Magnetic Stirring Assisted Demulsification Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction for Preconcentration of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Grilled Pork Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Chromatographic Conditions
2.3. Sample Preparation of Grilled Pork Samples
2.4. Magnetic Stirring Assisted Demulsified Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction
2.5. Method Validation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
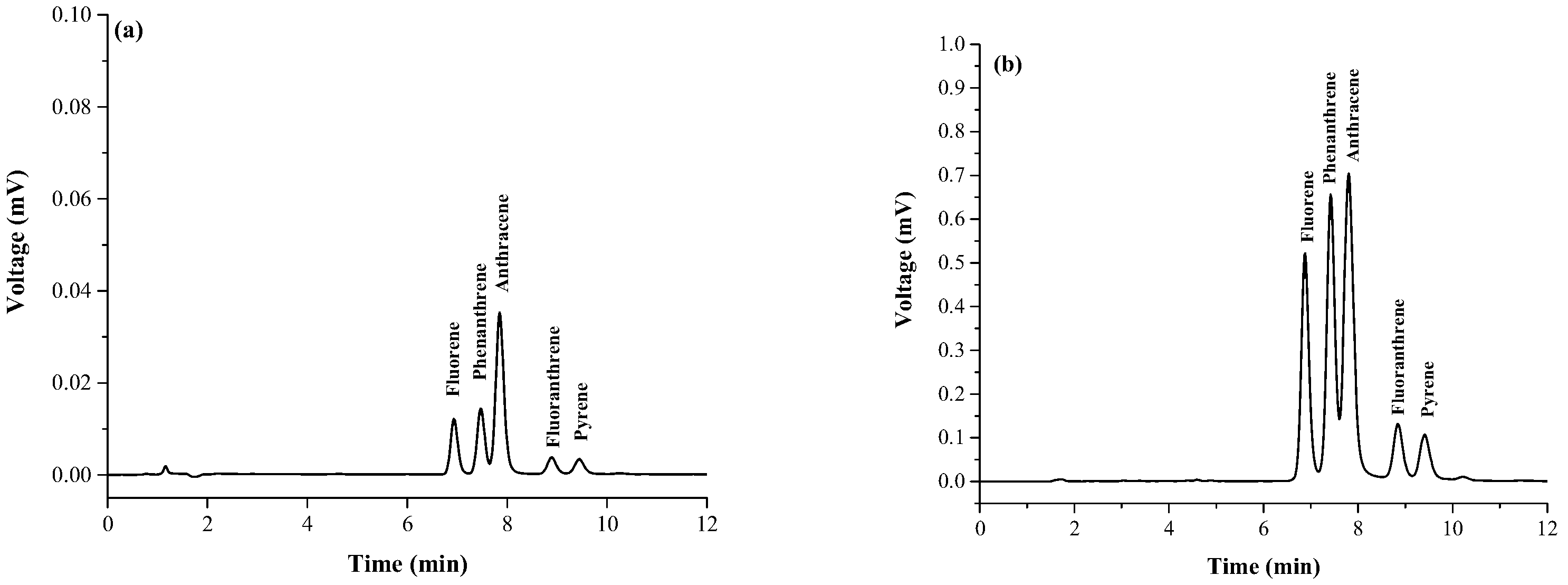
3.1. Optimization of Magnetic Stirring Assisted Demulsified Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Condition
3.2. Analytical Performance of the Proposed Method
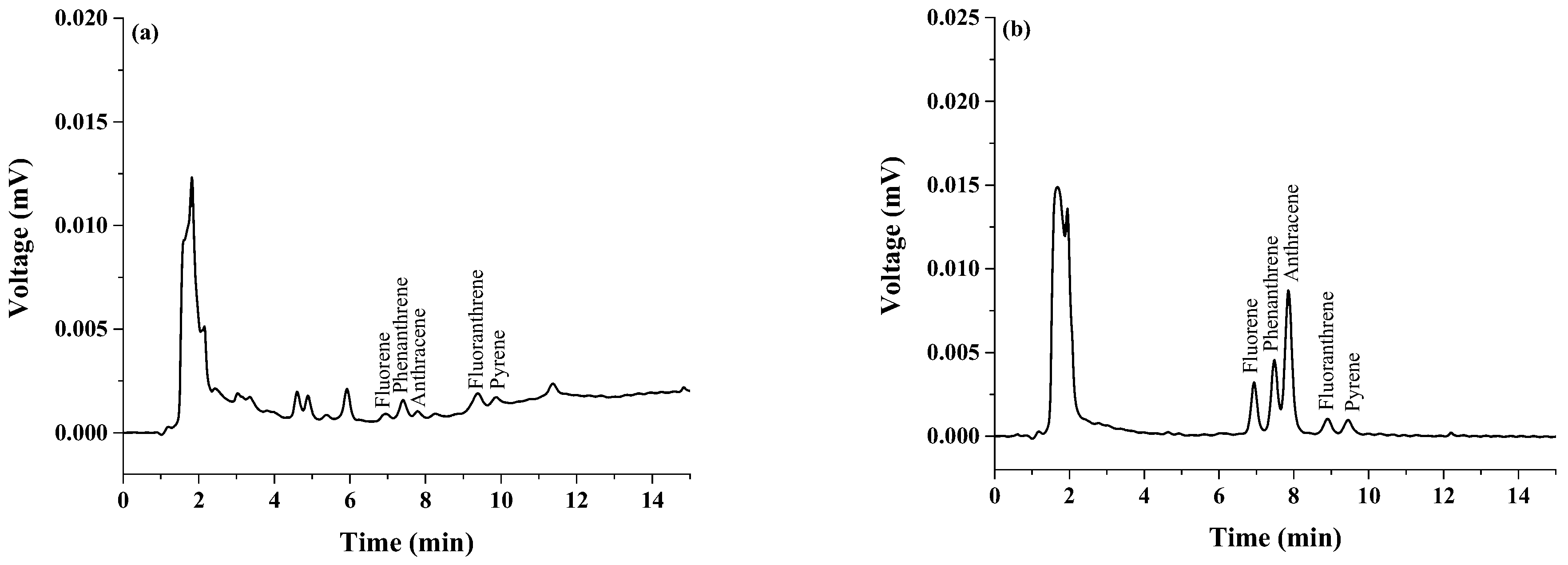
3.3. Grilled Pork Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dost, K.; İdeli, C. Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in edible oils and barbecued food by HPLC/UV–Vis detection. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Ghasemzadeh-Mohammadi, V.; Haratian, P.; Khaksar, R.; Chaichi, M. Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in smoked fish samples by a new microextraction technique and method optimisation using response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2459–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Hassan, F.W.; Raoov, M.; Kamaruzaman, S.; Sanagi, M.M.; Yoshida, N.; Hirota, Y.; Nishiyama, N.; Yahaya, N. Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with dispersive solid-phase extraction for gas chromatography with mass spectrometry determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous matrices. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 3751–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, C.; Guo, X.; Du, J.; Du, L. Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in coffee and tea samples by magnetic solid-phase extraction coupled with HPLC–FLD. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Bolanos, P.; Frenich, A.G.; Vidal, J.L.M. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in food and beverages. Analytical methods and trends. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 6303–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ma, R.; Wu, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. Magnetic microsphere-confined graphene for the extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from environmental water samples coupled with high performance liquid chromatography–fluorescence analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1293, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Jiang, R.; Pawliszyn, J. Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in solid matrices using automated cold fiber headspace solid phase microextraction technique. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1307, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.-B.; Chen, X.-J.; Zhang, H.-F.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Li, X.; Li, X.-Y.; Zhu, F.-P.; Pang, Y.-Q.; Hou, H.-W. Simultaneous determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and tobacco-specific N-nitrosamines in mainstream cigarette smoke using in-pipette-tip solid-phase extraction and on-line gel permeation chromatography-gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1460, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, W.; Ren, F.; Tang, L.; Dong, D. Analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in cigarette samples using gel permeation chromatography clean-up by gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2016, 129, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Feng, J.; Bu, Y.; Luo, C. Highly sensitive copper fiber-in-tube solid-phase microextraction for online selective analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons coupled with high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1408, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.; Clavijo, S.; Forteza, R.; Cerdà, V. Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons using lab on valve dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled to high performance chromatography. Talanta 2015, 138, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moazzen, M.; Ahmadkhaniha, R.; Gorji, M.E.; Yunesian, M.; Rastkari, N. Magnetic solid-phase extraction based on magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes for the determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in grilled meat samples. Talanta 2013, 115, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.-W.; Tang, M.-Q.; Xu, L.; Shi, Z. Magnetic nanoparticles with hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity for solid-phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1411, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payanan, T.; Leepipatpiboon, N.; Varanusupakul, P. Low-temperature cleanup with solid-phase extraction for the determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in edible oils by reversed phase liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2720–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Yu, W. Liquid–liquid extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in four different edible oils from China. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, O.; Christoph, G.; Kalbe, U.; Berger, W. Comparison of stir bar sorptive extraction (SBSE) and liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) for the analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in complex aqueous matrices. Talanta 2011, 85, 1428–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaee, M.; Assadi, Y.; Hosseini, M.R.M.; Aghaee, E.; Ahmadi, F.; Berijani, S. Determination of organic compounds in water using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1116, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Chen, R.; Li, Sh. Low-density extraction solvent-based solvent terminated dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of carbamate pesticides in water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 1244–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharis, C.K.; Tzanavaras, P.D.; Roubos, K.; Dhima, K. Solvent-based de-emulsification dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry for determination of trace organochlorine pesticides in environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 5896–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichapong, J.; Burakham, R.; Srijaranai, S. Vortex-assisted surfactant-enhanced-emulsification liquid–liquid microextraction with solidification of floating organic droplet combined with HPLC for the determination of neonicotinoid pesticides. Talanta 2013, 117, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichapong, J.; Burakham, R. Novel ultrasound-assisted mixed anionic–cationic surfactant-enhanced emulsification microextraction combined with HPLC for the determination of carbamate pesticides. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 2101–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstkotte, B.; Suárez, R.; Solich, P.; Cerdà, V. In-syringe-stirring: A novel approach for magnetic stirring-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 788, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.-P.; Shi, Z.-G.; Yu, Q.-W.; Feng, Y.-Q. A new device for magnetic stirring-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of UV filters in environmental water samples. Talanta 2011, 83, 1711–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seebunrueng, K.; Santaladchaiyakit, Y.; Srijaranai, S. Vortex-assisted low density solvent liquid–liquid microextraction and salt-induced demulsification coupled to high performance liquid chromatography for the determination of five organophosphorus pesticide residues in fruits. Talanta 2015, 132, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regueiro, J.; Llompart, M.; Garcia-Jares, C.; Garcia-Monteagudo, J.C.; Cela, R. Ultrasound-assisted emulsification–microextraction of emergent contaminants and pesticides in environmental waters. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1190, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seebunrueng, K.; Santaladchaiyakit, Y.; Srijaranai, S. Vortex-assisted low density solvent based demulsified dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides in water samples. Chemosphere 2014, 103, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Cheng, M.; Guo, F.; Wang, X.; Cheng, J. In-syringe demulsified dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and high performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry for the determination of trace fungicides in environmental water samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 724, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Cheng, M. Development of a simple combining apparatus to perform a magnetic stirring-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and its application for the analysis of carbamate and organophosphorus pesticides in tea drinks. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 787, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichapong, J.; Santaladchaiyakit, Y.; Burakham, R.; Srijaranai, S. Determination of Benzimidazole Anthelminthics in Eggs by Advanced Microextraction with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Lett. 2015, 48, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
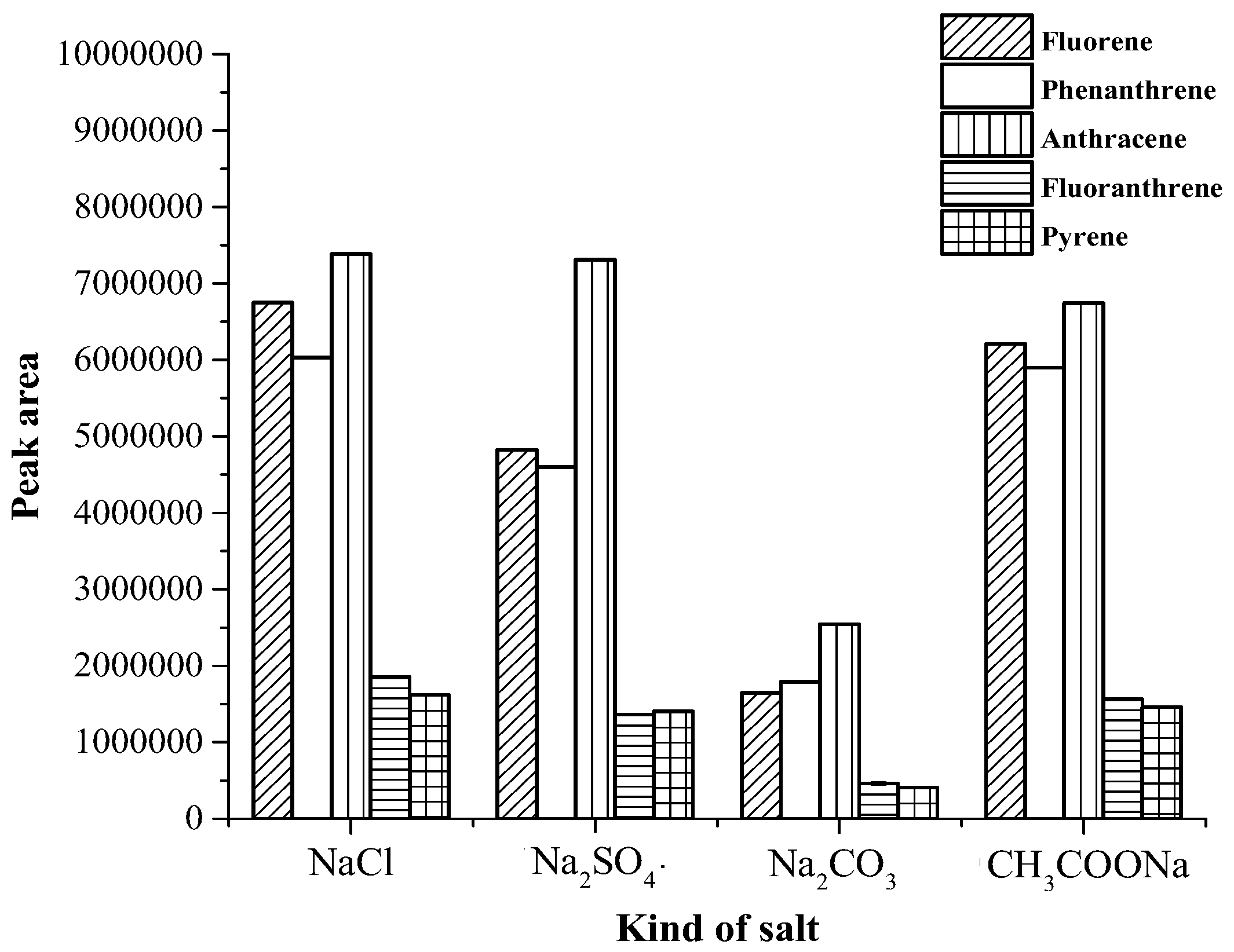
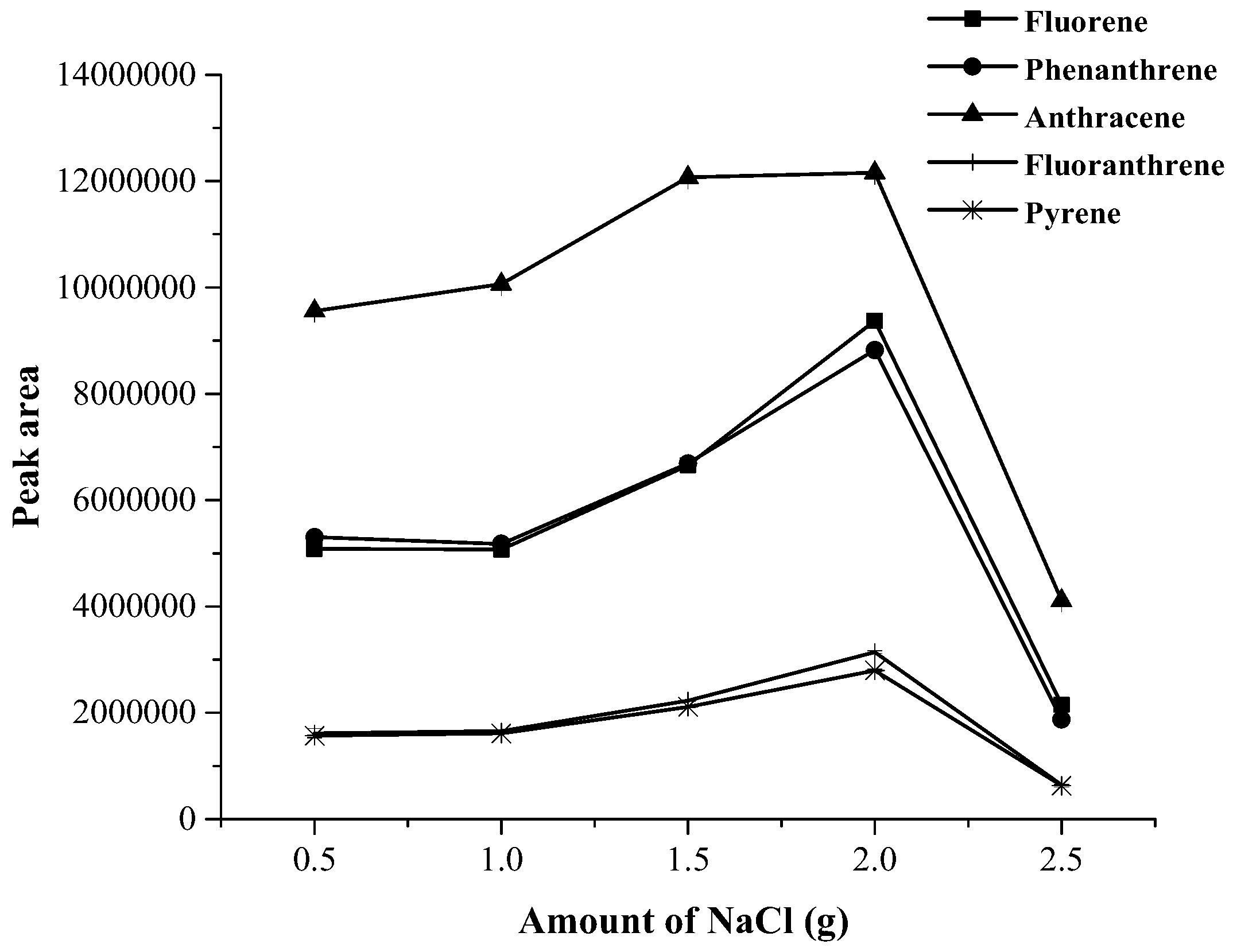
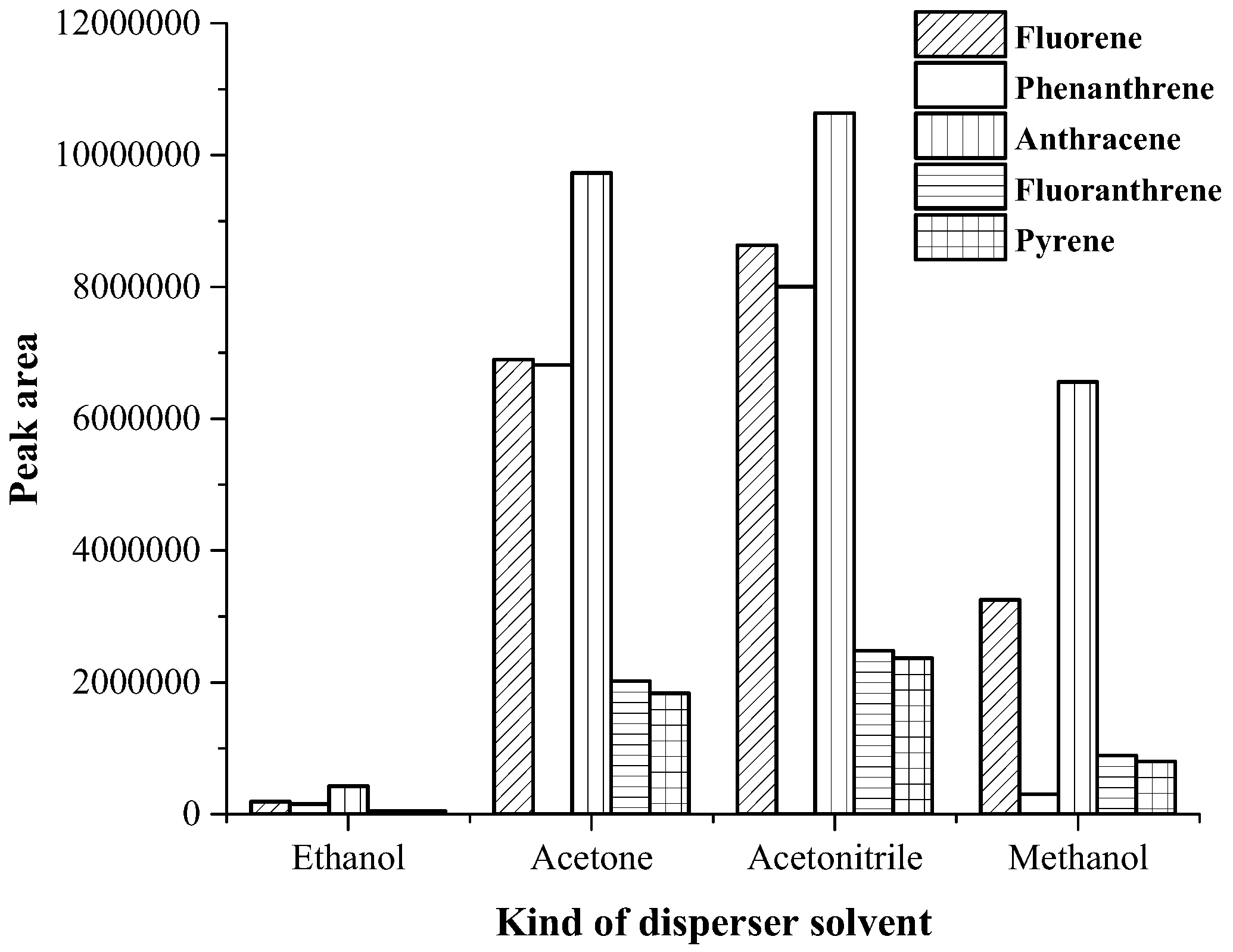
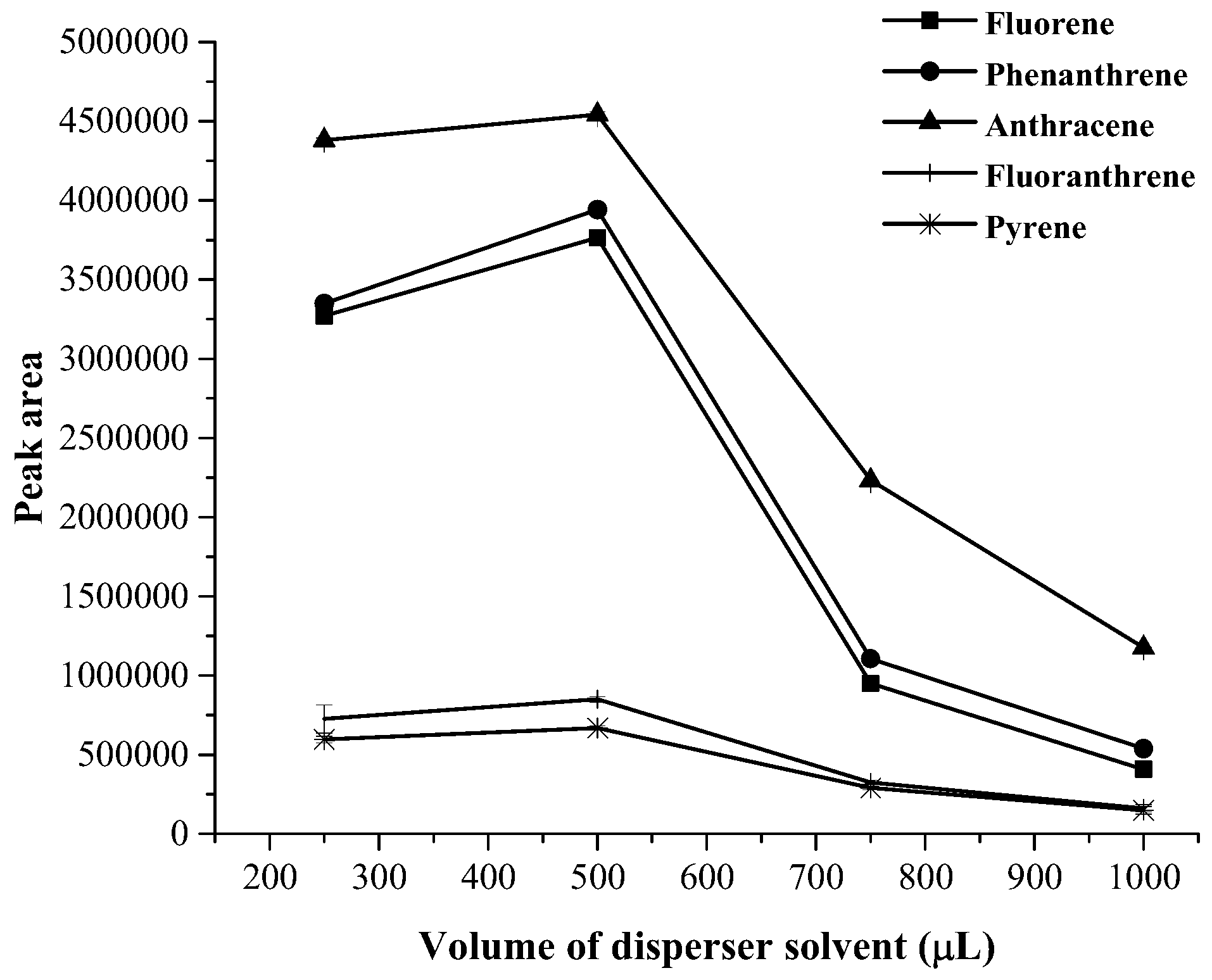


| Analyte | Linear range (µg·mL−1) | Linear equation | R2 | EF | LOD (µg·mL−1) | LOQ (µg·mL−1) | Intra-day a (n = 5) | Inter-day (n = 3 × 5) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tR | Area | tR | Area | |||||||
| Fluorene | 0.0005–1 (0.03–1) b | y = (7 × 106x) + 87,587 | 0.9992 | 65 | 0.0001 | 0.0003 | 0.15 (0.17) | 2.18 (2.51) | 0.39 (0.50) | 6.72 (7.44) |
| Phenanthrene | 0.0005–1 (0.03–1) | y = (7 × 106x) + 87,587 | 0.9973 | 64 | 0.0001 | 0.0003 | 0.17 (0.19) | 2.79 (3.08) | 0.22 (0.29) | 2.73 (3.19) |
| Anthracene | 0.0005–1 (0.03–1) | y = 401,767x + 32,354 | 0.9993 | 60 | 0.0003 | 0.0005 | 0.24 (0.39) | 2.58 (3.70) | 0.37 (0.60) | 5.68 (6.25) |
| Fluoranthrene | 0.0005–1 (0.03–1) | y= (2 × 106x) + 20,850 | 0.9989 | 66 | 0.0003 | 0.0005 | 0.20 (0.49) | 3.55 (4.34) | 0.33 (0.48) | 5.51 (7.05) |
