The History of Bovine Genital Campylobacteriosis in the Face of Political Turmoil and Structural Change in Cattle Farming in Germany
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. A Short Excursion into Recent ‘German’ History
3. Campylobacter fetus Subspecies venerealis, a Quiet but Steady Companion of (German) Cattle Breeding
4. The Wings of Change in Agriculture: Industrialization of Cattle Breeding
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WOAH. Chapter 3.4.4—Bovine genital campylobacteriosis. In OIE Terrestrial Manual; OIE: Paris, France, 2021; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- WOAH. Chapter 11.3—Bovine Genital Campylobacteriosis. Available online: https://www.woah.org/en/what-we-do/standards/codes-and-manuals/terrestrial-code-online-access/?id=169&L=1&htmfile=chapitre_bovine_genital_campylobacteriosis.htm (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- More, S.; Botner, A.; Butterworth, A.; Calistri, P.; Depner, K.; Edwards, S.; Garin-Bastuji, B.; Good, M.; Gortazar Schmidt, C.; Michel, V.; et al. Assessment of listing and categorisation of animal diseases within the framework of the Animal Health Law (Regulation (EU) No 2016/429): Bovine genital campylobacteriosis. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mshelia, G.D.; Amin, J.D.; Woldehiwet, Z.; Murray, R.D.; Egwu, G.O. Epidemiology of bovine venereal campylobacteriosis: Geographic distribution and recent advances in molecular diagnostic techniques. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2010, 45, e221–e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iraola, G.; Forster, S.C.; Kumar, N.; Lehours, P.; Bekal, S.; Garcia-Pena, F.J.; Paolicchi, F.; Morsella, C.; Hotzel, H.; Hsueh, P.R.; et al. Distinct Campylobacter fetus lineages adapted as livestock pathogens and human pathobionts in the intestinal microbiota. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Glil, M.Y.; Hotzel, H.; Tomaso, H.; Didelot, X.; Brandt, C.; Seyboldt, C.; Linde, J.; Schwarz, S.; Neubauer, H.; El-Adawy, H. Genomic epidemiology of Campylobacter fetus subsp. venerealis from Germany. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 9, 1069062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadyean, J.; Stockman, S. Report of the Departmental Committee Appointed by the Board of Agriculture and Fisheries to Inquire into Epizootic Abortion, Part III 1-64; Eyre and Spottiswoode: London, UK, 1913. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, T.; Taylor, M.S. Some morphological and biological characters of the Spirilla (Vibrio fetus, N. Sp.) associated with disease of the fetal membranes in cattle. J. Exp. Med. 1919, 30, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, A. Sporadic cases of bovine abortion. J. Comp. Pathol. Therapeut. 1926, 39, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gminder, A. Nachweis von Spirillen als Ursache des ansteckenden Verkalbens auch in Deutschland; Berliner Tierärztliche Wochenschrift: Berlin, Germany, 1922; Volume 38, p. 184. [Google Scholar]
