Simple Summary
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius is commonly found in dogs and is occasionally linked to infections in humans. The growing concern over S. pseudintermedius stems not only from its pathogenic potential but also from its rising resistance to multiple antibiotic classes. This resistance makes treatment more difficult and underscores the importance of identifying alternative strategies for managing infections. We conducted a comparative genomics analysis of S. pseudintermedius isolates. Interestingly, the genes similar to those coding for subtilisin A, a bacteriocin originally produced by Bacillus subtilis, were detected in S. pseudintermedius genomes. The core gene, sboA, was present in 657 S. pseudintermedius isolates from infected animals and humans, 1,031 S. pseudintermedius isolated from the environment, and 487 S. pseudintermedius isolates from unclassified sources, while the complete gene cluster was identified in only 395, 593, and 417 isolates, respectively. This discrepancy may reflect natural genetic variation or limitations in genome assembly quality. Our results show that S. pseudintermedius carries the genetic potential to produce subtilosin A, a bacteriocin known to kill a broad range of both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. These findings may support the development of new treatments that harness such natural antimicrobial compounds to help combat bacterial infections and address the growing challenge of antibiotic resistance.
Abstract
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius, an opportunistic pathogen of veterinary and zoonotic concern, harbors diverse biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) that may contribute to its ecological fitness and virulence. In this study, we performed a comparative genomic analysis of 6815 S. pseudintermedius isolates. Using Roary, we identified core and accessory genomes, revealing the subtilosin A gene (sboA) as part of the accessory genome, present in a subset of S. pseudintermedius isolates from clinical (n = 657), environmental (n = 1031), and unclassified sources (n = 487). AntiSMASH v8.0.0 analysis confirmed the presence of subtilosin A BGCs annotated as a sactipeptide with low similarity confidence to Bacillus subtilis subsp. spizizenii ATCC 6633 subtilosin A cluster. Further characterization using BAGEL4 identified multiple genes homologous to the Bacillus subtilis subtilosin A biosynthetic machinery (sbo-albABCDEFG), although albB, albG, and sboX were not annotated, raising questions about cluster completeness and functionality. BLAST v2.12.0 analysis of the full BGC identified by BAGEL4, revealing high conservation (99.6–100% pairwise identity) of gene content and order in 395 clinical, 593 environmental, and 417 unclassified S. pseudintermedius isolates. Incomplete clusters were identified in 763 clinical, 942 environmental, and 201 unclassified S. pseudintermedius isolates. The discrepancy between the number of isolates containing sboA and those harboring the full cluster may reflect evolutionary divergence or could be attributed to limitations in assembly quality. The functional implications of the identified cluster in S. pseudintermedius remain to be elucidated; however, its potential role in conferring competitive fitness by inhibiting closely related species is supported by previous findings in other staphylococci.
1. Introduction
The rise of antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections has intensified the search for novel antimicrobial agents, including naturally occurring peptides known as bacteriocins. Bacteriocins are ribosomally synthesized antimicrobial peptides produced by bacteria to inhibit the growth of closely related or competing bacterial species. Among these, subtilosin A, a bacteriocin produced by Bacillus subtilis strain 168, has garnered considerable interest due to its broad-spectrum activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including Enterococcus faecalis OGX-1, Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 19115, Porphyromonas gingivalis ATCC 33277, Kocuria rhizophila ATCC 9341, Enterobacter aerogenes ATCC 13408, Streptococcus pyogenes ATCC 19615, and Shigella sonnei ATCC 25931 [1]. Subtilosin A belongs to a group of ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs) called sactipeptides, which are characterized by sulfur-to-alpha carbon thioether cross-linked peptides. The biosynthesis of subtilosin is governed by the sbo-albABCDEFG gene cluster. The structural gene sbo encodes the subtilosin precursor peptide Sbo, which contains a leader peptide of eight residues and a core peptide of thirty-five residues. The radical S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) enzyme AlbA (an albA gene product), which contains a [4Fe-4S] cluster, catalyzes the formation of unique intramolecular thioether bonds of Sbo that crosslink the α-carbon of acceptor residues and the sulfur atom of cysteine residues. This thioether bond formation is dependent on the intact Sbo leader peptide sequence. The leader peptide is subsequently cleaved, and macrocyclization of the core peptide is mediated by AlbE and AlbF, encoded by the albE and albF genes. The final mature peptide is exported via the ABC transporter AlbC, encoded by the albC gene [2,3].
