Abstract
Poly- and perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) are a group of chemicals that are widely used, prevalent in the environment, associated with several toxic effects, and often have long half-lives. Their persistence and relevant toxicity are the primary causes of environmental and human health concerns, and they are referred to as “forever chemicals” because of their persistence. Environmental accumulation caused by slow natural biodegradation and subsequent long environmental half-lives leads to bioaccumulation and makes PFAS more likely to be chronically toxic with potential transgenerational effects. Ultimately, it is this persistence that causes the greatest concern because PFAS-contaminated sites need costly remediation techniques, or else the contaminated areas will not be available for proper economic development because of social and economic suppression. Non-PFAS, alternative Aqueous Film Forming Foams (AFFF) that are considered environmentally friendly, are being heavily considered or currently used for fire suppression instead of PFAS-based products. The bioaccumulation and toxicity of alternative AFFF are just starting to be studied. The purpose of this review is to discuss the basic environmental and human health effects of PFAS and alternative AFFF that propel regulatory changes, increase clean-up costs, reduce economic development, and drive the development of novel alternatives.
Keywords:
PFAS; PFOS; bioaccumulation; biodegradation; half-life; forever chemical; regulation; economic; chronic toxicity 1. Background
On 29 July 1967, the USS Forrestal caught fire, killing 134 sailors and injuring 161 more [1,2]. Improper safety measures and the lack of high-quality fire suppressants were in part to blame. This fire helped usher in the development and use of new Aqueous Film-Forming Foams (AFFF) that contained poly- and perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) [3]. These PFAS-containing AFFF were highly effective at fighting fires and became widely used in multiple other products, but led to widespread environmental contamination due to their persistence and toxicity.
PFAS are synthetic chemicals that have been used widely as surfactants and polymerization aids, non-stick coatings for cookware, food packaging, finishes for clothing, upholstery, and as firefighting foams for approximately ninety years [4,5,6]. PFAS come in multiple lengths with multiple functional groups. These diverse functional groups may include carboxylic acids, sulfonic acids, sulfonamide, iodides, ethers, and phosphonic or phosphinic acids. The two major forms are sulfonates such as perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) and carboxylic acids such as pefluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) [6]. Characterization may also be based on the number of carbons in the chain, with six-carbon chains or less typically considered short-chain PFAS and seven carbons or more considered long-chain PFAS. Chain length is important as it is directly correlated to bioaccumulation [6,7]. With more than 7 million PFAS structures [8], many with long chemical half-lives, these ‘forever chemicals’ have raised several human health and environmental concerns, as exposure is widespread [9,10].
Human PFAS exposure remains prevalent for common PFAS such as PFOS, PFOA, and perfluorohexane sulfonic acid (PFHxS) despite U.S. and European manufacturing phase-outs in the early 2000s and listing in the Stockholm Convention [6,11]. Contaminated food and water, household dust, and indoor air continue to be important sources. Furthermore, these chemicals and other PFAS are produced internationally by multiple countries and imported in consumer goods such as firefighting foams, non-stick cookware, stain-resistant products, clothing, mattress pads, table cloths, personal care products, and cleaning products [12], which means the exposure, bioaccumulation, and toxicity risks of PFAS will continue.
The manufacturing and subsequent persistence of PFAS led to significant contamination in several areas or hotspots [13,14]. These hotspots affect human and environmental health, leading to increased healthcare and compliance costs, and adversely impacting property values and economic development due to potential clean-up costs. Therefore, PFAS significantly reduce investment in these regions [15,16,17]. It is the widespread use and persistence of PFAS that lead to downstream adverse effects on human health, the environment, and the economy (Figure 1).
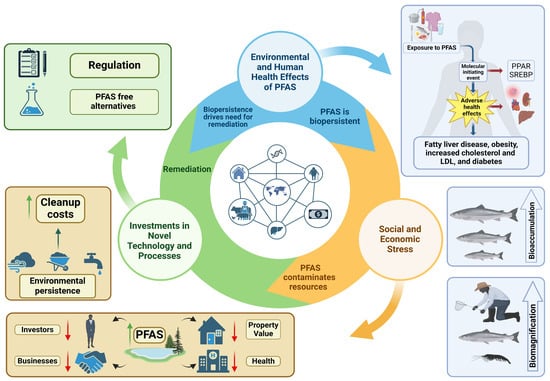
Figure 1.
PFAS exposure has negative consequences on the environment and human health, and in turn negative social and economic impacts related to it’s toxicity and persistence. As toxicologists, we often consider only the bioaccumulation or toxic responses; however, the novel properties of PFAS have led to reduced economic investment, repressed property values, expensive remediation and clean-up costs, and ultimately a search for alternatives. Adverse environmental and human health effects caused by PFAS are often the result of biomagnification and bioaccumulation (blue). PFAS’s persistence and toxic effects leads to the need for regulations and novel remediation strategies (green). In addition, there are social and economic stresses caused by PFAS bioaccumulation and toxicity such as increased clean up costs, reduced property value, reduced investment, and increased healthcare costs. This figure was created using Biorender.
Multiple PFAS, including PFOA, PFOS, and long-chain fluorotelomers, have been used in AFFF as firefighting foams since the 1970s. AFFF are typically used as class B firefighting foams to extinguish gas, oil, and jet fuel fires (flammable liquids, gases, or greases), and therefore are commonly available at airports and military bases [18,19]. The ensuing contamination threatens the health and well-being of the environment, firefighters, and local communities [19]. Therefore, synthetic fluorine-free foams, also known as “F3” foams, that are effective at putting out fires are being developed.
In February 2024, the U.S. FDA announced that PFAS-containing grease-proofing agents that come into contact with food, such as in cookware and food packaging products, are no longer being sold [20]. In April 2024, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) established enforceable drinking water limits for PFOS, PFOA, hexafluoropropylene oxide dimer acid [GenX (HFPO-DA)], perfluorononanoic acid (PFNA), and PFHxS, with limits ranging from 4 to 10 parts per trillion (pptr). Specifically, PFOA and PFOS were capped at 4 pptr; GenX, PFNA, and PFHxS were capped at 10 pptr as a Maximum Contaminant Level (MCL). This regulation also includes mixtures of two or more of PFHxS, PFNA, perfluorobutane sulfonic acid (PFBS), and HFPO-DA. Public water systems have until 2027 to complete initial monitoring and until 2029 to implement solutions to reduce these PFAS in accordance with the MCLs [21]. However, in May 2025, the USEPA announced its intent to rescind its drinking water standards for GenX, PFHxS, PFNA, and PFBS. The proposed rule redefining PFAS standards should come into effect in the spring of 2026 [22].
The following review examines PFAS persistence, toxicity, costs, and potential alternatives.
2. PFAS Exposure and Bioaccumulation
Decades of widespread use, along with mobility and persistence, have resulted in PFAS contamination worldwide. Recent studies revealed widespread contamination of U.S. municipal drinking water supplies with detectable levels of PFAS, with PFOA and PFOS being most consistently reported [23,24,25]. Importantly, these and other PFAS have been measured in the vast majority of biological samples, such as serum and urine collected from nationally representative studies of U.S. children and adults [26,27]. For example, 97% of human samples contained measurable PFAS in the NHANES study [27,28]; other studies found as many as 100% of samples contained PFAS [28]. Such findings present important public health concerns given bioaccumulation within humans, persistence in the environment, and their continued production and use in many areas [29,30,31]. To further complicate matters, recent studies reveal that exposures do not occur in isolation, but rather as combinations of substances, indicating that real-world exposures to PFAS occur as complex mixtures with unknown biological implications [28,32]. For example, some studies have found that mixtures of PFAS work in a predictable manner that leads to neurotoxicity and cytotoxicity and follow typical concentration-addition mixture type dose–response curves [32]. However, other studies found that specific combinations of chemicals (with both PFAS and other persistent organic pollutants or metals) were more likely to cause adverse outcomes in children [28]. In addition, other studies found that PFOA antagonized PFOS’s ability to form reactive oxygen species and cause acute toxicity [33].
In addition to human exposures, the presence of PFASs in tissues of aquatic and terrestrial species has been documented in studies conducted across every continent, including remote regions far from direct sources of emission, such as the high Arctic, Antarctica, and oceanic islands [34,35]. Further, some PFAS compounds (e.g., PFOS) have the potential to biomagnify with increasing trophic levels in a variety of both freshwater and marine ecosystems [6,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. The bioaccumulation of PFAS has been noted to be greater in marine environments compared to terrestrial systems [44]. Some of the greatest accumulations of PFAS have been shown in marine mammals, compared to aquatic animals with gills [45,46]. PFAS accumulation within an organism’s tissues may cause adverse health effects directly, through maternal transfer, and also cause indirect effects to higher-trophic-level predators, including human consumers of fish and shellfish.
Bioaccumulation potential generally increases with PFAS carbon chain length, and sulfonic acids are more bioaccumulative than carboxylic acids of the same carbon chain length [6]. Short-chain carboxylic acids (C < 7) were determined to have log bioconcentration (BCF) values < 1 in fish and thus would not be considered bioaccumulative [44]. Bioaccumulation of both linear and branched isomers of PFOS has been shown in Eastern oysters, but the branched isomers were more readily eliminated than the linear isomers [47]. Our understanding of bioconcentration and bioaccumulation is crucial as biological persistence is still considered the most prominent toxicology issue in marine and aquatic toxicology today, with PFOS and other, mostly legacy, PFAS of highest concern [48].
Typical bioaccumulation models based on chemical partitioning into lipids are not applicable to most PFAS, in part due to their lipophobic properties and in part due to their affinity for proteins that bind to lipids, making lipid partitioning models inaccurate [49,50]. Fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs), serum albumin, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), organic anion transporters (OATs), and organic anion transport proteins (OATPs) are some of the proteins that bind PFAS. Of these, FABPs, serum albumin, and OATs are involved in PFAS’s bioaccumulation [51]. FABPs bind PFAS with high affinity, and the greater the induction and binding to FABP and serum albumin, the greater the half-life [52,53,54,55,56,57]. PPARs are nuclear receptors that respond to fatty acids and modify lipid uptake, metabolism, and storage, and therefore regulate liver lipid accumulation [58,59,60,61,62].
Both albumin and FABPs bind numerous fatty acids in addition to PFASs. FABPs even change conformation upon binding [51]. The Posterior Inclusion Probabilities (PIPs) obtained from molecular descriptor analysis revealed that molecular flexibility, atomic polarizabilities, and the number of carbon atoms were the primary molecular characteristics that led to binding of PFASs to (liver) L-FABP [56]. Species differences in L-FABP binding were also noted, with human, rat, and rainbow trout having stronger binding affinities than Japanese medaka and fathead minnow [63]. The number of carbons may also have an effect, as eight-carbon compounds increased lipid synthesis more, while ten-carbon PFAS decreased lipid excretion [64]. Albumin binds PFAS at multiple positions, but does not change conformation as FABP does [51]. Serum albumin binds PFAS in the blood, inhibiting filtration and excretion by the kidneys [51]. In summary, L-FABP helps transport and keep PFASs in the liver where they preferentially bioaccumulate. The liver and serum are typically the tissues with the greatest bioaccumulation because of PFAS binding to FABP and albumin [6,51,56].
In addition to binding proteins, OATs and OATPs also enhance bioaccumulation. The four proteins most associated with bioaccumulation in the liver due to enterohepatic circulation are L-FABP, serum albumin, apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter (ASBT), and sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide (NTCP) [65,66] as NTCP transports PFAS to the bile but ASBT reabsorbs them from the intestines. Once PFAS are absorbed, most are excreted through the kidney. However, reabsorption is common through OATP1A1 as well as OATP1B3 and OATP2B1 [67]. Some species and sex differences [45,68] in bioaccumulation are likely caused by transporters. The half-life of PFOA is only hours in female rats, but several days in male rats [69], probably because of reduced expression of OATP1A1 in female rats [70]. The role of transporters in bioaccumulation is not fully understood. For example, L-FABP protein and fatp1 gene expression were associated with differences in liver PFOS retention between Cyp2b-null and hCYP2B6-Tg mice [53]; however, the role of fatp1 in PFOS liver absorption has not been studied to our knowledge.
Exposure to mixtures of PFAS will also influence uptake, binding, transformation, and toxicity. In fish, differential protein-binding interactions between PFOS and PFOA were observed, where PFOS did not upregulate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (pparα) but did significantly upregulate a downstream product, apolipoprotein A4 (apoa4) [33]. PFOA had the opposite binding pattern and resulted in decreased toxicity when mixed with PFOS [33].
Environmental exposure conditions such as salinity and temperature may also influence bioavailability and resulting toxicity of PFAS compounds. Chung et al. [71] reported that PFOS toxicity was greater at higher temperatures for C. variegatus, and greater at lower salinities for grass shrimp (Palaemon pugio) and eastern mud snail (T. obsoleta).