- Lerche, M. Spirillen als Ursache des ansteckenden Verkalbens; Berliner Tierärztliche Wochenschrift: Berlin, Germany, 1922; Volume 38, pp. 281–282. [Google Scholar]
- Felius, M.; Beerling, M.; Buchanan, D.; Theunissen, B.; Koolmees, P.; Lenstra, J.A. On the history of cattle genetic resources. Diversity 2014, 6, 705–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florent, A. Les deux Vibrioses génitales de la bête bovine: La vibriose vénérienne, due àV. fœtus venerialis, et la Vibriose d’origine intestinale due àV. fœtus intestinalis. In Proceedings of the 16th International Veterinary Congress, Madrid, Spain, 20–27 May 1960; pp. 489–493. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffer, M.A. Bovine campylobacteriosis: A review. Can. Vet. J. 1981, 22, 327–330. [Google Scholar]
- Veron, M.; Chatelain, R. Taxonomic study of the genus Campylobacter Sebald and Veron and designation of the neotype strain for the type species, Campylobacter fetus (Smith and Taylor) Sebald and Veron. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1973, 23, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, G. Die Krankheiten des Rindes; Paul Parey: Berlin, Germany, 1978; pp. 773–778. [Google Scholar]
- Mitscherlich, E.; Ließ, B.; Prange, H.; Baumgarte, G.; Lietsch, C.D. Die Verbreitung der Vibrio fetus-Infektion des Rindes in den Südlichen Kreisen Niedersachsen. DTW 1958, 65, 490–497. [Google Scholar]
- Mitscherlich, E. Zur Epidemiologie und Tilgung der Vibriosis Genitalis des Rindes; Dtsch. tierärztl. Wschr. Schlütersche Verl.-Ges. Schaper: Berlin, Germany, 1962; pp. 189–199. [Google Scholar]
- Blaser, M.J.; Newell, D.G.; Thompson, S.A.; Zechner, E.L. Pathogenesis of Campylobacter fetus. In Campylobacter, 3rd ed.; Nachamkin, I., Szymanski, C.M., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 401–428. [Google Scholar]
- Mshelia, G.D.; Singh, J.; Amin, J.D.; Woldehiwet, Z.; Egwu, G.O.; Murray, R.D. Bovine venereal campylobacteriosis: An overview. CABI Rev. 2007, 1–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J. Registration and use of veterinary medicines in New Zealand. N. Z. Vet. J. 2002, 50, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, C.J.; Ginja, C.; Kantanen, J.; Perez-Pardal, L.; Tresset, A.; Stock, F.; Gama, L.T.; Penedo, M.C.; Bradley, D.G.; Lenstra, J.A.; et al. Dual origins of dairy cattle farming--evidence from a comprehensive survey of European Y-chromosomal variation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanel, I.; Hotzel, H.; Muller, W.; Tomaso, H. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of German Campylobacter fetus subsp. venerealis isolates by agar disk diffusion method. Berl. Munch Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2011, 124, 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Wennigstedt, R.; Messerschmidt, M.; Haring, F.; Siebitz, K. Handbuch der Tierzüchtung; Bd.3 Rassenkunde. Rinderrassen in Nordwesteuropa; Paul Parey: Hamburg, Germany; Berlin, Germany, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Brade, W.; Brade, E. Zuchtgeschichte der Deutschen Holsteinrinder. 2013. Available online: https://buel.bmel.de/index.php/buel/article/view/25/brade2-html (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Pusch, G. Lehrbuch der Allgemeinen Tierzucht; Enke: Stuttgart, Germany, 1904. [Google Scholar]