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius is primarily associated with companion animals, particularly dogs and cats, where it acts as both a commensal and an opportunistic pathogen. It is the most common cause of skin infections in dogs, including pyoderma, and can also cause wound infections, otitis, and post-surgical complications [4]. Though historically considered an animal-specific pathogen, S. pseudintermedius has increasingly been recognized as a zoonotic agent capable of causing infections in humans, particularly in those with close contact with pets [5,6,7,8]. The growing concern over S. pseudintermedius stems not only from its pathogenic potential but also from its rising resistance to multiple antibiotic classes, including β-lactams and macrolides [9,10,11,12,13]. This resistance complicates treatment and underscores the importance of identifying alternative strategies for managing infections.
To better understand the genetic factors that may contribute to its antimicrobial capabilities and pathogenicity, we conducted a comparative genomics analysis of S. pseudintermedius isolates. Interestingly, the genes similar to those coding for subtilisin A, a bacteriocin originally produced by Bacillus subtilis, were detected in S. pseudintermedius genomes. Our findings suggest the potential for subtilosin production in this species.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolates Included in the Study
We used the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Pathogen Detection system (BETA) (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pathogens/, accessed in January 2025) to obtain Staphylococcus pseudintermedius genome sequences for this study. This integrated system compiles bacterial and fungal genomic data from ongoing surveillance and research efforts, including isolates obtained from food, environmental sources, and clinical samples from patients. The NCBI Pathogen Detection system clusters related pathogen genome sequences to help identify potential transmission chains, supporting outbreak investigations by public health officials, and screens genome sequences as part of the National Database of Antibiotic Resistant Organisms (NDARO) using the AMRFinderPlus tool [14]. This allows for the detection of genes coding for antimicrobial resistance, stress response, and virulence proteins, providing insight into the spread and evolution of resistance and pathogenicity.
We filtered S. pseudintermedius isolates by source, including those isolated from clinical, environmental, or unclassified sources, to ensure that both infection-related and putative environmental reservoirs were adequately represented.
2.2. Genome Mining by antiSMASH and BAGEL4
To identify biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) associated with secondary metabolite production, we employed antiSMASH v8.0 (https://antismash.secondarymetabolites.org) [15] and BAGEL4 (http://bagel4.molgenrug.nl/) [16]—two widely used web-based platforms for genome mining. AntiSMASH analyzes bacterial genomes for potential BGCs by comparing gene architectures with a curated database of known biosynthetic pathways, while BAGEL4 is tailored to detect bacteriocins and ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs) in bacterial (meta-) genomic DNA. The default parameters were applied, and only high-quality assemblies were included to ensure accurate annotation and characterization of candidate clusters.
2.3. Sequence Analysis
All sequence analyses were conducted using Geneious Prime® 2025.1.3 software [17], which integrates a variety of bioinformatics tools. Multiple sequence alignments were performed using Clustal Omega v1.2.3. For homology and identity searches, we generated and queried a custom BLAST database within Geneious Prime® 2025 software to ensure accurate comparison against genome sequences from reference, clinical, and environmental S. pseudintermedius isolates and those isolated from unclassified sources. For the pangenomic analysis, S. pseudintermedius genome assemblies were downloaded from NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). The assemblies were subjected to prokka v1.14.5 annotation (https://github.com/tseemann/prokka) [18] and the Roary v3.13.0 pangenome pipeline (https://github.com/sanger-pathogens/Roary) [19]. The default parameters were applied.
