Abstract
Riparian zones play an important role in the ecological stability of rivers. In particular, the quality of the riparian vegetation is a significant component of the hydromorphological status. In Europe, the QBR index (Qualitat del Bosc de Ribera) and the River Habitat Survey (RHS) are commonly used for the qualitative assessment of the riparian vegetation. In this study, we estimated the QBR index and the Riparian Quality index, which is derived from the RHS method, for 123 river reaches of the National Monitoring Network of Greece. Our field work included the completion of RHS and QBR protocols, as well as the use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). The aim of this study is to assess the riparian vegetation status and to identify linkages with the dominant land uses within the catchment. Correlation analysis was used to identify the relationships between hydromorphological alterations and the degradation of the riparian vegetation, as well as their connection to land uses in the catchment area. Our results highlighted severe modifications of the riparian vegetation for the majority of the studied reaches. We also showed a differentiation of the QBR with respect to changes in the altitude and the land uses in the catchment area. Overall QBR reflects the variation in the riparian vegetation quality better than RQI. Our findings constitute an assessment of the status of the riparian zones in Greek rivers and set the basis for further research for the development of new and effective tools for a rapid quality assessment of the riparian zones.
1. Introduction
1.1. Riparian Zones and WFD
Riparian areas in Europe are undoubtedly threatened by many stressors, with hydromorphological alterations and expansion of agricultural land uses being the most common and serious causes for their ecological degradation [1,2]. The importance of riparian zones in the ecological functioning of river systems has been widely recognized in recent European policies. Thus, the Water Framework Directive [3] includes the structure of the riparian zone in the morphological conditions that, together with the hydrological regime and river continuity, represent the main hydromorphological elements supporting the biological communities. The Directive recommends that the structure of riparian zones should be analyzed systematically and that their restoration and conservation should be included within the programmes of measures that form part of the Integrated Basin Management Plans [4]. As the Directive (WFD) requires from member states to monitor hydromorphological features of rivers in order to assess their ecological quality, numerous hydromorphological assessment methods have been developed with most of them focusing on the dynamics of hydrology, geomorphology, and riparian zone extent [5]. The riparian zones consist of a wide variety of structures. They are of great value to humans, as they are complex and extremely sensitive areas that connect the aquatic and the terrestrial ecosystems [6]. Through their functions, they strongly influence the biodiversity as well as the landscape of an area. However, the assessment of riparian zones, and specifically the assessment of riparian vegetation, is not often included in research concerning the evaluation of the ecological status of rivers, despite their importance [7]. This is evident in various Mediterranean countries, including Greece [8]. Riparian vegetation is known to provide numerous functions to lotic ecosystems. The production of food and nutrients in rivers is one of them. As trees and plants absorb soil nutrients, they produce organic matter that ends up in rivers, making up most of the nutrient availability to aquatic organisms [9,10]. Furthermore, plant assemblages within the channel and along the banks form buffer zones that mediate nutrient and sediment transport from the land into the watercourse. In addition, riparian vegetation prevents erosion by stabilizing the channel bed and the banks [11]. At the same time, riparian plant communities provide many habitats for fish, amphibia, birds, and invertebrates [11,12,13]. Plants on the banks also provide shade and influence the light availability in the water column and the thermal regime [14,15]. This function is of particular importance for the stream productivity and the overall ecosystem metabolism [16,17].
1.2. Riparian Vegetation and Hydromorphological Alterations
Hydromorphological changes are considered responsible for the degradation of the riparian vegetation which in turn impacts the ecological integrity of the riparian ecosystems [18,19,20]. Hence, hydromorphological assessments incorporate the evaluation of the riparian vegetation status placing emphasis on various features such as the total cover, the cover structure and the continuity along the riparian corridor. These assessments of riparian zone that are using various protocols and indices are in global practice [7,8,16,21,22,23,24,25]. According to historical sources [26], from the beginning of the Middle Ages, various interventions took place in the riparian zones of the Mediterranean rivers, aiming to protect crops, livestock, and humans, living in areas susceptible of flooding. The construction of large dams over the years has reduced the amount of water in downstream areas, subjecting others to long-term or permanent inundation [27]. Furthermore, the transport and deposition of sediments changed the hydrology of the riparian areas, leading to an increase in groundwater depth [28]. As a result, valuable habitats and high biological diversity areas, such as the riparian zones, have been affected by water scarcity [29]. Nowadays, typical riparian vegetation is found in a small number of river ecosystems in most Mediterranean countries [30]. Crop expansion, uncontrolled grazing, increased timber demand, illegal logging, and deforestation have reduced rivers’ natural vegetation areas to narrow linear strips along their banks [31,32]. Furthermore, agriculture, urbanization, hydropower, and flood protection are the most common and important drivers of hydromorphological modifications in the rivers of Europe [18]. As a result, dams, bridges, weirs, channelization, embankments, deepening, resectioning, and many others are some examples of the modifications that threaten the river connectivity, the riparian corridor’s naturalness, and the overall ecosystem health. Identifying these pressures at reach scale is often accomplished through monitoring activities in accordance with the implementation of the WFD [5].
Regarding Greece, the Institute of Marine Biological Resources and Inland Waters (IMBRIW) of Hellenic Centre for Marine research (HCMR) has been assigned by the special Water Secretariat, of the Greek Ministry of the Environment, Energy and Climate Change to implement the WFD in Greek rivers, at a national level. Reference conditions were defined for each Mediterranean River Type according to the available information for the Biological Quality Elements (BQEs), the physicochemical, and hydromorphological conditions. Mediterranean river types are described as follows [33,34]: R-M1: Small–medium altitude Mediterranean streams (<100 km2 catchment area) with strong seasonal flow, R-M2: Small–medium lowland Mediterranean streams (100–1000 km2 catchment area), R–M3:Large Mediterranean streams (1000–10,000 km2 catchment area) with strong seasonal flow, R-M4: Small–medium Mediterranean mountain streams with strong seasonal flow, R-M5: Small lowland temporary streams with temporary flow, VL: Very Large Rivers: (>10,000 km2 catchment area) . Mediterranean River Types refer to the river typology used by each geographic intercalibration group to identify river systems with common characteristics.