- Schwark, H.J. Rinderzucht; VEB Deutscher Landwirtschafts, Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1989; pp. 22–100. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, J. Lehrbuch der Rinderzucht; Paul Parey: Berlin, Germany, 1921. [Google Scholar]
- Götze, R. Paarung- und Besamungsinfektionen beim Rind. Dtsch. Tierärztl. Wschr. 1950, 57, 377–382. [Google Scholar]
- Hellich, M.; Störiko, K.R. Die Deutsche Tierseuchengesetzgebung—Verordnung über die Einführung der Anzeigepflicht für die Deckinfektion des Rindes; Paul Parey: Hamburg/Berlin, Germany, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Wohanka, K. Besamungsinfektionen und die Verordnung zur Bekämpfung der Deckinfektionen vom 5. Februar 1951; Mh. Vet.-Med.: Berlin, Germany, 1957; pp. 307–308. [Google Scholar]
- Mitscherlich, E.; Prange, H. Die Vibriosis Genitalis des Rindes; Mh. Vet.-Med.: Berlin, Germany, 1959; pp. 516–521. [Google Scholar]
- Blobel, H.; Schliesser, T. Handbuch der Bakteriellen Infektionen bei Tieren, III. Enzootischer Campylobacter-Abort des Rindes; VEB Gustav Fischer Verlag: Jena, Germany, 1982; pp. 9–27. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament and the Council Regulation (EU) 2016/429 on Transmissible Animal Diseases (“Animal Health Law”). April 2021. Available online: https://food.ec.europa.eu/animals/animal-health/animal-health-law_de (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Sieblitz, K. Das deutsche Höhenvieh. Handbuch der Tierzüchtung; Bd3 Rassenkunde; Paul Parey: Hamburg/Berlin, Germany, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Schwark, H.J. Rinderzucht; Dt. Landwirtschaftsverl.: Berlin, Germany, 1983; pp. 32–96. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, W.; Weiher, O. Vierzehn Europäische Fleischrind-Bzw. Fleischbetonte Zweinutzungsrassen im Leistungsvergleich; Wilhelm-Pieck-Universität: Rostock, Germany, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Dedié, K.; Voigt, A. Die Vibriosis Genitalis des Rindes in Mitteldeutschland; Mh. Vet.-Med.: Berlin, Germany, 1955; pp. 463–468. [Google Scholar]
- Wohanka, K. Die Leistungen der künstlichen Besamung bei der Bekämpfung von Vibriose und Trichomoniasis und deren Voraussetzungen; Mh. Vet.-Med.: Berlin, Germany, 1964; pp. 213–216. [Google Scholar]
- Pilz, K. Latest Developments in Artificial Insemination of Cattle in the German Democratic Republic. Monatshefte Veterinaermedizin 1967, 22, 681–684. [Google Scholar]
