Characterization and Seasonal Dynamics of Tick Populations in Dairy Cattle Production Systems of Northwestern Colombian Amazon
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
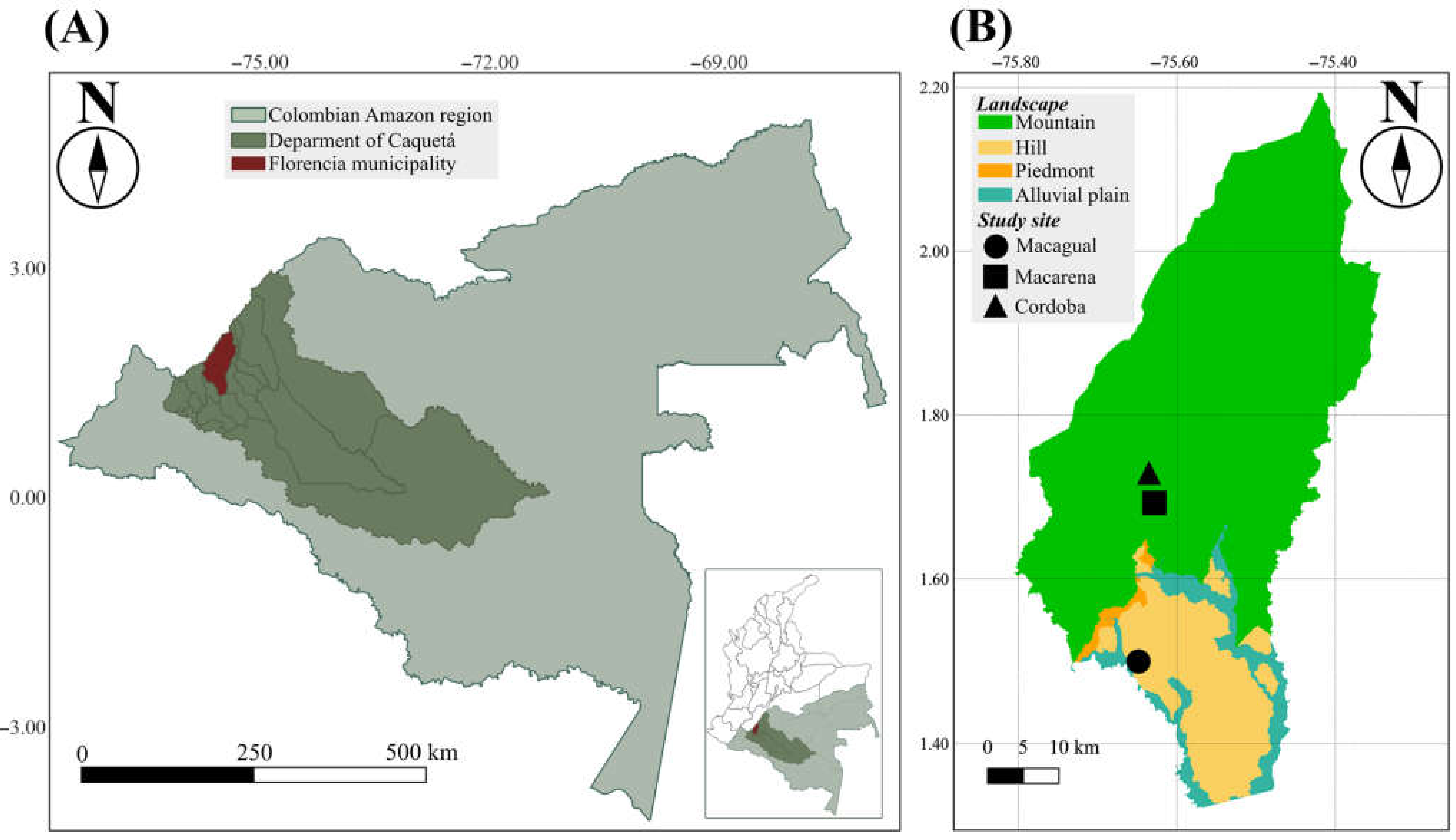
2.1. Description of the Study Area
