Brewing Beer in Microgravity: The Effect on Rate, Yeast, and Volatile Compounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Wort
2.2. Yeast Propagation
2.3. Miniature Fermentation Assay
2.4. Clinostats
2.5. Density
2.6. Yeast in Suspension
2.7. Total Yeast and Viability
2.8. Volatile Extraction
2.9. Gas Chromatography (GC-MS)
2.10. Volatile Identification
2.11. Free Amino Nitrogen (FAN)
2.12. RNA Extraction and Gene Expression Analysis
2.13. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
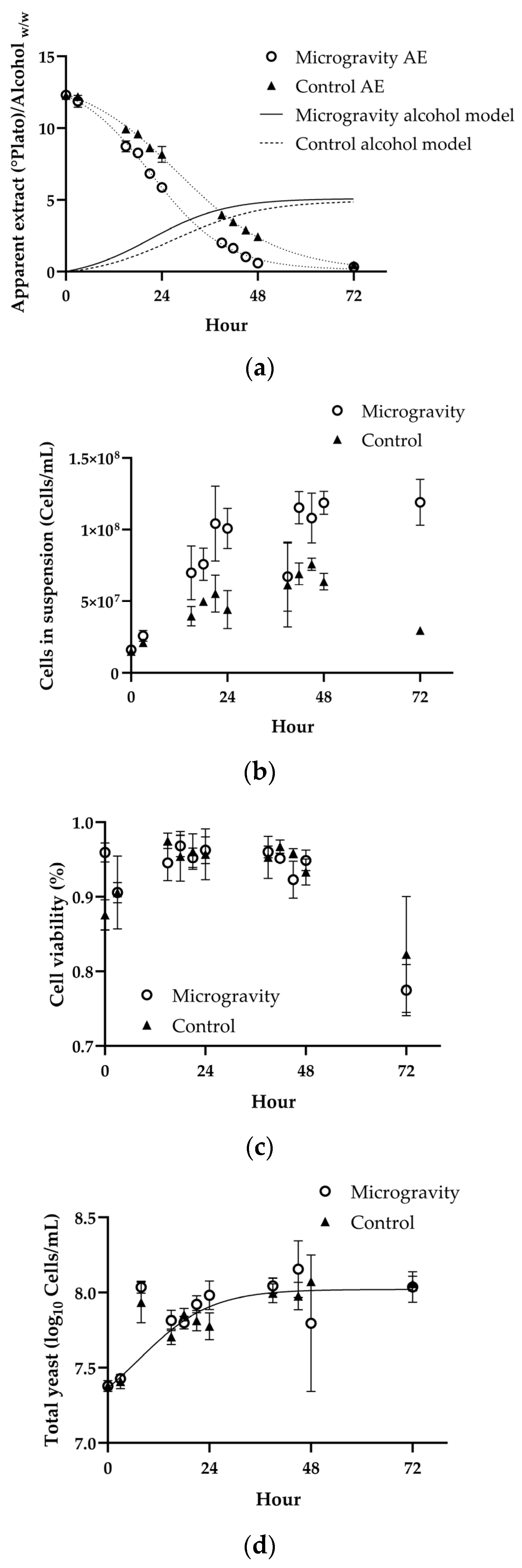
3.1. Yeast Growth Kinematics
3.2. Free Amino Nitrogen and Volatile Compound Analysis
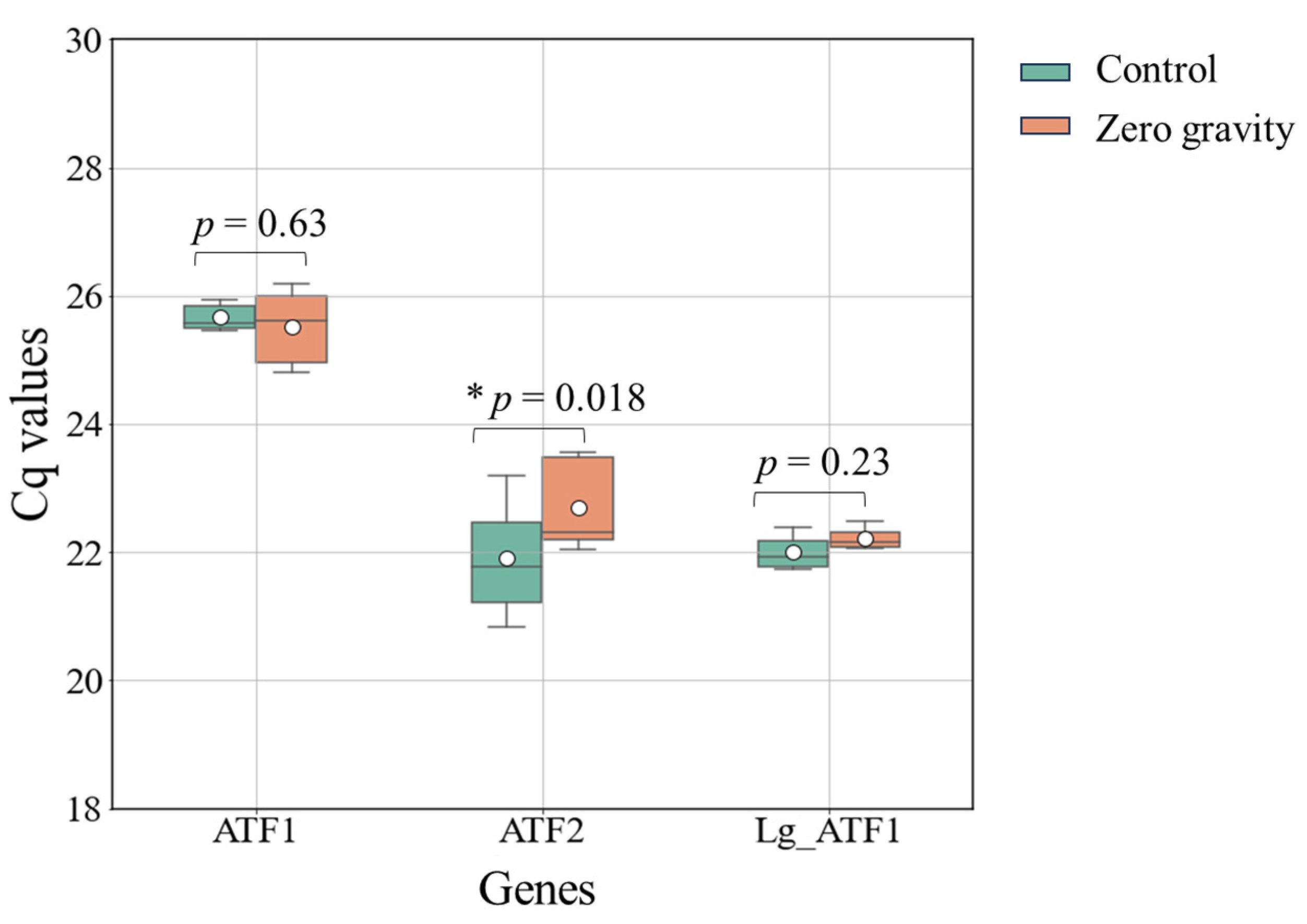
3.3. Gene Expression
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klaus, D. Microgravity and its implications for fermentation biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Li, D.G.; Huang, Y.; Liu, C.T. Effects of spaceflight and simulated microgravity on microbial growth and secondary metabolism. Mil. Med. Res. 2018, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parapouli, M.; Vasileiadis, A.; Afendra, A.S.; Hatziloukas, E. Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its industrial applications. AIMS Microbiol. 2020, 6, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kulagina, N.; Besseau, S.; Godon, C.; Goldman, G.H.; Papon, N.; Courdavault, V. Yeasts as biopharmaceutical production platforms. Front. Fungal Biol. 2021, 2, 733492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez Castro, E.; Memari, G.; Ata, Ö.; Mattanovich, D. Carbon efficient production of chemicals with yeasts. Yeast 2023, 40, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rivero, C.; López-Gómez, J.P. Unlocking the potential of fermentation in cosmetics: A review. Fermentation 2023, 9, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.; Pontes, A.; Almeida, P.; Barbosa, R.; Serra, M.; Libkind, D.; Hutzler, M.; Goncalves, P.; Sampaio, J. Distinct domestication trajectories in top-fermenting beer yeasts and wine yeasts. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 2750–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiano, A. Craft beer: An overview. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 20, 1829–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, S.; Verstrepen, K.; Saels, V.; Rouck, G.; Aerts, G.; Verstrepen, K. A large set of newly created interspecific Saccharomyces hybrids increases aromatic diversity in lager beers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 8202–8214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Niu, C.; Zheng, F.; Li, Q. Evaluating the physiology and fermentation performance of the lager yeast during very high gravity brewing with increased temperature. LWT 2023, 173, 114312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, P.; Bryce, J.; Stewart, G. The effects of osmotic pressure and ethanol on yeast viability and morphology. J. Inst. Brew. 2003, 109, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purevdorj-Gage, B.; Sheehan, K.; Hyman, L. Effects of low-shear modeled microgravity on cell function, gene expression, and phenotype in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 4569–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versari, S.; Longinotti, G.; Barenghi, L.; Maier, J.; Bradamante, S. The challenging environment on board the international space station affects endothelial cell function by triggering oxidative stress through thioredoxin interacting protein overexpression: The Esa-sphinx experiment. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 4466–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, S.; Ohnuki, S.; Abe, F.; Ohya, Y. Simulated microgravity triggers characteristic morphology and stress response in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Yeast 2018, 36, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, T.; Allen, P.; Gunter, M.; Chiang, J.; Giaever, G.; Nislow, C.; Birdsall, H. Physical forces modulate oxidative status and stress defense mediated metabolic adaptation of yeast colonies: Spaceflight and microgravity simulations. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 2017, 30, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, V.; Gonçalves, J.; Figueira, J.A.; Ornelas, L.P.; Branco, R.N.; Câmara, J.S.; Pereira, J.A.M. Beer volatile fingerprinting at different brewing steps. Food Chem. 2020, 326, 126856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Nagasawa, N.; Iwamatsu, A.; Bogaki, T.; Tamai, Y.; Hamachi, M. Molecular cloning, sequence