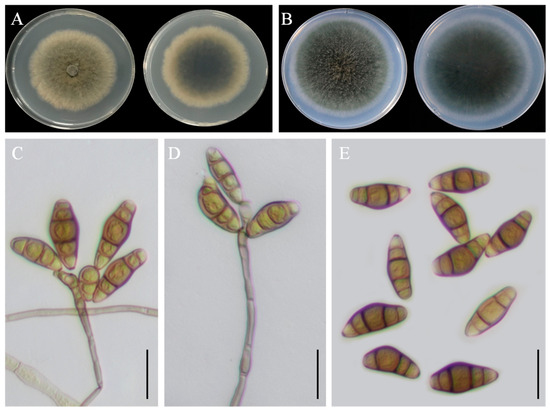
Figure 5.
Morphological characteristics of Curvularia geniculata YZU 191548. (A) Colony on PDA for 7 days at 25 °C; (B) colony on PCA for 7 days at 25 °C; (C–E) conidiophores and conidia. Scale bars, (C–E) = 20 µm.
Asexual morphology: Hyphae were thin, smooth-walled to verruculose, septate, subhyaline, and measured 2.5–4 µm in diameter. Conidiophores were mononematous, septate, straight or flexuous, mostly geniculate, unbranched or slightly branched, pale brown to brown, and measured 20(–190) µm in length. Conidia were subcylindrical to ellipsoidal, with broad central cells, verruculose and guttulate, pale brown, and 3–4 distoseptate, measuring 15(–25) × 5(–12) µm (Figure 5C–E). Conidiogenous loci were terminal or intercalary, mono- or sympodially proliferating, pale brown, subcylindrical, and 3–6 µm in width. The sexual morph was not observed.
Note: Based on phylogenetic analysis using ITS and GAPDH gene sequences, strain YZU 191548 was identified as Colletotrichum geniculata. This study represents the first identification of this fungus in association with tuber rot of Dioscorea esculenta.
3.4. Taxonomy: Curvularia muehlenbeckiae YZU 191566
Colony morphology: On PDA, the colony reached 85–86 mm in diameter after 7 days at 25 °C. It was olivaceous to yellowish-brown, with cottony aerial mycelium and a yellowish-brown reverse side (Figure 6A). On PCA, the colony reached 84–86 mm in diameter after 7 days at 25 °C. It was dark brown with a white margin, and the reverse side was dark (Figure 6B).
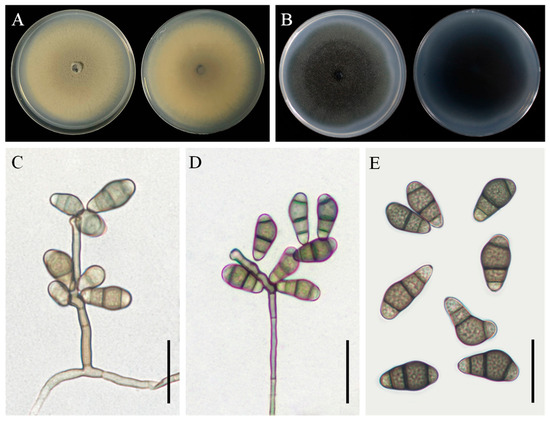
Figure 6.
Morphological characteristics of Curvularia muehlenbeckiae YZU 191566. (A) Colony on PDA for 7 days at 25 °C; (B) colony on PCA for 7 days at 25 °C; (C–E) conidiophores and conidia. Scale bars, (C–E) = 20 µm.
Asexual morphology: Hyphae were subhyaline to pale brown, branched, septate, and measured 1.5–5 µm in diameter. Conidiophores occurred singly or in groups, were septate, straight or flexuous, smooth-walled, mononematous, and sometimes branched, with lengths ranging up to 300 µm. Conidia were slightly verruculose, with middle cells unequally enlarged, subhyaline to pale brown, ellipsoidal to obovoid, and 3–4 distoseptate, measuring 14(–19) × 7(–9) µm (Figure 6C–E). Conidiogenous cells were smooth-walled, terminal or intercalary, sympodially proliferating, pale brown, and subcylindrical to swollen, measuring 4.5–14 µm in width. The sexual morph was not observed.
