Poisoning by Atractylus gummifera L. Roots in Grazing Cattle of a Sicilian Farm
Simple Summary
Abstract
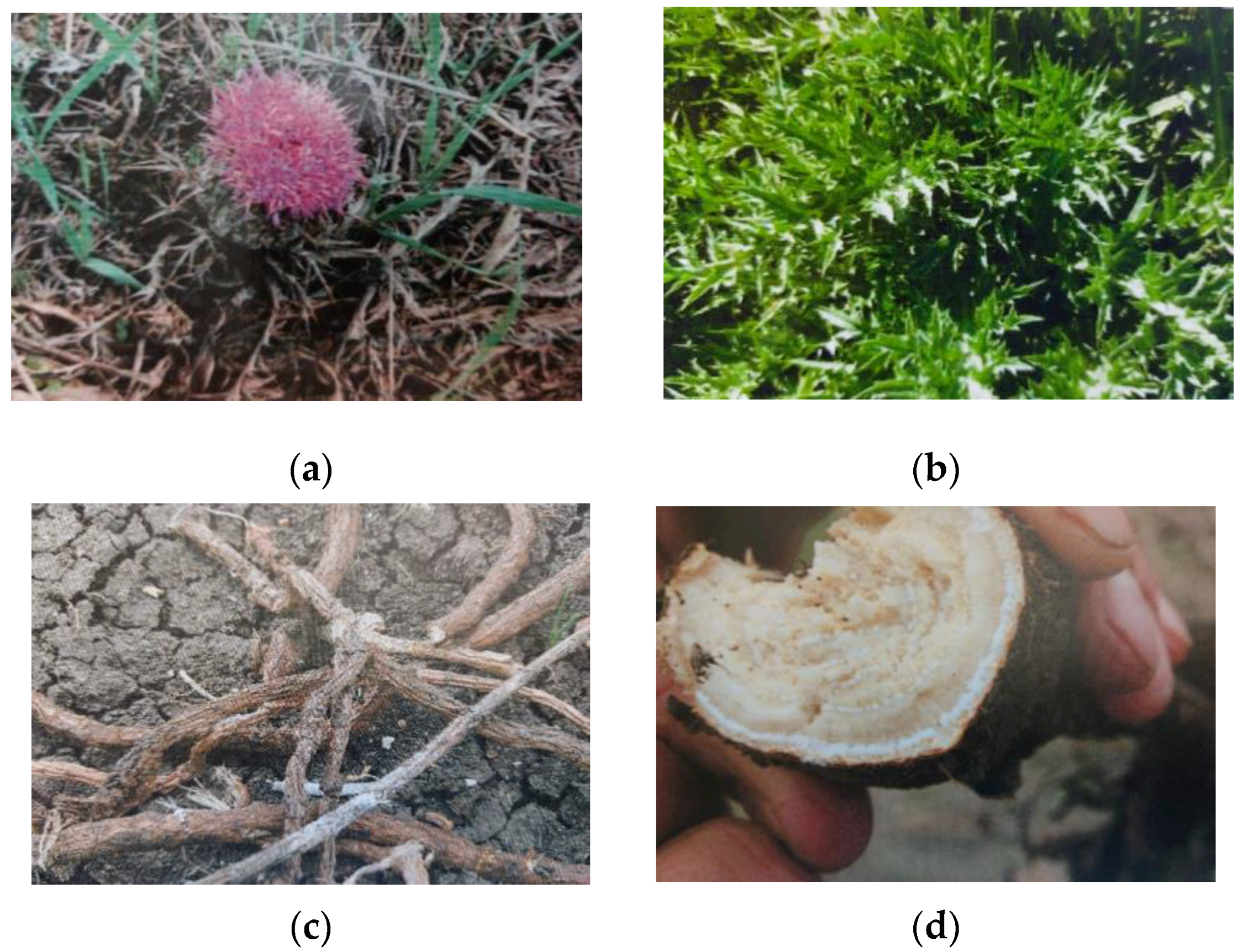
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Information on Poisoning of Grazing Cattle
2.2. Medical History
Clinical Symptoms
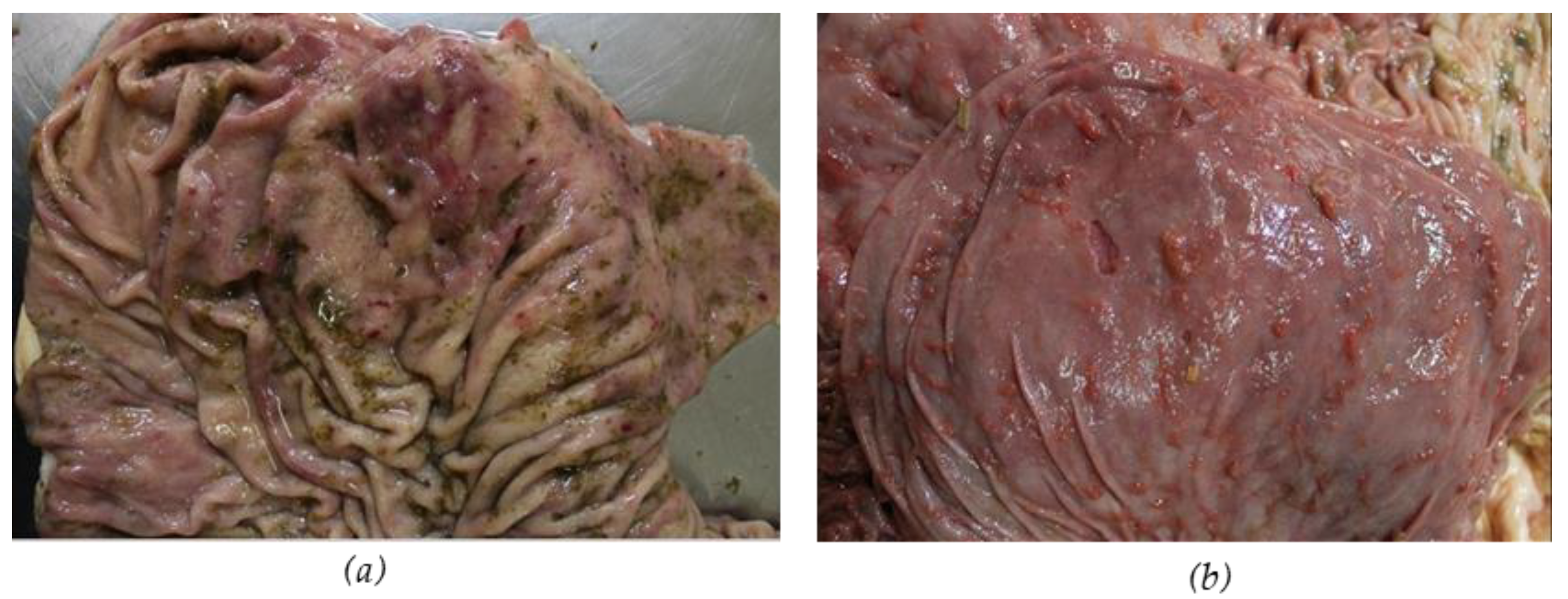
2.3. Necropsy Examination
2.4. Clinical Analyses
2.5. Pharmacological Therapy
3. Results
3.1. Necropsy Examination
3.2. Clinical–Pathological Analyses
3.3. Pharmacological Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daniele, C.; Dahamna, S.; Firuzi, O.; Sekfali, N.; Saso, L.; Mazzanti, G. Atractyligummifera L. poisoning: An ethnopharmacological review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 97, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejdoub, K.; Mami, I.R.; Belabbes, R.; Dib, M.E.A.; DJabou, N.; Tabti, B.; Benyelles, N.G.; Costa, J.; Muselli, A. Chemical Variability of Atractylis gummifera Essential Oils at Three Developmental Stages and Investigation of Their Antioxidant, Antifungal and Insecticidal Activities. Curr. Bioact. Compd. 2020, 16, 489–497. [Google Scholar]
- Bouabid, K.; Lamchouri, F.; Toufik, H.; Boulfia, M.; Senhaji, S.; Faouzi, M.E.A. In vivo anti-diabetic effect of aqueous and methanolic macerated extracts of Atractylis gummifera. Bangl. J. Pharmac. 2019, 14, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Hamouda, C.; Hédhili, A.; Ben Salah, N.; Zhioua, M.; Amamou, M. A review of acute poisoning from Atractylisgummifera L. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 2004, 46, 144–146. [Google Scholar]
- Hamouda, C.; Amamou, M.; Thabet, H.; Yacoub, M.; Hedhili, A.; Bescharnia, F.; Ben Salah, N.; Zhioua, M.; Abdelmoumen, S.; El Mekki Ben Brahim, N. Plant poisonings from herbal medication admitted to a Tunisian toxicologic intensive care unit, 1983–1998. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 2000, 42, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Vallejo, J.R.; Peral, D.; Gemio, P.; Carrasco, M.C.; Heinrich, M.; Pardo-de-Santayana, M. Atractylis gummifera and Centaureaornata in the Province of Badajoz (Extremadura, Spain)—Ethnopharmacological importance and toxicological risk. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 126, 366–370. [Google Scholar]
