Abstract
High energy consumption in size reduction operations is one of the most significant issues concerning the sustainability of raw material beneficiation. Thus, process optimization should be done to reduce energy consumption. This study aimed to investigate the applicability of artificial neural networks (ANNs) to predict the particle size distributions (PSDs) of mill products. PSD is one of the key sources of information after milling since it significantly affects the subsequent beneficiation processes. Thus, precise PSD prediction can contribute to process optimization and energy consumption reduction by avoiding over-grinding. In this study, coal particles (−2 mm) were ground with a rod mill under different conditions, and their PSDs were measured. The variables studied included volume% (vol.%) of feed (coal particle), vol.% rod load, and grinding time. Our supervised ANN models were developed to predict PSDs and trained by experimental data sets. The trained models were verified with the other experimental data sets. The results showed that the PSDs predicted by ANN fitted very well with the experimental data after the training. Root mean squared error (RMSE) was calculated for each milling condition, with results between 0.165 and 0.965. Also, the developed ANN models can predict the PSDs of ground products under different milling conditions (i.e., vol.% feed, vol.% rod load, and grinding time). The results confirmed the applicability of ANNs to predict PSD and, thus the potential contribution to reducing energy consumption by optimizing the grinding conditions.
1. Introduction
High energy consumption in size reduction operations is one of the biggest concerns in terms of the sustainability of raw material processing. One report stated that approximately 3% of the world’s energy is consumed by this process []. Thus, the process optimization of size reduction should contribute to energy reduction for our sustainable society. Proper prediction of size reduction and thus the particle size distributions (PSDs) avoid over-grinding and therefore reduce energy consumption to plant operations.
An artificial neural network (ANN) or knowledge-based artificial neural network (KBANN) is a parallel computation model inspired by the human brain and is categorized under the framework of machine learning []. While the human brain processes highly complex computations by billions of neutrons, ANN works with sequentially constructed input, hidden, and output layers consisting of several computation nodes called artificial neurons or simply neurons. Neurons in each layer are fully interconnected to other neurons in the adjacent layers, with weight vectors representing the strength of their connections. Similar to the human brain, a neuron receives signals from neurons in the pre-layer and signals can be intensified or weakened by the assigned activation functions. Their connections weight modulates input signals as synapsis does in the brain. The structure of the ANN model is different case-by-case. The independent and dependent parameters of a subjected conundrum are allocated to the input and output layers, respectively. In a forward process of ANN, the neutrons in the input layers receive the data from a database and transfer the data to neurons in the hidden layer through interconnected weight vectors. Subsequently, the forwarded values are processed by an assigned transfer function in the hidden neutrons and then sent to the output layer through interlinked weight vectors between the hidden and output layers. Consequently, an output value is obtained at an output layer. The neurons in the input and output layers are the data receivers. Computed value providers and only hidden neurons converse with other neurons.
Coal has been an energy source for several hundred years and has become increasingly significant. In 2011, it constituted 42% of the world’s electricity, and was recognized as one of the fastest-growing energy sources []. There are two types of coal in use: thermal and metallurgical. Thermal coal is used mainly for power generation. Metallurgical coal, on the other hand, is used in steel manufacturing. Coal can be obtained from either surface or underground mines; for example, in Australia, the majority is surface-mined. This determines how the coal is recovered and used as an energy source. The closer to the surface it is recovered from, the more weathered and oxidized it becomes. The oxidized coal shows different physical and/or surface properties from the underground coal with unoxidized surfaces. This oxidation can make coal difficult to process, especially in flotation, where particle surface properties are highly influenced [,].
Once the coal is mined, it can be classified into four size categories, i.e., coarse (+10 mm), intermediate (1–10 mm), fine (150 µm–1 mm), and ultrafine (−150 µm) particles []. Density separation of larger particles is performed to separate the coal from gangue minerals, while froth flotation is used for the fine and ultrafine particles.
