1. Introduction
The ecological status of water bodies is an expression of the quality of the structure and functioning of water systems, classified according to the composition and abundance of biological elements, hydromorphological conditions, and the physico-chemical conditions supporting the biological elements [
1,
2]. The importance of hydromorphological conditions for river ecosystem quality, related to channel morphology and the presence of natural riverine habitat features and riverbank vegetation, has long been taken into consideration. In December 2000, the Directive 2000/60/EC–Water Framework Directive (WFD) for river ecosystem assessment considered this factor in its implementation [
2].
The observation of river dynamics has led several researchers to classify such environments according to their different features. This type of approach has a strong geomorphological appeal, seeking to evaluate and compare the different basins/drainages [
3,
4]. From an ecological point of view, several studies proposed the classification of river environments, applied not only to environmental analysis but also to biomonitoring [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11]. The literature also presents combinations of grouped information related to the physical environment, biological aspects, and chemical analyses [
8,
12,
13], as in the case of the Environmental Protection Agency [
14] and Directive 2000/60/EC [
1]. The WFD introduced an obligatory hydromorphological quality element to assess the ecological status of European rivers [
15], underlining its importance in the classification of river systems [
16,
17]. Raven et al. [
17] conducted a comparative study in order to provide the European Committee for Standardisation (CEN) with technical guidance for establishing a standard for assessing the hydromorphological features of rivers [
1,
16,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23]. Several methods for characterizing the physical structure of rivers and assessing habitat quality have been independently developed across Europe since the early 1990s [
15,
17,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34]. Much of these methods are not suitable for some types of rivers, particularly those that are very long or have highly seasonal flows [
17], and require a certain scientific knowledge, materials, and time for their calculation [
34], making it difficult to perform a quick assessment from a technical point of view [
35].
Moreover, under the influence of the overall purpose and specific content of the WFD [
15,
17], the British Environment Agency developed the RHS project [
36]. The main objective of the project was to establish an accessible methodology from a technical–scientific point of view for denoting habitat features and evaluating the importance of wildlife in a river ecosystem [
37,
38]. These specially targeted “benchmark” surveys, implemented in Britain and Ireland, were extended to mainland Europe, including rivers in Finland, Norway, Slovenia, Bavaria, the Tyrolean Alps, the Cévennes in south-eastern France, Poland, northern Spain, and southern Portugal [
30,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44]. Medeiros [
45] reported that this methodology has been consistently tested in several countries [
39,
40,
41,
43,
46,
47,
48,
49], proving advantageous in different lines of research, from habitat assessment for the establishment of various species [
50], to erosion risk assessment [
51]. The RHS method is also commonly used for river ecological valorization in Switzerland, Germany, Czech Republic, Denmark, and Latvia. In a modified form [
39,
45] it was used in Italy, Greece, and Poland, mainly in scientific research [
21,
47], and also in Spain for hydrographic basin management purposes [
48]. The comparison of RHS and other habitat assessment methods has also been part of this European wide initiative [
17]. The RHS assessment parameters can also be used directly for river protection and restoration [
52,
53,
54]. The RHS has been used for many types of studies for WFD compliant monitoring of water bodies [
55,
56,
57,
58,
59,
60]: the STAR project [
45]; national research projects [
56,
61,
62,
63]; and environmental impact assessment studies [
15]. The RHS made an important contribution to determining the degree of modification of river hydromorphology [
39] and in the development of the CEN standard “water quality: guidance standard for assessing the hydromorphological features of rivers (EN 14,614 of 2004)” [
38]. As highlighted by Newson et al. [
54], RHS is not a directly geomorphological assessment, but rather a diagnosis of ecological status.
The first attempts to apply RHS in Portugal were made at the beginning of the 1990s, in association with research projects on limnology and aquatic ecology [
64,
65], and using global indexes to assess human disturbance and establish links between the river biota and hydromorphological modifications [
15]. Since no standard national protocol existed before WFD implementation, the Portuguese Environment Agency (PEA) adopted the RHS as an official hydromorphological quality assessment tool in 2011 [
15,
39,
43,
44,
55]. The PEA has developed partnerships to adapt the RHS as a method for the morphological analysis of rivers, taking advantage of the fact that in some national universities there is already research experience related to the application of this method [
39,
45,
66]. RHS was first used on the island of Madeira by Hughes [
61], followed by Cortes et al. [
56,
62] on the Portuguese mainland, with the purpose of identifying priority areas for restoration measures along disturbed rivers [
15]. The RHS was also applied in two river segments in the North of Portugal, subject to different anthropogenic pressures [
34]. Currently, the main practical uses of RHS fall within the scope of river basin management plans [
52], the ecological characterization of requalification projects [
67], and the environmental impact of river works [
34].
