Influence of Chemical and Physical Variables on 87Sr/86Sr Isotope Ratios Determination for Geographical Traceability Studies in the Oenological Food Chain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
3. Experimental
3.1. Soil Sampling
3.2. Vine Branch Sampling
3.3. Wine Sampling
4. Sample Processing
4.1. Soil
4.2. Vine Branches and Wines
4.3. Strontium/Rubidium Spiking Solutions
4.4. Strontium Isotopic Ratio Determination on Real Samples
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Results and Discussion
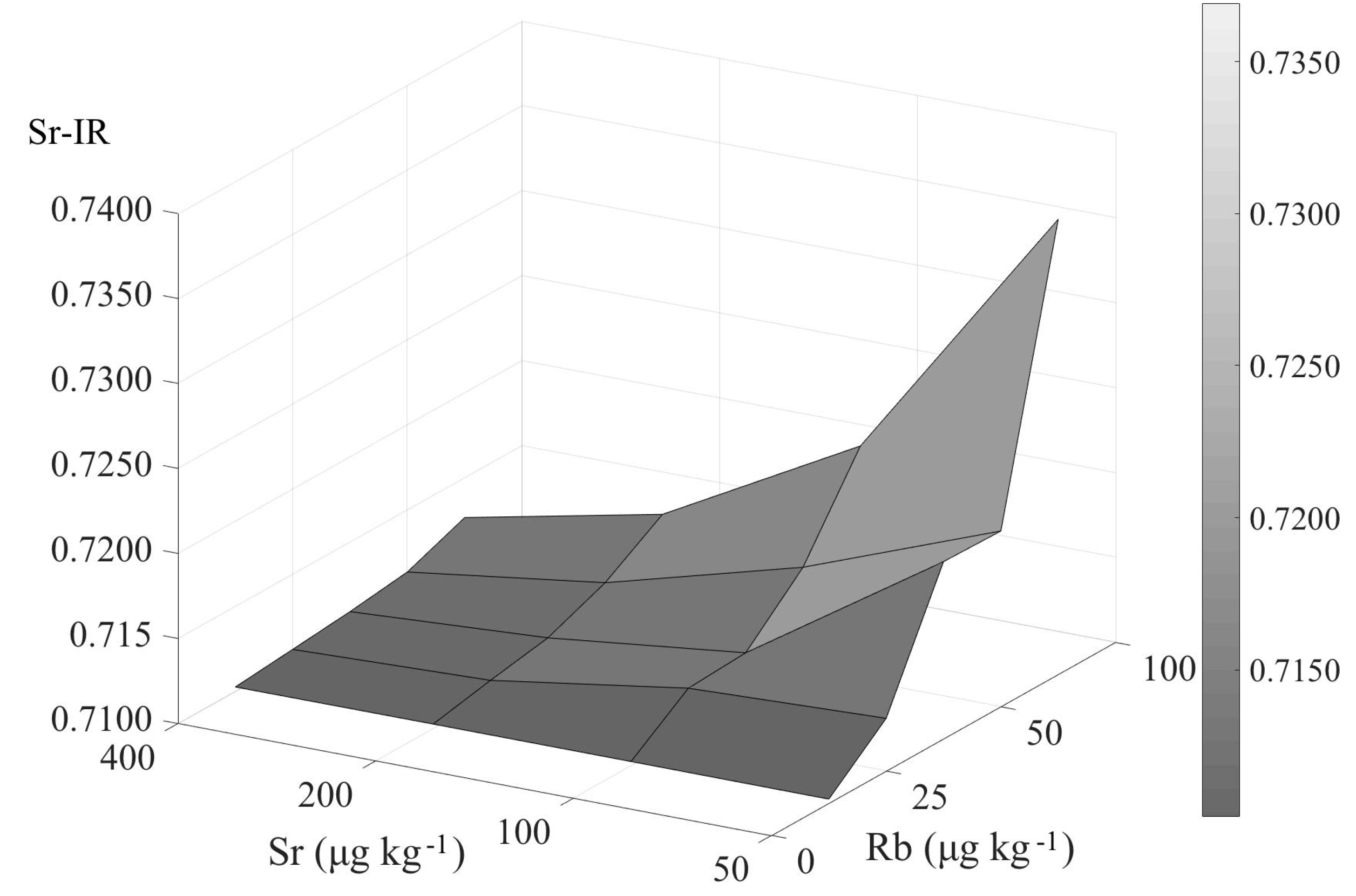
5.1. Influence of the Residual Rb on the Accuracy of the 87Sr/86Sr Ratio
5.2. Influence of the Milling Process
5.3. 87Sr/86Sr Ratio as Geographical Indicator in the Chianti Classico Production Area
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EU Agricultural Product Quality Policy. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/agriculture/quality_en (accessed on 25 July 2018).
