Factors Predicting Acute Brain Injury in Cases of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: A Prospective Registry-Based Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population and Measures
2.3. Treatment Protocol
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Comparison of Clinical Characteristics and Laboratory Findings Based on the Presence of ABI
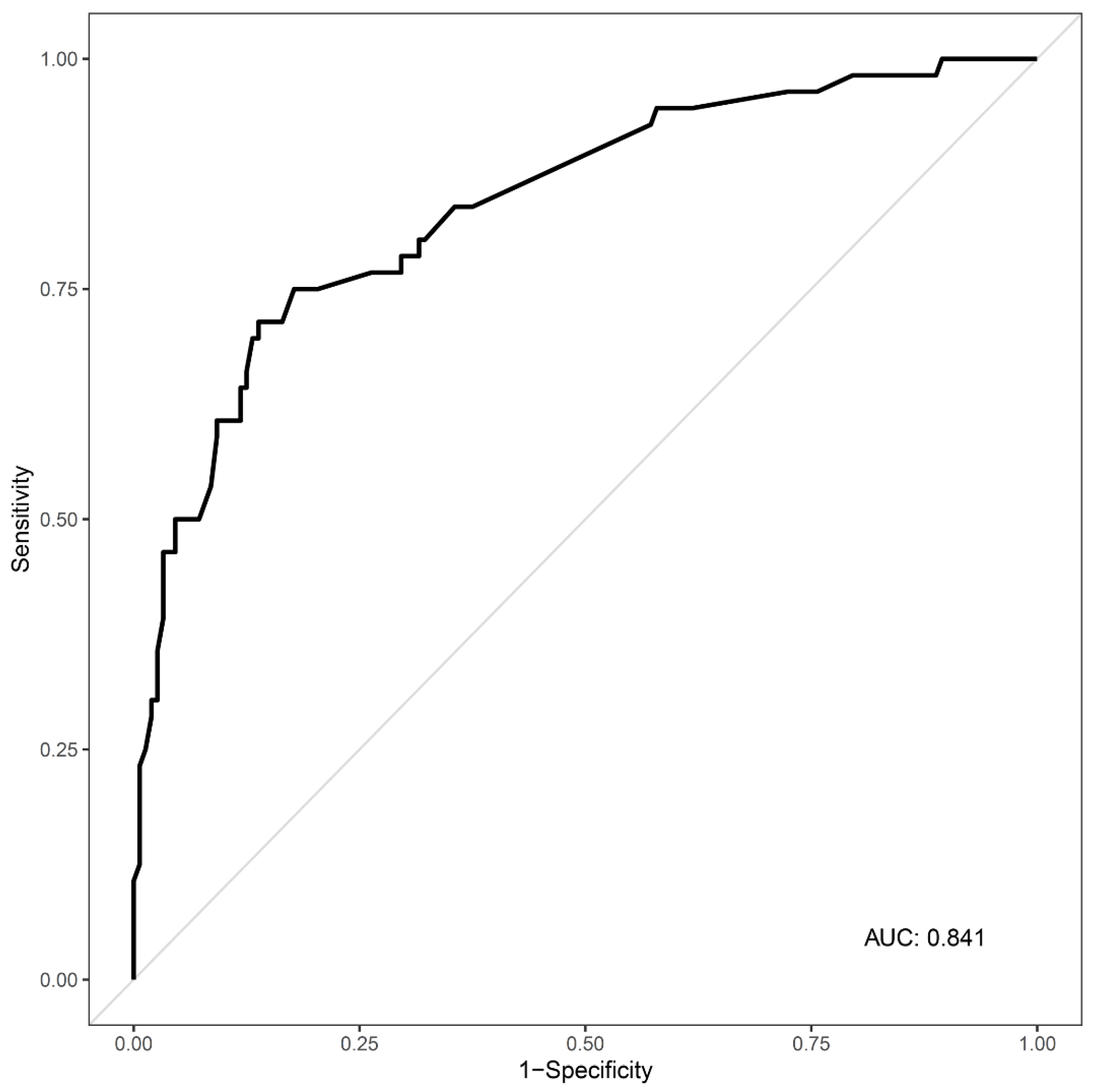
3.3. Predictors of ABI in Cases of Acute CO Poisoning
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hampson, N.B.; Weaver, L.K. Carbon monoxide poisoning: A new incidence for an old disease. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2007, 34, 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, J.J.; Wang, L.; Xu, Q.; McTiernan, C.F.; Shiva, S.; Tejero, J.; Gladwin, M.T. Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Pathogenesis, Management, and Future Directions of Therapy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, N.B. US mortality due to carbon monoxide poisoning, 1999–2014. Accidental and intentional deaths. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13, 1768–1774. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, A.; Zibrak, J.D. Carbon monoxide poisoning. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, L.K. Carbon monoxide poisoning. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-C.; Chung, M.-H.; Weng, S.-F.; Chien, C.-C.; Lin, S.-J.; Lin, H.-J.; Guo, H.-R.; Su, S.-B.; Hsu, C.-C.; Juan, C.-W. Long-Term Prognosis of Patients with Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: A Nationwide Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.-F.; Guo, Q.; Shao, H.; Li, B.; Du, Y.; Liu, M.; Liu, F.; Dai, L.; Chung, M.-H.; Lin, H.-J.; et al. A Positive Babinski Reflex Predicts Delayed Neuropsychiatric Sequelae in Chinese Patients with Carbon Monoxide Poisoning. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 814736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jeon, S.-B.; Sohn, C.H.; Seo, D.-W.; Oh, B.J.; Lim, K.S.; Kang, D.-W.; Kim, W.Y. Acute Brain Lesions on Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Delayed Neurological Sequelae in Carbon Monoxide Poisoning. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampson, N.B.; Piantadosi, C.A.; Thom, S.R.; Weaver, L.K. Practice recommendations in the diagnosis, management, and prevention of carbon monoxide poisoning. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Wang, Y.; Cao, L.; Huang, W.; Zhang, J.; Gao, X.; Lin, C. Glasgow Coma Scale is a better delayed neurological sequelae risk factor than neurological examination abnormalities in carbon monoxide poisoning. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 38, 2468–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, C.M.; Pinto, D.S.; Murphy, S.A.; Morrow, D.A.; Hobbach, H.P.; Wiviott, S.D.; Giugliano, R.P.; Cannon, C.P.; Antman, E.M.; Braunwald, E.; et al. Association of creatinine and creatinine clearance on presentation in acute myocardial infarction with subsequent mortality. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 42, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, K.; Rastelli, E.; Schoser, B. A systematic review on the definition of rhabdomyolysis. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nah, S.; Choi, S.; Kim, H.B.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.U.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, G.W.; Han, S. Cerebral white matter lesions on diffusion-weighted images and delayed neurological sequelae after carbon monoxide poisoning: A prospective observational study. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, L.K.; Hopkins, R.O.; Chan, K.J.; Churchill, S.; Elliott, C.G.; Clemmer, T.P.; Orme, J.F.; Thomas, F.O.; Morris, A.H. Hyperbaric Oxygen for Acute Carbon Monoxide Poisoning. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Yip, P.S.; Chan, C.H.; Fu, K.W.; Chang, S.S.; Lee, W.J.; Gunnell, D. The impact of a celebrity’s suicide on the introduction and establishment of a new method of suicide in South Korea. Arch. Suicide Res. 2014, 18, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.-W.; Gunnell, D.; Chou, Y.-H.; Kuo, C.-J.; Lee, M.-B.; Chen, Y.-Y. Why do people choose charcoal burning as a method of suicide? An interview based study of survivors in Taiwan. J. Affect. Disord. 2011, 131, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieb, G.; Simons, D.; Schmitz, L.; Piatkowski, A.; Grottke, O.; Pallua, N. Glasgow Coma Scale and laboratory markers are superior to COHb in predicting CO intoxication severity. Burns 2011, 37, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Choi, S.; Nah, S.; Lee, S.-U.; Cho, Y.S.; Kim, G.W.; Lee, Y.H. Cox regression model of prognostic factors for delayed neuropsychiatric sequelae in patients with acute carbon monoxide poisoning: A prospective observational study. Neurotoxicology 2021, 82, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, P.; Buxton, P.J.; Pitkin, A.; Jarvis, L.J. The magnetic resonance imaging appearances of the brain in acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Clin. Radiol. 2000, 55, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Durey, A.; Han, S.B.; Kim, J.H. Predictive factors for acute brain lesions on magnetic resonance imaging in acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 38, 1825–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.W.; Lee, J.H. Serum lactate as a predictor of neurologic outcome in ED patients with acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 37, 823–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Sohn, C.H.; Seo, D.-W.; Oh, B.J.; Lim, K.S.; Chang, J.W.; Kim, W.Y. Analysis of the development and progression of carbon monoxide poisoning–related acute kidney injury according to the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) criteria. Clin. Toxicol. 