The RHS is a versatile field method used to “characterise and assess, in broad simple terms, the physical character of freshwater streams and rivers” [
39], and as a result of accurately defined parameters [
21,
68]. The assessment of habitat quality and extent of channel modification can be derived from RHS data [
39], reflected in indexes used for setting physical quality objectives for rivers [
69]. The RHS database allows sites of a similar nature to be grouped together for comparative purposes [
39]. Channel slope, distance from source, height of source, and site altitude are used to cluster RHS sample sites for the so-called “context analysis”, based on principal components analysis (PCA) plots [
70]. The RHS is used in the hydromorphological evaluation of homogenous river sections (not surface water bodies) and is compatible with European standards [
21,
71]. The application of the RHS takes into account the need to characterize the intervention areas from an environmental point of view, to assess the impact of the disturbances along the sections under study, and in order to introduce corrective measures aimed at restoring degraded habitats and increasing local biodiversity [
34].
With this article we intended to test this quality index of riverside habitats and its ease of application, thinking about its usefulness as a tool for assessing the conservation status of a river course, from hydromorphology, to the structure of riverside and aquatic vegetation. It is concerned with evaluating the applicability of the RHS method in water courses and its utility for daily decision-making processes in activities covered by the licensing regime for the use of water resources. Consequently, we considered the implementation of this methodology in our study area of great value, and our proposal was to characterize transects selected in the River Selho from a hydromorphological point of view and to evaluate their vulnerability and state of conservation.
2. Materials and Methods
The River Selho basin is a sub-basin of the River Ave, which is located between parallels 41°23′33.2″ N and 41°31′18.6″ N, and meridians 8°12′48.6″ W and 8°22′41.7″ W, with a predominant NE–SW direction. The area of this basin is 68 km
2, and it is located almost entirely within the Guimarães municipality (
Figure 1).
With the river’s source at 580 m altitude, the watershed totals an extension of 236 km. The River Selho covers a distance of almost 21 km, resulting in a medium-low average slope of only 2.4% in its main course [
72]. The area is thus strongly prone to flooding, since river flow is hindered by the low average longitudinal slope. In most of the middle and lower course of the River Selho there is a slow discharge that encourages silting of the channel, obstructing the river system and making the flood flows more severe [
72].
There have been very few river restoration projects in the Guimarães Council [
73], and even these have not been continued or monitored. Our proposal is thus intended as an intervention methodology for the River Selho in the Guimarães Municipality, and in identified locations with major hydrological, environmental, and landscape problems.
The RHS evaluates the physical structure of watercourses based on a standard 500 m sampling transect [
45,
74], which requires extensive fieldwork to identify visually predefined features and to draft survey forms. The RHS offers a semi-objective method developed and tested in scenarios different from those that normally characterize Portuguese river ecosystems [
34]. Therefore, adaptations of the RHS form and methodology were required in order to fulfil some WFD requirements not covered by the original methodology. The RHS form is divided into 18 sections [
14] and includes the characteristics of fluvial channel, land use, and adjacent river corridor attributes, such as geology, slope, or distance from the source [
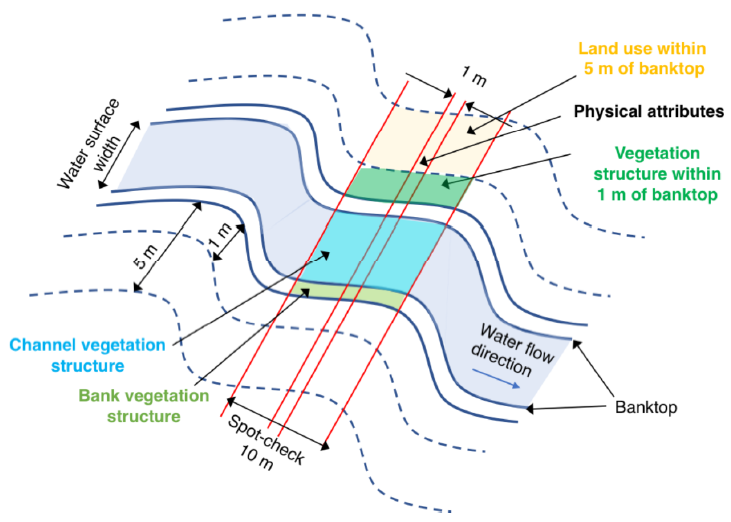
37]. A field survey obtains the data pertaining to both in-stream and bank features, collected in 10 spot-checks, with a 50 m distance between each (
Figure 2).