With this study, we evaluated the riparian vegetation status of 123 reaches in Greece by applying two discrete methodological approaches. The QBR index (“Qualitat del Bosc de Ribera” or riparian forest quality) [35] and the River Habitat Survey (RHS) [36]. We also enabled the use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) aiming to an accurate and detailed depiction of riparian vegetation and hydromorphological alterations at every site where the flights were allowed. The main objective is to present an overview of the riparian vegetation status in rivers and streams of Greece and provide a first assessment based on preliminary results. In addition, this work explores significant variations of the riparian vegetation quality among water districts and river intercalibration types, as well as their relationships with the dominant land uses in the catchments. In contrast to other works that attempt to assess riparian vegetation status in limited ecoregions or water districts, our study is set on a national scale and utilizes a large data set that will continuously expand in the next three years during standardized sampling methods under the scope of the WFD national monitoring program. In addition, our methodological approach ensures homogenous results that cover all areas of national territory and can be utilized to assess and extract useful conclusions for future river management practices. However, it requires a careful examination of the riparian cover in relation to topography and drainage, river channel morphology, watershed land use and the ecosystems in the adjacent water body, as often times assessments are carried out too quickly.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Area
Our study was carried out through the implementation of the Greek National Monitoring Program in compliance with the Water Framework Directive (WFD). Distributed among 11 Water Districts (Northern and Western Peloponnese (GR 01,02), Eastern Peloponnese (GR03), Western Central Greece (GR04), Epirus (GR05), Attica (GR06), Eastern Central Greece (GR07), Thessaly (GR08), Western Macedonia (GR09), Central Macedonia (GR10) and Eastern Macedonia (GR11)) and 42 river basins, 123 river reaches were visited in total during summer of 2018, 2019 and 2020 when there is a low flow condition [37] and therefore the access is easier (Figure 1).
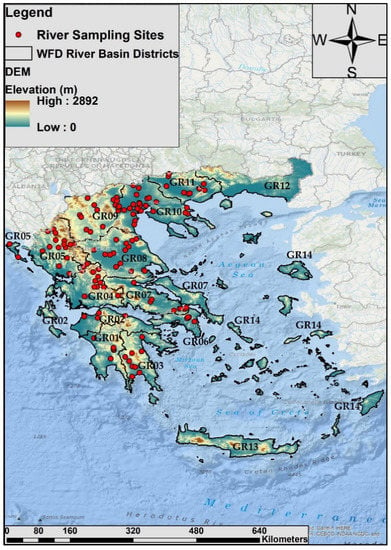
Figure 1.
Distribution of the sampling sites (n = 123) among water districts: GR01: Western Peloponnese, GR02: Northern Peloponnese, GR03: Eastern Peloponnese, GR04: Western Central Greece, GR05: Epirus, GR06: Attica, GR07: Eastern Central Greece, GR08: Thessaly, GR09: Western Macedonia, GR10: Central Macedonia, GR11: Eastern Macedonia, GR12: Thrace, GR13: Crete, GR14: North Aegean Islands.
The climate of the studied areas is characterized by hot summers and wet but mild winters. However, sudden weather changes are often occurred with torrential rains and strong winds that have a significant effect on vegetation [38]. According to data from the river basin management plans elaborated by the Greek Ministry of Environment and Energy and the Special Secretariat for Water [39], GR06 is the most populated water district characterized by intense urban development and the lowest rainfalls in Greece. On the contrary, GR05 and GR09 located on altitudes above 500 meters from the sea level in the north part of the country are the less developed ones. They host large undisturbed forest areas and exhibit high levels of rain and snow, while the average annual temperatures range from 10 to 14 °C. However, GR01 is the water district with the highest precipitation level. There are also large forests and rural areas there characterized by a semi-mountainous climate with mean temperatures ranging from 14 to 18 °C. In GR08, the presence of vast agricultural areas and low rainfalls are typical, with July and August being extremely hot and dry months in terms of hydrology. Generally, the rivers in which our research was carried out present intense natural relief, with their altitude ranging from sea level to 936 m. Most river catchments are characterized by intensive agricultural activities (median of agricultural land use 39.7%). Water abstractions for irrigation combined with limited water availability during summer influence the structure of the riparian vegetation and the overall hydromorphological status [40].
2.2. Methods and Tools for the Evaluation of Riparian Vegetation Quality and Hydromorphological Assessment
The QBR index (Qualitat del Bosc de Ribera) is an easy-to-use field method for assessing riparian forests’ habitat quality. It was designed and developed for use in Mediterranean streams in Spain [22]. There are no strictly defined research sections when applying QBR. Instead, there is only a recommendation that an optimal section length should be 100 m. QBR is easy to apply, as it is based on visual estimates of the total coverage of the riparian vegetation. It takes into consideration the characteristics of the horizontal cohesion of the river and riparian vegetation in relation to the surrounding ecosystems [22]. Taxonomical knowledge is not necessary, the knowledge of local plants is sufficient, as well as the ability to distinguish between native and introduced species [23,35]. Therefore, the chances of error or differences in the overall assessment by different groups is extremely small. After determining the flood zone, it is necessary to divide the river into two parts, the main channel and the riparian area. The analysis does not focus on the physical assessment of the channel and the surrounding area, but on the bank vegetation, assumed to be all the vegetation growing on the flooded areas [41]. The bank vegetation mainly consists of trees (riparian forest), but also includes bushes and shrubs and lower plants, excluding annual plants. The classification is based in a score-based index which includes four categories, representing: (1) overall bank vegetation cover, (2) structure of cover, (3) quality of cover, and (4) changes in the river bed. According to methodological criteria, each of these categories can be assigned 0 to 25 points (with a five-point interval); hence, the overall score can range from 0 to 100 points. The QBR method uses a classification which is in line with the Water Framework Directive (WFD), with five quality classes (Table 1).