2.2. Tick Sampling Periods
2.3. Tick Collection
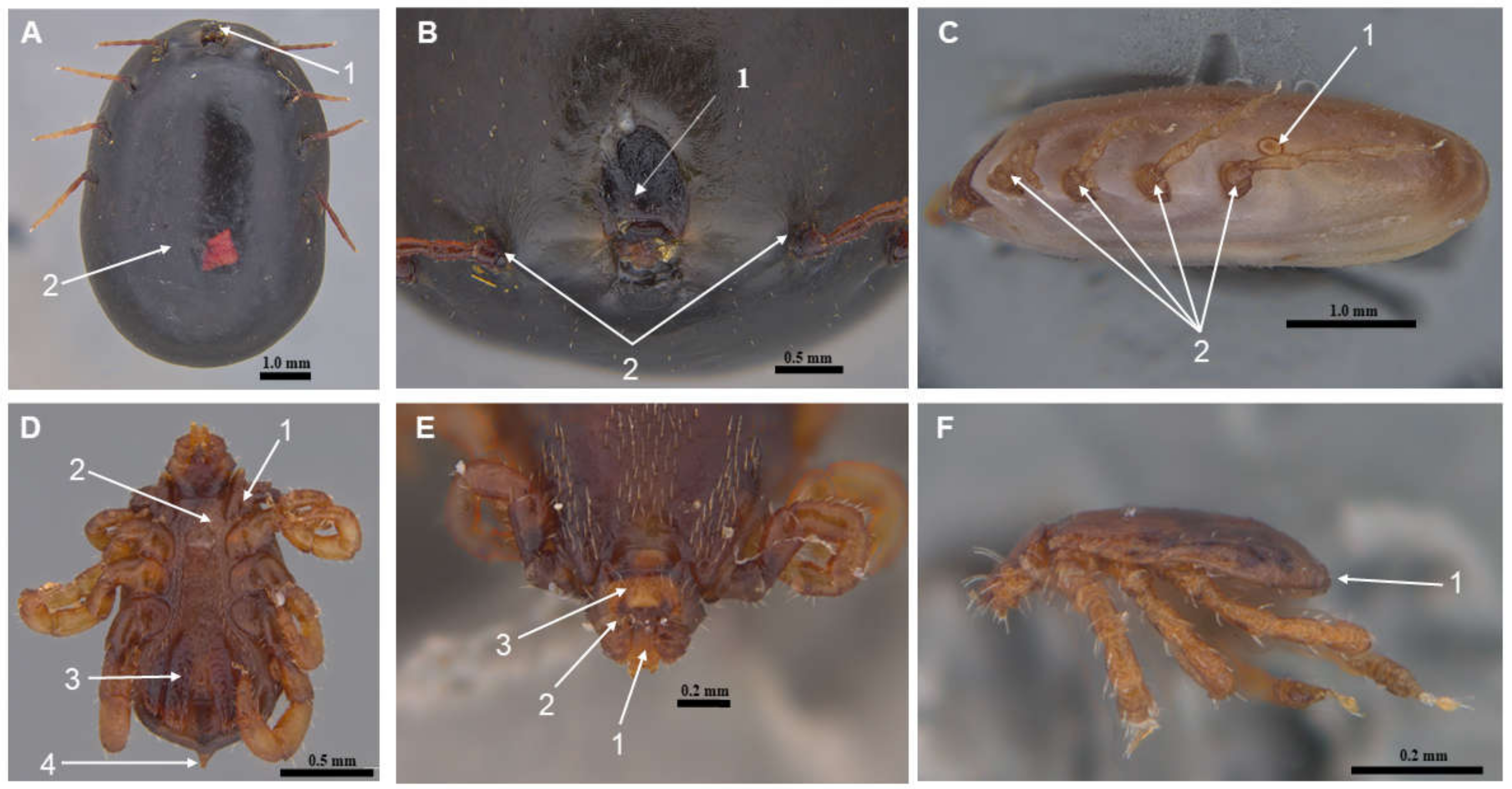
2.4. Tick Morphological Characterization
2.5. DNA Extraction, PCR, and Sequencing
2.6. Sequence Analysis
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
