Molecular and Serological Footprints of Mycobacterium avium Subspecies Infections in Zoo Animals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.1.1. Serum Samples
2.1.2. Fecal and Environmental Samples
2.1.3. Tissue Samples
2.2. Serological Survey
2.2.1. Mycobacterium avium Complex (MAC) ELISA
2.2.2. Mycobacterium avium Subspecies Paratuberculosis (MAP) ELISA
2.3. Molecular Survey
3. Results
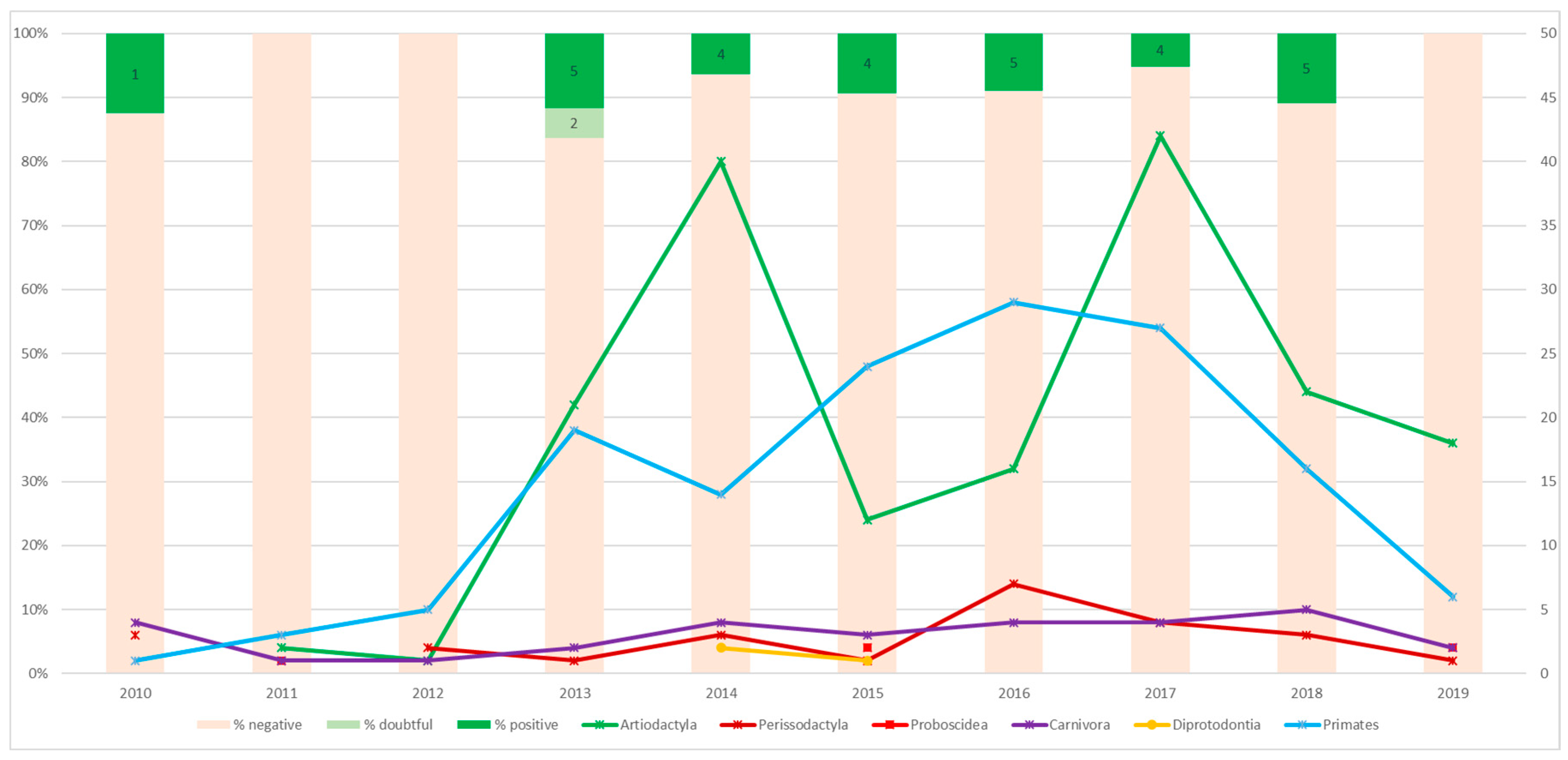
3.1. Serological Survey
3.2. Molecular Survey
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thorel, M.F.; Krichevsky, M.; Lévy-Frébault, V.V. Numerical taxonomy of mycobactin-dependent mycobacteria, emended description of Mycobacterium avium, and description of Mycobacterium avium subsp. avium subsp. nov., Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis subsp. nov., and Mycobacterium avium subsp. silvaticum subsp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1990, 40, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijs, W.; de Haas, P.; Rossau, R.; Van Der Laan, T.; Rigouts, L.; Portaels, F.; van Soolingen, D. Molecular evidence to support a proposal to reserve the designation Mycobacterium avium subsp. avium for bird-type isolates and ‘M. avium subsp. hominissuis’ for the human/porcine type of M. avium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turenne, C.Y.; Alexander, D.C. Mycobacterium avium complex. In Paratuberculosis; Organism, Disease, Control; Behr, M.A., Collins, D.M., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2010; pp. 60–72. [Google Scholar]
- Inderlied, C.B.; Kemper, C.A.; Bermudez, L.E. The Mycobacterium avium complex. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1993, 6, 266–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamberski, N. Nontuberculous mycobacteria: Potential for zoonosis. In Fowler’s Zoo and Wild Animal Medicine: Current Therapy 4; Fowler, M.E., Miller, R.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Isaza, R. Tuberculosis in all taxa. In Fowler’s Zoo and Wild Animal Medicine: Current Therapy 5; Fowler, M.E., Miller, R.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 689–696. [Google Scholar]
- Riggs, G. Avian mycobacterial disease. In Fowler’s Zoo and Wild Animal Medicine 7; Fowler, M.E., Miller, R.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 266–274. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, N.B.; Barletta, R.G. Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosisin veterinary medicine. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 489–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitlock, R.H.; Buergelt, C. Preclinical and clinical manifestations of paratuberculosis (including pathology). Vet. Clin. North. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 1996, 12, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, E.J.; Sleeman, J.M. Johne’s disease and free-ranging wildlife. In Fowler’s Zoo and Wild Animal Medicine: Current Therapy; Fowler, M.E., Miller, R.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 7, pp. 628–635. [Google Scholar]
- Manning, E.J.; Collins, M.T. Paratuberculosis in zoo animals. In Fowler’s Zoo and Wild Animal Medicine: Current Therapy 4; Fowler, M.E., Miller, R.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 612–616. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchings, M.R.; Stevenson, K.; Greig, A.; Davidson, R.S.; Marion, G.; Judge, J. Infection of non-ruminant wildlife by Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. In Paratuberculosis; Organism, Disease, Control; Behr, M.A., Collins, D.M., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2010; pp. 188–200. [Google Scholar]