- Regulation (EU) 1151/2012 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 November 2012 on Quality Schemes for Agricultural Products and Foodstuffs; L 343/1; Official Journal of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 14 December 2012.
- Danezis, G.P.; Tsagkaris, A.S.; Camin, F.; Brusic, V.; Georgiou, C.A. Food authentication: Techniques, trends & emerging approaches. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Baroni, M.V.; Podio, N.S.; Badini, R.G.; Inga, M.; Ostera, H.A.; Cagnoni, M.; Gallegos, E.; Gautier, E.; Peral-García, P.; Hoogewerff, J.; et al. How Much Do Soil and Water Contribute to the Composition of Meat? A Case Study: Meat from Three Areas of Argentina. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 11117–11128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voerkelius, S.; Lorenz, G.D.; Rummel, S.; Quétel, C.R.; Heiss, G.; Baxter, M.; Brach-Papa, C.; Deters-Itzelsberger, P.; Hoelzl, S.; Hoogewerff, J.; et al. Strontium isotopic signatures of natural mineral waters, the reference to a simple geological map and its potential for authentication of food. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, P.; Schaaf, P.; Holbach, B.; Holzl, S.; Eschnauer, H. 87Sr/86Sr from rock and soil into vine and wine. Z. Lebensm. Unters. Forsch. 1993, 196, 407–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.M. Geochemistry; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-470-65667-9. [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti, A.; Durante, C.; Bertacchini, L. Heavy isotopes: A powerful tool to support geographical traceability of food. In Food Authentication, Management, Analysis and Regulation; Georgiou, C.A., Danezis, G.P., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781118810255. [Google Scholar]
- Fortunato, G.; Mumic, K.; Wunderli, S.; Pillonel, L.; Bosset, J.; Gremaud, G. Application of strontium isotope abundance ratios measured by MC-ICP-MS for food authentication. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2004, 19, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, K.; Nakano, T.; Shin, K.C.; Izawa, A.; Morita, S. Variation of strontium stable isotope ratios and origins of strontium in Japanese vegetables and comparison with Chinese vegetables. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchionni, S.; Buccianti, A.; Bollati, A.; Braschi, E.; Cifelli, F.; Molin, P.; Parotto, M.; Mattei, M.; Tommasini, S.; Conticelli, S. Conservation of 87Sr/86Sr isotopic ratios during the winemaking processes of ‘Red’ wines to validate their use as geographic tracer. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trincherini, P.R.; Baffi, C.; Barbero, P.; Pizzoglio, E.; Spalla, S. Precise determination of strontium isotope ratios by TIMS to authenticate tomato geographical origin. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, R.J.; Carlson, R.W.; Shirey, S.B.; Boyd, F.R. Os, Sr, Nd, and Pb isotope systematics of southern African peridotite xenoliths: Implications for the chemical evolution of the subcontinental mantle. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 1583–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, T.D.; Burton, J.H.; Bentley, R.A. The characterization of biologically available strontium isotope ratios for the study of prehistoric migration. Archaeometry 2002, 44, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmes, M.; Bataille, C.P.; James, H.F.; Moffat, I.; McMorrow, L.; Kinsley, L.; Armstrong, R.A.; Eggins, S.; Grün, R. Mapping of bioavailable strontium isotope ratios in France for archaeological provenance studies. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 90, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, C.; Baschieri, C.; Bertacchini, L.; Bertelli, D.; Cocchi, M.; Marchetti, A.; Manzini, D.; Papotti, G.; Sighinolfi, S. An analytical approach to Sr isotope ratio determination in Lambrusco wines for geographical traceability purposes. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sillen, A.; Hall, G.; Richardson, S.; Armstrong, R. 87Sr/86Sr ratios in modern and fossil food-webs of the Sterkfontein Valley: Implications for early hominid habitat preference. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 2463–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, C.; Bertacchini, L.; Cocchi, M.; Manzini, D.; Marchetti, A.; Rossi, M.C.; Sighinolfi, S.; Tassi, L. Development of 87Sr/86Sr maps as targeted strategy to support wine quality. Food Chem. 2018, 255, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durante, C.; Baschieri, C.; Bertacchini, L.; Cocchi, M.; Sighinolfi, S.; Silvestri, M.; Marchetti, A. Geographical traceability based on 87Sr/86Sr indicator: A first approach for PDO Lambrusco wines from Modena. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2779–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durante, C.; Bertacchini, L.; Bontempo, L.; Camin, F.; Manzini, D.; Lambertini, P.; Marchetti, A.; Paolini, M. From soil to grape and wine: Variation of light and heavy elements isotope ratios. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchionni, S.; Braschi, E.; Tommasini, S.; Bollati, A.; Cifelli, F.; Mulinacci, N.; Mattei, M.; Conticelli, S. High-precision 87Sr/86Sr analyses in wines and their use as a geological fingerprint for tracing geographic provenance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 6822–6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braschi, E.; Marchionni, S.; Priori, S.; Casalini, M.; Tommasini, S.; Natarelli, L.; Buccianti, A.; Bucelli, P.; Costantini, E.A.C.; Conticelli, S. Tracing the 87Sr/86Sr from rocks and soils to vine and wine: An experimental study on geologic and pedologic characterisation of vineyards using radiogenic isotope of heavy elements. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarède, F.; Telouk, P.; Blichert-Toft, J.; Boyet, M.; Agranier, A.; Nelson, B. Precise and accurate isotopic measurements using multiple-collector ICPMS. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 2725–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, M.E.; Schwieters, J.B. The development of multiple collector mass spectrometry for isotope ratio measurements. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 242, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, C.P.; Sharp, B.L.; Horstwood, M.S.A.; Parrish, R.R.; Lewis, D.J. Instrument response functions, mass bias and matrix effects in isotope ratio measurements and semi-quantitative analysis by single and multi-collector ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2003, 18, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowell, G.M.; Pearson, D.G.; Ottley, C.J.; Schwieters, J.; Dowall, D. Long term performance characteristics of a plasma ionization multi collector mass spectrometer (PIMMS): The Thermo Finnigan Neptune. In Plasma Source Mass Spectrometry, Application and Emerging Technologies; Holland, J.G., Tanner, S.D., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2003; pp. 307–320. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich, S.; Gavrieli, I.; Dor, L.B.; Halicz, L. Direct high-precision measurements of the 87Sr/86Sr isotope ratio in natural water, carbonates and related materials by multiple collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (MC-ICP-MS). J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2001, 16, 1389–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.J.; Yoon, J.K.; Kim, T.S.; Yang, J.E.; Owen, G.; Kim, K.R. Bioavailability of heavy metals in soils: definitions and practical implementation—A critical review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2015, 37, 1041–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, J.D.; Taliaferro, E.H.; Weisse, M.T.; Holmes, R.T. Changes in Sr/Ca, Ba/Ca and 87Sr/86Sr ratios between trophic levels in two forest ecosystems in the northeastern U.S.A. Biogeochemistry 2000, 49, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberg, G. The use of natural strontium isotopes as tracers in environmental studies. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1995, 79, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberg, G.; Fosse, G.; Stray, H. Man, nutrition and mobility: A comparison of teeth and bone from the Medieval era and the present from Pb and Sr isotopes. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 224, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlkea, J.K.; Horan, M. Strontium isotope geochemistry of ground waters and streams affected by agriculture, Locust Grove, MD. Appl. Geochem. 2000, 15, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, M.; Starinsky, A.; Katz, A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Machlus, M.; Schramm, A. Strontium isotopic, chemical and sedimentological evidence for the evolution of lake Lisan and the Dead sea. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 3975–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. Soil Quality—Extraction of Trace Elements from Soil Using Ammonium Nitrate Solution; DIN ISO 19730 (2009-07); ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cocchi, M.; Durante, C.; Marchetti, A.; Li Vigni, M.; Baschieri, C.; Bertacchini, L.; Sighinolfi, S.; Tassi, L.; Totaro, S. Optimization of microwave assisted digestion procedure by means of chemometric tools. In Microwaves: Theoretical Aspects and Practical Applications in Chemistry; Marchetti, A., Ed.; Transworld Research Network: Trivandrum, Kerala, India, 2011; pp. 203–223. ISBN 978-81-7895-508-7. [Google Scholar]