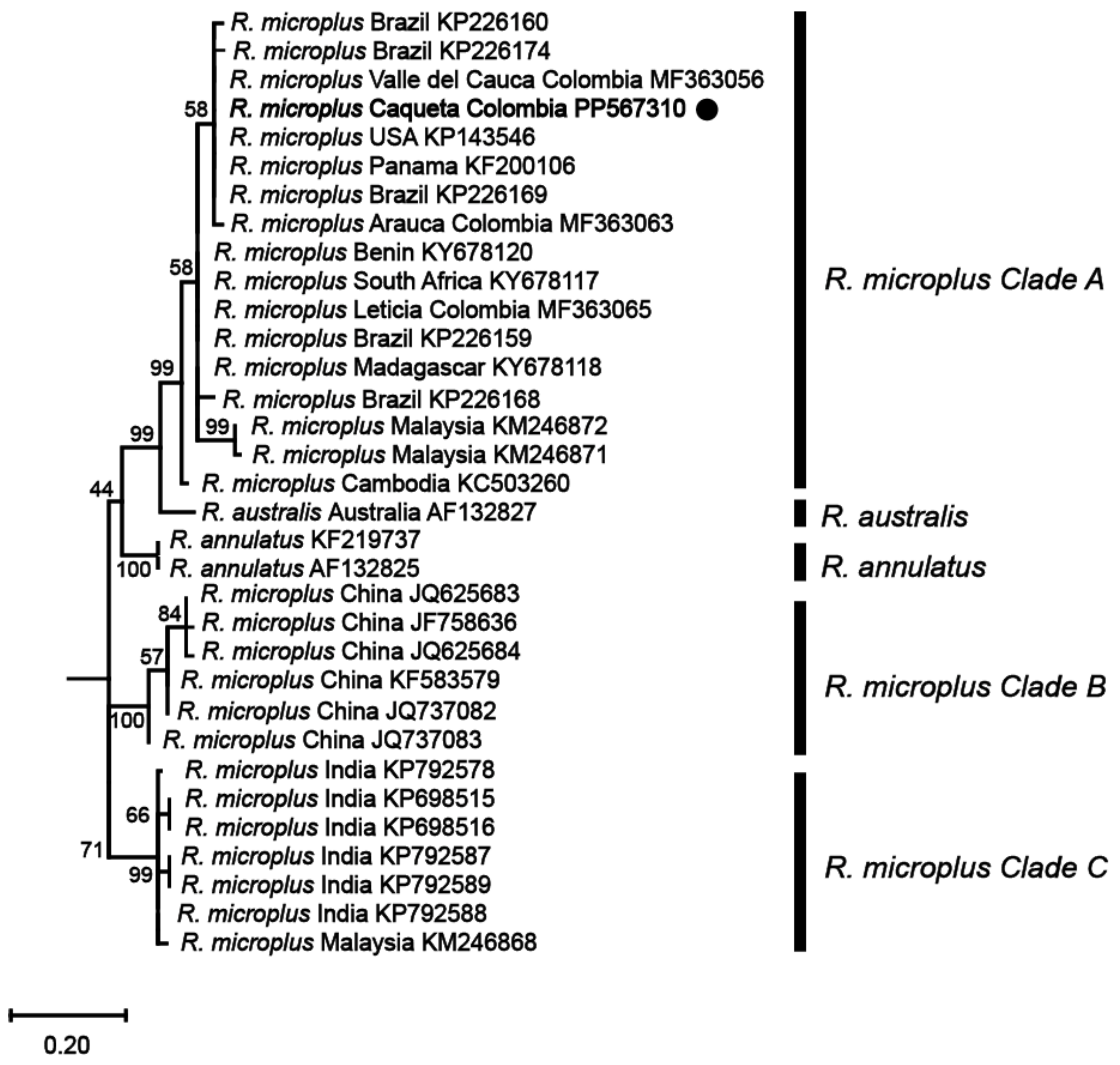
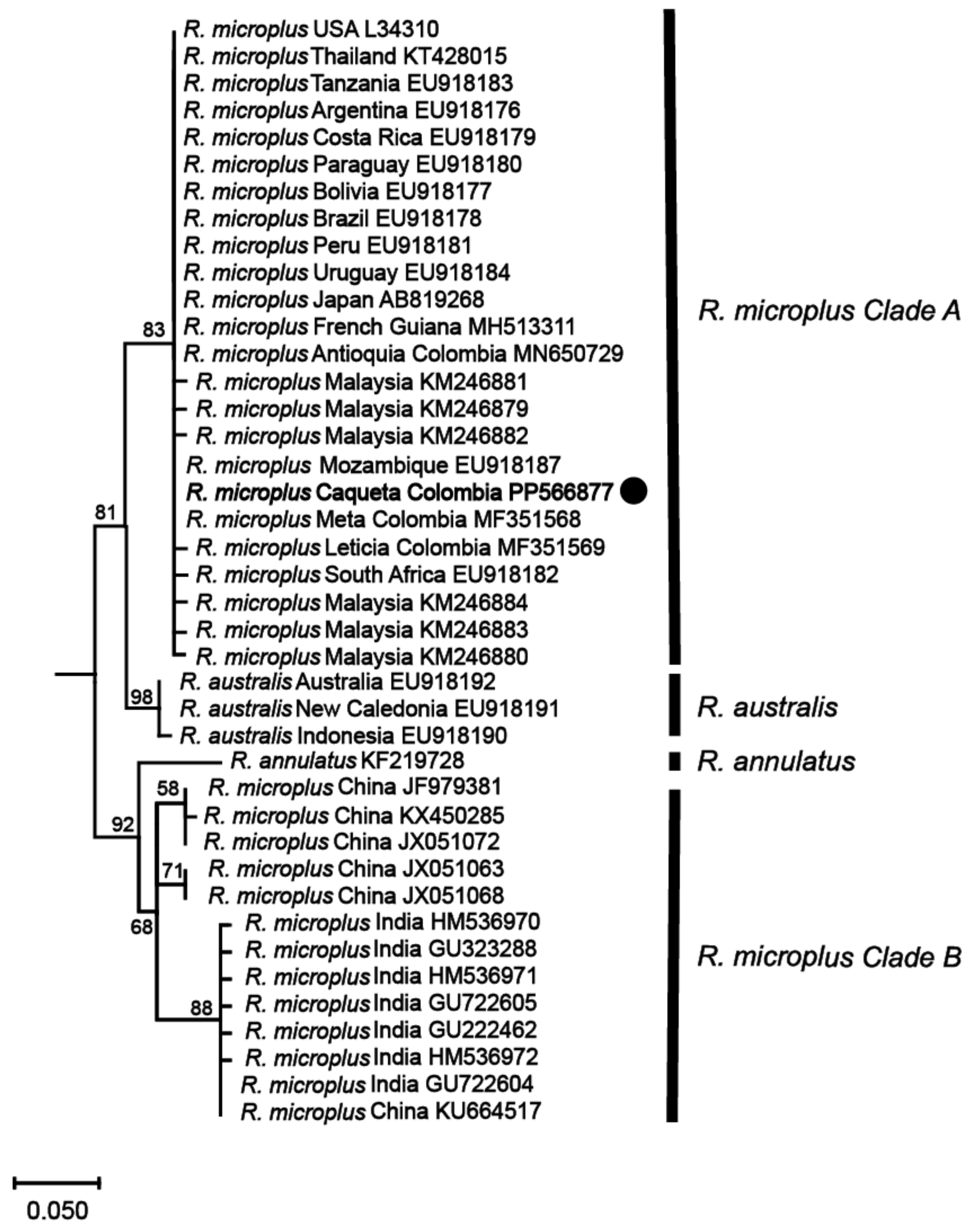
3.1. Ticks Present on Cattle in the Colombian Amazon Belong to the Rhipicephalus microplus Complex
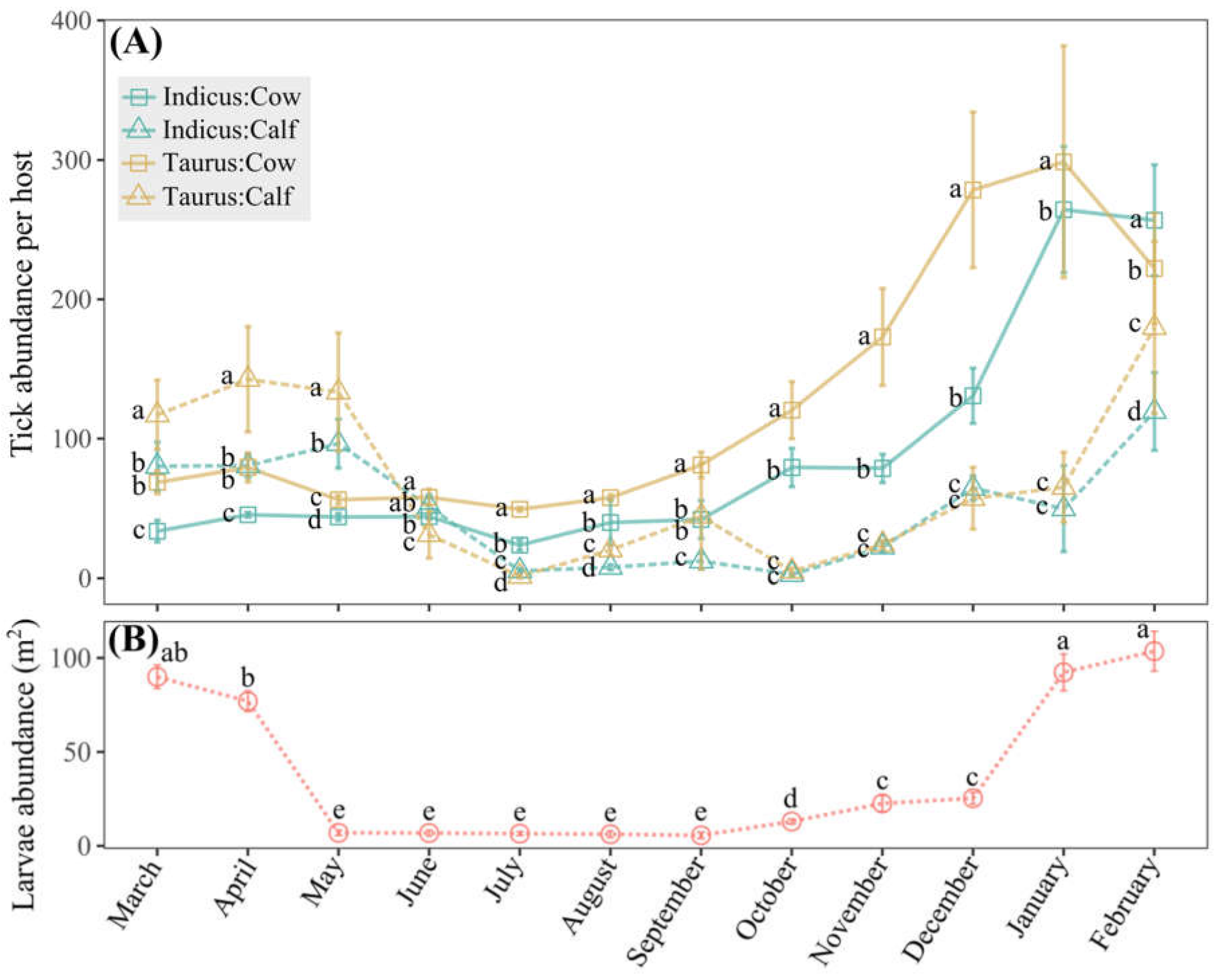
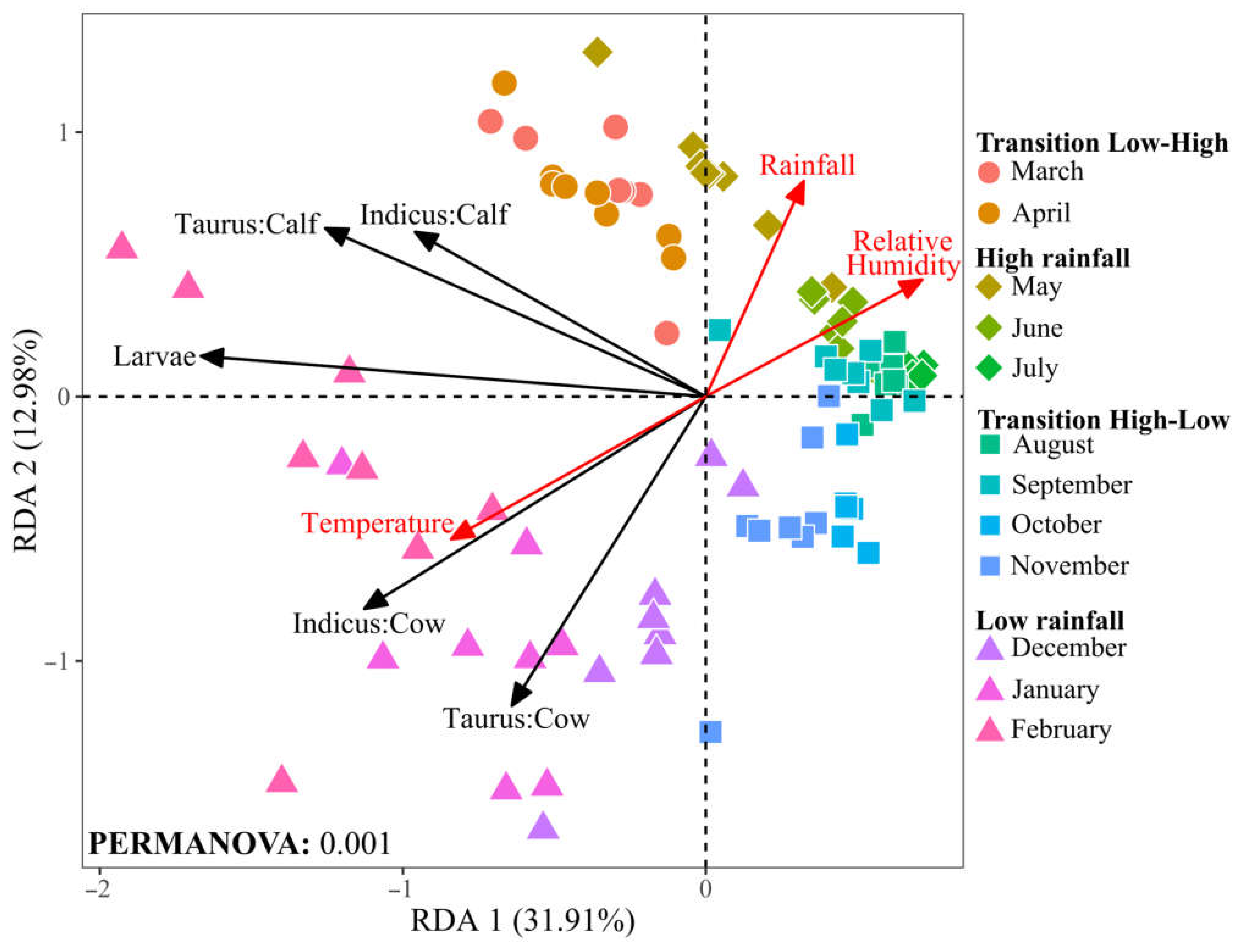
3.2. Host Race, Age, and Seasonal Dynamics Shape Tick Infestation Severity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FEDEGAN—Federación Colombiana de Ganaderos. Cifras de Referencia del Sector Ganadero Colombiano. 2017. Available online: https://estadisticas.fedegan.org.co (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- ICA—Instituto Colombiano Agropecuario. Censo Pecuario Nacional 2023. Censo Bovino en Colombia. 2023. Available online: https://bit.ly/2RUsZV5 (accessed on 9 July 2023).
