Genetic Variations Associated with Sleep Disorders in Patients with Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
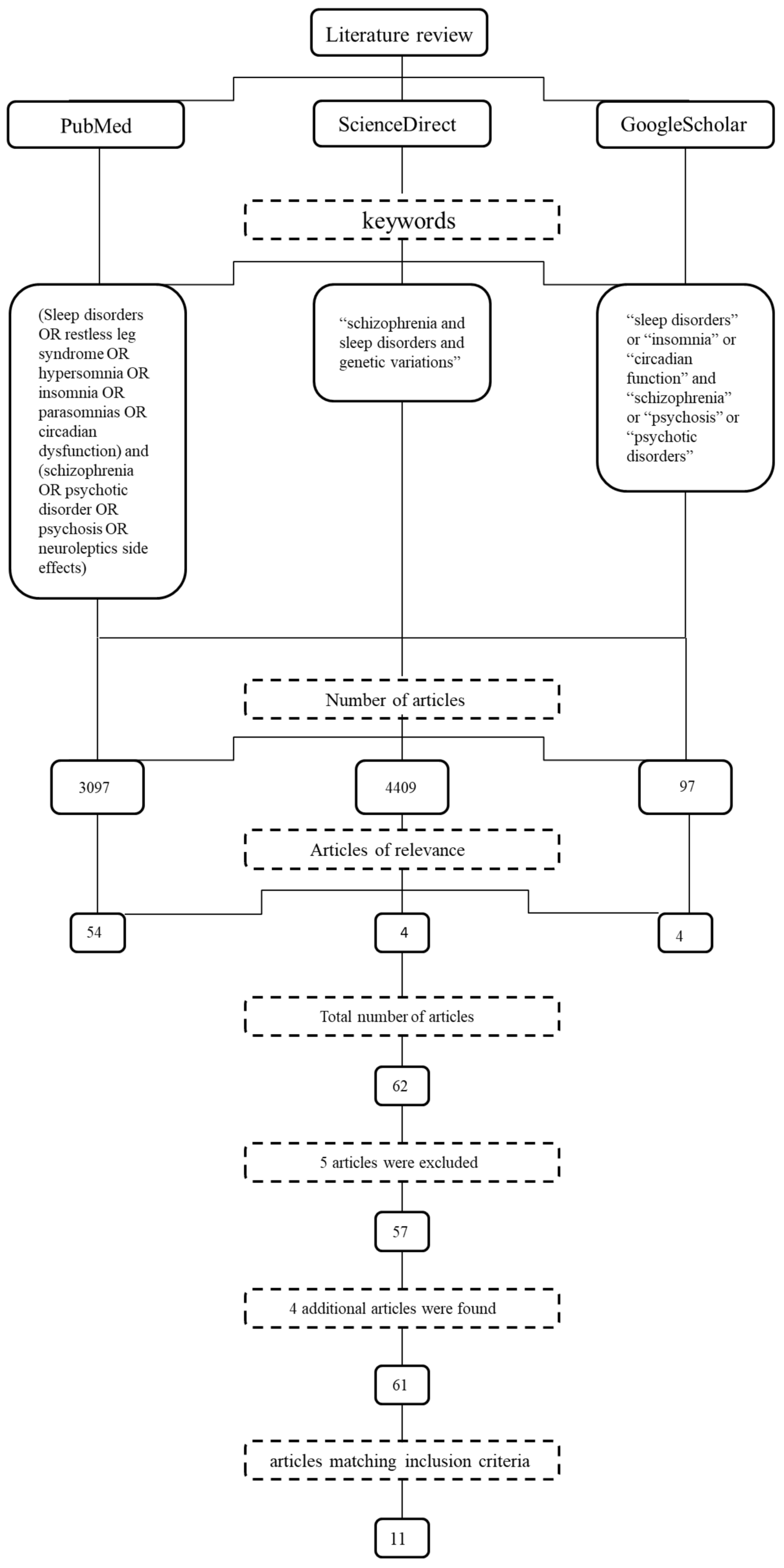
2. Materials and Methods
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of Studies
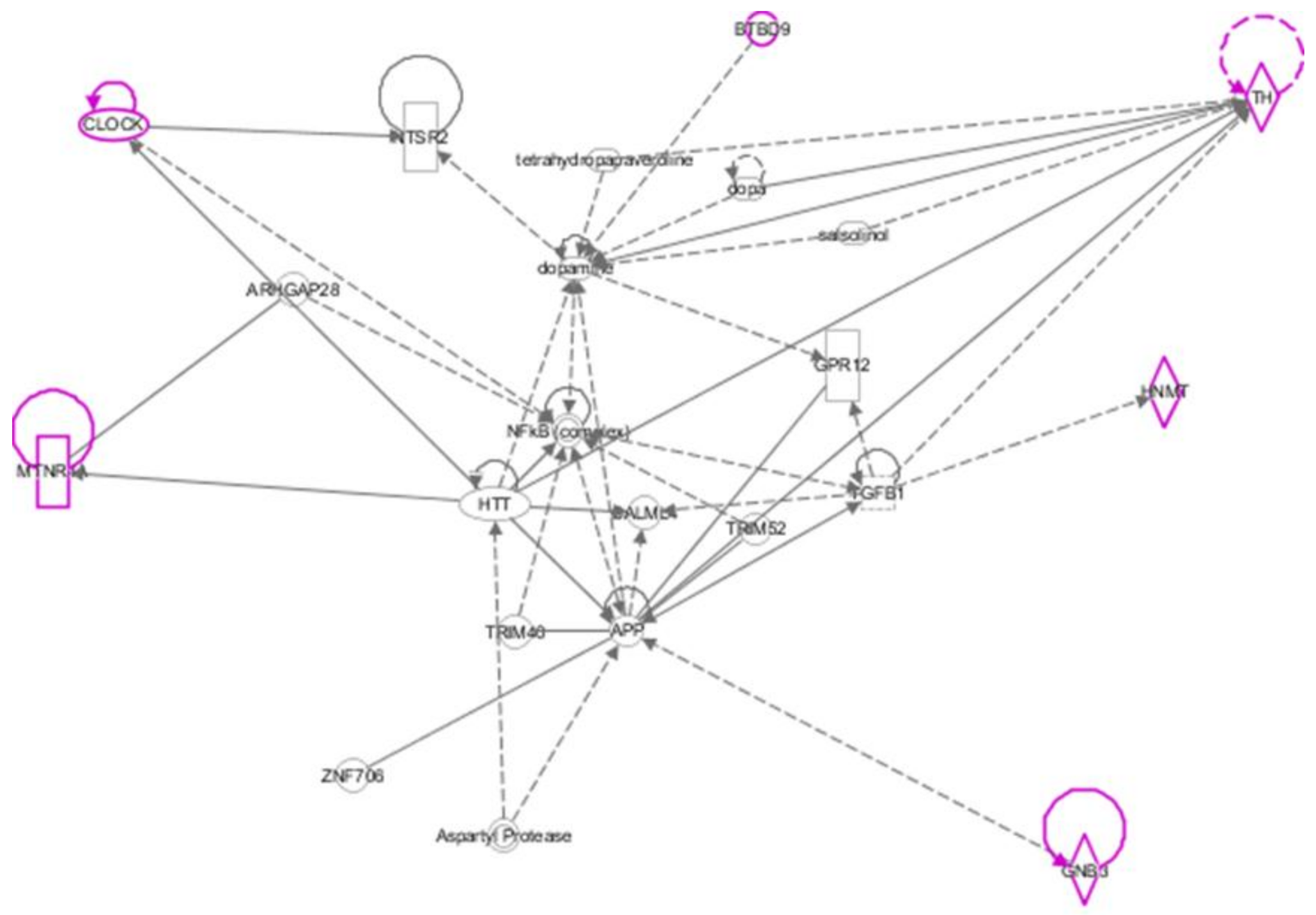
3.2. Associations between Genetic Variations and Specific Sleep Disorders
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohrs, S. Sleep disturbances in patients with schizophrenia: Impact and effect of antipsychotics. CNS Drugs 2008, 22, 939–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofstetter, J.R.; Lysaker, P.H.; Mayeda, A.R. Quality of sleep in patients with schizophrenia is associated with quality of life and coping. BMC Psychiatry 2005, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, P.; Brissos, S.; Figueira, M.L.; Paiva, T. Schizophrenia patients with predominantly positive symptoms have more disturbed sleep-wake cycles measured by actigraphy. Psychiatry Res. 2011, 189, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, K.L. Sleep in schizophrenia: Impairments, correlates, and treatment. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2006, 29, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulff, K.; Dijk, D.-J.; Middleton, B.; Foster, R.G.; Joyce, E.M. Sleep and circadian rhythm disruption in schizophrenia. Br. J. Psychiatry 2012, 200, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.-T.; Weng, Y.-Z.; Leung, C.-M.; Tang, W.-K.; Lai, K.Y.C.; Ungvari, G.S. Prevalence and correlates of insomnia and its impact on quality of life in Chinese schizophrenia patients. Sleep 2009, 32, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manoach, D.S.; Pan, J.Q.; Purcell, S.M.; Stickgold, R. Reduced Sleep Spindles in Schizophrenia: A Treatable Endophenotype That Links Risk Genes to Impaired Cognition? Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 80, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshavan, M.S.; Reynolds, C.F.; Miewald, J.M.; Montrose, D.M. A longitudinal study of EEG sleep in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 1996, 59, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouinard, S.; Poulin, J.; Stip, E.; Godbout, R. Sleep in untreated patients with schizophrenia: A meta-analysis. Schizophr. Bull. 2004, 30, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaskie, R.E.; Graziano, B.; Ferrarelli, F. Schizophrenia and sleep disorders: Links, risks, and management challenges. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2017, 9, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, J.M.; Vlasac, I.; Anderson, S.G.; Kyle, S.D.; Dixon, W.G.; Bechtold, D.A.; Gill, S.; Little, M.A.; Luik, A.; Loudon, A.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies novel loci for chronotype in 100,420 individuals from the UK Biobank. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, J.M.; Liang, J.; Vlasac, I.; Anderson, S.G.; Bechtold, D.A.; Bowden, J.; Emsley, R.; Gill, S.; Little, M.A.; Luik, A.I.; et al. Genome-wide association analyses of sleep disturbance traits identify new loci and highlight shared genetics with neuropsychiatric and metabolic traits. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sateia, M.J. International classification of sleep disorders-third edition: Highlights and modifications. Chest 2014, 146, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnbaum, R.; Weinberger, D.R. Genetic insights into the neurodevelopmental origins of schizophrenia. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. PRISMA Group Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. The ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders DSM-5, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, C.-H.; Kang, S.-G.; Choi, J.-E.; Park, Y.-M.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, L. Association between Antipsychotics-Induced Restless Legs Syndrome and Tyrosine Hydroxylase Gene Polymorphism. Psychiatry Investig. 2009, 6, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.-G.; Lee, H.-J.; Choi, J.-E.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, S.-S.; Han, C.; Kim, Y.-K.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, M.-S.; Joe, S.-H.; et al. Possible association between G-protein β3 subunit C825T polymorphism and antipsychotic-induced restless legs syndrome in schizophrenia. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2007, 19, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.-G.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, L. MEIS1, a Promising Candidate Gene, Is Not Associated with the Core Symptoms of Antipsychotic-Induced Restless Legs Syndrome in Korean Schizophrenia Patients. Psychiatry Investig. 2015, 12, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.-G.; Park, Y.-M.; Choi, J.-E.; Lim, S.-W.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-K.; Kim, S.-H.; Cho, S.N.; Kim, L. Association study between antipsychotic-induced restless legs syndrome and polymorphisms of monoamine oxidase genes in schizophrenia. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2010, 25, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.-G.; Lee, H.-J.; Choi, J.-E.; Park, Y.-M.; Park, J.-H.; Han, C.; Kim, Y.-K.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, M.-S.; Joe, S.-H.; Jung, I.-K.; Kim, L. Association study between antipsychotics- induced restless legs syndrome and polymorphisms of dopamine D1, D2, D3, and D4 receptor genes in schizophrenia. Neuropsychobiology 2008, 57, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.-G.; Lee, H.