Note: Based on phylogenetic analysis using ITS and GAPDH gene sequences, strain YZU 191566 was identified as Colletotrichum muehlenbeckiae. This species was identified for the first time in association with tuber rot of Dioscorea esculenta.
3.5. Taxonomy: Fusarium commune YZU 201358
Colony morphology: On PDA, the colony reached 88–89 mm in diameter after 7 days at 25 °C. The front side was pink with a white margin and center, and the reverse side was yellow (Figure 7A).
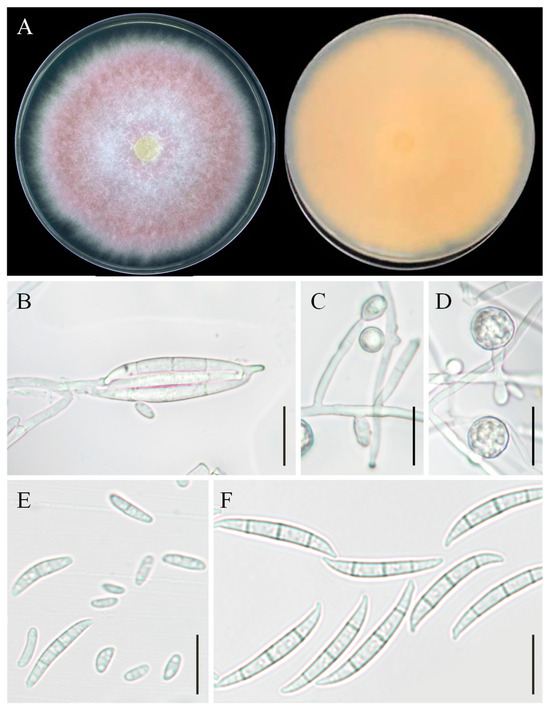
Figure 7.
Morphological characteristics of Fusarium commune YZU 201358. (A) Colony on PDA for 7 days at 25 °C; (B,F) macroconidia; (E) microconidia; (C,D) chlamydospores. Scale bars, (B–F) = 30 µm.
Asexual morphology: Macroconidia were abundant, elongate, and straight, measuring 3 × 35 μm, with 3–4 septa. The apical cells were tapered and curved, and the basal cell was developed, foot-shaped, 8–13 μm long, elongated, and barely to distinctly notched, measuring 9–14 μm in length (Figure 7B,F). Microconidia were fusiform to obovoid, measuring 5–16 × 2.5 μm, with 0–1 septa (Figure 7E). Chlamydospores were globose or subglobose (Figure 7C,D). Conidiogenous cells were monophialidic or polyphialidic, formed from aerial mycelium, measuring 6–30 × 3–3.5 μm in size.
Note: Strain YZU 201358 was identified as Fusarium commune based on phylogenetic analysis using concatenated sequences of the ITS, TUB2, TEF1, and RPB2 regions. This is the first report of F. commune being associated with tuber rot of Dioscorea esculenta.
3.6. Taxonomy: Penicillium sclerotigenum YZU 211050
Colony morphology: On CYA, colonies were velvety, with an aniline yellow reverse side, displaying a darker yellow center (Figure 8A). On MEA, colonies were floccose, devoid of exudates, with moderate sporulation. The reverse side was reddish-yellow to orange (Figure 8B). On YES, colonies were floccose, with moderate to abundant sporulation, dull green in color, and the reverse side was light yellow with a dark-yellow center (Figure 8C).
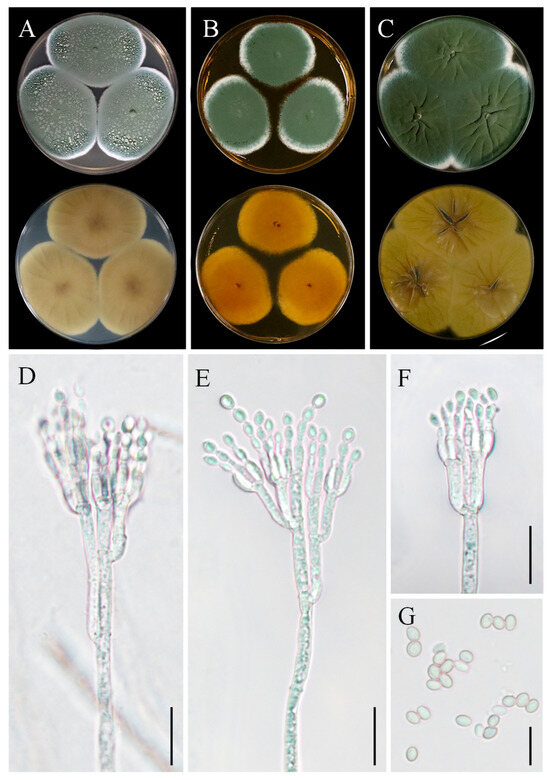
Figure 8.