3. Results
A total of 6815 S. pseudintermedius isolates were retrieved from the NCBI Pathogen Detection database. We performed pan-genome analysis using Roary, which enabled the identification of core and accessory genes among the genomes. Through this analysis, we observed that the subtilosin A core gene (sboA) was present in 657 of 1724 clinical isolates (38.1%), 1031 of 3176 environmental isolates (32.5%), and 487 of 1915 unclassified isolates (25.4%) Figure 1.
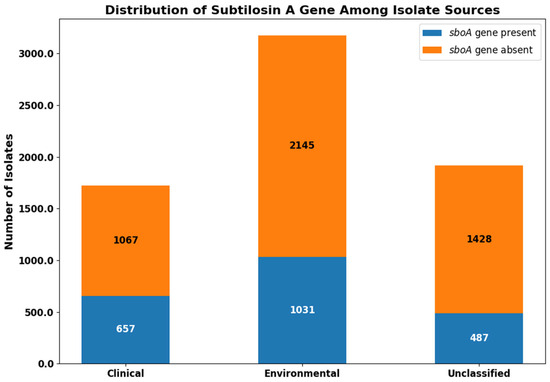
Figure 1.
Distribution of the subtilosin A core gene (sboA) among Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolates. The sboA gene was detected in 657 of 1724 clinical isolates, 1031 of 3176 environmental isolates, and 487 of 1915 unclassified isolates. Bar segments represent the number of isolates present (blue) or absent (orange) for the sboA gene in each source category.
To explore whether the entire subtilosin A secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene cluster (BGC) was present, the complete genome of S. pseudintermedius isolates was analyzed using antiSMASH version 8.0.0 [15]. The tool was run with default parameters, allowing for the detection of a wide range of BGC types. Each cluster’s similarity to known BGCs was evaluated using the built-in similarity comparison module. The number and types of BGCs varied across genomes, reflecting strain-specific biosynthetic diversity. S. speudintermedius 081661 was selected for detailed visualization, as shown in Figure 2. Notably, region 8 in this isolate was identified as a sactipeptide with low similarity confidence to the known and well-characterized subtilosin A cluster in the database. The low similarity confidence reflects limited homology to characterized clusters, suggesting either sequence divergence or novel gene architecture.
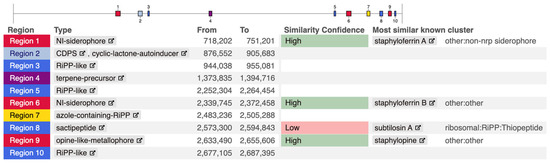
Figure 2.
Biosynthetic gene clusters identified in Staphylococcus pseudintermedius 081661 using antiSMASHV8.0.0.
The genetic similarity and organization of the BGCs were analyzed using the “Minimum Information about a Biosynthetic Gene Cluster” (MIBiG) database. The BGC from S. pseudintermedius 081661 showed a similarity score of 0.60 with subtilosin A-producing Bacillus subtilis subsp. spizizenii ATCC 6633 Figure 3. A similarity score of 0.45 was observed with a thurincin H-producing Bacillus thuringiensis, and a score of 0.40 was linked to an enterocin F4-9-producing Enterococcus faecalis Figure 3.
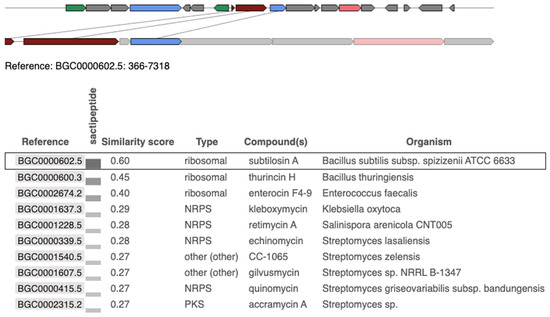
Figure 3.
