Avian Orexin: Feed Intake Regulator or Something Else?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Orexin
3. Central Role of Orexin
3.1. Feeding Behavior, Wake-Sleep Cycle, and Stress
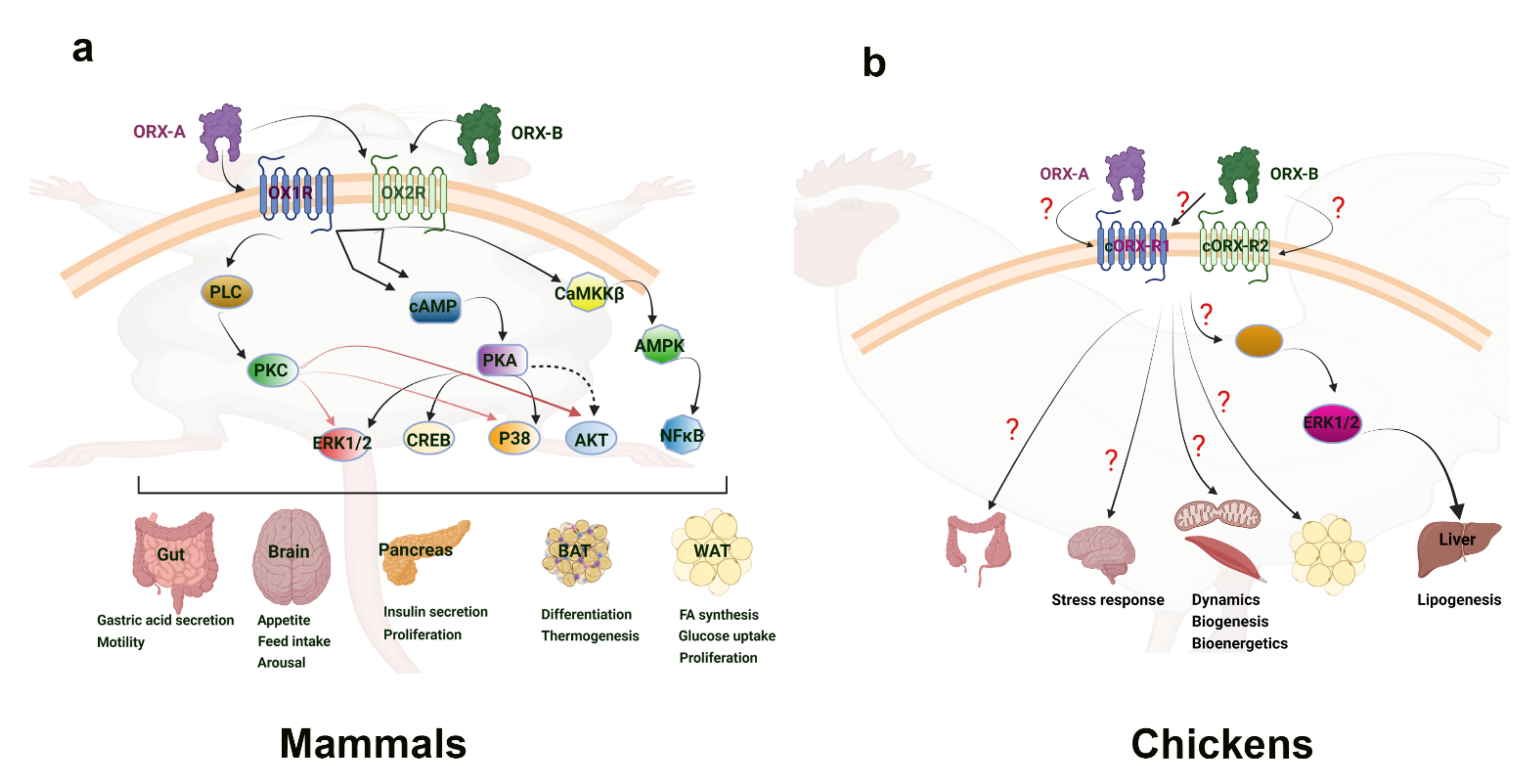
3.2. Central Orexin Signaling Pathways
3.3. Orexin in the Avian Central Nervous System
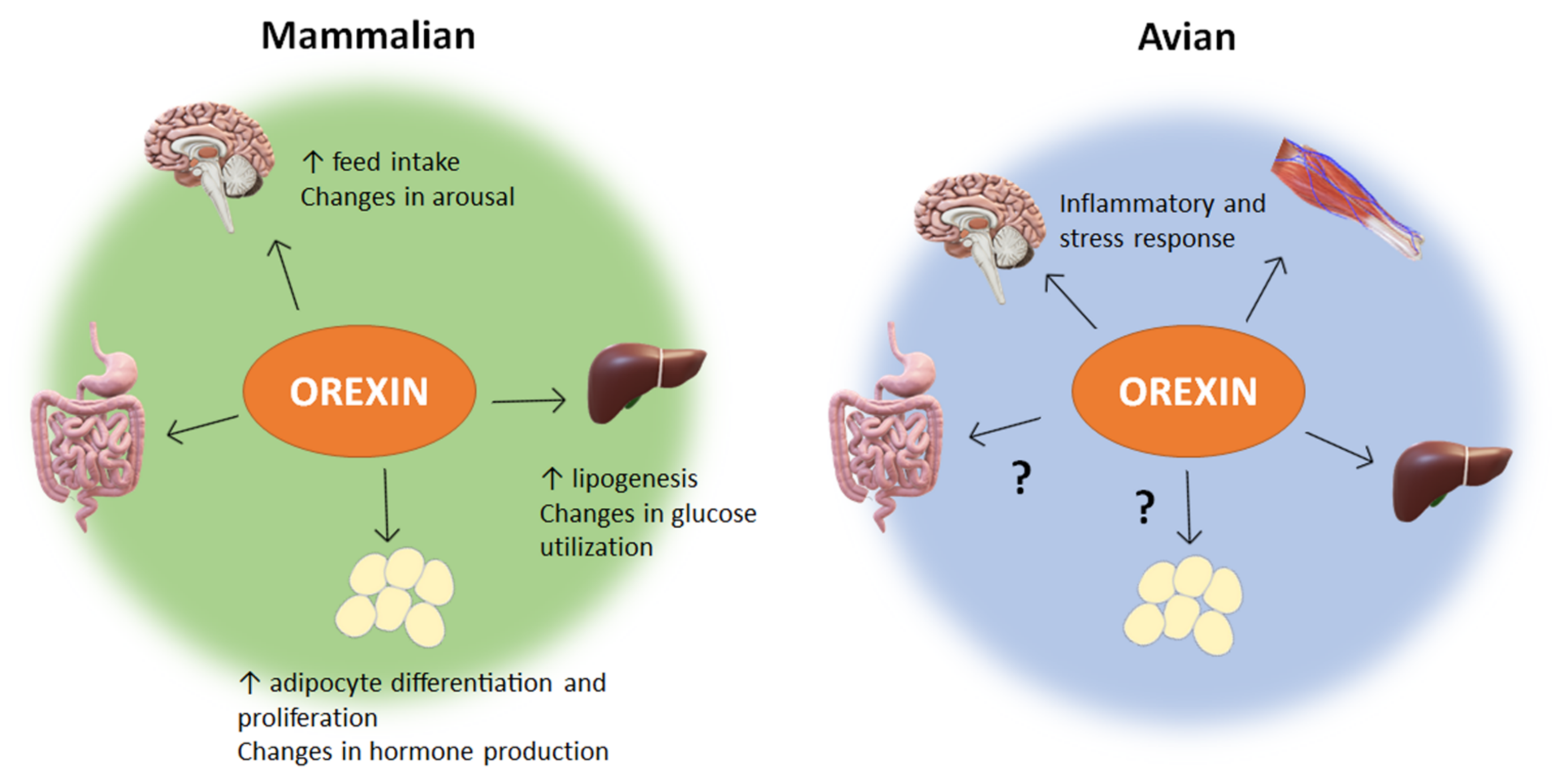
4. Peripheral Role of Orexin
4.1. Intestinal Tract and Digestion
4.2. Adipose Tissue
4.3. Liver
4.4. Peripheral Orexin Signaling Pathways
4.5. Orexin in Avian Peripheral Tissues
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baumann, C.R.; Bassetti, C.L. Hypocretins (orexins) and sleep–wake disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2005, 4, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehr, J.B.; Bilotti, M.M.; James, M.H. Orexin (hypocretin) and addiction. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 852–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.J.; Lister, C.A.; Buckingham, R.E.; Pickavance, L.; Wilding, J.; Arch, J.R.S.; Wilson, S.; Williams, G. Down-regulation of orexin gene expression by severe obesity in the rats: Studies in Zucker fatty and Zucker diabetic fatty rats and effects of rosiglitazone. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2000, 77, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunematsu, T.; Yamanaka, A. The role of orexin/hypocretin in the central nervous system and peripheral tissues. Vitam. Horm. 2012, 89, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Grasselli, F.; Bussolati, S.; Grolli, S.; Di Lecce, R.; Dall’Aglio, C.; Basini, G. Effects of Orexin B on Swine Granulosa and Endothelial Cells. Animals 2021, 11, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levanti, M.; Germanà, A.; Abbate, F. Orexin A Expression in the Ovary of Dog and Cat. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2015, 50, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zu, N.; Zhang, C.S.; Xie, M.Y.; Liu, Y.Z.; Xu, X.J. Orexin A promotes granulosa cell secretion of progesterone in sheep. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 20, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leone, A.; Spatola, G.F.; Cucco, D.; Tessitore, V.; Bonaventura, G.; Uzzo, M.L. Immunohistochemical expression and distribution of orexin, orphanin and leptin in the major salivary glands of some mammals. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2012, 50, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, Z.; Lecea, L. The hypocretins/orexins: Integrators of multiple physiological functions. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 332–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, T.; Amemiya, A.; Ishii, M.; Matsuzaki, I.; Chemelli, R.M.; Tanaka, H.; Williams, S.C.; Richardson, J.A.; Kozlowski, G.P.; Wilson, S.; et al. Orexins and Orexin Receptors: A Family of Hypothalamic Neuropeptides and G Protein-Coupled Receptors that Regulate Feeding Behavior. Cell 1998, 92, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lecea, L.; Kilduff, T.S.; Peyron, C.; Gao, X.; Foye, P.E.; Danielson, P.E.; Fukuhara, C.; Battenberg, E.L.; Gautvik, V.T.; Bartlett, F.S., II; et al. The Hypocretins: Hypothalamus-Specific Peptides with Neuroexcitatory Activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, T. Orexins and orexin receptors: Implication in feeding behavior. Regul. Pept. 1999, 85, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, T.; Moriguchi, T.; Furuya, K.; Kajiwara, N.; Nakamura, T.; Yanagisawa, M.; Goto, K. Structure and Function of Human Prepro-orexin Gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 17771–17776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkubo, T.; Tsukada, A.; Shamoto, K. cDNA cloning of chicken orexin receptor and tIssue distribution: Sexually dimorphic expression in chicken gonads. