Toxicity in Peripheral Nerves: An Overview
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sources of Entry into the Body
3. Environmental Toxicity
4. Clinical Features of TNs
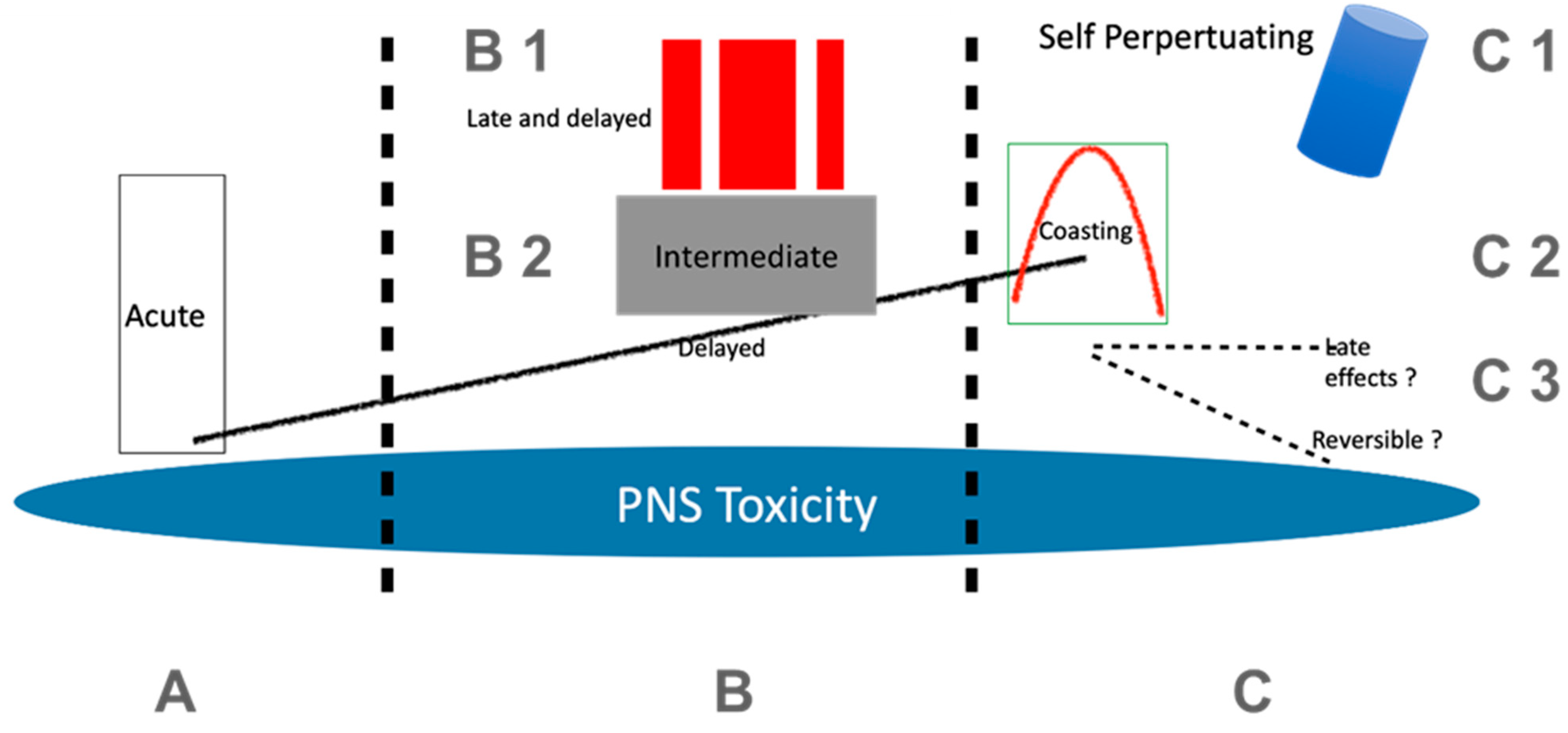
4.1. Acute Toxicity
4.2. Cumulative Toxicity
4.3. Multiple Timely Presentations (Different Types of Toxicity of the Same Substance in Sequential Temporal Relationships)
4.4. Delayed Toxicity, Long-Term and Indirect Effects
5. Pathogenesis and Prognosis
6. Criteria Useful to Classify TNs: The “Bradford Hill Criteria”
7. Targets and Mechanisms of Neurotoxicants
7.1. The Nerve Axon as a Target of Neurotoxins
7.2. Schwann Cells and Myelin as Targets of Neurotoxicity
7.3. Peripheral Neurons and Satellite Glial Cells as Targets of Neurotoxicity
7.4. Other Mechanisms
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hill, A.B. The Environment and Disease: Association or Causation? Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1965, 58, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, A.B. The environment and disease: Association or causation? 1965. J. R. Soc. Med. 2015, 108, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franquet-Griell, H.; Gómez-Canela, C.; Ventura, F.; Lacorte, S. Predicting concentrations of cytostatic drugs in sewage effluents and surface waters of Catalonia (NE Spain). Environ. Res. 2015, 138, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretti, M.; Bonfiglioli, R.; Feretti, D.; Pavanello, S.; Mussi, F.; Grollino, M.G.; Villarini, M.; Barbieri, A.; Ceretti, E.; Carrieri, M.; et al. A study protocol for the evaluation of occupational mutagenic/carcinogenic risks in subjects exposed to antineoplastic drugs: A multicentric project. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachisuka, J.; Chiang, M.C.; Ross, S.E. Itch and neuropathic itch. Pain 2018, 159, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oaklander, A.L. Common neuropathic itch syndromes. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2012, 92, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saviuc, P.F.; Danel, V.C.; Moreau, P.A.; Guez, D.R.; Claustre, A.M.; Carpentier, P.H.; Mallaret, M.P.; Ducluzeau, R. Erythromelalgia and mushroom poisoning. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 2001, 39, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimolai, N.; Cimolai, T. Erythromelalgia accompanying rosuvastatin-associated myopathy. J. Dermatol. Case Rep. 2009, 3, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grzybowski, A.; Zulsdorff, M.; Wilhelm, H.; Tonagel, F. Toxic optic neuropathies: An updated review. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015, 93, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasinska-Borowiec, W.; Aghdam, K.A.; Saari, J.M.; Grzybowski, A. An Updated Review on the Most Common Agents Causing Toxic Optic Neuropathies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 586–595. [Google Scholar]
- Lindhard Madsen, M.; Du, H.; Ejskjær, N.; Jensen, P.; Madsen, J.; Dybkær, K. Aspects of vincristine-induced neuropathy in hematologic malignancies: A systematic review. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2019, 84, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fehm, T.; Marme, A.; Lipp, H.P.; Schumacher, K. Paravasation von Zytostatika. Der Gynäkologe 2008, 41, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emre, A.U. Median Nerve Injury Due to High-Pressure Water Jet Injection: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2009, 35, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, O.; Aigner, K.; Wilimzig, H. Peripheral nerve damage following isolated extremity perfusion with cis-platinum. Recent Results Cancer Res. 1983, 86, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peel, N.; Kandler, R. Localized neuropathy following jellyfish sting. Postgrad. Med J. 1990, 66, 953–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebl, J.R.; Horlocker, T.T.; Pritchard, D.J. Diffuse Brachial Plexopathy after Interscalene Blockade in a Patient Receiving Cisplatin Chemotherapy: The Pharmacologic Double Crush Syndrome. Anesth. Analg. 