analysis, and expression of the yeast alcohol acetyltransferase gene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 2786–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, M.J.; Huttenhower, C.; Airoldi, E.M.; Rosenstein, R.; Matese, J.C.; Gresham, D.; Boer, V.M.; Troyanskaya, O.G.; Botstein, D. Coordination of growth rate, cell cycle, stress response, and metabolic activity in yeast. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 352–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Luo, Q.; Lin, C.; Kuang, D.; Song, G. Simulated microgravity inhibits osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via depolymerizing f-actin to impede taz nuclear translocation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajardo-Cavazos, P.; Nicholson, W. Mechanotransduction In Prokaryotes: A possible mechanism of spaceflight adaptation. Life 2021, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollero, S.; Roberts, S.; Bauer, F.F.; Divol, B. Agitation impacts fermentation performance as well as carbon and nitrogen metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae under winemaking conditions. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2018, 24, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delente, J.; Akin, C.; Krabbe, E.; Ladenburg, K. Carbon dioxide in fermenting beer—Part II. MBAA TQ 1968, 5, 228–234. [Google Scholar]
- Boswell, C.D.; Nienow, A.W.; Hewitt, C.J. Studies on the effect of mechanical agitation on the performance of brewing fermentations: Fermentation rate, yeast physiology, and development of flavor compounds. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2002, 60, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASBC Methods of Analysis. MALT-4: Extract. In American Society of Brewing Chemists; ASBC Methods of Analysis: 2011.
- ASBC Methods of Analysis. YEAST-14: Miniature fermentation assay. In American Society of Brewing Chemists; ASBC Methods of Analysis: 2011.
- ASBC Methods of Analysis. Beer-2: Specific Gravity, B. By digital density meter. In American Society of Brewing Chemists; ASBC Methods of Analysis: 2014.
- ASBC Methods of Analysis. YEAST—4: Microscopic yeast cell counting. In American Society of Brewing Chemists; ASBC Methods of Analysis: 2016.