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 31, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, C.S.; Kukkonen, J.P. Orexin/hypocretin receptor signalling: A functional perspective. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkonen, J.P.; Leonard, C.S. Orexin/hypocretin receptor signalling cascades: Orexin receptor signalling cascades. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Babaoglu, K.; Brautigam, C.A.; Clark, L.; Shao, Z.; Scheuermann, T.H.; Harrell, C.M.; Gotter, A.L.; Roecker, A.J.; Winrow, C.J.; et al. Structure and ligand-binding mechanism of the human OX1 and OX2 orexin receptors. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, T.; Takaya, T.; Nakano, M.; Akutsu, H.; Nakagawa, A.; Aimoto, S.; Nagai, K.; Ikegami, T. Orexin-A is composed of a highly conserved C-terminal and a specific, hydrophilic N-terminal region, revealing the structural basis of specific recognition by the orexin-1 receptor. J. Pept. Sci. 2006, 12, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuki, T.; Sakurai, T. Orexins and orexin receptors: From molecules to integrative physiology. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 2008, 46, 27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heinonen, M.V.; Purhonen, A.K.; Makela, K.A.; Herzig, K.H. Functions of orexins in peripheral tissues. Acta Physiol. 2008, 192, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, C.J.; Tupone, D.; Morrison, S.F. Orexin modulates brown adipose tissue thermogenesis. Biomol. Concepts 2012, 3, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassiter, K.; Dridi, S. Orexin System and Avian Muscle Mitochondria. In Muscle Cells-Recent Advances and Future Perspectives; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wojciechowicz, T.; Skrzypski, M.; Szczepankiewicz, D.; Hertig, I.; Kołodziejski, P.A.; Billert, M.; Strowski, M.Z.; Nowak, K.W. Original Research: Orexins A and B stimulate proliferation and differentiation of porcine preadipocytes. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 241, 1786–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrzypski, M.; Billert, M.; Nowak, K.W.; Strowski, M.Z. The role of orexin in controlling the activity of the adipo-pancreatic axis. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 238, R95–R108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, C.M.; Abusnana, S.; Sunter, D.; Murphy, K.G.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. The effect of the orexins on food intake: Comparison with neuropeptide Y, melanin-concentrating hormone and galanin. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 160, R7–R12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, A.C.; Jackson, B.; Chapman, H.; Tadayyon, M.; Johns, A.; Porter, R.A.; Arch, J.R.S. A selective orexin-1 receptor antagonist reduces food consumption in male and female rats. Regul. Pept. 2000, 96, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, C.J.; Touchette, K.J.; Carroll, J.A.; Allee, G.L.; Matteri, R.L. Cloning of Porcine Prepro-Orexin cDNA and Effects of an Intramuscular Injection of Synthetic Porcine Orexin-B on Feed Intake in Young Pigs. Domest. Anim. Endorinol. 