Kinetic Study of the Ultrasound Effect on Acid Brown 83 Dye Degradation by Hydrogen Peroxide Oxidation Processes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
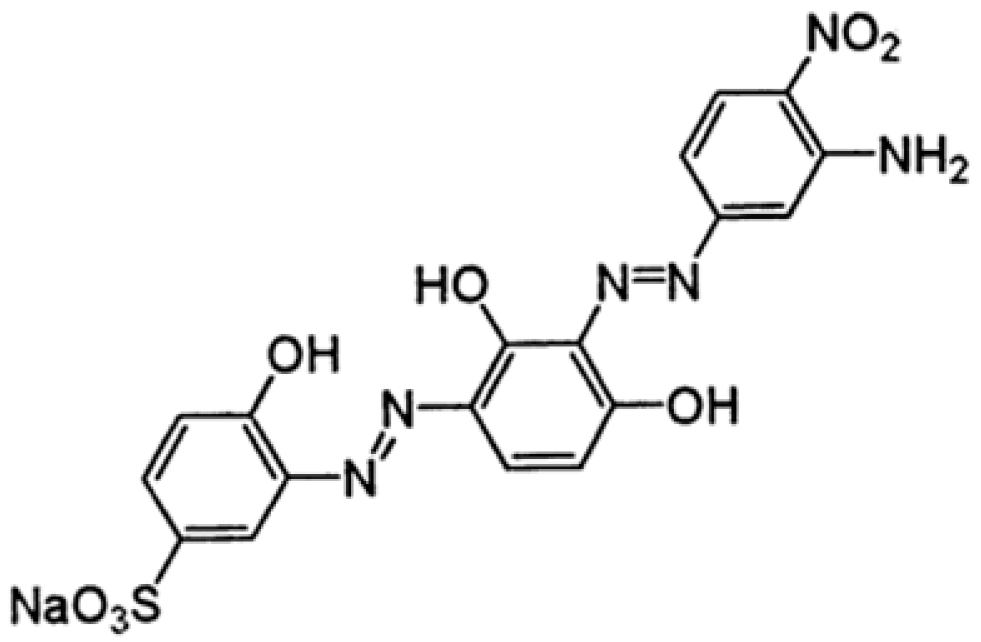
2.1. Chemicals
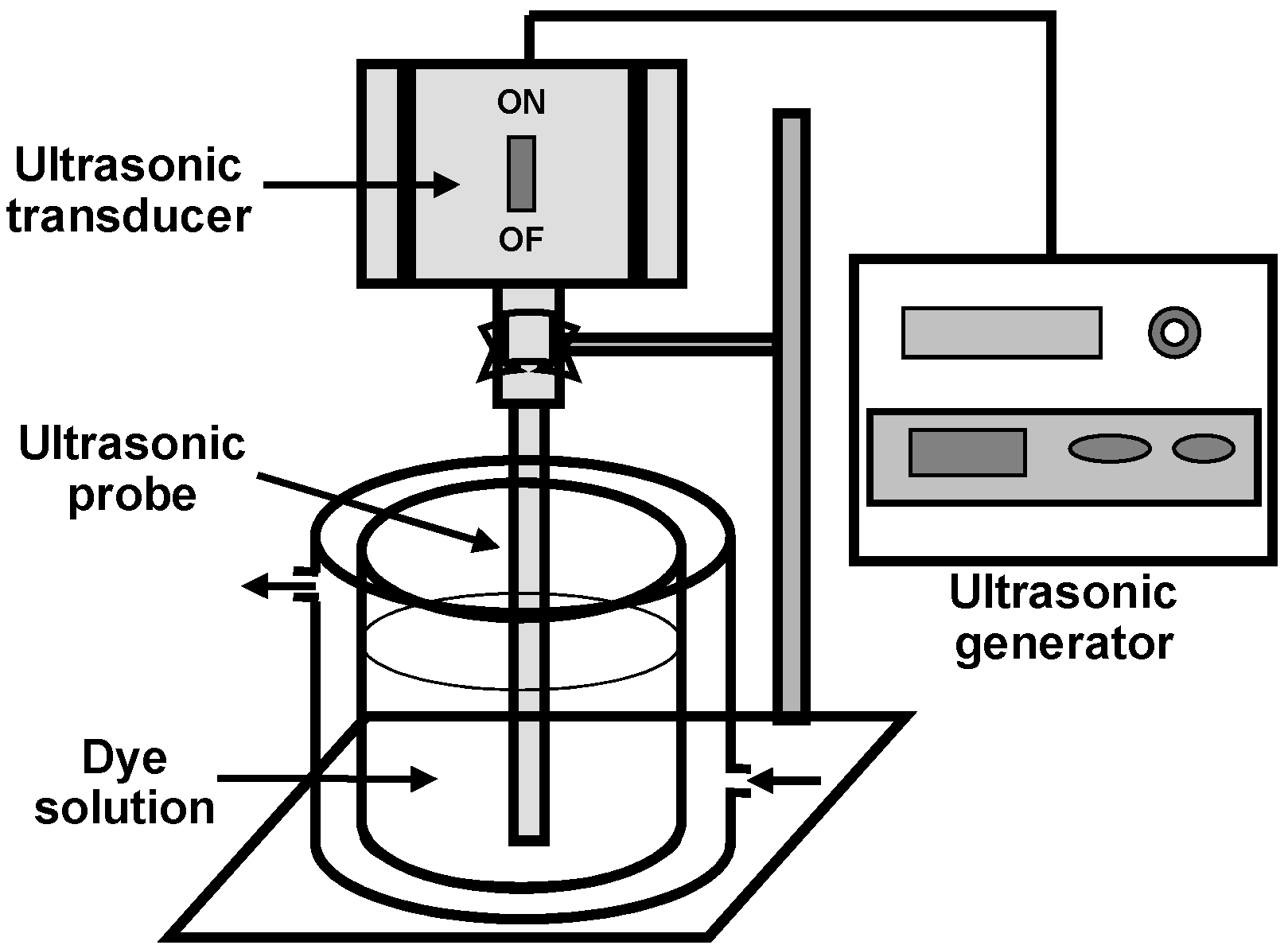
2.2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
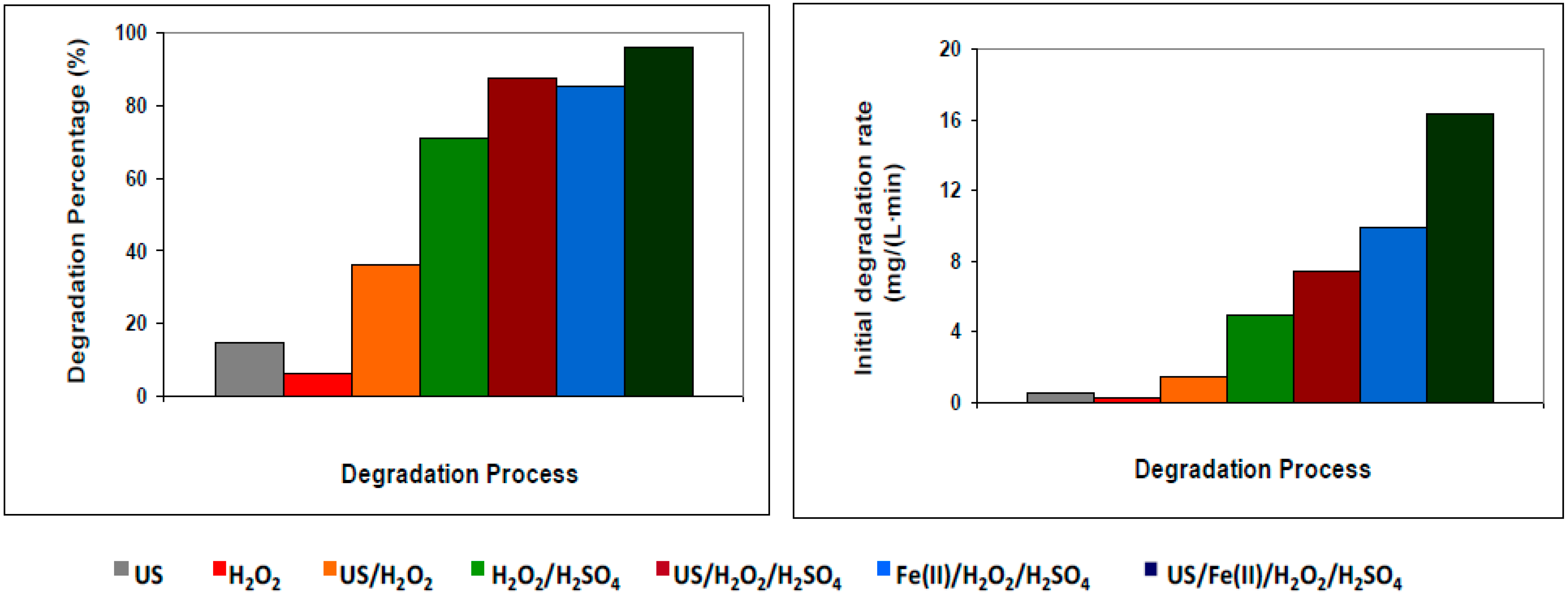
3.1. Effect of Ultrasound on the Degradation of Acid Brown 83 by Different Methods
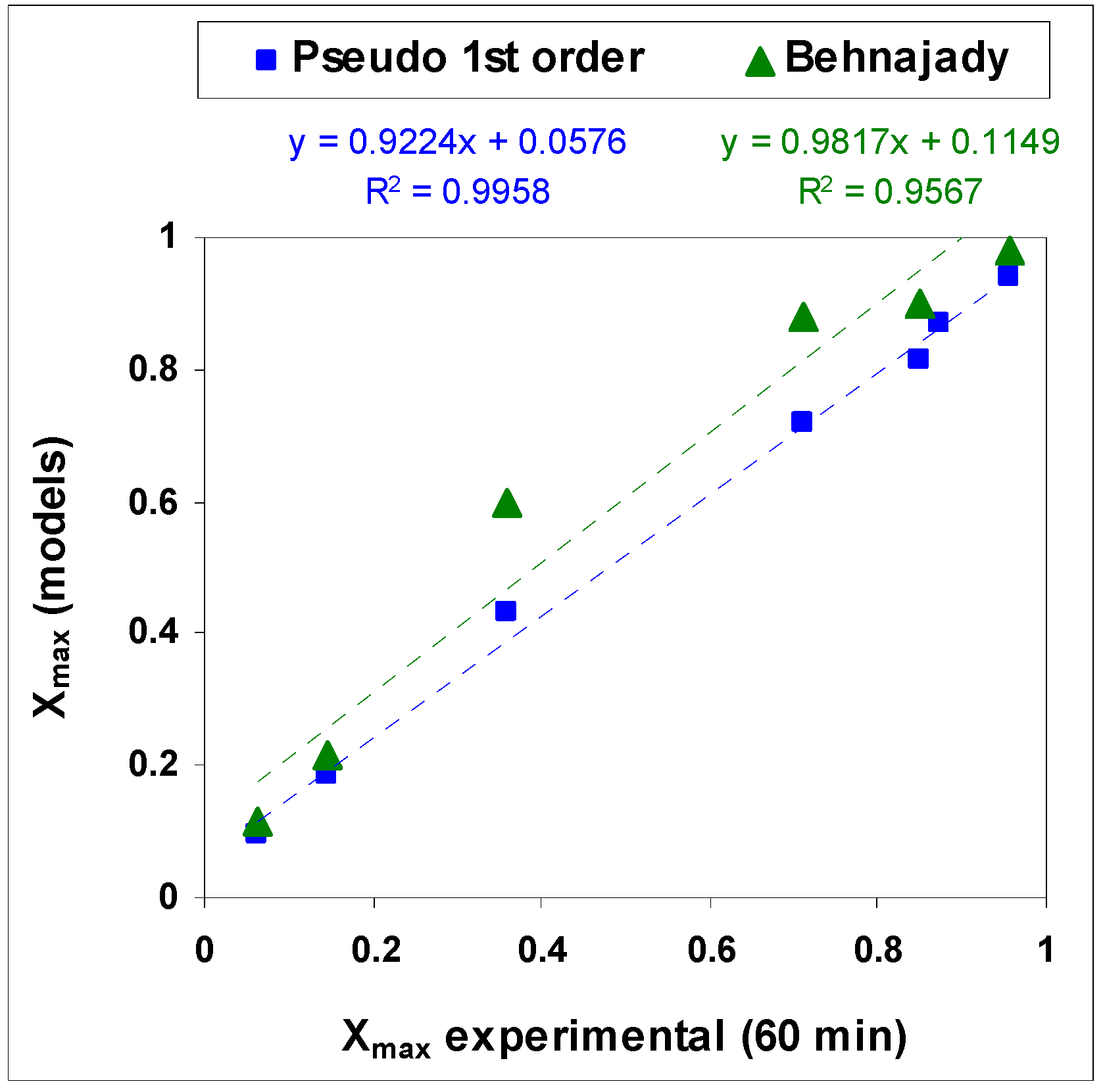
3.2. Kinetics Study of the AB83 Degration Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Wei, J.; Lv, S.; Guo, Z.; Jiang, F. Removal of organic dyes in environmental water onto magneticsulfonic graphene