Characterization of Musts, Wines, and Sparkling Wines Based on Their Elemental Composition Determined by ICP-OES and ICP-MS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Solutions
2.2. Must, Wine, and Sparkling Wine Samples
2.3. Analytical Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
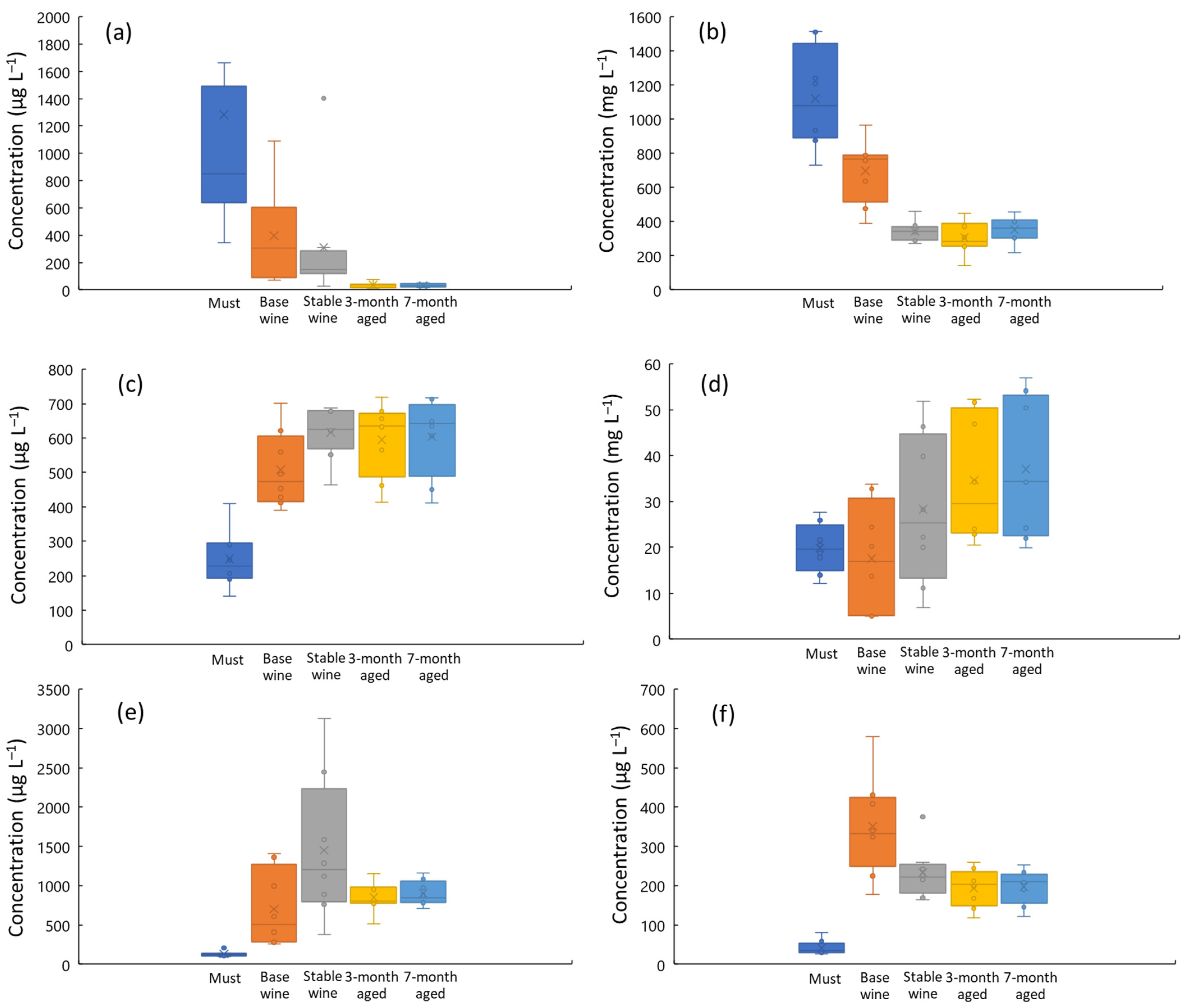
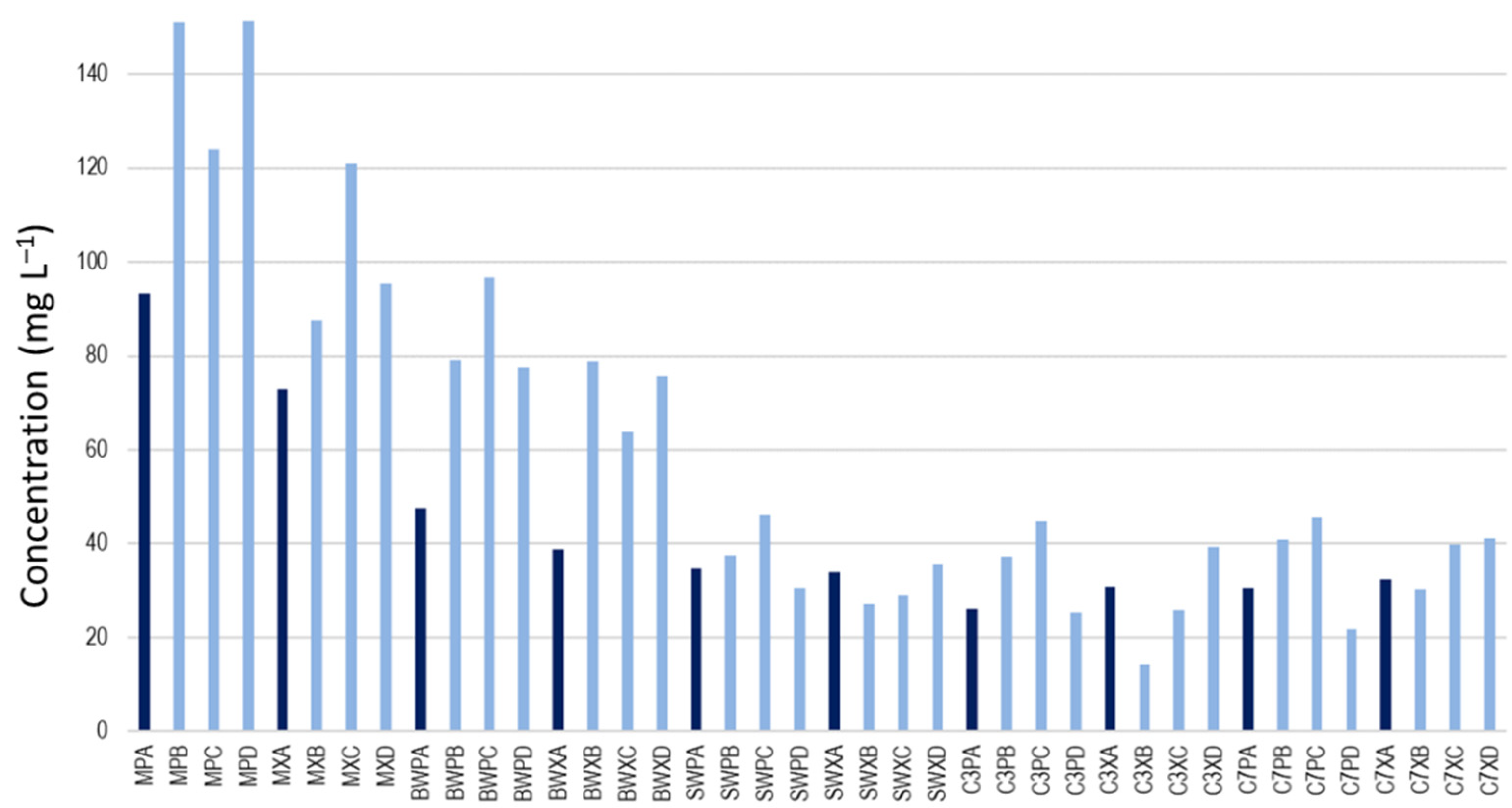
3.1. Must, Wine, and Cava Analysis
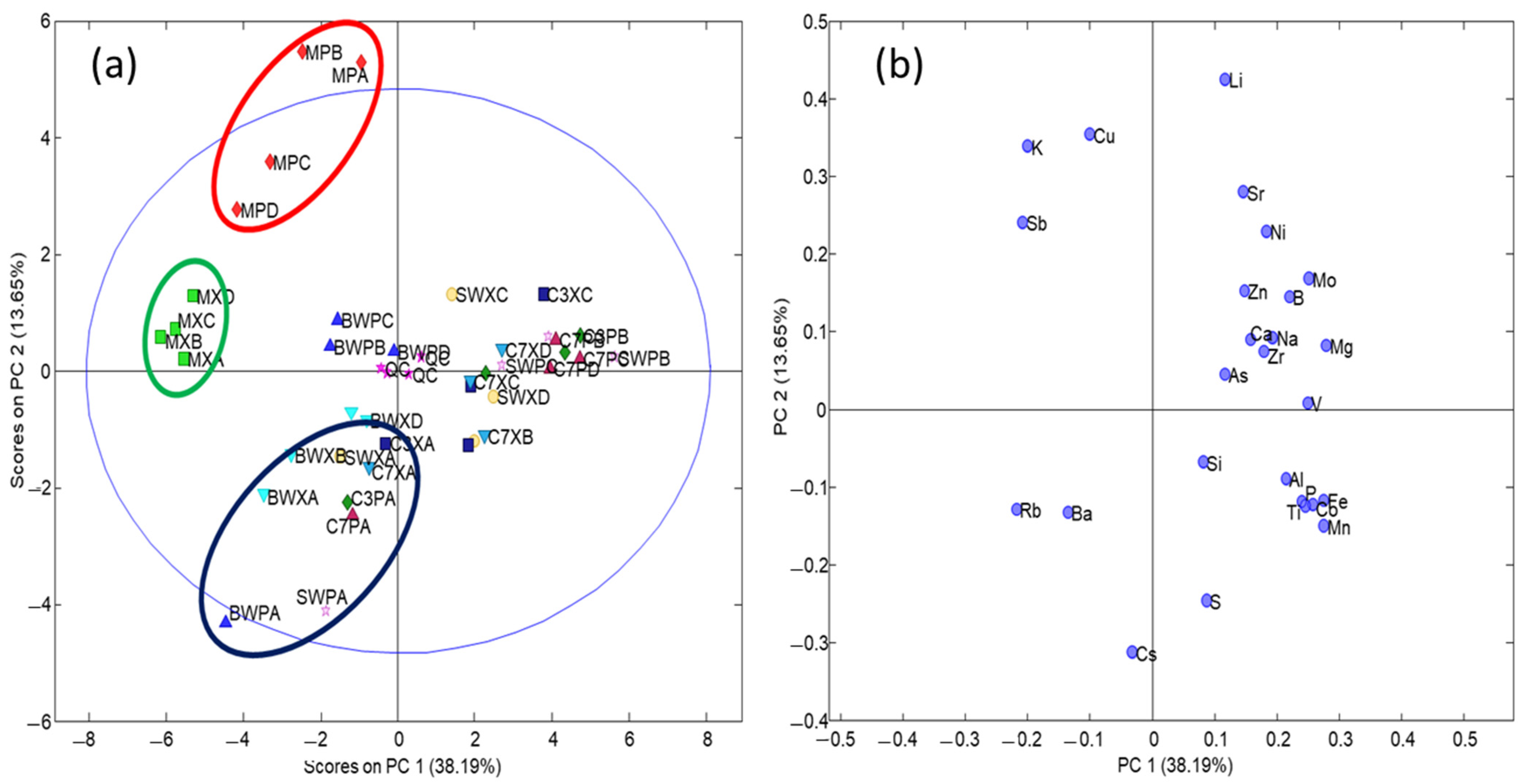
3.2. Chemometric Evaluation of Samples by PCA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D.O. Cava. The Traditional Method or Méthode Champenoise. Available online: https://www.cava.wine/en/origin-cava/traditional-method-champenoise/ (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Izquierdo-Llopart, A.; Saurina, J. Multi-Sensor Characterization of Sparkling Wines Based on Data Fusion. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Llopart, A.; Saurina, J. Liquid Chromatographic Approach for the Discrimination and Classification of Cava Samples Based on the Phenolic Composition Using Chemometric Methods. Beverages 2020, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Llopart, A.; Carretero, A.; Saurina, J. Organic Acid Profiling by Liquid Chromatography for the Characterization of Base Vines and Sparkling Wines. Food Anal. Methods 2020, 13, 1852–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiloglu, S. Authenticity and traceability in beverages. Food Chem. 2018, 277, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Sun, D.-W.; Pu, H.; Cheng, J.-H. Quality analysis, classification, and authentication of liquid foods by near-infrared spectroscopy: A review of recent research developments. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1524–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkytė, V.; Longo, E.; Windisch, G.; Boselli, E. Phenolic Compounds as Markers of Wine Quality and Authenticity. Foods 2020, 9, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danezis, G.P.; Tsagkaris, A.S.; Camin, F.; Brusic, V.; Georgiou, C.A. Food authentication: Techniques, trends & emerging approaches. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucci, P.; Saurina, J.; Nuñez, O. Trends in LC-MS and LC-HRMS analysis and characterization of polyphenols in food. Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 88, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esteki, M.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Shahsavari, Z.; Zandbaaf, S.; Dashtaki, E.; Heyden, Y.V. A review on the application of chro-matographic methods, coupled to chemometrics, for food authentication. Food Control 2018, 93, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callao, M.P.; Ruisánchez, I. An overview of multivariate qualitative methods for food fraud detection. Food Control 2018, 86, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versari, A.; Laurie, F.; Ricci, A.; Laghi, L.; Parpinello, G.P. Progress in authentication, typification and traceability of grapes and wines by chemometric approaches. Food Res. Int. 2014, 60, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Lourido, D.; Saurina, J.; Hernández-Cassou, S.; Checa, A. Classification and characterisation of Spanish red wines according to their appellation of origin based on chromatographic profiles and chemometric data analysis. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saurina, J. Characterization of wines using compositional profiles and chemometrics. Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drivelos, S.A.; Georgiou, C.A. Multi-element and multi-isotope-ratio analysis to determine the geographical origin of foods in the European Union. Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 40, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husted, S.; Persson, D.P.; Laursen, K.H.; Hansen, T.H.; Pedas, P.; Schiller, M.; Hegelund, J.N.; Schjoerring, J.K. Review: The role of atomic spectrometry in plant science. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2010, 26, 52–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Armesto, A.; Carballeira-Díaz, J.; Pérez-Rodríguez, P.; Fernández-Calviño, D.; Arias-Estévez, M.; Muñoz, J.C.N.; Álvarez-Rodríguez, E.; Fernández-Sanjurjo, M.J.; Núñez-Delgado, A. Copper content and distribution in vineyard soils from Betanzos (A Coruña, Spain). Span. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Hernández, E.; Andrades, M.S.; Rodríguez-Cruz, M.S.; Arienzo, M.; Sánchez-Martín, M.J. Long-term variability of metals from fungicides applied in amended young vineyard fields of La Rioja (Spain). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 184, 3359–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orescanin, V.; Katunar, A.; Kutle, A.; Valkovic, V. Heavy metals in soil, grape, and wine. J. Trace Microprobe Tech. 2003, 21, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Code of Oenological Practices. International Organization of Vine and Wine. Annex: Maximum Acceptable Limits. 2021. Available online: https://www.oiv.int/public/medias/7713/en-oiv-code-2021.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Katerinopoulou, K.; Kontogeorgos, A.; Salmas, C.E.; Patakas, A.; Ladavos, A. Geographical Origin Authentication of Agri-Food Products: A Review. Foods 2020, 9, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhaj, M.; Korenovska, M. Application of elemental analysis for identification of wine origin—A review. Acta Aliment. 2005, 34, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubadda, F. Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry for the Determination of Elements and Elemental Species in Food: A Review. J. AOAC Int. 2004, 87, 173–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzálvez, A.; Llorens, A.; Cervera, M.; Armenta, S.; de la Guardia, M. Elemental fingerprint of wines from the protected designation of origin Valencia. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šelih, V.S.; Šala, M.; Drgan, V. Multi-element analysis of wines by ICP-MS and ICP-OES and their classification according to geographical origin in Slovenia. Food Chem. 2014, 153, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horii, S.; Hashiguchi, T.; Izu, H.; Sudo, S. Analysis of element composition of Japanese and other wine and their classifica-tion. J. Jap. Soc. Horticul. Sci. 2011, 80, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Paola-Naranjo, R.D.; Baroni, M.V.; Podio, N.S.; Rubinstein, H.R.; Fabani, M.P.; Badini, R.G.; Inga, M.; Ostera, H.A.; Cagnoni, M.; Gallegos, E.; et al. Fingerprints for Main Varieties of Argentinean Wines: Terroir Differentiation by Inorganic, Organic, and Stable Isotopic Analyses Coupled to Chemometrics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 7854–7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geana, I.; Iordache, A.; Ionete, R.; Marinescu, A.; Ranca, A.; Culea, M. Geographical origin identification of Romanian wines by ICP-MS elemental analysis. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azcarate, S.; Martinez, L.D.; Savio, M.; Camiña, J.M.; Gil, R.A. Classification of monovarietal Argentinean white wines by their elemental profile. Food Control 2015, 57, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, F.; Anzanello, M.J.; Fogliatto, F.S.; Marcelo, M.C.; Ferrão, M.F.; Manfroi, V.; Pozebon, D. Element selection and concentration analysis for classifying South America wine samples according to the country of origin. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 150, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, G.H.; Anzanello, M.J.; Soares, F.; Rocha, M.K.; Fogliatto, F.S.; Rodrigues, N.P.; Rodrigues, E.; Celso, P.G.; Manfroi, V.; Hertz, P.F. Hierarchical classification of sparkling wine samples according to the country of origin based on the most informative chemical elements. Food Control 2019, 106, 106737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, N.P.; Rodrigues, E.; Celso, P.G.; Kahmann, A.; Yamashita, G.H.; Anzanello, M.J.; Manfroi, V.; Hertz, P.F. Dis-crimination of sparkling wines samples according to the country of origin by ICP-OES coupled with multivariate analysis. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 131, 109760. [Google Scholar]
- Kozak, M.; Scaman, C.H. Unsupervised classification methods in food sciences: Discussion and outlook. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2008, 88, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, D.; Putnik, P.; Kovačević, D.B.; Santos, J.S.; Calado, V.; Rocha, R.S.; Da Cruz, A.G.; Jarvis, B.; Rodionova, O.Y.; Pomerantsev, A. Trends in Chemometrics: Food Authentication, Microbiology, and Effects of Processing. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cruz, T.L.E.; Esperanza, M.G.; Wrobel, K.; Barrientos, E.Y.; Aguilar, F.J.A.; Wrobel, K. Determination of major and minor elements in Mexican red wines by microwave-induced plasma optical emission spectrometry, evaluating different calibration methods and exploring potential of the obtained data in the assessment of wine provenance. Spectrochim. Acta Part B Atom. Spectrosc. 