2001, 92, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, P.; Pimentel, D.A.; Sundar, B.; Moonis, M.; Qin, L.; Novak, V. Association of Statins with Sensory and Autonomic Ganglionopathy. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giannoccaro, M.P. Somatic and autonomic small fiber neuropathy induced by bortezomib therapy: An immunofluorescence study. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 32, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremedhn, E.G.; Shortland, P.J.; Mahns, D.A. The incidence of acute oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy and its impact on treatment in the first cycle: A systematic review. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alcaraz, A.; Rey, C.; Concha, A.; Medina, A. Intrathecal vincristine: Fatal myeloencephalopathy despite cerebrospinal fluid perfusion. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, R.; Iwasa, S.; Yanai, T.; Hirano, H.; Shoji, H.; Honma, Y.; Okita, N.; Takashima, A.; Kato, K.; Hashimoto, H.; et al. Impact of peripheral neuropathy induced by platinum in first-line chemotherapy on second-line chemotherapy with paclitaxel for advanced gastric cancer. Int. J Clin. Oncol. 2020, 25, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, L.A., Jr. Modernizing the Bradford Hill criteria for assessing causal relationships in observational data. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2018, 48, 682–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahi, M.; Karami-Mohajeri, S. A comprehensive review on experimental and clinical findings in intermediate syndrome caused by organophosphate poisoning. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 258, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haliga, R.E.; Morarasu, B.B.; Ursaru, M.; Irimioaia, V.; Sorodoc, L. New insights into the organophosphate-induced intermediate syndrome. Arh. Hig. Rada. Toksikol. 2018, 69, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasconcellos, L.F.; Leite, A.C.; Nascimento, O.J. Organophosphate-induced delayed neuropathy: Case report. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2002, 60, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agalave, N.M.; Mody, P.H.; Szabo-Pardi, T.A.; Jeong, H.S.; Burton, M.D. Neuroimmune Consequences of eIF4E Phosphorylation on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 642420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, G.; Monza, L.; Cavaletti, G.; Rigolio, R.; Meregalli, C. Neuroinflammatory Process Involved in Different Preclinical Models of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 626687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehr, D. Sulfonamide vasculitis. J. Clin. Pharmacol. New Drugs. 1972, 12, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjemian, J.; Howell, J.; Holzbauer, S.; Harris, J.; Recuenco, S.; McQuiston, J.; Chester, T.; Lynfield, R.; Devries, A.; Belay, E.; et al. A clustering of immune-mediated polyradiculoneuropathy among swine abattoir workers exposed to aerosolized porcine brains, Indiana, United States. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2009, 15, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelpi, E.; Posada de la Paz, M.; Terracini, B.; Abaitua, I.; Gómez de la Cámara, A.; Kilbourne, E.M.; Lahoz, C.; Nemery, B.; Philen, R.M.; Soldevilla, L.; et al. The Spanish toxic oil syndrome 20 years after its onset: A multidisciplinary review of scientific knowledge. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grisold, W.; Mamoli, B. The syndrome of continuous muscle fibre activity following gold therapy. J. Neurol. 1984, 231, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jortner, B.S. Mechanisms of toxic injury in the peripheral nervous system: Neuropathologic considerations. Toxicol. Pathol. 2000, 28, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kist, A.M.; Sagafos, D.; Rush, A.M.; Neacsu, C.; Eberhardt, E.; Schmidt, R.; Lunden, L.K.; Ørstavik, K.; Kaluza, L.; Meents, J.; et al. SCN10A Mutation in a Patient with Erythromelalgia Enhances C-Fiber Activity Dependent Slowing. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161789. [Google Scholar]
