Genomic Analysis of Third Generation Cephalosporin Resistant Escherichia coli from Dairy Cow Manure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
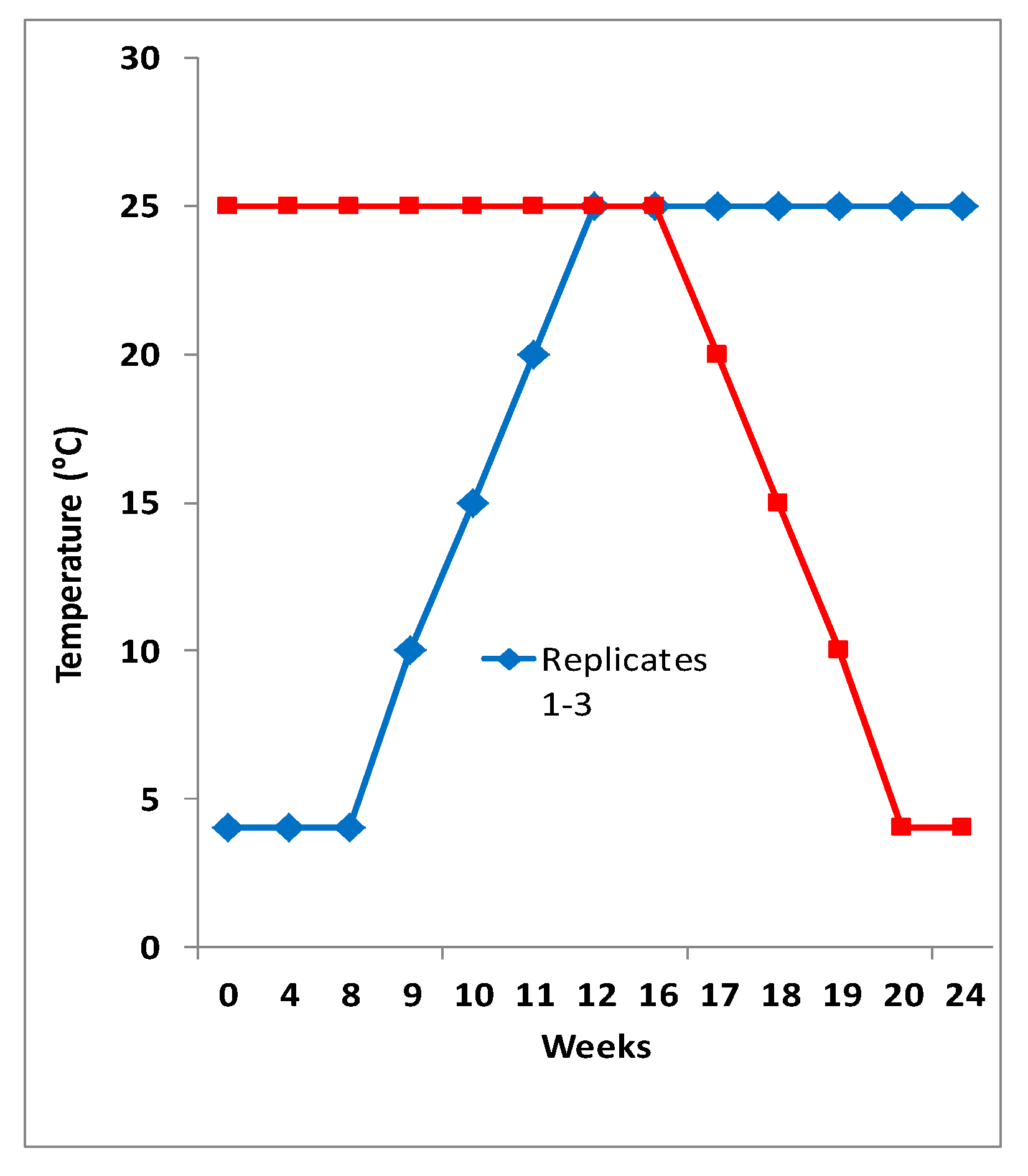
2.1. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
2.2. Minimal Inhibitory Concentrations
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Genome Sequencing, Assembly and Pan-Genome Analysis
2.5. Virulence and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
2.6. Plasmids
2.7. Statistical Analyses
2.8. Genome Sequence Accession Numbers
3. Results
3.1. Cephalosporin Resistant Escherichia coli
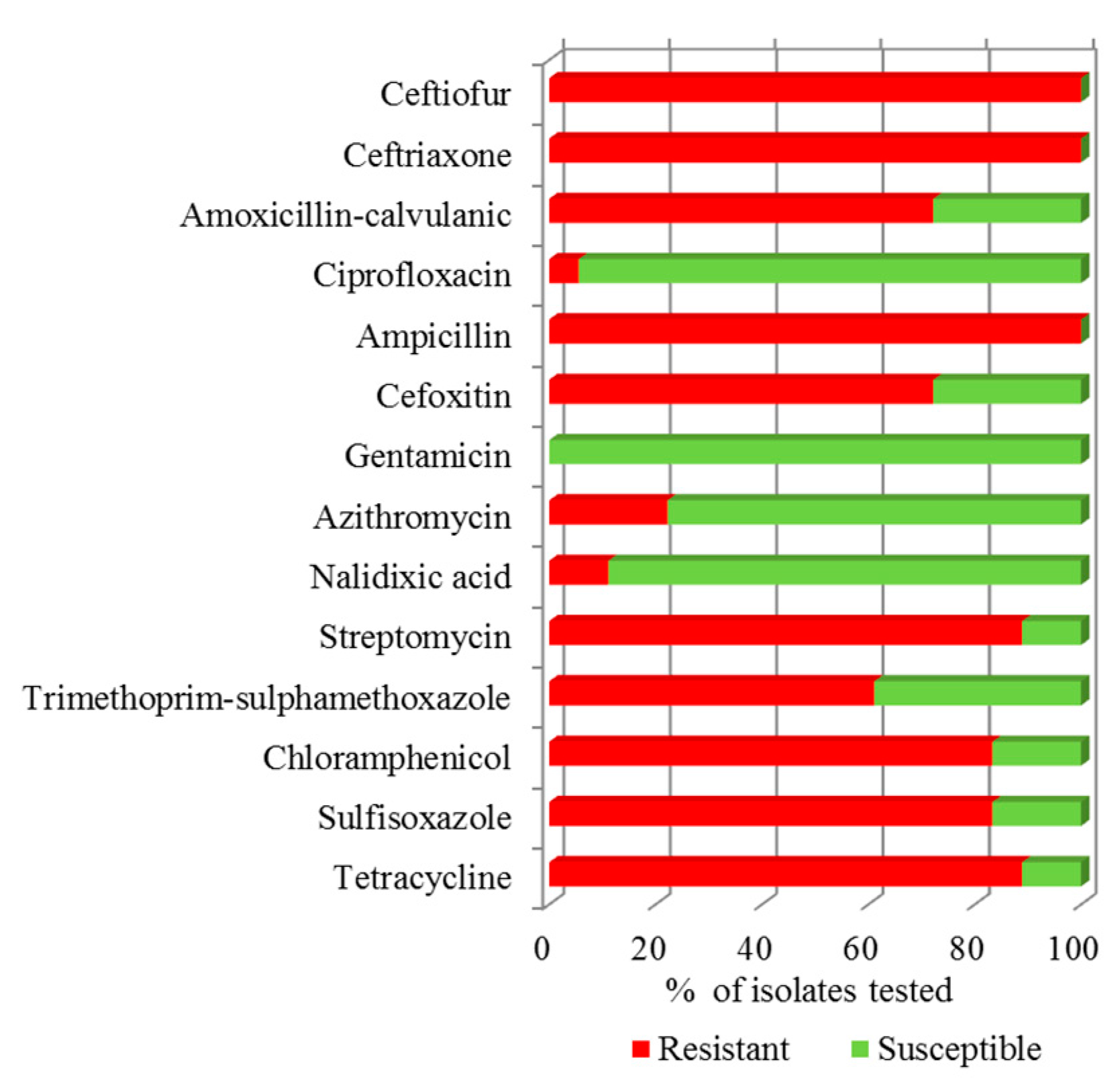
3.2. Antibiotic Susceptibility
3.3. Sequencing, Assembly and Annotation
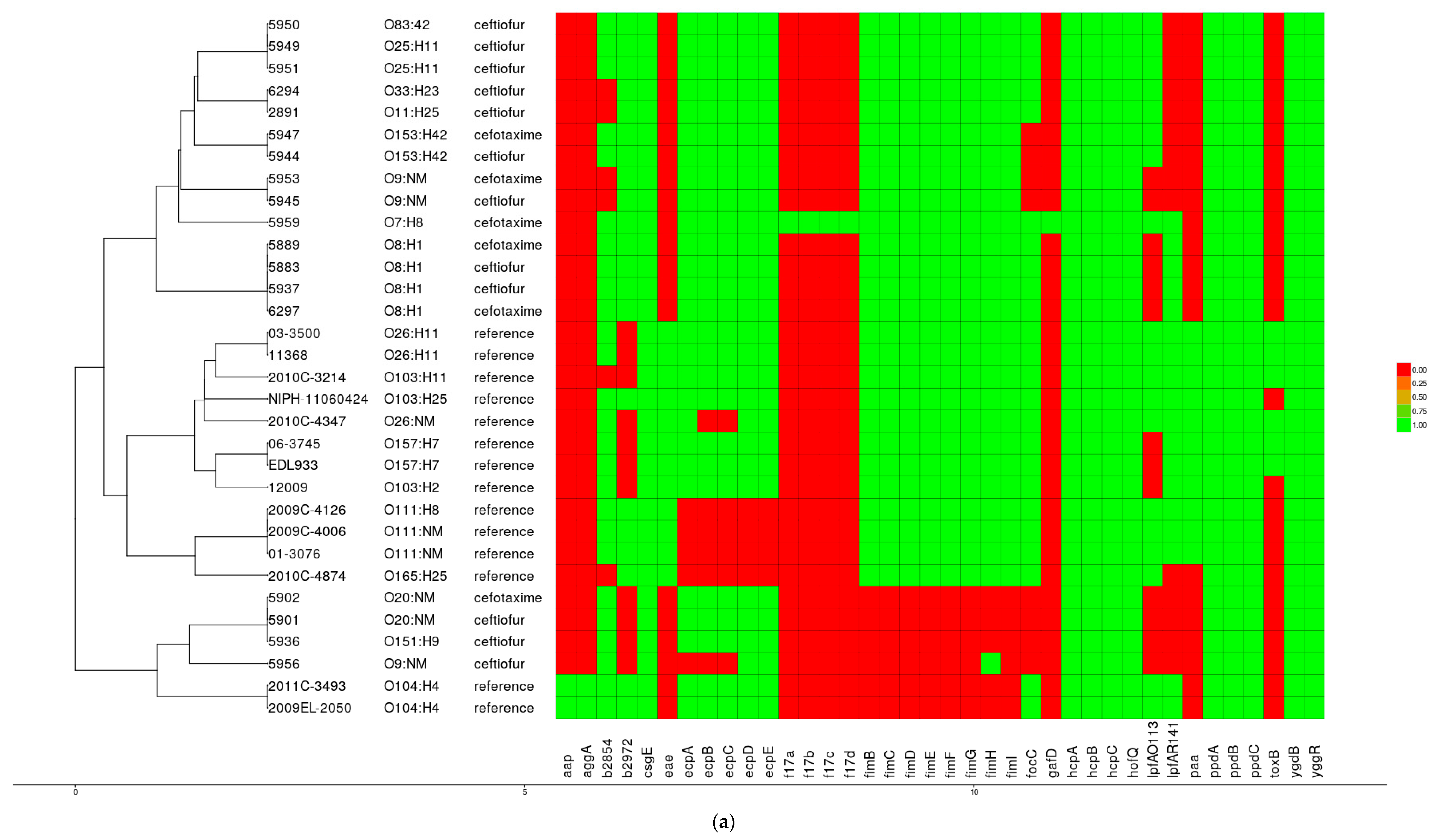
3.4. Virulence Factors
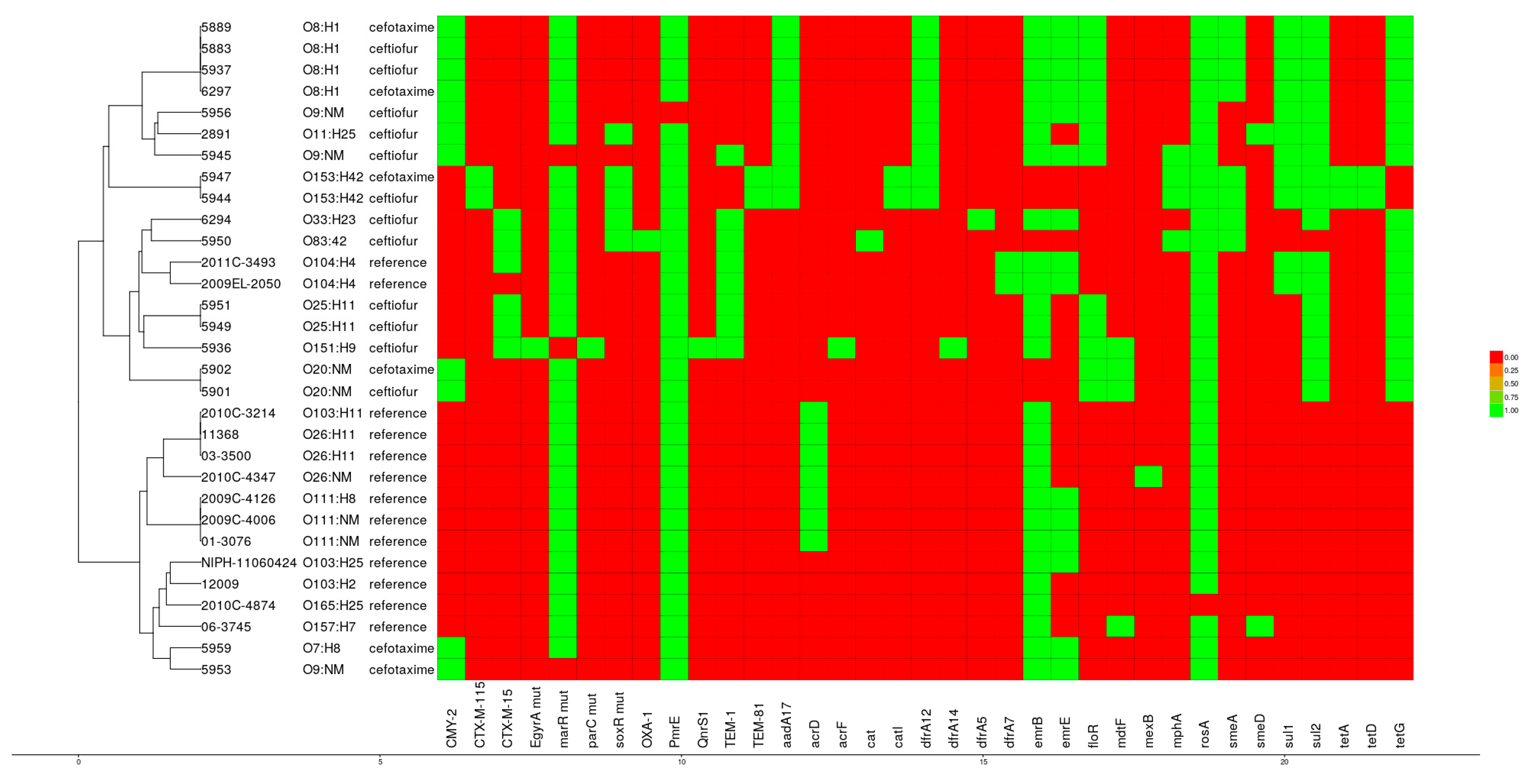
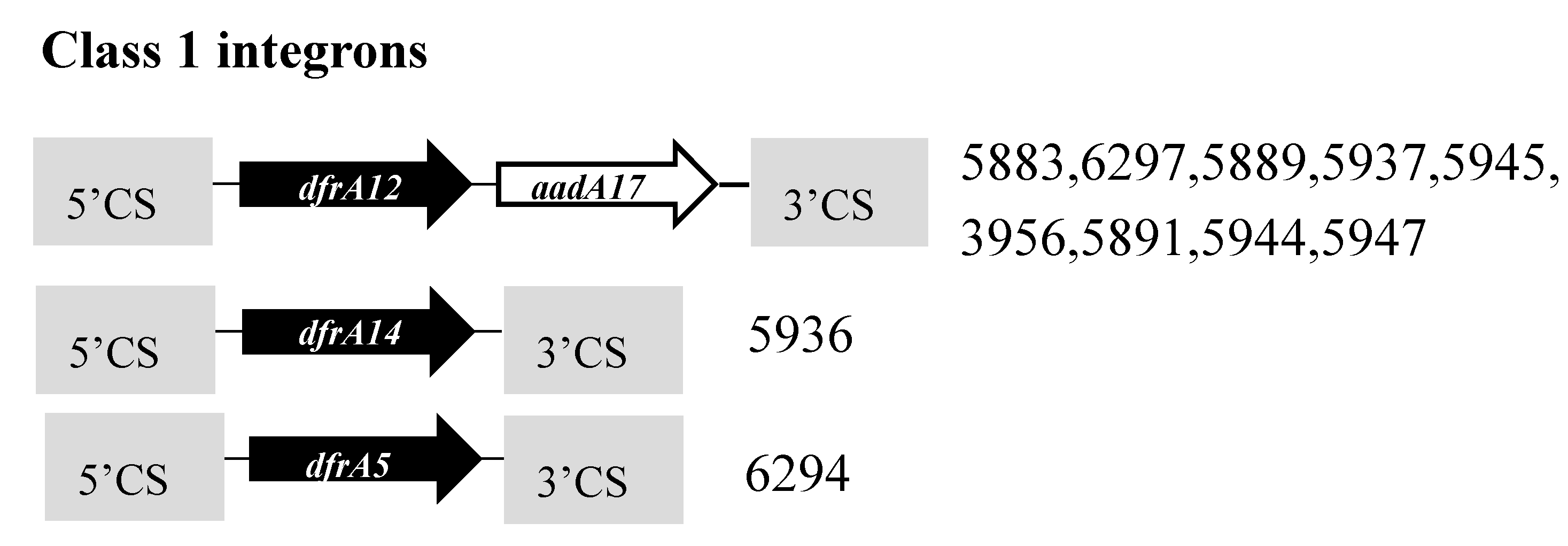
3.5. Antibiotic Resistance Genes
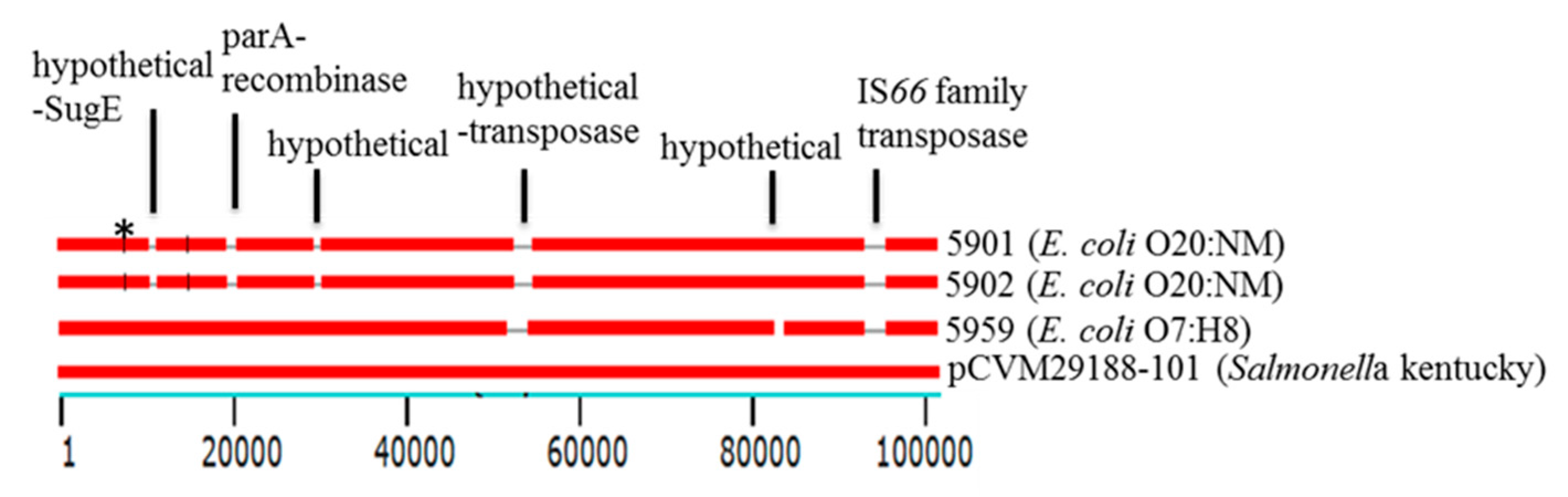
3.6. Mobile Genetic Elements (MGEs)
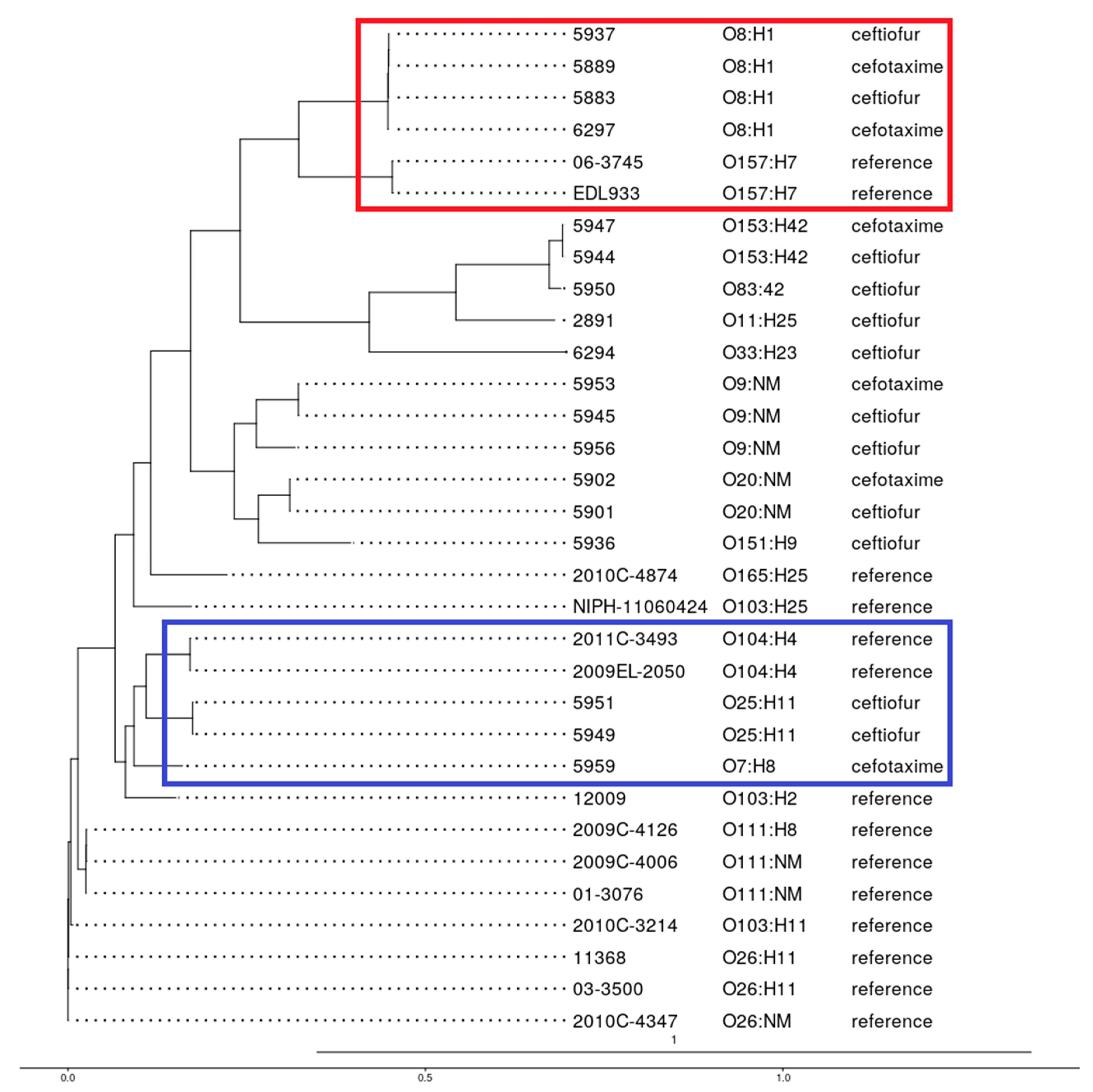
3.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
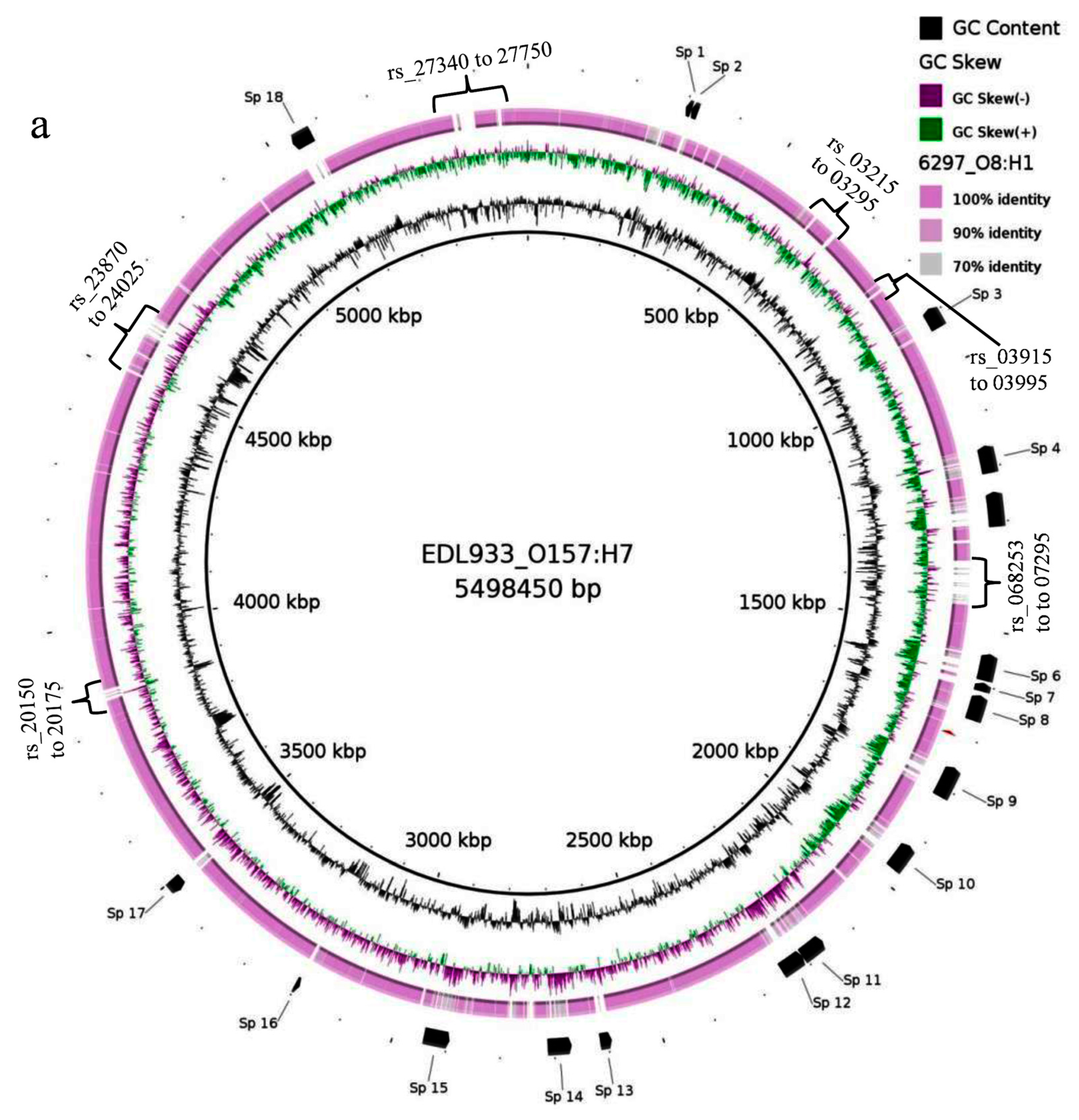
3.8. Comparative Genomics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Statistics Canada. Available online: http://www5.Statcan.Gc.Ca/access_acces/ (accessed on 17 October 2014).
- Udikovic-Kolic, N.; Wichmann, F.; Broderick, N.A.; Handelsman, J. Bloom of resident antibiotic-resistant bacteria in soil following manure fertilization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15202–15207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manyi-Loh, C.E.; Mamphweli, S.N.; Meyer, E.L.; Makaka, G.; Simon, M.; Okoh, A.I. An overview of the control of bacterial pathogens in cattle manure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.Y.; Yoon, J.; Hovde, C.J. A brief overview of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and its plasmid o157. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harris, A.M.; Marshall, M.J.; Curtis, R.; Watson, D.J.; Evans, J.M. Cephalosporins in the prevention and treatment of mastitis. Vet. Rec. 1976, 99, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suojala, L.; Kaartinen, L.; Pyorala, S. Treatment for bovine Escherichia coli Mastitis—An evidence-based approach. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 36, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinthong, W.; Pumipuntu, N.; Santajit, S.; Kulpeanprasit, S.; Buranasinsup, S.; Sookrung, N.; Chaicumpa, W.; Aiumurai, P.; Indrawattana, N. Detection and drug resistance profile of Escherichia coli from subclinical mastitis cows and water supply in dairy farms in Saraburi province, Thailand. PeerJ 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichmann, F.; Udikovic-Kolic, N.; Andrew, S.; Handelsman, J. Diverse antibiotic resistance genes in dairy cow manure. mBio 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noyes, N.R.; Yang, X.; Linke, L.M.; Magnuson, R.J.; Cook, S.R.; Zaheer, R.; Yang, H.; Woerner, D.R.; Geornaras, I.; McArt, J.A.; et al. Characterization of the resistome in manure, soil and wastewater from dairy and beef production systems. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsberg, K.J.; Reyes, A.; Wang, B.; Selleck, E.M.; Sommer, M.O.; Dantas, G. The shared antibiotic resistome of soil bacteria and human pathogens. Science 2012, 337, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, C.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Kristiansson, E.; Larsson, D.G. The structure and diversity of human, animal and environmental resistomes. Microbiome 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Guo, X.; Yan, Z.; Wang, W.; Chen, B.; Ge, F.; Ye, B. A comprehensive analysis on spread and distribution characteristic of antibiotic resistance genes in livestock farms of southeastern China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Wintersdorff, C.J.; Penders, J.; van Niekerk, J.M.; Mills, N.D.; Majumder, S.; van Alphen, L.B.; Savelkoul, P.H.; Wolffs, P.F. Dissemination of antimicrobial resistance in microbial ecosystems through horizontal gene transfer. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salverda, M.L.; de Visser, J.A.; Barlow, M. Natural evolution of tem-1 beta-lactamase: Experimental reconstruction and clinical relevance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 1015–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathys, D.A.; Mathys, B.A.; Mollenkopf, D.F.; Daniels, J.B.; Wittum, T.E. Enterobacteriaceae harboring ampc (blaCMY) and ESBL (blaCTX-M) in migratory and nonmigratory wild songbird populations on Ohio dairies. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2017, 17, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyles, C.; Boerlin, P. Horizontally transferred genetic elements and their role in pathogenesis of bacterial disease. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, R.M. Mobile gene cassettes and integrons: Moving antibiotic resistance genes in gram-negative bacteria. Ciba Found. Symp. 1997, 207, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Logan, L.K.; Weinstein, R.A. The epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae: The impact and evolution of a global menace. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, S28–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.; Davies, D. Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, S.D.; Ahmed, M.F.; El-Adawy, H.; Hotzel, H.; Engelmann, I.; Weiss, D.; Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R. Surveillance of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in dairy cattle farms in the Nile Delta, Egypt. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horigan, V.; Kosmider, R.D.; Horton, R.A.; Randall, L.; Simons, R.R. An assessment of evidence data gaps in the investigation of possible transmission routes of extended spectrum beta-lactamase producing Escherichia coli from livestock to humans in the UK. Prev. Vet. Med. 2016, 124, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luby, E.; Ibekwe, A.M.; Zilles, J.; Pruden, A. Molecular methods for assessment of antibiotic resistance in agricultural ecosystems: Prospects and challenges. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, L.E.; Rempel, H.; Forge, T.; Kannangara, T.; Bittman, S.; Delaquis, P.; Topp, E.; Ziebell, K.A.; Diarra, M.S. Characterization of antibiotic-resistant and potentially pathogenic Escherichia coli from soil fertilized with litter of broiler chickens fed antimicrobial-supplemented diets. Can. J. Microbiol. 2012, 58, 1084–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, B.; Diarra, M.S.; Giguere, K.; Roy, G.; Michaud, S.; Malouin, F. Antibiotic resistance and hypermutability of Escherichia coli O157 from feedlot cattle treated with growth-promoting agents. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 2411–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. Spades: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laing, C.; Buchanan, C.; Taboada, E.N.; Zhang, Y.; Kropinski, A.; Villegas, A.; Thomas, J.E.; Gannon, V.P. Pan-genome sequence analysis using panseq: An online tool for the rapid analysis of core and accessory genomic regions. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. Fasttree 2—Approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteside, M.D.; Laing, C.R.; Manji, A.; Kruczkiewicz, P.; Taboada, E.N.; Gannon, V.P. Superphy: Predictive genomics for the bacterial pathogen Escherichia coli. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArthur, A.G.; Waglechner, N.; Nizam, F.; Yan, A.; Azad, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Bhullar, K.; Canova, M.J.; de Pascale, G.; Ejim, L.; et al. The comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 3348–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; Garcia-Fernandez, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Moller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using plasmidfinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, C.; Diarrassouba, F.; Brousseau, R.; Masson, L.; Topp, E.; Diarra, M.S. Pathotype and antibiotic resistance gene distributions of Escherichia coli isolates from broiler chickens raised on antimicrobial-supplemented diets. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6955–6962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Decousser, J.W.; Nordmann, P. Insertion sequence isecp1b is involved in expression and mobilization of a bla (CTX-M) beta-lactamase gene. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 2938–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thungapathra, M.; Amita; Sinha, K.K.; Chaudhuri, S.R.; Garg, P.; Ramamurthy, T.; Nair, G.B.; Ghosh, A. Occurrence of antibiotic resistance gene cassettes aac(6′)-ib, dfra5, dfra12, and ereA2 in class I integrons in non-O1, non-O139 Vibrio cholerae strains in India. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2948–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keen, P.L.; Montforts, M.H.M.M. Seasonal Dynamics of Tetracycline Resistance Genes and Antibiotics in a British Columbia Agricultural Watershed; University of British Columbia: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sawant, A.A.; Hegde, N.V.; Straley, B.A.; Donaldson, S.C.; Love, B.C.; Knabel, S.J.; Jayarao, B.M. Antimicrobial-resistant enteric bacteria from dairy cattle. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, A.; Locatelli, A.; Amoureux, L.; Depret, G.; Jolivet, C.; Gueneau, E.; Neuwirth, C. Occurrence of CTX-M producing Escherichia coli in soils, cattle, and farm environment in France (Burgundy region). Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebana, E.; Carattoli, A.; Coque, T.M.; Hasman, H.; Magiorakos, A.P.; Mevius, D.; Peixe, L.; Poirel, L.; Schuepbach-Regula, G.; Torneke, K.; et al. Public health risks of enterobacterial isolates producing extended-spectrum beta-lactamases or AmpC beta-lactamases in food and food-producing animals: An EU perspective of epidemiology, analytical methods, risk factors, and control options. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, R.A.; Duncan, D.; Randall, L.P.; Chappell, S.; Brunton, L.A.; Warner, R.; Coldham, N.G.; Teale, C.J. Longitudinal study of ctx-m ESBL-producing E. coli strains on a UK dairy farm. Res. Vet. Sci. 2016, 109, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santman-Berends, I.M.; Gonggrijp, M.A.; Hage, J.J.; Heuvelink, A.E.; Velthuis, A.; Lam, T.J.; van Schaik, G. Prevalence and risk factors for extended-spectrum beta-lactamase or ampc-producing Escherichia coli in organic dairy herds in The Netherlands. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonggrijp, M.A.; Santman-Berends, I.M.; Heuvelink, A.E.; Buter, G.J.; van Schaik, G.; Hage, J.J.; Lam, T.J. Prevalence and risk factors for extended-spectrum beta-lactamase- and ampc-producing Escherichia coli in dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 9001–9013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, D.R.; Dodd, C.E.; Stekel, D.J.; Ramsden, S.J.; Hobman, J.L. Multidrug resistant, extended spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli isolated from a dairy farm. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storteboom, H.N.; Kim, S.C.; Doesken, K.C.; Carlson, K.H.; Davis, J.G.; Pruden, A. Response of antibiotics and resistance genes to high-intensity and low-intensity manure management. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1695–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, L.; Yang, Y.; Littier, H.; Ray, P.; Zhang, T.; Pruden, A.; Strickland, M.; Knowlton, K. Metagenomic analysis of antibiotic resistance genes in dairy cow feces following therapeutic administration of third generation cephalosporin. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peirano, G.; Costello, M.; Pitout, J.D. Molecular characteristics of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli from the Chicago area: High prevalence of st131 producing CTX-M-15 in community hospitals. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 36, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaita, K.; Aoki, K.; Suzuki, T.; Nakaharai, K.; Yoshimura, Y.; Harada, S.; Ishii, Y.; Tachikawa, N. Epidemiology of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase producing Escherichia coli in the stools of returning Japanese travelers, and the risk factors for colonization. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangden, T.; Cars, O.; Melhus, A.; Lowdin, E. Foreign travel is a major risk factor for colonization with Escherichia coli producing CTX-M-type extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: A prospective study with Swedish volunteers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3564–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nüesch-Inderbinen, M.; Stephan, R. Epidemiology of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in the human-livestock environment. Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep. 2016, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, K.; Islam, M.R.; Rempel, H.; Block, G.; Topp, E.; Diarra, M.S. Antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia fergusonii isolated from broiler chickens. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricke, W.F.; McDermott, P.F.; Mammel, M.K.; Zhao, S.; Johnson, T.J.; Rasko, D.A.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; Pedroso, A.; Whichard, J.M.; Leclerc, J.E.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance-conferring plasmids with similarity to virulence plasmids from avian pathogenic Escherichia coli strains in Salmonella enterica serovar kentucky isolates from poultry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5963–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Tyson, G.H.