2019, 164, 105754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalafyan, A.A.; Temerdashev, Z.A.; Kaunova, A.A.; Abakumov, A.G.; Titarenko, V.O.; Akin’shina, V.A.; Ivanovets, E.A. Determination of the Wine Variety and Geographical Origin of White Wines Using Neural Network Technologies. J. Anal. Chem. 2019, 74, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, N.L.; Ximenez, J.P.B.; Rodrigues, J.L.; Barbosa, F.; Barbosa, R. Characterization of Cabernet Sauvignon wines from California: Determination of origin based on ICP-MS analysis and machine learning techniques. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, F.D.; Donici, A.; Rusu, T.; Bunea, A.; Popescu, D.; Bunea, C. Elemental Profile and Pb-207/Pb-206, Pb-208/Pb-206, Pb-204/Pb-206, Sr-87/Sr-86 Isotope Ratio as Fingerprints for Geographical Traceability of Romanian Wines. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobo. 2018, 46, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geana, E.I.; Sandru, C.; Stanciu, V.; Ionete, R.E. Elemental Profile and Sr-87/Sr-86 Isotope Ratio as Fingerprints for Geo-graphical Traceability of Wines: An Approach on Romanian Wines. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova-Petropulos, V.; Balabanova, B.; Bogeva, E.; Frentiu, T.; Ponta, M.; Senila, M.; Gulaboski, R.; Irimie, F.D. Rapid De-termination of Trace Elements in Macedonian Grape Brandies for Their Characterization and Safety Evaluation. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Grape Variety | Quality | Must | Base Wine | Stabilized Wine | 3 Months Sparkling Wine | 7 Months Sparkling Wine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pinot Noir | A | MPA | BWPA | SWPA | C3PA | C7PA |
| B | MPB | BWPB | SWPB | C3PB | C7PB | |
| C | MPC | BWPC | SWPC | C3PC | C7PC | |
| D | MPD | BWPD | SWPD | C3PD | C7PD | |
| Xarel·lo | A | MXA | BWXA | SWXA | C3XA | C7XA |
| B | MXB | BWXB | SWXB | C3XB | C7XB | |
| C | MXC | BWXC | SWXC | C3XC | C7XC | |
| D | MXD | BWXD | SWXD | C3XD | C7XD |
| Sample Origin | Instrumental Technique | Sample Pretreatment | Dilution | Measured Elements | Chemometric Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japan, Chile, United States, France and Italy | ICP-OES | Acid digestion | 2:5:1 (v/v/v) with 60% HNO3 and 30% H2O2 Final 1:5 dilution with 1% HNO3 | Al, B, Ba, Ca, Cd, Cr, Cs, Cu, Fe, K, Li, Mg, Mn, Mo, Na, Ni, P, Pb, Sr, V, Y and Zn | PCA and LDA | [25] |