- Abshagen, H.; Beduhn, M. Ein Jahr Gesundheitsdienst für Bullen der VdgB und LPG im Einzugsgebiet des Veterinäruntersuchungs- und Tiergesundheitsamtes Greifswald; Mh. Vet.-Med.: Berlin, Germany, 1959; pp. 494–496. [Google Scholar]
- Krippner, S.; Nopper, P.; Herold, H.; Pollandt, P.; Steuer, D. Zur Bekämpfung von Campylobacter fetus in einer Zentralen Bullenaufzuchtstation; Mh. Vet.-Med.: Berlin, Germany, 1986; pp. 388–390. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, D.G.; Duim, B.; Van Bergen, M.A.P.; Grogono-Thomas, R.; Wagenaar, J.A. Speciation, Subspeciation and Subtyping of Campylobacter spp. Associated with Bovine Infertility and Abortion. Cattle Pract. 2000, 8, 421–425. [Google Scholar]
- Gellner, K.; Schwarzwälder, M. Bullensperma geschmuggelt: Die ersten Bio-Bauern der DDR. In Mitteldeutscher Rundfunk; Bazydło, G., Ed.; MDR: Leipzig, Germany, 2022; Available online: https://www.mdr.de/geschichte/ddr/wirtschaft/bio-bauern-oekologische-landwirtschaft-bullensperma-schmuggel-grenze-100.html (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Schulze, F.; Bagon, A.; Müller, W.; Hotzel, H. Identification of Campylobacter fetus subspecies by phenotypic differentiation and PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2019–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engeler, W. Das Eringervieh. In Handbücher der Tierzüchtung, Rassenkunde; Hammond, J., Johansson, I., Haring, F., Eds.; Paul Parey: Hamburg, Germany, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- BLE. Einheimische Nutztierrassen in Deutschland und Rote Liste Gefährdeter Nutztierrassen 2021; Bundesanstalt für Landwirtschaft und Ernährung (BLE): Bonn, Germany, 2021; 236p. [Google Scholar]
- BMEL. Rinderhaltung in Deutschland; Bundesanstalt für Landwirtschaft und Ernährung (BLE): Bonn, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Häfner, K.; Thiede, G. Statistisches Handbuch über Landwirtschaft und Ernährung der Bundesrepublik Deutschland; Paul Parey: Hamburg, Germany; Berlin, Germany, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Reidt, L. Rinderwahnsinn BSE: 25 Jahre Nach der Notschlachtung von Importrindern. Available online: https://www.deutschlandfunk.de/bse-krise-rinderwahnsinn-25-jahre-spaeter-100.html: (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Dedié, K.; Fischer, A.; Pohl, R.; Schababerle, H. Bekämpfung und Verhütung der Venerischen Campylobacteriose in Besamungsstationen. Tierärz. Umschau. 1982, 37, 604–612. [Google Scholar]
- Dedié, K.; Pohl, R.; Romer, H.; Wagenseil, F.; Albrecht, E.; Hühnermund, G. Zur Verbreitung, Ermittlung und Bekämpfung der Venerischen Campylobacteriose (Vibriosis genitalis) beim Rind in Beständen mit Bullenhaltung. Tierärz. Umschau. 1982, 37, 80–96. [Google Scholar]