3. Bioanalytical Challenges for Identification and Quantitation of PFAS
Exposure studies, both in vivo and in vitro, require quantitation of dosed PFASs. Biomonitoring studies aim to confidently identify and quantify PFASs that are present in a biological matrix. However, PFAS identification and quantitation are not straightforward. Not only are PFAS ubiquitous, but the number of chemicals classified as PFAS is as high as 7 million [8]. Other factors such as the physiochemical properties of PFAS, the lack of standard methods, the need for low detection limits, the presence of analytical interferences, and the ability to biotransform can lower confidence in correct identification and accurate quantitation. Few standard methods are available for the detection and quantitation of PFAS, and several that are available are intended for aqueous matrices [72]. Quantitation can be difficult due to the lack of appropriate, PFAS-free control matrices, limited commercial availability of analytical standards and reference materials, and paucity of commercial isotope-labeled internal standards.
Quantities of biological samples are often small and prevent accurate quantitation of PFAS that are present at low concentrations. This is especially true for human biomonitoring, for which both sample volumes are minimal and PFAS concentrations are typically close to detection limits. PFAS exposure can occur through multiple pathways [73], which makes the selection of appropriate models for understanding potential health effects challenging, as does the variety of biological systems impacted by PFAS. Due to the ubiquitous nature of PFAS, care must be taken to minimize and avoid contaminated laboratory animal feed that could influence a toxic response as well as contribute to internal dose measurements for exposure studies [74,75].
Further complicating the accurate quantitation of PFAS in biological matrices is the ubiquitous nature of PFAS in common laboratory materials. Care must be taken to minimize and avoid contamination of samples from typical analytical chemistry laboratory sources such as solvents, water, plasticware including pipette tips and 96-well plates, glassware, filters, foil, vials, septa, manifold lids, nitrogen evaporation needles, and analytical instrumentation. PFAS adhere to both glass and plastics [76], which leads to often conflicting advice on the use of labware such as recommendations to avoid using glass [77,78], only use polypropylene (PP) [79], use polystyrene (PS) but not PP [80], use glass instead of PP, PS, and polycarbonate [76], and avoid use of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) [5]. Filters used during sample collection and preparation have been shown to contain PFAS that can contaminate samples or bind and remove PFAS from the sample [81,82]. Instrument manufacturers offer specialized kits and parts to reduce PFAS contamination that occurs during separation and/or mass spectrometry analysis due to PFAS-containing instrument components. Best practices for laboratories determining PFAS include testing all solvents and supplies for PFASs prior to use on samples, replacing solvent lines and seals on liquid chromatographs with PEEK tubing and other PFAS-free substitutes, use of an in-line delay column, use of blanks to monitor contaminants, and frequently cleaning mass spectrometer sources.
Some PFAS have properties including varied solubility and air sensitivity that may make them difficult to handle in the laboratory [83]. PFAS may sublime [8], leach into extracts during sample preparation [84], or decompose during storage or dosing [85]. Control matrices used for the preparation of calibration curves and quality control samples may also be a source of potential contamination. Fetal bovine calf serum is used by some researchers as a control matrix due to the assumption that it is PFAS-free [24,86]. In other instances, solvent-based standards may be used due to the lack of availability of an appropriate PFAS-free control matrix [87,88].
Detection of PFAS in biological matrices is hampered by the lack of published methods. Few standard methods are available for the detection of PFAS, and they are only applicable to a small number of semi-volatile compounds [72,75,89,90]. For example, most standard USEPA analytical methods for the detection of PFAS are validated for aqueous samples [72], target fewer than 25 common PFAS, and employ liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) performed on triple-quadrupole mass spectrometry systems. A few standard methods are available for use with biological matrices such as cells, cell media, biofluids, or tissues that are relevant to toxicity studies. The USEPA Method 1633 expands detection to 40 PFAS in fish tissue, along with environmental matrices [91]. A worldwide inter-laboratory assessment of targeted analyses of 22 PFAS in matrices including human milk and plasma demonstrated that PFAS measurements between laboratories are comparable [90]. The U.S. Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) uses an on-line solid-phase extraction (SPE) method for the analysis of 17 PFAS in human serum [92]. Researchers may be able to modify standard methods to fit with the matrices they are interested in, such as human plasma, rodent liver and other organs, milk, and zebrafish embryos. But in many instances, new analytical methods must be developed and validated.
A literature search using Abstract Sifter with terms including PFAS, rat liver, plasma, and mass spectrometry yields hundreds of articles, most related to the detection of PFAS in human matrices for biomonitoring [93]. An LC-MS/MS method with matrix-specific sample preparation procedures was used for the detection and quantitation of PFAS in milk from healthy human mothers, as well as liver samples collected postmortem from human donors [87]. A review of analytical methods for the detection and quantitation of PFAS in human matrices provides additional examples [94]. Other recent publications describe LC-MS/MS methods for the determination of PFAS in rat livers and plasma [95,96,97]. Huang et al. [98] included methods for the detection of PFAS in rat plasma, liver, kidney, and brain for a toxicokinetics study. The detection of PFAS and glucuronide metabolites was documented in a recent study [99]. Toxicokinetic studies have made use of both LC-MS/MS and gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for detection and quantitation of PFASs in plasma, serum albumin, and hepatocyte media [55,99,100].
Analytical interferences from endogenous chemicals in biomatrices can lead to false identifications or miscalculation of PFAS concentrations [101]. Steroid sulfates have common tandem mass spectrometry transitions with perfluorohexane sulfonic acid (PFHxS) that can lead to false identifications or overestimation of concentrations in human serum unless alternate transitions were selected, high-resolution mass spectrometry was employed, or the compounds were chromatographically separated [102]. Similarly, taurodeoxycholic acid and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) share a common transition that could confuse identification or quantitation in biomatrices [103]. An interference in a chemical standard of perfluoro-3,5,7,9,11-pentaoxadodecanoic acid (PFO5DoA), a novel PFAS observed in human blood, was identified by Kotlarz after it had contributed to an overestimation of concentrations in human serum [24].
PFAS are commonly known as “forever chemicals”, but some including perfluorosulfonamides and fluorotelomers are able to biotransform to generate metabolites [104]. For example, PFAS-based fluorotelomer alcohols (FTOH) biotransform to perfluorocarboxylic acids such as PFOA and perfluorohexanoic acid (PFHxA). The Total Oxidizable Precursors (TOP) assay can be used to detect FTOH as it oxidizes the unknown precursors and intermediates into stable PFAS [105]. Because of concerns surrounding precursor chemicals, Europe is considering adding FTOH 6:2 and FTOH 8:2 to the regulatory sum of PFAS of primary concern in drinking water [106].
Other examples of dosing studies with precursor compounds that yield metabolites that may be toxic include perfluorohexanesulfonamide (PFHxSA), which is known to metabolize to PFHxS [104]. PFHxS is highly toxic and included in a USEPA national drinking water standard [107]. Exposure studies evaluating the toxicity of PFHxSA may assume toxic effects are related to PFHxSA, while being unaware of the presence of PFHxS. Other recent studies have observed biotransformation of dosed PFAS compounds [99,100,108]. Biomonitoring studies may detect metabolites at higher concentrations than chemical precursors [109] or may use targeted methods that do not include precursors. Incorporation of nontarget analysis (NTA) using high-resolution/accurate mass LC-MS/MS into study designs may provide insights into the full distribution of PFAS present in biomatrices [110,111]. Another NTA method that may prove useful is Combustion Ion Chromatography (CIC), which quantifies total organofluorine content after high-temperature combustion [112]. It is complementary to LC-MS/MS; however, it does not identify individual PFAS.
4. PFAS and the One Health Concept
The One Health concept aims to balance and optimize the health of humans, animals, and ecosystems [113]. In the field of toxicology, One Health recognizes that shared environments allow potential exposure to the same toxic agents and chemical-associated health risks. This approach is particularly relevant for studies of PFAS exposure and toxicity [48,114,115,116,117,118,119]. In the context of One Health, biomonitoring studies have demonstrated that shared environments, food, and water sources can contribute to similarities in human and animal PFAS exposure profiles. Recent results demonstrate similar adverse system toxicology effects across taxa and even common toxicity themes across PFAS classes [120,121]. Key findings from these studies include differences in spatial and temporal trends in PFAS contamination and exposure, the prevalence of PFAS within food webs, including livestock and crops for human consumption, and overlap in adverse health effects between humans and animals, including three primary targets of PFAS toxicity: the immune system, kidneys, and liver [73,119,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129].
5. Human Health Effects and Systemic Toxicity of PFASs
Improved understanding of the health effects of PFAS is a current research priority for epidemiologists in the environmental health research community. Epidemiological studies have shown that exposures to some PFAS have been associated with a wide variety of health effects, including immune suppression, high cholesterol, liver toxicity, fetal growth restriction, and certain types of cancer [6,73,130,131]. Results from observational/epidemiological studies in human populations are mixed; however, continued research is yielding greater health concerns [132,133]. PFAS cross the placental barrier, resulting in fetal exposure [134], with potential developmental sequelae. Recent meta-analyses of studies in human populations have reported lower birth weight and birth length associated with greater PFAS exposure, as well as greater risks of preterm birth and small-for-gestational-age infants [135,136]. A greater risk of thyroid disease and altered thyroid hormone levels has also been reported in human studies of PFAS exposure in adults and children [137,138], which could have a myriad of downstream adverse health impacts. However, contradictory study results and some methodological concerns also preclude a causal connection at present [139,140]. Other evidence from human studies suggests adverse effects on metabolism, including diabetes, lipid homeostasis, body composition/obesity, and vascular health, in association with greater gestational and postnatal PFAS exposure, but again with mixed results [141,142,143]. Less common PFAS [144], replacement PFAS [145] and PFAS mixtures [146] are also areas of concern, but less research has been performed compared to legacy PFAS.
Toxicological evidence is growing as results from a number of experimental studies, both in vitro and in vivo, indicate adverse human health effects from PFASs [147,148]. Several PFASs and their replacements have been identified as endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in experimental studies, altering the function of sex steroid and thyroid hormones [97,137,149,150]. Other studies show binding to PPARs, with potential developmental and metabolic effects [151,152,153]. Furthermore, a U.S. National Toxicology Program literature review identified PFOA and PFOS as human immune hazards [154], and a collaboration of industry and academic experts called for further investigation [155].
PFAS cause a large number of negative effects on multiple organ systems. Toxicology studies in animal models, cell models, and key molecular initiating events such as PPARα and sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP/SREBF) activation provide mechanisms for PFAS-mediated metabolic diseases such as fatty liver disease, obesity, increased cholesterol and LDL, and diabetes [6,52,60,68,145,156,157].
Both legacy and alternative PFAS appear to activate similar pathways [60,145]. For example, a recent toxicogenomics study indicates that most legacy and alternative PFAS activate PPARα; many also activate SREBP, constitutive androstane receptor (CAR), and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2), and some inhibit signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b (STAT5b) [60]. These key molecular initiating events with PPARα activation are central to the disruption of most pathways associated with obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, and other metabolic-dysfunction-associated fatty liver diseases (MAFLDs). The large overlap between legacy and alternative PFAS is interesting. Evidence from epidemiology studies confirms most if not all of the disease results (see below), including studies that demonstrate an association between concentrations of PFAS or PFAS-containing mixtures in mothers and childhood obesity [28,142,158,159]. Overall, it is not surprising that PFAS bind albumin, fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs), and PPARs, and disrupt energy signaling given their similar structure to short- and mid-chain fatty acids (Figure 2) depending on the length of the PFAS [56,160].
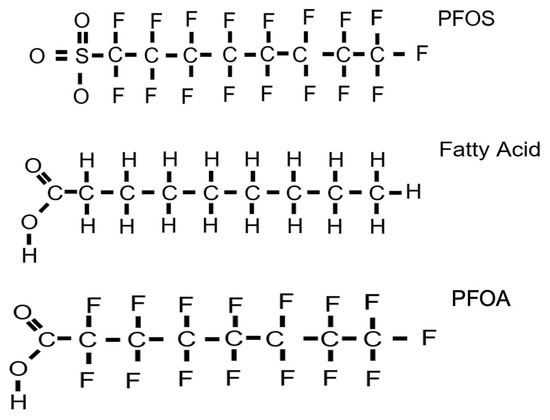
Figure 2.
The structure of many PFAS shows high similarity to fatty acids, with the replacement of hydrogens with fluorines. An eight-carbon mid-chain fatty acid is compared to PFOS and PFOA.