- Carozzi, V.; Chiorazzi, A.; Canta, A.; Oggioni, N.; Gilardini, A.; Rodriguez-Menendez, V.; Avezza, F.; Crippa, L.; Ceresa, C.; Nicolini, G.; et al. Effect of the chronic combined administration of cisplatin and paclitaxel in a rat model of peripheral neurotoxicity. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meregalli, C.; Bonomo, R.; Cavaletti, G.; Carozzi, V.A. Blood molecular biomarkers for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: From preclinical models to clinical practice. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 749, 135739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benbow, S.J.; Cook, B.M.; Reifert, J.; Wozniak, K.M.; Slusher, B.S.; Littlefield, B.A.; Wilson, L.; Jordan, M.A.; Feinstein, S.C. Effects of Paclitaxel and Eribulin in Mouse Sciatic Nerve: A Microtubule-Based Rationale for the Differential Induction of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Neurotox. Res. 2016, 29, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.A.; Slusher, B.S.; Wozniak, K.M.; Farah, M.H.; Smiyun, G.; Wilson, L.; Feinstein, S.; Jordan, M.A. Structural Basis for Induction of Peripheral Neuropathy by Microtubule-Targeting Cancer Drugs. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5115–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herskowitz, A.; Ishii, N.; Schaumburg, H. n-Hexane neuropathy: A syndrome occurring as a result of industrial exposure. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 285, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzuto, N.; De Grandis, D.; Di Trapani, G.; Pasinato, E. n-Hexane polyneuropathy: An occupational disease of shoemakers. Eur. Neurol. 1980, 19, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C. Patients with n-hexane induced polyneuropathy: A clinical follow up. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1990, 47, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.C. Polyneuropathy induced by n-hexane intoxication in Taiwan. Acta Neurol. Taiwanica 2008, 17, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- De Waegh, S.M.; Lee, V.M.; Brady, S.T. Local modulation of neurofilament phosphorylation, axonal caliber, and slow axonal transport by myelinating Schwann cells. Cell 1992, 68, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, M.; Kupina, N.; Fink, D.J. Phosphorylation-dependent neurofilament epitopes are reduced at the node of Ranvier. J. Neurocytol. 1992, 21, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, S.T.; Kidd, G.J.; Crawford, T.O.; Xu, Z.; Lin, W.M.; Trapp, B.D.; Cleveland, D.W.; Griffin, J.W. Regional modulation of neurofilament organization by myelination in normal axons. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 6392–6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shemesh, O.A.; Spira, M.E. Paclitaxel induces axonal microtubules polareconfiguration and impaired organelle transport: Implications for the pathogenesis of paclitaxel-induced polyneuropathy. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Crawford, T.O.; Griffin, J.W.; Tu, P.H.; Lee, V.M.; Li, C.; Roder, J.; Trapp, B.D. Myelin-associated glycoprotein is a myelin signal that modulates the caliber of myelinated axons. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cosgaya, J.M.; Chan, J.R.; Shooter, E.M. The neurotrophin receptor p75NTR as a positive modulator of myelination. Science 2002, 298, 1245–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syroid, D.E.; Maycox, P.R.; Burrola, P. Cell death in the Schwann cell lineage and its regulation by neuregulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9229–9234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guenard, V.; Gwynn, L.A.; Wood, P.M. Transforming growth factor-beta blocks myelination but not ensheathment of axons by Schwann cells in vitro. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towfighi, J.; Gonatas, N.K.; McCree, L. Hexachlorophene-induced changes in central and peripheral myelinated axons of developing and adult rats. Lab. Investig. 1974, 31, 712–721. [Google Scholar]
- Tripier, M.F.; Berard, M.; Toga, M.; Martin-Bouyer, G.; Le Breton, R.; Garat, J. Hexachlorophene and the central nervous system. Toxic effects in mice and baboons. Acta Neuropathol. 1981, 53, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.I.; de Jesus, P.V.; Pleasure, D.E.; Gonatas, N.K. Triethyltin sulfateinduced neuropathy in rats. Electrophysiologic, morphologic, and biochemical studies. Arch. Neurol. 1976, 33, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanz, S.; Fainzilber, M. Retrograde signaling in injured nerve–the axon reaction revisited. J. Neurochem. 2006, 99, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheib, J.; Ho¨ke, A. Advances in peripheral nerve regeneration. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adelsberger, H.; Quasthoff, S.; Grosskreutz, J.; Lepier, A.; Eckel, F.; Lersch, C. The chemotherapeutic oxaliplatin alters voltage-gated Na(þ) channel kinetics on rat sensory neurons. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 406, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.B.; Lin, C.S.Y.; Krishnan, A.V.; Goldstein, D.; Friedlander, M.L.; Kiernan, M.C. Dose effects of oxaliplatin on persistent and transient Naþ conductances and the development of neurotoxicity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18469. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.N.; Chen, B.S.; Wu, Y.H.; Peng, H.; Chen, L.T. The mechanism of the actions of oxaliplatin on ion currents and action potentials in differentiated NG108-15 neuronal cells. Neurotoxicology 2009, 30, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.G.; Brain, K.L.; Wilson, R.H.; Grem, J.L.; Vincent, A. Oxaliplatin induces hyperexcitability at motor and autonomic neuromuscular junctions through effects on voltage-gated sodium channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 146, 1027–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartu, M.; Carozzi, V.A.; Dorsey, S.G.; Serra, M.P.; Poddighe, L.; Picci, C.; Boi, M.; Melis, T.; Del Fiacco, M.; Meregalli, C.; et al. Bortezomib treatment produces nocifensive behavior and changes in the expression of TRPV1, CGRP, and substance P in the rat DRG, spinal cord, and sciatic nerve. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 180428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwick, R.A.; Hanani, M. The contribution of satellite glial cells to chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pain 2013, 17, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.U.; Fitzpatrick-Lewis, D.; Kenny, M.; Raina, P.; Atkins, D.L.; Soar, J.; Nolan, J.; Ristagno, G.; Sherifali, D. Effectiveness of antiarrhythmic drugs for shockable cardiac arrest: A systematic review. Resuscitation 2018, 132, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Anti-Microbials | Anti-Cancer Drugs | Cardiovascular | Psychiatric/Central Nervous System Disorders | Vitamins | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chloroquine | Brentuximab vedotin | Amiodarone | Chlorprothixene | Vitamin B6 overdose | Allopurinol |
| Chloramphenicol | Epothilones | Perhexilene | Glutethimide | Vitamin B12 deficiency | Colchicin |