- Vansnick, E.; Vercammen, F.; Bauwens, L.; D’Haese, E.; Nelis, H.; Geysen, D. A survey for Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis in the Royal Zoological Society of Antwerp. Vet. J. 2005, 170, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, A.D.; Richardson, D.; Sellar, M.; Harley, J.; Philbey, A.W.; Girling, S.J. Clinical Signs, antemortem diagnostics, and pathological findings associated with Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis infection in Mishmi Takin (Budorcas taxicolor taxicolor). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2018, 49, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erume, J.; Spergser, J.; Rosengarten, R. Rapid detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis from cattle and zoo animals by nested PCR. Afr. Health Sci. 2001, 1, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Witte, C.L.; Hungerford, L.L.; Rideout, B.A. Association between Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis infection among offspring and their dams in nondomestic ruminant species housed in a zoo. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2009, 21, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, T.L.; Witte, C.L.; Rideout, B.A. Early-life exposures and Johne’s disease risk in zoo ruminants. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2018, 30, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst, C.; Speck, S.; Hofer, H. Serosurvey of zoo ungulates in central Europe. Int. Zoo Yearb. 2011, 45, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, M.S.; Olsen, J.H.; Ball, R.L.; Dumonceaux, G.A. Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis infection in an addax (Addax nasomaculatus). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2001, 32, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Münster, P.; Fechner, K.; Volkel, I.; von Buchholz, A.; Czerny, C.P. Distribution of Mycobacterium avium ssp. paratuberculosis in a German zoological garden determined by IS900 semi-nested and quantitative real-time PCR. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 163, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fechner, K.; Matz-Rensing, K.; Lampe, K.; Kaup, F.J.; Czerny, C.P.; Schafer, J. Detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in non-human primates. J. Med. Primatol. 2017, 46, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fechner, K.; Schafer, J.; Munster, P.; Ternes, K.; Doring, S.; Volkel, I.; Kaup, F.J.; Czerny, C.P. Detection of Mycobacterium avium Subspecies Paratuberculosis in Rock Hyraxes (Procavia Capensis) Imported from South Africa. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2017, 48, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwick, L.S.; Walsh, T.F.; Barbiers, R.; Collins, M.T.; Kinsel, M.J.; Murnane, R.D. Paratuberculosis in a mandrill (Papio sphinx). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2002, 14, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, B.; Blyde, D.; Eamens, G.; Whittington, R. Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis cultured from the feces of a Southern black rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis minor) with diarrhea and weight loss. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2012, 43, 391–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. Proceedings of the Workshop on Diagnosis, Prevention, and Control of Johne’s Disease in Non-Domestic Hoofstock; White Oak Conservation Center: Yulee, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg, T.; Wolter, W.; Lenz, M.; Schlez, K.; Zschöck, M. Boot swabs to collect environmental samples from common locations in dairy herds for Mycobacterium avium ssp. paratuberculosis (MAP) detection. J. Dairy Res. 2013, 80, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodini, R.J.; Van Kruiningen, H.J.; Merkal, R.S. Ruminant paratuberculosis (Johne’s disease): The current status and future prospects. Cornell Vet. 1984, 74, 218–262. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, S.; Roller, M.; Alslim, L.; Böhlken-Fascher, S.; Fechner, K.; Czerny, C.P.; Abd El Wahed, A. Development of rapid extraction method of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis dna from bovine stool samples. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.; Schafer, J.; Fechner, K.; Czerny, C.P.; Abd El Wahed, A. Development of a recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of the Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocchetti, T.T.; Silbert, S.; Gostnell, A.; Kubasek, C.; Widen, R. Validation of a multiplex real-time PCR assay for detection of Mycobacterium spp., Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex, and Mycobacterium avium complex directly from clinical samples by use of the BD max open system. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1644–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fechner, K.; Schafer, J.; Wiegel, C.; Ludwig, J.; Munster, P.; Sharifi, A.R.; Wemheuer, W.; Czerny, C.P. Distribution of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in a Subclinical Naturally Infected German Fleckvieh Bull. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 916–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slana, I.; Kaevska, M.; Kralik, P.; Horvathova, A.; Pavlik, I. Distribution of Mycobacterium avium subsp. avium and M. a. hominissuis in artificially infected pigs studied by culture and IS901 and IS1245 quantitative real time PCR. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 144, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münster, P.; Völkel, I.; Wemheuer, W.; Petschenka, J.; Wemheuer, W.; Steinbrunn, C.; Campe, A.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J.; Kreienbrock, L.; Czerny, C.P. Detection of Mycobacterium avium ssp. paratuberculosis in ileocaecal lymph nodes collected from elderly slaughter cows using a semi-nested IS900 polymerase chain reaction. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 154, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münster, P.; Völkel, I.; Wemheuer, W.; Schwarz, D.; Döring, S.; Czerny, C.P. A longitudinal study to characterize the distribution patterns of Mycobacterium avium ssp. paratuberculosis in Semen, Blood and Faeces of a Naturally Infected Bull by IS 900 Semi-Nested and Quantitative Real-Time PCR. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2013, 60, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.T.; Oosterhuis, J.E. Diagnosis and control of paratuberculosis in exotic hoofed stock. Proc. Am. Assoc. Zoo Vet. 1993, 386–387. [Google Scholar]
- Münster, P.; Völkel, I.; von Buchholz, A.; Czerny, C.P. Detection of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis by is 900-based PCR assays from an alpaca (Vicugna pacos) kept in a German Zoological Garden. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2013, 44, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, A.C.; Figueira, L.; Matos, M.; Pinto, M.L.; Coelho, A.C. Seroprevalence of Mycobacterium avium complex in wild mammals in the Iberian Peninsula. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2015, 66, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stevenson, K.; Alvarez, J.; Bakker, D.; Biet, F.M.; de Juan, L.; Denham, S.; Dimareli, Z.; Dohmann, K.; Gerlach, G.F.; Heron, I. Occurrence of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis across host species and European countries with evidence for transmission between wildlife and domestic ruminants. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, R.L.; Kearney, C.; Burton, M.S.; Dumoneux, G.; Olsen, J.H. Morbidity and mortality related to hypoglycemia and chronic energy malnutrition in captive giraffe. Proc. Am. Assoc. Zoo Vet. 2002, 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Whittington, R.J.; Begg, D.J.; de Silva, K.; Purdie, A.C.; Dhand, N.K.; Plain, K.M. Case definition terminology for paratuberculosis (Johne’s disease). BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittington, R.J.; Marsh, I.B.; Reddacliff, L.A. Survival of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in dam water and sediment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5304–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, D.; Ghosh, P.; Khan, M.A.A.; Hossain, F.; Böhlken-Fascher, S.; Matlashewski, G.; Kroeger, A.; Olliaro, P.; El Wahed, A.A. Mobile suitcase laboratory for rapid detection of Leishmania donovani using recombinase polymerase amplification assay. Parasit Vectors 2016, 9, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Wahed, A.A.; Weidmann, M.; Hufert, F.T. Diagnostics-in-a-Suitcase: Development of a portable and rapid assay for the detection of the emerging avian influenza A (H7N9) virus. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 69, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Wahed, A.A.; Patel, P.; Faye, O.; Thaloengsok, S.; Heidenreich, D.; Matangkasombut, P.; Manopwisedjaroen, K.; Sakuntabhai, A.; Sall, A.A.; Hufert, F.T. Recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid diagnostics of dengue infection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Wahed, A.A.; El-Deeb, A.; El-Tholoth, M.; El Kader, H.A.; Ahmed, A.; Hassan, S.; Hoffmann, B.; Haas, B.; Shalaby, M.A.; Hufert, F.T. A portable reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of foot-and-mouth disease virus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, M.A.; El-Deeb, A.; El-Tholoth, M.; Hoffmann, D.; Czerny, C.-P.; Hufert, F.T.; Weidmann, M.; El Wahed, A.A. Recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of lumpy skin disease virus. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkinham, J.O. Surrounded by mycobacteria: Nontuberculous mycobacteria in the human environment. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 107, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salchow, A. Untersuchung Zum Vorkommen Und zur Bedeutung Ausgewählter Mykobakterien bei Zootieren. Ph.D. Thesis, Freie Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 23 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, I.; Schettler, E.; Hotzel, H.; Herzog, S.; Frölich, K. Mycobacterial infections in free-living cervids in Germany (2002–2006). J. Wildl. D 2011, 47, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravkova, M.; Trcka, I.; Lamka, J.; Pavlik, I. A mixed infection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis and M. a. hominissuis in one red deer (Cervus elaphus) studied by IS900 BstEII and IS1245 PvuII RFLP analyses: A case report. Vet. Med. 2008, 53, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möbius, P.; Lentzsch, P.; Moser, I.; Naumann, L.; Martin, G.; Köhler, H. Comparative macrorestriction and RFLP analysis of Mycobacterium avium subsp. avium and Mycobacterium avium subsp. hominissuis isolates from man, pig, and cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 2006, 117, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriz, P.; Jahn, P.; Bezdekova, B.; Blahutkova, M.; Mrlik, V.; Slana, I.; Pavlik, I. Mycobacterium avium subsp. hominissuis infection in horses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1328–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haist, V.; Seehusen, F.; Moser, I.; Hotzel, H.; Deschl, U.; Baumgärtner, W.; Wohlsein, P. Mycobacterium avium subsp. hominissuis infection in 2 pet dogs, Germany. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 988–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campora, L.; Corazza, M.; Zullino, C.; Ebani, V.V.; Abramo, F. Mycobacterium avium subspecies hominissuis disseminated infection in a Basset Hound dog. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2011, 23, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-C.; Kim, J.; Kang, W.; Jang, Y.B.; Kim, Y.-H. Systemic infection of Mycobacterium avium subspecies hominissuis and fungus in a pet dog. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2016, 78, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hobi, S.; Bettenay, S.; Majzoub, M.; Mueller, R.; Moser, I. Mycobacterium avium subspecies hominissuis infection in a dog from Germany with multifocal alopecia, exfoliative dermatitis, hypercalcaemia and subsequent sebaceous atrophy. Vet. Rec. Case Rep. 2015, 3, e000168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klang, A.; Staffler, C.; Mascherbauer, C.; Spergser, J.; Rütgen, B.C.; Hinney, B.; Luckschander-Zeller, N.; Kuenzel, F. Mycobacterium avium subspecies hominissuis infection in a domestic European shorthair cat. Wien. Tierarztl. Monatsschr. 2014, 101, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Shitaye, E.J.; Grymova, V.; Grym, M.; Halouzka, R.; Horvathova, A.; Moravkova, M.; Beran, V.; Svobodova, J.; Dvorska-Bartosova, L.; Pavlik, I. Mycobacterium avium subsp. hominissuis infection in a pet parrot. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 617–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorska, L.; Matlova, L.; Ayele, W.Y.; Fischer, O.A.; Amemori, T.; Weston, R.T.; Alvarez, J.; Beran, V.; Moravkova, M.; Pavlik, I. Avian tuberculosis in naturally infected captive water birds of the Ardeideae and Threskiornithidae families studied by serotyping, IS901 RFLP typing, and virulence for poultry. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 119, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravkova, M.; Mrlik, V.; Parmova, I.; Kriz, P.; Pavlik, I. High incidence of Mycobacterium avium subspecies hominissuis infection in a zoo population of bongo antelopes (Tragelaphus eurycerus). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2013, 25, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenker, C.; Wyss, F.; Hoby, S.; Ghielmetti, G.; Friedel, U.; Gurtner, C.; Posthaus, H. Non-tuberculous mycobacterial lung infection in an African elephant (Loxodonta africana) and a greater one-horned rhinoceros (Rhinoceros unicornis) caused by Mycobacterium avium ssp. hominissuis and Mycobacterium nebraskense and the reaction to ante- and postmortem tests. Proc. Europ. Assoc. Zoo Vet. 2018, 288–290. [Google Scholar]
- Glawischnig, W.; Steineck, T.; Spergser, J. Infections caused by Mycobacterium avium subspecies avium, hominissuis, and paratuberculosis in free-ranging red deer (Cervus elaphus hippelaphus) in Austria, 2001–2004. J. Wildl. D 2006, 42, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montali, R.J.; Mikota, S.K.; Cheng, L.I. Mycobacterium tuberculosis in zoo and wildlife species. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2001, 20, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Park, N.-Y. Disseminated mycobacteriosis due to Mycobacterium avium in captive Bengal tiger (Panthera tigris). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2006, 18, 312–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, H.; Choi, G.-E.; Lee, B.S.; Whang, J.; Shin, S.J. Disseminated infection due to Mycobacterium avium subsp. avium in an Asian elephant (Elephas maximus). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2011, 42, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Order | Family | Species | Common Name | No. Tested | Ind. Tested | No. (+) | Ind. (+) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diprotodontia | Macropodidae | Macropus rufus | Red kangaroo | 3 | 3 | ||