- Brade, W. Auf Dem Weg Zum Deutschen Holstein. Available online: https://www.bauernzeitung.de/agrarpraxis/tierhaltung/auf-dem-weg-zum-deutschen-holstein/ (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Statistisches-Bundesamt. Produktion von Trinkmilch im Jahr 2021 um 7% Niedriger als im Vorjahr. Available online: https://www.destatis.de/DE/Presse/Pressemitteilungen/2022/05/PD22_N034_51.html#:~:text=Auch%20der%20Pro%2DKopf%2DVerbrauch,den%20niedrigsten%20Wert%20seit%201991 (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- BLE. Genetische Ressourcen: Rind. Available online: https://tgrdeu.genres.de/nutztiere/liste-tierarten/liste-genetik-plugin/?tx_sttgrdeu_nutztier%5Baction%5D=genetikList&tx_sttgrdeu_nutztier%5Ba_id%5D=3&tx_sttgrdeu_nutztier%5Bcontroller%5D=Nutztier&cHash=b0cb5054315d7b342249727c370a2e36 (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Deutscher-Bundestag. Förderungen in der Weidetierhaltung. Available online: https://www.bundestag.de/resource/blob/627298/f1d7c5b3de111d08e6a5a163578d4e71/WD-5-158-18-pdf-data.pdf (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Kögler, J. Monitoring regional livestock breeds in zoological gardens as basis for an ex-situ in-vivo conservation strategy. Zool. Garten N. F. 2021, 89, 57–66. Available online: https://www.zootier-lexikon.org/lebensraeume/images/haustiere/index.php?option=com_k2&view=item&id=7959:koegler-j-2021&Itemid=217 (accessed on 8 November 2023).
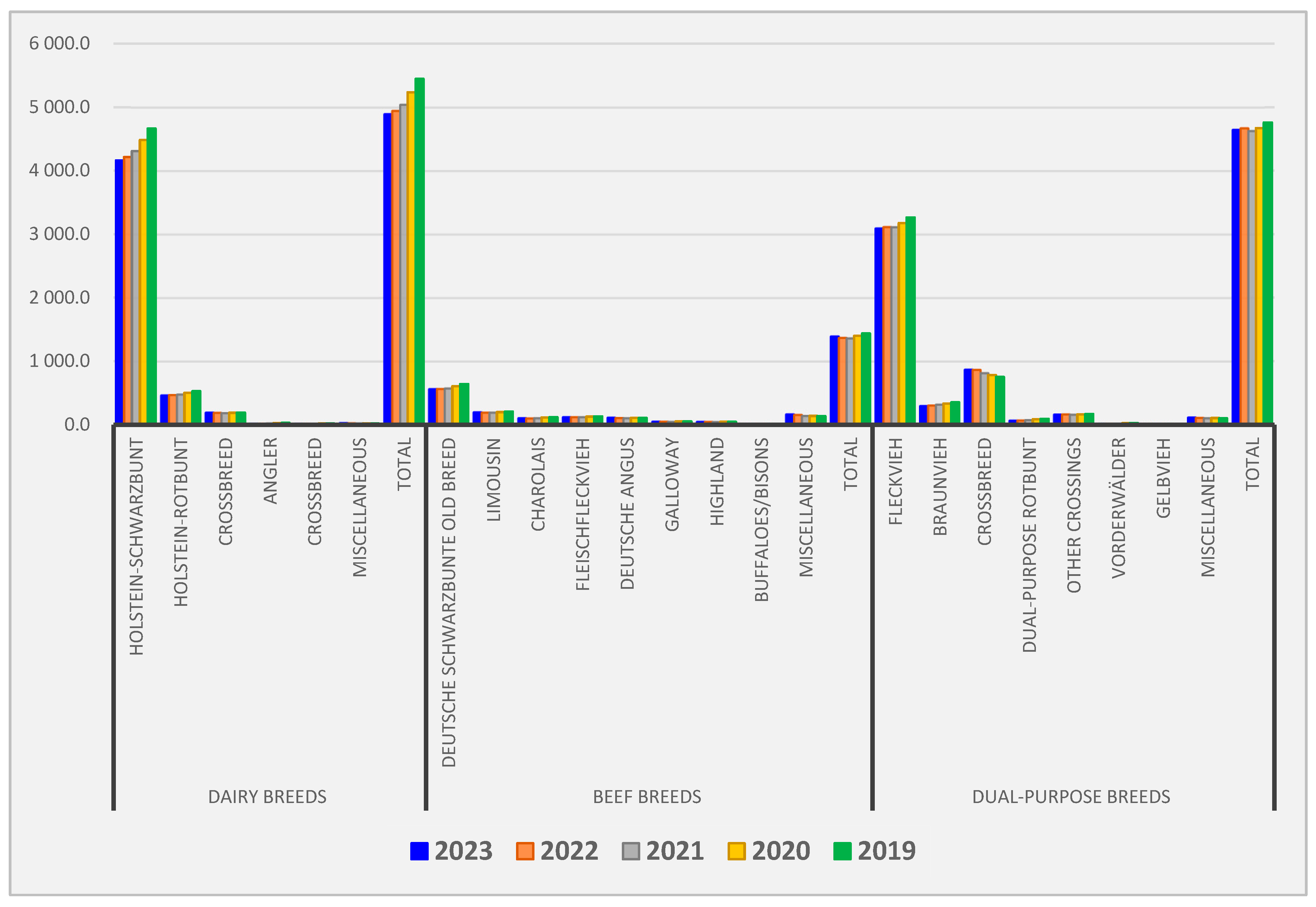
| Cattle Breed | Total | Calves ≤8 m. | Calves >8 m.–1 y | Cattle >1–≤2 y | Cattle >2 y | Cows |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dairy breeds (numbers × 1000) | ||||||
| Holstein-Schwarzbunt | 4160.2 | 750.6 | 290.6 | 811.3 | 209.8 | 2097.9 |
| Holstein-Rotbunt | 466.1 | 82.8 | 33.8 | 94.0 | 30.1 | 225.4 |
| Crossbreed | 194.7 | 38.1 | 16.0 | 43.7 | 10.7 | 86.2 |
| Angler | 23.6 | 4.1 | 1.4 | 4.5 | 1.6 | 12.0 |
| German Schwarzbunte (old breed) | 18.9 | 3.6 | 1.7 | 4.3 | 1.9 | 7.3 |
| Miscellaneous | 31.1 | 5.3 | 2.4 | 6.5 | 2.6 | 14.3 |
| Beef breeds (numbers × 1000) | ||||||
| Crossbreed | 564.8 | 126.9 | 64.4 | 152.5 | 42.1 | 179.0 |
| Limousin | 199.6 | 43.2 | 19.4 | 52.8 | 20.7 | 63.5 |
| Charolais | 108.4 | 22.7 | 8.1 | 28.0 | 10.7 | 38.9 |
| Fleckvieh (Beef) | 124.1 | 25.1 | 12.0 | 29.8 | 10.0 | 47.2 |
| German Angus | 116.4 | 26.9 | 8.6 | 28.4 | 11.3 | 41.2 |
| Galloway | 51.7 | 7.4 | 4.6 | 10.4 | 9.9 | 19.4 |
| Highland | 49.7 | 6.1 | 4.3 | 8.6 | 10.6 | 20.1 |
| Buffaloes/Bisons | 11.4 | 1.4 | 1.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 4.7 |
| Miscellaneous | 168.3 | 33.1 | 16.4 | 39.3 | 23.5 | 56.0 |
| Dual-purpose breeds (milk/meat) (numbers × 1000) | ||||||
| Fleckvieh | 3094.7 | 688.0 | 331.3 | 824.5 | 183.0 | 1068.0 |
| Braunvieh | 298.6 | 48.3 | 21.5 | 62.2 | 21.8 | 144.8 |
| Crossbreed | 872.1 | 266.0 | 123.3 | 292.0 | 48.2 | 142.7 |
| Dual-purpose Rotbunt | 69.9 | 12.3 | 6.0 | 16.8 | 7.4 | 27.4 |
| Other crossbreed | 166.2 | 38.7 | 18.9 | 46.1 | 9.7 | 52.8 |
| Vorderwälder | 20.1 | 3.5 | 1.4 | 4.0 | 1.7 | 9.5 |
| Gelbvieh | 8.8 | 1.6 | 0.8 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 3.3 |
| Miscellaneous | 117.5 | 26.0 | 10.4 | 31.0 | 13.0 | 37.1 |