New shorter-living, typically short-chain PFAS and PFAS-forming formulations have been tested recently. There is still much to be learned about the bioaccumulation profiles of these PFAS-containing compounds, including PFAS-containing AFFF. In addition, they are not as strictly regulated as legacy PFAS, as total PFAS in drinking water can legally reach 0.5 μg/L [161,162]. A recent study comparing legacy, short-chain, and precursor PFAS [i.e., substances that can transform into perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs)] that form PFOS in primary human hepatocytes found that the replacement short-chain PFAS and precursor PFOS were more potent at inducing steatosis and lipogenic gene expression than legacy PFAS [145]. PFAS precursors are also likely to add to the total PFAS accumulation in human tissues; however, their role in bioaccumulation is not known.
Other adverse health effects include endocrine disruption, some of it mediated through nuclear receptors, increased oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, reproductive and developmental toxicity, pulmonary toxicity, and cancer, of which some of these effects may be elicited through reduced immune surveillance [6]. For example, PFAS levels have been associated with cancer in humans, and PFAS have been shown to increase cancer incidence in laboratory animals [131,163,164,165]. In the Danish population, the greater the level of PFAS, especially PFOA and PFOS, the greater the risk of cancer [166]. Concentrations of PFOS, PFOA, PFNA, and PFHxS are inversely associated with income [167]. In addition, non-Hispanic Black populations may be exposed to more PFAS and have higher serum levels of some PFAS than other racial and ethnic groups, and this may manifest itself in increased cancer risk and other diseases such as hypertension [164,168,169,170,171].
The long half-lives of many PFAS allow for bioaccumulation and the time necessary for transgenerational effects to occur. PFAS have been associated with reproductive problems and developmental delays [96,134,172] that in part may be due to the disruption of PPARγ signaling [173]. Other toxicity and health issues include cardiovascular disease, hypothyroidism, neurotoxicity, and many other adverse effects associated with human PFAS exposure in agreement with PFAS toxicity assessments performed in laboratories [154,174,175,176,177,178,179]. Immunotoxicity [154,180] and reduced responses to vaccines have also been measured [181]. In summary, there are a multitude of potential adverse health effects that might be caused by PFAS exposure based on laboratory evidence and epidemiological studies.
Figure 3 is a summary figure presenting some possible molecular initiating mechanisms of PFASs and their ultimate systemic effects. Many of PFASs’ negative effects are linked to their environmental persistence and bioaccumulation, which is also stressed in Figure 3. OATs and OATPs increase the retention of PFAS in the kidney due to tubular reabsorption [53,67,69,182]. This can also lead to kidney toxicity and cancer [54,70,183,184,185,186]. Proteins such as serum albumin and FABP bind PFOA, PFOS, and other PFASs and increase their half-lives [56,160,187]. L-FABP also helps transport PFASs to the PPARs, where they may activate PPARs such as PPARα or potentially inhibit PPARγ [56,188]. Disruption of PPAR activity is associated with metabolic disease following PFAS exposure, including altered mitochondrial function, changes in lipid metabolism, and fatty liver disease. These effects may lead to obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease [6,52,60,159,189,190,191,192,193].
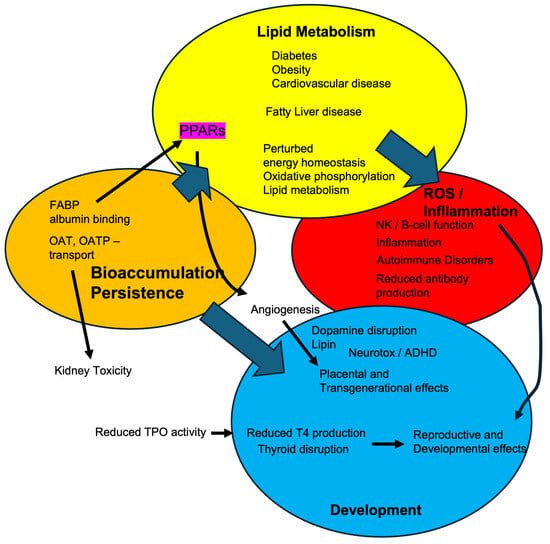
Figure 3.
PFOS, PFOA, and other PFAS have multiple effects on several different organ systems. Most of these adverse effects are complicated or worsened by the bioaccumulation of some PFAS. This allows for disruption of lipid metabolism and other metabolic pathways, subsequent perturbations in reactive oxygen species and inflammation, and development, including neurodevelopment, and immune surveillance.
In addition to metabolic changes, PPARγ disruption by PFASs alters angiogenesis and placental function [173,193,194]. In turn, PFAS exposure can lead to developmental effects in children from exposed mothers, including neurotoxicity, immune surveillance issues, and childhood obesity [96,172,195]. Immune suppression may occur through multiple pathways. PFAS can disrupt PPARs and NF-kB, perturb fatty acid metabolism, or induce oxidative stress (reactive oxygen species/ROS) [53,196,197,198]. These molecular events can cause changes in cytokine release, B-cell, T-cell, and natural killer cell functions [196,199,200] that lead to repression of antibody production, increased asthma, autoimmune disease, and a reduced response to vaccines [196,199,201,202,203]. The nervous system and thyroid are also targets. Enzymes such as thyroid peroxidase (TPO) or tyrosine hydroxylase are inhibited or down-regulated, leading to reduced thyroid hormone or dopamine release and signaling [137,204], which can lead to alterations in neurodevelopment, neurotoxicity [205], and recently reported increases in Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and potentially autism [206,207].
6. Regulation of PFAS
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has the authority to regulate PFAS at the national level through the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA), and the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) [208]. Owing to concerns regarding the persistence and toxicity of long-chain PFASs, the EPA began regulating these chemicals in 2002 with Significant New Use Rules (SNURs) requiring manufacturers to provide advanced notification about the production or import of perfluorooctane sulfonyl fluoride (POSF) and some of its salts and homologs [208,209,210,211]. Shortly thereafter, in January 2006, the EPA implemented the 2010/2015 PFOA Stewardship Program [212]. This program invited eight major companies in the PFAS industry to commit to reducing PFOA in factory emissions and products by 95% by 2010 and to work toward eliminating PFOA from emissions and products by 2015. All eight companies, which operate globally, committed to this stewardship program and to working towards a global phase-out of PFOA and related chemicals. In conjunction with these phase-outs, the fluorochemical industry has introduced replacement chemistries, prioritizing shorter-chain PFAS and perfluoroalkyl ether moieties, claiming they are less bioaccumulative and toxic [209,213]. Through the SDWA, the EPA continues to monitor concentrations of PFAS in drinking water supplies and has made modifications to lifetime drinking water health advisories in response to accumulating evidence of toxicity [213]. These modifications include reducing the health advisory levels for PFOS and PFOA, from 70 parts per trillion (pptr) established in 2016 to 0.02 pptr PFOS and 0.004 pptr PFOA in 2022, and establishing health advisory levels for some of the replacement chemistries, including HFPO-DA (also known as GenX) and PFBS. Health advisory levels are not enforceable standards; however, the EPA finalized a National Primary Drinking Water Regulation (NPDWR) to establish legally enforceable concentrations, known as MCLs, for six PFAS in drinking water in 2024 [162]. Note however that in 2025, the EPA proposed that it will keep the MCLs only for PFOA and PFOS and rescind or reconsider the limits for PFHxS, HFPO-DA, PFNA, and mixtures of these with PFBS (https://www.epa.gov/newsreleases/epa-announces-it-will-keep-maximum-contaminant-levels-pfoa-pfos, accessed on 18 June, 2025) [214]. With the vast structural diversity of PFAS, consisting of many thousands to millions of different compounds, regulations could benefit from a change in strategy from the current approach of regulating a single compound and related substances to regulating large groups of PFAS based on chemical class (i.e., physiochemical, environmental, and toxicological properties) [209,215]. This is especially true of PFAS because while six PFAS are tightly regulated in drinking water, total PFAS concentrations of non-legacy compounds can reach up to 0.5 μg/L in drinking water, probably due to uncertainty in their bioaccumulation and human toxicity.
7. Impacts of PFAS on Economic Development, Business, and Property Value
PFAS are also of concern due to their potential economic impacts. Companies involved in the manufacturing or use of PFAS-containing products may encounter legal responsibilities and lawsuits initiated by affected individuals, communities, and government entities seeking compensation for health issues and property harm resulting from PFAS contamination. Notably, compensation in some states in the U.S., such as Minnesota (USD 850 million), Alabama (USD 39 million), and Michigan (USD 168 million), highlights the substantial legal costs associated with defending against or resolving such litigations, presenting a considerable financial burden to state or federal agencies in addition to the companies involved [15]. Conversely, state and local governments may also face lawsuits from manufacturers due to PFAS reduction policies and health regulations related to drinking water. In addition to direct liability and legal costs, companies associated with PFAS contamination may face reputational damage, leading to reduced sales and market share.
Growing concerns about PFAS may result in restrictions or bans on international trade in products containing PFAS. For instance, a report released by the US Chamber of Commerce in September 2023 revealed that the economic and fiscal impacts of PFAS-containing goods exported from the United States to the European Union amounted to USD 314 billion in value and over 500,000 jobs [216]. These could be jeopardized if the European Union enforces its proposed PFAS ban from February 2023. Consequently, these regulations can impact industries reliant on the global supply chain for PFAS-containing materials and products.
Moreover, PFAS contamination can dissuade potential investors, businesses, and residents from considering locations affected by contamination, potentially negatively affecting the economic growth and overall economic well-being of a region [16]. Properties located in proximity to PFAS-contaminated sites may witness a decline in their worth (Figure 4). Research from Australia demonstrated that property values in Williamtown, New South Wales, an area contaminated with PFAS, fell by 15% compared to the current market value had contamination not existed [17,217]. This can result in financial losses for property owners and local governments, along with potential reductions in property tax revenues. This may be even more so in some minority communities where PFAS contamination is greater due to local factories and municipal pollution sources [12,218,219].
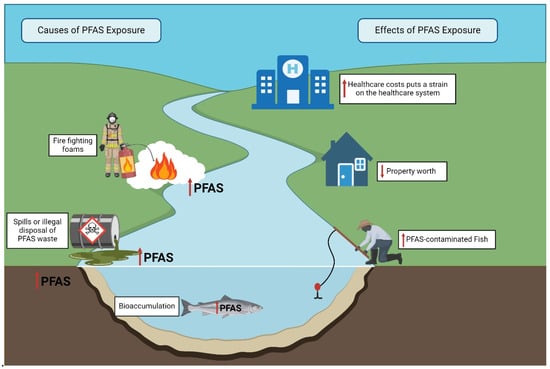
Figure 4.
PFAS contamination has negative consequences on property values and healthcare costs. These problems are especially acute in poor or minoritized areas where factories, landfills, testing grounds, and waste facilities are more likely to be found. This figure was created with Biorender.
8. PFAS and Healthcare Costs
The health repercussions of PFAS exposure can lead to escalated healthcare costs, as individuals affected may require medical treatment and monitoring. As an illustration, a study assessed healthcare expenses in Nordic countries for populations impacted by PFAS exposure through occupation, drinking water, or background exposure. According to this study, communities exposed to PFAS in their drinking water due to proximity to chemical plants or other industries incurred estimated annual healthcare costs ranging from EUR 2.1 to 2.4 million [16]. These expenses can place a strain on healthcare systems and insurance providers.
Finally, the insurance sector may face increased costs and losses due to PFAS-related claims, as indicated in a report from the Hinshaw Law Firm [220]. These can subsequently translate into higher insurance premiums for businesses and individuals.
To tackle these economic challenges, governmental bodies, corporations, and local communities are collaborating to institute regulations, execute clean-up initiatives, and innovate new technologies to reduce the adverse effects of PFAS contamination and the costs linked to it. Nonetheless, the economic consequences of PFAS contamination are intricate and enduring, demanding continued dedication and resources to effectively address the issue.
9. Clean-Up and Compliance Costs Due to PFAS
Of course, clean-up costs are also expensive. One of the major economic challenges associated with PFAS concerns the costs incurred in the remediation of contaminated sites, encompassing both surface and groundwater. PFAS have prolonged environmental persistence, resulting in costly and time-consuming efforts to cleanse polluted soil, water, and air. For instance, the endeavor to bring drinking water in Orange County, California, to the state’s recommended PFAS levels is projected to amount to at least USD 1 billion [15]. In March 2023, the USEPA introduced new regulations under the SDWA for PFAS, entailing total annualized expenses ranging from USD 772 million to USD 1.2 billion [221]. These fiscal responsibilities can be borne by state and federal agencies, as well as the public through utility costs. Additionally, these requirements can impose compliance costs on local and smaller businesses, resulting in investments in novel technologies and processes to minimize PFAS emissions and contamination. This has been an impetus for the development of alternatives to PFAS.
10. Economic Impacts Lead to PFAS-Free Alternatives—AFFF as an Example
As mentioned previously, the untimely death of 134 sailors and more injured in July 1967 on the USS Forrestal led to the development and use of PFAS-containing AFFF. These highly effective foams would be used for years and lead to environmental and clean-up issues costing billions. The US Department of Defense (DOD) has been funding the development of fluorine-free foams (F3) since 2017. The DOD released specifications for F3 in January 2023, and was required to stop buying PFAS-containing foam by October 2023 and replace all AFFFs by October 2024 [222]. The U.S. military is currently transitioning to F3 products.