| Argentina | ICP-MS | Mineralization followed by acid digestion | 5:6 (v/v) with HNO3(cc) Final 1:5 dilution with H2O | Al, B, Ba, Ca, Cd, Ce, Co, Cs, Cu, Eu, Ga, K, La, Li, Lu, Mg, Mn, Mo, Na, Ni, Nd, Pb, Rb, Se, Sm, Sr, Tl, U, V, Yb, and Zn | DA | [26] |
| Romania | ICP-MS | Acid digestion | 1:1 (v/v) with HNO3(cc) Final 1:20 dilution with H2O | Ag, Be, Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb, Rb, Sr, V and Zn | PCA | [27] |
| Slovenia | ICP-OES | Only dilution | 1:3 (v/v) with 2% HNO3 | Al, B, Ca, Cu, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, Na and Zn | PCA and CPANN | [28] |
| ICP-MS | Only dilution | 1:10 (v/v) with 2% HNO3 | Ag, Au, As, Ba, Be, Bi, Ce, Co, Cr, Dy, Ga, Gd, Ge, Hg, Ir, La, Li, Mo, Nb, Nd, Ni, Os, Pb, Pd, Pt, Re, Rh, Ru, Sb, Sc, Se, Sn, Ta, Ti, Tl V, W, Y, and Zr | PCA and CPANN | ||
| Argentina | ICP-MS | Only dilution | 1:10 (v/v) with 1% HNO3 | As, Ba, Be, Bi, Cd, Co, Cu, Hg, Li, Mn, Mo, Ni, Pb, Rb, Sr, Tl and V | PCA and LDA | [29] |
| Argentina, Brazil, Chile and Uruguay | ICP-OES | Acid digestion | 1:3 (v/v) with 2% HNO3, followed by 1:25 dilution with H2O, and final 1:10 dilution with 5% HNO3 | Al, Ba, Ca, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, Na, P, Rb, Sr, Ti, and Zn | NN, LDA, NB and SVM | [30] |
| ICP-MS | Acid digestion | 1:3 (v/v) with 2% HNO3, followed by 1:25 dilution with H2O, and final 1:2 dilution with 5% HNO3 | Ag, As, Be, Bi, Cd, Ce, Co, Cr, Cu, Dy, Er, Eu, Gd, Ho, La, Li, Lu, Mo, Nd, Ni, Pb, Pr, Sb, Se, Sm, Sn. Tb, Tl, Tm, U, V and Yb | NN, LDA, NB and SVM | ||
| Argentina, Brazil, France and Spain | ICP-OES | Degasification | 1:10 (v/v) with 1 M HNO3 for major elements, while minor elements are non-diluted | Al, B, Ba, Ca, Cu, Fe, K, Li, Mg, Mn, Na, and Sr | LDA and NB | [31] |
| Brazil, Argentina, Spain and France | ICP-OES | Degasification using ultrasonic bath | 1:10 (v/v) with 1 M HNO3 for major elements, while minor elements are non-diluted | Al, B, Ba, Ca, Cu, Fe, K, Li, Mg, Mn, Na, and Sr | LDA, PCA and LR | [32] |
| Mexico | MIP-OES | Only dilution | 1:100, 1:50, 1:10, and 1:4 (v/v) with 1 M HNO3 depending on concentrations | Al, Ca, Cu, Cr, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, Na, Rb, and Sr | PCA | [35] |
