Influence of Pyrolysis Parameters Using Microwave toward Structural Properties of ZnO/CNS Intermediate and Application of ZnCr2O4/CNS Final Product for Dark Degradation of Pesticide in Wet Paddy Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material of Research
2.2. Procedures of Research
2.2.1. Synthesis of ZnO/CNS and ZnCr2O4/CNS
- Rice husk without ZnCl2 activator—GM4, GM6, GM8;
- Rice husk with ZnCl2 activator (Z)—GMZ4, GMZ6, GMZ8;
- Sawdust without ZnCl2 activator—SGM4, SGM6, SGM8;
- Sawdust with ZnCl2 activator (Z)—SGMZ4, SGMZ6, SGMZ8.
- Rice husk without ZnCl2 activator—TGM4, TGM6, TGM8;
- Rice husk with ZnCl2 activator (Z)—TGMZ4, TGMZ6, TGMZ8;
- Sawdust without ZnCl2 activator—TSGM4, TSGM6, TSGM8;
- Sawdust with ZnCl2 activator (Z)—TSGMZ4, TSGMZ6, TSGMZ8.
- Rice husk with ZnCl2 activator (Z)—CTGMZ4, CTGMZ8;
- Sawdust with ZnCl2 activator (Z)—CTSGMZ4, CTSGMZ8.
2.2.2. Characterization
2.2.3. Application of Composite for Dark Degradation Reaction of Pesticide
3. Results and Discussion
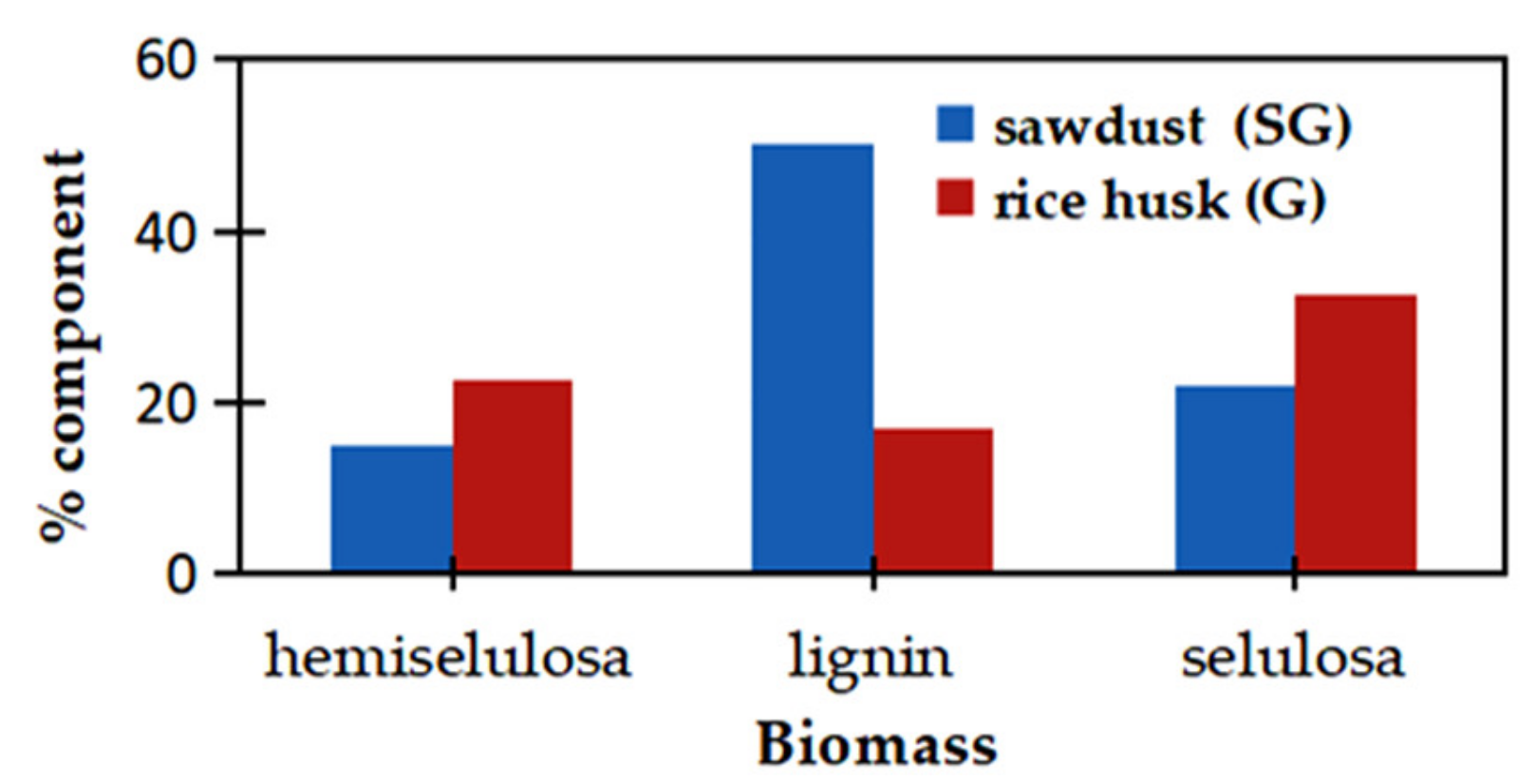
3.1. Synthesis of ZnO/CNS from Different Biomass
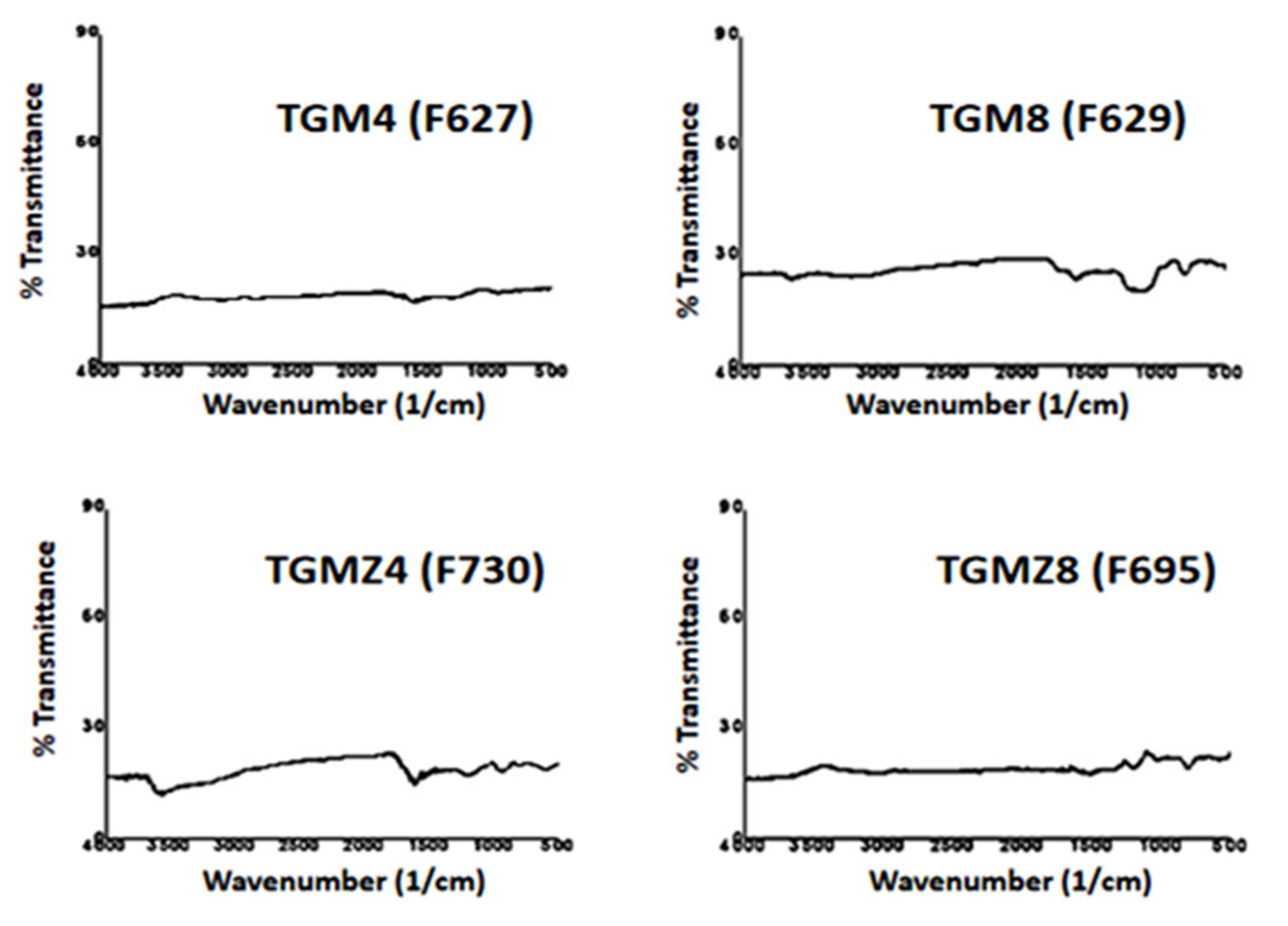
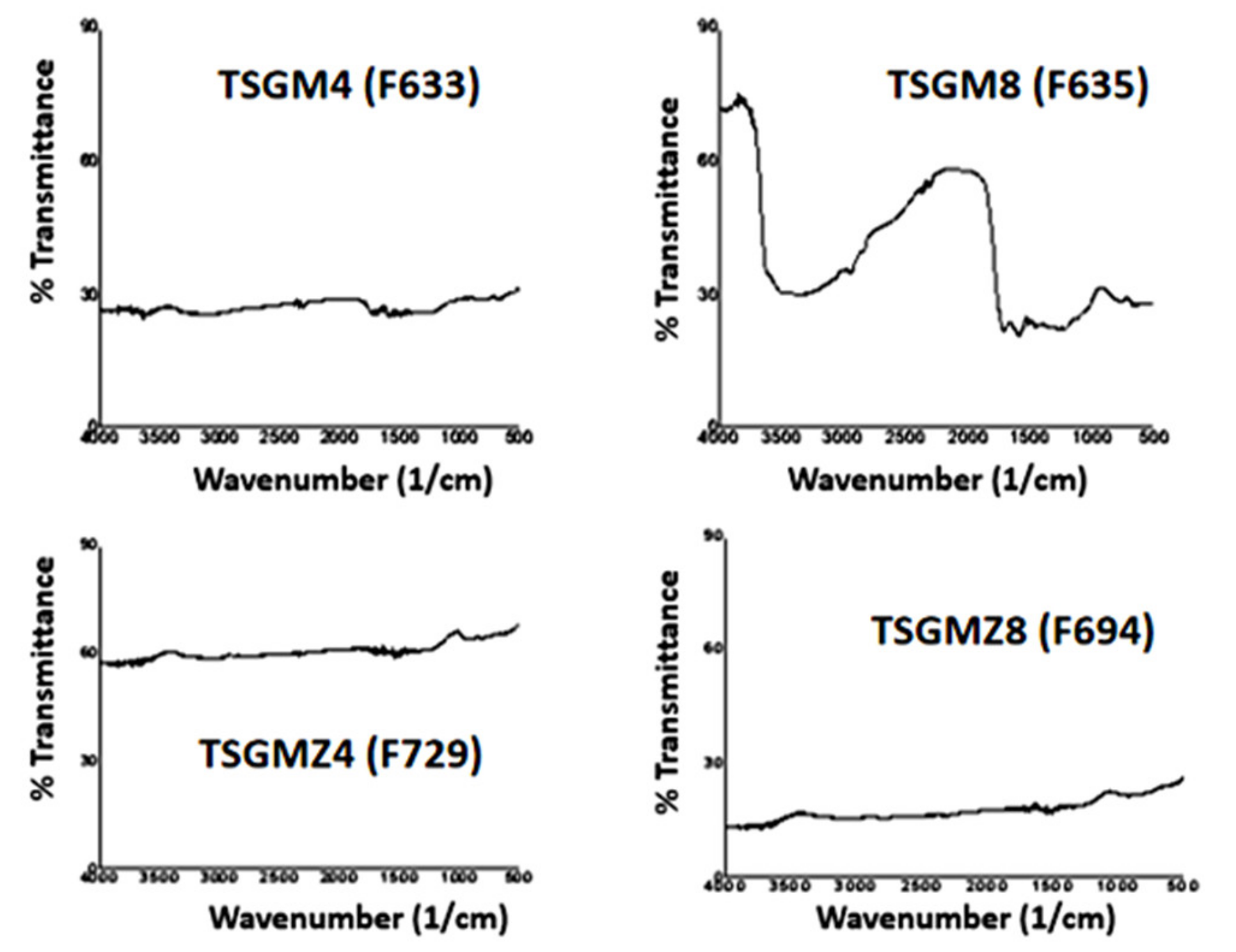
3.2. Influence of Biomass Type and Microwave Pyrolysis Parameters toward Functional Groups of the ZnO/CNS Composites
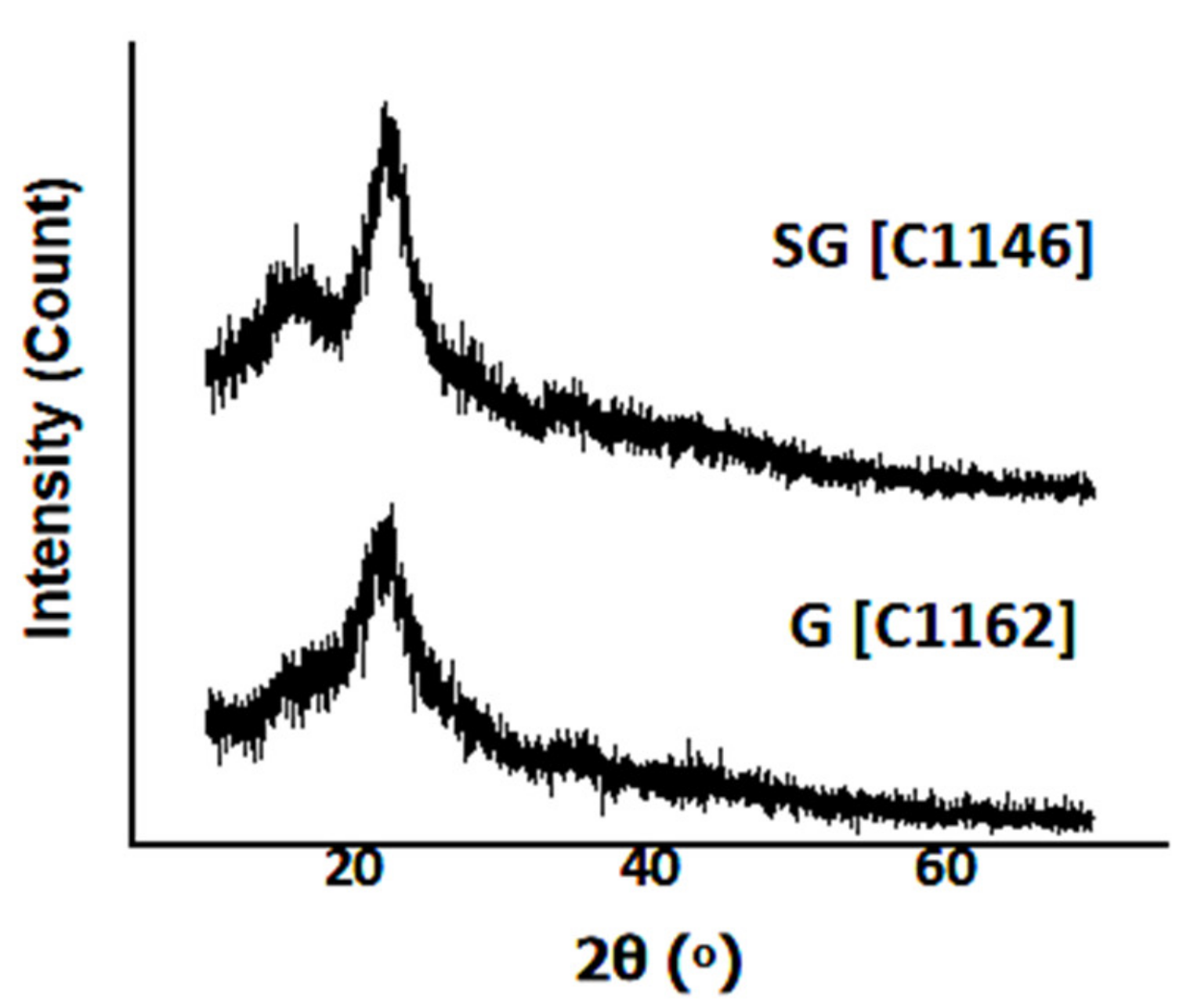
3.3. Influence of Biomass and Microwave Pyrolysis Parameters toward Structure of the ZnO/CNS
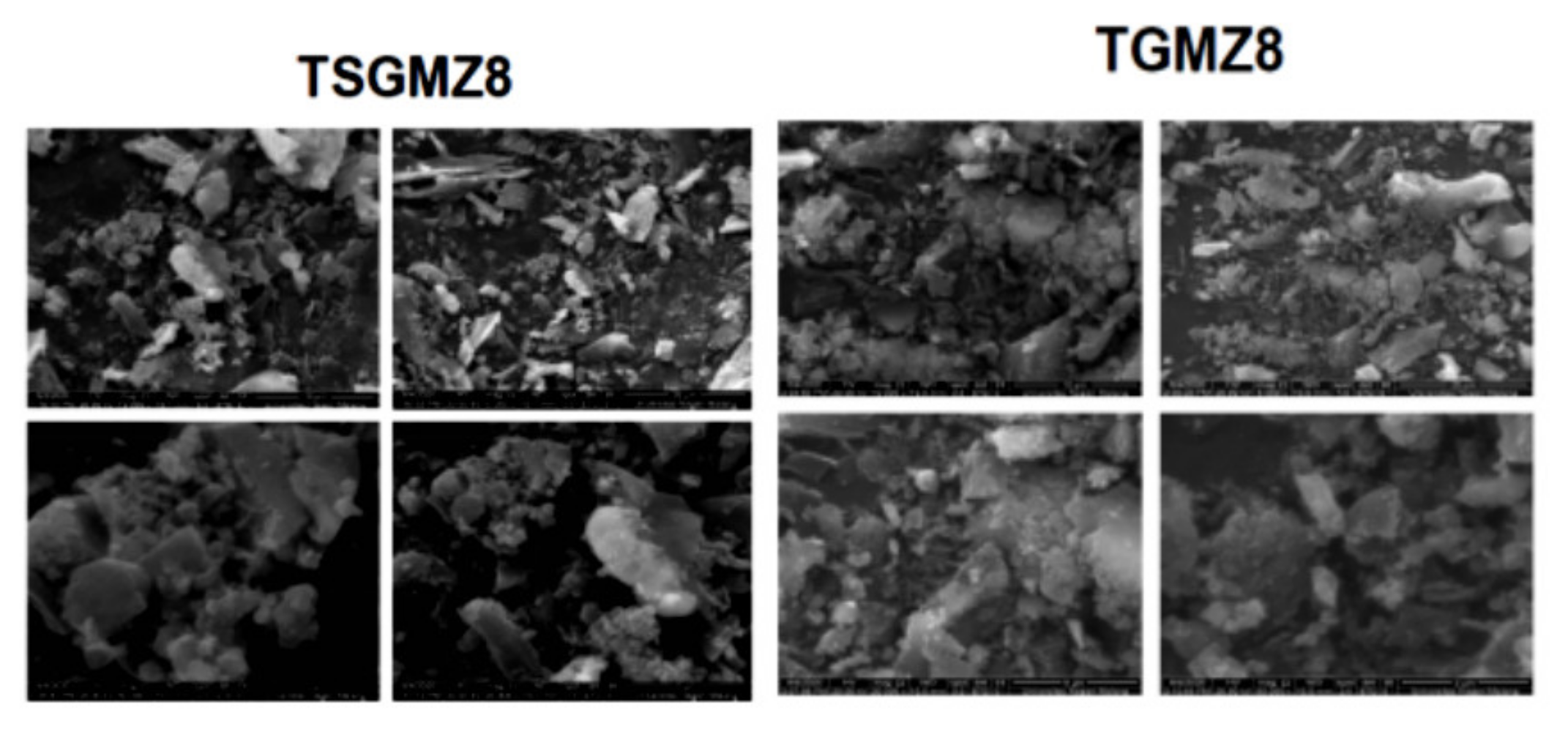
3.4. Influence of Biomass and Microwave Pyrolysis Parameters toward Morphology of the ZnO/CNS
3.5. Influence of Biomass and Microwave Pyrolysis Parameters toward Stability of the ZnO/CNS Colloid
3.6. Characterization of the Final Product ZnCr2O4/CNS Composite by XRD and SEM-EDX
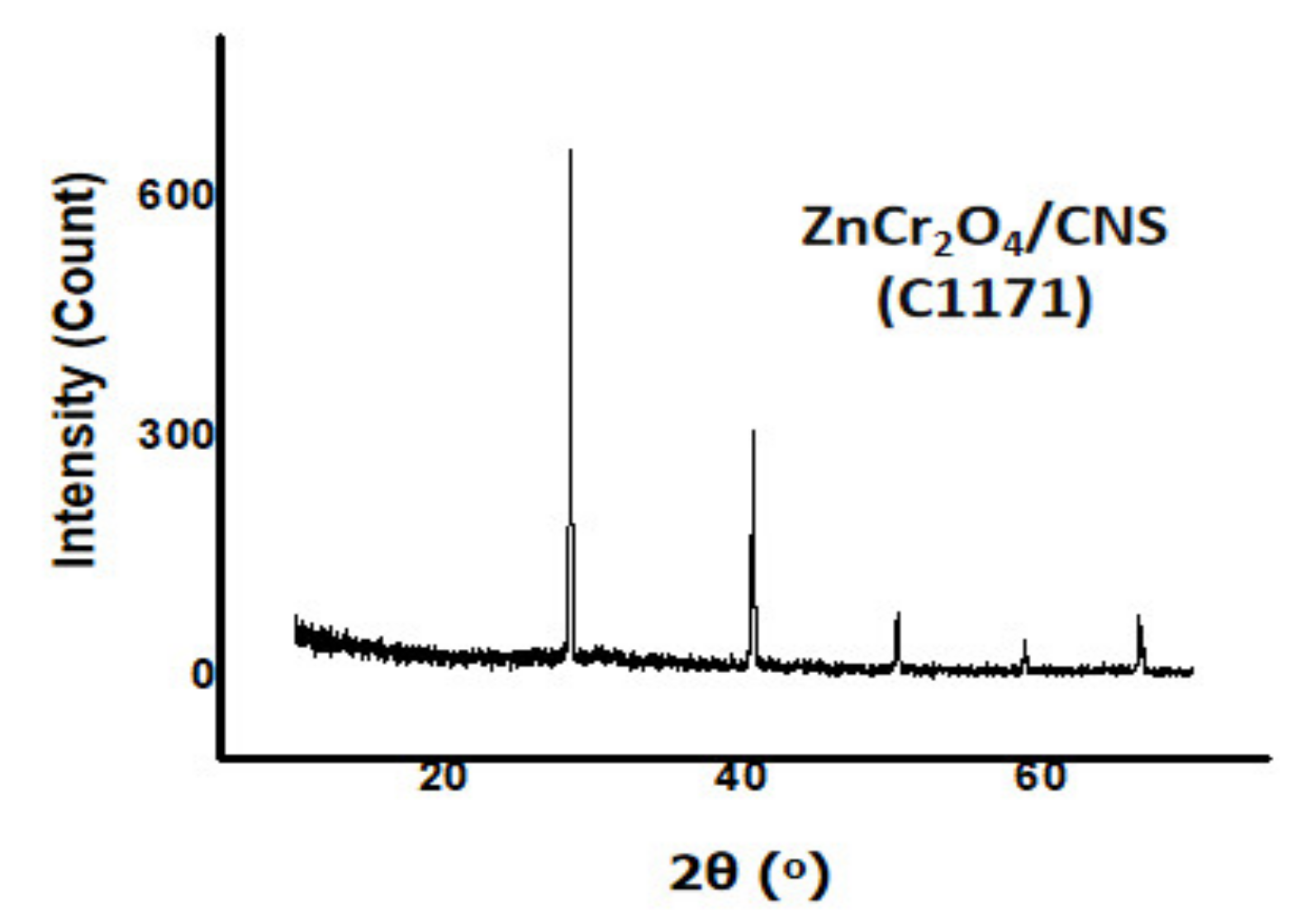
3.6.1. Characterization by XRD
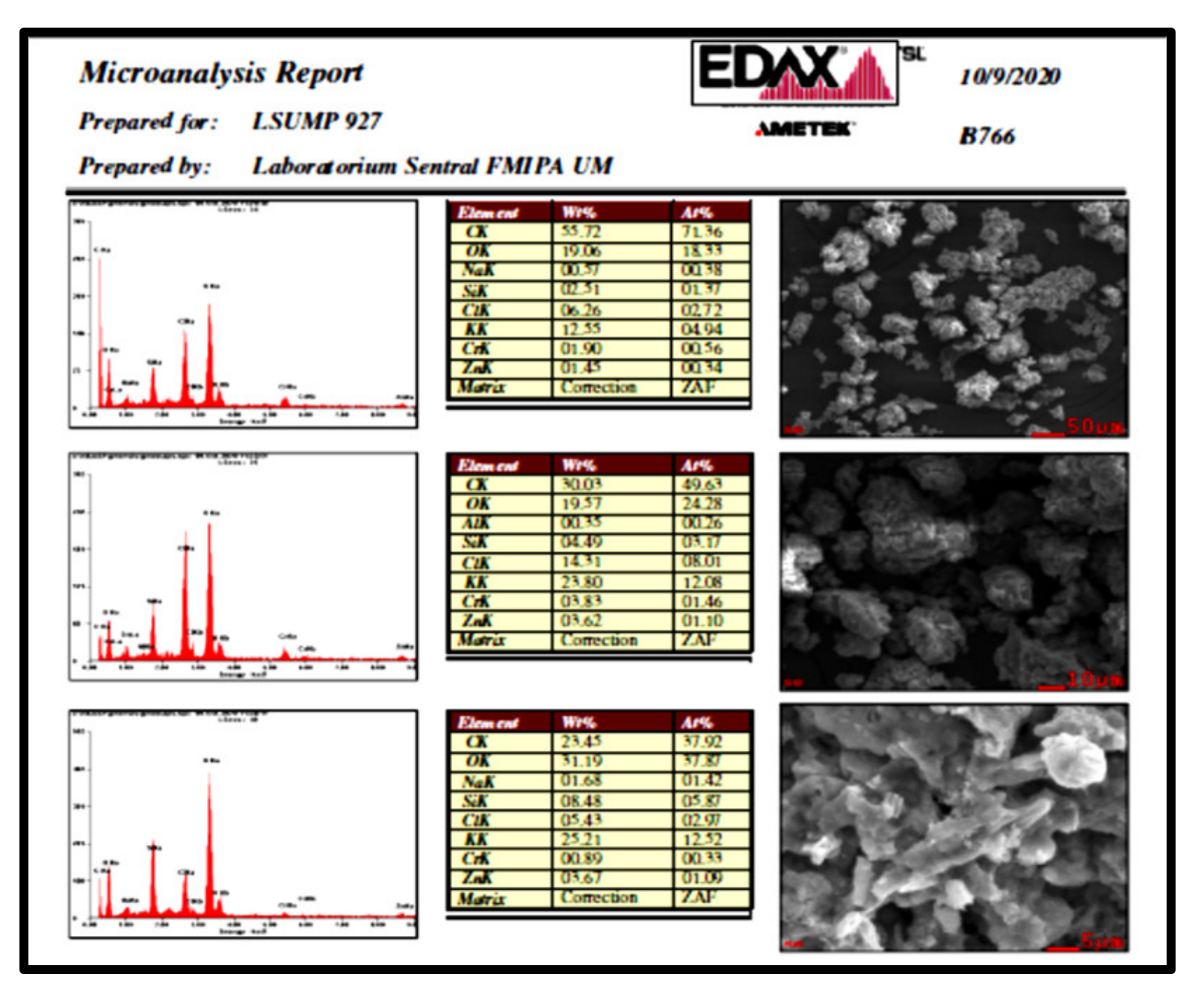
3.6.2. Characterization by SEM-EDX
3.7. Application of ZnCr2O4 Composite for Dark Degradation of Pesticide in Soil
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Subandi, M.; Chaidir, L.; Nurjanah, U. Keefektifan Insektisida BPMC dan Ekstrak Daun Suren terhadap Hama Wereng Batang Coklat (Nilaparvata lugens Stal.) dan Populasi Musuh Alami pada Padi Varietas Ciherang. J. Agrik. 2016, 27, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardiwinata, A.N.; Nursyamsi, D. Residu Pestisida di Sentra Produksi Padi di Jawa Tengah. Pangan 2012, 21, 39–58. Available online: https://jurnalpangan.com/index.php/pangan/article/view/103/90 (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Fitriadi, B.R.; Putri, A.C. Metode-Metode Pengurangan Residu Pestisida pada Hasil Pertanian. J. Rekayasa Kim. Lingkung. 