nanocomposite. Clean Soil Air Water 2013, 41, 992–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, S.; Renganathan, V. Non enzymatic reduction of azo dyes by NADH. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosz-Wilkolazka, A.; Kochmanska-Rdest, J.; Malarczyk, E.; Wardas, W.; Leonowicz, A. Fungi and their ability to decolorize azo and anthraquinonic dyes. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2002, 30, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, J.M.; Rocha-Filho, R.C.; Ruotolo, L.A.; Bocchi, N.; Biaggio, S.R. Electrochemical degradation of a real textile wastewater using PbO2 and DSA anodes. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 251, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, J.; Nidheesh, P.V.; Singh, T.A.; Kumar, M.S. Advanced oxidation processes based on zero-valent aluminium for treating textile wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhya, S. Biodegradation of azo dyes under anaerobic condition: Role of azoreductase. In Biodegradation of Azo Dyes (The Handbook of Environmental Ehemistry, Volume 9), 1st ed.; Erkur, H.A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 52–70. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Malik, A. Toxicity evaluation of textile effluents and role of native soil bacterium in biodegradation of a textile dye. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 4446–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copaciu, F.; Opris, O.; Coman, V.; Ristoiu, D.; Niinemets, Ü.; Copolovici, L. Diffuse water pollution by anthraquinoneand azo dyes in environment importantly alters foliage volatiles, carotenoids and physiology in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, P. Toxicology of textile dyes. In Environmental Aspects of Textile Dyeing, 1st ed.; Christie, R.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 44–73. [Google Scholar]
- Shaul, G.M.; Lieberman, R.J.; Dempsey, C.R.; Dostal, K.A. Treatability of Water Soluble Azo Dyes by the Activated Sludge Process; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1986.