- Torrijos, R.; Eslava, F. Cifras de Contexto Ganadero Caquetá 2017. Editorial Comité de Ganaderos del Caquetá. 2018. Available online: https://acortar.link/juHDpE.Florencia–Caquetá–Colombia (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- Strydom, T.; Lavan, R.P.; Torres, S.; Heaney, K. The Economic Impact of Parasitism from Nematodes, Trematodes and Ticks on Beef Cattle Production. Animals 2023, 13, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulanger, N.; Boyer, P.; Talagrand-Reboul, E.; Hansmann, Y. Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases. Med. Mal. Infect. 2019, 49, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, B.C.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Krücken, J.; Rehman, A.; Nijhof, A.M. Morphological and Phylogenetic Analyses of Rhipicephalus microplus Ticks from Bangladesh, Pakistan and Myanmar. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, T.D.; Shao, R.; Barker, S.C. Phylogenetic Analysis of Mitochondrial Genome Sequences Indicates That the Cattle Tick, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, Contains a Cryptic Species. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 76, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, V.L.; Tay, S.T.; Kho, K.L.; Koh, F.X.; Tan, T.K.; Lim, Y.A.L.; Ong, B.L.; Panchadcharam, C.; Norma-Rashid, Y.; Sofian-Azirun, M. Molecular Characterisation of the Tick Rhipicephalus microplus in Malaysia: New Insights into the Cryptic Diversity and Distinct Genetic Assemblages throughout the World. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvano, M.P.C.A.; Brumatti, R.C.; Garcia, M.V.; Barros, J.C.; Andreotti, R. Economic Efficiency of Rhipicephalus microplus Control and Effect on Beef Cattle Performance in the Brazilian Cerrado. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2019, 79, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, C. Long-Term Pressures and Prospects for the U.S. Cattle Industry; Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City: Kansas City, MO, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, A.K.; Jacob, S.S.; RamVerma, M.; Singh, N.K.; Shakya, M.; Sankar, M.; Ghosh, S. Economic Impact of Predominant Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases on Indian Dairy Production Systems. Exp. Parasitol. 2022, 243, 108408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicaretta, J.E.; Zapa, D.M.B.; Couto, L.F.M.; Heller, L.M.; Cavalcante, A.S.d.A.; Cruvinel, L.B.; Melo Júnior, R.D.d.; Ferreira, L.L.; Nascimento, R.M.d.; Soares, V.E.; et al. Rhipicephalus microplus Seasonal Dynamic in a Cerrado Biome, Brazil: An Update Data Considering the Global Warming. Vet. Parasitol. 2021, 296, 109506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, R.; Krüger, R.F.; Peterson, A.T.; De Melo, L.F.; Vicenzi, N.; Jiménez-García, D. Climate Change Implications for the Distribution of the Babesiosis and Anaplasmosis Tick Vector, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, A.Z.; Kamal, N. Identification of Ticks and Detection of Blood Protozoa in Friesian Cattle by Polmerase Chain Reacton Test and Estimation of Blood Parameters in District Kasur, Pakistan. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2008, 40, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, J.C.; Menne, B. Climate Change and Infectious Diseases in Europe. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastropaolo, M.; Mangold, A.J.; Guglielmone, A.A.; Nava, S. Non-Parasitic Life Cycle of the Cattle Tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus in Panicum maximum Pastures in Northern Argentina. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 115, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randolph, S.E. Dynamics of Tick-Borne Disease Systems: Minor Role of Recent Climate Change. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2008, 27, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecino, J.A.C.; Echeverri, J.A.B.; Cárdenas, J.A.; Herrera, L.A.P. Distribution of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus Ticks on Cattle and Farms from Altiplano cundiboyacense (Colombia). Corpoica Cienc. Tecnol. Agropecu. 2010, 11, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Gutiérrez, L.Y.; Paternina, L.E.; Pérez-Pérez, J.C.; Londoño, A.F.; López, G.; Rodas, J.D. Garrapatas duras (Acari: Ixodidae) de Colombia, una revisión a su conocimiento en el país. Acta Biol. Colomb. 2020, 25, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata-Serna, Y.; Rojas-Rodríguez, A.E.; Pérez-Cárdenas, J.E.; Aricapa-Giraldo, H.J.; Hidalgo-Diaz, M.; Rivera-Páez, F.A. Prevalence of Rickettsias in Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) Collected in Domestic Animals of the Northern Region of Caldas Department, Colombia. Rev. U. D. C. A. Actual. Divulg. Científica 2022, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.F.; Martínez, R.; López-Villalobos, N.; Morris, S.T. Tick Burden in Bos Taurus Cattle and Its Relationship with Heat Stress in Three Agroecological Zones in the Tropics of Colombia. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Instituto Geografico Agustín. Codazzi Estudio General de Suelos y Zonificación de Tierras: Departamento de Caquetá; Imprenta Nacional de Colombia: Bogotá, Colombia, 2014; ISBN 9789588323732. [Google Scholar]