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Mukherjee, S.; Young, S.; Lam, C.; Folster, J.P.; Whichard, J.M.; McDermott, P.F. Whole-genome sequencing analysis accurately predicts antimicrobial resistance phenotypes in Campylobacter spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 82, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, P.F.; Tyson, G.H.; Kabera, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Folster, J.P.; Ayers, S.L.; Lam, C.; Tate, H.P.; Zhao, S. Whole-genome sequencing for detecting antimicrobial resistance in nontyphoidal Salmonella. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 5515–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manges, A.R. Escherichia coli and urinary tract infections: The role of poultry-meat. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, H.L.T.; Conover, M.S.; Chou, W.C.; Hibbing, M.E.; Manson, A.L.; Dodson, K.W.; Hannan, T.J.; Roberts, P.L.; Stapleton, A.E.; Hooton, T.M.; et al. Bacterial virulence phenotypes of Escherichia coli and host susceptibility determine risk for urinary tract infections. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Serotype | C3 | C4 | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 4 | Week 8 | Week 4 | Week 8 | ||
| O7:H8 | 1 | 1 | |||
| O8:H1 | 8 | 9 | 17 | ||
| O9:NM | 6 | 6 | |||
| O11:H25 | 1 | 1 | |||
| O20:NM | 2 | 2 | |||
| O25:H11 | 2 | 2 | |||
| O33:H23 | 1 | 1 | |||
| O83:42 | 1 | 1 | |||
| O151:H9 | 1 | 1 | |||
| O153:H42 | 5 | 5 | |||
| Strain ID | Serotype | Treatment | Genome Size (bp) | Coding Sequences | Source | Location | Year | Putative Plasmid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5883 | O8:H1 | ceftiofur | 5,244,652 | 5230 | Bovine manure | Canada | 2014 | IncA/IncFIB |
| 5889 | O8:H1 | cefotaxime | 5,238,639 | 5135 | Bovine manure | Canada | 2014 | IncA/IncFIB |
| 5891 | O11:H25 | ceftiofur | 5,069,111 | 4957 | Bovine manure | Canada | 2014 | IncA |
| 5901 | O20:NM | ceftiofur | 4,776,338 | 4708 | Bovine manure | Canada | 2015 | IncI1/IncQ1/IncFIA/IncFII |
| 5902 | O20:NM | cefotaxime | 4,772,820 | 4698 | Bovine manure | Canada | 2015 | IncI1/IncQ1/IncFIA/IncFII |
| 5936 | O151:H9 | ceftiofur | 4,869,431 | 4753 | Bovine manure | Canada | 2015 | IncN/IncFIB |
| 5937 | O8:H1 | ceftiofur | 5,195,554 | 5061 | Bovine manure | Canada | 2015 | IncA/IncFIB |
| 5944 | O153:H42 | ceftiofur | 5,101,758 | 4973 | Bovine manure | Canada | 2015 | IncI1/IncQ1 |
| 5945 | O9:NM | ceftiofur | 4,766,659 | 4685 | Bovine manure | Canada | 2015 | IncI2/IncFIB |
