Molecular Characterization of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Isolated over a 15-Year Period in Switzerland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolates
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Nitrate Reductase Gene
2.4. Diphtheria-Like Toxin Gene
2.5. Multilocus Sequencing
2.6. In Silico Sequence Analysis
2.7. Multilocus Sequence Analysis (MLSA)
2.8. Discriminatory Index
2.9. Whole-Genome Sequencing
Virulence Factor Analysis
3. Results
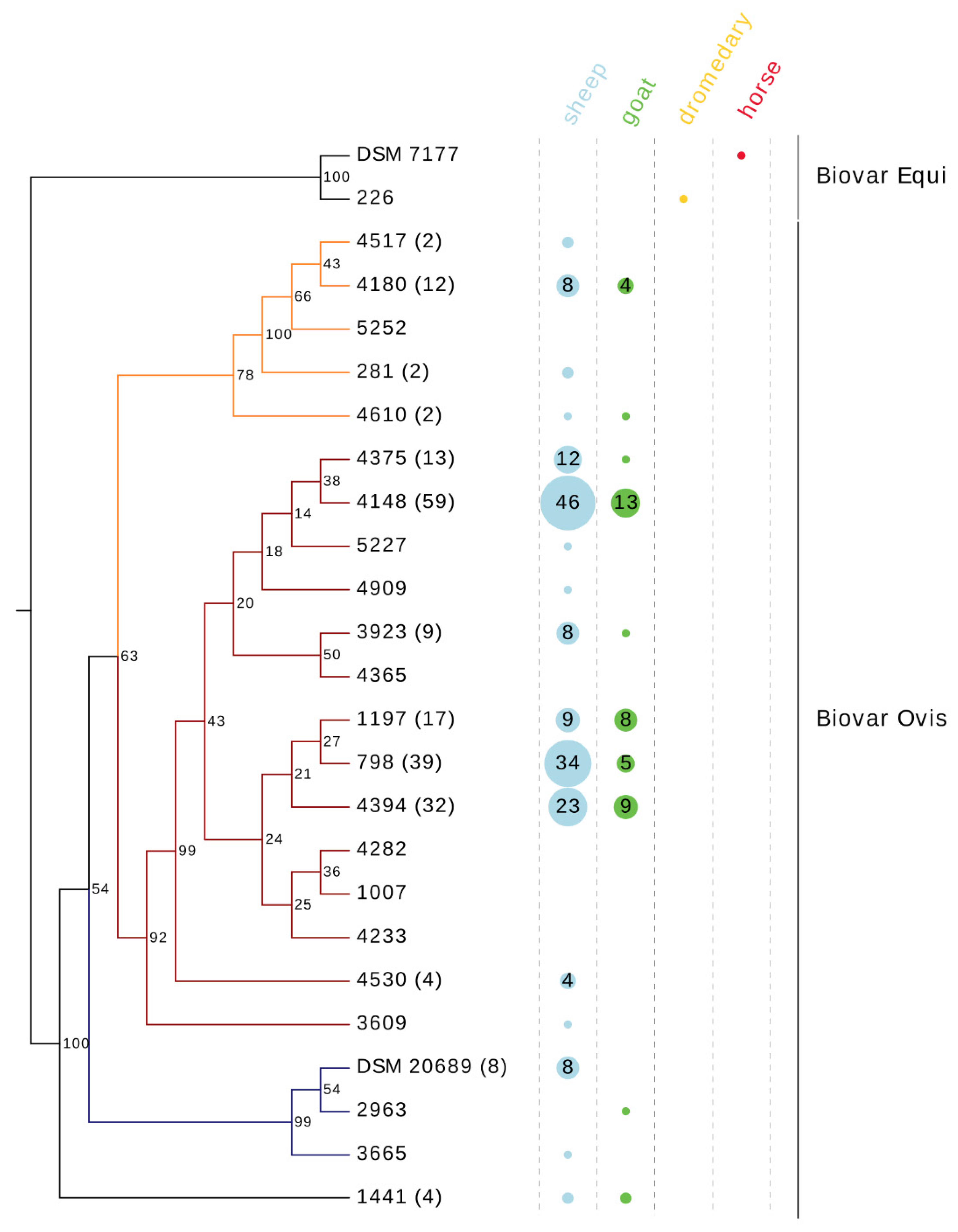
3.1. Biovar Classification
3.2. Temporal Distribution
3.3. Allelic Variation
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
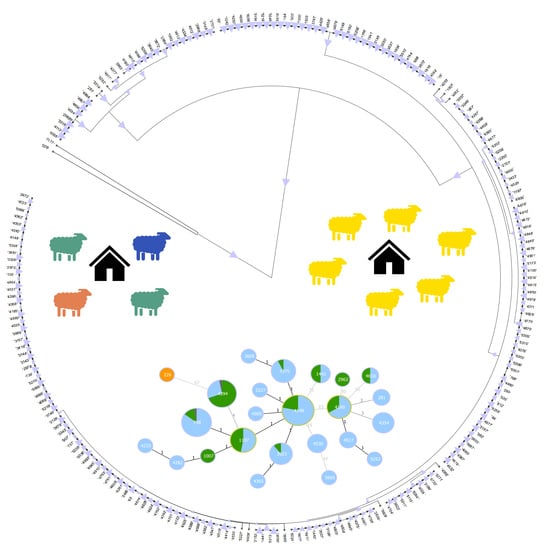
3.5. goeBURST Analysis
3.6. Discriminatory Index
3.7. SNP Analysis of Six Sequenced Isolates
3.8. Association between Sequence Type and Farms
3.9. Association between ST and Virulence
3.10. Diphtheria-Like Toxin Gene
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dorella, F.A.; Pacheco, L.; Oliveira, S.C.; Miyoshi, A.; Azevedo, V. Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis: Microbiology, biochemical properties, pathogenesis and molecular studies of virulence. Vet. Res. 2006, 37, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Sá Guimarães, A.; Ribeiro, D.; Lage, A.P.; Heinemann, M.B.; Miyoshi, A.; Gouveia, A.M.G. Caseous lymphadenitis: Epidemiology, diagnosis and control. IIOAB J. 2011, 2, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, G.; Fontaine, M. Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis and its role in ovine caseous lymphadenitis. J. Comp. Pathol. 2007, 137, 179–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilcoyne, I.; Spier, S.J.; Carter, C.N.; Smith, J.L.; Swinford, A.K.; Cohen, N.D. Frequency of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis infection in horses across the United States during a 10-year period. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2014, 245, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, T.; Silva, A.; Thiago, R.; Carneiro, A.; Dorella, F.A.; Rocha, F.S.; Santos, A.; Lima, A.R.J.; Guimarães, L.C.; Barbosa, E.G.V.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis strain Cp267, isolated from a llama. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 3567–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peel, M.M.; Palmer, G.G.; Stacpoole, A.M.; Kerr, T.G. Human lymphadenitis due to Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis: Report of ten cases from Australia and review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 24, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selim, S.E. Oedematous skin disease of buffalo in Egypt. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 2001, 48, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejedor-Junco, M.T.; Lupiola, P.; Schulz, U.; Gutierrez, C. Isolation of nitrate-reductase positive Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis from dromedary camels. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2008, 40, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeruham, I.; Elad, D.; Friedman, S.; Perl, S. Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis infection in Israeli dairy cattle. Epidemiol. Infect. 2003, 131, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colom-Cadena, A.; Velarde, R.; Salinas, J.; Borge, C.; García-Bocanegra, I.; Serrano, E.; Gassó, D.; Bach, E.; Casas-Díaz, E.; Lopezolvera, J.R.; et al. Management of a caseous lymphadenitis outbreak in a new Iberian ibex (Capra pyrenaica) stock reservoir. Acta Vet. Scand. 2014, 56, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domenis, L.; Spedicato, R.; Pepe, E.; Orusa, R.; Robetto, S. Caseous lymphadenitis caused by Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis in Alpine Chamois (Rupicapra r. Rupicapra): A review of 98 cases. J. Comp. Pathol. 2018, 161, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, D.; Sisay Tessema, T. Determination of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of isolates from lymph nodes of sheep and goats at an organic export abattoir, Modjo, Ethiopia. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 61, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pointon, A.; Hamilton, D.; Kiermeier, A. Comparison of postmortem inspection procedures for detecting caseous lymphadenitis of Australian sheep and goats. Vet. Rec. 2019, 185, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, L.H. Caseous lymphadenitis in small ruminants. Vet. Clin. North Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2001, 17, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, M.W.; Buller, N.B.; Rose, I.R.; Ellis, T.M. Effect of the interval between shearing and dipping on the spread of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis infection in sheep. Aust. Vet. J. 2002, 80, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, T.M.; Sutherland, S.S.; Wilkinson, F.C.; Mercy, A.R.; Paton, M.W. The role of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis lung lesions in the transmission of this bacterium to other sheep. Aust. Vet. J. 1987, 64, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, M.; Stewart, A.; Passler, T.; Wooldridge, A.; Van Santen, E.; Chamorro, M.; Cattley, R.; Hathcock, T.; Hogsette, J.; Hu, X. Experimental transmission of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis biovar equi in horses by house flies. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2015, 29, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braverman, Y.; Chizov-Ginzburg, A.; Saran, A.; Winkler, M. The role of houseflies (Musca domestica) in harbouring Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis in dairy herds in Israel. Rev. Sci. Tech. (Int. Off. Epizoot.) 1999, 18, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeruham, I.; Braverman, Y.; Shpigel, N.; Chizov-Ginzburg, A.; Saran, A.; Winkler, M. Mastitis in dairy cattle caused by Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosisand the feasibility of transmission by houseflies I. Vet. Q. 1996, 18, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, S.; Dorneles, E.M.S.; Diniz, C.; Abreu, V.; Sousa, C.; Alves, J.; Carneiro, A.; Bagano, P.; Spier, S.; Barh, D.; et al. Quadruplex PCR assay for identification of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis differentiating biovar Ovis and Equi. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biberstein, E.L.; Knight, H.D.; Jang, S. Two biotypes of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis. Vet. Rec. 1971, 89, 691–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songer, J.G.; Beckenbach, K.; Marshall, M.M.; Olson, G.B.; Kelley, L. Biochemical and genetic characterization of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1988, 49, 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Pratt, S.M.; Spier, S.J.; Carroll, S.; Vaughan, B.; Whitcomb, M.B.; Wilson, W.D. Evaluation of clinical characteristics, diagnostic test results, and outcome in horses with internal infection caused by Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis: 30 cases (1995–2003). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2005, 227, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorneles, E.M.S.; Santana, J.A.; Ribeiro, D.; Dorella, F.A.; Guimarães, A.S.; Moawad, M.S.; Selim, S.A.; Garaldi, A.L.M.; Miyoshi, A.; Ribeiro, M.G.; et al. Evaluation of ERIC-PCR as genotyping method for Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis isolates. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, M.W.; Walker, S.B.; Rose, I.R.; Watt, G.F. Prevalence of caseous lymphadenitis and usage of caseous lymphadenitis vaccines in sheep flocks. Aust. Vet. J. 2003, 81, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, L.; Huerta, B.; Galán-Relaño, Á.; Gómez-Gascón, L.; Almeida, A.; Viegas, I.; Maldonado, A. Utility assessment of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of subclinical cases of caseous lymphadenitis in small ruminant flocks. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 6, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, A.S.; Carmo, F.B.; Heinemann, M.B.; Portela, R.W.; Meyer, R.; Lage, A.P.; Seyffert, N.; Miyoshi, A.; Azevedo, V.; Gouveia, A.M. High sero-prevalence of caseous lymphadenitis identified in slaughterhouse samples as a consequence of deficiencies in sheep farm management in the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil. BMC Vet. Res. 2011, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arsenault, J.; Girard, C.; Dubreuil, P.; Daignault, D.; Galarneau, J.