The high applicability of ANN for simulating multi-parameter systems has received significant attention in many different fields (e.g., color coordinates in dyeing [], energy storage tanks [], and concrete [,]). Details of ANN and other soft computing technologies applications on mining engineering can be found in Jang and Topal (2014) []. In relation to PSD prediction, ANN has been applied to the crystallization process with mechano-chemical alloying [], the prediction of rock fragmentation after blasting [], and the prediction of PSD in a granulation process []. On the other hand, based on our literature review, the ANN-based predictive modeling of size reduction in milling processes has not been found. This is even though milling/comminution processes in mineral processing plants are one of the most energy-intensive operations in industries, and the presence of conventional approaches for predicting the PSDs of milling products involve discrete element methods (DEMs) [] and population balance modeling []. Thus, this paper details our attempt to apply ANN to predict PSDs during a size reduction process with a rod mill, which is one of the most common milling/comminution units.
This study aimed to generate ANN-based simulation models to predict the PSDs of comminution/mill products, address the above-noted issues, and substantially improve the model’s accuracy. In this study, ANN was used to develop reliable predicting models to predict PSDs of comminution products. The developed models allow us to predict the PSDs precisely to avoid over-grinding and reduce the energy consumption of plant operations. The logical basis of adopting ANN is its significant ability in terms of nonlinear approximation in comparison with common statistical prediction methods.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The coal sample used in this study was oxidized metallurgical coal, i.e., a run-of-mine sample from the Bowen Basin, Queensland, Australia. The experimental parts were divided into two: (1) feed coal sample preparation for the rod-milling experiments; (2) using the feed generated in part 1 and the rod-milling experiments to generate the PSD data for the ANN modeling and simulation. Firstly, the coal sample was spread onto a clean sheet, and the large coal particles not suitable for immediate rod milling were crushed through a cone crusher, then sent back into the sample pile. Then, the sample was milled in batches using a rod mill (ESSA, 520490). Each batch was milled for 5 min, with 10 or 20 vol.% of the mill volume loaded with the sample. The milled samples were then sorted into plus or minus 2 mm fractions using the Ro-tap (Tyler Industrial products, Testing sieve shaker model B). The minus-2 mm fraction was then split into subsamples to obtain approximately 10% to 20% feed volume of the rod mill, with each using a riffle splitter for each comminution/milling experiment. To characterize the feed, each split sample was sieved using sieves with openings of 2 mm, 1 mm, 500 µm, 250 µm, 125 µm, 63 µm, and 38 µm to obtain the particle size distribution of the feed in each set by sieving the sample for 5 min in a vibrating sieve shaker.
Secondly, to generate the milling experimental results used in this study, using the feed coal sample generated in the above procedure in the first step, the load of the coal sample (i.e., minus 2 mm) was 10 or 20 vol.% of the mill with 9 or 19 rods (i.e., 10 or 20 vol.% of the mill), and the sample was ground for 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32 min. After each grinding time, the ground coal particles were riffled to obtain two 250 g representative samples and their size classifications were performed separately with the same sieve set mentioned above in the first step to obtain the PSDs. The average of the two PSDs was used for the modeling and simulation. Since we needed to have changes in the PSDs for the ANN modeling and simulation to capture the trend in PSD changes, 1–2 mm size fraction data sets (with a passing cumulative that was always 100%) were not used, but the minus-1 mm size fraction data sets were used in this study.
2.2. Methods-ANN Model Predicting Percentage Passing Cumulative
The percentage passing cumulative (PPC: %) is generally expressed as a function of sieve opening size (SO:). A total of 56 datasets were collected and randomly divided into training (40 datasets: 70%), validation (8 datasets: 15%), and training (8 datasets: 15%) datasets. For the milling study, 56 experimental datasets are considered more than enough [,,]. The used datasets split% is common in the literature [,,]. The training datasets were used to train the ANN model, while the validation datasets were employed to validate each iteration. At the end of the training process, the generalization of the trained ANN model was checked by inputting the untrained test datasets.
To generate a potential PPC, a PPC prediction ANN was formulated for the SO values of 1000, 500, 250, 125, 63, and 38 µm. The basic structures of the six ANNs were identical to each other. It consisted of feed load (FL: Vol.%), rod load (RL: Vol.%), and grinding time (GT: min) as input parameters and PPC as an output. In addition, all of the six PPC prediction ANN models were formulated with ten hidden neurons determined by trial and error. The structure of the proposed ANN models is illustrated in Figure 1.
