Water Quality in a Small Lowland River in Different Land Use
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
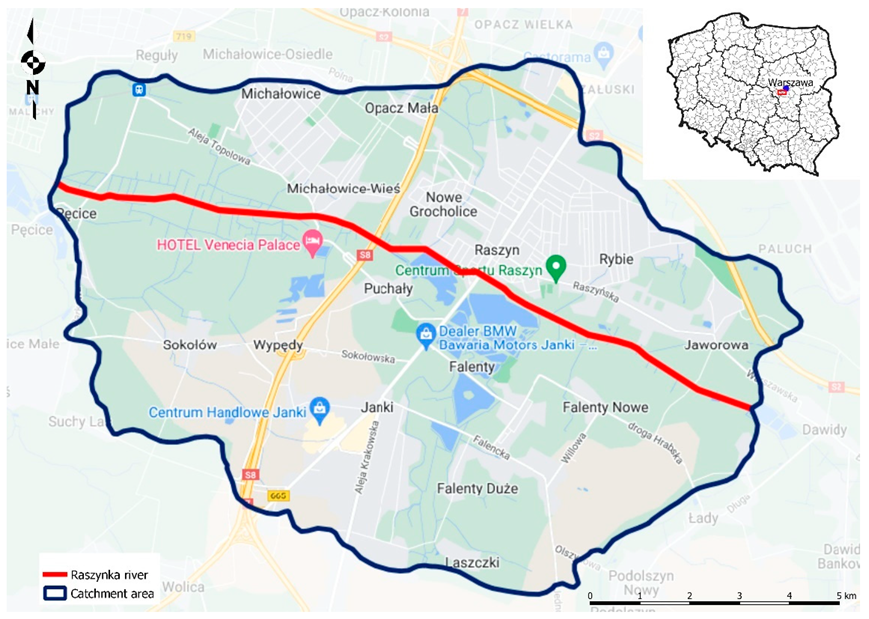
2.1. Characteristics of the Raszynka River Catchment
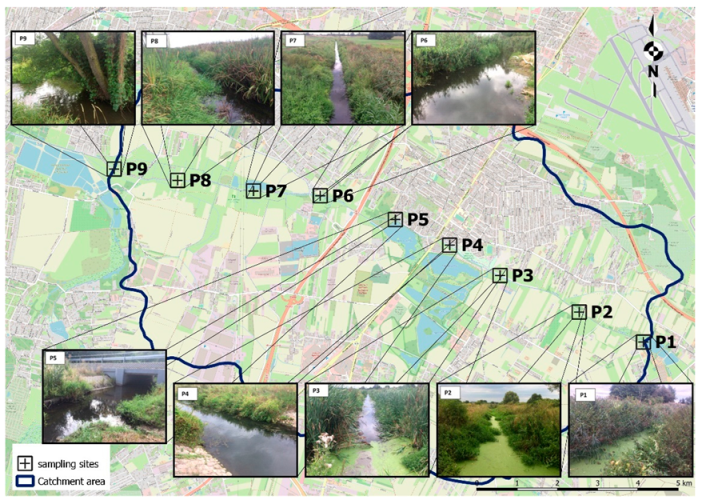
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Methodology of Determination of Selected Physicochemical Indices
- Ammonium (NH4+) was determined by means of the flow injection analysis method (FIA) with spectrophotometric detection [38].
- Nitrates (NO3−) were determined by means of the flow injection analysis (FIA) with spectrophotometric detection [39].
- Total phosphorus (TP) was determined by means of the method with the application of ascorbic acid [40].
- Chlorides (Cl−) were determined by means of the titration method with the application of silver nitrate (Mohr method) [41].
- Chemical oxygen demand (COD) was determined by means of the titration method with the application of potassium permanganate [42].
- EC was determined conductometrically [43].
- pH was determined by means of the potentiometric method [44].
- Total alkalinity was determined by means of the titration method against phenolphthalein and methyl orange [45].