Comparison of the subtilosin A biosynthetic gene cluster (BGC) identified in Staphylococcus pseudintermedius 081661 with reference BGCs from the MIBiG database using antiSMASHV8.0.0 analysis. The top panel shows a visual representation of the query region from S. pseudintermedius (bottom track) aligned with the best-matching reference cluster, subtilosin A from Bacillus subtilis subsp. spizizenii ATCC 6633 (top track). Genes are represented as arrows, with lines connecting orthologous genes based on the best 1:1 BLAST matches. The lower panel shows the genetic similarity analysis of the identified subtilosin A BGC from S. pseudintermedius 081661. The highlighted row (black border) indicates the currently selected match, subtilosin A (BGC0000615), which shares 60% similarity with the query cluster and is classified as a ribosomal sactipeptide cluster. Red: core biosynthetic genes; Orange: additional biosynthetic genes; Blue: transport-related genes; Green: regulatory genes; Gray: other or uncharacterized genes.
To further validate and refine these findings, the BAGEL4 web server was utilized to mine S. pseudintermedius genome assemblies for bacteriocins and ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs). BAGEL4 analysis helped to better characterize the components of the subtilosin A biosynthetic gene cluster, providing additional insights into gene content. BAGEL4 analysis of S. pseudintermedius genome assemblies confirmed the presence of a biosynthetic cluster associated with subtilosin A biosynthesis in some S. pseudintermedius isolates. The cluster was annotated as Subtilosin A and included several hallmark genes involved in sactipeptide biosynthesis. Key components identified within the cluster included albA (encoding an antilisterial bacteriocin subtilosin biosynthesis protein albA; BmbF), albD (encoding an antilisterial bacteriocin subtilosin biosynthesis protein albD; orf00020), albE (encoding an antilisterial bacteriocin subtilosin biosynthesis protein albE; orf00023), and albF, the latter annotated as a putative zinc-dependent protease (OS = Bacillus subtilis, GN = albF). An ABC transporter protein (ALBC_BACSU, PF00005) was also present, indicating a potential role in peptide export or immunity. However, albB, albG, and sboX were not annotated/detected.
Additional open reading frames (ORFs), such as orf00022 and orf00025, remained functionally uncharacterized, suggesting possible novel or accessory functions within the identified subtilosin cluster. The detection of these genes in several isolates supports the hypothesis of a conserved, yet potentially divergent, subtilosin A bacteriocin system in S. pseudintermedius.
The overall genetic architecture of the subtilosin A gene cluster in S. pseudintermedius 081661 is illustrated in Figure 4.
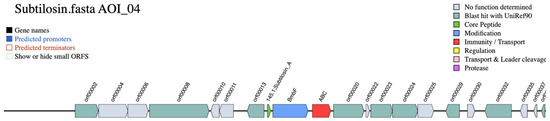
Figure 4.
Genetic organization of the subtilosin A biosynthetic gene cluster identified by BAGEL4 in Staphylococcus pseudintermedius 081661. The cluster was visualized with predicted functions color-coded according to gene classification. The core peptide (green), the protein involved in the modification process (blue), and transport (red).
To assess the conservation and synteny of the subtilosin A biosynthetic gene cluster (BGC), we performed a BLAST analysis of the entire cluster identified by BAGEL4 against all downloaded S. pseudintermedius genomes. This analysis revealed that the full cluster, including gene content and order, was conserved in a subset of the genomes. Specifically, the subtilosin A biosynthetic gene cluster was detected in 395 clinical isolates, with sequence lengths ranging from 6315 to 6325 bps and nucleotide identity of 99.6–100% to the S. pseudintermedius 081661 subtilosin A BGC Figure 5. Additionally, 593 isolates from environmental sources harbored the cluster with lengths of 6316 to 6328 bps and nucleotide identity of 99.6–99.98% to the S. pseudintermedius 081661 subtilosin A BGC. Furthermore, 417 isolates from unclassified sources carried the cluster with lengths of 6316 to 6326 bps and nucleotide identity of 99.6-99.98% to the S. pseudintermedius 081661 subtilosin A BGC Figure 5. These findings demonstrate the widespread but not universal conservation of the subtilosin A cluster among S. pseudintermedius isolates from clinical, environmental, and unclassified sources Figure 5. Importantly, incomplete or partial subtilosin A clusters were observed in a greater number of genomes. These truncated clusters may reflect technical limitations, such as incomplete genome assemblies, fragmented contigs, or variations in sequencing technology, depth, and quality. Alternatively, they could indicate evolutionary differences in the BGC architecture.