Spot-check observations, complemented with surveillance between them, provide an image of river values as a natural ecosystem. The insights into hydromorphological state elements are input: predominant valley form, information about riffles, pools and point bars, artificial features, the material of banks, their modifications and features, land use, bank profile shape, channel dimensions, and others are presented. Apart from the presence of plants on banks, bars, and those within the channel, such elements describing the vegetation structure can be distinguished as: the type of vegetation in the adjacent area (scrubs, shrubs, orchard, woodland etc.), vegetation structure uniformity level, bryophytes and lichens presence, free-floating, floating leaved plants, amphibious, submerged plant appearance, and algae presence [
37].
There are some elements in the form that are not completely applicable to the river Selho, which is consistent with other studies performed in mainland Portugal [
39,
45,
66]. Thus, we opted for a Portuguese version prepared by the INAG in 2010, adapting some aspects related to: Section Q, a section open to the identification of relevant regional problems; Section O, where the local species are registered; and Section F, related to uses and structure of the vegetation of the margins in a 10 m strip to count the bed-limit line, as stipulated in Portuguese Law No. 54/2005, of 15 November.
One of the determining concerns in the application of the RHS in the river Selho was the definition of the sampling program, regarding the representativeness of the sample vis-à-vis the population [
70]. In the present work, 5 transepts were carried out on the main course of the river Selho, having accessibility as a fundamental aspect, guaranteeing not only safe conditions, but also that the field work could be effective. Sampling also involves, according to the described methodology, an assessment of risks for the observer. For this, there is an additional form, in which some questions about the location are prior evaluated, so that the observer can indicate the degree of associated risk; classified as low, moderate, and high. In the case of the present study, sampling was limited to places with a high probability of success, that is, with the possibility of being able to evaluate sections with a continuous extension of 500 m, avoiding areas whose characteristics could prevent this objective from being reached. The selection of the sampling sites includes the completion of complete transepts and in safe conditions [
45].
The selection of transects is based on the collection of systematic samples that are representative of watercourses with problems, in terms of flow and physical degradation [
45]. The sampled sections were located in urbanized and industrialized areas, areas with alterations essentially associated with agricultural, livestock, and forestry exploration, as well as areas occupied by weed vegetation (
Figure 3). In general, the main landscape units existing in the region that had already been defined in previous projects, and visited in field work for recognition [
72,
73,
75], were covered. The samples were therefore representative of all water courses in the basin.
The RHS system has four distinct components: (i) a field survey method; (ii) a computer database for entering results from survey sites; (iii) a set of methods for assessing the habitat quality; and (iv) a system for describing the level of man-made channel modification [
76]. RHS data recorded on the field sheets have to be manually introduced into the freely downloadable Rapid 2.1 software developed by the Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, UK [
77]. Implemented using Microsoft Access for Windows, Rapid 2.1 can be used to store RHS data and calculate HMS and HQA indexes [
55]. Hydromorphological river quality is expressed via the habitat quality assessment (HQA) and habitat modification score (HMS) indexes, two quantitative parameters calculated from RHS survey information. The HQA provides information about the level of the naturalness of the section. HMS describes the modification degree of the chosen reach, i.e., if there is a measure of the deviation in a section from its natural, intact state.
Based on previous surveys and contacts established with authorities from the Guimarães municipality, 5 transects (
Figure 1 and
Figure 3) were selected, validated from criteria defined by the security protocol, so that the fieldwork could be effective [
75].