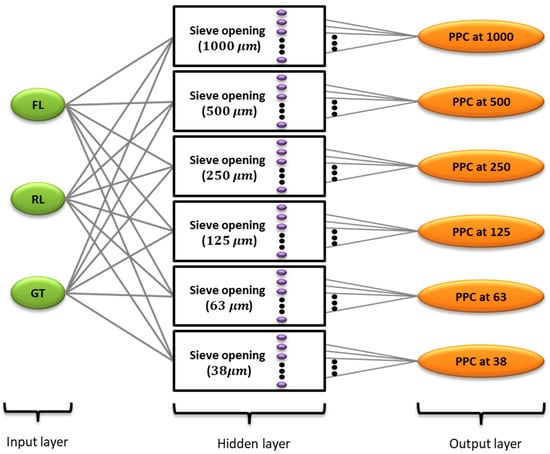
Figure 1.
Schematic of the proposed ANN models for PPC predictions. (FL—Feed Load (Vol.%), RL—Rod Load (Vol.%), GT—Grinding Time (min.), SO—Sieve Opening (), and PPC—Percentage of Passing Cumulative (%)).
An output of an artificial node can be calculated as follows []:
where f is the transfer function, n is the input vector dimension, is the connection weight of input , and is a bias value of the node.
In these PPC-prediction ANN models, the hyperbolic tangent function was applied in hidden neurons as a transfer function that receives values from −1 to 1. The mathematical equation of the hyperbolic tangent function is shown in Equation (2) [].
The input net () was connected to the hidden neurons in every hidden layer. For example, the net input values to the hidden layer of SO: 1000 were:
where, was a computed net value in the hidden layer for the sieve opening of 1000, was the input values, was the connection weights between the input neurons and hidden neurons in SO: 1000, and was a bias neuron from the input to the hidden layers. As the six hidden layers were identical to each other, the computation process of the net input values to the other SO hidden layers were also identical.
As the hyperbolic tangent function was adopted in the hidden layers, for example, the output of hidden layer of SO: 1000 was:
Thus, the input net to the output layer of SO: 1000 was:
where was connection weights between the hidden and output layers of SO: 1000, and was a bias neuron from hidden to output layers.
In the early backward process, the mean square error (MSE where and were measured and predicted the output of the testing or training data []) of the predicted output () and target experimental output () were calculated. For instance, the MSE for SO: 1000 was calculated as:
The was back-propagated to update the randomly assigned connection weights for the next iteration using the Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm (LMA) [,]. The LMA weights update rule, i.e., the learning rule, was:
where represents the updated connection weights for step, represents the weights for step, represents the Jacobian matrix for step, and the combination coefficient.
In order to develop ANN models, the following steps were taken: (1) experimental data collection (see Section 2.1); (2) division of the data for training, testing, and validation; (3) creation of the network for the selected parameters; (4) configuration of the network by selecting the number of hidden layers and the desired training and necessary learning functions; and (5) training of the ANN models to obtain the MSE target. Figure 2 shows an example of an ANN learning process results within the MATLAB neuron toolbox indicating the structure, learning algorithm, and results of the learning parameters. The ANN structure is 3-10-1 in all particle size fractions. It consists of the input and output layers as well as the 10 hidden nodes. The outcomes of the ANN represent the particle percentage passing of each size fraction.
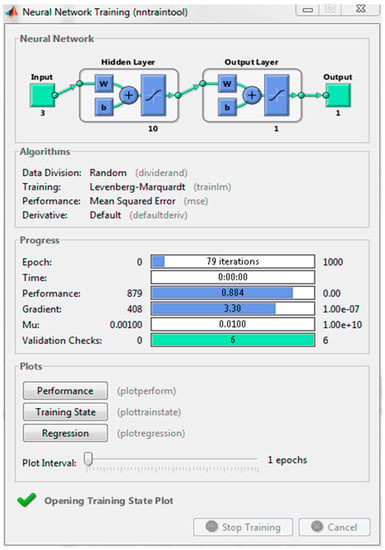
Figure 2.