- Baschieri, C. Food Traceability: A Multivariate Approach to Procedures Optimization and Models Development. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, Modena, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Berglund, M.; Wieser, M.E. Isotopic compositions of the elements 2009 (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 83, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample Size µm | Sample M1 %, w/w | Sample M2 %, w/w | Sample M3 %, w/w | Sample M4 %, w/w |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 315 | 0.10 | --- | --- | --- |
| 250 | 3.00 | 4.00 | 5.90 | --- |
| 180 | 6.90 | 13.00 | 12.20 | 14.40 |
| 125 | 16.10 | 17.10 | 13.60 | 21.50 |
| 90 | 26.80 | 28.00 | 19.40 | 14.20 |
| 63 | 32.10 | 29.20 | 25.80 | 26.00 |
| 50 | 9.90 | 7.30 | 12.40 | 11.30 |
| Collecting pan | 5.10 | 1.40 | 10.70 | 12.50 |
| Sample Size µm | (87Sr/86Sr)_M1 | (87Sr/86Sr)_M2 | (87Sr/86Sr)_M3 | (87Sr/86Sr)_M4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 250 | 0.710088 | 0.709778 | 0.709179 | 0.711348 |
| 180 | 0.710081 | 0.709769 | 0.709149 | 0.711369 |
| 125 | 0.710103 | 0.709804 | 0.709183 | 0.711377 |
| 90 | 0.710105 | 0.709791 | 0.709183 | 0.711382 |
| 63 | 0.710090 | 0.709784 | 0.709194 | 0.711380 |
| 50 | 0.710092 | 0.709782 | 0.709192 | 0.711375 |
| Collecting pan | 0.710109 | 0.709763 | 0.709199 | 0.711366 |
| Mean | 0.71010 | 0.70978 | 0.70918 | 0.71137 |
| SD | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.00002 | 0.00001 |
| Whole sample 1 | 0.71007 | 0.70978 | 0.70920 | 0.71136 |
| |ΔMean-Whole sample| | 0.00003 | 0.00000 | 0.00002 | 0.00001 |
| Site | Hole | 87Sr/86Sr Soil 1 | 87Sr/86Sr Branch 2 | 87Sr/86Sr Wine 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1up | 0.71002 | 0.70963 | 0.70943 |
| 1dw | 0.70994 | |||
| 2up | 0.70918 | 0.70914 | ||
| 2dw | 0.70922 | |||
| Mean ± SD | 0.70959 ± 0.00045 | 0.70939 ± 0.00035 | ||
| B | 3up | 0.70900 | 0.70905 | 0.70941 |
| 3dw | 0.70900 | |||
| 4up | 0.70945 | 0.70924 | ||
| 4dw | 0.70954 | |||
| 5up | 0.70978 | 0.70977 | ||
| 5dw | 0.71006 | |||
| 6up | 0.70977 | 0.70941 | ||
| 6dw | 0.71034 | |||
| 7up | 0.70992 | 0.70929 | ||
| 7dw | 0.70986 | |||
| Mean ± SD | 0.70967 ± 0.00043 | 0.70935 ± 0.00027 |
| Source of Variation | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | F | F crit (α = 0.05) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between groups | 4.17004 × 10−7 | 2 | 1.530 | 3.492 |
| Within groups | 2.72386 × 10−6 | 20 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sighinolfi, S.; Durante, C.; Lisa, L.; Tassi, L.; Marchetti, A. Influence of Chemical and Physical Variables on 87Sr/86Sr Isotope Ratios Determination for Geographical Traceability Studies in the Oenological Food Chain. Beverages 2018, 4, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4030055
Sighinolfi S, Durante C, Lisa L, Tassi L, Marchetti A. Influence of Chemical and Physical Variables on 87Sr/86Sr Isotope Ratios Determination for Geographical Traceability Studies in the Oenological Food Chain. Beverages. 2018; 4(3):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4030055
Chicago/Turabian StyleSighinolfi, Simona, Caterina Durante, Lancellotti Lisa, Lorenzo Tassi, and Andrea Marchetti. 2018. "Influence of Chemical and Physical Variables on 87Sr/86Sr Isotope Ratios Determination for Geographical Traceability Studies in the Oenological Food Chain" Beverages 4, no. 3: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4030055
APA StyleSighinolfi, S., Durante, C., Lisa, L., Tassi, L., & Marchetti, A. (2018). Influence of Chemical and Physical Variables on 87Sr/86Sr Isotope Ratios Determination for Geographical Traceability Studies in the Oenological Food Chain. Beverages, 4(3), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4030055