2016, 11, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Young, R.O. Colloids and Colloidal Systems in Human Health and Nutrition. Int. J. Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinko, P.J.; Singh, Y. Martin’s Physical Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 6th ed.; Physical, Chemical and Biopharmaceutical Principles in the Pharmaceutical Sciences; Wolters Kluwer Health, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006; p. 1. Available online: https://innocentbalti.files.wordpress.com/2015/01/martins-physical-pharmacy-6th-ed-2011-dr-murtadha-alshareifi.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Hielscher, T. Ultrasonic Production of Nano—Size Dispersions and Emulsions. In Proceedings of the ENS’05, Paris, France, 14–16 December 2005; Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/0708.1831 (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Milanovi, M.; Stijepovi, I.; Pavlovi, V.; Srdi, V. Functionalization of Zinc Ferrite Nanoparticles: Influence of Modification Procedure on Colloidal Stability. Process. Appl. Ceram. 2016, 10, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setianingsih, T.; Mutrofin, S. Sintesis Karbon Nanomaterial dari Limbah Biomassa yang Dimodifikasi MFe2O4 Secara Green Technology Sebagai Campuran Pupuk Cair Untuk Remediator Tanah Sawah dan Saluran Irigasi Tercemar Pesticida. In Laporan akhir HPU.; Universitas Brawijaya: Malang, Indonesia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zaytseva, O.; Neumann, G. Carbon Nanomaterials: Production, Impact on Plant Development. Agric. Environ. Appl. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2016, 3, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowell, S.; Shields, J.E.; Thomas, M.A.; Thommes, M. Characterization of Porous Solids and Powders: Surface Area, Pore Size and Density; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; Available online: https://3lib.net/book/2086739/44936e (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Li, L.; Sun, Z.; Li, H.; Keener, T.C. Effects of activated carbon surface properties on theadsorption of volatile organic compounds. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2012, 62, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Qu, Y.; Xu, J. Microwave-Assisted Conversion of Lignin. In Production of Biofuels and Chemicals with Microwave; Fang, Z., Smith, R.L., Jr., Qi, X., Eds.; Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Shra’ah, A.; Helleur, R. Microwave pyrolysis of cellulose at low temperature. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2014, 105, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chem, P.; Liu, S.; Peng, P.; Min, M.; Cheng, Y.; Anderson, E.; Zhou, N.; Fan, L.; Liu, L.; et al. Effects of Feedstock Characteristics on Microwave-assisted Pyrolisis—A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 230, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoan, B.T.; Tam, P.D.; Pha, V.H. Green Synthesis of Highly Luminescent Carbon Quantum Dots from Lemon Juice. Hindawi J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 2019, 2852816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewumi, G.A.; Revaprasadu, N.; Eloka-Eboka, A.C.; Inambao, F.L.; Gervas, C. A Facile Low-cost Synthesis of Carbon Nanosphere from Coconut Fibre. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science (WCECS) 2017, San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–27 October 2017; Volume II. Available online: http://www.iaeng.org/publication/WCECS2017/WCECS2017_pp577-582.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Schwenke, A.M.; Hoeppener, S.; Schubert, U.S. Synthesis and Modification of Carbon Nanomaterials Utilizing Microwave Heating. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4113–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.F.; Chiueh, P.T.; Shih, C.H.; Lo, S.L.; Sun, L.; Zhong, Y.; Qiu, C. Microwave Pyrolisis of Rice Straw to Produce Biochar as Adsorbent for CO2 Capture. Energy 2015, 84, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyang, M.; Gao, B.; Zimmerman, A.; Zhang, M.; Chena, H. Synthesis, Characterization, and Dye Sorption Ability of Carbon Nanotube—Biochar Nanocomposites. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Park, M.; Park, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; Akanda, M.R.; Park, B.Y.; Kim, H.Y. Green Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots from Carrot Juice for In Vitro Cellular Imaging. Carbon Lett. 2017, 21, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauzi, N.; Zain, N.M.; Yusof, N.A.A. Microwave-assisted Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Stabilized with Gum Arabic: Effect of Microwave Irradiation Time on ZnO Nanoparticles Size and Morphology. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal. 2019, 14, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.Z.; Khorasani-Motlagh, M.; Jahani, S.; Yousefi, M. Synthesis and Characterization of α-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles by Microwave Method. Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 8, 87–92. Available online: http://www.ijnnonline.net/article_3909_75ca9bcd50a49f70f707d5a9ef0848fc.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Taylor, L.A.; Meek, T.T. Microwave Sintering of Lunar Soil: Properties, Theoy, and Practice. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2005, 18, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setianingsih, T.; Purwonugroho, D.; Prananto, Y.P.; Mutrofin, S. Sintesis Nanokarbon dan Komposit Nanokarbon dari Biomassa dengan Metode Pirolisis Fasa Padat dengan Mirowave—Sonikasi untuk Remediator Lahan Tanah Pertanian Tercemar Pestisida. In Laporan akhir Hibah Doktor Lektor Kepala; Universitas Brawijaya: Malang, Indonesia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dippong, T.; Andrea, E.; Cadar, O. Review Recent Advances in Synthesis and Applications of MFe2O4 (M = Co, Cu, Mn, Ni, Zn) Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayedwa, N.; Mulaudzi-Masuku, T.; Matinise, N.; Nkosi, M. Biosynthesis and characterization of multifunctional mixed oxides of ZnCr2O4/ZnCrO4 nanoparticulate from natural leaf extracts of Hibiscus Rosa Sinensis. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 36, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Laudenschleger, D.; Carey, J.J.; Ruland, H.; Nolan, M.; Muhler, M. Spinel-Structured ZnCr2O4 with Excess Zn Is the Active ZnO/Cr2O3 Catalyst for High-Temperature Methanol Synthesis. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 7610–7622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Chakra, C.H.S. Synthesis and Structural Characterization of ZnCr2O4 Nano Particles Prepared by Citrate-gel Auto Combustion Method. Asian J. Phys. Chem. Sci. 2017, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dumitru, R.; Manea, F.; Păcurariu, C.; Lupa, L.; Pop, A.; Cioablă, A.; Surdu, A.; Ianculescu, A. Synthesis, Characterization of Nanosized ZnCr2O4 and Its Photocatalytic Performance in the Degradation of Humic Acid from Drinking Water. Catalysts 2018, 8, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarulzaman, N.; Kasim, M.F.; Rusdi, R. Band Gap Narrowing and Widening of ZnO Nanostructures and Doped Materials. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keihan, E.R.; Aliabadi, H.A.M.; Radinekiyan, F.; Sobhani, M.; Khalili, F.; Maleki, A.; Madanchi, H.; Mahdavi, M.; Shalan, A.E. Investigation of the biological activity, mechanical properties and wound healing application of a novel scaffold based on lignin–agarose hydrogel and silk fibroin embedded zinc chromite nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 17914–17923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assem, L.; Zhu, H. Chromium, Toxicological Overview; Cranfield University: Bedford, UK, 2007; pp. 1–14. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/338694/Chromium_toxicological_overview.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Sun, H.; Brocato, J.; Costa, M. Oral Chromium Exposure and Toxicity. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2015, 2, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.; Maignan, A.; Simon, C.; Martin, C. FeCr2O4 and CoCr2O4 spinels: Multiferroicity in the collinear magnetic state? Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielicka, A.; Bojanowska, I.; Wiśniewski, A. Two Faces of Chromium—Pollutant and Bioelement. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2005, 14, 5–10. Available online: http://www.pjoes.com/Two-Faces-of-Chromium-Pollutant-and-Bioelement,87721,0,2.html (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Chen, Y.; Wu, H.; Sun, P.; Liu, J.; Qiao, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Z. Remediation of Chromium-Contaminated Soil Based on Bacillus cereus WHX-1 Immobilized on Biochar: Cr(VI) Transformation and Functional Microbial Enrichment. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, D.; Tiwari, M.; Dutta, P.; Singh, P.; Chawda, K.; Kumari, M.; Chakrabarty, D. Chromium Stress in Plants: Toxicity, Tolerance and Phytoremediation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; Choudhury, S. Chromium stress in plant. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 17, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, A.K.; Cervantes, C.; Loza-Tavera, H.; Avudainayagam, S. Chromium toxicity in plants. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Regional Office for Europe. Chromium. In Air Quality Guidelines, 2nd ed.; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2000; pp. 1–4. Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/document/e71922.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- DesMarias, T.L.; Costa, M. Mechanisms of chromium-induced toxicity. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2019, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triyanto, K.B.T. Manfaat Hidrogen Peroksida (H2O2) Bagi Tanaman, Kabar Tani.com, 2016, 18/11/2016. Available online: https://kabartani.com/manfaat-hidrogen-perok (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Hany, R.C.R. Efektivitas Pemberian Hidrogen Peroksida terhadap Kualitas Media, Kelangsungan Hidup dan Pertumbuhan Benih Ikan Patin Pangasius sp. Skripsi, Departemen Budidaya Perairan, Fakultas Perikanan dan Ilmu Kelautan, IPB, Bogor. 2014. Available online: https://repository.ipb.ac.id/handle/123456789/74423 (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Yang, H.; Yan, R.; Chen, H.; Lee, D.H.; Zheng, C. Characteristics of Hemicellulose, Cellulose, and Lignin Pyrolysis. Fuel 2007, 86, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balat, M. Experimental Study on Pyrolysis of Black Alder Wood. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2008, 26, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, H.; Reinoso, F.R. Activated Carbon; Elsevier Sci.: Alpharetta, GA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bergna, D.; Varila, T.; Romar, H.; Lassi, U. Comparison of the Properties of Activated Carbons Produced in One-Stage andTwo-Stage Processes. C J. Carbon Res. 2018, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setianingsih, T.; dan Prananto, Y.P. Spektroskopi Inframerah Untuk Material Anorganik; UB Press: Malang, Indonesia, 2020; pp. 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Bakti, A.I.; Gareso, P.L. Characterization of Active Carbon Prepared From Coconuts Shells Using FTIR, XRD and SEM Techniques. J. Ilm. Pendidik. Fis. Al-Biruni 2018, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, J.; Kazehaya, A.; Muroyama, K.; Watkinson, A.P. Preparation of activated carbon from lignin by chemical activation. Carbon 2000, 38, 1873–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomboan, F.O.; Kumaat, E.J.; Windah, R.S. Pengujian Kuat Tekan Mortar dan Beton Ringan Dengan Menggunakan AgregatRingan Batu Apung Dan Abu Sekam Padi Sebagai Substitusi Parsial Semen. J. Sipil Statik 2016, 4, 271–278. Available online: https://ejournal.unsrat.ac.id/index.php/jss/article/view/11918/11507 (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Lukmandaru, G.; Hidayah, R.N. Studi Mutu Kayu Jati di Hutan Rakyat Gunungkidul. VI. Kadar Zat Anorganik dan Keasaman. J. Ilmu Kehutan. 2017, 10, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ummah, H.; Suriamihardja, D.A.; Selintung, M.; Wahab, A.W. Analysis of Chemical Composition of Rice Husk Used as Absorber Plates Sea Water into Clean Water. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2015, 10, 6046–6050. Available online: http://digilib.unhas.ac.id/uploaded_files/temporary/DigitalCollection/YzdkNDNjZjU5OTYwYThjZTM2YzYyNzllYzFkNzE0MjYzNmQ4NWE0Ng==.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Ghani, W.A.W.A.K.; da Silva, G.; Alias, A.B. Physico-chemical characterizations of sawdust-derived biochar as potential solid fuels. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2014, 18, 724–729. Available online: http://www.ukm.my/mjas/v18_n3/Wan%20Azlina_18_3_30.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Li, S.; Zhu, H.; Xi, G.; Lin, Q.; Wang, C.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z. Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous carbon spheres. Mater. Sci. Pol. 2019, 37, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufford, T.E.; Hulicova-Jurcakova, D.