| Proboscidea | Elephantidae | Elephas maximus | Asian elephant | 5 | 3 | ||
| Primates | Lemuridae | Varecia rubra | Red ruffed lemur | 1 | 1 | ||
| Atelidae | Ateles hybridus | Brown spider monkey | 16 | 10 | 2 | 1 | |
| Alouatta caraya | Black howler | 6 | 4 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Pitheciidae | Pithecia pithecia | White-faced saki | 4 | 2 | |||
| Cercopithecidae | Trachypithecus auratus auratus | Eastern Javan langur | 11 | 7 | 1 | 1 | |
| Macaca fuscata | Japanese macaque | 9 | 8 | ||||
| Mandrillus leucophaeus | Drill | 9 | 3 | ||||
| Theropithecus gelada | Gelada baboon | 33 | 32 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Hylobatidae | Hylobates lar | Lar gibbon | 7 | 5 | |||
| Pongidae | Pongo abelii | Sumatran orangutan | 9 | 6 | 1 | 1 | |
| Gorilla gorilla gorilla | Western lowland gorilla | 17 | 11 | 2 | 2 | ||
| Pan paniscus | Bonobo | 22 | 12 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Carnivora | Procyonidae | Nasua nasua | South American coati | 1 | 1 | ||
| Ursidae | Ursus arctos syriacus | Syrian brown bear | 4 | 3 | |||
| Ursus maritimus | Polar bear | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Tremarctos ornatus | Spectacled bear | 2 | 2 | ||||
| Canidae | Speothos venaticus | Bush dog | 1 | 1 | |||
| Chrysocyon brachyurus | Maned wolf | 3 | 3 | ||||
| Otariidae | Zalophus californianus | California sea lion | 3 | 3 | |||
| Felidae | Panthera uncia | Snow leopard | 5 | 4 | |||
| Panthera leo persica | Asiatic lion | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Panthera onca | Jaguar | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Panthera pardus saxicolor | Persian leopard | 5 | 3 | ||||
| Panthera tigris sumatrae | Sumatran tiger | 2 | 2 | ||||
| Acinonyx jubatus | Cheetah | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Perissodactyla | Rhinocerotidae | Rhinoceros unicornis | Indian rhino | 4 | 2 | ||
| Tapiridae | Tapirus indicus | Malayan tapir | 1 | 1 | |||
| Equidae | Equus asinus asinus | Poitou-ass | 2 | 1 | |||
| Equus africanus somaliensis | Somali wild ass | 4 | 3 | ||||
| Equus ferus przewalskii | Przewalski’s horse | 2 | 2 | ||||
| Equus grevyi | Grevy’s zebra | 8 | 6 | ||||
| Equus hemionus onager | Onager | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | ||
| Artiodactyla | Suidae | Sus scrofa f. domestica | Domestic pig | 2 | 2 | ||
| Babyrousa babyrussa | Buru babirusa | 8 | 7 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Pecari tajacu | Collared peccary | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Hippopotamidae | Hippopotamus amphibius | Common hippopotamus | 1 | 1 | |||
| Choeropsis liberiensis | Pygmy hippopotamus | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Camelidae | Camelus bactrianus | Bactrian camel | 4 | 3 | |||
| Lama pacos | Alpaca | 16 | 11 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Vicugna vicugna | Vicuña | 5 | 5 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Cervidae | Dama mesopotamica | Persian fallow deer | 14 | 14 | 3 (2) | 3 (2) | |
| Giraffidae | Giraffa camelopardalis reticulata | Reticulated giraffe | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Okapia johnstoni | Okapi | 8 | 5 | ||||
| Bovidae | Tragelaphus eurycerus | Eastern bongo | 5 | 5 | 1 | 1 | |
| Tragelaphus imberbis | Lesser kudu | 14 | 12 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Bos taurus f. domesticus | Domestic cattle | 13 | 9 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Bubalus depressicornis | Lowland anoa | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Bison bison | American bison | 3 | 3 | ||||
| Addax nasomaculatus | Addax | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Oryx dammah | Scimitar-horned oryx | 4 | 4 | ||||