Table 1.
Quality classes according to the QBR index [35].
The River Habitat Survey (RHS) is a systematic framework for collecting and analyzing data associated with the physical structure of water courses. Data collection is based on a standard 500 m length of river channel. It includes observations of substrate, flow, erosion, and deposition features in the channel, morphological and vegetation structure on the banks, and land use in the adjacent river corridor. During the field survey, features of the channel (both in-stream and banks), and adjacent river corridor are recorded in accordance with the relevant protocol [42]. Channel substrate, habitat features, aquatic vegetation types, the complexity of bank vegetation structure and the type of artificial modification to the channel and banks are recorded at each of 10 spot-checks located at 50 m intervals. A sweep-up checklist is also completed to ensure that features and modifications not occurring at the spot-checks are recorded. Cross-section measurements of water and bankfull width, bank height, and water depth are made at one representative transect, to provide information about the channel’s geomorphological processes. The number of riffles, pools, and point bars found in the site is also recorded. In the case of RHS, the experience and familiarity of the evaluators regarding the physical structure of water courses as well as the monitoring of hydrological alterations and habitat modifications seem to be more substantial issues in order to avoid different assessments due to subjectivity.
Habitat Modification Score (HMS) is a metric derived from the RHS method and consists of an indication of artificial modification to river channel morphology. Its calculation incorporates the presence and extent of artificial features such as culverts and weirs, as well as modifications caused by the re-profiling and reinforcement of banks. The cumulative points provide the Habitat Modification Score (HMS). High HMS scores (>500) reflect more artificial intervention and modification of the river channel within a site (Table 2).

Table 2.
Habitat Modification Classes according to HMS and their correspondence with ecological quality classes according to WFD.
The Riparian Quality Index (RQI) is another metric derived from the RHS method and represents the complexity, naturalness, and continuity of the riparian zone. It features three sub-scores for the aforementioned riparian zone factors, calculated separately for each bank and added to yield a final site score between 0 and 120. It can be a useful tool for monitoring and evaluating riparian zones’ structure, an element of the river morphological conditions which is considered as important by the Water Framework Directive. The RQI scores are classified into six quality categories to represent increasing riparian quality from ‘Very Bad’ to ‘Very good’ quality status (Table 3). In addition, RQI provides helpful criteria for evaluating the present status of riparian systems and formulating diagnosis and rehabilitation options. It represents a checklist of riparian natural characteristics and possible human-impacted riparian features.

Table 3.
Riparian Status according to RQI.
QBR and RHS methods were conducted covering stretches of 100 m and 500 m respectively and filling in the relevant protocols. Additionally, there was an aerial depiction of these sections by Unmanned Aerial Vehicles’ (UAVs) flights.
For the evaluation of the riparian vegetation status, the QBR score, as well as the RQI (Riparian Quality Index) sub-scores for complexity, naturalness, and continuity, were assessed initially. Then, the two indices (QBR and RQI) were compared, in order to examine whether they present common assessment results, as well as to identify possible relationships with the dominant land uses in the catchment.
2.3. Drone Flights
Complementary to field surveys, we used Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) to produce aerial orthophoto maps of the examined reaches. The high spatial resolution orthophoto maps offered the advantage of assessing riparian and geomorphological features that were not easily distinct in the field. As the technological advances in unmanned aerial vehicles and systems have offered new possibilities in monitoring stream morphology and riparian vegetation through photos at a high level of accuracy [43,44], we tried to exploit the high-quality output offered by UAV in this study. The flight campaign was conducted in every site where it was allowed according to the legislation regulations, with a DJI Mavic Pro Professional UAV (https://www.dji.com/gr/mavic/info (accessed on 21 April 2020)) equipped with a 12 megapixel camera. The Pix4Dcapture software was used for flight planning using the single grid mission. Specifically, a 500 m stretch of the surveyed length of the river was captured with a width of 120 m to ensure that both the channel and the whole extent of the riparian zone was recorded along with the completion of QBR and HMS indices. The flight altitude was 50 m according to the legislation regulations. Due to dense vegetation and man-made constructions, an 80% overlap rate of the images was selected. The collected image (approximately 70 to 90 photos per site) was then processed with the Pix4Dmapper software, using photogrammetric algorithms to produce an orthophoto map of the site. In some cases, the completion of the RHS and QBR protocols was done in office by the careful observations of such maps in various photo viewers (Figure 2), when this was not possible to be achieved in situ, due to the difficulties in accessing the river reaches.

Figure 2.
High spatial resolution’s orthophotomaps of 3 different sites: (a) Matesi, (b) Ladon, and (c) Sarantaporos by DJI Mavic Pro.
The images of Figure 2 depict three visited river reaches with different riparian vegetation status. (a) Matesi (R-M2) in Western Peloponnese water district, (b) Ladon (R-M2) in Northern Peloponnese water district, and (c) Sarantaporos (R-M2) in Epirus water district. Apparently, the differences between the extent and the continuity of the riparian vegetation, the type of flow and substrate of the river, as well as information on anthropogenic activities can be clearly distinguished, facilitating in more ways the better monitoring of these areas.