2.4. Statistical Analysis of Results
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mosiej, J.; Skrzypski, J.; Suchecka, T. Impact of the Łódź Agglomeration on water quality indicators and load of pollutants in Ner and Warta rivers, in the period 1995–2011. Acta Sci. Pol. Form. Circumiectus 2019, 18, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemirycz, E.; Gozdek, J.; Koszka-Maroń, D. Variability of Organic Carbon in Water and Sediments of the Odra River and Its Tributaries. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2006, 15, 557–563. [Google Scholar]
- Strzebońska, M.; Kostka, A. Geochemical State of Wilga River Environment in Kraków (Poland)—Historical Aspects and Existing Issues. Minerals 2021, 11, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhoff-Wrześniewska, A.; Strzelczyk, M.; Helis, M.; Paszkiewicz-Jasińska, A.; Gruss, Ł.; Pulikowski, K.; Skorulski, W. Identification of catchment areas with nitrogen pollution risk for lowland river water quality. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2022, 48, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Węsławski, J.M. Zdrowe rzeki, zdrowy Bałtyk. Acad.-Mag. Pol. Akad. Nauk. 2020, 62, 81–83. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Deluga, W. Znaczenie marketingu ekologicznego w zachowaniu czystości wód Morza Bałtyckiego. Folia Pomeranae Univ. Technol. Stetin. Oeconomica 2018, 92. (In Polish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhao, D.; Fan, X.; Liu, C.; Zhao, G. Landscape dynamics facilitated non-point source pollution control and regional water security of the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Environ. Impact Assess. 2022, 92, 106696, ISSN 0195-9255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowska, E.; Matej-Łukowicz, K.; Nawrot, N.; Gajewska, M.; Obarska-Pempkowiak, H. Wstępna ocena wielkości stężeń związków azotu i fosforu odprowadzanych z wodami powierzchniowymi do Zatoki Puckiej z terenu gminy Puck. Technol. Wody 2019, 4, 14–21. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Cvetkovic, V.; Destouni, G. Scenarios of Nutrient-Related Solute Loading and Transport Fate from Different Land Catchments and Coasts into the Baltic Sea. Water 2019, 11, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fiedler, H.; Liu, W.; Pan, T.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, T. Influence of land use type and urbanization level on the distribution of pharmaceuticals and personal care products and risk assessment in Beiyun River, China. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132075, ISSN 0045-6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bol, R.; Gruau, G.; Mellander, P.-E.; Dupas, R.; Bechmann, M.; Skarbøvik, E.; Bieroza, M.; Djodjic, F.; Glendell, M.; Jordan, P.; et al. Challenges of Reducing Phosphorus Based Water Eutrophication in the Agricultural Landscapes of Northwest Europe. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromiec, M. Nowe koncepcje gospodarki wodno-ściekowej-osadowej. Ocena Gospod. Ściekowo-Osadowej Polsce 2020, 7. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Piekar, S.; Urbaś, M. Ocena skuteczności usuwania zanieczyszczeń w gminnej oczyszczalni ścieków w Chwałkowie. Współczesne Probl. Ochr. Sr. Energetyki 2020, 161. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Gracia-Gracia, G.; Jagtap, S. Enhancement of a Spent Irrigation Water Recycling Process: A Case Study in a Food Business. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristi, I.; von Schiller, D.; Arroita, M.; Barceló, D.; Ponsatí, L.; García-Galán, M.J.; Sabater, S.; Elosegi, A.; Acuña, V. Mixed effects of effluents from a wastewater treatment plant on river ecosystem metabolism: Subsidy or stress? Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 1398–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Büttner, O.; Kumar, R.; Jäger, C.; Jawitz, J.W.; Rao, P.S.C.; Borchardt, D. Spatial patterns of water quality impairments from point source nutrient loads in Germany’s largest national River Basin (Weser River). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotova, G.; Lazarova, S.; Kudłak, B.; Zlateva, B.; Mihaylova, V.; Wieczerzak, M.; Venelinov, T.; Tsakovski, S. Assessment of the Bulgarian Wastewater Treatment Plants’ Impact on the Receiving Water Bodies. Molecules 2019, 24, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Cui, N.; Cheng, S. Water quality assessment of an urban river receiving tail water using the single-factor index and principle component analysis. Water Supply 2019, 19, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim Dantas, M.; Rodrigues Barroso, G.; Corrêa Oliveira, S. Performance of sewage treatment plants and impact of effluent discharge on receiving water quality within an urbanized area. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, V.; Yotova, G.; Kudłak, B.; Venelinov, T.; Tsakovski, S. Chemometric Evaluation of WWTPs’ Wastewaters and Receiving Surface Waters in Bulgaria. Water 2022, 14, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiak-Wójcicka, K. Assessment of Water Resources in Poland. In Quality of Water Resources in Poland; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, J.; von Fumetti, S.; Kelly-Quinn, M. The importance of small waterbodies for biodiversity and ecosystem services: Implications for policy makers. Hydrobiologia 2017, 793, 3–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, S.; Rasmussen, J.J.; Süß, A. Specifics and challenges of assessing exposure and effects of pesticides in small water bodies. Hydrobiologia 2017, 793, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crnobrnja-Isailović, J.; Adrović, A.; Bego, F.; Čađenović, N.; Hadžiahmetović, J.; Jablonski, D.; Sterijovski, B.; Jovanović Glavaš, O. The Importance of Small Water Bodies’ Conservation for Maintaining Local Amphibian Diversity in the Western Balkans. In Small Water Bodies of the Western Balkans; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 351–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfrin, A.; Bombi, P.; Traversetti, L.; Larsen, S.; Scalici, M. A landscape-based predictive approach for running water quality assessment a Mediterranean case study. J. Nat. Conserv. 2016, 30, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara, M.; Jamil, N.R.; Bin Abdullah, A.F. Impact of land uses on water quality in Malaysia a review. Ecol. Process. 2019, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, R.O.; Hochmuth, G.J.; Martinez, C.J.; Boyer, T.H.; Dukes, M.D.; Toor, G.S.; Cisar, J.L. Evaluating nutrient impacts in urban water-sheds challenges and research opportunities. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 173, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dudgeon, D.; Cheng, D.; Thoe, W.; Fok, L.; Wang, Z.; Lee, J.H.W. Impacts of land use and water quality on macroinvertebrate communities in the Pearl River drainage basin, China. Hydrobiologia 2010, 652, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, R.; Zhang, J. Relationship between landscape pattern and water quality of the multi-scale effects in the Yellow River Basin. J. Lake Sci. 2021, 33, 737–748. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, B.; Ju, X.; Chang, J.; Ge, Y.; Vitousek, P.M. Integrated reactive nitrogen budgets and future trends in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8792–8797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, N.A.; Groffman, P.M.; Keller, A.A.; Prager, J.C. A watershed nitrogen and phosphorus balance the upper Potomac River basin. Estuaries 1992, 15, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzha, A.C.; Rufino, M.C.; Okoth, S.; Jacobs, S.; Nobrega, R.L.B. Impacts of land use and land cover change on surface runoff, dis-charge and low flows evidence from East Africa. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 15, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yang, P.; Geng, J.; Yin, H.; Chen, K. Sediment internal nutrient loading in the most polluted area of a shallow eutrophic lake (Lake Chaohu, China) and its contribution to lake eutrophication. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PWN. Kondracki Geografia Regionalna Polski; PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 2002; p. 440. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Woś, A. Klimat Polski; PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 1999; p. 301. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Burzyńska, I. Evaluation of selected physical and chemical indicators in Raszynka River. Water-Environ.-Rural. Areas 2016, 16, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Regulation of the Minister of Maritime Economy and Inland Navigation. on 11 October 2019. On the classification of ecological condition, ecological potential, chemical condition, and the method of classification of the state of surface water bodies, as well as environmental quality standards for priority substances. Journal of Laws 2019, 21, 255. [Google Scholar]
- PN-EN ISO 11732; Water Quality—Determination of Ammonium Nitrogen by Flow Analysis (CFA and FIA) and Spectrometric Detection. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warszawa, Poland, 2007.