- Mahajan, P.; Kaushal, J. Phytoremediation of azo dye methyl red by macroalgae Chara vulgaris L.: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 26406–26418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Zhou, B.; Xing, K.; Tan, L. Co-enhanced activated sludge system by static magnetic field and two halotolerant yeasts for azo dye treatment. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 2095–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.; Dineshram, R.; Hemalatha, K.R.; Dhassiah, M.P.; Gopal, D.; Kumar, A. Bio-Decolorization of Synthetic Dyes by a Halophilic Bacterium Salinivibrio sp. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 594011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majul, L.; Sonia Wirth, S.; Levin, L. High dye removal capacity of Peniophora laxitexta immobilized in a combined support based on polyurethane foam and lignocellulosic substrates. Environ. Technol. 2020, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojsov, K.; Andronikov, D.; Janevski, A.; Kuzelov, A.; Gaber, S. The application of enzymes for the removal of dyes from textile effluents. Adv. Technol. 2016, 5, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Recent advances for dyes removal using novel adsorbents: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonetto, L.R.; Crespo, J.S.; Guégan, R.; Esteves, V.I.; Giovanela, M. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions using a solid residue of the apple juice industry: Full factorial design, equilibrium, thermodynamics and kinetics aspects. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1224, 129296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadekar, M.R.; Ahammed, M.M. Coagulation/flocculation process for dye removal using water treatment residuals: Modelling through artificial neural networks. Desal. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 26392–26400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.V.; Zhou, M.; Oturan, M.A. An overview on the removal of synthetic dyes from water by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 210–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, H.; Umar, M.; Ullah, A.; Razzaq, H.; Zia, K.M.; Liu, X. Polyvinylidene fluoride nanocomposite super hydrophilic membrane integrated with Polyaniline-Graphene oxide nano fillers for treatment of textile effluents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Xie, Y.; Gu, Y.H.; Yan, X.; Chen, Y.; Guo, X.J.; Lang, W.Z. PVDF-CaAlg nanofiltration membranes with dual thin-filmcomposite (TFC) structure and high permeation flux for dye removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 255, 117739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, R.J.; Al-Ani, F.H.; Al-shaeli, M.; Alsalhy, Q.F.; Figoli, A. Removal of Dyes Using Graphene Oxide (GO) Mixed Matrix Membranes. Membranes 2020, 10, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasperchik, V.P.; Yaskevich, A.; Bil’dyukevich, A.V. Wastewater treatment for removal of dyes by coagulation and membrane processes. Pet. Chem. 2012, 52, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alardhi, S.M.; Albayati, T.M.; Jamal, M.; Alrubaye, J.M. A hybrid adsorption membrane process for removal of dye from synthetic and actual wastewater. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2020, 157, 108113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikuku, V.O.; Nyairo, W.N. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Dye Removal from Wastewater. In Impact of Textile Dyes on Public Health and the Environment, 1st ed.; Wani, N.K.A., Jangid, N.K., Bhat, A.R., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 205–238. [Google Scholar]
- Korpe, S.; Rao, P.V. Application of advanced oxidation processes and cavitation techniques for treatment of tannery wastewater. A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledakowicz, S.; Pazdzior, K. Recent Achievements in Dyes Removal Focused on Advanced Oxidation Processes Integrated with Biological Methods. Molecules 2021, 26, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuerda-Correa, E.M.; Alexandre-Franco, M.F.; Fernández-González, C. Advanced Oxidation Processes for the Removal of Antibiotics from Water. An Overview. Water 2020, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merouani, S.; Hamdaoui, O.; Rezgui, Y.; Guemini, M. Theoretical estimation of the temperature and pressure within collapsing acoustical bubbles. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matouq, M.; Al-Anber, Z.; Susumu, N.; Tagawa, T.; Karapanagioti, H. The kinetic of dyes degradation resulted from food industry in wastewater using high frequency of ultrasound. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 135, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Ren, S.; Zhang, H. Kinetic studies of direct blue photodegradation over flower-like TiO2. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2017, 43, 1529–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnajady, M.A.; Modirshahla, N.; Ghanbary, F. A kinetic model for the decolorization of C.I. Acid Yellow 23 by Fenton process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murcia, M.D.; Gómez, M.; Gómez, E.; Gómez, J.L.; Christofi, N. Photodegradation of Congo red using XeBr, KrCl and Cl2 barrier discharge excilamps: A kinetics study. Desalination 2011, 281, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thasilu, K.; Karthikeyan, J. Chemical oxidation for degradation of textile dyes using hydrogen peroxide. Int. J. Control Theory Applicat. 2016, 9, 9055–9062. [Google Scholar]
- Özdemir, C.; Öden, M.K.; Sahinkaya, S.; Güclu, D. The sonochemical decolorisation of textile azo dye CI Reactive Orange 127. Color. Technol. 2011, 127, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckett, M.A.; Hua, I. Elucidation of the 1,4-dioxane decomposition pathway at discrete ultrasonic frequencies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3944–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, R.; Qazi, U.Y. Catalytic Oxidation Process for the Degradation of Synthetic Dyes: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahdar, S.; Igwegbeb, C.A.; Ghasemi, M.; Ahmadi, S. Degradation of aniline by the combined process of ultrasound and hydrogen peroxide (US/H2O2). MethodsX 2019, 6, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basturk, E.; Karatas, M. Advanced oxidation of Reactive Blue 181 solution: A comparison between Fenton and Sono-Fenton Process. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 1881–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, P.; Saha, S. Oxidation of direct dyes with hydrogen peroxide using ferrous ion as catalyst. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2003, 31, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, F.; Santana, C.S.; Aguiar, A. Behavior of dihydroxybenzenes and gallic acid on the Fenton-based decolorization of dyes. Desal. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, C.S.; Ramos, M.D.N.; Velloso, C.C.V.; Aguiar, A. Kinetic Evaluation of Dye Decolorization by Fenton Processes in the Presence of 3-Hydroxyanthranilic Acid. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

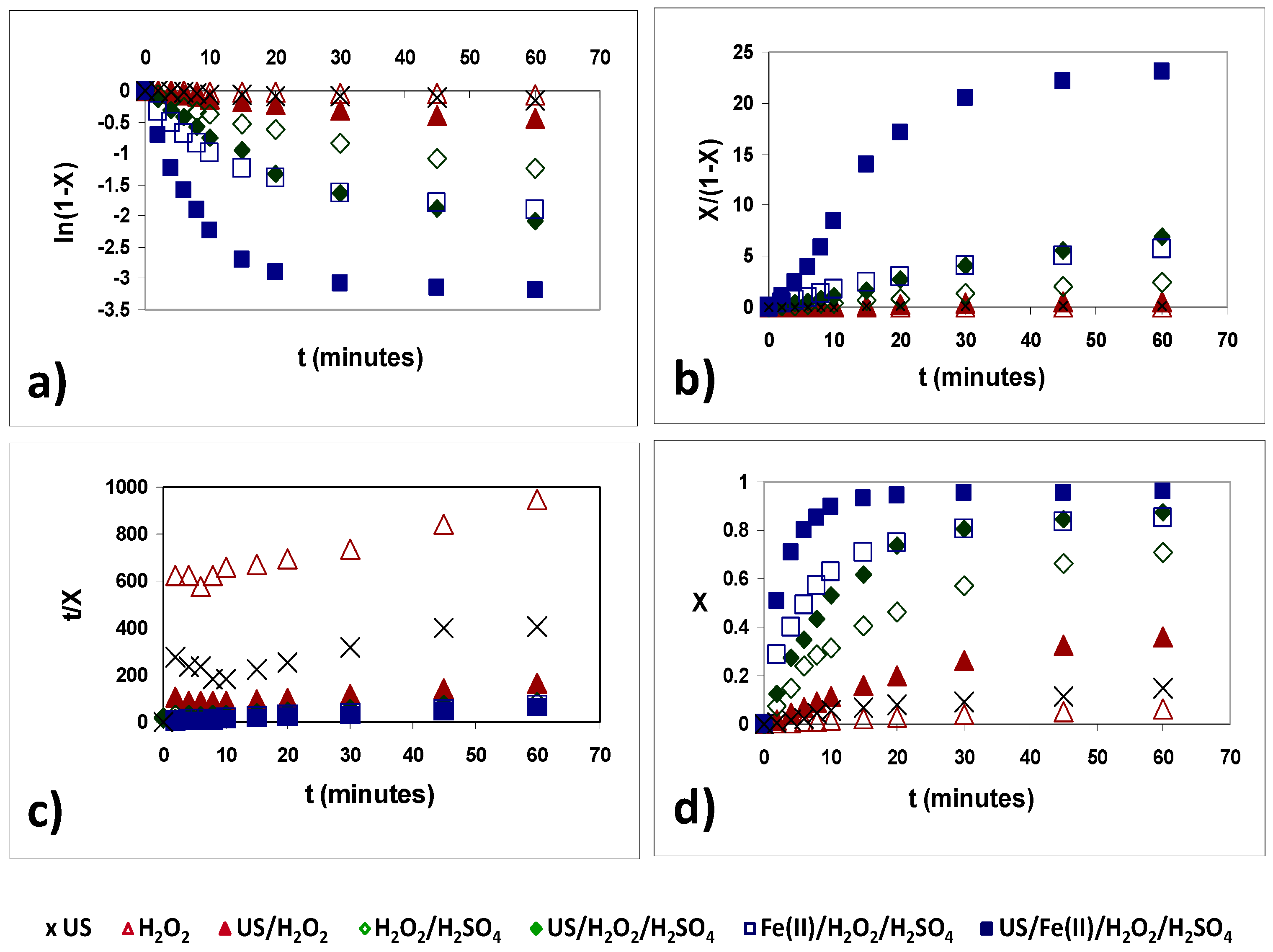
| Process | First Order | Second Order | Behnajady Model | Pseudo-First Order | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | k1 (min−1) | R2 | k2 (L·mg−1·min−1) | R2 | a (min) | B | R2 | kps1 (min−1) | Xmax | |
| 1 | 0.9367 | 0.0025 | 0.9462 | 0.00002 | 0.6333 | 163.22 | 4.6305 | 0.9991 | 0.02712 | 0.18503 |
| 2 | 0.981 | 0.0011 | 0.9832 | 0.00001 | 0.4960 | 478.97 | 8.6474 | 0.9998 | 0.01792 | 0.09640 |
| 3 | 0.9647 | 0.0077 | 0.9826 | 0.00008 | 0.6225 | 67.11 | 1.6769 | 0.9998 | 0.03044 | 0.43215 |
| 4 | 0.9565 | 0.0208 | 0.9968 | 0.00033 | 0.9218 | 17.773 | 1.1386 | 0.9974 | 0.05692 | 0.71953 |
| 5 | 0.9057 | 0.0353 | 0.9897 | 0.00098 | 0.9684 | 8.8707 | 0.9888 | 0.9989 | 0.08817 | 0.87110 |
| 6 | 0.8089 | 0.0289 | 0.948 | 0.00078 | 0.995 | 4.2467 | 1.1092 | 0.9938 | 0.15682 | 0.81581 |
| 7 | 0.6197 | 0.0438 | 0.8309 | 0.00334 | 0.9994 | 1.0462 | 1.0222 | 0.9976 | 0.34859 | 0.94094 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
León, G.; Miguel, B.; Manzanares, L.; Saavedra, M.I.; Guzmán, M.A. Kinetic Study of the Ultrasound Effect on Acid Brown 83 Dye Degradation by Hydrogen Peroxide Oxidation Processes. ChemEngineering 2021, 5, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5030052
León G, Miguel B, Manzanares L, Saavedra MI, Guzmán MA. Kinetic Study of the Ultrasound Effect on Acid Brown 83 Dye Degradation by Hydrogen Peroxide Oxidation Processes. ChemEngineering. 2021; 5(3):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5030052
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeón, Gerardo, Beatriz Miguel, Laura Manzanares, María Isabel Saavedra, and María Amelia Guzmán. 2021. "Kinetic Study of the Ultrasound Effect on Acid Brown 83 Dye Degradation by Hydrogen Peroxide Oxidation Processes" ChemEngineering 5, no. 3: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5030052
APA StyleLeón, G., Miguel, B., Manzanares, L., Saavedra, M. I., & Guzmán, M. A. (2021). Kinetic Study of the Ultrasound Effect on Acid Brown 83 Dye Degradation by Hydrogen Peroxide Oxidation Processes. ChemEngineering, 5(3), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering5030052