| Federal State | 2022 | 2023 | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Baden-Wuerttemberg | 912, 467 (8.3%) | 903, 858 (8.26%) | −0.9 |
| Bavaria | 2, 867, 085 (26.1%) | 2, 833, 433 (25.90%) | −1.2 |
| Berlin | 784 (0.01%) | 741 (0.007%) | −5.5 |
| Brandenburg | 448, 309 (4.10%) | 446, 303 (4.08%) | −0.4 |
| Bremen | 8, 274 (0.075%) | 8, 269 (0.076%) | −0.1 |
| Hamburg | 5, 861 (0.053%) | 5, 793 (0.053%) | −1.2 |
| Hesse | 391, 587 (3.56%) | 392, 436 (3.59%) | +0.2 |
| Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania | 458, 837 (4.17%) | 461, 394 (4.22%) | +0.6 |
| Lower-Saxony | 2, 350, 584 (21.37%) | 2, 352, 926 (21.51%) | +0.1 |
| North Rhine-Westphalia | 1, 272, 505 (11.57%) | 1, 260, 319 (11.52%) | −1.0 |
| Rhineland-Palatinate | 299, 575 (2.72%) | 298, 020 (2.72%) | −0.5 |
| Saarland | 39, 575 (0.36%) | 39, 355 (0.36%) | −0.6 |
| Saxony | 435, 024 (3.96%) | 435, 284 (3.98%) | +0.1 |
| Saxony-Anhalt | 278, 086 (2.53%) | 276, 488 (2.53%) | −0.6 |
| Schleswig-Holstein | 950, 534 (8.64%) | 949, 171 (8.68%) | −0.1 |
| Thuringia | 277, 876 (2.53%) | 273, 008 (2.50%) | −1.8 |
| Total | 10, 996, 963 | 10, 936, 798 | −0.5 |
| 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baden-Wuerttemberg | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Bavaria | 4 | 6 | 8 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Brandenburg | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Lower-Saxony | - | - | - | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| North Rhine-Westphalia | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Rhineland-Palatinate | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Saxony | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Total | 6 | 7 | 9 | 6 | - | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Adawy, H.; Hotzel, H.; Tomaso, H.; Neubauer, H. The History of Bovine Genital Campylobacteriosis in the Face of Political Turmoil and Structural Change in Cattle Farming in Germany. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10120665
El-Adawy H, Hotzel H, Tomaso H, Neubauer H. The History of Bovine Genital Campylobacteriosis in the Face of Political Turmoil and Structural Change in Cattle Farming in Germany. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(12):665. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10120665
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Adawy, Hosny, Helmut Hotzel, Herbert Tomaso, and Heinrich Neubauer. 2023. "The History of Bovine Genital Campylobacteriosis in the Face of Political Turmoil and Structural Change in Cattle Farming in Germany" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 12: 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10120665
APA StyleEl-Adawy, H., Hotzel, H., Tomaso, H., & Neubauer, H. (2023). The History of Bovine Genital Campylobacteriosis in the Face of Political Turmoil and Structural Change in Cattle Farming in Germany. Veterinary Sciences, 10(12), 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10120665