However, F3 and other green chemistry firefighting foams are not a direct replacement for PFAS-containing AFFF because they vary in performance for class B fire suppression across different fuel types [223]. Whatever the military decides and what alternatives the military deems best, based on its criteria of efficacy, safety, cost, and environmental health concerns, will affect local municipal and airport fire stations, forest services, chemical plants, oil refineries, oil tankers, and offshore platforms because these military-preferred foams will most likely become the new standard.
Switching from PFAS is not an easy task. There are several types of new synthetic firefighting foams to work with and learn, and each type may work differently from traditional AFFF or other modern non-PFAS synthetic foams. For example, the specific type of fire or size of the fire may impact the foam’s performance or preferred use. Some firefighting equipment may need to be modified or completely replaced to handle the new foams because of different application densities, proportioning rates, viscosities, and flows. How long the new synthetic foams last under variable storage conditions also needs to be considered. Lastly, firefighters will need training to learn how to properly use the new foams [222].
As PFAS-containing AFFF compounds are being phased out due to their toxicity and bioaccumulative potential, there is an urgent need to assess the bioaccumulation potential and toxicity of the PFAS-free AFFF replacement products. The Strategic Environmental Research and Development Program (SERDP) run by the DoD has been studying potential PFAS-free AFFF. Early data suggest that the PFAS-free AFFF products are predicted to have a much lower likelihood of environmental persistence and bioaccumulation [224,225]. For example, the toxicity of six replacement products was assessed: BIOEX ECOPOL A 3%, Fomtec Enviro USP, National Foam 20-391, National Foam AvioF3 Green KHC 3%, National Research Lab (NRL)-502W, and Solberg Re-Healing Foam RF3 3%. These PFAS-free alternatives were compared to Buckeye Platinum 3% PFAS-containing AFFFs and showed greater biodegradability. ToxPi 2.3, a free downloadable software package for prioritizing and visualizing data, was used to rank toxicity [226]. ToxPi indicates that BIOEX ECPOL was the least hazardous to human and animal health based on the hazard assessment criteria, and Solberg Re-Healing Foam RF3 3% was the most hazardous replacement product. Comparatively, the short-chain PFAS Buckeye Platinum 3% was the second-least hazardous [224].
A recent investigation of the biodegradability of those same six alternative PFAS-free AFFF formulations (BIOEX ECOPOL A 3%, Fomtec Enviro USP, National Foam 20-391, National Foam AvioF3 Green KHC 3%, National Research Lab (NRL)-502W, and Solberg Re-Healing Foam RF3 3%) revealed that most formulations had similar metabolite formation and were readily degraded within the 28-day trial [227]. Ecotoxicity studies indicate that F3 may exhibit similar or even greater toxicity to aquatic biota than AFFFs [223]. The acute toxicity of these six PFAS-free compounds and one PFAS-containing reference compound was evaluated with 14 freshwater, marine, and terrestrial species. These studies determined that exposure to some PFAS-free AFFF formulations can result in equal or greater acute toxicity in aquatic species compared to PFAS-containing AFFF [228]. Species-specific differences were noted, such as lower toxicity thresholds for estuarine invertebrates such as the mud snail (Tritia obsoleta) and the sheepshead minnow (Cyprinodon variegatus) than corresponding freshwater species [228].
Standard chronic toxicity tests with a suite of freshwater and marine species and the same set of alternative AFFF formulations revealed significant effects on growth (Daphinia magna, Chironomus dilutus, Pimephales promelas, and Americamysis bahia) and reproduction (D. magna, Ceriodaphnia dubia, C. dilutus) [229]. While in many cases the PFAS-free AFFF products exhibited greater toxicity than the reference legacy AFFF, it should be noted that observed effect thresholds were generally >1 ppm [229]. More comprehensive toxicological profiles of F3 formulations are needed to determine mechanisms of action and degradation pathways under variable exposure conditions and to further characterize chronic toxicity, reproductive toxicity, and endocrine disruption [50,223]. The good news is that while these compounds exert greater acute toxicity in some cases, they have much lower bioaccumulation potential and therefore are less likely to cause persistent effects.
The primary purpose for switching to alternatives is the environmental health issues and subsequent clean-up costs. There are 714 military installations that are being assessed for PFAS contamination. As of 30 June 2023, 466 installations have been assessed, of which 359 of these installations are proceeding with further testing and risk assessments per CERCLA processes. Sites identified as imminent risks to human health after the Relative Risk Site Evaluations (RRSEs) will be prioritized. The Department of Defense (DoD) will take immediate action (provide bottled water, water filters, municipal filtration systems, etc.) at any site with PFOA or PFOS at drinking water concentrations above the EPA’s former 70 pptr threshold set in 2016 [230]. The immediate costs of the PFAS clean-up obligations are estimated at USD 2.02 billion; however, this estimate is expected to increase as the DoD completes its initial assessments and determines what actions are required [231]. In 2021, it was estimated that the total costs of PFAS remediation at 50 contaminated military sites would be USD 3.7 billion; however, just 2 years later, and those estimates had ballooned to USD 31 billion. These are just the costs associated with military installations [232]. Therefore, it is unaffordable for most municipalities or states to clean up PFAS from wastewater. For example, Minnesota estimates its PFAS clean-up costs to approach USD 28 billion over the next 20 years [233]. Sadly, the new short-chain PFAS are more water-soluble and difficult to destroy, and therefore, it could be 70% more expensive to mitigate their contamination in water through conventional means such as activated carbon [233]. Thus, new and potentially more expensive methods may need to be developed. However, expectations are that some or all of them will have shorter half-lives, and this could reduce that concern.
Another way to reduce the use of PFAS-based AFFFis to reduce the potential for fires or limit the number of alcohol- and fuel-based fires. The move to electric vehicles (EVs) should continue to reduce fires despite the problems associated with certain EV models. Fires occur most often in hybrids with a frequency of 3475/100,000 vehicles. Fires occur in gas-powered vehicles at a frequency of 1530/100,000 vehicles, whereas fires occur in EVs at a frequency of 25/100,000 vehicles. This is an incredible 61X decrease from gas-powered vehicles [234]. It should be noted that EV fires can burn longer because of the Li-ion batteries and bring a new set of firefighting challenges. Included in these challenges is lithium bis ((trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl)imide (HQ-115), a more water-soluble PFAS that is considered safer than the lithium hexafluorophosphate that it replaced [235]. The USEPA has made a call for further research on the economic, environmental, and human health impacts of HQ-115 [236]. Current research data indicates that HQ-115 has hazardous effects on the kidney, testes, and liver; however, it is not as toxic as PFOA or PFOS [237,238,239]. Overall, the move to EVs and electric sources of power instead of liquid-ignition fuels could reduce the reliance on AFFF and alternative foams, providing a different means of reducing AFFF’ environmental contamination and adverse human health effects.
11. Conclusions
Significant knowledge gaps remain about the fate, exposure, and effects of PFAS, particularly on human and ecosystem health. There are even more gaps in the knowledge of the bioaccumulation and toxicity of PFAS-free formulations such as F3. Additional testing of PFAS alternative products (F3) will be beneficial for ensuring the human and environmental safety of replacement compounds. Very little research has addressed the chronic toxicity of the new AFFF on the market, also an area of research needed for legacy and emerging PFAS [50,223]. In addition, much PFAS research has evaluated exposure scenarios involving food or water resources; however, consumer products have been understudied and are an area that some states in the USA require further information [240,241]. In the USA, there are several state-specific guidelines that affect policies and provide policy challenges for drinking water, remediation, AFFF, consumer products, and food packaging [241,242,243].
Drawing from historical examples in the One Health literature, it will be crucial to move past conventional interdisciplinary barriers that separate human health, veterinary, ecological, environmental, and computational sciences to develop novel PFAS control and remediation strategies and reduce the risks that PFAS pose to human, animal, and ecosystem health [244]. To address these needs, future studies should prioritize the collection of physiochemical property data, determine effect-based toxicity values in a variety of matrices, and establish methods to effectively measure the bioaccumulation and biomagnification potential of PFAS-containing and PFAS-free AFFF formulations for the development of predictive models [57,245]. In addition, prospective and longitudinal human studies are indispensable, with a focus on the complex PFAS mixtures that reflect real-life exposure scenarios, to more definitively assess the health risks of legacy, emerging, and PFAS alternatives, which can help to prioritize investment in mitigation strategies and ecological health, sensitive populations, public health, and clinical interventions. These studies may help enable better regulation of specific classes of PFASbased on their properties, toxicity, and bioaccumulation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.S.B.; investigation, W.S.B., M.S.B., K.W.C., S.D., M.E.D., K.J.H., P.B.K., J.L.P., K.D.R., P.T., M.A.J., M.M.G. and L.J.B.; writing—original draft preparation, W.S.B., M.S.B., K.W.C., S.D., M.E.D., K.J.H., P.B.K., J.L.P., K.D.R., P.T. and L.J.B.; writing—review and editing, W.S.B., M.S.B., K.W.C., S.D., M.E.D., K.J.H., P.B.K., J.L.P., K.D.R. and L.J.B.; visualization, W.S.B., M.A.J. and M.M.G.; project administration, W.S.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Support for this research has been provided by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA), the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and the Save our Seas Foundation. The views expressed are the authors’ and do not necessarily represent the views of NIH, USEPA, NOAA, or Save our Seas. The research herein has not been formally reviewed by the funding providers nor are there any endorsements of any products or commercial services in the publication. Specific funding sources include: NIH grants UG3OD035543 (K.J.H.; M.S.B), R03ES036327 (S.D.), R03ES035536 (M.S.B.), R15ES017321 (W.S.B.) USEPA Assistance Agreement no84046001 (K.J.H.; J.L.P.; W.S.B.; L.J.B.) and Save our Seas Foundation grant number 669 (K.D.R.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Denise MacMillan for her thoughtful, helpful comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. All opinions expressed in this paper are the authors’ and do not necessarily reflect the policies and views of the Department of Commerce (DOC) or National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Any use of trade, firm, or product names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Government.