- Thompson-Witrick, K.A.; Rouseff, R.L.; Cadawallader, K.R.; Duncan, S.E.; Eigel, W.N.; Tanko, J.M.; O’Keefe, S.F. Comparison of two extraction techniques, solid-phase microextraction versus continuous liquid–liquid extraction/solvent-assisted flavor evaporation, for the analysis of flavor compounds in gueuze lambic beer. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, C571–C576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butzke, C.E. Survey of yeast assimilable nitrogen status in musts from California, Oregon, and Washington. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1998, 49, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstehen, K.J.; Van Laere, S.D.M.; Vanderhaegen, B.M.P.; Derdelinckx, G.; Dufour, J.P.; Pretorius, I.S.; Winderickx, J.; Thevelein, J.M.; Delvaux, F.R. Expression levels of the yeast alcohol acetyltransferase genes ATF1, Lg-ATF1, and ATF2 control the formation of a broad range of volatile esters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5228–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.J.; Josey, M.; MacIntosh, A.J.; Maskell, D.L.; Alex Speers, R. Predicting fermentation rates in Ale, Lager and Whisky. Fermentation 2021, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, A.; MacIntosh, A.J.; Speers, R.A.; St Mary, C. Modeling yeast in suspension during laboratory and commercial fermentations to detect aberrant fermentation processes. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2020, 78, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson-Witrick, K.A.; Pitts, E. Nitrogen content in craft malts: Effects on total ester concentration in beer. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2020, 78, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.E.; Stewart, G.G. Free Amino Nitrogen in Brewing. Fermentation 2019, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meilgaard, M.C. Flavour chemistry of beer. Part II: Flavor and threshold of 239 aroma volatiles. MBAA. Technol. Q. 1975, 12, 151–168. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, D.-Y.; Ge, J.-L.; Song, Y.-M.; Feng, P.-P.; Lin, L.-C.; Guo, L.-Y.; Zhang, C.-Y. Regulating the ratio of higher alcohols to esters by simultaneously overexpressing ATF1 and deleting BAT2 in brewer’s yeast Saccharomyces pastorianus. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, E.J.; Teixeira, J.A.; Brányik, T.; Vicente, A.A. Yeast: The soul of beer’s aroma—A review of flavour-active esters and higher alcohols produced by the brewing yeast. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 1937–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meilgaard, M.C. Flavor chemistry of beer: Part I: Flavor interactionbetween principal volatiles. MBAA. Technol. Q. 1975, 12, 107–117. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, S.; Miks, M.H.; de Carvalho, B.T.; Foulquié-Moreno, M.R.; Thevelein, J.M. The molecular biology of fruity and floral aromas in beer and other alcoholic beverages. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 43, 193–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaniran, A.O.; Hiralal, L.; Mokoena, M.P.; Pillay, B. Flavour-active volatile compounds in beer: Production regulation control. J. Inst. Brew. 2017, 123, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhsler, M.; Leitsch, D.; Müller, N.; Walochnik, J. Validation of reference genes for the normalization of RT-qPCR gene expression in Acanthamoeba spp. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadai, C.; Campanaro, S.; Giacomini, A.; Corich, V. Selection and validation of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR studies during Saccharomyces cerevisiae alcoholic fermentation in the presence of sulfite. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 215, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Song, X.; Feng, W.; Xiong, A.S. Suitable reference genes for accurate gene expression analysis in parsley (Petroselinum crispum) for abiotic stresses and hormone stimuli. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, H.; Fujiwara, D.; Momma, T.; Tanaka, K.; Sone, H.; Nagasawa, N.; Tamai, Y. Isolation and characterization of the ATF2 gene encoding alcohol acetyltransferase II in the bottom fermenting yeast Saccharomyces pastorianus. Yeast 1999, 15, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procopio, S.; Qian, F.; Becker, T. Function and regulation of yeast genes involved in higher alcohol and ester metabolism during beverage fermentation. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2011, 233, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dack, R.E.; Black, G.W.; Koutsidis, G.; Usher, S.J. The effect of Maillard reaction products and yeast strain on the synthesis of key higher alcohols and esters in beer fermentations. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Average FAN (mg/L) | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| Control 0 h | 104.482 a | 8.034 |