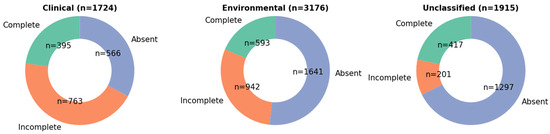
Figure 5.
The distribution of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolates containing subtilosin A genes across three sources: clinical, environmental, and unclassified. Each pie chart displays the proportion of isolates with complete, incomplete, or absent subtilosin A gene clusters. Complete: Isolates with full subtilosin A gene cluster; Incomplete: Isolates with partial/subset of subtilosin A genes; Absent: No detectable subtilosin A gene components. Colors: greenish = #66c2a5, orange = #fc8d62, blueish = #8da0cb.
4. Discussion
In this study, we focused on Staphylococcus pseudintermedius, an opportunistic pathogen that primarily colonizes the skin and mucosal surfaces of dogs and other companion animals. It is increasingly recognized as a significant cause of veterinary infections, including pyoderma, otitis, and postoperative wound infections [20]. Moreover, S. pseudintermedius has zoonotic potential, with reports of transmission to humans, particularly among pet owners and veterinary personnel. The clinical relevance of this study is underscored by the growing global concern surrounding methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius (MRSP). Currently, MRSP presents a veterinary health challenge comparable to the public health crisis posed by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in human medicine. The increasing spread of multidrug-resistant MRSP and methicillin-susceptible S. pseudintermedius (MSSP) strains, coupled with the lack of effective new antibiotics, highlights the limited therapeutic possibilities and the urgent need for alternative strategies such as bacteriocin-based interventions to control and treat infections [1,21].
Among the bacteriocins, subtilosin A—a ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide (RiPP)—is known for its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, particularly against Gram-positive bacteria [22]. The biosynthesis of subtilosin is governed by the sbo-albABCDEFG gene cluster. Our analysis revealed that the subtilosin A biosynthetic gene cluster (BGC) is conserved in a subset of S. pseudintermedius isolates. Notably, the presence of key genes coding for subtilosin A (sboA), albA, albD, albE, and albF, along with an associated ABC transporter, suggests a functional sactipeptide biosynthetic pathway. However, we also observed incomplete or partial clusters in a greater number of genomes, which may be attributed to technical limitations like incomplete genome assemblies or sequencing technology and quality. Alternatively, these variations could reflect evolutionary differences in the BGC architecture. Importantly, these observations emphasize the need for experimental validation. Techniques such as RNA-seq and proteomics are essential to confirm not only the transcription and translation of these genes but also the actual production of subtilosin A in vitro and its functional role as a bacteriocin.
A recently published comprehensive population and pan-genomic study of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius by Zehr et al., which we came across during manuscript submission, supports our findings [23].
A previous study has identified the subtilosin A BGC in Staphylococcus felis and Staphylococcus delphini [2]. The identified cluster in S. felis included Sbo, AlbA, AlbC, AlbD, AlbE, AlbF, and AlbG, but lacked AlbB, whereas in S. delphini, the cluster included Sbo, AlbA, AlbB, AlbC, AlbD, AlbE, and AlbF, but lacked AlbG [2].
Zheng et al. demonstrated that Bacillus subtilis mutants lacking albE and albF exhibited reduced or abolished subtilosin production, highlighting the essential role of these genes in subtilosin maturation [24]. Intriguingly, our bioinformatic analysis revealed that albB, albG, and sboX are absent/not annotated in all examined clinical and environmental isolates of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius and even those from unclassified sources. This raises important questions about whether S. pseudintermedius employs an alternative mechanism for subtilosin processing or produces a structurally distinct, functionally analogous molecule. Further transcriptomic and proteomic analyses are warranted to determine whether subtilosin or a related compound is synthesized and matured through a different pathway in this species.