The survey and fieldwork were implemented by walking, from May 2018 to September 2018. The data collection was made with the support of a checklist [
74], and part of the RHS methodology, with some adaptations implemented to the specific study area. Various tools were used in this survey (measuring tape, camera, GPS, among others).
The method used to collect data was based on the RHS form and was designed to be robust, associated with a good database and geographical information system, and intended to support management measures, public information, and future interventions [
70].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Results from the RHS Implementation
The RHS form is divided into 18 sections, regarding which we present a brief analysis for each of the 5 transects of the River Selho.
- -
Section B: Predominant valley form.
Despite some local particularities, there is a certain homogeneity in the valley forms in the basins studied, given their small size and similar geological origin. V-shaped valleys prevail, with gentle, not very pronounced slopes, which are sometimes asymmetric.
- -
Section C: Number of riffles, pools, and point bars.
The natural features we identified appeared, essentially, in the form of riffles (17 occurrences) and point bars (39 of 41 corresponding to vegetated point bars), reflecting the orographic characteristics associated with the basin (
Figure 4a,b), such as its short length and high average slopes. They stand out for their impacts on habitats, flow regulation and, consequently, risk management. The presence of point bars indicates the capacity for sediment transport, the greater or lesser dynamic of which is reflected in the rooting or not of vegetation.
- -
Section D: Artificial features (
Table 1).
The number of artificial features reflects a significant degree of anthropic modifications, essentially associated with water use or improving mobility and security conditions. Among the wide range of structures provided in the RHS form, we found most types represented by structures of different sizes (
Figure 5a,b). We highlight the transversal structures, particularly the importance of weirs for agricultural activity and hydroelectric production. The description of the types of structure is related not only to their size, but also to their possible impact on the structure and functionality of the watercourse.
- -
Section E: Physical attributes (1-m wide transect) (
Table 2 and
Table 3).
As far as the bank material is concerned, natural and traditional processes prevail, and boulders and stone walls abound. It should also be noted that cement/concrete elements appear frequently. The composition of the bank material was confirmed, with modifications mostly associated to interventions to reinforce and resect stretches of the River Selho. There was also many vegetated side bars, which show the high capacity of the river’s hydrodynamics.
Regarding the channels (
Table 3), we noted significant granulometric variability that ranged from transects filled with boulders, to sand (
Figure 6a,b), predominant materials in the River Selho. The low turbulence of the flow is also worth mentioning.
- -
Sections F and H: Banktop land-use and vegetation structure (
Table 4).
Most of the land use provided for in the survey form can be observed on the River Selho, within 50 m of the banktop. This situation reflects the region’s typical land use, where housing and industry are diffuse in the countryside, which is dominated by cropland and some woodlands. As for vegetation structure, the four types defined in the survey form (bare, uniform, simple, and complex) were recorded in almost all the transects identified (
Figure 7).
We highlighted the prevalence of more complex structures along the River Selho, both on the banks and on the slopes of its watercourses.
- -
Section G: Channel vegetation types (
Table 5).
The type of vegetation found in a watercourses may reflect not only the surrounding habitats, but also the flow dynamics. As a result of rooted vegetation, conditions are created for the establishment of specific communities. Many of the flora species observed in the channels were similar to the usual vegetation in areas along the banks, or even in areas further away from the watercourses. The type of flora reflected the high degree of habitat changes, although there were still some areas with a lower degree of change, bearing vegetation structures in a better state of conservation.
- -
Section I: Bank profiles (
Table 6).
The bank profiles of the transects analyzed revealed an imbalance, when considering natural and artificial/modified typology. This situation reflected signs of erosion processes, which, in the case of modified profiles, had been mitigated, or had generated new risks, caused by design errors in these artificial structures. Bank reinforcements do indeed highlight these different risk situations, associated with possible erosion and mass movement processes.
- -
Section J: Extent of trees and associated features (
Table 7).
The presence of trees and their dispersion may stabilize the banks, or cause obstructions due to their fall. Considering the distribution of trees and associated features in biogeographical terms, this can be very useful in the planning of management actions, particularly to identify segments where clearance is needed.
- -
Section L: Channel dimensions (
Table 8).
In this section, we present an overview of the measurements made in the transects (
Figure 8a,b).
- -
Section M: Features of special interest.