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, G.Q. A comparative study of chemical treatment by FeCl3, MgCl2, and ZnCl2 on microstructure, surface chemistry, and double-layer capacitance of carbons from waste biomass. J. Mater. Res. 2010, 25, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windolz, M.; Budavari, S.; Blumeti, R.F.; Otterbein, E.S. The Merc Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals, 10th ed.; Merck & Co, Inc.: Kenilworth, NJ, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Setianingsih, T.; Sutarno, M. Prinsip Dasar dan Aplikasi Metode Difraksi Sinar-X untuk Karakterisasi Material; UB Press, Universitas Brawijaya: Malang, Indonesia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, M. Isolation and Characterization of Cellulose Nanofiber from Bambusa Rigida. BioResources 2013, 8, 5678–5689. Available online: https://ojs.cnr.ncsu.edu/index.php/BioRes/article/view/BioRes_08_4_5678_He_Nanofiber_Bambusa/2364 (accessed on 1 June 2021). [CrossRef]
- Tsaneva, V.N.; Kwapinski, W.; Teng, X.; Glowacki, B.A. Assessment of the Structural Evolution of Carbons from Microwave Plasma Natural Gas Reforming and Biomass Pyrolisis Using Raman Spectroscopy. Carbon 2014, 80, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Verma, P.; Baskey, H.B.; Agarwala, R.C.; Agarwala, V.; Shami, T.C. Microwave Absorption Study of Carbon Nano Tube Dispersed Hard/Soft Ferrite Nanocomposite. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 4561–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Wang, Y.; Huo, J. Porous graphitic carbon materials prepared from cornstarch with the assistance of microwaveirradiation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 210, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setianingsih, T. Mikroskop Elektron Transmisi: Teori dan Aplikasinya untuk Karakterisasi Material; UB Press: Malang, Indonesia, 2017; pp. 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mahbubul, M.; Chong, T.H.; Khaleduzzaman, S.S.; Shahrul, I.M.; Saidur, R.; Long, B.D.; Amalina, M.A. Effect of Ultrasonication Duration on Colloidal Structure and Viscosity of Alumina−Water Nanofluid I. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 6677–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirankumar, V.S.; Sumathi, S. A Review on Photodegradation of Organic Pollutants Using Spinel Oxide. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataramana, C.; Botsa, S.M.; Shyamala, P.; Muralikrishna, R. Photocatalytic degradation of polyethylene plastics by NiAl2O4 spinels-synthesis and characterization. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shriver, D.F.; Atkins, P.W.; Langford, C.H. Inorganic Chemistry; Oxford University Press: Oxford, MI, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Tsou, T.; Yang, J. Formation of Reactive Oxygen Species and DNA Strand Breakage During Interaction of Chromium(III) and Hydrogen Peroxide in Vitro: Evidence for a Chromium(III)-mediated Fenton-like Reaction. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1996, 02, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, F.A.; Wilkinson, G. Kimia Anorganik Dasar; Suharto, S., Translator; UI Press: Jakarta, Indonesia, 1989; pp. 23–26. [Google Scholar]