Interestingly, the presence of subtilosin A biosynthetic gene cluster (BGC) in S. pseudintermedius adds to a growing body of evidence suggesting that staphylococci possess diverse and potentially bioactive bacteriocin gene clusters [25,26,27,28]. For instance, Staphylococcus hyicus 4244 was recently reported to produce a novel sactibiotic, hyicin 4244, the first of its kind identified in staphylococci. This bacteriocin exhibits a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity, including efficacy against multidrug-resistant staphylococcal strains, and has demonstrated the ability to prevent biofilm formation and reduce established biofilms on abiotic surfaces in vitro [29]. These findings highlight the biotechnological potential of sactibiotics not only in therapeutic settings but also in the development of antimicrobial coatings for medical devices.
The widespread presence of the subtilosin A BGC in a substantial subset of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolates, spanning both clinical and environmental origins, suggests that this cluster may play an important role in the ecological success of this species.
In microbial ecosystems, species often compete for limited resources such as nutrients, colonization sites, and ecological space. One common strategy for gaining a competitive advantage involves the secretion of antimicrobial compounds, including bacteriocins, which target closely related species [30,31,32,33,34,35]. The identification of subtilosin A gene clusters in S. pseudintermedius suggests this bacterium may utilize such a strategy to enhance its ecological success. If functionally expressed, subtilosin A could enable S. pseudintermedius to inhibit the growth of competing skin-associated microbes, thereby promoting its persistence on host surfaces and increasing its colonization efficiency [35,36]. This is particularly relevant in polymicrobial environments, where subtle shifts in microbial population dynamics can determine pathogenic potential or persistence. The conservation of the subtilosin A cluster in many S. pseudintermedius genomes underscores its likely benefit; however, the absence of key genes in some genomes, as well as the lack of annotation for potential regulatory elements such as sboX, raises questions about whether the cluster is universally functional in these strains.
Ultimately, the detection of these clusters at the genomic level does not confirm functional expression. To determine whether the subtilosin A BGC is actively transcribed and translated into a functional antimicrobial product, further studies incorporating RNA-seq, proteomics, and biochemical assays are needed [37,38]. These approaches will be critical for verifying bacteriocin production and understanding its regulatory mechanisms, as well as elucidating its role in inter-bacterial interactions and potential contribution to virulence or colonization. Confirming the functional activity of subtilosin A in S. pseudintermedius may also open new avenues for exploring its therapeutic potential as a targeted antimicrobial agent.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our genomic analysis of S. pseudintermedius revealed the widespread presence and conservation of the subtilosin A biosynthetic gene cluster in both clinical and environmental isolates. Although some genomes contained incomplete clusters, likely due to sequencing quality or evolutionary divergence, the core components were consistently identified in a significant subset of isolates. The findings suggest that subtilosin A, if functionally expressed, may contribute to the competitive fitness of S. pseudintermedius in complex microbial environments. However, the absence of key genes in some isolates and the lack of annotation for regulatory elements such as sboX highlight the need for further experimental validation. Future work integrating transcriptomic and proteomic approaches is essential to confirm subtilosin A expression and elucidate its functional role in bacterial competition and pathogenesis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.A.; methodology, O.K.E.; software, O.K.E.; validation, M.A.A. and O.K.E.; formal analysis, O.K.E.; investigation, M.A.A. and O.K.E.; resources, M.A.A.; data curation, O.K.E.; writing—original draft preparation, O.K.E.; writing—review and editing, M.A.A.; visualization, O.K.E.; supervision, M.A.A.; project administration, M.A.A.; funding acquisition, M.A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Shelburne, C.E.; An, F.Y.; Dholpe, V.; Ramamoorthy, A.; Lopatin, D.E.; Lantz, M.S. The spectrum of antimicrobial activity of the bacteriocin subtilosin A. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 59, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, K.; Nakamura, A.; Kojima, S. Crystal structure of the AlbEF complex involved in subtilosin A biosynthesis. Structure 2022, 30, 1637–1646.E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Yan, L.Z.; Vederas, J.C.; Zuber, P. Genes of the sbo-alb locus of Bacillus subtilis are required for production of the antilisterial bacteriocin subtilosin. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 7346–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, V.; Oliveira, A.; Manageiro, V.; Caniça, M.; Contente, D.; Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Carvalho, I.; Capelo, J.L.; Igrejas, G.; et al. Clonal Diversity and Antimicrobial Resistance of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius Isolated from Canine Pyoderma. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viñes, J.; Verdejo, M.Á.; Horvath, L.; Vergara, A.; Vila, J.; Francino, O.; Morata, L.; Espasa, M.; Casals-Pascual, C.; Soriano, À.; et al. Isolation of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in Immunocompromised Patients from a Single Center in Spain: A Zoonotic Pathogen from Companion Animals. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, N.C.; Moodley, A.; Ghibaudo, G.; Guardabassi, L. Carriage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in small animal veterinarians: Indirect evidence of zoonotic transmission. Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, M.; Sabala, R.F.; Morita, S.; Fukuda, A.; Tsuyuki, Y.; Torii, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Okamura, K.; Komatsu, T.; Sasaki, J.; et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility and genetic diversity of staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolated from companion animals and human clinical patients in Japan: Potential zoonotic implications. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2025, 42, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, I.B.; Santos, F.F.; Gales, A.C. Human Colonization and Infection by Staphylococcus pseudintermedius: An Emerging and Underestimated Zoonotic Pathogen. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayem, S.A.J.; Lee, G.Y.; Abbas, M.A.; Park, S.C.; Lee, S.J. Pharmacodynamic Profiling of Amoxicillin: Targeting Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Positive Pathogens Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in Canine Clinical Isolates. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grist, L.F.; Brown, A.; Fitzpatrick, N.; Mariano, G.; La Ragione, R.M.; Van Vliet, A.H.M.; Mehat, J.W. Global phylogenomic analysis of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius reveals genomic and prophage diversity in multidrug-resistant lineages. Microb. Genom. 2025, 11, 001369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrenås, M.; Pedersen, K.; Windahl, U. Genomic Analyses of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius from Companion Animals Reveal Changing Clonal Populations, Multidrug Resistance, and Virulence. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phophi, L.; Abouelkhair, M.; Jones, R.; Henton, M.; Qekwana, D.N.; Kania, S.A.; Zhang, K. The molecular epidemiology and antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius canine clinical isolates submitted to a veterinary diagnostic laboratory in South Africa. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phophi, L.; Abouelkhair, M.A.; Jones, R.; Zehr, J.; Kania, S.A. Temporal changes in antibiotic resistance and population structure of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius between 2010 and 2021 in the United States. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 100, 102028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldgarden, M.; Brover, V.; Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Frye, J.G.; Haendiges, J.; Haft, D.H.; Hoffmann, M.; Pettengill, J.B.; Prasad, A.B.; Tillman, G.E.; et al. AMRFinderPlus and the Reference Gene Catalog facilitate examination of the genomic links among antimicrobial resistance, stress response, and virulence. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Vader, L.; Szenei, J.; Reitz, Z.L.; E Augustijn, H.; Cediel-Becerra, J.D.D.; de Crécy-Lagard, V.; A Koetsier, R.; E Williams, S.; et al. antiSMASH 8.0: Extended gene cluster detection capabilities and analyses of chemistry, enzymology, and regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, gkaf334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Heel, A.J.; de Jong, A.; Song, C.; Viel, J.H.; Kok, J.; Kuipers, O.P. BAGEL4: A user-friendly web server to thoroughly mine RiPPs and bacteriocins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W278–W281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.G.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannoehr, J.; Guardabassi, L. Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in the dog: Taxonomy, diagnostics, ecology, epidemiology and pathogenicity. Vet. Dermatol. 