| Pyrene | 0.0005–1 (0.03–1) | y = (4 × 106x) + 30,813 | 0.9997 | 67 | 0.0001 | 0.0003 | 0.32 (1.06) | 3.89 (5.40) | 0.48 (1.48) | 7.22 (8.12) |
| Samples | Amount found ± SD, mg·kg−1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluorene | Phenanthrene | Anthracene | Fluoranthrene | Pyrene | |
| Grilled pork I (n = 3) | 0.50 ± 0.10 | 1.00 ± 0.10 | 0.50 ± 0.10 | 0.80 ± 0.20 | 0.50 ± 0.01 |
| Grilled pork II (n = 3) | - | 0.70 ± 0.20 | 0.30 ± 0.20 | 0.50 ± 0.01 | 0.40 ± 0.01 |
| Grilled pork III (n = 3) | 0.30 ± 0.02 | - | 0.50 ± 0.20 | 0.70 ± 0.01 | 0.30 ± 0.20 |
| Grilled pork IV (n = 3) | 0.40 ± 0.10 | 0.40 ± 0.01 | 0.50 ± 0.10 | 0.60 ± 0.20 | 0.20 ± 0.10 |
| Analytes | Spiked (mg·kg−1) | Grilled pork I | Grilled pork II | Grilled pork III | Grilled pork IV | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR (%) | RSD (%) | RR (%) | RSD (%) | RR (%) | RSD (%) | RR (%) | RSD (%) | ||
| Fluorene | 0.01 | 83.45 | 1.52 | 87.64 | 4.73 | 95.73 | 6.63 | 91.57 | 8.76 |
| 0.05 | 87.93 | 3.30 | 90.62 | 5.67 | 90.67 | 2.54 | 89.72 | 6.78 | |
| 0.10 | 84.63 | 6.35 | 96.87 | 3.79 | 85.33 | 2.63 | 98.74 | 6.87 | |
| Phenanthrene | 0.01 | 82.93 | 5.36 | 92.39 | 4.33 | 87.73 | 3.87 | 89.30 | 7.45 |
| 0.05 | 91.58 | 4.74 | 83.76 | 5.76 | 93.48 | 4.57 | 95.78 | 6.87 | |
| 0.10 | 98.74 | 6.79 | 90.78 | 7.63 | 90.63 | 7.86 | 90.87 | 7.86 | |
| Anthracene | 0.01 | 82.97 | 4.53 | 87.33 | 3.63 | 92.78 | 6.75 | 90.63 | 3.67 |
| 0.05 | 87.62 | 5.73 | 88.63 | 4.76 | 90.78 | 7.67 | 89.78 | 4.38 | |
| 0.10 | 90.73 | 8.63 | 93.74 | 6.78 | 91.87 | 1.56 | 89.90 | 3.78 | |
| Fluoranthrene | 0.01 | 89.97 | 3.44 | 93.35 | 4.32 | 94.67 | 3.39 | 89.93 | 3.45 |
| 0.05 | 91.56 | 4.67 | 89.90 | 6.32 | 91.75 | 4.13 | 83.63 | 6.78 | |
| 0.10 | 95.73 | 7.78 | 91.72 | 4.36 | 89.73 | 5.62 | 90.57 | 8.98 | |