| Krasnodar | ICP-OES | Only dilution | 1:10 (v/v) with 1 M HNO3 | Fe, Mg, Rb, Ti, and Na | NN | [36] |
| California | ICP-MS | Only dilution | 1:10 (v/v) with 1 M HNO3 | Al, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Li, Mn, Ni, P, Pb, Rb, Sr, and Zn | SVM | [37] |
| Romania | ICP-MS | Dilution and microwave digestion | 1:16 (v/v) with HNO3 + H2O2 | Ag, Al, As, Ba, Be, Bi, Ca, Cd, Co, Cr, Cs, Cu, Fe, Ga, In, K, Li, Mg, Mn, Na, Ni, Pb, Rb, Se, Sr, Tl, V, U, Zn, and Hg. Isotope ratios; 207Pb/206Pb, 208Pb/206Pb, 204Pb/206Pb, and 87Sr/86Sr | LDA | [38] |
| Romania | FAAS, GFAAS, and ICP-MS | Dilution and microwave digestion | 1:1 (v/v) with HNO3 Final 1:20 dilution with H2O | Li, Ga, Se, Ag, Tl, Pb, Ni, Cr, Ba, Zn, Sr, Rb, Al, Cu, Mn, Fe, Ca, Mg, Na, K, and 87Sr/86Sr | LDA | [39] |
| Macedonia (brandy) | GFAAS | - | Direct injection | Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn | PCA | [40] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Granell, B.; Izquierdo-Llopart, A.; Sahuquillo, À.; López-Sánchez, J.F.; Saurina, J. Characterization of Musts, Wines, and Sparkling Wines Based on Their Elemental Composition Determined by ICP-OES and ICP-MS. Beverages 2022, 8, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages8010003
Granell B, Izquierdo-Llopart A, Sahuquillo À, López-Sánchez JF, Saurina J. Characterization of Musts, Wines, and Sparkling Wines Based on Their Elemental Composition Determined by ICP-OES and ICP-MS. Beverages. 2022; 8(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages8010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleGranell, Biel, Anaïs Izquierdo-Llopart, Àngels Sahuquillo, José F. López-Sánchez, and Javier Saurina. 2022. "Characterization of Musts, Wines, and Sparkling Wines Based on Their Elemental Composition Determined by ICP-OES and ICP-MS" Beverages 8, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages8010003
APA StyleGranell, B., Izquierdo-Llopart, A., Sahuquillo, À., López-Sánchez, J. F., & Saurina, J. (2022). Characterization of Musts, Wines, and Sparkling Wines Based on Their Elemental Composition Determined by ICP-OES and ICP-MS. Beverages, 8(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages8010003