1999, 16, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Volkoff, H.; Narnaware, Y.; Bernier, N.J.; Peyon, P.; Peter, R.E. Brain regulation of feeding behavior and food intake in fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2000, 126, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartin, J.L.; Dyer, C.; Matteri, R.; Buxton, D.; Buonomo, F.; Shores, M.; Baker, J.; Osborne, J.A.; Braden, T.; Steele, B. Effect of intracerebroventricular orexin-B on food intake in sheep. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 79, 1573–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, A.; Beuckmann, C.T.; Willie, J.T.; Hara, J.; Tsujino, N.; Mieda, M.; Tominaga, M.; Yagami, K.-I.; Sugiyama, F.; Goto, K.; et al. Hypothalamic Orexin Neurons Regulate Arousal According to Energy Balance in Mice. Neuron 2003, 38, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdakov, D.; Gerasimenko, O.; Verkhratsky, A. Physiological Changes in Glucose Differentially Modulate the Excitability of Hypothalamic Melanin-Concentrating Hormone and Orexin Neurons In Situ. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 2429–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuneki, H.; Wada, T.; Sasaoka, T. Role of orexin in the central regulation of glucose and energy homeostasis. Endocr. J. 2012, 59, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokołowska, P.; Urbańska, A.; Biegańska, K.; Wagner, W.; Ciszewski, W.; Namiecińska, M.; Zawilska, J.B. Orexins Protect Neuronal Cell Cultures Against Hypoxic Stress: An Involvement of Akt Signaling. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 52, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterick, T.A.; Nixon, J.P.; Billington, C.J.; Kotz, C.M. Orexin A decreases lipid peroxidation and apoptosis in a novel hypothalamic cell model. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 524, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.; Yan, Y.; Tang, Y.; Dong, X.; Chen, G.; Kang, J.; Huang, L.; Xiong, Q.; Feng, Z. Orexin-A Attenuates Inflammatory Responses in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neural Stem Cells by Regulating NF-KB and Phosphorylation of MAPK/P38/Erk Pathways. J. Inflam. Res. 2021, 14, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Kong, T.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, B.; Chen, J.; Wang, C. Orexin-A protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting excessive autophagy through OX1R-mediated MAPK/ERK/mTOR pathway. Cell. Signal. 2021, 79, 109839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Kong, T.; Cheng, B.; Zhang, R.; Yang, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, C. Orexin-A alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignot, E. Sleep, sleep disorders and hypocretin (orexin). Sleep Med. 2004, 5, S2–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Faraco, J.; Li, R.; Kadotani, H.; Rogers, W.; Lin, X.; Qiu, X.; de Jong, P.J.; Nishino, S.; Mignot, E. The Sleep Disorder Canine Narcolepsy Is Caused by a Mutation in the Hypocretin (Orexin) Receptor 2 Gene. Cell 1999, 98, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- España, R.A.; Baldo, B.A.; Kelley, A.E.; Berridge, C.W. Wake-promoting and sleep-suppressing actions of hypocretin (orexin): Basal forebrain sites