This section covers a range of structures that can be observed in watercourses that provide additional information, particularly regarding their dynamics and potential habitats. We highlighted the low number of features of special interest and their poor representativeness, apart from the large boulders, typical of the dominant geological substrate in this region, porphyroid granite rock.
- -
Section P: Overall characteristics.
The features recorded in this section directly reflect permanent or recent activities that may decisively influence aspects of river management, such as runoff, water quality, and habitat integrity. We highlighted problematic and urgent situations such as accumulated debris, polluting discharges, and sewage. On this last point, we highlighted the works and structures associated with the Ave Valley Integrated Pollution Management System, which sometimes interferes with the stability of the banks and the regular water flow. Some activities observed were also considered, such as deforestation, associated with forest exploitation, or fisheries management, associated with fish restocking.
3.2. The Habitat Quality Assessment (HQA) and Human Modification Score (HMS) Indices
HQA provides a broad indication of the overall habitat diversity provided by natural features in the channel and river corridor, whereas HMS is an indication of artificial modifications to river channel morphology [
39,
43]. HQA scoring considers: (i) flow types, (ii) channel substrates, (iii) channel features, (iv) bank features, (v) bank vegetation structure, (vi) instream channel vegetation, (viii) land use within 50 m, (ix) trees and associated features, and (x) special features. Consequently, its sum is calculated. This can be used to quantify improvement or degradation of habitat quality. This scoring system basically shows the features of the physical structure of the site (including channel and river corridor). Points are scored for the presence of features such as point, side and mid-channel bars, eroding cliffs, large woody debris, waterfalls, backwaters, and floodplain wetlands. Additional points reflect the variety of channel substratum, flow-types, in-channel vegetation, and also the extent of banktop trees and the extent of near-natural land use adjacent to the river.
HQA is a score of habitat quality and the diversity of features, such as substrate and flow types, as well as other in-channel features, such as deposition bars. The diversity and character of features at any site is influenced by natural variations and also the extent of human intervention, both in the channel and on adjacent land. Comparisons between different HQA’s should only occur for rivers of a similar character, or for sections of the same river [
34]. The RHS database allows HQA scores to be compared using sites with similar physical characteristics (e.g., bedslope, distance from source) and geology. This index is normally expressed in absolute values, which increase with the increase in the quality of the habitat. High values of HQA demonstrate high diversity and a significant number of natural elements in a channel and within the surrounding area [
37]. The higher the HQA, the more diverse the river habitat and the potential for supporting biodiversity.
The second index concerns the HMS and allows measuring the extent to which the natural characteristics of the sampling section have been anthropically modified. The HMS provides an estimate of the degree of modification and presence of artificial features.
This includes such parameters as the quantity and size of particular types of water structures (dams, crossings, culverts, groynes, bridges), anthropogenic bank profile transformations (reinforcing, resectioning, embanking, bank devastation by cattle, riparian plants mowing), and bottom modifications (reinforcing, resectioning, dredging, artificial bottom material, carving water plants).
HMS values increase with the increasing degree of modification, and a value of zero indicates that there are no significant anthropogenic changes. The cumulative points provide the HMS. Habitat modification class (HMC) has been developed, which allocates a site into one of five modification classes, based on the total score (1 = semi-natural; 5 = severely modified). In contrast to HQA, low HMS values indicate the lack of modification or insignificant hydromorphological transformations of rivers, whereas high HMS indicates extensive changes. A cumulative HMS score can be used to summarize the significance and the extent of structural alteration of the channel.
Although some subjective assumptions are considered (such as the value/weight of the score for each characteristic), it is an objective measure, allowing a consistent comparison between locations, regardless of the type of river. This is a more robust index for the simulation/prediction of the consequences of certain interventions on the beds and margins of watercourses, in terms of their structural alteration.
The HQA and HMS numerical indices are inversely proportional; two ecologically similar river sections could be characterized by different anthropogenic influences [
37], which do not necessarily lead to a drop in the hydromorphological quality of a river. This is the case for human efforts in river restoration that lead to increasing the naturalness of a habitat [
21].
The two quality indices, HQA and HMS, were applied to the sampled transects in the River Selho using Rapid 2.1 software (
Table 9).