References
- Naval History and Heritage Command. This Day in Naval History, 29 July 1967. 2025. Available online: https://www.history.navy.mil/today-in-history/july-29.html (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Cox, S.J. H-008-6: Uss Forrestal Disaster, 29 July 1967; Naval History and Heritage Command: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- GZA GeoEnvironmental, Inc. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances–Part i–A Focus on the History of Aqueous Film-Forming Foams. Available online: https://www.gza.com/insights/per-and-polyfluoroalkyl-substances-part-i-focus-history-aqueous-film-forming-foams#:~:text=The%20Forrestal%20disaster%20drove%20the,vessels%20by%20the%20late%201960s (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Buck, R.C.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; de Voogt, P.; Jensen, A.A.; Kannan, K.; Mabury, S.A.; van Leeuwen, S.P.J. Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the Environment: Terminology, Classification, and Origins. Integr. Env. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevedouros, K.; Cousins, I.T.; Buck, R.C.; Korzeniowski, S.H. Sources, Fate and Transport of Perfluorocarboxylates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, W.S.; Davis, T.T.; Eccles, J.A. Per- and Polyfluoroalkylsubstances (PFAS) and Their Toxicology as Evidenced Through Disease and Biomarkers. In Biomarkers in Toxicology. Biomarkers in Disease: Methods, Discoveries and Applications; Patel, V.B., Preedy, V.R., Rajendram, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 989–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Burkhard, L.P. Evaluation of published bioconcentration factor (BCF) and bioaccumulation factor (BAF) data for per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances across aquatic species. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 1530–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Zhang, J.; Thiessen, P.A.; Chirsir, P.; Kondic, T.; Bolton, E.E. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in PubChem: 7 Million and Growing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 16918–16928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartell, S.M.; Calafat, A.M.; Lyu, C.; Kato, K.; Ryan, P.B.; Steenland, K. Rate of Decline in Serum PFOA Concentrations after Granular Activated Carbon Filtration at Two Public Water Systems in Ohio and West Virginia. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, G.W.; Burris, J.M.; Ehresman, D.J.; Froelich, J.W.; Seacat, A.M.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Zobel, L.R. Half-Life of Serum Elimination of Perfluorooctanesulfonate, Perfluorohexanesulfonate, and Perfluorooctanoate in Retired Fluorochemical Production Workers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United National Environmental Programme (UNEP). Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs); UNEP/POPS/COP.10/33. United National Environmental Programme (UNEP): Chatelaine, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, R.; Villanueva, C.M.; Beene, D.; Cradock, A.L.; Donat-Vargas, C.; Lewis, J.; Martinez-Morata, I.; Minovi, D.; Nigra, A.E.; Olson, E.D.; et al. US drinking water quality: Exposure risk profiles for seven legacy and emerging contaminants. J. Exp. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2024, 34, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, A.L.B.; Geiger, T.C.; Pansari, G.O.; Justen, P.T.; Richardson, S.D. Identifying PFAS hotspots in surface waters of South Carolina using a new optimized total organic fluorine method and target LC-MS/MS. Water Res. 2024, 256, 121570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evich, M.G.; Davis, M.J.B.; McCord, J.P.; Acrey, B.; Awkerman, J.A.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Speth, T.F.; Tebes-Stevens, C.; Strynar, M.J.; et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment. Science 2022, 375, eabg9065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordner, A.; Goldenman, G.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Brown, P.; Miller, M.F.; Mueller, R.; Patton, S.; Salvatore, D.H.; Trasande, L. The true cost of PFAS and the benefits of acting now. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 9630–9633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldenman, G.; Fernandes, M.; Holland, M.; Tugran, T.; Nordin, A.; Schoumacher, C.; McNeill, A. The Cost of Inaction: A Socioeconomic Analysis of Environmental and Health Impacts Linked to Exposure to PFAS; Nordic Council of Ministers: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, R.; Tachovsky, M. Real estate damage economics: The impact of PFAS “Forever chemicals” on real estate valuation. Environ. Claims J. 2022, 34, 136–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellows, N.; Wetzstein, D.; Lee, S.; Stockinger, J. PFCS and Class B Firefighting Foam; Minnesota Pollution Control Agency: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Conder, J.; Zodrow, J.; Arblaster, J.; Kelly, B.; Gobas, F.; Suski, J.; Osborn, E.; Frenchmeyer, M.; Divine, C.; Lesson, A. Strategic resources for assessing PFAS ecological risks at AFFF sites. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2021, 17, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinges, E.; Jones, J. FDA, Industry Actions End Sales of PFAS Used in Us Food Packaging. 2024. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-industry-actions-end-sales-pfas-used-us-food-packaging (accessed on 6 September 2024).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. PFAS National Primary Drinking Water Regulation; Volume EPA-HQ-OW-2022-0114, FRL 8543-02-OW; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2024; pp. 32532–32757. [Google Scholar]
- Zarghamee, R.; Halter, A.G.; Marullo, J. EPA to Reconsider Drinking Water Standards for Several PFAS. 2025. Available online: https://pfas.pillsburylaw.com/epa-reconsider-drinking-water-standards-pfas/ (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Hu, X.C.; Andrews, D.Q.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Bruton, T.A.; Schaider, L.A.; Grandjean, P.; Lohmann, R.; Carignan, C.C.; Blum, A.; Balan, S.A.; et al. Detection of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in U.S. Drinking Water Linked to Industrial Sites, Military Fire Training Areas, and Wastewater Treatment Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlarz, N.; McCord, J.; Collier, D.; Lea, C.S.; Strynar, M.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Wilkie, A.A.; Islam, J.Y.; Matney, K.; Tarte, P.; et al. Measurement of Novel, Drinking Water-Associated PFAS in Blood from Adults and Children in Wilmington, North Carolina. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 77005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalling, K.L.; Romanok, K.M.; Bradley, P.M.; Morriss, M.C.; Gray, J.L.; Kanagy, L.K.; Gordon, S.E.; Williams, B.M.; Breitmeyer, S.E.; Jones, D.K.; et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in United States tapwater: Comparison of underserved private-well and public-supply exposures and associated health implications. Environ. Int. 2023, 178, 108033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Disease Control. CDC National Report on Human Exposure to Environmental Chemicals—Biomonitoring Data Tables for Environmental Chemicals. 2024. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/exposurereport/index.html (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Botelho, J.C.; Kayoko, K.; Lee-Yang, W.; Calafat, A.M. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Exposure in the U.S. Population: NHANES 1999–March 2020. Environ. Res. 2025, 270, 120916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, J.L.; Neelon, B.; Bloom, M.S.; Buckley, J.P.; Ananth, C.V.; Perera, F.; Vena, J.; Hunt, K. Exploring associations between prenatal exposure to multiple endocrine disruptors and birth weight with exposure continuum mapping. Environ. Res. 2021, 200, 111386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheringer, M.; Trier, X.; Cousins, I.T.; de Voogt, P.; Fletcher, T.; Wang, Z.; Webster, T.F. Helsingor Statement on Poly- and Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances (PFASs). Chemosphere 2014, 114, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Cousins, I.T.; Scheringer, M.; Buck, R.C.; Hungerbuhler, K. Global Emission Inventories for C-4-C-14 Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylic Acid (PFCA) Homologues from 1951 to 2030, Part I: Production and Emissions from Quantifiable Sources. Environ. Int. 2014, 70, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, K.; Wong, L.-Y.; Jia, L.T.; Kuklenyik, Z.; Calafat, A.M. Trends in Exposure to Polyfluoroalkyl Chemicals in the U.S. Population: 1999−2008. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8037–8045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Bonilla, K.M.; Aga, D.S.; Lee, J.; Konig, M.; Qin, W.; Cristobal, J.R.; Atilla-Gokcumen, G.E.; Escher, B.I. Neurotoxic Effects of Mixtures of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) at Environmental and Human Blood Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 16774–16784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, P.; Key, P.B.; Chung, K.W.; Pisarski, E.C.; Reiner, J.L.; Rodowa, A.E.; Magnuson, J.T.; DeLorenzo, M.E. Mixture Effects of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances on Embryonic and Larval Sheepshead Minnows (Cyprinodon variegatus). Toxics 2024, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giesy, J.P.; Kannan, K. Global distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate in wildlife. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houde, M.; De Silva, A.O.; Muir, D.C.G.; Letcher, R.J. Monitoring of perfluorinated compounds in aquatic biota: An updated review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7962–7973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, M.G.; Huijbregts, M.A.; van den Heuvel-Greve, M.J.; Vethaak, A.D.; Van de Vijver, K.I.; Leonards, P.E.; van Leeuwen, S.P.; de Voogt, P.J.H.A. Accumulation of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) in the food chain of the Western Scheldt estuary: Comparing field measurements with kinetic modeling. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 1766–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, K.; Tao, L.; Sinclair, E.; Pastva, S.D.; Jude, D.J.; Giesy, J.P. Perfluorinated compounds in aquatic organisms at various trophic levels in a Great Lakes food chain. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2005, 48, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.W.; Smithwick, M.M.; Braune, B.M.; Hoekstra, P.F.; Muir, D.C.; Mabury, S.A. Identification of long-chain perfluorinated acids in biota from the Canadian Arctic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penland, T.N.; Cope, W.G.; Kwak, T.J.; Strynar, M.J.; Grieshaber, C.A.; Heise, R.J.; Sessions, F.W. Trophodynamics of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the Food Web of a Large Atlantic Slope River. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6800–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powley, C.R.; George, S.W.; Russell, M.H.; Hoke, R.A.; Buck, R.C. Polyfluorinated chemicals in a spatially and temporally integrated food web in the Western Arctic. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomy, G.T.; Tittlemier, S.A.; Palace, V.P.; Budakowski, W.R.; Braekevelt, E.; Brinkworth, L.; Friesen, K. Biotransformation of N-Ethyl Perfluorooctanesulfonamide by Rainbow Trout (Onchorhynchus mykiss) Liver Microsomes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Guo, C.S.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, W. Bioaccumulation and trophic transfer of perfluorinated compounds in a eutrophic freshwater food web. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, E.; Yeung, I.L.W.; Taniyasu, S.; Lam, P.K.; Kannan, K.; Yamashita, N. Trophic Magnification of Poly- and Perfluorinated Compounds in a Subtropical Food Web. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5506–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassen, C.; Jensen, A.A.; Potrykus, A.; Christensen, F.; Kjølholt, J.; Jeppesen, C.N.; Mikkelsen, S.H.; Innanen, S. Survey of PFOS, PFOA and Other Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances; Part of the LOUS-Review; Environmental Project No. 1475; Danish Ministry of the Environment, Environmental Protection Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fair, P.A.; House, M.; Hulsey, T.C.; Bossart, G.D.; Adams, J.; Balthis, L.; Muir, D.C.G. Assessment of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in plasma of bottlenose dolphins from two southeast US estuarine areas: Relationship with age, sex and geographic locations. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fair, P.A.; Wolf, B.; White, N.D.; Arnott, S.A.; Kannan, K.; Karthikraj, R.; Vena, J.E. Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in edible fish species from Charleston Harbor and tributaries, South Carolina, United States: Exposure and risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2019, 171, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquilina-Beck, A.A.; Reiner, J.L.; Chung, K.W.; DeLise, M.J.; Key, P.B.; DeLorenzo, M.E. Uptake and biological effects of perfluorooctane sulfonate exposure in the adult Eastern oyster Crassostrea virginica. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 79, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, W.S.; Bain, L.J.; Di Giulio, R.; Kullman, S.; Rice, C.D.; Ringwoo, A.H.; van den Hurk, P. 20th pollutant responses in marine organisms (PRIMO): Global issues and fundamental mechanisms caused by pollutant stress in marine and freshwater organisms. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 227, 105620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhore, R.; Murthy, G.S. Per/polyfluoroalkyl substances production, applications and environmental impacts. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMillan, D.K.; Wetmore, B.A.; Dasgupta, S.; Baldwin, W.S. Closing the Gaps in Understanding PFAS Toxicology and Metabolism. Toxics 2025, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Teng, M.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhao, W.; Ruan, Y.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Wu, F. Insight into the binding model of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances to proteins and membranes. Environ. Int. 2023, 175, 107951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfohl, M.; Marques, E.; Auclair, A.; Barlock, B.; Jamwal, R.; Goedken, M.; Akhlaghi, F.; Slitt, A.L. An ‘Omics Approach to Unraveling the Paradoxical Effect of Diet on Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid (PFOS) and Perfluorononanoic Acid (PFNA)-Induced Hepatic Steatosis. Toxicol. Sci. 2021, 180, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.A.; Hamilton, M.C.; Edin, M.L.; Lih, F.B.; Eccles-Miller, J.A.; Tharayil, T.; Leonard, E.; Baldwin, W.S. Increased Perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) Toxicity and Accumulation Is Associated with Perturbed Prostaglandin Metabolism and Increased Organic Anion Transport Protein (OATP) Expression. Toxics 2024, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Cao, Y.; Chen, R.; Bedi, M.; Sanders, A.P.; Ducatman, A.; Ng, C. A State-of-the-Science Review of Interactions of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) with Renal Transporters in Health and Disease: Implications for Population Variability in PFAS Toxicokinetics. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 076002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Burchett, W.; Zhang, S.; Modaresi, S.M.S.; Areiza, J.A.; Fischer, F.C.; Slitt, A.L. Species-Specific Unbound Fraction Differences in Highly Bound PFAS: A Comparative Study across Human, Rat, and Mouse Plasma and Albumin. Toxics 2024, 12, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Shi, X.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, S.; Lin, Y.; Wei, X.; Li, Y.; Tang, X. Hepatotoxicity assessment investigations on PFASs targeting L-FABP using binding affinity data and machine learning-based QSAR model. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, D.E.; Lau, C.; Pradeep, P.; Sayre, R.R.; Judson, R.S.; Tornero-Velez, R.; Wambaugh, J.F. A Machine Learning Model to Estimate Toxicokinetic Half-Lives of Per- and Polyfluoro-Alkyl Substances (PFAS) in Multiple Species. Toxics 2023, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corton, J.C.; Cunningham, M.L.; Hummer, B.T.; Lau, C.; Meek, B.; Peters, J.M.; Popp, J.A.; Rhomberg, L.; Seed, J.; Klaunig, J.E. Mode of action framework analysis for receptor-mediated toxicity: The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) as a case study. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Klaunig, J.E. The effects of perfluorooctanoate on high fat diet induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Tociology 2019, 416, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robarts, D.R.; Dai, J.; Lau, C.; Apte, U.; Corton, J.C. Hepatic Transcriptome Comparative In Silico Analysis Reveals Similar Pathways and Targets Altered by Legacy and Alternative Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Mice. Toxics 2023, 11, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mello, T.; Materozzi, M.; Galli, A. PPARs and Mitochondrial Metabolism: From NAFLD to HCC. PPAR Res. 2016, 7403230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccles, J.A.; Baldwin, W.S. Detoxification Cytochrome P450s (CYPs) in Families 1-3 Produce Functional Oxylipins from Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. Cells 2023, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Doering, J.A.; LaLone, C.; Ng, C. Integrative computational approaches to inform relative bioaccumulation potential of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) across species. Toxicol. Sci. 2022, 180, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Chen, P.; Yang, L.; Zhu, L. Probing the hepatotoxicity mechanisms of novel chlorinated polyfluoroalkyl sulfonates to zebrafish larvae: Implication of structural specificity. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, Z.; Wei, C.L.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; et al. Effect of Enterohepatic Circulation on the Accumulation of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Evidence from Experimental and Computational Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 3214–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zitzow, J.D.; Ehresman, D.J.; Chang, S.C.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Forster, J.; Hagenbuch, B. Na+/Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide and Apical Sodium-Dependent Bile Acid Transporter Are Involved in the Disposition of Perfluoroalkyl Sulfonates in Humans and Rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 146, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zitzow, J.D.; Weaver, Y.; Ehresman, D.J.; Chang, S.-C.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Hagenbuch, B. Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptides Contribute to the Disposition of Perfluoroalkyl Acids in Humans and Rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 156, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, M.C.; Heintz, M.M.; Pfohl, M.; Marques, E.; Ford, L.; Slitt, A.L.; Baldwin, W.S. Increased toxicity and retention of perflouroctane sulfonate (PFOS) in humanized CYP2B6-transgenic mice compared to Cyp2b-null mice is relieved by a high-fat diet (HFD). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 152, 112175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loccisano, A.E.; Campbel, J.L., Jr.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Andersen, M.E.; Clewell, H.J.I. Comparison and evaluation of pharmacokinetics of PFOA and PFOS in the adult rat using a phsiologically based pharmacokinetic model. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 33, 452–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, R.R.; Fisher, J. Application of physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modeling to explore the role of kidney transporters in renal reabsorption of perfluorooctanoic acid in the rat. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 289, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.W.; Key, P.B.; Tanabe, P.; DeLorenzo, M.E. Effects of Temperature and Salinity on Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) Toxicity in Larval Estuarine Organisms. Toxics 2024, 12, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). PFAS Analytical Methods Development and Sampling Research; United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sunderland, E.M.; Hu, X.C.; Dassuncao, C.; Tokranov, A.K.; Wagner, C.C.; Allen, J.G. A review of the pathways of human exposure to poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and present understanding of health effects. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Rericha, Y.; Powley, C.; Truong, L.; Tanguay, R.L.; Field, J.A. Background Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Laboratory Fish Diet: Implications for Zebrafish Toxicological Studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 842, 156831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Food and Drug Administration; USFDA. Determination of 30 Per and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Food and Feed Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), C-010.03; United States Food and Drug Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lath, S.; Knight, E.R.; Navarro, D.A.; Kookana, R.S.; McLaughlin, M.J. Sorption of PFOA onto different laboratory materials: Filter membranes and centrifuge tubes. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 25101; Water Quality—Determination of Perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoate (PFOA)—Method for Unfiltered Samples Using Solid Phases Extraction and Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Shoemaker, J.; Boutin, B.; Grimmett, P. Development of a U. S. EPA drinking water method for the analysis of selected perfluoroalakl acids by solid=phase extraction and LC-MS-MS. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2009, 47, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellsing, M.S.; Josefsson, S.; Hughes, A.V.; Ahrens, L. Sorption of perfluoroalkyl substances to two types of minerals. Chemosphere 2016, 159, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, C.P.; Luthy, R.G. Sorption of perfluorinated surfactants on sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7251–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, J.H.; Berger, U.; Cousins, I.T. Can the use of deactivated glass fibre filters eliminate sorption artifacts associated with active air sampling of perfluorooctanoicacid? Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorengard, M.; Franke, V.; Troger, R.; Ahrens, L. Losses of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances to syringe filter materials. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1690, 460430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, S.C.E.; Wanninayake, D.; Chen, D.; Nguyen, N.-T. Physiochemical properties and interactions of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)—Challenges and opportunities in sensing and remediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 166764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.W.; Kannan, K.; Berger, U.; De Voogt, P.; Field, J.; Franklin, J.; Giesy, J.P.; Harner, T.; Muir, D.C.G.; Scott, B.; et al. Analytical Challenges Hamper Perfluoroalkyl Research. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 248A–255A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberatore, H.K.; Jackson, S.R.; Strynar, M.J.; McCord, J.P. Solvent Suitability for HFPO-DA (“GenX” Parent Acid) in Toxicological Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangma, J.T.; Reiner, J.; Fry, R.C.; Manuck, T.; McCord, J.; Strynar, M.J. Identification of an Analytical Method Interference for Perfluorobutanoic Acid in Biological Samples. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karrman, A.; Domingo, J.L.; Llebaria, X.; Nadal, M.; Bigas, E.; van Bavel, B.; Lindstrom, G. Biomonitoring perfluorinated compounds in Catalonia, Spain: Concentrations and trends in human liver and milk samples. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, M.; Smith, J.; Steed, J.; McMillan, D.; Stahl-Zeng, J. Quantitation of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Foodstuffs; Volume Sciex Technical Note MKT-28758-B2023; Sciex: Marlborough, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Young, W.; Wiggins, S.; Limm, W.; Fisher, C.M.; DeJager, L.; Genualdi, S. Analysis of Per- and Poly(fluoroalkyl) Substances (PFASs) in Highly Consumed Seafood Products from U. S. Markets. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 13535–13553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Veen, I.; Fielder, H.; de Boer, J. Assessment of the per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances analysis under the Stockholm Convention—2018/2019. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137549–137556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA 821-R-24-001; Method 1633 Analysis of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Aqueous, Solid, Biosolids, and Tissue Samples by LC-MS/MS. United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2024.
- Nhanes 2017–2018, Method 6304.09; Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances, Online Solid Phase Extraction-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Turbo Ion Spray-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Atlanta, Georgia, 2017–2018. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/public/2013/labmethods/PFAS_H_MET.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Baker, N.; Knudsen, T.; Williams, A. Abstract Sifter: A comprehensive front-end system to PubMed. F1000Research 2017, 6, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comito, R.; Porru, E.; Violante, F.S. Analytical methods employed in the identification and quantification of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in human matrices—A scoping review. Chemosphere 2023, 345, 140433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, J.; Lambright, C.S.; Evans, N.; McCord, J.; Strynar, M.J.; Hill, D.; Medlock-Kakaley, E.; Wilson, V.; Gray, L.E., Jr. Hexafluorpropylene oxide-dimer acid (HFPO-DA or GenX) alters maternal and fetal glucose and lipid metabolism and produces neonatal mortality, low birthweight, and hepatomegaly in the Sprague-Dawley rat. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, J.; Lambright, C.S.; Evans, N.; Medlock-Kakaley, E.; Hill, D.; McCord, J.; Strynar, M.J.; Wehmas, L.C.; Hester, S.; MacMillan, D.K.; et al. Developmental toxicity of Nafion byproduct 2 (NBP2) in the Sprague-Dawley rat with comparisons to hexafluoropropylene oxide-dimer acid (HFPO-DA or GenX) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS). Environ. Int. 2022, 160, 107056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renyer, A.; Ravindra, K.; Wetmore, B.A.; Ford, J.L.; DeVito, M.; Hughes, M.F.; Wehmas, L.C.; MacMillan, D.K. Dose Response, Dosimetric, and Metabolic Evaluations of Replacement PFAS Perfluoro-(2,5,8-trimethyl-3,6,9-trioxadodecanoic) Acid (HFPO-TeA). Toxics 2023, 11, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.C.; Dzierlenga, A.L.; Robinson, V.G.; Waidyanatha, S.; DeVito, M.J.; Elfrid, M.A.; Granville, C.A.; Gibbs, S.T.; Blystone, C.R. Toxicokinetics of perfluorobutane sulfonate (PFBS), perfluorohexane-1-sulphonic acid (PFHxS), and perfluorooctane sulfonic acid in male and female Hsd:Sprague SD rats after intravenous and gavage administration. Toxicol. Rep. 2019, 6, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dukes, D.A.; McDonough, C.A. N-glucuronidation and Excretion of Perfluoroalkyl Sulfonamides in Mice Following Ingestion of Aqueous Film-Forming Foam. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2024, 43, 2274–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutz, A.; Clifton, M.S.; Henderons, W.M.; Smeltz, M.G.; Phillips, M.; Wambaugh, J.F.; Wetmore, B.A. Category-Based Toxicokinetic Evaluations of Data-Poor Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) using Gas Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry. Toxics 2023, 11, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangma, J.; Barry, K.M.; Fisher, C.M.; Genualdi, S.; Guillette, T.C.; Huset, C.A.; McCord, J.; Ng, B.; Place, B.J.; Reiner, J.L.; et al. PFAS Ghosts: How to identify, evaluate, and exorcise new and existing analytical interference. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, E.; Sandhu, M.; Benskin, J.P.; Ralitsch, M.; Thibault, N.; Birkholz, D.; Martin, J.W. Endogenous high performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry interferences and the case of perfluorohexane sulfonate (PFHxS) in human serum; are we overestimating exposure? Rapid. Comm. Mass. Spectrom. 2009, 23, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benskin, J.P.; Bataineh, M.; Martin, J.W. Simultaneous Characterization of Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylate, Sulfonate, and Sulfonamide Isomers by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 6455–6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolanczyk, R.C.; Saley, M.R.; Serrano, J.A.; Daley, S.M.; Tapper, M.A. PFAS Biotransformation Pathways: A Species Comparison Study. Toxics 2023, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ateia, M.; Chiang, D.; Cashman, M.; Acheson, C. Total Oxidizable Precursor (TOP) Assay—Best Practices, Capabilities and Limitations for PFAS Site Investigation and Remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2024, 10, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. A9-0238; Proposal for a Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council Amending Directive 2000/60/Ec Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy, Directive 2006/118/Ec on the Protection of Groundwater Against Pollution and Deterioration and Directive 2008/105/Ec on Environmental Quality Standards in the Field of Water Policy. European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2023.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Final PFAS National Primary Drinking Water Regulation; United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Licul-Kucera, V.; Ragnarsdottir, O.; Fromel, T.; van Wezel, A.P.; Knepper, T.P.; Harrad, S.; Abdallah, M.A.-E. Interspecies comparison of metabolism of two novel prototype PFAS. Chemosphere 2024, 351, 141237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergren, R.; Cousins, I.T.; Trudel, D.; Wormuth, M.; Scheringer, M. Estimating the contribution of precursor compounds in consumer exposure to PFOS and PFOA. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCord, J.; Strynar, M. Identification of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the Cape Fear River by High Resolution Mass Spectrometry and Nontargeted Screening. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4717–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, S.; McCord, J.; Bangma, J.; Sobus, J. Establishing performance metrics for quantitative non-targeted analysis: A demonstration using per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 1249–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idjaton, B.I.T.; Togola, A.; Ghestem, J.P.; Kastler, L.; Bristeau, S.; Ronteltap, M.; Colombano, S.; Devau, N.; Lions, J.; van Hullebusch, E.D. Determination of organic fluorinated compounds content in complex samples through combustion ion chromatography methods: A way to define a “Total Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)” parameter? Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 932, 172589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidaisee, S.; Macpherson, C.N.L. Zoonoses and One Health: A Review of the Literature. J. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 2014, 874345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bečanová, J.; Komprdová, K.; Vrana, B.; Klánová, J. Annual dynamics of perfluorinated compounds in sediment: A case study in the Morava River in Zlín district, Czech Republic. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribble, M.O.; Bartell, S.M.; Kannan, K.; Wu, Q.; Fair, P.A.; Kamen, D.L. Longitudinal measures of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in serum of Gullah African Americans in South Carolina: 2003–2013. Environ. Res. 2015, 143, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, J.S.; Schaefer, A.M.; Bossart, G.D.; Fair, P.A. Health and Environmental Risk Assessment Project for bottlenose dolphins Tursiops truncatus from the southeastern USA. II. Environmental aspects. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2017, 125, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossart, G.D.; Fair, P.; Schaefer, A.M.; Reif, J.S. Health and Environmental Risk Assessment Project for bottlenose dolphins Tursiops truncatus from the southeastern USA. I. Infectious diseases. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2017, 125, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, P. A review of sources, multimedia distribution and health risks of novel fluorinated alternatives. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiteux, V.; Dauchy, X.; Bach, C.; Colin, A.; Hemard, J.; Sagres, V.; Rosin, C.; Munoz, J.-F. Concentrations and patterns of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in a river and three drinking water treatment plants near and far from a major production source. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Pan, X.; Wang, T.; Li, X.; Luo, Y. Toxicity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances to Nematodes. Toxics 2023, 11, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beccacece, L.; Costa, F.; Pascali, J.P.; Giorgi, F.M. Cross-species transcriptomics analysis highlights conserved molecular responses to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Toxics 2023, 11, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, K.D.; Polera, M.E.; Guillette, T.C.; Starnes, H.M.; Dean, K.; Watters, M.; Stevens-Stewart, D.; Belcher, S.M. Domestic Dogs and Horses as Sentinels of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Exposure and Associated Health Biomarkers in Gray’s Creek North Carolina. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 9567–9579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkwood, K.I.; Fleming, J.; Nguyen, H.; Reif, D.M.; Baker, E.S.; Belcher, S.M. Utilizing Pine Needles to Temporally and Spatially Profile Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 3441–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, J.-M.; Chen, D.; Han, F.-J.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, F. A short review on human exposure to and tissue distribution of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.-S.; Wen, L.-L.; Chu, P.-L.; Lin, C.-Y. Association among total serum isomers of perfluorinated chemicals, glucose homeostasis, lipid profiles, serum protein and metabolic syndrome in adults: Nhanes, 2013–2014. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 232, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greaves, A.K.; Letcher, R.J.; Sonne, C.; Dietz, R. Brain region distribution and patterns of bioaccumulative perfluoroalkyl carboxylates and sulfonates in East Greenland polar bears (Ursus maritimus). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillette, T.C.; Jackson, T.W.; Guillette, M.; McCord, J.; Belcher, S.M. Blood concentrations of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances are associated with autoimmune-like effects in American alligators from Wilmington, North Carolina. Front. Toxicol. 2022, 4, 1010185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bost, P.C.; Strynar, M.J.; Reiner, J.L.; Zweigenbaum, J.A.; Secoura, P.L.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Dye, J.A. U.S. domestic cats as sentinels for perfluoroalkyl substances: Possible linkages with housing, obesity, and disease. Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, A.O.; Spencer, C.; Ho, K.C.D.; Tarhuni, M.A.; Go, C.; Houde, M.; de Solla, S.R.; Lavoie, R.A.; King, L.E.; Muir, D.C.G.; et al. Perfluoroalkylphosphinic Acids in Northern Pike (Esox lucius), Double-Crested Cormorants (Phalacrocorax auritus), and Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in Relation to Other Perfluoroalkyl Acids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10903–10913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Health Effects Support Document for Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA); United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Steenland, K.; Winquist, A. PFAS and cancer, a scoping review of the epidemiologic evidence. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, S.E.; Ducatman, A.; Boobis, A.; DeWitt, J.C.; Lau, C.; Ng, C.; Smith, J.S.; Roberts, S.M. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Toxicity and Human Health Review: Current State of Knowledge and Strategies for Informing Future Research. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 606–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappazzo, M.K.; Coffman, E.; Hines, P.E. Exposure to Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances and Health Outcomes in Children: A Systematic Review of the Epidemiologic Literature. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appel, M.; Forsthuber, M.; Ramos, R.; Widhalm, R.; Granitzer, S.; Uhl, M.; Hengstschlaeger, M.; Stamm, T.; Gundacker, C. The Transplacental Transfer Efficiency of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): A First Meta-Analysis. J. Toxicol. Environ. Healtth-Part B-Crit. Rev. 2022, 25, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, S.-Y.; Chen, Y.-N.; Wu, K.-J.; Liu, W.; Wang, W.-J.; Liang, H.-R.; Jiang, Z.-X.; Li, Z.-L.; Hu, C.-Y. Association between Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Birth Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 855348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.M.; Lee, A.L.; Rappazzo, K.M.; Ru, H.; Radke, E.G.; Bateson, T.F. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Birth Weight and PFNA Exposures. Environ. Res. 2023, 222, 115357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coperchini, F.; Croce, L.; Ricci, G.; Magri, F.; Rotondi, M.; Imbriani, M.; Chiovato, L. Thyroid Disrupting Effects of Old and New Generation PFAS. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 11, 612320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Moon, S.; Oh, B.-C.; Jung, D.; Ji, K.; Choi, K.; Park, Y.J. Association between Perfluoroalkyl Substances Exposure and Thyroid Function in Adults: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzierlenga, M.W.; Allen, B.C.; Clewell, H.J.; Longnecker, M.P. Pharmacokinetic Bias Analysis of an Association between Clinical Thyroid Disease and Two Perfluoroalkyl Substances. Environ. Int. 2020, 141, 105784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzierlenga, M.W.; Moreau, M.; Song, G.; Mallick, P.; Ward, P.L.; Campbell, J.L.; Housand, C.; Yoon, M.; Allen, B.C.; Clewell, H.J.I.; et al. Quantitative Bias Analysis of the Association between Subclinical Thyroid Disease and Two Perfluoroalkyl Substances in a Single Study. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.M.; Braun, J.M. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Outcomes Related to Metabolic Syndrome: A Review of the Literature and Current Recommendations for Clinicians. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2023, 19, 15598276231162802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratakis, N.; Rock, S.; La Merrill, M.A.; Saez, M.; Robinson, O.; Fecht, D.; Vrijheid, M.; Valvi, D.; Conti, D.V.; McConnell, R.; et al. Prenatal Exposure to Persistent Organic Pollutants and Childhood Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Human Studies. Obes. Rev. 2022, 23, e13383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, S.-Y.; Qiao, J.-C.; Xu, K.-X.; Li, Z.-L.; Chen, Y.-N.; Wu, K.-J.; Jiang, Z.-X.; Hu, C.-Y. Association between Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Exposure and Risk of Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Exp. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2023, 33, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radke, E.G.; Wright, J.M.; Christensen, K.; Lin, C.J.; Goldstone, A.E.; Lemeris, C.; Thayer, K.A. Epidemiology Evidence for Health Effects of 150 Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: A Systematic Evidence Map. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 096003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, E.; Pfohl, M.; Wei, W.; Tarantola, G.; Ford, L.; Amaeze, O.; Alesio, J.; Ryu, S.; Jia, X.; Zhu, H.; et al. Replacement per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are potent modulators of lipogenic and drug metabolizing gene expression signatures in primary human hepatocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 442, 115991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Kuiper, J.R.; Chen, Y.; Feuerstahler, L.; Teresi, J.; Buckley, J.P. Developing an Exposure Burden Score for Chemical Mixtures Using Item Response Theory, with Applications to PFAS Mixtures. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 117001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.T.; Song, B.; Xiao, R.; Zeng, G.M.; Gong, J.L.; Chen, M.; Xu, P.A.; Zhang, P.; Shen, M.C.; Yi, H. Assessing the Human Health Risks of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate by in Vivo and in Vitro Studies. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, E.; Metruccio, F.; Guercio, V.; Tosti, L.; Benfenati, E.; Bonzi, R.; La Vecchia, C.; Moretto, A. Exposure to PFOA and PFOS and Fetal Growth: A Critical Merging of Toxicological and Epidemiological Data. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2017, 47, 482–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokra, K. Endocrine Disruptor Potential of Short- and Long-Chain Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs)—A Synthesis of Current Knowledge with Proposal of Molecular Mechanism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Kumar, P.; Fahmi, N.; Garg, B.; Dutta, S.; Sachar, S.; Matharu, A.S.; Vimaleswaran, K.S. Endocrine disruption and obesity: A current review on environmental obesogens. Curr. Res. Green. Sustain. Chem. 2020, 3, 100009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behr, A.-C.; Plinsch, C.; Braeuning, A.; Buhrke, T. Activation of human nuclear receptors by perfluoroalkylated substances (PFAS). Toxicology 2020, 62, 104700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heindel, J.J.; Blumberg, B. Environmental Obesogens: Mechanisms and Controversies. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 59, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, G.A.; Norris, D.O.; Kloas, W.; Kullman, S.W.; Baldwin, W.S.; Greally, J.M. Detailed Review Paper on the State of the Science on Novel In Vitro and In Vivo Screening and Testing Methods and Endpoints for Evaluating Endocdrine Disruptors; Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development: Paris, France, 2012; p. 213. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences. National Toxicology Program (NTP). Monograph on Immunotoxicity Associated with Exposure to Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS); National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences: Durham, NC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, E.T.; Adami, H.-O.; Boffetta, P.; Wedner, H.J.; Mandel, J.S. A critical review of perfluorooctanoate and perfluorooctanesulfonate exposure and immunological health conditions in humans. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2016, 46, 279–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, Y.J. Investigating fatty liver disease-associated adverse outcome pathways of perfluorooctane sulfonate using a systems toxicology approach. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 176, 113781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrabadi, F.; Alarcan, J.; Sprenger, H.; Braeuning, A.; Buhrke, T. Impact of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and PFAS mixtures on lipid metabolism in differentiated HepaRG cells as a model for human hepatocytes. Arch. Toxicol. 2024, 98, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangione, B.; Birk, S.; Benzouak, T.; Rodriguez-Villamizar, L.A.; Karim, F.; Dugandzic, R.; Villeneuve, P.J. Exposure to perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances and pediatric obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratakis, N.; Vrijheid, M. Invited Perspective: PFAS and the Childhood Obesity Phenotype—Challenges and Opportunities. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 061301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, M.B.; Das, K.P.; Wood, C.R.; Wolf, C.J.; Abbott, B.D.; Lau, C. Evaluation of perfluoroalkyl acid activity using primary mouse and human hepatocytes. Toxicology 2013, 308, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, C.A.; Choyke, S.; Ferguson, P.L.; DeWitt, J.C.; Higgins, C.P. Bioaccumulation of Novel Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Mice Dosed with an Aqueous Film-Forming Foam. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 5700–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). PFAS National Primary Drinking Water Regulation Rulemaking; United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Takeda, K.; Saito, T.; Sasaki, S.; Eguchi, A.; Sugiyama, M.; Eto, S.; Suzuki, K.; Kamata, R. Toxicity Assessment of Mixed Exposure of Nine Perfluoroalkyl Substances at Concentrations Relevant to Daily Intake. Toxics 2024, 12, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, J.J.; Callahan, C.L.; Calafat, A.M.; Huang, W.-Y.; Jones, R.R.; Sabbisetti, V.S.; Freedman, N.D.; Sampson, J.N.; Silverman, D.T.; Purdue, M.P.; et al. Serum concentrations of per- and polyfluoroaklyl substances and risk of renal cell carcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021, 113, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalmendulis, L.M.; Hocevar, J.M.; Stephens, M.; Sandusky, G.E.; Hacevar, B.A. Exposure to perflurooctanoic acid leads to promotion of pancreatic cancer. Carcinogenesis 2022, 43, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, K.T.; Sørensen, M.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Lipworth, L.; Tjønneland, A.; Overvad, K.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O. Perfluorooctanoate and perfluorooctanesulfonate plasma levels and risk of cancer in the general Danish population. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.W.; Scammell, M.K.; Hatch, E.E.; Webster, T.F. Social disparities in exposures to bisphenol A and polyfluoroalkyl chemicals: A cross-sectional study within Nhanes 2003–2006. Environ. Health 2012, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Karvonen-Gutierrez, C.A.; Zota, A.R.; Mukherjee, B.; Harlow, S.D.; Park, S.K. The role of exposure to per and polyfluroalkyl substances in racial/ethic disparities in hypertension: Results from the study of women’s health across the nation. Environ. Res. 2023, 227, 115813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, J.; Chang, V.C.; Cheng, I.; Calafat, A.M.; Botelho, J.C.; Shearer, J.J.; Sampson, J.N.; Setiawan, V.W.; Wilkens, L.R.; Silverman, D.T.; et al. Serum concentrations of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and risk of renal cell carcinoma in the multiethnic cohort study. Environ. Int. 2023, 180, 108197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calafat, A.M.; Wong, L.Y.; Kuklenyik, Z.; Reidy, J.A.; Needham, L.L. Polyfluoroalkyl Chemicals in the U.S. Population: Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (Nhanes) 2003–2004 and Comparisons with Nhanes 1999–2000. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1596–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.K.; Kahana, A.; Heidt, J.; Polemi, K.; Kvasnicka, J.; Jolliet, O.; Colacino, J.A. A Comprehensive Analysis of Racial Disparities in Chemical Biomarker Concentrations in United States Women, 1999–2014. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, K.N.; Judson, R.S.; Hill, B.N.; Jarema, K.A.; Olin, J.K.; Knapp, B.R.; Lowery, M.; Feshuk, M.; Brown, J.; Padilla, S. Using Zebrafish to Screen Developmental Toxicity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). Toxics 2024, 12, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Quan, X.; Lei, S.