- Bruneton, J. Toxic Plants Dangerous to Humans and Animals; Tec & Doc: Paris, France, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ahid, S.; El Cadi, M.A.; Meddah, B.; Cherah, Y. Atractylis gummifera: De l’intoxication aux méthodes analytiques. Ann. Biol. Clin. 2012, 70, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammich, V.; Merad, R.; Azzouz, M. Plantes Toxiques à Usage Médicinal du Pourtour Méditerranéen; Springer: Paris, France, 2013; p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Fakchich, J.; Elachouri, M. Ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants used by people in Oriental Morocco to manage various ailments. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 154, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegi, L.; Pieroni, A.; Guarrera, P.M.; Vangelisti, R. A review of plants used in folk veterinary medicine in Italyasbasis for a databank. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 89, 221–244. [Google Scholar]
- Nya, S.; Abouzahir, H.; Dami, A.; Saif, Z.; Najdi, A.; Belhouss, A.; Benyaich, H. Death in Children After Atractylis gummifera L. Poisoning in Morocco-Report of Three Cases and Review of Literature. Am. J. Forensic Med. Pathol. 2021, 42, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stickel, F.; Egerer, G.; Seitz, H.K. Hepatotoxicity of botanicals. Public Health Nutr. 2000, 3, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carlier, J.; Romeuf, L.; Guitton, J.M.; Priez-Barallon, C.; Bevalot, F.; Fanton, L.; Gaillard, Y. A validated method for quantifying atractyloside and carboxyatractyloside in blood by HPLCHRMS/MS, a non-fatal case of intoxication with Atractylis gummifera L. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2014, 38, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Achour, S.; Rhalem, N.; Elfakir, S.; Khattabi, A.; Nejjari, C.; Mokhtari, A.; Soulaymani, A.; Soulaymani, R. Prognostic factors of Atractylis gummifera L. poisoning, Morocco. East. Mediterr. Health J. 2013, 19, 901–965. [Google Scholar]