Morphological characteristics of Penicillium sclerotigenum YZU 211050. (A) Colony on CYA; (B) colony on MEA; (C) colony on YES; (D–F) conidiophores and conidia; (G) conidia; scale bars, (D–F) = 15 µm, (G) = 10 µm.
Asexual morphology: Conidiophores were borne from surface hyphae. On MEA, stipes were mostly straight, measuring 200–600 µm in length, smooth-walled, rough-walled, biverticillate, and quadriverticillate. Metulae were cylindrical, measuring 15–25 µm in length. Phialides were smooth-walled, measuring 8–12 µm in length. Conidia were ellipsoidal, measuring 4–5 µm × 2.5–3.5 µm (Figure 8D–G).
Note: Morphologically, this fungus was similar with the previous description of P. sclerotigenum [39]. Phylogenetically, strain YZU 21050 clustered with reference strains of P. sclerotigenum. This is the first report of this fungus being associated with tuber rot of D. esculenta.
3.7. Taxonomy: Penicillium oxalicum YZU 201352
Colony morphology: On CYA, colonies were light yellow to dark yellow on the reverse side, with a dark-brown center and a whitish margin. The colonies were velutinous to floccose, with abundant sporulation (Figure 9A). On MEA, the colony margin was velutinous to lanose (Figure 9B). On YES, colonies were sulcate, whitish to light green, with the reverse side yellow to light greenish-yellow (Figure 9C).
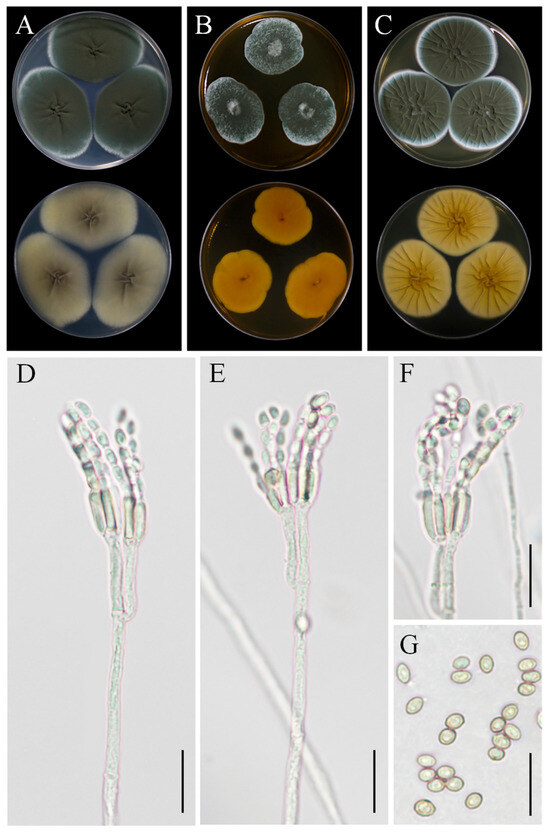
Figure 9.
Morphological characteristics of Penicillium oxalicum YZU 201352. (A) Colony on CYA; (B) colony on MEA; (C) colony on YES; (D–F) conidiophores and conidia; (G) conidia; scale bars, (D–F) = 30 µm, (G) = 15 µm.
Asexual morphology: Conidiophores were terminal, branched, typically biverticillate with 2–3 adpressed metulae or monoveticillate. Stipes were smooth, measuring mostly 75–400(–550) × 2.5–3.0 μm. Metulae were 11–25 × 2.5–4.5 μm. Phialides were cylindrical with a distinct collula, 2–6 per metula, measuring 8.5–15(–19) × 2.0–4.0 μm. Conidia were finely roughened, ellipsoidal, measuring 4–5.5 × 2.7–3.5 μm (Figure 9D–G). The sexual state was not known.