| 5947 | O153:H42 | cefotaxime | 5,101,804 | 4979 | Bovine manure | Canada | 2015 | IncI1/IncQ1 |
| 5949 | O25:H11 | ceftiofur | 4,994,147 | 5007 | Bovine manure | Canada | 2015 | IncI1/IncQ1/IncFIA/IncFII |
| 5950 | O83:42 | ceftiofur | 5,311,653 | 5236 | Bovine manure | Canada | 2015 | IncB/IncFIB/IncFIC/IncFII |
| 5951 | O25:H11 | ceftiofur | 4,992,789 | 4993 | Bovine manure | Canada | 2015 | IncI1/IncQ1/IncFIA/IncFII |
| 5953 | O9:NM | cefotaxime | 4,691,236 | 4600 | Bovine manure | Canada | 2015 | IncI2 |
| 5956 | O9:NM | ceftiofur | 4,674,446 | 4565 | Bovine manure | Canada | 2015 | IncI2/IncFII |
| 5959 | O7:H8 | cefotaxime | 5,198,736 | 5217 | Bovine manure | Canada | 2015 | IncI1/IncFIB/IncFII |
| 6294 | O33:H23 | ceftiofur | 5,047,447 | 4959 | Bovine manure | Canada | 2015 | IncI1/IncFIB/IncFII/IncQ1 |
| 6297 | O8:H1 | cefotaxime | 5,188,526 | 5050 | Bovine manure | Canada | 2015 | IncA/IncFIB |
| 12009 | O103:H2 | reference | 5,449,314 | 5121 | Human stool | Japan | 2001 | IncFIB |
| 11368 | O26:H11 | reference | 5,697,240 | 5519 | Human stool | Japan | 2001 | IncB/IncFIB/IncFII |
| NIPH-11060424 | O103:H25 | reference | 5,159,902 | 5327 | Human stool | Norway | 2006 | col156/IncFIB |
| 2009EL-2050 | O104:H4 | reference | 5,253,138 | 5183 | Human stool | USA | 2009 | IncP/IncQ1/IncFIB/IncFII |
| 2011C-3493 | O104:H4 | reference | 5,273,097 | 5138 | Human stool | USA | 2011 | IncP/IncQ/IncFIB/IncFII |
| 2010C-4347 | O26:NM | reference | 5,293,499 | 5477 | Not known | USA | 2013 | IncB/IncFIB |
| 2010C-3214 | O103:H11 | reference | 5,398,184 | 5493 | Not known | USA | 2013 | IncB/IncFIB |
| 06-3745 | O157:H7 | reference | 5,316,785 | 5384 | Human stool | USA | 2013 | IncFII |
| 2010C-4874 | O165:H25 | reference | 5,123,375 | 5211 | Not known | USA | 2013 | IncFIB/IncFII |
| 2009C-4006 | O111:NM | reference | 5,146,824 | 5263 | Not known | USA | 2013 | col156/IncFII |
| 03-3500 | O26:H11 | reference | 5,337,704 | 5531 | Not known | USA | 2013 | col156/IncFIB |
| 2009C-4126 | O111:H8 | reference | 5,093,584 | 5189 | Not known | USA | 2013 | IncFII |
| 01-3076 | O111:NM | reference | 5,038,636 | 5170 | Not known | USA | 2013 | IncFII |
| EDL933 | O157:H7 | reference | 5,547,323 | 5645 | ground beef | USA | 1982 | IncFIB/IncFII |
| Strain ID | Serotype | Resistance Phenotypes a | Resistance Genotypes b |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5959 | O7:H8 | AMC, AMP, FOX, TIO, CRO | blaCMY-2 |
| 5883 | O8:H1 | AMC, AMP, FOX, TIO, CRO, STR, SXT, CHL, SUL, TET | blaCMY-2, aadA-17, floR, dfrA-12, sul1-sul-2, tetG, strA, strB |
| 6297 | O8:H1 | AMC, AMP, FOX, TIO, CRO, STR, SXT, CHL, SUL, TET | blaCMY-2, aadA-17, floR, dfrA-12, sul1-sul-2, tetG, strA, strB |