-J.; Park, Y.-M.; Yang, H.J.; Song, H.M.; Lee, Y.J.; Cho, S.-J.; Cho, S.N.; Kim, L. The BTBD9 gene may be associated with antipsychotic-induced restless legs syndrome in schizophrenia. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 28, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.-S.; Lee, H.-J.; Cho, C.-H.; Kang, S.-G.; Yoon, H.-K.; Park, Y.-M.; Moon, J.-H.; Yang, H.-J.; Song, H.-M.; Kim, L. Association between restless legs syndrome and CLOCK and NPAS2 gene polymorphisms in schizophrenia. Chronobiol. Int. 2014, 31, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J.; Park, J.K.; Kim, S.K.; Cho, A.-R.; Kim, J.W.; Yim, S.-V.; Chung, J.-H. Association of polymorphism in the promoter of the melatonin receptor 1A gene with schizophrenia and with insomnia symptoms in schizophrenia patients. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 45, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viikki, M.; Kampman, O.; Seppälä, N.; Mononen, N.; Lehtimäki, T.; Leinonen, E. CYP1A2 polymorphism -1545C > T (rs2470890) is associated with increased side effects to clozapine. BMC Psychiatry 2014, 14, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almoguera, B.; Riveiro-Alvarez, R.; Lopez-Castroman, J.; Dorado, P.; Vaquero-Lorenzo, C.; Fernandez-Piqueras, J.; Llerena, A.; Abad-Santos, F.; Baca-García, E.; Dal-Ré, R.; et al. Spanish Consortium of Pharmacogenetics Research in Schizophrenia Association of common genetic variants with risperidone adverse events in a Spanish schizophrenic population. Pharmacogenomics J. 2013, 13, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gómez-Santos, C.; Ambrosio, S.; Ventura, F.; Ferrer, I.; Reiriz, J. TGF-beta1 increases tyrosine hydroxylase expression by a mechanism blocked by BMP-2 in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Brain Res. 2002, 958, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konturek, P.C.; Brzozowski, T.; Konturek, S.J. Gut clock: Implication of circadian rhythms in the gastrointestinal tract. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2011, 62, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trbovic, S.M. Schizophrenia as a possible dysfunction of the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Med. Hypotheses 2010, 74, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, A.-S.; Owe-Larsson, B.; Hetta, J.; Lundkvist, G.B. Altered circadian clock gene expression in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2016, 174, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.-Q.; Li, S.-X.; Chen, F.-B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Jin, M.; Sun, Y.; Wang, F.; Mi, W.-F.; Shi, L.; et al. Diurnal neurobiological alterations after exposure to clozapine in first-episode schizophrenia patients. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 64, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poceta, J.S.; Parsons, L.; Engelland, S.; Kripke, D.F. Circadian rhythm of CSF monoamines and hypocretin-1 in restless legs syndrome and Parkinson’s disease. Sleep Med. 2009, 10, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, M.W.; Roberts, R.C.; Melendez-Ferro, M.; Perez-Costas, E. Mapping dopaminergic deficiencies in the substantia nigra/ventral tegmental area in schizophrenia. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dauvilliers, Y.; Winkelmann, J. Restless legs syndrome: Update on pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2013, 19, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunugi, H.; Kawada, Y.; Hattori, M.; Ueki, A.; Otsuka, M.; Nanko, S. Association study of structural mutations of the tyrosine hydroxylase gene with schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1998, 81, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, M.; Yamauchi, K.; Satoh, Y.-I.; Yamaji, R.; Inui, K.; Jonker, J.W.; Schinkel, A.H.; Maeyama, K. Recent advances in molecular pharmacology of the histamine systems: Organic cation transporters as a histamine transporter and histamine metabolism. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 101, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solismaa, A.; Kampman, O.; Lyytikäinen, L.-P.; Seppälä, N.; Viikki, M.; Mononen, N.; Lehtimäki, T.; Leinonen, E. Histaminergic gene polymorphisms associated with sedation in clozapine-treated patients. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 27, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, H.L.; Sergeeva, O.A.; Selbach, O. Histamine in the nervous system. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 1183–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamm, H.E. The many faces of G protein signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J.; Cha, J.-H.; Ham, B.-J.; Han, C.-S.; Kim, Y.-K.; Lee, S.-H.; Ryu, S.-H.; Kang, R.-H.; Choi, M.-J.; Lee, M.-S. Association between a G-protein beta 3 subunit gene polymorphism and the symptomatology and treatment responses of major depressive disorders. Pharmacogenomics J. 2004, 4, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Müller, D.J.; De Luca, V.; Sicard, T.; King, N.; Hwang, R.; Volavka, J.; Czobor, P.; Sheitman, B.B.; Lindenmayer, J.-P.; Citrome, L.; McEvoy, J.P.; et al. Suggestive association between the C825T polymorphism of the G-protein beta3 subunit gene (GNB3) and clinical improvement with antipsychotics in schizophrenia. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2005, 15, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefansson, H.; Rye, D.B.; Hicks, A.; Petursson, H.; Ingason, A.; Thorgeirsson, T.E.; Palsson, S.; Sigmundsson, T.; Sigurdsson, A.P.; Eiriksdottir, I.; et al. A genetic risk factor for periodic limb movements in sleep. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stogios, P.J.; Downs, G.S.; Jauhal, J.J.S.; Nandra, S.K.; Privé, G.G. Sequence and structural analysis of BTB domain proteins. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, R82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Granger, A.J.; Tran, T.; Saulnier, J.L.; Kirkwood, A.; Sabatini, B.L. Endogenous Gαq-Coupled Neuromodulator Receptors Activate Protein Kinase A. Neuron 2017, 96, 1070–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hasani, R.; Bruchas, M.R. Molecular mechanisms of opioid receptor-dependent signaling and behavior. Anesthesiology 2011, 115, 1363–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcdonald, J.; Dg, P.; Frca, L.P. Opioid receptors. In Continuing Education in Anaesthesia, Critical Care & Pain; 2015; Volume 15, pp. 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanini, M.; Castro, J.; Coelho, F.M.; Bittencourt, L.; Bressan, R.A.; Tufik, S.; Brietzke, E. Do sleep abnormalities and misaligned sleep/circadian rhythm patterns represent early clinical characteristics for developing psychosis in high risk populations? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 2631–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Assimakopoulos, K.; Karaivazoglou, K.; Skokou, M.; Kalogeropoulou, M.; Kolios, P.; Gourzis, P.; Patrinos, G.P.; Tsermpini, E.E. Genetic Variations Associated with Sleep Disorders in Patients with Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review. Medicines 2018, 5, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5020027
Assimakopoulos K, Karaivazoglou K, Skokou M, Kalogeropoulou M, Kolios P, Gourzis P, Patrinos GP, Tsermpini EE. Genetic Variations Associated with Sleep Disorders in Patients with Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review. Medicines. 2018; 5(2):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5020027
Chicago/Turabian StyleAssimakopoulos, Konstantinos, Katerina Karaivazoglou, Maria Skokou, Marina Kalogeropoulou, Panagiotis Kolios, Philippos Gourzis, George P. Patrinos, and Evangelia Eirini Tsermpini. 2018. "Genetic Variations Associated with Sleep Disorders in Patients with Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review" Medicines 5, no. 2: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5020027
APA StyleAssimakopoulos, K., Karaivazoglou, K., Skokou, M., Kalogeropoulou, M., Kolios, P., Gourzis, P., Patrinos, G. P., & Tsermpini, E. E. (2018). Genetic Variations Associated with Sleep Disorders in Patients with Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review. Medicines, 5(2), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5020027






