The Development of a Menthol Solution for Use during Sport and Exercise
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Solution Concentration
3.2. Solution Colour
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dawes, C. Physiological factors affecting salivary flow rate, oral sugar clearance, and the sensation of dry mouth in man. J. Dent. Res. 1987, 66, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaven, C.M.; Maulder, P.; Pooley, A.; Kilduff, L.; Cook, C. Effects of caffeine and carbohydrate mouth rinses on repeated sprint performance. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 38, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, C.J.; Best, R. Menthol: A fresh ergogenic aid for athletic performance. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peart, D.J. Quantifying the Effect of Carbohydrate Mouth Rinsing on Exercise Performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, N.D.; Kornilios, E.; Richardson, D.L. Carbohydrate and Caffeine Mouth Rinses Do Not Affect Maximum Strength and Muscular Endurance Performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 2926–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doering, T.M.; Fell, J.W.; Leveritt, M.D.; Desbrow, B.; Shing, C.M. The effect of a caffeinated mouth-rinse on endurance cycling time-trial performance. IJSNEM 2014, 24, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, L.M.; Maughan, R.J. The Governor has a sweet tooth—Mouth sensing of nutrients to enhance sports performance. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2014, 15, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stellingwerff, T.; Cox, G.R. Systematic review: Carbohydrate supplementation on exercise performance or capacity of varying durations 1. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 39, 998–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riera, F.; Trong, T.T.; Sinnapah, S.; Hue, O. Physical and Perceptual Cooling with Beverages to Increase Cycle Performance in a Tropical Climate. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran Trong, T.; Riera, F.; Rinaldi, K.; Briki, W.; Hue, O. Ingestion of a cold temperature/menthol beverage increases outdoor exercise performance in a hot, humid environment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, R.; Payton, S.; Spears, I.; Riera, F.; Berger, N. Topical and Ingested Cooling Methodologies for Endurance Exercise Performance in the Heat. Sports 2018, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccles, R. Menthol and Related Cooling Compounds. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1994, 46, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eccles, R. Role of cold receptors and menthol in thirst, the drive to breathe and arousal. Appetite 2000, 34, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eccles, R.; Du-Plessis, L.; Dommels, Y.; Wilkinson, J.E. Cold pleasure. Why we like ice drinks, ice-lollies and ice cream. Appetite 2013, 71, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillis, D.J.; Barwood, M.J.; Newton, P.S.; House, J.R.; Tipton, M.J. The influence of a menthol and ethanol soaked garment on human temperature regulation and perception during exercise and rest in warm, humid conditions. J. Therm. Biol. 2016, 58, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mündel, T.; Jones, D.A. The effects of swilling an l(−)-menthol solution during exercise in the heat. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 109, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, C.J.; Bennett, K.J.M.; Sculley, D.V.; Callister, R.; Taylor, L.; Dascombe, B.J. A comparison of mixed-method cooling interventions on pre-loaded running performance in the heat. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, C.J.; Thoseby, B.; Sculley, D.V.; Callister, R.; Taylor, L.; Dascombe, B.J. Running performance and thermal sensation in the heat are improved with menthol mouth rinse but not ice slurry ingestion. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 26, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riera, F.; Trong, T.; Rinaldi, K.; Hue, O. Precooling does not Enhance the Effect on Performance of Midcooling with Ice-Slush/Menthol. Int. J. Sports Med. 2016, 37, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eccles, R. Menthol: Effects on nasal sensation of airflow and the drive to breathe. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2003, 3, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meamarbashi, A.; Rajabi, A. The effects of peppermint on exercise performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2013, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Craen, A.J.M.; Roos, P.J.; de Vries, A.L.; Kleijnen, J. Effect of colour of drugs: Systematic review of perceived effect of drugs and of their effectiveness. BMJ 1996, 313, 1624–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenko, A.; Schifferstein, H.N.J.; Hekkert, P. Looking hot or feeling hot: What determines the product experience of warmth? Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 1325–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, G.A.; Rolhion, P. Cool colors: Color-induced nasal thermal sensations. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 436, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, A.; Bérdi, M.; Köteles, F.; Bárdos, G. Perceptual characteristics of nutritional supplements determine the expected effectiveness in boosting strength, endurance, and concentration performances. IJSNEM 2013, 23, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briki, W.; Rinaldi, K.; Riera, F.; Trong, T.T.; Hue, O. Perceiving red decreases motor performance over time: A pilot study. Rev. Eur. Psychol. Appl./Eur. Rev. Appl. Psychol. 