-R.; Boisclair, J.; Simard, C.; Bélanger, D. Prevalence of and carcass condemnation from maedi–visna, paratuberculosis and caseous lymphadenitis in culled sheep from Quebec, Canada. Prev. Vet. Med. 2003, 59, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heggelund, L.; Gaustad, P.; Håvelsrud, O.E.; Blom, J.; Borgen, L.; Sundset, A.; Sørum, H.; Frøland, S.S. Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis pneumonia in a veterinary student infected during laboratory work. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2015, 2, ofv053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres, L.d.F.C.; Ribeiro, D.; Hirata, R., Jr.; Pacheco, L.G.C.; Souza, M.C.; dos Santos, L.S.; dos Santos, C.S.; Salah, M.; da Costa, M.M.; Ribeiro, M.G.; et al. Multiplex polymerase chain reaction to identify and determine the toxigenicity of Corynebacterium spp with zoonotic potential and an overview of human and animal infections. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2013, 108, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, E.; Ott, L.; Schneider, J.; Schröder, J.; Jaenicke, S.; Goesmann, A.; Husemann, P.; Stoye, J.; Dorella, F.A.; Rocha, F.S.; et al. The complete genome sequence of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis FRC41 isolated from a 12-year-old girl with necrotizing lymphadenitis reveals insights into gene-regulatory networks contributing to virulence. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKean, S.C.; Davies, J.K.; Moore, R.J. Expression of phospholipase D, the major virulence factor of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis, is regulated by multiple environmental factors and plays a role in macrophage death. Microbiology 2007, 153, 2203–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weibel, J.C. Cell Invasion and Intracellular Survival of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Maximescu, P.; Oprisan, A.; Pop, A.; Potorac, E. Further studies on Corynebacterium species capable of producing diphtheria toxin (C. diphtheriae, C. ulcerans, C. ovis). J. Gen. Microbiol. 1974, 82, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Selim, S.A.; Mohamed, F.H.; Hessain, A.M.; Moussa, I.M. Immunological characterization of diphtheria toxin recovered from Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, N.C.; Efstratiou, A.; Mokrousov, I.; Mutreja, A.; Das, B.; Ramamurthy, T. Diphtheria. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, S. Genetic differences between nitrate-negative and nitrate-positive C. pseudotuberculosis strains using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Vet. Microbiol. 1996, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, K.M.; Fontaine, M.C.; Rudge, K.; Baird, G.J.; Donachie, W. Molecular genotyping of multinational ovine and caprine Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis isolates using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Vet. Res. 2007, 38, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, L.R.; Spier, S.J.; Hirsh, D.C. Comparative molecular characterization of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis of different origin. Vet. Microbiol. 1998, 62, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorneles, E.; Santana, J.A.; Andrade, G.; Santos, E.; Guimarães, A.; Mota, R.; Santos, A.; Miyoshi, A.; Azevedo, V.; Gouveia, A.; et al. Short communication molecular characterization of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis isolated from goats using ERIC-PCR. Genet. Mol. Res. 2012, 11, 2051–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, A.D.S.; Dorneles, E.M.S.; Andrade, G.I.; Lage, A.P.; Miyoshi, A.; Azevedo, V.; Gouveia, A.M.G.; Heinemann, M.B. Molecular characterization of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis isolates using ERIC-PCR. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 153, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meacham, K.J.; Zhang, L.; Foxman, B.; Bauer, R.J.; Marrs, C.F. Evaluation of genotyping large numbers of Escherichia coli isolates by Enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus-PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5224–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tyler, K.D.; Wang, G.; Tyler, S.D.; Johnson, W.M. Factors affecting reliability and reproducibility of amplification-based DNA fingerprinting of representative bacterial pathogens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wijetunge, D.S.; Dunn, P.; Wallner-Pendleton, E.; Lintner, V.; Lu, H.; Kariyawasam, S. Fingerprinting of poultry isolates of Enterococcus cecorum using three molecular typing methods. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2012, 24, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gevers, D.; Cohan, F.M.; Lawrence, J.G.; Spratt, B.G.; Coenye, T.; Feil, E.J.; Stackebrandt, E.; Van de Peer, Y.; Vandamme, P.; Thompson, F.L.; et al. Re-evaluating prokaryotic species. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 3, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaeser, S.P.; Kämpfer, P. Multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) in prokaryotic taxonomy. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 38, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiden, M.C.J.; Bygraves, J.A.; Feil, E.; Morelli, G.; Russell, J.E.; Urwin, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zurth, K.; Caugant, D.A.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing: A portable approach to the identification of clones within populations of pathogenic microorganisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3140–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sellyei, B.; Bányai, K.; Bartha, D.; Hajtos, I.; Fodor, L.; Makrai, L. Multilocus sequencing of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis biotype Ovis strains. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1762162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- König, C.; Meinel, D.; Margos, G.; Konrad, R.; Sing, A. Multilocus sequence typing of Corynebacterium ulcerans provides evidence for zoonotic transmission and for increased prevalence of certain sequence types among toxigenic strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4318–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bolt, F.; Cassiday, P.; Tondella, M.L.; DeZoysa, A.; Efstratiou, A.; Sing, A.; Zasada, A.; Bernard, K.; Guiso, N.; Badell, E.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing identifies evidence for recombination and two distinct lineages of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 4177–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prohaska, S.; Regenscheit, N.; Hilbe, M.; Gerspach, C.; Wittenbrink, M.M. Visceral form of pseudotuberculosis in a dromedary with biovar equi. Vet. Rec. Case Rep. 2013, 1, e000010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, F.; Monaco, M.; Pataracchia, M.; von Hunolstein, C.; Pantosti, A.; Ciervo, A. Identification and molecular discrimination of toxigenic and nontoxigenic diphtheria Corynebacterium strains by combined real-time polymerase chain reaction assays. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 73, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gao, S.; Lercher, M.; Chen, W.-H.; Hu, S. Evolview v2: An online visualization and management tool for customized and annotated phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W236–W241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, A.P.; Vaz, C.; Monteiro, P.T.; Melo-Cristino, J.; Ramirez, M.; Carriço, J.A. PHYLOViZ: Phylogenetic inference and data visualization for sequence based typing methods. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hunter, P.R.; Gaston, M.A. Numerical index of the discriminatory ability of typing systems: An application of Simpson’s index of diversity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 2465–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, D.J.; Dorneles, E.M.S.; Spier, S.J.; Carroll, S.P.; Edman, J.; Azevedo, V.A.; Heinemann, M.B.; Lage, A.P. Molecular epidemiology of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis isolated from horses in California. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 49, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, S.D.C.; Silva, A.; Trost, E.; Blom, J.; Ramos, R.; Carneiro, A.; Ali, A.; Santos, A.; Pinto, A.C.; Diniz, C.; et al. The pan-genome of the animal pathogen Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis reveals differences in genome plasticity between the biovar ovis and equi strains. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz, J.C.; D’Afonseca, V.; Silva, A.; Ali, A.; Pinto, A.C.; Santos, A.R.; Rocha, A.A.M.C.; Lopes, D.O.; Dorella, F.A.; Pacheco, L.; et al. Evidence for reductive genome evolution and lateral acquisition of virulence functions in two Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis strains. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, S.; Loureiro, D.; Portela, R.W.; Mariano, D.C.B.; Sousa, T.J.; Pereira, F.L.; Dorella, F.A.; Carvalho, A.F.; Moura-Costa, L.F.; Leal, C.A.G.; et al. Complete genome sequence of the attenuated Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis strain T1. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00947-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pethick, F.E.; Lainson, A.F.; Yaga, R.; Flockhart, A.; Smith, D.; Donachie, W.; Cerdeira, L.; Silva, A.; Bol, E.; Lopes, T.S.; et al. Complete genome sequences of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis strains 3/99-5 and 42/02-A, isolated from sheep in Scotland and Australia, respectively. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 4736–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, T.D.J.; Parise, D.; Profeta, R.; Parise, M.T.D.; Gomide, A.C.P.; Kato, R.; Pereira, F.L.; Figueiredo, H.C.P.; Ramos, R.; Brenig, B.; et al. Re-sequencing and optical mapping reveals misassemblies and real inversions on Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis genomes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerdeira, L.; Pinto, A.C.; Schneider, M.P.C.; de Almeida, S.S.; Santos, A.; Barbosa, E.G.V.; Ali, A.; Barbosa, M.S.; Carneiro, A.R.; Ramos, R.; et al. Whole-genome sequence of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis PAT10 strain isolated from sheep in Patagonia, Argentina. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 6420–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ibraim, I.C.; Parise, M.T.D.; Parise, D.; Sfeir, M.Z.T.; Castro, T.L.D.P.; Wattam, A.R.; Ghosh, P.; Barh, D.; Souza, E.M.; Góes-Neto, A.; et al. Transcriptome profile of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis in response to iron limitation. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Primer Name | Putative Gene Function | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| groEL1_F groEL1_R | Heat-shock protein | ACCTTCACCGGATCATTG TTGGTGATCGTCGTAAAGC | 655 | Sellyei et al. 2017 [48] |
| leuA_F leuA_R | 2-isopropylmalate synthase | AGCTCAGTGCGCGGTTGACC ATGGCGTCGCGGGTTCG | 664 | Sellyei et al. 2017 [48] |
| infB_F infB_R | Translation initiation factor IF2 | ATTGCGGGACTTGGACG GCATTATGCTGCACAAGACG | 642 | Sellyei et al. 2017 [48] |
| dnaK_F dnaK_R | Chaperone Hsp70 | TCCTTACCAGTGCCCTTATCC GAGTTCCAGCGCATCACC | 580 | Sellyei et al. 2017 [48] |
| aspT_F aspT_R | Aspartate aminotransferase | TCCCGCTGAGAACCTGGTTG GATCACTGCCTAGCCCACAT | 1102 | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schlicher, J.; Schmitt, S.; Stevens, M.J.A.; Stephan, R.; Ghielmetti, G. Molecular Characterization of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Isolated over a 15-Year Period in Switzerland. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8080151
Schlicher J, Schmitt S, Stevens MJA, Stephan R, Ghielmetti G. Molecular Characterization of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Isolated over a 15-Year Period in Switzerland. Veterinary Sciences. 2021; 8(8):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8080151
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchlicher, Jessica, Sarah Schmitt, Marc J. A. Stevens, Roger Stephan, and Giovanni Ghielmetti. 2021. "Molecular Characterization of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Isolated over a 15-Year Period in Switzerland" Veterinary Sciences 8, no. 8: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8080151
APA StyleSchlicher, J., Schmitt, S., Stevens, M. J. A., Stephan, R., & Ghielmetti, G. (2021). Molecular Characterization of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Isolated over a 15-Year Period in Switzerland. Veterinary Sciences, 8(8), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8080151