2.4. Watershed Delineation and Definition of Main Land Uses
The watersheds’ delineation was based on the location of the 96 sites. The methodological process involved the following steps: (1) watershed automatic delineation using GIS routines, (2) Manual delineation and/or correction of the automated watersheds. Integrated use of contours with 20 m interval, Google earth satellite images, aerial photographs from National Surface Cadastre and Mapping Agency S.A., and a Digital Elevation Model (25m pixel size) were utilized for the evaluation of the watershed polygon. Except for the optical inspection using the sources mentioned above, each watershed was examined based on literature review if any modifications altered the water course. After the final evaluation, the delineated watersheds were used to extract the land uses based on the CORINE 2018 maps [45]. Land uses were aggregated at the 1st level of CORINE classification. Three main classes of land uses were defined (artificial, agriculture and near natural) that correspond to the CORINE classes: 1. Artificial surfaces, 2. Agricultural areas, 3. Forests and semi-natural areas.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Descriptive statistics were calculated for each Mediterranean River Type for the total of 123 sites in order to identify river systems with common characteristics, as well as to show the variations between QBR and HMS in different water districts. A Kruskal–Wallis non-parametrical test was implemented to determine if there are statistically significant differences for the QBR, RQI, and HMS between Mediterranean River Types and Water Districts. Additionally, post hoc comparisons were implemented with the use of a Mann–Whitney test. Spearman correlations were conducted between the indices and the land uses in the catchment to identify possible significant relationships.
3. Results and Discussion
A synoptic version of the data set we used in order to extract our results is shown in Table 4. For each Water District, the number of sites, the type of RMs, the range of the values of selected land use categories, as well as the range of HMS, RQI, and QBR scores are presented.

Table 4.
Main parameters of the examined data set for each Water District (GR01: Western Peloponnese, GR02: Northern Peloponnese, GR03: Eastern Peloponnese, GR04: Western Central Greece, GR05: Epirus, GR06: Attica, GR07: Eastern Central Greece, GR08: Thessaly, GR09: Western Macedonia, GR10: Central Macedonia, GR11: Eastern Macedonia) and each Mediterranean River Type according to Van de Bund [33] and Lazaridou et al. [34] (R-M1: Small–mid altitude Mediterranean streams (<100 km2 catchment area) with strong seasonal flow, R-M2: Small mid-lowland Mediterranean streams (100–1000 km2 catchment area), R-M3: Large Mediterranean streams (1000–10,000 km2 catchment area) with strong seasonal flow, R-M4: Small–mid Mediterranean mountain streams with strong seasonal flow, R-M5: Small lowland temporary streams with temporary flow, VL: Very Large Rivers: (>10,000 km2 catchment area).
The minimum, maximum, and median values of the dominant land uses, altitudes, HMS, QBR, and RQI are presented in Table 5. With the exception of urban land uses, we found considerable differences between minimum and maximum values for all of the above-mentioned parameters.

Table 5.
Min, 25th percentile, median, 75th percentile and max of Land Uses (LUs), altitude, QBR, RQI, and HMS.
With regard to the classification of the sites to quality classes according to the QBR index, 67% of the sites were classified as of less than Good quality (Very Bad n = 26, Bad n = 29 and Fair n = 29, Figure 3). Conversely, 26 sites belonged to Good quality class and only 13 sites were in a very good natural condition. Most of these sites belong to R-M2 river type, while 15 sites (12%) belong to R-M4, which corresponds to water districts with higher altitude.
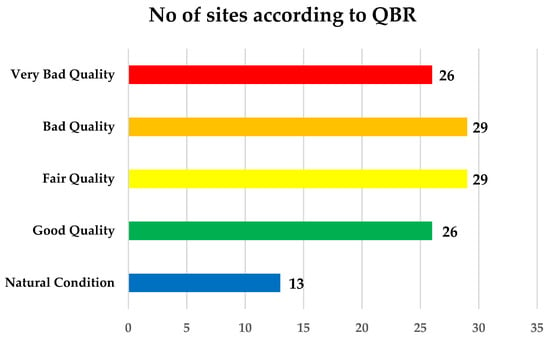
Figure 3.
Number of sites per class according to QBR Index.
Figure 4 shows the distribution of sites among the six quality classes of RQI Index. Again, most of the sites presented Moderate (n = 42), Poor (n = 30), Bad (n = 12) and Very Bad (n = 17) qualities, overall a not good status. Only 22 sites were characterized of Good quality, while none of the sites presented Very Good quality. These findings agree with the latest report from the European Environmental Agency (EEA) [46], which reported that 82% of all surface water bodies did not achieve good ecological status, while at the same time it listed hydromorphological modification as one of the most common pressures for the reduction of riparian vegetation.
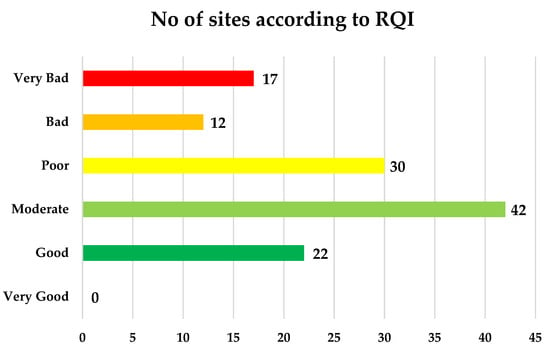
Figure 4.
Number of sites per class according to River Quality Index (RQI).
According to HMS, the majority of sites were characterized as Obviously (n = 40), Significantly (n = 37) and Severely (n = 17) modified in terms of hydromorphological alterations (Figure 5). Conversely, only 29 out of 123 sites achieved predominantly unmodified and pristine scores (HMS < 199). The fact that at least 70% of the studied sites presented severe hydromorphological modifications is in line with the general trend for all Europe [46]. The construction of dams and barriers are among the most important factors for the decrease of the riparian vegetation, due to the hydrological regime’s alterations. Recently, a study by Stefanidis et al. [5] showed that bank and channel modifications (i.e., resectioning, reinforcement) were a common hydromorphologic modification in Greek rivers. These modifications are used as a flood defense management practice. However, these changes inevitably cause significant alterations in the riparian zone affecting the vegetation’s structure and cover [4]. Other pressure that contributes to the gradual reduction of riparian vegetation, especially at lower altitude sites, is the large expansion of agricultural activity. According to the implementation of RQI, 82% belongs to moderate, poor bad and very bad quality, while for fair, bad, and very bad quality classes QBR gives a smaller percentage (69%).