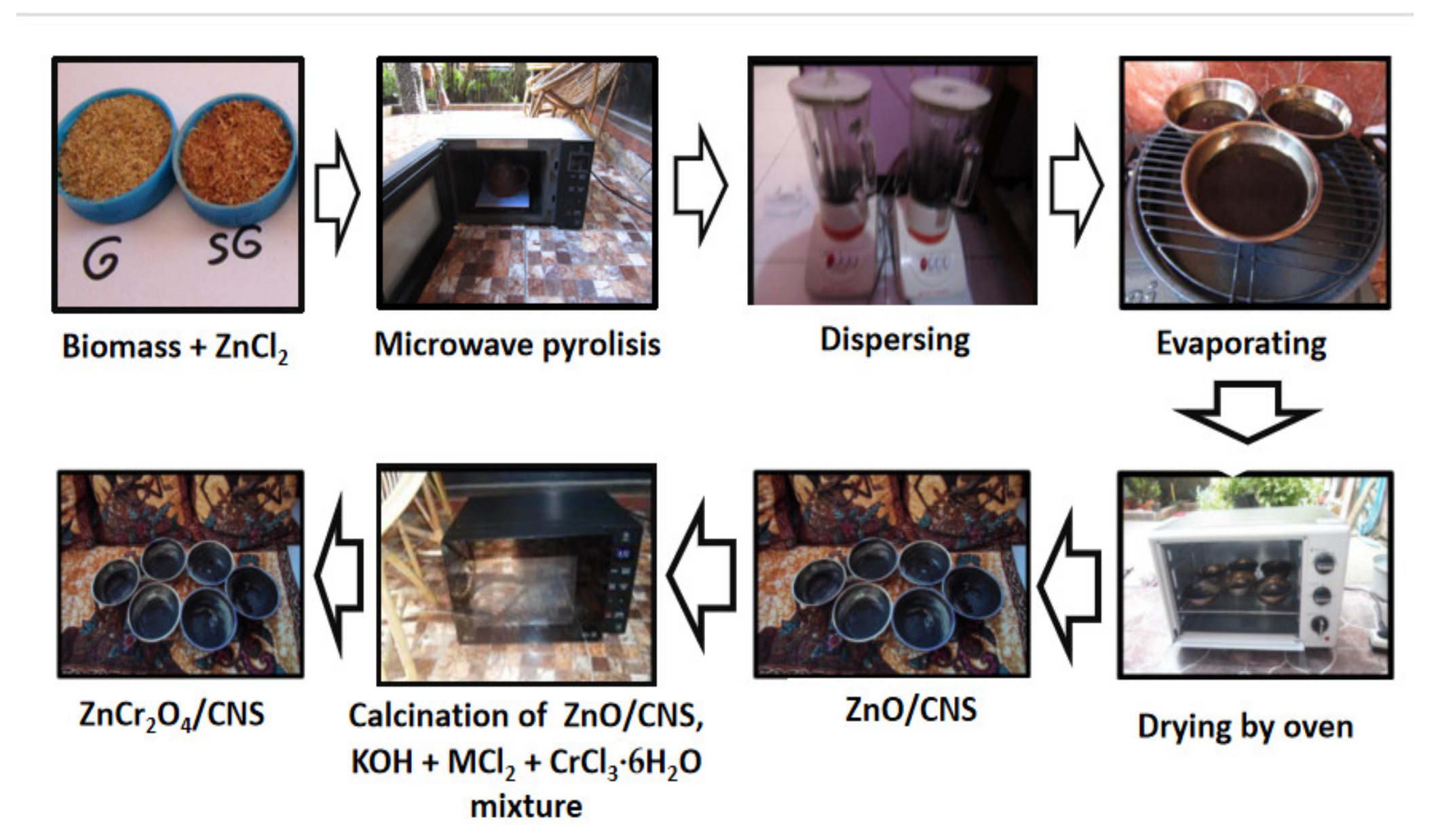
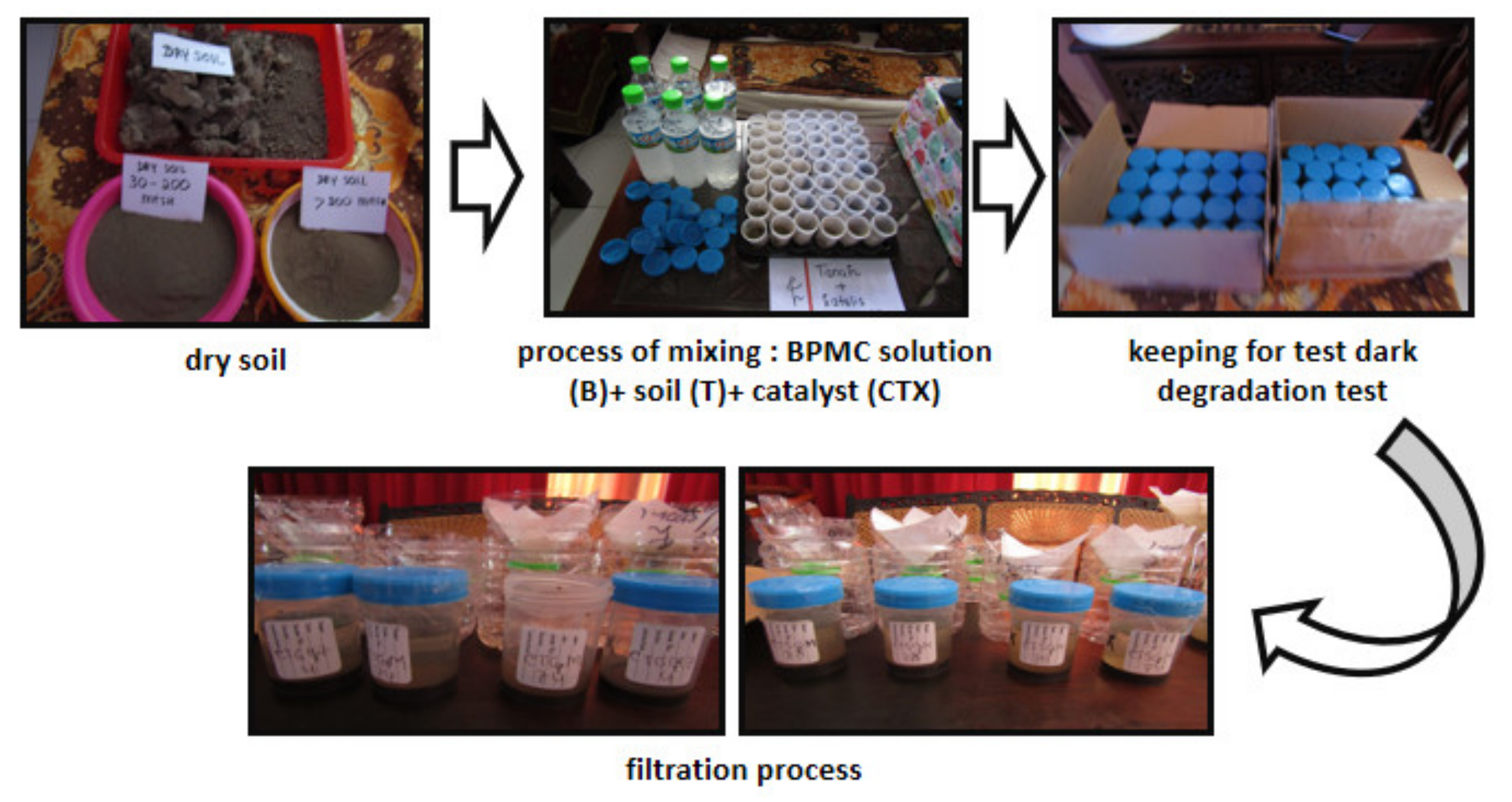
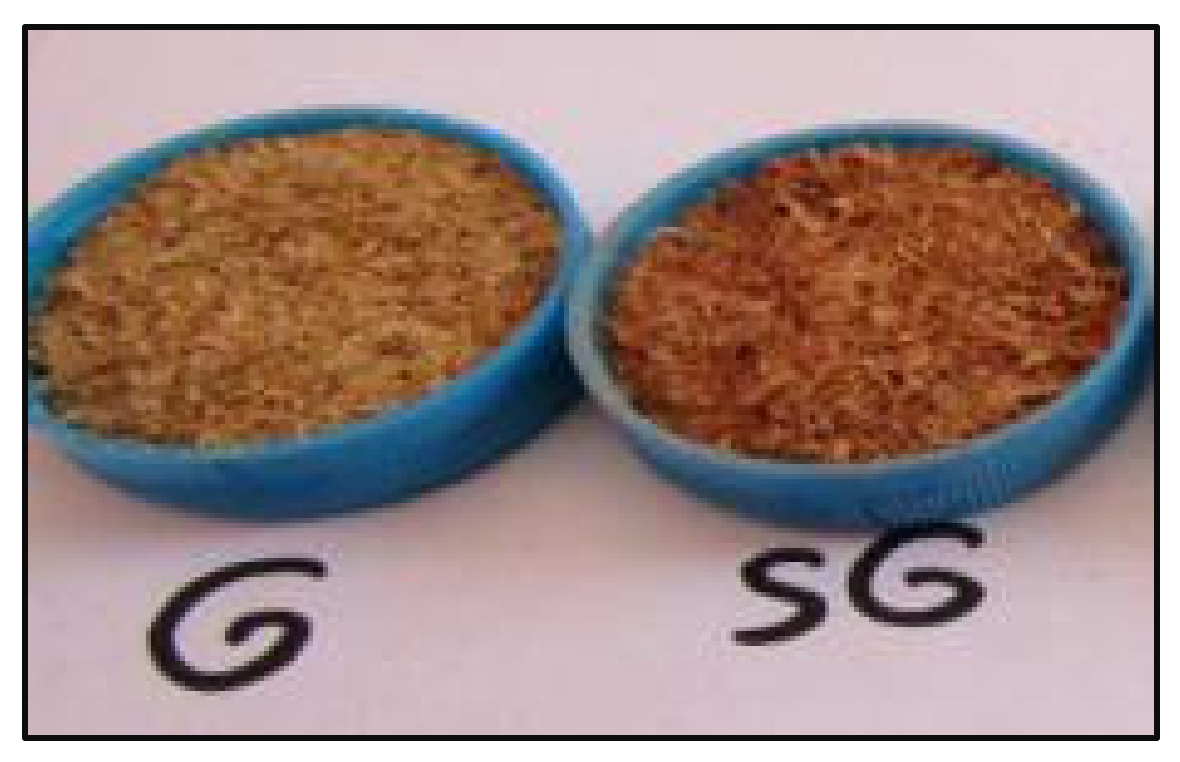













| No. | Purpose | Code | Experiment | Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Adsorption test of pesticide by the thermal deactivated soil | BT | A 5 g of dry soil + 25 mL of BPMC solution (0.5 g/L) + 10 mL water, kept in the dark for 5 days. | TOC |
| 2. | Degradation test of pesticide by catalytic oxidation reaction with H2O2–ZnCr2O4 | CTGMZX | A 5 g of dry soil + 25 mL of BPMC solution (0.5 g/L) + 10 mL of H2O2 solution (0.15%) + 0.1 g of composite, kept in the dark for 5 days. | TOC |
| Biomass | I200 | Iam | CI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sawdust (SG) | 4.3 | 1.6 | 62.8 |
| Rice husk (G) | 2.7 | 1.0 | 63.0 |
| Substance | 2θ(IR) | 2θ(IR) | 2θ(IR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO | 31.00(53) | 34.47(40) | 36.29(100) |
| ZnCr2O4 | 30.35(43) | 35.75(100) | 63.15(38) |
| Cr2O3 | 33.65(100) | 36.27(93) | 54.94(85) |
| KCl | 28.39(100) | 40.58(63) | 50.26(20) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Setianingsih, T.; Purwonugroho, D.; Prananto, Y.P. Influence of Pyrolysis Parameters Using Microwave toward Structural Properties of ZnO/CNS Intermediate and Application of ZnCr2O4/CNS Final Product for Dark Degradation of Pesticide in Wet Paddy Soil. ChemEngineering 2021, 5, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5030058
Setianingsih T, Purwonugroho D, Prananto YP. Influence of Pyrolysis Parameters Using Microwave toward Structural Properties of ZnO/CNS Intermediate and Application of ZnCr2O4/CNS Final Product for Dark Degradation of Pesticide in Wet Paddy Soil. ChemEngineering. 2021; 5(3):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5030058
Chicago/Turabian StyleSetianingsih, Tutik, Danar Purwonugroho, and Yuniar Ponco Prananto. 2021. "Influence of Pyrolysis Parameters Using Microwave toward Structural Properties of ZnO/CNS Intermediate and Application of ZnCr2O4/CNS Final Product for Dark Degradation of Pesticide in Wet Paddy Soil" ChemEngineering 5, no. 3: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5030058
APA StyleSetianingsih, T., Purwonugroho, D., & Prananto, Y. P. (2021). Influence of Pyrolysis Parameters Using Microwave toward Structural Properties of ZnO/CNS Intermediate and Application of ZnCr2O4/CNS Final Product for Dark Degradation of Pesticide in Wet Paddy Soil. ChemEngineering, 5(3), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5030058