of action. Neuroscience 2001, 106, 699–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgin, P.; Huitron-Resendiz, S.; Spier, A.D.; Fabre, V.; Morte, B.; Criado, J.R.; Sutcliffe, J.G.; Henriksen, S.J.; de Lecea, L. Hypocretin-1 Modulates Rapid Eye Movement Sleep through Activation of Locus Coeruleus Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 7760–7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, A.A.; Joyal, A.A.; Yamanaka, A.; Scammell, T.E. The Impacts of Age and Sex in a Mouse Model of Childhood Narcolepsy. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 644757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonstein, J.S.; Linning-Duffy, K.; Tang, Y.; Moody, A.; Yan, L. Impact of daytime light intensity on the central orexin (hypocretin) system of a diurnal rodent (Arvicanthis niloticus). Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 54, 4167–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhla, B.; Goers, S.; Metges, C.C. Hypothalamic orexin A expression and the involvement of AMPK and PPAR-gamma signalling in energy restricted dairy cows. Arch. Tierzucht. 2011, 54, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’neill, H.M. Review: AMPK and Exercise: Glucose Uptake and Insulin Sensitivity. Diabetes Metab. J. 2013, 37, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzig, S.; Shaw, R.J. AMPK: Guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janani, C.; Ranjitha Kumari, B.D. PPAR gamma gene—A review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2014, 9, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-N.; Wu, P.-F.; Zhou, J.; Guan, X.-L.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.-J.; Long, L.-H.; Xie, N.; Chen, J.-G.; Wang, F. Orexin-A Activates Hypothalamic AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling through a Ca2+-Dependent Mechanism Involving Voltage-Gated L-Type Calcium Channel. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 84, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.; Seoane-Collazo, P.; Contreras, C.; González-García, I.; Martínez-Sánchez, N.; González, F.; Zalvide, J.; Gallego, R.; Diéguez, C.; Nogueiras, R.; et al. A Functional Link between AMPK and Orexin Mediates the Effect of BMP8B on Energy Balance. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 2231–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuse, M.; Ando, R.; Bungo, T.; Shimojo, M.; Masuda, Y. Intracerebroventricular injection of orexins does not stimulate food intake in neonatal chicks. Br. Poult. Sci. 1999, 40, 698–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkubo, T.; Boswell, T.; Lumineau, S. Molecular cloning of chicken prepro-orexin cDNA and preferential expression in the chicken hypothalamus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Struct. Expr. 2002, 1577, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, B.; Esposito, V.; de Girolamo, P.; Sharp, P.J.; Wilson, P.W.; Dunn, I.C. Orexin in the chicken hypothalamus: Immunocytochemical localisation and comparison of mRNA concentrations during the day and night, and after chronic food restriction. Brain Res. 2013, 1513, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soya, S.; Sakurai, T. Evolution of Orexin Neuropeptide System: Structure and Function. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singletary, K.G.; Deviche, P.; Strand, C.; Delville, Y. Distribution of orexin/hypocretin immunoreactivity in the brain of a male songbird, the house finch, Carpodacus mexicanus. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2007, 33, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Li, C.; Xin, H.; Li, S.; Bi, Y.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Bao, J. Keel Fracture Causes Stress and Inflammatory Responses and Inhibits the Expression of the Orexin System in Laying Hens. Animals 2019, 9, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Hepeng, L.; Xianlei, L.; Hongchao, J.; Hai, L.; Sheikhahmadi, A.; Yufeng, W.; Zhigang, S. Effects of acute heat stress on gene expression of brain-gut neuropeptides in broiler chickens. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 5194–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchgessner, A.L.; Liu, M.-T. Orexin Synthesis and Response in the Gut. Neuron 1999, 24, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naslund, E.; Ehrstrom, M.; Ma, J.; Hellstrom, P.M.; Kirchgessner, A.L. Localization and effects of orexin on fasting motility in the rat duodenum. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002, 282, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nakabayashi, M.; Suzuki, T.; Takahashi, K.; Totsune, K.; Muramatsu, Y.; Kaneko, C.; Date, F.; Takeyama, J.; Darnel, A.D.; Moriya, T.; et al. Orexin-A expression in human peripheral tissues. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2003, 205, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korczynski, W.; Ceregrzyn, M.; Matyjek, R.; Kato, I.; Kuwahara, A.; Wolinski, J.; Zabielski, R. Central and Local (Enteric) Action of Orexins. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2006, 57, 17–42. [Google Scholar]
- Satoh, Y.; Uchida, M.; Fujita, A.; Nishio, H.; Takeuchi, T.; Hata, F. Possible role of orexin A in nonadrenergic, noncholinergic inhibitory response of muscle of the mouse small intestine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 428, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, Y.; Okishio, Y.; Azuma, Y.-T.; Nakajima, H.; Hata, F.; Takeuchi, T. Orexin A affects ascending contraction depending on downstream cholinergic neurons and descending relaxation through independent pathways in mouse jejunum. Neuropharmacology 2006, 51, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, M.W.; Makela, K.; Herzig, K.-H.; Flemstrom, G. Short food deprivation inhibits orexin receptor 1 expression and orexin-A induced intracellular calcium signaling in acutely isolated duodenal enterocytes. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 296, G651–G658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, E.S.; Zampiga, M.; Sirri, F.; Ohkubo, T.; Dridi, S. Orexin system is expressed in avian liver and regulates hepatic lipogenesis via ERK1/2 activation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassiter, K.; Greene, E.; Piekarski, A.; Faulkner, O.B.; Hargis, B.M.; Bottje, W.; Dridi, S. Orexin system is expressed in avian muscle cells and regulates mitochondrial dynamics. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2015, 308, R173–R187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouedraogo, R.; Naslund, E.; Kirchgessner, A.L. Glucose Regulates the Release of Orexin-A From the Endocrine Pancreas. Diabetes 2003, 52, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, K.W.; Strowski, M.Z.; Switonska, M.M.; Kaczmarek, P.; Singh; Fabis, M.; Mackowiak, P.; Nowak, M.; Malendowicz, L.K. Evidence that orexins A and B stimulate insulin secretion from rat pancreatic islets via both receptor subtypes. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2005, 15, 969–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrzypski, M.; Le, T.T.; Kaczmarek, P.; Pruszynska-Oszmalek, E.; Pietrzak, P.; Szczepankiewicz, D.; Kolodziejski, P.A.; Sassek, M.; Arafat, A.; Wiedenmann, B.; et al. Orexin A stimulates glucose uptake, lipid accumulation and adiponectin secretion from 3T3-L1 adipocytes and isolated primary rat adipocytes. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 1841–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, D.; Chang, X.; Ju, S.; Guo, L. Effects of orexin A on GLUT4 expression and lipid content via MAPK signaling in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 138, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruszynska-Oszmalek, E.; Kolodziejski, P.A.; Kaczmarek, P.; Sassek, M.; Szczepankiewicz, D.; Mikula, R.; Nowak, K.W. Orexin A but not orexin B regulates lipid metabolism and leptin secretion in isolated porcine adipocytes. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2018, 63, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypski, M.; Kaczmarek, P.; Le, T.T.; Wojciechowicz, T.; Pruszyńska-Oszmalek, E.; Szczepankiewicz, D.; Sassek, M.; Arafat, A.; Wiedenmann, B.; Nowak, K.W.; et al. Effects of orexin A on proliferation, survival, apoptosis and differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes into mature adipocytes. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 4157–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, P.; Skrzypski, M.; Pruszynska-Oszmalek, E.; Sassek, M.; Kolodziejski, P.A.; Billert, M.; Szczepankiewicz, D.; Wojciechowicz, T.; Maechler, P.; Nowak, K.W.; et al. Chronic orexin-A (hypocretin-1) treatment of type 2 diabetic rats improves glucose control and beta-cell functions. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 68, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Świtońska, M.M.; Kaczmarek, P.; Malendowicz, L.K.; Nowak, K.W. Orexins and adipoinsular axis function in the rat. Regul. Pept. 2002, 104, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Shim, H.-M.; Na, A.-Y.; Bae, J.-H.; Im, S.-S.; Song, D.-K. Orexin A regulates plasma insulin and leptin levels in a time-dependent manner following a glucose load in mice. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 1542–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hara, J.; Beuckmann, C.T.; Nambu, T.; Willie, J.T.; Chemelli, R.M.; Sinton, C.M.; Sugiyama, F.; Yagami, K.-I.; Goto, K.; Yanagisawa, M.; et al. Genetic Ablation of Orexin Neurons in Mice Results in Narcolepsy, Hypophagia, and Obesity. Neuron 2001, 30, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, A.; Nakayama, K.; Nakamura, S.; Dantsuji, M.; Kamijo, R.; Shioda, S.; Sakurai, T.; Ozeki, M.; Inoue, T. Involvement of orexin in lipid accumulation in the liver. J. Oral Biosci. 2018, 60, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.; Adeleye, S.; Hudson, T.; Richardson, K.; Lee, D. Differential Exposure to Chronic vs. Acute Palatable Food Intake on Rat Renal Orexin Receptor 1 and NOX-4 Liver Expression. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 818–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Sun, C.; Wang, B.; Yan, P.; Wu, A.; Yang, G.; Li, W. Orexin-A stimulates the expression of GLUT4 in a glucose dependent manner in the liver of orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2016, 199, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Lei, T.; Guo, P.; Yu, J.; Xu, Q.; Luo, Y.; Ke, R.; Huang, D. Mechanisms shaping the role of ERK1/2 in cellular senescence. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, H.-Y.; Koh, M.-S.; Moon, A. The p38 MAPK inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases and cancer. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 1893–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuneki, H.; Murata, S.; Anzawa, Y.; Soeda, Y.; Tokai, E.; Wada, T.; Kimura, I.; Yanagisawa, M.; Sakurai, T.; Sasaoka, T. Age-related insulin resistance in hypothalamus and peripheral tissues of orexin knockout mice. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdar, M.; Liang, A.; Rajput, S.A.; Abbas, N.; Zubair, M.; Shaukat, A.; Rehman, A.u.; Jamil, H.; Guo, Y.; Ullah, F.; et al. Orexin-A Regulates Follicular Growth, Proliferation, Cell Cycle and Apoptosis in Mouse Primary Granulosa Cells via the AKT/ERK Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2021, 26, 5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Liao, Q.; Su, M.; Huang, K.; Jin, J.; Cao, D. AKT and ERK dual inhibitors: The way forward? Cancer Lett. 2019, 459, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcamone, N.; D’Angelo, L.; de Girolamo, P.; Lucini, C.; Pelagalli, A.; Castaldo, L. Orexin and orexin receptor like peptides in the gastroenteric tract of Gallus domesticus: An immunohistochemical survey on presence and distribution. Res. Vet. Sci. 2014, 96, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferver, A.; Greene, E.; Dridi, S. Hormonal regulation of visfatin gene in avian Leghorn male hepatoma (LMH) cells. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2020, 240, 110592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, E.; Khaldi, S.; Ishola, P.; Bottje, W.; Ohkubo, T.; Anthony, N.; Dridi, S. Heat and oxidative stress alter the expression of orexin and its related receptors in avian liver cells. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2016, 191, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.H.; Greene, E.; Kong, B.W.; Bottje, W.; Anthony, N.; Dridi, S. Acute Heat Stress Alters the Expression of Orexin System in Quail Muscle. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, O.; Tuzcu, M.; Sahin, N.; Orhan, C.; Tuzcu, Z.; Sahin, K. Organic chromium modifies the expression of orexin and glucose transporters of ovarian in heat-stressed laying hens. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2017, 63, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramser, A.; Dridi, S. Avian Orexin: Feed Intake Regulator or Something Else? Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9030112
Ramser A, Dridi S. Avian Orexin: Feed Intake Regulator or Something Else? Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(3):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9030112
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamser, Alison, and Sami Dridi. 2022. "Avian Orexin: Feed Intake Regulator or Something Else?" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 3: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9030112
APA StyleRamser, A., & Dridi, S. (2022). Avian Orexin: Feed Intake Regulator or Something Else? Veterinary Sciences, 9(3), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9030112