- Giovambattista, G.; Ripoli, M.V.; De Luca, J.C.; Mirol, P.M.; Liron, J.P.; Dulout, F.N. Male-Mediated Introgression of Bos indicus Genes into Argentine and Bolivian Creole Cattle Breeds. Anim. Genet. 2000, 31, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermani, R.H.; Garris’, G.I. Sampling Efficiency of Three Dragging Techniques for the Collection of Nonparasitic Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) Larvae in Puerto Rico. J. Econ. Entomol. 1985, 78, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, S.; Mangold, A.J.; Simonato, G.E.; Puntin, E.; del Sproat, C.M. Guía Para La Identificación de Las Principales Especies de Garrapatas Que Parasitan a Los Bovinos en La Provincia de Entre Ríos, 1st ed.; INTA Ediciones, Ed.; INTA Ediciones: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2019; ISBN 9789875219816. [Google Scholar]
- Oteo, J.A.; Nava, S.; de Sousa, R.; Mattar, S.; Venzal, J.M.; Abarca, K.; Labruna, M.B.; Zavala-Castro, J. Guías Latinoamericanas de La RIICER Para El Diagnóstico de Las Rickettsiosis Transmitidas Por Garrapatas. Rev. Chil. Infectol. 2014, 31, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.R.; Bouattour, A.; Camicas, J.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Horak, I.; Latif, A.; Pegram, R.; Preston, P.M. Ticks of Domestic Animals in Municipal Abattoir for Their Technical Support. In Africa: A Guide to Identification of Tick Species; Bioscience Reports: Edinburgh, UK, 2003; ISBN 0-9545173-0-X. [Google Scholar]
- Black, W.C.; Piesmant, J. Phylogeny of Hard-and Soft-Tick Taxa (Acari: Ixodida) Based on Mitochondrial 16S RDNA Sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 10034–10038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA Primers for Amplification of Mitochondrial Cytochrome C Oxidase Subunit I from Diverse Metazoan Invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.-I.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A Novel Method for Rapid Multiple Sequence Alignment Based on Fast Fourier Transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. TrimAl: A Tool for Automated Alignment Trimming in Large-Scale Phylogenetic Analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hothorn, T.; Bretz, F.; Westfall, P. Simultaneous Inference in General Parametric Models. Biom. J. 2008, 50, 346–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Wagner, H. Vegan community ecology package version 2.6—2 April 2022. In The Comprehensive R Archive Network; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Husson, F.; Josse, J.; Le, S.; Maintainer, J.M.; Package “FactoMineR”. Multivariate Exploratory Data Analysis and Data Mining. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/FactoMineR/FactoMineR.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F. Package ‘factoextra’. Extract and Visualize the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=factoextra (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- Dray, S.; Dufour, A.-B. The Ade4 Package: Implementing the Duality Diagram for Ecologists. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 22, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- Posit Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; Posit Software, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2024; Available online: https://posit.co/ (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- Estrada-Peña, A.; Bouattour, A.; Camicas, J.L.; Guglielmone, A.; Horak, I.; Jongejan, F.; Latif, A.; Pegram, R.; Walker, A.R. The Known Distribution and Ecological Preferences of the Tick Subgenus Boophilus (Acari: Ixodidae) in Africa and Latin America. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2006, 38, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Vivas, R.I.; Jonsson, N.N.; Bhushan, C. Strategies for the Control of Rhipicephalus microplus Ticks in a World of Conventional Acaricide and Macrocyclic Lactone Resistance. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, S.; van der Merwe, N.A.; Maritz-Olivier, C. The Genetic Relationship between R. microplus and R. decoloratus Ticks in South Africa and Their Population Structure. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 129, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silatsa, B.A.; Jules-Roger, K.; Njiokou, F.; Simo, G.; Jean-Marc, F.K.; Tunrayo, A.; Amzati, G.S.; Bett, B.; Bishop, R.; Githaka, N.; et al. A Countrywide Molecular Survey Leads to a Seminal Identification of the Invasive Cattle Tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus in Cameroon, a Decade after It Was Reported in Cote d’Ivoire. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanduma, E.G.; Emery, D.; Githaka, N.W.; Nguu, E.K.; Bishop, R.P.; Šlapeta, J. Molecular Evidence Confirms Occurrence of Rhipicephalus microplus Clade A in Kenya and Sub-Saharan Africa. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sungirai, M.; Baron, S.; Van der Merwe, N.A.; Moyo, D.Z.; De Clercq, P.; Maritz-Olivier, C.; Madder, M. Population Structure and Genetic Diversity of Rhipicephalus microplus in Zimbabwe. Acta Trop. 2018, 180, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Páez, F.A.; Labruna, M.B.; Martins, T.F.; Perez, J.E.; Castaño-Villa, G.J.; Ossa-López, P.A.; Gil, C.A.; Sampieri, B.R.; Aricapa-Giraldo, H.J.; Camargo-Mathias, M.I. Contributions to the Knowledge of Hard Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in Colombia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattioli, R.C.; Pandey, V.S.; Murray, M.; Fitzpatrick, J.L. Immunogenetic Influences on Tick Resistance in African Cattle with Particular Reference to Trypanotolerant N’Dama (Bos taurs) and Trypanosusceptible Gobra Zebu (Bos indicus) Cattle. Acta Trop. 2000, 75, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piper, E.K.; Jackson, L.A.