- PN-EN ISO 13395; Water Quality—Determination of Nitrite Nitrogen by and Nitrate Nitrogen and the sum by Flow Analysis (CFA and FIA) and Spectrometric Detection. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warszawa, Poland, 2001.
- PN-EN ISO 6878:2006; Total Phosphorus (P) Was Determined by the Ascorbic Acid Method. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warszawa, Poland, 2006.
- PN-ISO 9297:1994; Water Quality—Determination of Chloride—Silver Nitrate Titration with Chromate Indicator (Mohr’s Method). Polish Committee for Standardization: Warszawa, Poland, 1994.
- PN-ISO 6060:2006; Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) Was Determined by Titration Using Potassium Permanganate. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warszawa, Poland, 2006.
- PN-EN 27888:1999; Water Quality—Determination of Electrical Conductivity. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warszawa, Poland, 1999.
- PN-EN ISO 10523:2012; Water Quality—Determination of pH. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warszawa, Poland, 2012.
- PN-EN ISO 9963-1:2001; Water Quality—Determination of Alkalinity—Part 1: Determination of Total and Composite Alkalinity. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warszawa, Poland, 2001.
- Nanda, A.; Mohapatra, B.B.; Mahapatra, A.P.K.; Mahapatra, A.P.K.; Mahapatra, A.P.K. Multiple comparison test by Tukey’s honestlysignificant difference (HSD): Do the confident levelcontrol type I error. Int. J. Stat. Appl. Math. 2021, 6, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Zarzuela, I.; Halaihel, N.; Balcázar, J.L.; Ortega, C.; Vendrell, D.; Perez, T.; Alonso, J.L.; de Blas, I. Effect of fish farming on the water quality of rivers in northeast Spain. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raczyńska, M.; Machula, S.; Choiński, A.; Sobkowiak, L. Influence of the fish pond aquaculture effluent discharge on abiotic environmental factors of selected rivers in Northwest Poland. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartnicki, J. Atmospheric Contribution to Eutrophication of the Baltic Sea. Air Pollut. Model. Its Appl. 2019, XXVI, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paule-Mercado, M.A.; Lee, B.Y.; Memon, S.A.; Umer, S.R.; Salim, I.; Lee, C.-H. Influence of land development on storm water runoff from a mixed land use and land cover catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 2142–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abobakr Yahya, A.S.; Ahmed, A.N.; Binti Othman, F.; Ibrahim, R.K.; Afan, H.A.; El-Shafie, A.; Fai, C.M.; Hossain, M.S.; Ehteram, M.; Elshafie, A. Water Quality Prediction Model Based Support Vector Machine Model for Ungauged River Catchment under Dual Scenarios. Water 2019, 11, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhamalov, R.G.; Kosolapov, A.E.; Vlasov, K.G.; Myagkova, K.G.; Reshetnyak, O.S.; Safronova, T.I. Pollution Degree of the Don River Water. Water Resour. Regime Water Bodies 2019, 46, S1–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, H.; Cruz, P.S.; Viana, L.G.; de Lucena Silva, D.; de Lucena Barbosa, J.E. Influence of the use and the land cover of the catchment in the water quality of the semiarid tropical reservoirs. J. Hyperspectral Remote Sens. 2017, 7, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Xu, G. Influence of land use and land cover patterns on seasonal water quality at multi-spatial scales. Catena 2017, 151, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro, P.; Bertrán, C.; Tapia, J.; Hauenstein, E.; Peña-Cortés, F.; Vergara, C.; Cerna, C.; Vargas-Chacoff, L. Effects of local land-use on riparian vegetation, water quality, and the functional organization of macroinvertebrate assemblages. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torma, S.; Koco, Š.; Vilček, J.; Čermák, P. Nitrogen and phosphorus transport in the soil from the point of view of water pollution. Folia Geogr. 2019, 61, 143–156, ISSN 1336-6157. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.Q.; Amatulli, G.; Sethi, T. Estimating nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations in streams and rivers, within a machine learning framework. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattan, K.J.; Corriveau, J.C.; Brua, R.B.; Clup, J.M.; Yates, A.G.; Chambers, P.A. Quantifying seasonal variation in total phosphorus and nitrogen from prairie streams in the Red River Basin, Manitoba Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 575, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, C.; Jarvie, H.P. Agriculture, Community, River Eutrophication and the Water Framework Directive. Hydrol. Process 2005, 19, 1895–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.; Kline, K.M. Nutrient Concentrations in Maryland Non-Tidal Streams. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 178, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingming, H.; Yuchun, W.; Pengcheng, D.; Yong, S.; Aiminc, C.; Cong, L.; Yufei, B.; Yanhui, L.; Shanze, L.; Panwei, Z. Tracing the sources of nitrate in the rivers and lakes of the southern areas of the Tibetan Plateau using dual nitrate isotopes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawłat-Zawrzykraj, A. Inwentaryzacja i waloryzacja przyrodniczo-krajobrazowa górnego biegu rzeki Raszynka [Ecological and landscape inventory and evaluation of the upper course of the Raszynka River]. Woda-Sr. Obsz. Wiejskie. 2003, 3, 97–110. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Abed, A.A.; Ewaid, S.H.; Al-Ansari, N. Evaluation of Water quality in the Tigris River within Baghdad, Iraq using Multivariate Statistical Techniques. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1294, 072025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Kumar, R.; Parveen, S.; Verma, N. Reduction in water pollution in Yamuna River due to lockdown under COVID-19 Pandemic. Pharma Innov. J. 2020, 9, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Ren, N. Characterizing water pollution potential in life cycle impact assessment based on bacterial growth and water quality models. Water 2018, 10, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Singh, U.K.; Ojha, S.N. Evaluation of geochemical data of Yamuna River using WQI and multivariate statistical analyses: A case study. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2019, 17, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waziri, M. Physicochemical and Bacteriological Investigation of Surface and Groundwater of Kumadugu-Yobe Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Maiduguri, Maiduguri, Nigeria, 2006; pp. 88–89. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, C.E. The Chemical Oxygen Demand of Waters and Biological Materials from Ponds. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1973, 102, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, R.; Seeger, J.; Rupp, H. Lysimeter studies in East Germany concerning the influence of set aside of intensively farmed land on the seepage water quality. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1998, 67, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lax, S.M.; Peterson, E.W.; Van der Hoven, S.J. Stream chloride concentrations as a function of land use: A comparison of an agricultural watershed to an urban agricultural watershed. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Wagner, P.D.; Fohrer, N. Effects of land cover, topography, and soil on stream water quality at multiple spatial and seasonal scales in a German lowland catchment. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniewski, P. Sezonowe Zmiany Wybranych Cech Fizyczno-Chemicznych wód Małej Rzeki Podmiejskiej na Przykładzie Dzierżąznej; Monografie Komitetu Gospodarki Wodnej PAN: Warszawa, Poland, 2014; Volume 20, pp. 407–416. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Jarvie, H.P.; Neal, C.; Withers, P.J.A. Sewage-effluent phosphorus: A greater risk to river eutrophication than agricultural phosphorus? Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 360, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, J.; O’Hare, M.; Bowes, M.J.; Jones, I. How green is my river? A new paradigm of eutrophication in rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 365, 66–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Rozemeijer, J.; van Breukelen, B.M.; Ouboter, M.; van der Vlugt, C.; Broers, H.P. Groundwater impacts on surface water quality and nutrient loads in lowland polder catchments: Monitoring the greater Amsterdam area. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 487–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocka-Czubaszek, A.; Wojno, W. Seasonal changes of water chemistry in a small river in an urban catchment. Sci. Rev. Eng. Environ. Sci. 2014, 23, 64–76. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, S.; Chen, W. Modeling the relationship between land use and surface water quality. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 66, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwek, J.P.; Żelazny, M.; Chełmicki, W. The influence of water circulation on stream water electrical conductivity in catchments with different land use during flood periods (the carpathian foothills, Poland). In Proceedings of the 12th Biennial International Conference of the Euromediter-Ranean Network of Experimental and Representative Basins (ERB), Kraków, Poland, 18–20 September 2008; pp. 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, V.; Estrany, J.; Ranzini, M.; de Cicco, V.; Tarjuelo, M.-B.J.M.; Hedo, J.; Lucas-Borja, M.E. Effects of land use and seasonality on stream water quality in a small tropical catchment: The headwater of Córrego Água Limpa, São Paulo (Brazil). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Li, Z.; Miao, H. Budget and Control of Phosphorus in the Changjiang River Catchment and Its Mouth 2020. In Studies of the Biogeochemistry of Typical Estuaries and Bays in China; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, B.M.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Murphy, C.A.; Haring, H.J.; Jensen, K.M.; Smith, M.E. Determining the effects of ammonia on fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) reproduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 420, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sampling Locality | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Samples | Geographical Coordinates | Km River | Land Use |