- Steenkamp, P.A.; Harding, N.M.; van Heerden, F.R.; van Wyk, B.E. Identification of atractyloside by LC–ESI–MS in alleged herbal poisonings. Forensic Sci. Int. 2006, 163, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obatomi, D.K.; Brant, S.; Anthonypillai, V.; Bach, P.H. Toxicity of Atractyloside in Precision-Cut Rat and Porcine Renal and Hepatic Tissue Slices. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1998, 148, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Khanfri, L.; Madi, A.; Hajji, H.; Naji, S.E.; El Kettani, S.; Boughima, F.A. Fatal Atractylis gummifera L. poisoning: A case report of an autopsy. Med.-Leg. J. 2023, 93 (Suppl. S1), 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, M.; Biol, D.; Sianidou, L. Hepatotoxicity due to Atractylis gummifera L. J. Clin. Toxicol. 1988, 26, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalli, S.; Alaoui, I.; Pineau, A.; Zaid, A.; Soulaymani, R. Atractylis gummifera L poisoning: A case report. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 2002, 95, 284–2866. [Google Scholar]
- Madani, N.; Sbaï, H.; Harandou, M.; Boujraf, S.; Achour, S.; Khatouf, M.; Kanjaa, N. Atractylis gummifera poisoning in a pregnant woman. Presse Med. 2006, 35, 1828–1830. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano, P. Poisoning by white chameleon, Atractylis gummifera, L., in a herd of pigs in the Saida region (Algeria). Rev. Med. Vet. 1958, 109, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Bourke, C.A.; White, J.G. Reassessment of the toxicity of Hypericum perforatum (St John’s wort) for cattle. Aust. Vet. J. 2004, 82, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboling, S. Do Poisonous Plants in Pastures Communicate Their Toxicity? Meta-Study and Evaluation of Poisoning Cases in Central Europe. Animals 2023, 13, 3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, K.; Rahman, F.; Ullah, I.; Ahmad, Z.; Schickhoff, U. Animals Feed in Transition: Intricate Interplay of Land Use Land Cover Change and Fodder Sources in Kurram Valley, Pakistan. Resources 2024, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capela E Silva, F.; Sousa, A.C.; Pastorinho, M.R.; Mizukawa, H.; Ishizuka, M. Editorial: Animal Poisoning and Biomarkers of Toxicity. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 891483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortinovis, C.; Caloni, F. Epidemiology of intoxication of domestic animals by plants in Europe. Vet. J. 2013, 197, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swirski, A.L.; Pearl, D.L.; Berke, O.; O’Sullivan, T.L. Companion animal exposures to potentially poisonous substances reported to a national poison control center in the United States in 2005 through 2014. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2020, 257, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berny, P.; Caloni, F.; Croubels, S.; Sachana, M.; Vandenbroucke, V.; Davanzo, F. Animal poisoning in Europe. Part 2: Companion animals. Vet. J. 2010, 183, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naccari, V.; Trevisi, G.; Naccari, C.; Ferrara, G.; Bava, R.; Palma, E. Poisoning due to Spinosad in honey bees: Toxicological report. J. Apic. Res. 2024, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riet-Correa, F.; Machado, M.; Micheloud, J.F. Plants causing poisoning outbreaks of livestock in South America: A review. Toxicon X 2023, 17, 100150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.Y.; Lin, H.S.; Sun, Y.H.; Tsai, J.S. Factors affecting intentional bird poisoning on bean farms in Taiwan: Seeding methods and the presence of adjoining duck farms matter. Avian Conserv. Ecol. 2021, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, A.L. Animal Poisoning: Toxins from Plants or Feed—An Important Chemical Risk for Domestic Animals. Toxins 2024, 16, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashetti, P.N.; Rohit, K.; Amit, K.; Chaitrali, A.; Rajeshwar, K.; Ashvini, B.; Mukesh, T.N. Comparative pathology of different plant toxins in grazing animals. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Anim. Husb. 2024, 9, 1436–1440. [Google Scholar]
- Guitart, R.; Croubels, S.; Caloni, F.; Sachana, M.; Davanzo, F.; Vandenbroucke, V.; Berny, P. Animal poisoning in Europe. Part 1: Farm livestock and poultry. Vet. J. 2010, 183, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modra, H.; Svobodova, Z. Incidence of animal poisoning cases in the Czech Republic: Current situation. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2009, 2, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouaffak, Y.; Boutbaoucht, M.; Ejlaidi, A.; Toufiki, R.; Younous, S. Fatal poisoning by Atractylis gummifera L.: A case report. Arch. Pédiatrie 2013, 20, 496–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benlamkaddem, S.; Ouedghiri, Y.; Hoummani, H.; Adnane Berdai, M.; Achour, S.; Harandou, M. A fatal case of cutaneous “Atractylis gummifera L.” poisoning: Case report. Toxicol. Anal. Clin. 2023, 35, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hami, H.; Soulaymani, A.; Skalli, S.; Mokhtari, A.; Sefiani, H.; Soulaymani, R. Intoxication par Atractylis gummifera L. Données du centre antipoison et de pharmacovigilance du Maroc [Poisoning by Atractylis gummifera L. Morocco poison control center data]. Bull. Société Pathol. Exot. 2011, 104, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaim, N.; Guemouri, L.; Lamnaouer, D.; Benjouad, A. Study of four cases of poisoning by Atractylis gummifera L. in Morocco. Therapie 2008, 63, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouziri, A.; Hamdi, A.; Menif, K.; Ben Jaballah, N. Hepatorenal injury induced by cutaneous application of Atractylis gummifera L. Clinic. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 752–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelef, M.; Hemida, H.; Hassani, A.; Mazrou, K.; Mira, S.; Abdali, M. Phytochemical profile of Atractylis gummifera rhizome, acute toxicity to Wistar rat and rat poisoning effect in the field. J. Crop Prot. 2021, 10, 119–137. [Google Scholar]
- Ozturk, Y.; Keskin, Z.; Tanyildizi, S.; Baykalir, B.G.; Korkak, F.A.; Dagoglu Hark, B.; Dagoglu, G. Atractyloside levels in Xanthium strumarium and atractyloside concentrations in the serum of rats given Xanthium strumarium. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2021, 27, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
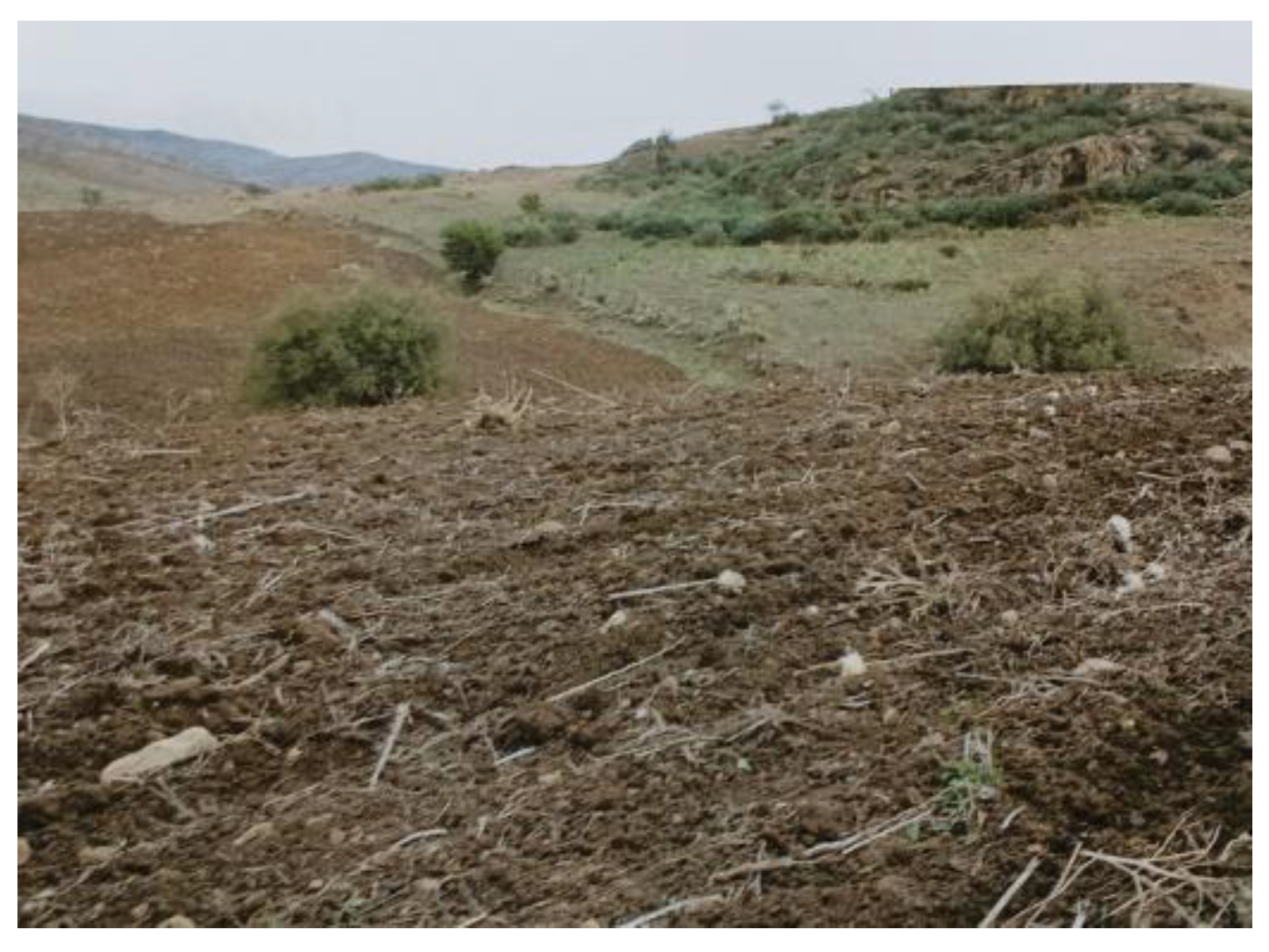