ANN toolbox indicating learning process and operational parameters.
3. Results and Discussion
The six ANN models were trained separately. Figure 3 shows typical correlation plots between the output and target during the training and validation. The correlation coefficient R for the trained model was close to 1 (i.e., R = 0.999), and thus it indicates the successful training of the model. As shown in the validation, the estimated ANN values were close to the experimental target results with R = 0.987. Therefore, the developed model can be used to predict the PSDs of milling products with good precision. In the literature, the other studies including the crystallization process with mechano-chemical alloying [], the prediction of rock fragmentation after blasting [], the prediction of PSD in a granulation process [], and also confirmed the applicability of ANN to predict PSD. Figure 4a shows the changes in parameters during the model optimization and indicates the validation process to prevent the over-fitting of the model. Figure 4b shows the mean squared errors (MSEs) and indicates that the MSE reached the best value after 30 epochs in the trial and 70 epochs in the validation. They are comparable with the number of epochs described in the literature [,]. The best validation performance was determined with a minimum MSE and thus the largest correlation with the experimental data/outcome [].
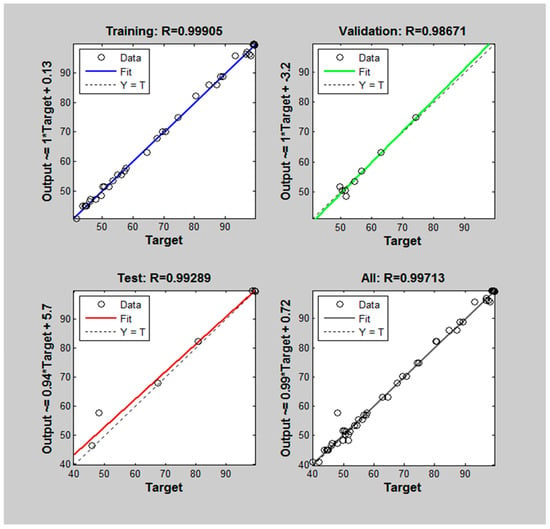
Figure 3.
Correlation plots between the output and target values for training, validation, and testing. The results of the 250 µm passing are plotted as an example.
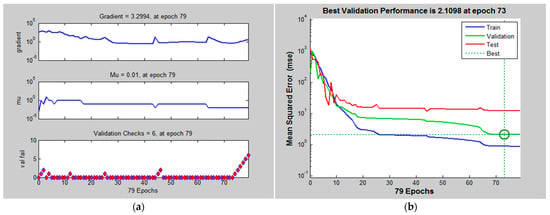
Figure 4.
(a) Changes in parameters and (b) mean squared error during the model optimization processes. The results of 250 µm passing are plotted as an example.
As introduced in the materials and methods, the six ANN models were trained separately, and the results are demonstrated in Table 1 and Figure 5. As shown in Table 1 and Figure 5, strong positive correlation coefficients (R > 0.90) were obtained in all the models, and thus confirmed the statistical reliability of the models. In terms of the correlations of SO: 38 are comparatively lower than other models, which could be due to the too-narrow ranges of the output datasets. As can be seen in Figure 6, among the eight datasets kept for testing the developed ANN models, four datasets were randomly selected, and the simulated data were compared by using the proposed ANN models with the experimental data.

Table 1.
Training results of six PPC prediction ANN models.
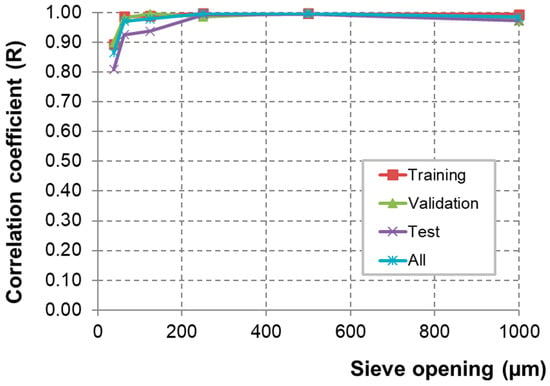
Figure 5.
Correlation coefficient (R) of the training, validation, and test datasets in the ANN models for six SO levels.