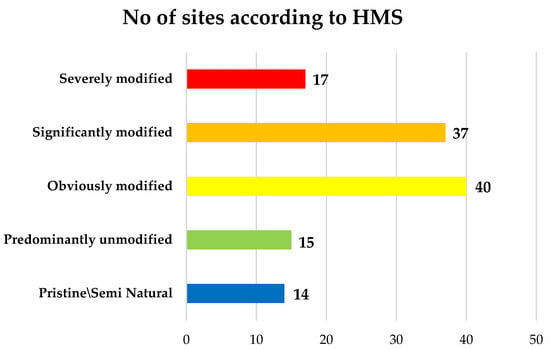
Figure 5.
Number of sites per class according to hydromorphological modification (HMS).
According to the results of the Kruskal–Wallis test, QBR and RQI were statistically different (p < 0.005 and p = 0.040, respectively) among the Water Districts. Specifically, post hoc comparisons showed several significant differences (p ≤ 0.002) for QBR such as between water districts GR04 (Western Central Greece) and GR01, 08, 10, and 11. Similarly for RQI, post hoc comparisons showed significant differences (p ≤ 0.004) between GR 01 (Western Peloponnese) as well as most of the other Water Districts and GR04, 03, 05, and 07. However, QBR was also statistically different among River types (p = 0.004), while RQI was not. Indicatively, QBR medians were statistically different between R-M2 and R-M4 river types. This could be explained by the fact that River Types are defined by specific typological criteria such as altitude, size of the catchment, etc., that can affect the type and structure of riparian vegetation. On the contrary, Water Districts are defined only by geographical criteria without taking into account the differences in their geomorphological characteristics. The only factor that could differentiate the riparian vegetation on Water District level is the climate (climatic zones).
In addition, RQI is a component of RHS which evaluates mostly the structure of vegetation on bank level, face and top, by characterizing it as complex, simple, uniform and bare, based on the number of different types of vegetation. In contrast, QBR is an integrated method of riparian vegetation assessment applied throughout the riparian area, aiming for the quantification of hydromorphological alterations, through the evaluation of vegetation cover, continuity, and structure disturbances.
The variations of QBR and RQI among Water districts and Mediterranean river types, as they result from the calibration of the typocharacteristic conditions of rivers [33,34], were visually assessed with strip charts and boxplots (Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8).
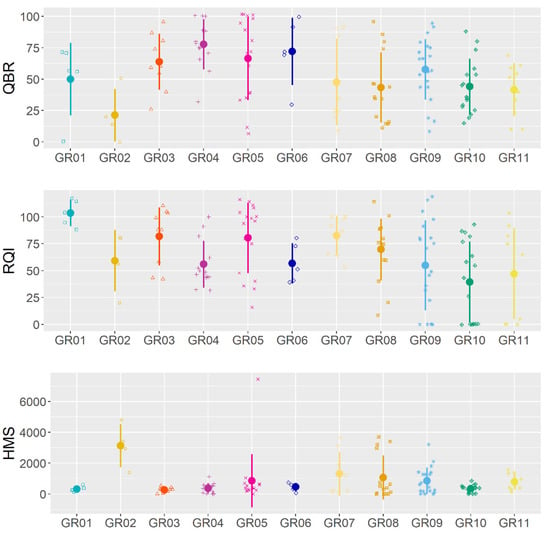
Figure 6.
Strip charts (1D scatter plots) of QBR, RQI and HMS per Water District. Mean values and standard deviations are also shown.
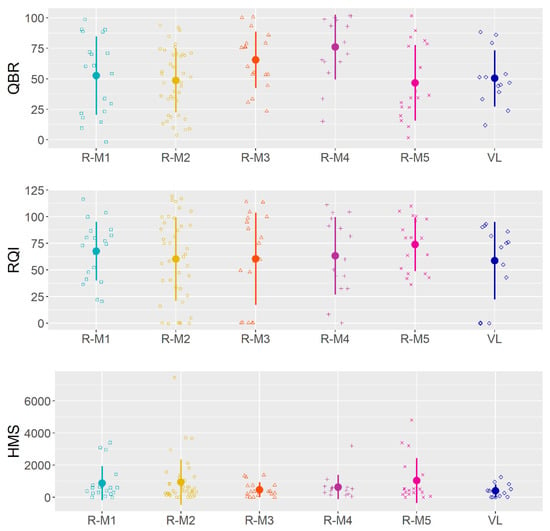
Figure 7.
Strip charts (1D scatter plots) of QBR, RQI, and HMS per Mediterranean River Types. Mean values and standard deviations are also shown.
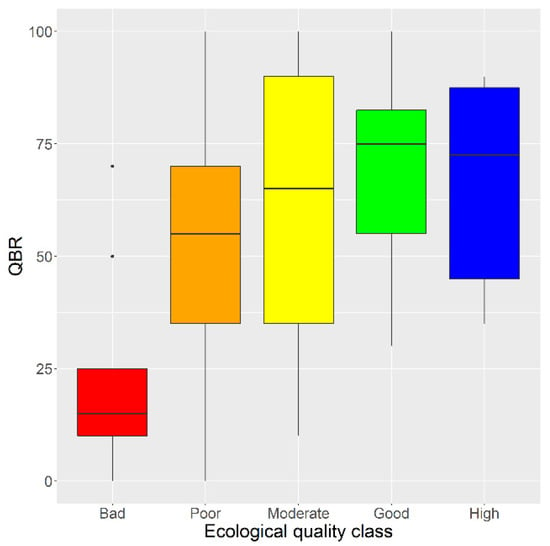
Figure 8.