The HQA scores obtained varied between 56 and 66, while the HMS scores were all 5. The high HMS scores reflect the intense influence of anthropogenic action on these riverside habitats, through the building of artificial channel structures and the urban occupation of both banks. This situation is severe throughout the River Selho. The wide range of features was influenced by natural variation and by the extent of human intervention, both in the channel and in adjacent areas. In relation to the HQA assessment, we obtained results that reflect the progressive degradation of biodiversity and the disappearance of existing vegetation along the river channel, a result of the high level of modification.
Considering the results obtained, we can point out the main problems that currently affect the hydromorphological quality in the River Selho (
Table 10), as well as the factors originating them.
Excessive silting of the watercourses, morphometric changes, with an emphasis on the narrowing and resectioning of the channel and banks, and massive destruction of the riparian zone were the most significant processes identified in the transects analyzed [
31].
3.3. Limitations and Advantages of the Application of the RHS
The RHS system was structured and developed for the situation in the United Kingdom and, therefore, it is shaped according to the river characteristics, occupation, and land uses that exist there. On the other hand, the RHS encompasses a set of technical terms that do not always have a direct correspondence in Portuguese, making it difficult to identify characteristics and collect field data [
34].
There are well-known difficulties in applying the RHS to Mediterranean rivers, and adaptations have been developed for southern Europe [
39,
78]. However, the rivers of the northwest of Portugal, where the River Selho is located, were not considered.
Some of the difficulties encountered in using the RHS methodology for the River Selho were related to the natural hydromorphological processes associated with Mediterranean rivers in northwest of Portugal, namely river flow variation, which can in some cases be influenced by processes resulting from human intervention. In these cases high annual and interannual flow variability increases the difficulty of recognizing and accurately recording the macrophyte growth, substrate type and composition, flow types, erosion, and depositional features directly affected [
15]. Especially in the case of rivers in the northwest of Portugal, their torrentiality and hydraulic seasonality limits to the summer the optimum period for the collection of field data [
34]. Thus, it became necessary to adapt the RHS form to allow greater sensitivity to anthropogenic changes, in addition to calibrating the values that emanated from them, to correctly assess the various stages of environmental degradation [
34].
These adaptations comprised necessary minor adjustments to lotic conditions and the re-definition of descriptions covering land use categories, special features, and notable nuisance plant species [
15]. Non-native invasive species are widely established along the River Selho, particularly in those areas which have been modified or have a high degree of disturbance. Thus, adaptations regarding riparian vegetation were also integrated into this version of the RHS form [
15,
79,
80].
We summarize some of the difficulties and uncertainties identified with the application of the RHS to the River Selho:
- -
Difficulty in classifying and identifying natural berms.
- -
Many streams and rivers are affected by minor fords and malls, and old dams and weirs. This affects both upstream (ponded) and downstream flow and substrate patterns.
- -
Subchannels are relatively common features, where seasonal flow has extreme variations.
- -
Small stretches of homogeneous smooth or non-perceptible flow make it difficult to separate artificial and naturally ponded flow.
- -
Due to the variation in flow regime, it is very difficult to define the banktop. Some sites have multiple side bars, recorded at several spot checks along the survey reach.
- -
Different types of land use occur along River Selho that are not included in the original RHS form.
- -
The annual flow variability directly affects features such as macrophyte development and complexity, substrate characteristics, and the accumulation of organic debris. In particular, the dominant flow types and flow diversity are affected.
To avoid misinterpretation the version of RHS we used included the count of side bars in the survey form. The banktop definition was determined using several clues (e.g., the “annual flood” trashline). The land use categories should reflect local/regional land management and included, wherever possible, additional categories within standard RHS types. Due to the flow seasonal variability, the timing of the survey is critical [
37]. We followed the period considered appropriate for southern Europe, coincident with the beginning of the summer [
39,
43]. Given the small size of the Selho river channel, it was also possible to carry out fieldwork to validate some of the RHS parameters in the winter, namely, type of flows, aquatic vegetation, and forms of sedimentation.