Note: Based on phylogenetic analysis using four markers (ITS, TUB2, CAL, and RPB2), strain YZU 201352 clustered closely with strains of P. oxalicum (XG6, CNU079938, and CBS 101033), with high statistical support. This fungus was identified here for the first time in association with tuber rot of Dioscorea esculenta.
3.8. Pathogenicity
The pathogenicity of the five fungal species was tested on healthy Foshou yam tubers using the following strains: YZU 191548 (C. geniculata), YZU 191566 (C. muehlenbeckiae), YZU 201358 (Fusarium commune), YZU 201352 (P. oxalicum), and YZU 211050 (P. sclerotigenum). Lesion diameters were measured 2 weeks post-inoculation. All fungal strains induced rot in yam tubers, while those in the control group remained healthy (Figure 10). Of all the tested strains, strain YZU 201352 (P. oxalicum) showed significantly higher pathogenicity than the others, with mean lesion diameters reaching 22.17 mm (Table 1). No significant difference was observed among the other four strains (Table 1). The mean lesion diameters caused by these four strains were similar: 10.65 mm for YZU 191548 (C. geniculata), 13.31 mm for YZU 191566 (C. muehlenbeckiae), 13.01 mm for YZU 201358 (Fusarium commune), and 11.50 mm for YZU 211050 (P. sclerotigenum). Each fungal pathogen was successfully reisolated from the inoculated tubers and reidentified by morphological and molecular methods, which confirms Koch’s postulates.
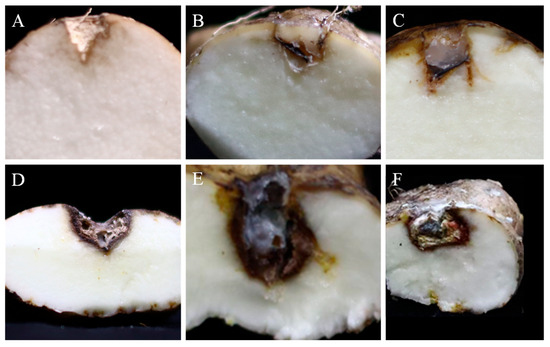
Figure 10.
Pathogenicity tests of fungal strains from this study on Foshou yam (Dioscorea esculenta) tubers. (A) Control; (B) Curvularia geniculata YZU 191548; (C) Curvularia muehlenbeckiae YZU 191566; (D) Fusarium commune YZU 201358; (E) Penicillium oxalicum YZU 201352; (F) Penicillium sclerotigenum YZU 211050.

Table 1.
Lesion diameters on Foshou yam (Dioscorea esculenta) tubers caused by different fungal species.
4. Discussion
Foshou yam (D. esculenta) is an agricultural product with geographical indication in Wuxue, China. In this study, tuber rot of Foshou yam was observed in Wuxue city from 2019 to 2021. Accurate identification of the pathogen is important for disease control. This study combined morphological analysis and multi-locus phylogeny to identify the fungal pathogens causing tuber rot in D. esculenta to the species level. The fungal species were identified as Curvularia geniculata, C. muehlenbeckiae, F. commune, P. oxalicum, and P. sclerotigenum based on combined analyses of morphology and multi-locus phylogeny. In addition, pathogenicity tests revealed differential pathogenicity among these species, with P. oxalicum showing the highest aggressiveness. To our knowledge, this is the first study to systematically characterize fungal pathogens involved in tuber rot in Foshou yam (D. esculenta).