| Case Report | Generalities | Clinical Symptoms | Pharmacological Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| N° 1 | One cross-breed cow, born on the farm, age approximately 5 years, weight 340 kg, reared in the wild, fed on pasture, rectal temperature 36.8 °C. Officially free from infectious diseases. | Anorexia, lack of rumination, tremors, jaundiced mucous membranes, aggressive behavior, hyperexcitability and dulling of the sensorium. Died 24 h after treatment. |
|
| N° 2 | One cross-breed cow, born on the farm, age approximately 6 years, weight 320 kg, reared in the wild, fed on pasture, rectal temperature 37 °C. Officially free from infectious diseases. | Anorexia, poor nutritional status, tremors, tonic spasms, dulling of the sensorium, poor elasticity of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, jaundiced mucous membranes, vomit, blackish diarrhea, mydriasis and dyspnea. * Died about 70 h after treatment. | |
| N° 3 | Group of n. 5 surviving cattle: Cross-breed cattle, born on the farm, age 2–3 years, weight 280–360 kg, reared in the wild, fed on pasture, rectal temperature 36.5–37.4 °C. Officially free from infectious diseases. | Clinical symptoms similar but of less intensity with respect to those described in the two deceased cows. The 5 cattle returned to normal health status (complete disappearance of clinical symptoms) approximately 30–40 days after the symptomatic treatment. |
| N. Case | Hematic Parameters | Leukocyte Formula | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBC (×106) | WBC (×103) | HGB (g/dL) | HCT (%) | Platelets (×105) | Neutrophils (%) | Eosinophils (%) | Basophils (%) | Lymphocytes (%) | Monocytes (%) | |
| Range | (5–10) | (4–12) | (8–15) | (24–46) | (2–7.3) | (15–45) | (0–20) | (0–2) | (45–75) | (2–7) |
| 1 | 7.6 | 6.5 | 9.5 | 28 | 2.9 | 36 | 4 | 2 | 56 | 2 |
| 2 * | 8.5 | 9.2 | 12.4 | 40 | 4.2 | 39 | 6 | 1 | 49 | 5 |
| 3 | 8 | 7.8 | 11.7 | 37 | 45 | 41 | 3 | 1 | 52 | 3 |
| 4 | 9.5 | 7.3 | 13.5 | 30 | 6.8 | 34 | 2 | 0 | 59 | 5 |
| 5 | 9.2 | 9.5 | 12.9 | 36 | 5.4 | 42 | 8 | 2 | 45 | 3 |
| 6 | 7.8 | 6.4 | 14.2 | 42 | 6.5 | 28 | 9 | 1 | 60 | 2 |
| N. Case | Hepatic Profile | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-ALT (I.U.) | GOT-AST (I.U.) | GGT (I.U.) | ALP (I.U.) | Bilirubin (µmol/L) | Glucose (mmol/L) | |
| Range | (17–37) | (48–100) | (18–30) | (80–156) | (1.20–1.90) | (2.1–3.9) |
| 1 | 320 | 380 | 162 | 299 | 6.5 | 1.9 |