2018, 56, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, D.; Drewry, A.; Huang, Y.L.; Sames, C. The clinical toxicology of carbon monoxide. Toxicology 2003, 187, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherpitel, C.J.; Borges, G.L.; Wilcox, H.C. Acute Alcohol Use and Suicidal Behavior: A Review of the Literature. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2004, 28, 18S–28S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.-H.; Peng, C.-K.; Chou, Y.-C.; Pan, K.-T.; Chang, S.-C.; Chang, S.-Y.; Huang, K.-L. Predicting duration of mechanical ventilation in patients with carbon monoxide poisoning: A retrospective study. J. Crit. Care 2015, 30, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Total | |
|---|---|
| (n = 231) | |
| Age, years | 43 (32–54) |
| Sex, n (%) | |
| Female | 88 (38.1) |
| Male | 143 (61.9) |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.44 (21.1–25.83) |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | |
| Hypertension | 23 (10.0) |
| Diabetes | 7 (3.0) |
| Current smoker, n (%) | 86 (38.1) |
| GCS score at presentation | 15 (12–15) |
| Exposure type of CO, n (%) | |
| Accidental | 69 (29.9) |
| Intentional | 162 (70.1) |
| Exposure time of CO, min | 180 (62.5–360) |
| Hyperbaric oxygen therapy, n (%) | 224 (97.0) |
| LOS on hospital, days | 3 (2–5) |
| Non-ABI | ABI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 167) | (n = 64) | ||
| Age, years | 40 (30–50.5) | 48 (39–57) | <0.001 |
| Age group, n (%) | 0.010 | ||
| <20 years | 14 (93.3) | 1 (6.7) | |
| 20–39 years | 74 (80.4) | 18 (19.6) | |
| 40–59 years | 61 (62.9) | 36 (37.1) | |
| ≥60 years | 18 (66.7) | 9 (33.3) | |
| Sex, n (%) | 0.383 | ||
| Female | 67 (75.9) | 21 (24.1) | |
| Male | 100 (69.9) | 43 (30.1) | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.52 (21.01–26.05) | 23.05 (21.21–25.39) | 0.575 |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | |||
| Hypertension | 18 (78.3) | 5 (21.7) | 0.668 |
| Diabetes | 4 (57.1) | 3 (42.9) | 0.400 |
| Current smoker, n (%) | 58 (67.4) | 28 (32.6) | 0.281 |
| Vital Signs | |||
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg | 130 (120–145.5) | 127 (110–140) | 0.075 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mmHg | 80 (75–90) | 80 (70–90) | 0.180 |
| Heart rate, /min | 89 (77.5–102) | 91.5 (83–101.25) | 0.224 |
| Respiratory rate, /min | 20 (18–20) | 20 (19–20) | 0.574 |
| Exposure type of CO, n (%) | 0.034 | ||
| Accidental | 57 (82.6) | 12 (17.4) | |
| Intentional | 110 (67.9) | 52 (32.1) | |
| Exposure time of CO, min * | 120 (40–198.75) | 240 (120–450) | 0.045 |
| GCS score at presentation | 15 (12.5–15) | 13 (9–15) | <0.001 |
| GCS score < 9 (%) | 9 (39.1) | 14 (60.9) | <0.001 |
| Symptoms, n (%) | |||
| Headache | 27 (84.4) | 5 (15.6) | 0.152 |
| Loss of consciousness | 33 (67.3) | 16 (32.7) | 0.489 |
| Dyspnea | 6 (85.7) | 1 (14.3) | 0.677 |
| Chest pain | 2 (50.0) | 2 (50.0) | 0.308 |