2012, 23, 253-e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, P.D.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. Bacteriocins—A viable alternative to antibiotics? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amrouche, T.; Noll, K.S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Chikindas, M.L. Antibacterial Activity of Subtilosin Alone and Combined with Curcumin, Poly-Lysine and Zinc Lactate Against Listeria monocytogenes Strains. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2010, 2, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehr, J.D.; Sun, Q.; Ceres, K.; Merrill, A.; Tyson, G.H.; Ceric, O.; Guag, J.; Pauley, S.; McQueary, H.C.; Sams, K.; et al. Population and pan-genomic analyses of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius identify geographic distinctions in accessory gene content and novel loci associated with AMR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2025, 91, e00010-25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Hehn, R.; Zuber, P. Mutational analysis of the sbo-alb locus of Bacillus subtilis: Identification of genes required for subtilosin production and immunity. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 3266–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freire Bastos, M.D.C.; de Farias, F.M.; Fagundes, P.C.; Coelho, M.L.V. Staphylococcins: An update on antimicrobial peptides produced by staphylococci and their diverse potential applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 10339–10368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Fernández, R.; Elsherbini, A.M.A.; Lozano, C.; Martínez, A.; de Toro, M.; Zarazaga, M.; Peschel, A.; Krismer, B.; Torres, C. Genomic Analysis of Bacteriocin-Producing Staphylococci: High Prevalence of Lanthipeptides and the Micrococcin P1 Biosynthetic Gene Clusters. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2025, 17, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wladyka, B.; Piejko, M.; Bzowska, M.; Pieta, P.; Krzysik, M.; Mazurek, Ł.; Guevara-Lora, I.; Bukowski, M.; Sabat, A.J.; Friedrich, A.W.; et al. A peptide factor secreted by Staphylococcus pseudintermedius exhibits properties of both bacteriocins and virulence factors. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Kim, J.; Quan, L.H.; Heu, S.; Roh, E. Purification and Characterization of Pasteuricin Produced by Staphylococcus pasteuri RSP-1 and Active against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 1768–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Duarte, A.F.; Ceotto-Vigoder, H.; Barrias, E.S.; Souto-Padrón, T.C.B.S.; Nes, I.F.; de Freire Bastos, M.D.C. Hyicin 4244, the first sactibiotic described in staphylococci, exhibits an anti-staphylococcal biofilm activity. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommineni, S.; Bretl, D.J.; Lam, V.; Chakraborty, R.; Hayward, M.; Simpson, P.; Cao, Y.; Bousounis, P.; Kristich, C.J.; Salzman, N.H. Bacteriocin production augments niche competition by enterococci in the mammalian gastrointestinal tract. Nature 2015, 526, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbing, M.E.; Fuqua, C.; Parsek, M.R.; Peterson, S.B. Bacterial competition: Surviving and thriving in the microbial jungle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, D.; Goncheva, M.I.; Flannagan, R.S.; Deecker, S.R.; Guariglia-Oropeza, V.; Ensminger, A.W.; Heinrichs, D.E. Coagulase-negative staphylococci release a purine analog that inhibits Staphylococcus aureus virulence. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leistikow, K.R.; May, D.S.; Suh, W.S.; Asensio, G.V.; Schaenzer, A.J.; Currie, C.R.; Hristova, K.R. Bacillus subtilis-derived peptides disrupt quorum sensing and biofilm assembly in multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. mSystems 2024, 9, e00712–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessandrini, G.; Mercuri, S.; Martella, A.; Ferrara, F.; Simonetti, V.; Trifirò, C.; Emanuele, E. Topical application of bacteriocins from Bacillus subtilis promotes Staphylococcus aureus decolonization in acneic skin and improves the clinical appearance of mild-to-moderate acne. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol./Postępy Dermatol. I Alergol. 2023, 40, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.; Levin, B.R. Structured habitats and the evolution of anticompetitor toxins in bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 6324–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, M.A.; Wertz, J.E. Bacteriocins: Evolution, Ecology, and Application. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2002, 56, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: A revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alajlani, M.M. Characterization of subtilosin gene in wild type Bacillus spp. and possible physiological role. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).