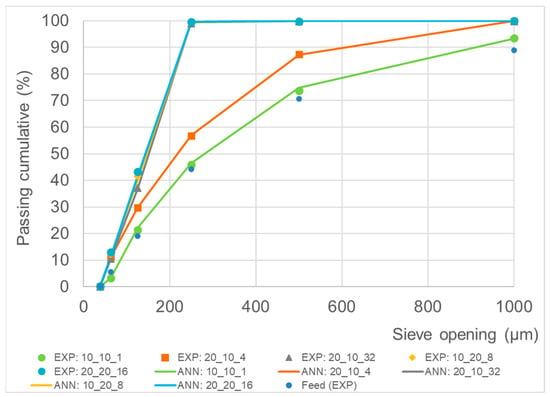
Figure 6.
Comparisons between the ANN-predicted PPC (ANN) and experimental PPC (EXP). The numbers in the figure legend represent FL (Vol.%), RL (Vol.%), and GT (Min.). The feed (EXP) particle size distribution without grinding (GT = 0 min) was also added as a reference value.
The results shown in Figure 6 indicate that very good predictions were made with our models of the PSDs of mill products under different conditions (i.e., feed load, rod load, and milling time). The root mean squared error (RMSE) was calculated for each milling condition, and it was between 0.165 and 0.965. These values are smaller than that of the literature [] on crystallite size prediction (RMSE = 3.34). It was found that with 1 min of milling at a 10 vol.% feed load and 10 vol.% rod load, there was no significant size reduction. On the other hand, with a higher rod load and milling time, the size reduction achieved and thus PSD of coal particles decreased, and this size reduction can be explained by the higher probability of collision between coal particles and mill media (i.e., rods in this study) (e.g., []). Our results confirmed the applicability of ANN to predict the particle size distributions of the milled products. Our proposed approach can be applicable not only to a specific mill type (i.e., rod mill in this study) and feed (i.e., coal in this study) but also to many other combinations (e.g., ball milling of gold-bearing ore), and can be beneficial for other scholars and practitioners.
4. Conclusions
This study aimed to investigate the applicability of artificial neural networks (ANNs) to predict the particle size distributions (PSDs) of mill products. Coal particles (−2 mm) were ground with a rod mill under different conditions, and we obtained their PSD. The parameters studied were vol.% feed (coal particle), vol.% rod load, and grinding time. The results showed that the particle size distributions predicted by ANN fit very well with the experimental data after training the dataset. The root mean squared error (RMSE) was calculated for each milling condition and it was significantly smaller (i.e., 0.165 and 0.965) than that found in the literature in terms of crystallite size prediction (RMSE = 3.34). Furthermore, the developed ANN models can predict the PSDs of ground products under different milling conditions (i.e., vol.% feed, vol.% rod load, and grinding time). The results indicated the applicability of ANN to predict PSD. The proposed approach can be used not only for coal particles but also for other minerals/materials to predict their PSD in order to reduce energy consumption by optimizing the grinding conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.O. and H.J.; methodology, A.O. and H.J.; software, A.O. and H.J.; validation, A.O. and H.J.; formal analysis, A.O. and H.J.; investigation, A.O. and H.J.; resources, A.O. and H.J.; data curation, A.O. and H.J.; writing—original draft preparation, A.O. and H.J.; writing—review and editing, A.O. and H.J.; visualization, A.O. and H.J.; supervision, A.O.; project administration, A.O.; funding acquisition, A.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Government of Canada. Tackling Comminution, the Largest Energy Consumer. Available online: https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/our-natural-resources/minerals-mining/mining-resources/tackling-comminution-largest-energy-consumer/18296 (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- Towell, G.G.; Shavlik, J.W. Knowledge-based artificial neural networks. Artif. Intell. 1994, 70, 119–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Coal Association. Coal Statistics. 2012. Available online: http://www.worldcoal.org/resources/coal-statistics/ (accessed on 4 April 2013).