| P1 | 52.160563 N 20.845211 E | 2.20 | Agricultural land |
| P2 | 52.158987 N 20.859988 E | 3.50 | Agricultural land |
| P3 | 52.157642 N 20.876194 E | 4.50 | Meadow |
| P4 | 52.156924 N 20.891203 E | 6.00 | Urbanized areas |
| P5 | 52.153720 N 20.908024 E | 7.20 | Urbanized areas |
| P6 | 52.150380 N 20.919491 E | 8.50 | Urbanized areas |
| P7 | 52.145495 N 20.933610 E | 10.20 | Agricultural land |
| P8 | 52.141619 N 20.948051 E | 13.90 | Meadow |
| P9 | 52.137210 N 20.963244 E | 16.30 | Meadow |
| Effect | SS | df | MS | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-NH4+ | |||||
| Intercept | 51.51406 | 1 | 51.51406 | 1949.577 | 0.000000 |
| Year | 0.32950 | 2 | 0.16475 | 6.235 | 0.003030 |
| Point | 17.85419 | 8 | 2.23177 | 84.463 | 0.000000 |
| Yearxpoint | 2.46053 | 16 | 0.15378 | 5.820 | 0.000000 |
| Error | 2.14028 | 81 | 0.02642 | ||
| N-NO3− | |||||
| Intercept | 134.5807 | 1 | 134.5807 | 2890.525 | 0.000000 |
| Year | 4.1392 | 2 | 2.0696 | 44.451 | 0.000000 |
| Point | 8.1390 | 8 | 1.0174 | 21.851 | 0.000000 |
| Yearxpoint | 6.6174 | 16 | 0.4136 | 8.883 | 0.000000 |
| Error | 3.7713 | 81 | 0.0466 | ||
| P | |||||
| Intercept | 2.418015 | 1 | 2.418015 | 1106.549 | 0.000000 |
| Year | 0.014735 | 2 | 0.007368 | 3.372 | 0.039219 |
| Point | 0.128169 | 8 | 0.016021 | 7.332 | 0.000000 |
| Yearxpoint | 0.045881 | 16 | 0.002868 | 1.312 | 0.210273 |
| Error | 0.177000 | 81 | 0.002185 | ||
| Cl− | |||||
| Intercept | 75,176.67 | 1 | 75,176.67 | 12,318.19 | 0.000000 |
| Year | 357.12 | 2 | 178.56 | 29.26 | 0.000000 |
| Point | 2579.05 | 8 | 322.38 | 52.82 | 0.000000 |
| Yearxpoint | 347.54 | 16 | 21.72 | 3.56 | 0.000078 |
| Error | 494.33 | 81 | 6.10 | ||
| COD | |||||
| Intercept | 8916.746 | 1 | 8916.746 | 2235.176 | 0.000000 |
| Year | 84.848 | 2 | 42.424 | 10.634 | 0.000079 |
| Point | 642.888 | 8 | 80.361 | 20.144 | 0.000000 |
| Yearxpoint | 39.479 | 16 | 2.467 | 0.619 | 0.860166 |
| Error | 323.132 | 81 | 3.989 | ||
| EC | |||||
| Intercept | 15,931,393 | 1 | 15,931,393 | 65,094.98 | 0.000000 |
| Year | 52 | 2 | 26 | 0.11 | 0.899610 |
| Point | 524,679 | 8 | 65,585 | 267.98 | 0.000000 |
| Yearxpoint | 3412 | 16 | 213 | 0.87 | 0.603027 |
| Error | 19824 | 81 | 245 | ||
| pH | |||||
| Intercept | 5720.333 | 1 | 5720.333 | 373,666.9 | 0.000000 |
| Year | 0.107 | 2 | 0.054 | 3.5 | 0.034777 |
| Point | 0.318 | 8 | 0.040 | 2.6 | 0.013953 |
| Yearxpoint | 0.341 | 16 | 0.021 | 1.4 | 0.166464 |
| Error | 1.240 | 81 | 0.015 | ||
| alkalinity | |||||
| Intercept | 3,078,136 | 1 | 3,078,136 | 27,355.67 | 0.000000 |
| Year | 509 | 2 | 254 | 2.26 | 0.110897 |
| Point | 56,971 | 8 | 7121 | 63.29 | 0.000000 |
| Yearxpoint | 3412 | 16 | 213 | 1.90 | 0.032603 |
| Error | 9114 | 81 | 113 | ||
| Year | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 | P8 | P9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH4+ (mg dm−3) | |||||||||
| 2017 | 0.24 a | 0.22 a | 0.27 a | 1.51 f | 0.92 e | 1.55 g | 0.28 a | 0.98 e | 0.60 c |
| 2018 | 0.47 b | 0.41 b | 0.48 c | 0.69 d | 0.97 e | 1.30 f | 0.21 a | 0.48 c | 0.50 c |
| 2019 | 0.41 b | 0.41 b | 0.48 c | 1.42 f | 0.96 e | 1.60 g | 0.21 a | 0.54 c | 0.55 c |
| NO3− (mg dm−3) | |||||||||
| 2017 | 0.97 d | 0.74 c | 0.22 a | 1.02 de | 0.84 cd | 1.38 f | 0.93 d | 0.76 c | 0.79 c |