Box plots of QBR score per class of hydromorphological modification (HMS).
From Figure 6, we can see some obvious variations of QBR and RQI in relation to Water districts. Specifically, both indices present the highest value in GR05 which includes sites of higher altitude in the water district of Epirus with extended vegetation (QBR average on these sites is up to 55%). According to [12,21,47], this happens also because these areas have a highly diverse relief and less human disturbance. At the same time, we can see a serious decrease of indices values in GR02 which represents sites of lower altitudes in Southern Greece (WD of Northern Peloponnese), as these sites are located mainly in agricultural plains. However, on GR01 sites, which again are reaches of lower altitudes in Western Peloponnese, the indices scored fair and good values. This probably occurs as there are climatic differences between these water districts. Specifically, Western Peloponnese exhibits higher rainfall rates than the Northern Peloponnese, which contributes to a higher quality vegetation status of the region. Furthermore, there are differences in relation to the land uses in each of them. In GR01, large rural areas are dominant with urban communities being greatly reduced, while, in GR02, anthropogenic pressures are more intense mainly due to the presence of large urban centers as well as the construction of major highways. Nevertheless, this contradiction needs further investigation. Finally, QBR and RQI do not present large variations in the majority of water districts of lowland Greece.
Figure 7 presents the spatial variation of QBR, RQI, and HMS in relation to Mediterranean River Types. There are high QBR values in the R-M4, which represents small–mid Mediterranean mountain streams. The strong seasonal flow combined with the high altitude of these sites result to an extended vegetation (QBR average on these sites is up to 56%) (Figure 7). On the contrary, for the same R-M, HMS values decrease. R-M3 river types also have relatively high QBR and RQI values which represents Large Mediterranean streams (1000–10,000 km2 catchment area) with strong seasonal flow. In general, in the Mediterranean River Types where the hydromorphological alteration is low (HMS <199), mainly due to the increased altitude or the presence of forest areas, the QBR scores high levels.
This is apparent in Figure 8 where we can note that sites with less hydromorphological degradation score higher QBR values. We assume that the riparian vegetation is of higher quality because of the lack of permanent structures (dams, etc.), or changes in river banks and channel. On the contrary, in areas of intense hydrological degradation, it is observed that QBR decreases, reinforcing the hypothesis that the hydromorphological degradation leads to the reduction of riparian vegetation [6].
Class differences per site are presented in the histogram of Figure 9 for the combinations of HMS-QBR and RQI-QBR indices. Generally, it seems that the classifications of the sites based on HMS and QBR are in concordance. Regarding the first combination, approximately one-third (35%) of the sites are characterized by the same class for HMS and QBR, while the 70% present zero or one class difference. This is a valuable result indicating that these two indices can produce similar results. RQI shows greater differences in relation to QBR. Consequently, for the second combination, about 23% of the sites show same classes while approximately 60% of the sites present zero or one class difference. Concerning the relationships between the indices and the land uses, the results of the Spearman’s correlation analysis are listed in Table 6.
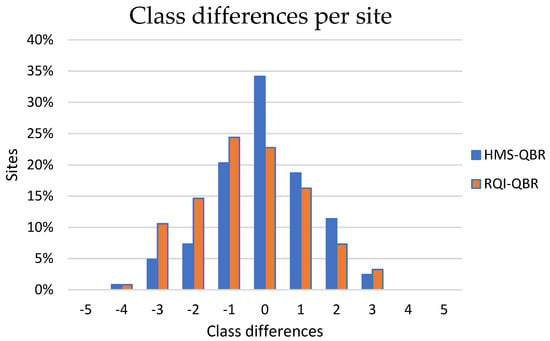
Figure 9.
HMS and RQI versus QBR Classes per site.

Table 6.
Spearman’s correlations between HMS, scores of QBR, RQI, altitude, and land uses.
The Spearman’s Correlation analysis was conducted in 96 out of 123 sites between the HMS, the scores of QBR and RQI, altitude, and the land uses according to CORINE land cover inventory by estimating the Spearman’s coefficient. Our aim was to identify the significant relationships between the scores and the dominant land uses and highlight further exploration issues. As shown in Τable 6, both QBR and RQI are positively correlated with altitude, which implies that at low altitude sites, where extended agricultural activities exist the riparian zone and thus the riparian vegetation is impacted. This is also shown by the significant negative correlation between agricultural land use and altitude. In contrast, natural land use is positively correlated with both indices (p ≤ 0.01 for QBR and p ≤ 0.05 for RQI). Finally, QBR correlates positively with RQI (p ≤ 0.01) which implies that both indices show similar results concerning the riparian quality status. A stronger correlation between QBR and HMS can be noted (p < 0.005), which confirms our hypothesis that riparian quality is affected by the hydromorphological modification. Overall, the correlations suggest that agriculture in the catchment and hydromorphological modification at reach scale are strongly correlated with the quality of the riparian vegetation.
4. Conclusions
This work presents the first results derived from the application of QBR and RHS indices in Greek rivers in line with the WFD. According to our findings, hydromorphological alterations impact the riparian vegetation and result in its gradual reduction. Changes in the structure and continuity of the riparian vegetation can also be observed in areas of lower altitudes, where a large expansion of agricultural activity exists. These two are the main factors which contribute mostly to the degradation of the riparian vegetation in the Mediterranean riparian ecosystems. In addition, we showed that agricultural land use was highly correlated with the QBR score, which implies a possible causal relationship.