2015, 65, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, W.G. Spreadsheet for analysis of controlled trials with adjustment for a predictor. Sportscience 2006, 10, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Marshall, S.W.; Batterham, A.M.; Hanin, J. Progressive Statistics for Studies in Sports Medicine and Exercise Science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Smith, G.D. Sifting the evidence-what’s wrong with significance tests? Phys. Ther. 2001, 81, 1464–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, C.J.; Taylor, L.; Dascombe, B.J. Cooling During Exercise: An Overlooked Strategy for Enhancing Endurance Performance in the Heat. Sports Med. 2016, 47, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flood, T.R.; Waldron, M.; Jeffries, O. Oral L-menthol reduces thermal sensation, increases work-rate and extends time to exhaustion, in the heat at a fixed rating of perceived exertion. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 117, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, K.; Sadofsky, L.R.; Morice, A.H. Genetic variants affecting human TRPA1 or TRPM8 structure can be classified in vitro as ‘well expressed’, ‘poorly expressed’ or ‘salvageable’. Biosci. Rep. 2015, 35, e00255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasnelli, J.; Albrecht, J.; Bryant, B.; Lundström, J.N. Perception of specific trigeminal chemosensory agonists. Neuroscience 2011, 189, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michlig, S.; Merlini, J.M.; Beaumont, M.; Ledda, M.; Tavenard, A.; Mukherjee, R.; Camacho, S.; le Coutre, J. Effects of TRP channel agonist ingestion on metabolism and autonomic nervous system in a randomized clinical trial of healthy subjects. Nat. Publish. Group 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, H.R.; Hems, R.; Rowsell, D.G.; Spring, D.J. New compounds with the menthol cooling effect. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1978, 29, 185–200. [Google Scholar]
- Cliff, M.A.; Green, B.G. Sensitization and desensitization to capsaicin and menthol in the oral cavity: Interactions and individual differences. Physiol. Behav. 1996, 59, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillis, D.J.; Weston, N.; House, J.R.; Tipton, M.J. Influence of repeated daily menthol exposure on human temperature regulation and perception. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 139, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botonis, P.G.; Geladas, N.D.; Kounalakis, S.N.; Cherouveim, E.D.; Koskolou, M.D. Effects of menthol application on the skin during prolonged immersion in swimmers and controls. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 27, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, A.H.; Carstens, M.I.; Zanotto, K.L.; Sawyer, C.M.; Ivanov, M.; Cheung, S.; Carstens, E. Self- and Cross-desensitization of Oral Irritation by Menthol and Cinnamaldehyde (CA) via Peripheral Interactions at Trigeminal Sensory Neurons. Chem. Senses 2010, 36, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantzis, A.; Robinson, P.P.; Loescher, A.R. Effects of capsaicin and menthol on oral thermal sensory thresholds. Arch. Oral Biol. 2007, 52, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, C. Just how