| Pyrene | 0.01 | 89.93 | 3.65 | 89.97 | 8.78 | 87.78 | 7.89 | 93.65 | 8.35 |
| 0.05 | 90.67 | 4.78 | 91.63 | 5.67 | 88.98 | 6.78 | 91.32 | 5.56 | |
| 0.10 | 89.92 | 7.87 | 89.73 | 6.72 | 90.56 | 5.76 | 90.01 | 4.65 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vichapong, J.; Santaladchaiyakit, Y.; Burakham, R.; Srijaranai, S. Magnetic Stirring Assisted Demulsification Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction for Preconcentration of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Grilled Pork Samples. Toxics 2019, 7, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics7010008
Vichapong J, Santaladchaiyakit Y, Burakham R, Srijaranai S. Magnetic Stirring Assisted Demulsification Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction for Preconcentration of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Grilled Pork Samples. Toxics. 2019; 7(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics7010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleVichapong, Jitlada, Yanawath Santaladchaiyakit, Rodjana Burakham, and Supalax Srijaranai. 2019. "Magnetic Stirring Assisted Demulsification Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction for Preconcentration of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Grilled Pork Samples" Toxics 7, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics7010008
APA StyleVichapong, J., Santaladchaiyakit, Y., Burakham, R., & Srijaranai, S. (2019). Magnetic Stirring Assisted Demulsification Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction for Preconcentration of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Grilled Pork Samples. Toxics, 7(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics7010008