| Dapsone | Platinum drugs (cisplatin and oxaliplatin) | Propafenone | Phenelzine | Cyclosporin A | |
| Ethambutol | Proteasome inhibitors (bortezomib) | Statins | Phenytoin | Dichloroacetate | |
| Fluoroquinolone | Taxanes (paclitaxel and docetaxel) | Disulfiram | |||
| Linezolid | Trastuzumab emtansine | Etanercept | |||
| Metronidazol | Vinca alkaloids (vincristine and vinblastine) | Gold | |||
| Nitrofurantoin | Hydralazine | ||||
| Nucleoside analogues | Infliximab | ||||
| Sulfasalazin | Interferon alpha | ||||
| Tuberculostatics | Leflunomid | ||||
| D-penicillamine | |||||
| Tacrolimus |
| Substance Groups | Examples |
|---|---|
| Anti-freeze substances | Diethylen glycole and methylbromide |
| Biological agents and venoms | Brevetoxin, ciguatera, domoic acid, lara toxin, saxitoxin, snake and spider venoms as well as tetrodoxin |
| Drugs, medicines and anesthesiology drugs | See dedicated table (Table 2), nitrous oxide Local toxicity (various agents) |
| Environment, water sources and wastewater | Wells: As, dioxin and Hg Chemotherapy excretions in wastewater |
| Food and diet | Examples: Spanish oil syndrome Fish poisoning |
| Industrial agents | Acrylamide, hexacarbone and solvents |
| Heavy metals | As, Hg, Pb, Th and Zn |
| Pesticide and herbicides | Dioxin, organophosphate and vacor |
| Plants | Example: sea buckthorn berry |
| “Recreational drugs” | Alcohol, methanol, (glue) “sniffing” |
| Source/Entry | Site of Entry | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Aerosols | Air tract | Aerosols, glue, NO and solvents |
| Ingestion | Mouth and intestine | Drugs, Food, Fluids (alcohol) |
| Local | Skin Paravasate Cavities—local toxicity and dissemination (e.g., intraperitoneal) Perfusion (e.g., limbs) | Local High-pressure device Grouting (+) (e.g., acrylamide) Anti-cancer drugs IT or IP chemotherapy Local tumor perfusion |
| Parenteral | Bloodstream | Medical treatment, drugs, IV and IT |
| Environmental (#) | Air Contamination Fumes Well water | Different dimensions of concentrations: see discussion |
| Target Site | Mechanisms | Toxic Substances | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Axon | Affected transport along axons Affected microtubule assembly Defects in neurofilament and actin microfilaments | Chemotherapeutic drugs Environmental chemicals | Adriamicine Anti-tubulin Bortezomib Epothilones Vinca alkaloids n-Hexane Carbon disulphide Acrylamide |
| Myelin and Schwann cells | Defects in key molecules for axon–Schwann cell signaling | Chemotherapy drugs Other drugs Adjuvants in soaps Contaminants in medication | Bortezomib Suramin Adalimumab Amiodorone Etanercept Infliximab Hexaclorophene Perhexiline Triethyltin |
| DRG | Organelle damage (mitochondria, ER, proteasome, etc.) Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA damage Defects in ion channels and receptors Defects in neuron–SGC signaling | Chemotherapeutic drugs Other drugs Venoms Vitamin excess | Bortezomib Platinum compounds Thalidomide Nitrofurantoin Isoniazid Mercury Pyridoxamine |
| Immune-mediated | Secondary induction of an immune response | Chemotherapeutic drugs Environmental substances | Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grisold, W.; Carozzi, V.A. Toxicity in Peripheral Nerves: An Overview. Toxics 2021, 9, 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9090218
Grisold W, Carozzi VA. Toxicity in Peripheral Nerves: An Overview. Toxics. 2021; 9(9):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9090218
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrisold, Wolfgang, and Valentina Alda Carozzi. 2021. "Toxicity in Peripheral Nerves: An Overview" Toxics 9, no. 9: 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9090218
APA StyleGrisold, W., & Carozzi, V. A. (2021). Toxicity in Peripheral Nerves: An Overview. Toxics, 9(9), 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9090218