| 5889 | O8:H1 | AMC, AMP, FOX, TIO, CRO, STR, SXT, CHL, SUL, TET | blaCMY-2, aadA-17, floR, dfrA-12, sul1-sul-2, tetG, strA, strB |
| 5937 | O8:H1 | AMC, AMP, FOX, TIO, CRO, STR, SXT, CHL, SUL, TET | blaCMY-2, aadA-17, floR, dfrA-12, sul1-sul-2, tetG, strA, strB |
| 5945 | O9:NM | AMC, AMP, FOX, TIO, CRO, AZM, STR, SXT, CHL, SUL, TET | blaCMY-2, blaTEM1, aadA-17, floR, dfrA-12, sul1-sul-2, tetG, strA, strB |
| 5956 | O9:NM | AMC, AMP, FOX, TIO, CRO, STR, SXT, CHL, SUL, TET | blaCMY-2, aadA-17, floR, dfrA-12, sul1-sul-2, tetG, strA, strB |
| 5953 | O9:NM | AMC, AMP, FOX, TIO, CRO | blaCMY-2 |
| 5891 | O11:H25 | AMC, AMP, FOX, TIO, CRO, STR, SXT, CHL, SUL, TET | blaCMY-2, aadA-17, floR, dfrA-12, sul1-sul-2, tetG, strA, strB |
| 5901 | O20:NM | AMC, AMP, FOX, TIO, CRO, STR, CHL, SUL, TET | blaCMY-2, floR, sul1-sul-2, tetG, strA, strB |
| 5902 | O20:NM | AMC, AMP, FOX, TIO, CRO, STR, CHL, SUL, TET | blaCMY-2, floR, sul1-sul-2, tetG, strA, strB |
| 5949 | O25:H11 | AMP, TIO, CRO, STR, CHL, SUL, TET | blaCTX-M15, blaTEM1, floR, dfrA-12, sul-2, tetG, strA, strB |
| 5951 | O25:H11 | AMP, TIO, CRO, STR, CHL, SUL, TET | blaCTX-M15, blaTEM1, floR, dfrA-12, sul-2, tetG, strA, strB |
| 6294 | O33:H23 | AMP, TIO, CRO, STR, SXT, SUL, TET | blaCTX-M15, blaTEM1, dfrA-5, sul-2, tetG, strA, strB |
| 5950 | O83:42 | AMC, AMP, TIO, CRO, AZM, NAL | blaCTX-M15, blaTEM1, OXA-1, cat, tetG |
| 5936 | O151:H9 | AMC, AMP, CIP, TIO, CRO, NAL, STR, SXT, CHL, SUL, TET | blaCTX-M15, blaTEM1, parC, qnrS1, floR, dfrA-14, sul-2, tetG, strA, strB |
| 5944 | O153:H42 | AMP, TIO, CRO, AZM, STR, SXT, CHL, SUL, TET | blaCTX-M115, blaTEM81, aadA17, cat1, dfrA12, suI1-sul-2, tetA tetD, strA,strB |
| 5947 | O153:H42 | AMP, TIO, CRO, AZM, STR, SXT, CHL, SUL, TET | blaCTX-M115, blaTEM81, aadA17, cat1, dfrA12, suI1-sul-2, tetA tetD, strA, strB |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rehman, M.A.; Yin, X.; Lepp, D.; Laing, C.; Ziebell, K.; Talbot, G.; Topp, E.; Diarra, M.S. Genomic Analysis of Third Generation Cephalosporin Resistant Escherichia coli from Dairy Cow Manure. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci4040057
Rehman MA, Yin X, Lepp D, Laing C, Ziebell K, Talbot G, Topp E, Diarra MS. Genomic Analysis of Third Generation Cephalosporin Resistant Escherichia coli from Dairy Cow Manure. Veterinary Sciences. 2017; 4(4):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci4040057
Chicago/Turabian StyleRehman, Muhammad Attiq, Xianhua Yin, Dion Lepp, Chad Laing, Kim Ziebell, Guylaine Talbot, Edward Topp, and Moussa Sory Diarra. 2017. "Genomic Analysis of Third Generation Cephalosporin Resistant Escherichia coli from Dairy Cow Manure" Veterinary Sciences 4, no. 4: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci4040057