- Otsuki, A.; Miller, T. Experimental Investigation on Safer Frother Option for Coal Flotation. Curr. Work. Miner. Process. 2019, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuki, A.; Miller, T. Safer Frother Option for Coal Flotation—A Review. Curr. Work. Miner. Process. 2019, 1, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaron, N.; Luttrell, G.H. A review of state-of-the-art processing operations in coal preparation. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2015, 25, 511–521. [Google Scholar]
- Vadood, M.; Haji, A. Application of ANN Weighted by Optimization Algorithms to Predict the Color Coordinates of Cellulosic Fabric in Dyeing with Binary Mix of Natural Dyes. Coatings 2022, 12, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, A.A.; Mokhtar, A.A.; Salilew, W.M.; Abdul Karim, Z.A.; Abbasi, A.; Lashari, N.; Jameel, S.M. Machine Learning Approach to Predict the Performance of a Stratified Thermal Energy Storage Tank at a District Cooling Plant Using Sensor Data. Sensors 2022, 22, 7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irandegani, M.A.; Zhang, D.; Shadabfar, M. Probabilistic assessment of axial load-carrying capacity of FRCM-strengthened concrete columns using artificial neural network and Monte Carlo simulation. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarir, P.; Armaghani, D.J.; Jiang, H.; Sabri, M.M.S.; He, B.; Ulrikh, D.V. Prediction of Bearing Capacity of the Square Concrete-Filled Steel Tube Columns: An Application of Metaheuristic-Based Neural Network Models. Materials 2022, 15, 3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Topal, E. A review of soft computing technology applications in several mining problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2014, 22, 638–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Ya, H.H.; Azeem, M.; Yusuf, M.; Soomro, I.A.; Masood, F.; Shozib, I.A.; Sapuan, S.M.; Akhter, J. Artificial Neural Network Modeling to Predict the Effect of Milling Time and TiC Content on the Crystallite Size and Lattice Strain of Al7075-TiC Composites Fabricated by Powder Metallurgy. Crystals 2022, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Huang, D.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, S. Combined ANN Prediction Model for Rock Fragmentation Distribution due to Blasting. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2013, 10, 3511–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Fu, J.; Dang, L.; Cheong, Y.; Tan, H.; Wei, H. Prediction of the particle size distribution parameters in a high shear granulation process using a key parameter definition combined artificial neural network model. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 10825–10834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasekara, N.S.; Liu, L.X.; Powell, M.S. Estimating energy in grinding using DEM modelling. Miner. Eng. 2016, 85, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esnault, V.P.B.; Zhou, H.; Heitzmann, D. New population balance model for predicting particle size evolution in compression grinding. Miner. Eng. 2015, 73, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kor, M.; Abkhoshk, E.; Tao, D.; Chen, G.L.; Modarres, H. Modeling and optimization of high chromium alloy wear in phosphate laboratory grinding mill with fuzzy logic and particle swarm optimization technique. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.K.; Dey, S.; Das, A. Comminution features in an impact hammer mill. Powder Technol. 2013, 235, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraschiv, G.; Moiceanu, G.; Voicu, G.; Chitoiu, M.; Cardei, P.; Dinca, M.N.; Tudor, P. Optimization Issues of a Hammer Mill Working Process Using Statistical Modelling. Sustainability 2021, 13, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulihonenahali Rajkumar, A.; Hemath, M.; Kurki Nagaraja, B.; Neerakallu, S.; Thiagamani, S.M.K.; Asrofi, M. An Artificial Neural Network Prediction on Physical, Mechanical, and Thermal Char-acteristics of Giant Reed Fiber Reinforced Polyethylene Terephthalate Composite. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 51, 769S–803S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picos-Benítez, A.R.; Martínez-Vargas, B.L.; Duron-Torres, S.M.; Brillas, E.; Peralta-Hernández, J.M. The use of artificial intelligence models in the prediction of optimum operational conditions for the treatment of dye wastewaters with similar structural characteristics. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 143, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenberg, K. A method for the solution of certain problems in least squares. Q. Appl. Math. 1944, 2, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, D.W. An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 1963, 11, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuki, A.; Pereira Gonçalves, P.; Leroy, E. Selective Milling and Elemental Assay of Printed Circuit Board Particles for Their Recycling Purpose. Metals 2019, 9, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).