much of what we taste derives from the sense of smell? Flavour 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, M.U.; Levitan, C.A.; Spence, C. Grape expectations: The role of cognitive influences in color–flavor interactions. Conscious. Cogn. 2010, 19, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Westland, S.; Li, Z.; Pan, Q.; Shin, M.J.; Won, S. The role of individual colour preferences in consumer purchase decisions. Color Res. Appl. 2017, 43, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, T.; Ishiuji, Y.; Yosipovitch, G. Menthol: A refreshing look at this ancient compound. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 57, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bligh, J.; Johnson, K.G. Glossary of terms for thermal physiology. J. Appl. Physiol. 1973, 35, 941–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabanac, M.; Massonnet, B. Thermoregulatory responses as a function of core temperature in humans. J. Physiol. 1977, 265, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenny, G.P.; Jay, O. Thermometry, calorimetry, and mean body temperature during heat stress. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 1689–1719. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Junge, N.; Jørgensen, R.; Flouris, A.D.; Nybo, L. Prolonged self-paced exercise in the heat—Environmental factors affecting performance. Temperature 2016, 3, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Rodriguez, R.; Ortega, J.F.; Hamouti, N. In a hot-dry environment racewalking increases the risk of hyperthermia in comparison to when running at a similar velocity. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Rodriguez, R.; Del Coso, J.; Estevez, E. Thermoregulatory responses to constant versus variable-intensity exercise in the heat. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreiskaemper, D.; Strauss, B.; Hagemann, N.; Büsch, D. Influence of red jersey color on physical parameters in combat sports. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2013, 35, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briki, W.; Hue, O. How Red, Blue, and Green are Affectively Judged. Appl. Cognit. Psychol. 2016, 30, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetterman, A.K.; Robinson, M.D.; Gordon, R.D.; Elliot, A.J. Anger as Seeing Red. Soc. Psychol. Pers. Sci. 2010, 2, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, S.G.; Elliot, A.J.; Feltman, R.; Ambady, N. Red enhances the processing of facial expressions of anger. Emotion 2013, 13, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcó, C.; Conchado, A.; Estevan, I. The Effect of Color on the Use of Electronic Body Protectors in Taekwondo Matches. Percept. Mot. Skills 2016, 122, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Vega, R.; Alberti, S.; Ruíz-Barquín, R.; Soós, I.; Szabo, A. Induced beliefs about a fictive energy drink influences 200-m sprint performance. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2017, 17, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, C.; Clifford, A.; Franklin, A. Color preferences are not universal. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2013, 142, 1015–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rasheed, A.S. An experimental study of gender and cultural differences in hue preference. Front. Psychol. 2015, 30, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokosawa, K.; Schloss, K.B.; Asano, M.; Palmer, S.E. Ecological Effects in Cross-Cultural Differences Between U.S. and Japanese Color Preferences. Cogn. Sci. 2016, 40, 1590–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
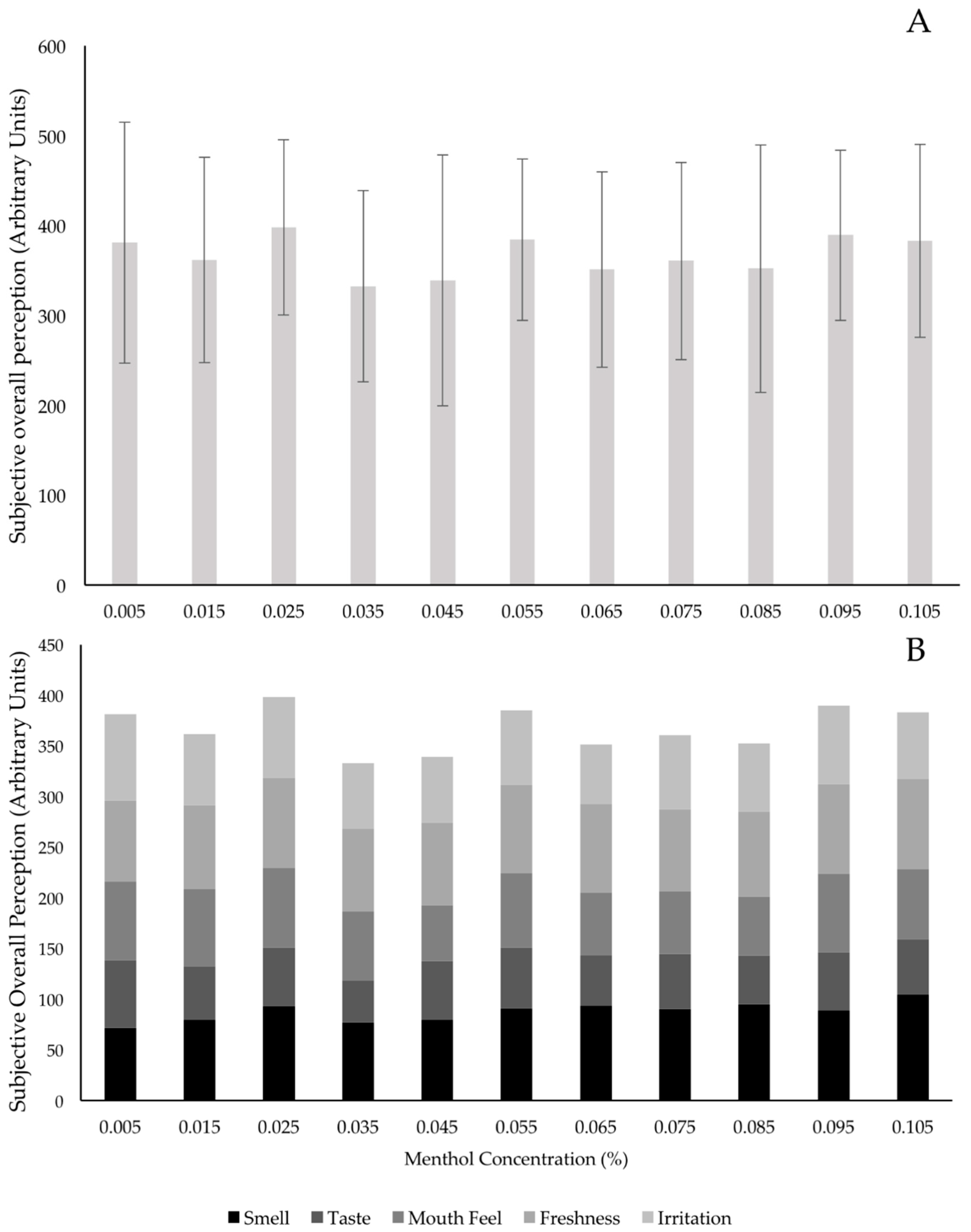
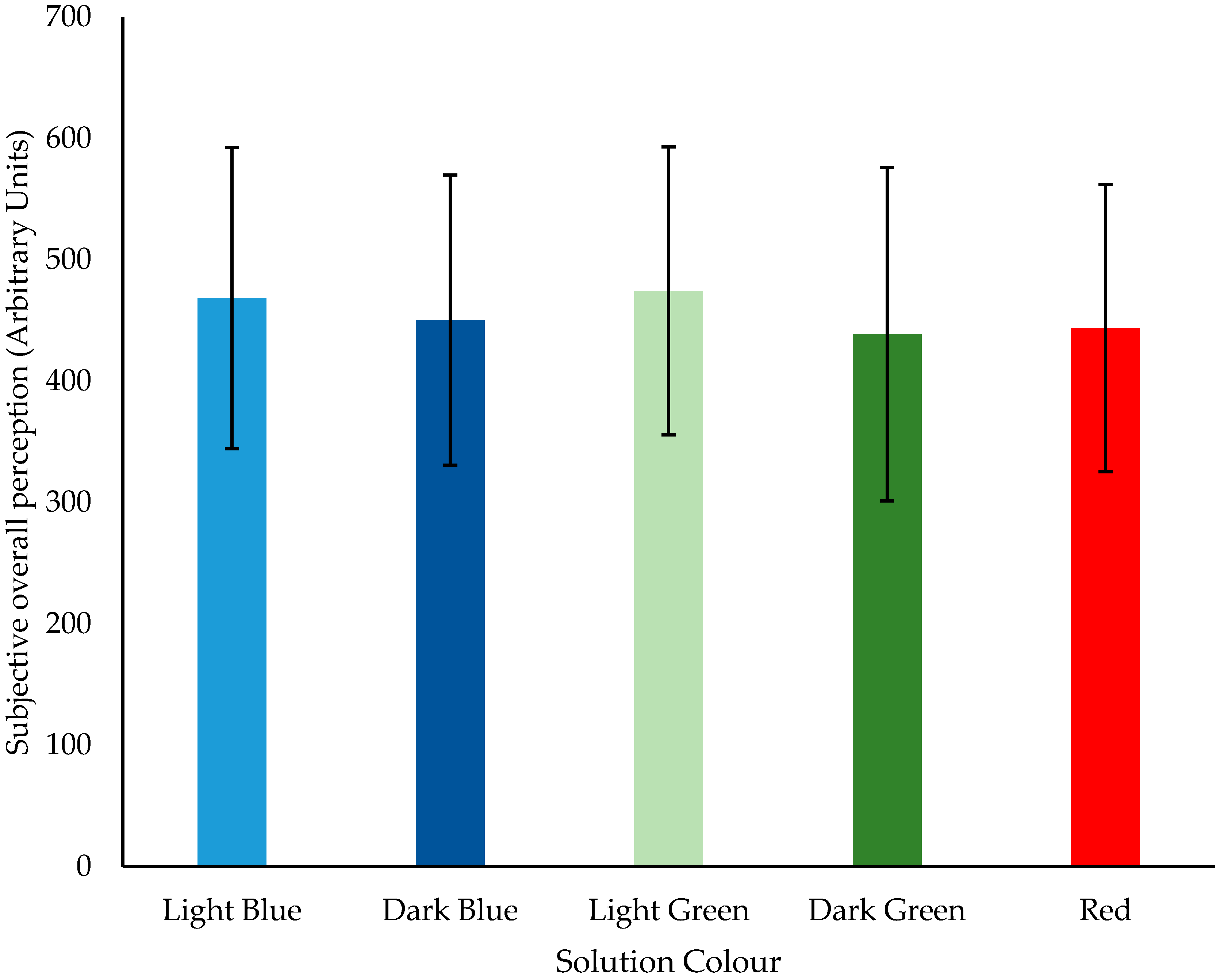
| 0.005 | 0.015 | 0.025 | 0.035 | 0.045 | 0.055 | 0.065 | 0.075 | 0.085 | 0.095 | 0.105 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | 0.27 ± 0.56 | 0.03 ± 0.59 | 0.52 ± 0.59 | 0.49 ± 0.54 | 0.16 ± 0.48 | 0.44 ± 0.50 | 0.29 ± 0.58 | 0.41 ± 0.35 * | 0.09 ± 0.48 | 0.20 ± 0.55 | 0.005 |
| - | x | 0.29 ± 0.32 | 0.24 ± 0.24 | 0.19 ± 0.26 | 0.20 ± 0.39 | 0.09 ± 0.37 | 0.01 ± 0.39 | 0.08 ± 0.51 | 0.23 ± 0.48 | 0.17 ± 0.44 | 0.015 |
| - | - | x | 0.24 ± 0.25 | 0.19 ± 0.27 | 0.19 ± 0.36 | 0.08 ± 0.31 | 0.01 ± 0.35 | 0.08 ± 0.49 | 0.24 ± 0.52 | 0.19 ± 0.47 | 0.025 |
| - | - | - | x | 0.05 ± 0.37 | 0.44 ± 0.36 * | 0.16 ± 0.35 | 0.25 ± 0.32 | 0.41 ± 0.39 * | 0.50 ± 0.48 * | 0.42 ± 0.35 * | 0.035 |
| - | - | - | - | x | 0.38 ± 0.41 | 0.10 ± 0.46 | 0.18 ± 0.50 | 0.10 ± 0.45 | 0.39 ± 0.53 | 0.34 ± 0.53 | 0.045 |
| - | - | - | - | - | x | 0.28 ± 0.39 | 0.20 ± 0.34 | 0.27 ± 0.46 | 0.04 ± 0.39 | 0.02 ± 0.44 | 0.055 |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | x | 0.08 ± 0.30 | 0.01 ± 0.53 | 0.31 ± 0.43 | 0.26 ± 0.33 | 0.065 |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - | x | 0.18 ± 0.51 | 0.25 ± 0.41 | 0.20 ± 0.33 | 0.075 |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | x | 0.13 ± 0.41 | 0.08 ± 0.56 | 0.085 |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | x | 0.06 ± 0.44 | 0.095 |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | x | 0.105 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Best, R.; Spears, I.R.; Hurst, P.; Berger, N.J.A. The Development of a Menthol Solution for Use during Sport and Exercise. Beverages 2018, 4, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4020044
Best R, Spears IR, Hurst P, Berger NJA. The Development of a Menthol Solution for Use during Sport and Exercise. Beverages. 2018; 4(2):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4020044
Chicago/Turabian StyleBest, Russ, Iain R. Spears, Philip Hurst, and Nicolas J. A. Berger. 2018. "The Development of a Menthol Solution for Use during Sport and Exercise" Beverages 4, no. 2: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4020044
APA StyleBest, R., Spears, I. R., Hurst, P., & Berger, N. J. A. (2018). The Development of a Menthol Solution for Use during Sport and Exercise. Beverages, 4(2), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4020044