Agricultural activity in particular is considered a major driver of hydromorphological modifications in Mediterranean rivers [4,21,47]. For instance, bank and channel resectioning is used as a practice of flood defense management to protect neighboring agricultural land from flood events. In addtion, bank reinforcement that uses hard materials (concrete, bricks, rip-rap, etc.) aims to mitigate bank erosion [5]. These changes inevitably are associated with significant alterations in the riparian zone affecting the structure and cover of the vegetation.
Concerning the use of the Riparian Quality Index, the RQI score correlates significantly with the QBR. However, Kruskal–Wallis analysis showed that QBR was statistically significant among water districts and River Types, while RQI was statistically different only among water districts. Therefore, it appears that QBR is better suited for distinguishing variations in the riparian quality status among different river typologies. It is also more effective on distinguishing sites with moderate impacts from sites with good quality status.
The use of UAVs in the field proved to be a valuable tool since it enabled the assessment of substrates, riparian cover, human alterations, and others, especially for sites where there was difficulty in access, in a cost-effective manner [43,44]. The filling in of the protocols improved positively, after the detailed investigation of the sampling areas through orthophoto maps and High Definition photography. The present work combines the traditional with a modern way of data collection enabling a more systematic application of automated photogrammetry in the monitoring of river riparian quality, which can provide greater accuracy in research on the conservation and management of river ecosystems.
As a concluding remark, constant monitoring of the riparian zones through the implementation of WFD is essential, since we need to achieve a better understanding on the impacts of hydromorphological changes in relation to riparian vegetation status. Rivers of poor and bad riparian vegetation quality must be identified and measures for their long-term restoration must be undertaken. Finally, we propose the need for further study, particularly on the effects of dams and other stable structures located mainly in higher altitudes of river basins, as well as the hydrological disturbances they cause, which have negative effects on riparian vegetation status.
Author Contributions
A.L., T.K., K.S., G.P., E.D.; methodology, A.L., T.K., K.S., G.P.; data curation, A.L., T.K., K.S., G.P., K.G., E.D., formal analysis, A.L., T.K., K.S., G.P.; visualization, A.L., T.K., K.S., G.P.; writing—original draft, A.L., T.K., K.S., G.P.; writing—review and editing, A.L., T.K., K.S., G.P., K.G., E.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been funded by the Project entitled: ‘Monitoring and Recording of the Water Status in Greece’, (MIS 5002739), funded by the Hellenic Republic, the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) & Cohesion Fund (CF).
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this study are available upon request at the Ministry of Environment and Energy: http://wfdver.ypeka.gr/en/geoportal-en/ (accessed on 21 April 2020).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Matono, P. Effects of Agricultural Land Use on the Ecohydrology of Small-Medium Mediterranean River Basins: Insights from a Case Study in the South of Portugal; Batista, T., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2019; pp. 29–51. ISBN 978-1-78985-704-7. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanidis, K.; Papaioannou, G.; Markogianni, V.; Dimitriou, E. Water quality and hydromorphological variability in Greek Rivers: A nationwide assessment with implications for management. Water 2019, 11, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European parliament and of the council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for community action in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2000, 327, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Del Tánago, M.G.; De Jalón, D.G. Riparian Quality Index (RQI): A methodology for characterising and assessing the environmental conditions of riparian zones. Limnetica 2011, 30, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, K.; Latsiou, A.; Kouvarda, T.; Lampou, A.; Kalaitzakis, N.; Gritzalis, K.; Dimitriou, E. Disentangling the main components of hydromorphological modifications at reach scale in rivers of Greece. Hydrology 2020, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefunkova, Z.; Neruda, M.; Vasekova, B. Impact Evaluation of riparian vegetation on aquatic habitat quality of rivers. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaimes, G.N.; Iakovoglou, V. Assessing riparian areas of Greece—An overview. Sustainability 2021, 13, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzinikolaou, Y.; Ntemiri, K.; Zogaris, S. River riparian zone assessment using a rapid site-based index in Greece. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2011, 20, 296–302. [Google Scholar]
- Walton, C.R.; Zak, D.; Audet, J.; Petersen, R.J.; Lange, J.; Oehmke, C.; Wichtmann, W.; Kreyling, J.; Grygoruk, M.; Jabłońska, E.; et al. Wetland Buffer zones for nitrogen and phosphorus retention: Impacts of soil type, hydrology and vegetation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkama, E.; Usva, K.; Saarinen, M.; Uusi-Kämppä, J. A meta-analysis on nitrogen retention by buffer zones. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutter, M.I.; Chardon, W.J.; Kronvang, B. Riparian Buffer strips as a multifunctional management tool in agricultural landscapes: Introduction. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, L.; Hasselquist, E.M.; Laudon, H. Towards ecologically functional riparian zones: A meta-analysis to develop guidelines for protecting ecosystem functions and biodiversity in agricultural landscapes. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, L.J.; Stockan, J.; Helliwell, R. Managing riparian buffer strips to optimise ecosystem services: A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 296, 106891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadmeadow, S.B.; Jones, J.G.; Langford, T.E.L.; Shaw, P.J.; Nisbet, T.R. The influence of riparian shade on lowland stream water temperatures in Southern England and their viability for brown trout. River Res. Appl. 2011, 27, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalny, G.; Laaha, G.; Melcher, A.; Trimmel, H.; Weihs, P.; Rauch, H.P. The influence of riparian vegetation shading on water temperature during low flow conditions in a medium sized river. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2017, 418, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornbach, D.J.; Beckel, R.; Hustad, E.N.; McAdam, D.P.; Roen, I.M.; Wareham, A.J. The influence of riparian vegetation and season on stream metabolism of valley creek, minnesota. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2015, 30, 569–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrell, T.K.; O’Brien, J.M.; Graham, S.E.; Simon, K.S.; Harding, J.S.; McIntosh, A.R. Riparian shading mitigates stream eutrophication in agricultural catchments. Freshw. Sci. 2014, 33, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasith, A.; Resh, V.H. Streams in mediterranean climate regions: Abiotic influences and biotic responses to predictable seasonal events. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1999, 30, 51–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonada, N.; Resh, V.H. Mediterranean-climate streams and rivers: Geographically separated but ecologically comparable freshwater systems. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershkovitz, Y.; Gasith, A. Resistance, resilience, and community dynamics in mediterranean-climate streams. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Lakhera, K.; Vyas, V. Status of riparian zone of river narmada in the central zone using QBR index. Int. J. Adv. For. Sci. Manag. 2019, 3, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Pascacio, E.; Ortega-Argueta, A.; Castillo-Uzcanga, M.M.; Ramírez-Marcial, N. Influence of land use on the riparian zone condition along an urban-rural gradient on the sabinal river, Mexico. Bot. Sci. 2018, 96, 180–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, S.R.; Hix, D.M. Adaptation of the QBR index for use in riparian forests of central ohio. Chapter: Forest Biometrics and Modeling. In Proceedings of the 16th Central Hardwoods Forest Conference, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 8–9 April 2008; pp. 331–340. [Google Scholar]
- Valerio, C.; De Stefano, L.; Martínez-Muñoz, G.; Garrido, A. A machine learning model to assess the ecosystem response to water policy measures in the tagus river basin (Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, J.; Pádua, J.; Hughes, S.J.; Cortes, R.M.; Varandas, S.; Holmes, N.; Raven, P. Adapting and adopting river habitat survey: Problems and solutions for fluvial hydromorphological assessment in Portugal. Limnetica 2011, 30, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, J. The “Design” of mediterranean landscapes: A millennial story of humans and ecological systems during the historic period. Hum. Ecol. 2006, 34, 713–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, T.; Xie, Z. Impacts of large dams on riparian vegetation: Applying global experience to the case of china’s three gorges dam. Biodivers. Conserv. 2008, 17, 3149–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zogaris, S.; Chatzinikolaou, Y.; Dimopoulos, P. Riparian woodland flora in upland rivers of western Greece. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2008, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdon, F.J.; Ramberg, E.; Sargac, J.; Forio, M.A.E.; de Saeyer, N.; Mutinova, P.T.; Moe, T.F.; Pavelescu, M.O.; Dinu, V.; Cazacu, C.; et al. Assessing the benefits of forested riparian zones: A qualitative index of riparian integrity is positively associated with ecological status in European streams. Water 2020, 12, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, T.E.; Figueroa, R.; Prat, N. Water management in mediterranean river basins: A comparison of management frameworks, physical impacts, and ecological responses. Hydrobiologia 2013, 719, 451–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, F.; Richards, K.; Girel, J.; Moss, T.; Muller, E.; Nilsson, C.; Rood, S. The Flooded Forest: Guidance for Policy Makers and River Managers in Europe on the Restoration of Floodplain Forests; Department of Geography, University of Cambridge: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Yon, D.; Tendron, G. Alluvial Forests of Europe; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 1981; ISBN 9789287107046. [Google Scholar]
- Van de Bund, W. Water Framework Directive Intercalibration Technical Report. Part 1: Rivers; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lazaridou, M.; Ntislidou, C.; Karaouzas, I.; Skoulikidis, N. Harmonisation of a new assessment method for estimating the ecological quality status of greek running waters. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munné, A.; Prat, N.; Solà, C.; Bonada, N.; Rieradevall, M. A Simple field method for assessing the ecological quality of riparian habitat in rivers and streams: QBR index. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2003, 13, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raven, P.J.; Dawson, F.H.; Everard, M. Quality assessment using river habitat survey data. Aquaic Conserv. 1998, 499, 477–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, D.; Mant, J.; Holloway, J.; Elbourne, N.; Janer, M. Practical River Restoration Appraisal Guidance for Monitoring Options (PRAGMO); The River Restoration Centre: Cranfield, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vaitis, M.; Feidas, H.; Symeonidis, P.; Kopsachilis, V.; Dalaperas, D.; Koukourouvli, N.; Simos, D.; Taskaris, S. Development of a spatial database and web-GIS for the climate of Greece. Earth Sci. Inform. 2019, 12, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environment and Energy-Special Secretariat for Water (MEE-SSW). River Basin Management Plans: Approved River Basin Management Plans. Available online: http://wfdver.ypeka.gr/en/management-plans-en/approved-management-plans-en/ (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Stefanidis, K.; Panagopoulos, Y.; Psomas, A.; Mimikou, M. Assessment of the natural flow regime in a mediterranean river impacted from irrigated agriculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 1492–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiatkowski, M.; Tomczyk, P. Comparative Assessment of the hydromorphological status of the rivers odra, bystrzyca, and ślȩza using the RHS, LAWA, QBR, and HEM methods above and below the hydropower plants. Water 2018, 10, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environment Agency. River Habitat Survey in Britain and Ireland—Field Survey Guidance Manual: 2003 Version; Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ourloglou, O.; Stefanidis, K.; Dimitriou, E. Assessing nature-based and classical engineering solutions for flood-risk reduction in urban streams. J. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 21, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, E.; Stavroulaki, E. Assessment of riverine morphology and habitat regime using unmanned aerial vehicles in a mediterranean environment. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2018, 175, 3247–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union; Copernicus Land Monitoring Service 2020; European Environment Agency (EEA) CORINE Land Cover 2018. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cover/clc2018 (accessed on 21 April 2020).
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Water and Agriculture: Towards Sustainable Solutions; Publications Office of the European Union: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kazoglou, Y.; Fotiadis, G.; Koutseri, I.; Vrahnakis, M. Assessment of structural components of riparian forest vegetation of the prespa basin with the means of the QBR index. In Proceedings of the BALWOIS Conference on Water Observation and Information System for Decision Support, Ohrid, Fyrom, 25–29 May 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).