| 2018 | 1.31 f | 1.04 e | 1.53 g | 1.41 f | 1.84 h | 1.13 e | 1.02 d | 0.85 d | 0.55 b |
| 2019 | 1.26 f | 1.22 e | 1.46 g | 1.13 e | 1.91 h | 2.13 i | 1.21 e | 0.85 d | 0.65 bc |
| TP (mg dm−3) | |||||||||
| 2017 | 0.12 b | 0.14 b | 0.13 b | 0.12 b | 0.16 bc | 0.16 bc | 0.11 a | 0.19 c | 0.19 c |
| 2018 | 0.14 b | 0.15 b | 0.18 c | 0.12 b | 0.18 c | 0.16 bc | 0.15 b | 0.21 c | 0.21 c |
| 2019 | 0.06 a | 0.11 a | 0.08 | 0.12 b | 0.13 b | 0.15 b | 0.14 b | 0.21 c | 0.26 d |
| COD (mg O2 dm−3) | |||||||||
| 2017 | 9.14 c | 9.41 c | 9.51 c | 9.43 c | 9.22 c | 9.50 c | 15.22 e | 10.51 d | 9.71 c |
| 2018 | 8.11 b | 9.49 c | 8.11 b | 7.85 b | 7.31 b | 7.66 b | 16.39 f | 8.35 b | 8.33 b |
| 2019 | 7.17 b | 6.45 a | 7.16 b | 7.67 b | 6.43 b | 5.84 a | 16.13 f | 7.38 b | 7.88 b |
| Year | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 | P8 | P9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl− (mg dm−3) | |||||||||
| 2017 | 28.8 e | 30.1 e | 26.8 d | 27.2 d | 27.9 d | 29.5 e | 13.3 a | 22.9 c | 21.6 b |
| 2018 | 29.4 e | 26.3 d | 28.3 e | 26.2 d | 25.9 d | 29.9 e | 15.7 a | 21.7 b | 20.6 b |
| 2019 | 27.1 d | 36.7 g | 37.1 g | 32.6 f | 31.1 e | 30.8 e | 18.2 b | 23.6 c | 23.4 c |
| EC (µS cm−1) | |||||||||
| 2017 | 401 d | 401 d | 414 d | 432 e | 384 c | 389 c | 195 a | 427 e | 422 e |
| 2018 | 410 d | 400 d | 426 e | 430 e | 373 b | 392 c | 179 a | 439 e | 401 d |
| 2019 | 401 d | 401 d | 417 d | 425 e | 373 b | 393 c | 204 ab | 432 e | 409 d |
| pH | |||||||||
| 2017 | 7.1 | 7.4 | 7.3 | 7.3 | 7.3 | 7.2 | 7.1 | 7.2 | 7.3 |
| 2018 | 7.2 | 7.2 | 7.3 | 7.3 | 7.2 | 7.2 | 7.3 | 7.2 | 7.3 |
| 2019 | 7.4 | 7.4 | 7.4 | 7.3 | 7.3 | 7.2 | 7.2 | 7.2 | 7.3 |
| total alkalinity (mg CaCO3 dm−3) | |||||||||
| 2017 | 166.4 b | 153.6 a | 150.8 a | 147.2 a | 158.4 a | 194.6 c | 139.2 a | 215.2 e | 220.4 e |
| 2018 | 156.8 a | 149.2 a | 152.5 a | 160.4 a | 155.2 a | 174.4 b | 148.8 a | 197.6 d | 204.4 d |
| 2019 | 152.8 a | 154.4 a | 148.8 a | 150.8 a | 156.4 a | 190.8 c | 156.8 a | 195.6 d | 207.2 d |
| Cl− | NH4+ | NO3− | P | COD | EC | pH | Total Alkalinity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural land | 25.06 a | 0.32 a | 1.08 b | 0.18 b | 10.83 b | 332.4 b | 7.27 a | 153.1 a |
| Meadow | 25.08 a | 0.54 b | 0.85 a | 0.12 a | 8.55 a | 420.8 a | 7.29 a | 188.0 c |
| Urbanized areas | 29.00 b | 1.21 c | 1.42 c | 0.14 a | 7.88 a | 399.0 a | 7.28 a | 165.4 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rutkowska, B.; Szulc, W.; Wyżyński, W.; Gościnna, K.; Torma, S.; Vilček, J.; Koco, Š. Water Quality in a Small Lowland River in Different Land Use. Hydrology 2022, 9, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology9110200
Rutkowska B, Szulc W, Wyżyński W, Gościnna K, Torma S, Vilček J, Koco Š. Water Quality in a Small Lowland River in Different Land Use. Hydrology. 2022; 9(11):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology9110200
Chicago/Turabian StyleRutkowska, Beata, Wieslaw Szulc, Wiktor Wyżyński, Katarzyna Gościnna, Stanislav Torma, Jozef Vilček, and Štefan Koco. 2022. "Water Quality in a Small Lowland River in Different Land Use" Hydrology 9, no. 11: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology9110200
APA StyleRutkowska, B., Szulc, W., Wyżyński, W., Gościnna, K., Torma, S., Vilček, J., & Koco, Š. (2022). Water Quality in a Small Lowland River in Different Land Use. Hydrology, 9(11), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology9110200