| Microgravity 0 h | 107.983 a | 2.880 |
| Control final | 20.506 b | 2.145 |
| Microgravity final | 22.981 b | 2.343 |
| Approximate Concentrations (mg/L) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | LRI | Control (T0) | Microgravity (T0) | Control Beer | Microgravity Beer |
| Acids | |||||
| 3-methylbutanoic acid (Isovaleric acid) | 936 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.0 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | ND |
| 2-methylbutanoic acid | 943 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.08 ± 0.01 G | 0.05 ± 0.02 G |
| Heptanoic acid | 1086 | ND | ND | 0.03 ± 0.01 G | 0.02 ± 0.01 G |
| Octanoic acid | 1176 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 1.69 ± 0.75 G | 0.72 ± 0.10 G |
| Nonanoic acid | 1265 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.15 ± 0.08 G | 0.15 ± 0.02 G |
| Decanoic acid | 1353 | ND | ND | 0.32 ± 0.17 G | 0.23 ± 0.12 G |
| Subtotal | 0.06 ± 0.03 G | 0.09 ± 0.01 G | 2.31 ± 0.97 G | 1.17 ± 0.16 G | |
| Alcohols | |||||
| 3-methylbutanol (Isoamyl alcohol) | 757 | 0.34 ± 0.04 | 0.39 ± 0.03 | 20.68 ± 0.76 G | 26.85 ± 6.41 G |
| 2-Ethylhexanol | 1040 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.01 B | 0.05 ± 0.01 A |
| 1-Octanol | 1074 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.02 G | 0.10 ± 0.01 G |
| Phenethyl alcohol | 1112 | 0.10 ± 0.04 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 9.79 ± 2.61 G | 12.07 ± 2.24 G |
| 1-Nonanol | 1172 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.01 B | 0.06 ± 0.01 A |
| 2-Decanol | 1203 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | ND | 0.06 ± 0.02 |
| Dodecanol | 1469 | ND | ND | 0.01 ± 0.01 G | 0.01 ± 0.01 G |
| Subtotal | 0.52 ± 0.03 G | 0.58 ± 0.04 G | 30.61 ± 2.79 G | 39.2 ± 8.54 G | |
| Aldehydes | |||||
| Furfural | 840 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.2 ± 0.02 | ND | ND |
| Benzeneacetaldehyde | 1044 | ND | ND | 0.03 ± 0.01 G | 0.04 ± 0.01 G |
| Nonanal | 1100 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.01 G | 0.08 ± 0.01 G |
| Decanal | 1206 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | ND | 0.04 ± 0.01 |
| 3-Phenylfuran | 1222 | ND | ND | 0.01 ± 0.01 | ND |
| Subtotal | 0.18 ± 0.01 A | 0.26 ± 0.01 B | 0.14 ± 0.02 G | 0.16 ± 0.02 G | |
| Esters | |||||
| 3-Methylbutyl acetate (Isoamyl acetate) | 882 | ND | ND | 8.19 ± 0.83 A | 1.52 ± 0.14 B |
| Ethyl hexanoate (caproate) | 1002 | ND | ND | 0.60 ± 0.25 G | 0.26 ± 0.06 G |
| Ethyl heptanoate | 1094 | ND | ND | 0.02 ± 0.01 A | 0.01 ± 0.01 B |
| Ethyl octanoate (caprylate) | 1197 | ND | ND | 3.75 ± 0.32 A | 2.47 ± 0.61 B |
| 2-Phenethyl acetate | 1249 | 0.08 ± 0.06 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 8.42 ± 0.51 A | 3.54 ± 1.27 B |
| Ethyl nonanoate | 1284 | ND | ND | 0.01 ± 0.01 G | 0.01 ± 0.01 G |
| Ethyl 9-decenoate | 1369 | ND | ND | 0.39 ± 0.03 G | 0.44 ± 0.12 G |
| Ethyl decanoate (caprate) | 1381 | ND | ND | 0.34 ± 0.01 A | 0.18 ± 0.05 B |
| Subtotal | 0.08 ± 0.06 G | 0.04 ± 0.00 G | 21.71 ± 0.36 A | 8.42 ± 2.22 B | |
| Ketones | |||||
| Damascenone | 1369 | 0.03 ± 0.00 G | 0.03 ± 0.00 G | 0.03 ± 0.01 G | 0.03 ± 0.01 G |
| Phenols | |||||
| 4-Vinylguaiacol | 1299 | 0.01 ± 0.00 A | 0.03 ± 0.00 B | 0.10 ± 0.04 G | 0.10 ± 0.03 G |
| Overall Total | 0.89 ± 0.11 G | 1.03 ± 0.05 G | 54.90 ± 3.47 G | 49.09 ± 10.95 G | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendoza, P.F.; Thompson-Witrick, K.A.; Moreno, S.R.; Cárdenas-Pinto, S.; Jia, Z.; Zotarelli, L.; Zhang, B.; MacIntosh, A.J. Brewing Beer in Microgravity: The Effect on Rate, Yeast, and Volatile Compounds. Beverages 2024, 10, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10020047
Mendoza PF, Thompson-Witrick KA, Moreno SR, Cárdenas-Pinto S, Jia Z, Zotarelli L, Zhang B, MacIntosh AJ. Brewing Beer in Microgravity: The Effect on Rate, Yeast, and Volatile Compounds. Beverages. 2024; 10(2):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10020047
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendoza, Pedro Fernandez, Katherine A. Thompson-Witrick, Skylar R. Moreno, Santiago Cárdenas-Pinto, Zhen Jia, Lincoln Zotarelli, Boce Zhang, and Andrew J. MacIntosh. 2024. "Brewing Beer in Microgravity: The Effect on Rate, Yeast, and Volatile Compounds" Beverages 10, no. 2: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10020047
APA StyleMendoza, P. F., Thompson-Witrick, K. A., Moreno, S. R., Cárdenas-Pinto, S., Jia, Z., Zotarelli, L., Zhang, B., & MacIntosh, A. J. (2024). Brewing Beer in Microgravity: The Effect on Rate, Yeast, and Volatile Compounds. Beverages, 10(2), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10020047