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Gondro, C.; Lew-Tabor, A.E.; Jonsson, N.N. Tick-Susceptible Bos taurus Cattle Display an Increased Cellular Response at the Site of Larval Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus Attachment, Compared with Tick-Resistant Bos indicus Cattle. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbertse, L.; Richards, S.A.; Maritz-Olivier, C. Bovine Immune Factors Underlying Tick Resistance: Integration and Future Directions. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Herrera, M.; Briceño-Arguedas, E. Comparación de los grupos raciales de bovinos en cuanto a incidencia de garrapatas (Acari: Ixodidae) y tórsalos (Diptera: Oestridae). Nutr. Anim. Trop. 2014, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, G.; Pino, L.A.; Sandoval, E.; Jiménez, D.; Morales, J. Relación Entre La Condición Corporal y El Nivel de Infestación Parasitaria en Bovinos a Pastoreo Como Criterio para El Tratamiento Antihelmíntico Selectivo Relationship between Body Condition and Level of Parasite Infestation in Grazing Cattle as a Criter. Rev. Inv. Vet. Perú 2012, 23, 80–89. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, M. Factores Genéticos y Ambientales Que Afectan El Crecimiento de Bovinos F1 (Bos taurus × Bos indicus) Manejados en El Trópico Húmedo de Méxino. 2001. Available online: https://acortar.link/V8irFC (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- Otto, P.I.; Guimarães, S.E.F.; Verardo, L.L.; Azevedo, A.L.S.; Vandenplas, J.; Sevillano, C.A.; Marques, D.B.D.; Pires, M.; de Freitas, C.; Verneque, R.S.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Studies for Heat Stress Response in Bos taurus × Bos indicus Crossbred Cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 8148–8158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Patra, G.; Borthakur, S.K.; Behera, P.; Tolenkhomba, T.C.; Das, M.; Lalnunpuia, C. Prevalence of Hard Tick Infestations in Cattle of Mizoram, India. Biol. Rhythm Res. 2019, 50, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, V.; Picozzi, K.; De Bronsvoort, B.M.C.; Majekodunmi, A.; Dongkum, C.; Balak, G.; Igweh, A.; Welburn, S.C. Ixodid Ticks of Traditionally Managed Cattle in Central Nigeria: Where Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus Does Not Dare (Yet?). Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Parizi, L.F.; Ferreira, B.R.; Vaz Junior, I.d.S. Uma Revisão Sobre Duas Espécies Distintas de Rhipicephalus R. microplus e R. australis. Cienc. Rural 2016, 46, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmeyer, K.H.; Pound, J.M.; May, M.A.; Kammlah, D.M.; Davey, R.B. Distribution of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus and Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) annulatus (Acari: Ixodidae) Infestations Detected in the United States Along the Texas/Mexico Border. J. Med. Entomol. 2011, 48, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condori, R.; Ibáñez, T.; Hernández, R.; Ochoa, R.; Loza-Murguía, M. Frecuencia Relativa de Boophilus microplus (Canestrini 1888) & Amblyomma cajennense (Fabricius 1787) (Acari: Ixodida) en Ganado Bovino, en La Zona de Colonización de Yucumo, Provincia Gral. José Ballivián Departamento Del Beni, Bolivia. J. Selva Andin. Res. Soc. 2010, 1, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Keesing, F.; Ostfeld, R.S.; Young, T.P.; Allan, B.F. Cattle and Rainfall Affect Tick Abundance in Central Kenya. Parasitology 2018, 145, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, B.C.; de Lima Mendes, A.F.; Maciel, W.G.; dos Santos, I.B.; Gomes, L.V.C.; Felippelli, G.; Teixeira, W.F.P.; Ferreira, L.L.; Soares, V.E.; Lopes, W.D.Z.; et al. Biological Parameters for Rhipicephalus microplus in the Field and Laboratory and Estimation of Its Annual Number of Generations in a Tropical Region. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 2421–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zapata, C.A.; Morea, E.G.O.; Mora-Motta, D.A.; Ojeda, D.M.M.; Quiceno-Mayo, E.J.; Toro, D.A.; Ortiz-Morea, F.A. Characterization and Seasonal Dynamics of Tick Populations in Dairy Cattle Production Systems of Northwestern Colombian Amazon. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11060244
Zapata CA, Morea EGO, Mora-Motta DA, Ojeda DMM, Quiceno-Mayo EJ, Toro DA, Ortiz-Morea FA. Characterization and Seasonal Dynamics of Tick Populations in Dairy Cattle Production Systems of Northwestern Colombian Amazon. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(6):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11060244
Chicago/Turabian StyleZapata, Cesar A., Edna G. O. Morea, Dúber A. Mora-Motta, Diana M. M. Ojeda, Esther J. Quiceno-Mayo, Diego A. Toro, and Fausto A. Ortiz-Morea. 2024. "Characterization and Seasonal Dynamics of Tick Populations in Dairy Cattle Production Systems of Northwestern Colombian Amazon" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 6: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11060244
APA StyleZapata, C. A., Morea, E. G. O., Mora-Motta, D. A., Ojeda, D. M. M., Quiceno-Mayo, E. J., Toro, D. A., & Ortiz-Morea, F. A. (2024). Characterization and Seasonal Dynamics of Tick Populations in Dairy Cattle Production Systems of Northwestern Colombian Amazon. Veterinary Sciences, 11(6), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11060244