In China, Neoscytalidium dimidiatum has recently been reported to cause dieback in D. esculenta [40]. In our study, three different genera (Curvularia, Fusarium, and Penicillium) were involved in the tuber rot of D. esculenta. The genus Curvularia contains various species, including saprophytes, endophytes, and pathogens. In this study, two species in this genus, C. geniculata and C. muehlenbeckiae, were isolated from yam tubers as pathogens. Curvularia geniculata has been reported on many different hosts, primarily plants in the Poaceae family. Curvularia muehlenbeckiae is a species first isolated from Muehlenbeckia sp. [41]. Later, this fungus was found on different hosts, including Cunninghamia lanceolata, Oryza sp., Saccharum officinarum, Sorghum spp., and Zizania latifolia [41,42,43,44,45,46]. According to the Fungus-Host database (https://fungi.ars.usda.gov/), C. eragrostidis has been found on Dioscorea spp. in Brazil. The present study expands the host range of C. geniculata and C. muehlenbeckiae. In addition, these two species showed similar aggressiveness toward their host, Foshou yam. Fusarium commune is one of the causal agents of fusarium wilt. This species can cause root rot disease in some plants, such as tomato, soybean, sugarcane, and horseradish [47,48,49,50]. In China, F. commune has frequently been found as the causal agent of fusarium wilt in Eleocharis dulcis [51]. This species has not previously been reported from Dioscorea spp. Our study revealed that F. commune is associated with tuber rot in Foshou yam (D. esculenta) in China. In this study, Penicillium oxalicum and P. sclerotigenum were also identified as pathogens in D. esculenta, with P. oxalicum showing stronger pathogenicity than P. sclerotigenum. According to the Fungus-Host database (https://fungi.ars.usda.gov/), these two species have been previously reported on Dioscorea sp. and D. batatas, respectively. Additionally, it has been reported that P. polonicum and P. sclerotigenum are associated with blue mold of yam (D. batatas) in Korea [39].
In conclusion, this study isolated and characterized five fungal species associated with tuber rot of D. esculenta in China. Their roles as causal pathogens of the disease were confirmed by pathogenicity tests. Since all five fungal species have not been previously reported in D. esculenta, increased attention and control efforts are needed to manage these new tuber rot pathogens in the future. Moreover, as plant diseases are dynamic and complex processes, further investigation is needed into additional factors contributing to infections in Foshou yam tubers in the field (e.g., soil conditions and plant–microbe interactions), as well as potential unknown pathogens.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jof11050380/s1, Table S1: GenBank accession numbers of fungal species used for phylogenetic analyses.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.D. and H.S.; methodology, H.L., A.A.H. and S.L.L.A.; formal analysis, S.L.L.A. and Y.T.; Investigation, A.A.H. and Y.T.; data curation, H.L. and A.A.H.; writing—original draft preparation, H.L. and A.A.H.; writing—review and editing, H.L., H.S. and J.D.; supervision, J.D.; project administration, J.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32270022).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The nucleotide sequences generated in this study were deposited in GenBank database.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mawuli K. Amenyogbe for his assistance in improving the English quality of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Aidoo, K.A. Identification of Yam Tuber Rot Fungi from Storage Systems at the Kumasi Central Market. Ph.D. Thesis, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi, Ghana, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Achar, K.; Vasanthakumari, M.; Mahishi, P.; Mallikarjunaswamy, G.; Shivanna, M. Prevalence and Severity of Anthracnose of Yam (Dioscorea alata and D. bulbifera) Caused by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides in Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary in Karnataka. J. Mycol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 43, 282–290. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Y.; Pearsall, D.M.; Gao, X.; Chen, F.; Pei, S.; Zhou, Z. Plant Use Activities during the Upper Paleolithic in East Eurasia: Evidence from the Shuidonggou Site, Northwest China. Quat. Int. 2014, 347, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, M.; Xue, J.; Hang, Y. Genetic Relationship and Identification of Dioscorea polystachya Cultivars Accessed by ISAP and SCAR Markers. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2017, 69, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Zhong, H.; Hu, B.; Tian, Z.; Sun, L.; Fischer, G.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Z. Agro-Ecological Suitability Assessment of Chinese Medicinal Yam under Future Climate Change. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 987–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Shan, N.; Ali, A.; Sun, J.; Luo, S.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, S.; Hu, R.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Q. Comprehensive Evaluation of Functional Components, Biological Activities, and Minerals of Yam Species (Dioscorea polystachya and D. alata) from China. LWT 2022, 168, 113964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ji, S.; Xu, T.; Zhong, Y.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Fan, B.; Wang, F.; Xiao, J.; et al. Chinese Yam (Dioscorea): Nutritional Value, Beneficial Effects, and Food and Pharmaceutical Applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 134, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Wang, F.; Liu, B.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, P.; Li, S. Novel Alkali Extraction, Optimisation, Characterisation, and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides from Foshou Yam. Int. Food Res. J. 2024, 31, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Yu, S.; Deng, X.; Hu, T. Research and Optimization of Foshou Yam and Honey Nutritional Can by Response Surface Methodology. J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 9, 156–161. [Google Scholar]
- Tariq, H.; Xiao, C.; Wang, L.; Ge, H.; Wang, G.; Shen, D.; Dou, D. Current Status of Yam Diseases and Advances of Their Control Strategies. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amusa, A.N.; Adegbite, A.A.; Muhammed, S.; Baiyewu, R.A. Yam Diseases and Its Management in Nigeria. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 2, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinbo, O. Pre and Post Harvest Studies of Yam Diseases and Their Control Measure in South Eastern Nigeria. Niger. Agric. J. 2019, 50, 193–197. [Google Scholar]
- Paparu, P.; Acur, A.; Kato, F.; Acam, C.; Nakibuule, J.; Nkuboye, A.; Musoke, S.; Mukankusi, C. Morphological and Pathogenic Characterization of Sclerotium rolfsii, the Causal Agent of Southern Blight Disease on Common Bean in Uganda. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 2130–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Xiao, C.; Zhou, K.; Fu, L.; Shen, D.; Dou, D. First Report of Nigrospora oryzae Causing Leaf Spot on Yam in China. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.-K.; Kim, W.-G.; Lee, Y.-K.; Choi, H.-W.; Choi, K.-J.; Lee, S.-Y. Leaf Spot of Yam Caused by Pseudophloeosporella dioscoreae in Korea. Mycobiology 2010, 38, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboagye-Nuamah, F.; Offei, S.K.; Cornelius, E.W.; Bancroft, R.D. Severity of Spoilage Storage Rots of White Yam (Dioscorea rotundata Poir.). Ann. Appl. Biol. 2005, 147, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, C.; Torino, V.; Minotti, P.; Pietrantonio, L.; Del Grosso, C.; Palmieri, D.; Palumbo, G.; Crawford, T.W.; Carfagna, S. Mycorrhized Wheat Plants and Nitrogen Assimilation in Coexistence and Antagonism with Spontaneous Colonization of Pathogenic and Saprophytic Fungi in a Soil of Low Fertility. Plants 2022, 11, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cubero, O.F.; Crespo, A.; Fatehi, J.; Bridge, P.D. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification Method Suitable for Fresh, Herbarium-Stored, Lichenized, and Other Fungi. Plant Syst. Evol. 1999, 216, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and Direct Sequencing of Fungal Ribosomal RNA Genes for Phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; Volume 18, pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, N.L.; Donaldson, G.C. Development of Primer Sets Designed for Use with the PCR to Amplify Conserved Genes from Filamentous Ascomycetes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-B.; Cho, H.-S.; Shin, H.-D.; Frisvad, J.C.; Samson, R.A. Novel Neosartorya Species Isolated from Soil in Korea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, I.; Kohn, L.M. A Method for Designing Primer Sets for Speciation Studies in Filamentous Ascomycetes. Mycologia 1999, 91, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbee, M.L.; Pirseyedi, M.; Hubbard, S. Cochliobolus Phylogenetics and the Origin of Known, Highly Virulent Pathogens, Inferred from ITS and Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Gene Sequences. Mycologia 1999, 91, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Whelen, S.; Hall, B.D. Phylogenetic Relationships among Ascomycetes: Evidence from an RNA Polymerse II Subunit. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A User-Friendly Biological Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Ferdinandez, H.S.; Manamgoda, D.S.; Udayanga, D.; Munasinghe, M.S.; Castlebury, L.A. Molecular Phylogeny and Morphology Reveal Two New Graminicolous Species, Curvularia aurantia sp. nov. and C. vidyodayana sp. nov. with New Records of Curvularia spp. from Sri Lanka. Fungal Syst. Evol. 2023, 12, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vuuren, N.; Yilmaz, N.; Wingfield, M.J.; Visagie, C.M. Five Novel Curvularia Species (Pleosporaceae, Pleosporales) Isolated from Fairy Circles in the Namib Desert. Mycol. Prog. 2024, 23, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crous, P.W.; Costa, M.M.; Kandemir, H.; Vermaas, M.; Vu, D.; Zhao, L.; Arumugam, E.; Flakus, A.; Jurjević, Ž.; Kaliyaperumal, M.; et al. Fungal Planet Description Sheets: 1550–1613. Persoonia 2023, 51, 280–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skovgaard, K.; Rosendahl, S.; O’Donnell, K.; Nirenberg, H.I. Fusarium commune Is a New Species Identified by Morphological and Molecular Phylogenetic Data. Mycologia 2003, 95, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.M.; Crous, P.W.; Sandoval-Denis, M.; Han, S.L.; Liu, F.; Liang, J.M.; Duan, W.J.; Cai, L. Fusarium and Allied Genera from China: Species Diversity and Distribution. Persoonia 2022, 48, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.L.; Wang, M.M.; Ma, Z.Y.; Raza, M.; Zhao, P.; Liang, J.M.; Gao, M.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, J.W.; Hu, D.M.; et al. Fusarium Diversity Associated with Diseased Cereals in China, with an Updated Phylogenomic Assessment of the Genus. Stud. Mycol. 2023, 104, 87–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.S.; Fong, J.J.; Oh, S.-Y.; Kwon, K.K.; Sohn, J.H.; Lim, Y.W. Marine-Derived Penicillium in Korea: Diversity, Enzyme Activity, and Antifungal Properties. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2014, 106, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Tan, T.; Tian, F.; Wang, Y.; Wen, T. OFPT: A One-Stop Software for Fungal Phylogeny. Mycosphere 2023, 14, 1730–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A Tool for Automated Alignment Trimming in Large-Scale Phylogenetic Analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast Model Selection for Accurate Phylogenetic Estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice across a Large Model Space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-K.; Hwang, Y.-S.; Yu, S.-H. Two Species of Penicillium Associated with Blue Mold of Yam in Korea. Mycobiology 2008, 36, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-X.; Liu, W.-B.; Wu, W.-Q.; Miao, W.-G.; Zheng, F.-C. First Report of Dioscorea esculenta Dieback Caused by Neoscytalidium dimidiatum in China. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid, H.; Da Cunha, K.C.; Gené, J.; Dijksterhuis, J.; Cano, J.; Sutton, D.A.; Guarro, J.; Crous, P.W. Novel Curvularia Species from Clinical Specimens. Persoonia 2014, 33, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemmuk, W.; Shivas, R.G.; Henry, R.J.; Geering, A.D.W. Fungi Associated with Foliar Diseases of Wild and Cultivated Rice (Oryza Spp.) in Northern Queensland. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2016, 45, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Hyde, K.D.; Diao, Y.-Z.; Cai, L. Culturable Plant Pathogenic Fungi Associated with Sugarcane in Southern China. Fungal Divers. 2019, 99, 1–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivas-Peraza, D.D.; Leyva-Madrigal, K.Y.; Maldonado-Mendoza, I.E.; Félix-Gastélum, R. Curvularia muehlenbeckiae Causing Leaf Spot on Johnson Grass in Mexico. Mycol. Progress 2022, 21, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.P.; Crous, P.W.; Shivas, R.G. Cryptic Species of Curvularia in the Culture Collection of the Queensland Plant Pathology Herbarium. Mycokeys 2018, 35, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Tang, T.; Chen, C.; Wei, L.; Zhou, D. First Report of Curvularia Leaf Spot Caused by Curvularia muehlenbeckiae on Zizania latifolia in China. J. Plant Pathol. 2021, 103, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chai, Z.; Bao, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Rao, G.P.; Zhang, M. First Report of Fusarium commune Causing Root Rot Disease of Sugarcane (Var. Badila) in China. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, M.L.; Arias, M.M.D.; Jimenez, D.R.C.; Munkvold, G.P.; Leandro, L.F. First Report of Fusarium commune Causing Damping-off, Seed Rot, and Seedling Root Rot on Soybean (Glycine max) in the United States. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamini-Kadar, N.; Edel-Hermann, V.; Gautheron, N.; Steinberg, C. First Report of Fusarium commune and Fusarium redolens Causing Crown and Root Rot on Tomato in Algeria. New Dis. Rep. 2010, 22, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.M.; Babadoost, M. Occurrence of Fusarium commune and F. oxysporum in Horseradish Roots. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zheng, L.; Pan, L.; Hsiang, T.; Huang, J. Identification and Characterization of Fusarium Species Associated with Wilt of Eleocharis dulcis (Chinese Water Chestnut) in China. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).