| Kobus ellipsiprymnus | Waterbuck | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Gazella dorcas | Dorcas gazelle | 7 | 4 | ||||
| Oreamnos americanus | Rocky Mountain goat | 4 | 2 | ||||
| Budorcas taxicolor taxicolor | Mishmi takin | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Ovis aries f. domestica | Domestic sheep | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Ammotragus lervia | Barbary sheep | 19 | 16 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Capra falconeri | Markhor | 24 | 22 | ||||
| Capra aegagrus | Wild goat | 5 | 5 | ||||
| Capra hircus f. domestica | Dwarf goat | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Capra ibex | Alpine ibex | 4 | 3 | ||||
| TOTAL | 62 | 381 | 296 | 28 (2) | 24 (2) |
| Family | Scientific Name | Common Name | Pop. | Fecal Samples | Environmental Samples | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16S rRNA | 16S rRNA | IS 1245 | |||||
| PRIMATES | Callimiconidae | Callimico goeldii | Goeldi’s monkey | 1.3 | pos | pos | - |
| Leontopithecus chrysomelas | Golden-headed lion tamarin | 1.1 | pos | pos | - | ||
| Saguinus imperator subgrisescens | Bearded emperor tamarin | 0.2 | pos | pos | - | ||
| Cebuella pygmaea | Pygmy marmoset | 2.2.1 | pos | pos | - | ||
| Atelidae | Ateles hybridus | Brown spider monkey | 1.2 | - | pos | - | |
| Alouatta caraya | Black howler | 2.2 | pos | pos | - | ||
| Cebidae | Saimiri boliviensis boliviensis | Bolivian squirrel monkey | 4.5 | pos | pos | - | |
| Pitheciidae | Pithecia pithecia | White-faced saki | 1.3 | pos | pos | - | |
| Cercopithecidae | Mandrillus leucophaeus | Drill | 1.1 | pos | pos | - | |
| Theropithecus gelada | Gelada baboon | 8.28.4 | pos | pos | - | ||
| Macaca fuscata | Japanese macaque | 2.3 | pos | pos | - | ||
| Trachypithecus auratus auratus | Eastern Javan langur | 3.7 | pos | pos | pos | ||
| Hylobatidae | Hylobates lar | Lar gibbon | 1.1 | pos | - | - | |
| Lemuridae | Varecia rubra | Red ruffed lemur | 0.1 | pos | pos | - | |
| Lorisidae | Nycticebus coucang | Slow loris | 0.1 | pos | pos | - | |
| Pongidae | Pan paniscus | Bonobo (Group I) | 2.4 | pos | pos | - | |
| Pan paniscus | Bonobo (Group II) | 4.6 | pos | pos | pos | ||
| Gorilla gorilla gorilla | Western lowland gorilla | 5.6 | pos | pos | - | ||
| Pongo abelii | Sumatran orangutan | 0.2 | pos | pos | - | ||
| ARTIODACTYLA | Bovidae | Capra hircus f. domestica | Dwarf goat | 1.6 | pos | pos | - |
| Capra ibex | Alpine ibex | 1.6 | pos | - | - | ||
| Bison bison | American bison | 1.2 | pos | pos | - | ||
| Tragelaphus eurycerus | Eastern bongo | 2.4.1 | pos | pos | - | ||
| Gazella dorcas | Dorcas gazelle | 2.5 | pos | pos | - | ||
| Bos taurus f. domesticus | Domestic cattle | 0.2.2 | - | - | - | ||
| Ovis aries f. domestica | Domestic sheep | 1.6 | pos | pos | - | ||
| Tragelaphus imberbis | Lesser kudu | 0.9 | pos | - | - | ||
| Bos taurus f. domesticus | Domestic cattle | 0.5.1 | pos | - | - | ||
| Ammotragus lervia | Barbary sheep | 4.8.2 | pos | - | - | ||
| Capra falconeri | Markhor | 1.7 | pos | - | - | ||
| Budorcas taxicolor taxicolor | Mishmi takin | 1.1 | pos | - | - | ||
| Oryx dammah | Scimitar-horned oryx | 0.2.2 | pos | - | - | ||
| Oreamnos americanus | Rocky Mountain goat | 0.2 | pos | - | - | ||
| Capra hircus f. domestica | Black Forest goat | 0.2 | pos | - | - | ||
| Ovis aries f. domestica | Domestic sheep | 1.6 | pos | - | - | ||
| Bison bison bonasus | European Bison | 1.0 | pos | pos | - | ||
| Camelidae | Lama pacos | Alpaca | 0.14 | pos | - | - | |
| Camelus bactrianus | Bactrian camel | 0.3 | pos | pos | - | ||
| Vicugna vicugna | Vicuña | 0.1 | pos | - | - | ||
| Cervidae | Dama mesopotamica | Persian fallow deer | 0.4 | pos | - | - | |
| Giraffidae | Giraffa camelopardalis reticulata | Reticulated giraffe | 2.2 | pos | pos | - | |