The most significant features of the method are its precision, reproducibility of scores, and the facility for carrying out a statistical analysis of the obtained results. Elements of the environment are evaluated objectively, and the method is quite cheap and easy to carry out [
21]. This technique presents a remarkable flexibility [
34], being suitable for small and medium-sized Mediterranean rivers when surveyed in the spring [
39], and having been used in several regions of mainland Portugal and Madeira island [
39,
45,
61,
62]. In terms of feasibility, the entire RHS sampling process is more suitable for rivers with a narrow and shallow channel, as is the case for the River Selho, as this allows better visibility of the opposite bank and the characteristics of the bed.
The results obtained show the need to develop the application of the RHS in other rivers in the northwest of Portugal, considering that:
- -
it is rapid, simple, and based on a standardized approach (strict field protocol) [
22,
23] and quality control procedures (training and accreditation, quality assurance routines);
- -
it was one of the methods used to develop the CEN Standard on Hydromorphology;
- -
it allows the production of comprehensive results for managers, scientists, and community groups [
39].
4. Conclusions
The RHS was developed in response to a need for information on the physical structure and quality of habitats in rivers. Its application considers the need to characterize the intervention areas from a hydromorphological point of view, to assess the impact of the disturbances along the sections under study, with the objective of introducing corrective measures aimed at restoring degraded sections and habitats, and increasing local biodiversity.
Using the RHS methodology, it was possible to identify the main problems currently affecting the hydromorphological quality of the transects analyzed in the River Selho, as well as to point out the factors behind them: excessive silting of the watercourses, and morphometric changes, with an emphasis on narrowing and resectioning of the channel and banks, as well as the massive destruction of the riparian zone.
Based on field studies in the River Selho and restoration works implemented we can conclude that the RHS method can be used, not only for the evaluation of present hydromorphological status, but also for forecasting the impact of morphological and habitat changes, namely the ones promoted by river restoration works. Furthermore, the implementation of RHS produces a significant quantity of data, extremely useful for comparative analysis of various ecological design solutions, and in considering different stages of ecological restoration processes [
21].
The method used to collect data was based on the RHS form and was designed to be robust and associated with a good database and geographical information system, as well as intended to support management measures, public information, and future interventions [
70].
The RHS was tested, within the scope of this work, from the perspective of considering its future use as a decision support tool in the management of water resources at a local level. At a regional scale, the RHS will have wide applications, regarding its integration with the WFD, and considering the identification of pressures on water bodies. In this context, the characterization of water courses, establishment of reference conditions, grouping of water courses in the respective typologies, and establishment and application of management measures are obligations of the administration that will clearly benefit from the adoption of this methodology [
45].
The application of RHS to the entire national territory, within the scope of the implementation of the WFD, will allow overcoming the local character with which this model was applied by us, and identifying the actual state of physical degradation of the river corridors [
34].
The attribution of numeric values to each hydromorphological element, assayed in RHS research, allows the identification of those which should be considered in describing the river restoration plans [
68]. Thus, the RHS provides basic information on the current situation of river habitats, enabling the formulation of very detailed environmental diagnoses. At the same time, it identifies the areas and factors that contribute to a certain degree of habitat quality, and the areas subject to changes in their natural state, as a result of pressures that are also characterized. This set of interconnected potentialities make the RHS system a very effective tool for identifying suitable areas for the environmental restoration of river ecosystems and the promotion of good channel management, and thus helping to plan and monitor the rehabilitation of riverside habitats [
34].
An inventory is also needed to develop a robust HQA scoring protocol for Mediterranean rivers [
39]. HQA constitutes a scoring system based on characteristics relevant to biodiversity. Regardless of its application, this index should only be used to compare rivers of the same type, so its calibration is suggested based on the classification obtained in the places considered to be of the highest quality; thereby establishing a reference for each type of river. A national scoring protocol should be developed in Portugal to reflect the river and riparian features that contribute to natural habitat diversity and quality [
81].
The single most important technical requirement is the development of a standard protocol for recording and assessing, in simple terms, the extent and character of riparian habitat that can be used as an addendum, and cross-referenced to the core RHS survey [
80]. Like other countries that have little baseline information on ecological and hydromorphological features required by the WFD, a cost-effective sampling strategy is needed [
39].
The application of the RHS methodology has undoubtedly proved to be a very re-liable tool for the management of degraded riparian areas. Following the hydromorphological assessment and definition of the intervention measures, the next step is to develop integrated intervention projects, adapted to the scale of the problems identified.