| 2 * | 365 | 420 | 179 | 285 | 7.8 | 1.4 |
| 3 | 205 | 310 | 140 | 190 | 4.7 | 1.7 |
| 4 | 180 | 270 | 158 | 178 | 3.5 | 2.2 |
| 5 | 168 | 255 | 142 | 164 | 2.8 | 2.4 |
| 6 | 125 | 210 | 124 | 172 | 1.9 | 2.1 |
| N. Case | Renal Profile | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Urea (mmol/L) | Creatinine (µmol/L) | Total Proteins (g/L) | |
| Range | (3.6–9.3) | (62–97) | (59–77) |
| 1 | 35.4 | 388 | 19 |
| 2 * | 39.7 | 362 | 23 |
| 3 | 23.2 | 198 | 38 |
| 4 | 19.4 | 212 | 42 |
| 5 | 18.2 | 187 | 34 |
| 6 | 20.2 | 223 | 45 |
| N. Case | Electrolytes Profile | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na (mmol/L) | K (mmol/L) | Mg (mmol/L) | Ca (mmol/L) | P (mmol/L) | Cl (mmol/L) | |
| Range | (132–144) | (4–5.3) | (0.7–1.1) | (1.9–3) | (1.5–2.9) | (90–104) |
| 1 | 232 | 7.8 | 0.95 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 95 |
| 2 * | 215 | 6.4 | 1.2 | 3.3 | 2.7 | 87 |
| 3 | 135 | 8.2 | 0.84 | 1.8 | 1.85 | 98 |
| 4 | 125 | 4.9 | 0.78 | 2.1 | 1.78 | 101 |
| 5 | 145 | 5.5 | 1.05 | 3.2 | 1.48 | 95 |
| 6 | 150 | 4.7 | 0.97 | 2.9 | 2.8 | 102 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naccari, C.; Donato, G.; Naccari, V.; Palma, E.; Niutta, P.P. Poisoning by Atractylus gummifera L. Roots in Grazing Cattle of a Sicilian Farm. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040305
Naccari C, Donato G, Naccari V, Palma E, Niutta PP. Poisoning by Atractylus gummifera L. Roots in Grazing Cattle of a Sicilian Farm. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(4):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040305
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaccari, Clara, Giulia Donato, Vincenzo Naccari, Ernesto Palma, and Pietro Paolo Niutta. 2025. "Poisoning by Atractylus gummifera L. Roots in Grazing Cattle of a Sicilian Farm" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 4: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040305
APA StyleNaccari, C., Donato, G., Naccari, V., Palma, E., & Niutta, P. P. (2025). Poisoning by Atractylus gummifera L. Roots in Grazing Cattle of a Sicilian Farm. Veterinary Sciences, 12(4), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040305