| Laboratory findings | |||
| COHb, % | 12.69 ± 11.11 | 10.14 ± 9.19 | 0.093 |
| White blood cell count, 103/μL | 11.5 ± 4.84 | 14.82 ± 6.56 | <0.001 |
| BUN, mg/dL | 13.79 ± 5.43 | 21.01 ± 8.82 | <0.001 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.98 ± 0.23 | 1.36 ± 1.16 | 0.013 |
| Creatine Kinase, U/L | 617.96 ± 2195.53 | 5390.73 ± 16,845.19 | 0.033 |
| pH | 7.41 ± 0.08 | 7.39 ± 0.09 | 0.177 |
| C-reactive protein, mg/L | 3.5 ± 8.7 | 31.8 ± 52.6 | <0.001 |
| Lactate, mg/dL | 2.93 ± 2.17 | 3.55 ± 2.88 | 0.154 |
| Troponin I, ng/mL | 25.61 ± 271.91 | 11.26 ± 69.92 | 0.567 |
| Hyperbaric oxygen therapy, n (%) | 162 (72.3) | 62 (27.7) | >0.999 |
| LOS at hospital, days | 3 (2–4) | 7 (3–14) | <0.001 |
| Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value | VIF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age group | ||||
| <20 years | 1 | |||
| 20–39 years | 2.24 | 0.22–23.22 | 0.499 | 8.901 |
| 40–59 years | 3.90 | 0.38–39.87 | 0.251 | 9.231 |
| ≥60 years | 1.99 | 0.15–25.91 | 0.598 | 4.182 |
| SBP ≥ 140 mmHg | 0.54 | 0.23–1.29 | 0.165 | 1.165 |
| GCS score < 9 | 3.28 | 1.08–10.01 | 0.037 | 1.050 |
| Intentional exposure | 1.45 | 0.53–3.95 | 0.469 | 1.217 |
| Headache | 0.97 | 0.24–3.87 | 0.963 | 1.123 |
| Laboratory findings | ||||
| WBC count > 10 × 103/μL | 2.46 | 1.00–6.06 | 0.051 | 1.066 |
| BUN > 17.71 mg/dL | 2.50 | 0.99–6.30 | 0.052 | 1.360 |
| Creatinine > 1.2 mg/dL | 3.04 | 1.16–8.01 | 0.024 | 1.089 |
| C-reactive protein > 9.2 mg/L | 4.38 | 1.41–13.65 | 0.011 | 1.400 |
| Creatine kinase > 1000 U/L | 1.80 | 0.59–5.45 | 0.299 | 1.386 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, H.; Lee, Y.H.; Nah, S.; Choi, S.; Cho, Y.S.; Kim, G.W.; Moon, J.E.; Han, S. Factors Predicting Acute Brain Injury in Cases of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: A Prospective Registry-Based Study. Toxics 2021, 9, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9060120
Lim H, Lee YH, Nah S, Choi S, Cho YS, Kim GW, Moon JE, Han S. Factors Predicting Acute Brain Injury in Cases of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: A Prospective Registry-Based Study. Toxics. 2021; 9(6):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9060120
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Hoon, Young Hwan Lee, Sangun Nah, Sungwoo Choi, Young Soon Cho, Gi Woon Kim, Ji Eun Moon, and Sangsoo Han. 2021. "Factors Predicting Acute Brain Injury in Cases of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: A Prospective Registry-Based Study" Toxics 9, no. 6: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9060120
APA StyleLim, H., Lee, Y. H., Nah, S., Choi, S., Cho, Y. S., Kim, G. W., Moon, J. E., & Han, S. (2021). Factors Predicting Acute Brain Injury in Cases of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: A Prospective Registry-Based Study. Toxics, 9(6), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9060120