| a | Procaviidae | Procavia capensis | Rock hyrax | 0.3.5 | - | - | - |
| b | Tapiridae | Tapirus indicus | Malayan tapir | 2.0 | pos | pos | - |
| Scientific Name | Common Name | Sex | Age (Year) | Cause of Death | Ileum | Ileocecal Lymph Node | Feces |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leontopithecus chrysomelas | Golden-headed lion tamarin | 1.0 | 1 | Deceased/Angiostrongylus | |||
| 1.0 | 1 | Euthanasia/Angiostrongylus | (pos) | ||||
| Saguinus imperator subgrisescens | Bearded emperor tamarin | 1.0 | 10 | Euthanasia/Phlegmon (Thigh) | |||
| Cebuella pygmaea | Pygmy marmoset | 1.0 | 0 | Deceased/Lissencephaly | pos | ||
| 0.1 | 0 | Deceased/Trauma | |||||
| Callithrix geoffroyi | Geoffroy’s tufted ear marmoset | 0.1 | 21 | Deceased/Neoplasia (Uterus) | pos | ||
| Ateles hybridus | Brown spider monkey | 1.0 | 1 | Deceased/Trauma/Enteritis (para.) | (pos) | ||
| Alouatta caraya | Black howler | 1.0 | 21 | Euthanasia/Colitis, Nephritis (bact.) | (pos) | pos | |
| Theropithecus gelada | Gelada baboon | 0.1 | 24 | Deceased/Age-related/Cardial Disease | pos | pos | |
| 1.0 | 1 | Euthanasia/Trauma | pos | ||||
| 0.1 | 2 | Euthanasia/Trauma | pos | ||||
| 0.1 | 22 | Deceased/Cardiomyopathy/Aneurysm | pos | ||||
| Trachypithecus auratus auratus | Eastern Javan langur | 0.1 | 21 | Euthanasia/Abscess (Lung)/Age-related | pos | (pos) | pos |
| Hylobates lar | Lar gibbon | 0.1 | 34 | Deceased/Pleuropneumonia, Septicaemia (bact.) | pos | ||
| 1.0 | 43 | Euthanasia/Septicaemia (bact.) | pos | ||||
| Ammotragus lervia | Barbary sheep | 0.1 | 7 | Euthanasia/Trauma/Cachexia | |||
| 1.0 | 0 | Deceased/Premature Birth | |||||
| 0.1 | 4 | Culling | (pos) | ||||
| Ovis aries f. domestica | Domestic sheep | 1.0 | 9 | Culling | pos | ||
| 0.1 | 7 | Culling | pos | ||||
| 0.1 | 8 | Culling | pos | ||||
| 0.1 | 4 | Culling | (pos) | ||||
| 0.1 | 3 | Culling | pos | ||||
| 0.1 | 6 | Culling | pos | ||||
| Oryx dammah | Scimitar-horned oryx | 1.0 | 0 | Euthanasia/Enteritis, Meningoencephalitis (bact.) | pos | ||
| Budorcas taxicolor taxicolor | Mishmi takin | 1.0 | 21 | Euthanasia/Age-related/Arthrosis | pos | pos | |
| Oreamnos americanus | Rocky Mountain goat | 0.1 | 14 | Deceased/Septicaemia (bact.) | pos | pos | |
| Dama mesopotamica | Persian fallow deer | 0.1 | 11 | Deceased/Age-related/Abomasitis (bact.) | pos | ||
| Procavia capensis | Rock hyrax | 0.1 | 7 | Deceased/Cachexia/Fatty Liver | pos | ||
| 0.1 | 8 | Deceased/Cachexia/Acute Circulatory Collapse | (pos) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roller, M.; Hansen, S.; Böhlken-Fascher, S.; Knauf-Witzens, T.; Czerny, C.-P.; Goethe, R.; Abd El Wahed, A. Molecular and Serological Footprints of Mycobacterium avium Subspecies Infections in Zoo Animals. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7030117
Roller M, Hansen S, Böhlken-Fascher S, Knauf-Witzens T, Czerny C-P, Goethe R, Abd El Wahed A. Molecular and Serological Footprints of Mycobacterium avium Subspecies Infections in Zoo Animals. Veterinary Sciences. 2020; 7(3):117. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7030117
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoller, Marco, Sören Hansen, Susanne Böhlken-Fascher, Tobias Knauf-Witzens, Claus-Peter Czerny, Ralph Goethe, and Ahmed Abd El Wahed. 2020. "Molecular and Serological Footprints of Mycobacterium avium Subspecies Infections in Zoo Animals" Veterinary Sciences 7, no. 3: 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7030117
APA StyleRoller, M., Hansen, S., Böhlken-Fascher, S., Knauf-Witzens, T., Czerny, C.-P., Goethe, R., & Abd El Wahed, A. (2020). Molecular and Serological Footprints of Mycobacterium avium Subspecies Infections in Zoo Animals. Veterinary Sciences, 7(3), 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7030117