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Xu, P. PFOS inhibited normal functional development of placenta cells via PPARg signaling. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, G.W.; Zobel, L.R. Assessment of lipid, hepatic, and thyroid parameters with serum perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) concentrations in fluorochemical production workers. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2007, 81, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, T.; Galloway, T.S.; Melzer, D.; Holcroft, P.; Cipelli, R.; Pilling, L.C.; Mondal, D.; Luster, M.; Harries, L.W. Associations between PFOA, PFOS and changes in the expression of genes involved in cholesterol metabolism in humans. Environ. Int. 2013, 57–58, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaunig, J.E.; Hocevar, B.A.; Kamendulis, L.M. Mode of Action analysis of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) tumorigenicity and Human Relevance. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 33, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-H.; Glover, K.P.; Han, X. Characterization of cellular uptake of Perfluorooctanoate via organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1A2, organic anion transporter 4, and urate transporter 1 for their potential roles in mediating human renal reabsorption of perflurocarboxylates. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 117, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, J.; Mylroie, J.; Kimble, A.; Steward, C.; Chapman, K.; Wilbanks, M.; Perkins, E.; Garcia-Reyero, N. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Impacts on Morphology, Behavior and Lipid Levels in Zebrafish Embryos. Toxics 2024, 12, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolewski, M.; Conrad, K.; Allen, J.L.; Weston, H.; Martin, K.; Lawrence, B.P.; Cory-Slechta, D.A. Sex-specific enhanced behavioral toxicity induced by maternal exposure to a mixture of low dose endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Neurotoxicology 2014, 45, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsini, E.; Avogadro, A.; Galbiati, V.; dell’Agli, M.; Marinovich, M.; Galli, C.L.; Germolec, D.R. In vitro evaluation of the immunotoxic potential of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 250, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermann, C.A.G.; Jensen, K.J.; Nielson, F.; Budtz-Jorgensen, E.; van der Klis, F.; Benn, C.S.; Grandjean, P.; Fisker, A.B. Serum Perfluoroalkyl Substances, Vaccine Responses, and Morbidity in a Cohort of Guinea-Bissau Children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 087002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louisse, J.; Dallafiora, L.; van den Heuvel, J.J.M.W.; Rijkers, D.; Leenders, L.; Dorne, J.-L.C.M.; Punt, A.; Russell, F.G.M.; Koenderink, J.B. Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) are substrates of the renal human organic anion transporter 4 (OAT4). Arch. Toxicol. 2022; 97, 685–696. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Nabb, D.L.; Russell, M.H.; Kennedy, G.L.; Rickard, R.W. Renal Elimination of Perfluorocarboxylates (PFCAs). Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.-L.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chou, H.-C.; Chang, C.-C.; Lo, H.-Y.; Juan, S.-H. Perfluorooctanesulfonate Mediates Renal Tubular Cell Apoptosis through PPARgamma Inactivation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Yan, S.; Wang, P.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Cui, J.; Liang, Y.; Ren, S.; Gao, Y. Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) exposure in relation to the kidneys: A review of current available literature. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1103141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, H.E.; Li, S.; Walker, D.I.; Wang, H.; Jia, Q.; Rock, S.; Costello, E.; Bjornstad, P.; Pyle, L.; Nelson, J.; et al. The potential mediating role of the gut microbiome and metabolites in the association between PFAS and kidney function in young adults: A proof-of-concept study. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Fu, J.; Sun, J.; Hall, D.R.; Yang, D.; Blatz, D.; Houck, K.A.; Ng, C.; Doering, J.A.; LaLone, C.; et al. Quantitative chemical proteomics reveals interspecies variations on binding schemes of L-FABP with perfluorooctanesulfonate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 55, 9012–9023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazaee, M.; Christie, E.; Cheng, W.; Michalsen, M.; Field, J.; Ng, C. Perfluoroalkyl Acid Binding with Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors α, γ, and δ, and Fatty Acid Binding Proteins by Equilibrium Dialysis with a Comparison of Methods. Toxics 2021, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, B.N.; Badders, A.N.; Costacou, T.; Arthur, J.M.; Innes, K.E. Perfluoroalkyl substances and kidney function in chronic kidney disease, anemia, and diabetes. Diab Met. Syn. Obes Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, E.; Marques, E.; Areiza, J.A.; Modaresi, S.M.S.; Slitt, A. Exposure to a PFOA, PFOS and PFHxS Mixture during Gestation and Lactation Alters the Liver Proteome in Offspring of CD-1 Mice. Toxics 2024, 12, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.T.; Zhao, Y.G.; Wei, X.; Hui, K.Y.; Giesey, J.P.; Wong, C.K.C. PFOS-induced hepatic steatosis, the mechanistic actions on β-oxidation and lipid transport. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takacs, M.L.; Abbott, B.D. Activation of mouse and human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (a,b/d,g) perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 95, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, A.; Zhang, J.; Feng, L. Exposure to perfluorobutane sulfonate and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid disrupts the production of angiogenesis factors and stress responses in human placental syncytiotrophoblast. Reprod. Toxicol. 2020, 98, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, M.S.; Varde, M.; Newman, R.B. Environmental Toxicants and Placental Function. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2022, 85, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.D.; Wolf, C.J.; Das, K.P.; Zehr, R.D.; Schmid, J.E.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Strynar, M.J.; Lau, C. Developmental toxicity of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) is not dependent on expression of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-alpha (PPAR alpha) in the mouse. Reprod. Toxicol. 2008, 27, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, V.; Bil, W.; Vandebriel, R.; Granum, B.; Luijten, M.; Lindeman, B.; Grandjean, P.; Kaiser, A.-M.; Hauzenberger, I.; Hartmann, C.; et al. Consideration of pathways for immunotoxicity of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Environ. Health 2023, 22, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, A.B.; Michelsen-Correa, S.; Rosen, C.; Martin, C.F.; Blumberg, B. PFAS and Potential Adverse Effects on Bone and Adipose Tissue Through Interactions With PPARγ. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.-Q.; Liu, T.; Yang, S.; Sun, L.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Li, L.-Y.; She, Y.-C.; Zheng, Y.-Y.; Bao, Q.; Dong, G.-H.; et al. Perfluoroalkyl substance pollutants activate the innate immune system through the AIM2 inflammasome. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bline, A.P.; DeWitt, J.C.; Kwiatkowski, C.F.; Pelch, K.E.; Reade, A.; Varshavsky, J.R. Public Health Risks of PFAS-Related Immunotoxicity Are Real. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2024, 11, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudzanová, B.; Thon, V.; Vespalcová, H.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Piler, P.; Zvonař, M.; Klánová, J.; Bláha, L.; Adamovsky, O. Altered Transcriptome Response in PBMCs of Czech Adults Linked to Multiple PFAS Exposure: B Cell Development as a Target of PFAS Immunotoxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beans, C. How “forever chemicals” might impair the immune system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2105018118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Holst, H.; Nayak, P.; Dembek, Z.; Buehler, S.; Echeverria, D.; Fallacara, D.; John, L. Perfluoroalkyl substances exposure and immunity, allergic response, infection, and asthma in children: Review of epidemiologic studies. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamen, D.L.; Peden-Adams, M.M.; Vena, J.E.; Gilkeson, G.S.; Hulsey, T.C.; Moultrie, L.; Stevens, B.E. Seafood consumption and persistent organic pollutants as triggers of autoimmunity among Gullah African Americans. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, A19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grønnestad, R.; Johanson, S.M.; Müller, M.H.B.; Schlenk, D.; Tanabe, P.; Krøkje, A.; Jaspers, V.L.B.; Jenssen, B.M.; Ræder, E.M.; Lyche, J.L.; et al. Effects of an environmentally relevant PFAS mixture on dopamine and steroid hormone levels in exposed mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2021, 428, 115670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Running, L.; Cristobal, J.R.; Karageorgiou, C.; Camdzic, M.; Aguilar, J.M.N.; Gokcumen, O.; Aga, D.S.; Atilla-Gokcumen, G.E. Investigating the Mechanism of Neurotoxic Effects of PFAS in Differentiated Neuronal Cells through Transcriptomics and Lipidomics Analysis. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2024, 15, 4568–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.I.; Kim, B.-N.; Lee, Y.A.; Shin, C.H.; Hong, Y.-C.; Døssing, L.D.; Dalgaard, L.; Hildebrandt, G.; Lim, Y.-H. Association between early-childhood exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances and ADHD symptoms: A prospective cohort study. Sci. Environ. 2023, 879, 163081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharal, B.; Ruchitha, C.; Kmar, P.; Pandey, R.; Rachamalla, M.; Niyogi, S.; Naidu, R.; Kaundal, R.V. Neurotoxicity of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances: Evidence and future directions. Sci. Environ. 2024, 955, 176941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, N.M.; Evans, A.T.; Fritz, M.K.; Peak, S.A.; von Holst, H.E. Trends in the Regulation of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cousins, I.T.; DeWitt, J.C.; Gluge, J.; Goldenman, G.; Herzke, D.; Lohmann, R.; Miller, M.; Ng, C.A.; Scheringer, M.; Vierkej, L.; et al. Strategies for grouping per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) to protect human and environmental health. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2020, 22, 1444–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.; Malek, A.; Arokianathar, J.; Haddad, E.; Matthew, J. Global Regulations Around PFAS: The Past, the Present and the Future. Int. Chem. Regul. Law Rev. 2023, 6, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Perfluoroalkyl Sulfonates; Significant New Use Rule; United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Fact Sheet: 2010/2015 PFOA Stewardship Program; United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cousins, I.T.; DeWitt, J.C.; Gluge, J.; Goldenman, G.; Herzke, D.; Lohmann, R.; Ng, C.A.; Scheringer, M.; Wang, Z. The high persistence of PFAS is sufficient for their management as a chemical class. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2020, 22, 2307–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency Press Office. EPA Announces It Will Keep Maximum Contaminant Levels for PFOA, PFOS: EPA Intends to Provide Regulatory Flexibility and Holistically Address These Contaminants in Drinking Water. 2025. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/newsreleases/epa-announces-it-will-keep-maximum-contaminant-levels-pfoa-pfos (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Kwiatkowski, C.F.; Andrews, D.Q.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Bruton, T.A.; DeWitt, J.C.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Maffini, M.V.; Miller, M.F.; Pelch, K.E.; Reade, A.; et al. Scientific Basis for Managing PFAS as a Chemical Class. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Chamber of Commerce. Impacts of the PFAS Restriction on Trade Between the U.S. and the European Union. 2023. Available online: https://www.uschamber.com/assets/documents/Impacts-of-PFAS-Restriction-on-Trade-Between-the-U.S.-and-the-European-Union_9.25.2023.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2023).
- Legg, R.; Prior, J. Toxic torts as compensation: Legal geographies of environmental contamination litigation. Geogr. Res. 2023, 61, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, K.; Salvatore, D.; Powers, M.; Brown, P.; Poehlein, M.; Conroy-Ben, O.; Cordner, A. Federal PFAS Testing and Tribal Public Water Systems. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 127701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedinick, K.; Taylor, S.; Roberts, M.; Moore, R.; Olson, E. Watered Down Justice; National Research Development Corporation (NRDC): Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.nrdc.org/sites/default/files/watered-down-justice-report.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2023).
- Hinshaw. Insurers Face Large PFAS-Related Losses: A Primer on Forever Chemical Regulation, Liabilities, and Insurance Coverage Issues. 2023. Available online: https://www.hinshawlaw.com/newsroom-updates-insights-for-insurers-insurers-face-large-pfas-related-losses.html (accessed on 3 November 2023).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Economic Analysis for the Proposed Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances National Primary Drinking Water Regulation; Division, Office of Ground Water and Drinking Water Standards and Risk Management Division Eds.; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2023; Available online: https://www.epa.gov/system/files/documents/2023-03/Proposed%20PFAS%20NPDWR%20EA_final_03_09_2023_0.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2023).
- Pepper, S. Transitioning from PFAS Firefighting Foam to Fluorine-Free Alternatives; Montrose Environmental: Little Rock, AR, USA, 2023; Available online: https://montrose-env.com/blog/transitioning-from-pfas-firefighting-foam-to-fluorine-free-alternatives/ (accessed on 3 November 2023).
- Jahura, F.T.; Mazumder, N.-U.S.; Hossain, M.T.; Kasebi, A.; Girase, A.; Ormond, R.B. Exploring the prospects and challenges of fluorine-free firefighting foams (F3) as alternatives to aqueous film-forming foams (AFFF): A review. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 37430–37444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, L.A.; East, A.G.; Narizzano, A.M.; Quinn, M.J., Jr. Toxicology assessment for six per- and polyfluoroalkyl (PFAS)-free aqueous film forming foam (AFFF) products. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2023, 19, 1609–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateia, M.; Van Buren, J.; Barrett, W.; Martin, T.; Back, G.G. Sunrise of PFAS Replacements: A Perspective on Fluorine-Free Foams. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 7986–7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvel, S.W.; To, K.; Grimm, F.A.; Wright, F.A.; Rusyn, I.; Reif, D.M. ToxPi Graphical User Interface 2.0: Dynamic exploration, visualization, and sharing of integrated data models. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharehveran, M.M.; Walus, A.M.; Anderson, T.A.; Subbiah, S.; Guelfo, J.; Frigon, M.; Longwell, A.; Suski, J.G. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)-free aqueous film forming foam formulations: Chemical composition and biodegradation in an aerobic environment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.K.; Quinlin, K.A.; Wigren, M.A.; Choi, Y.J.; Sepúlveda, M.S.; Lee, L.S.; Haskins, D.L.; Lotufo, G.R.; Kennedy, A.; May, L.; et al. Acute toxicity of eight aqueous film-forming foams to 14 aquatic species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 6078–6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, N.; Suski, J.G.; Lanasa, S.; Chanov, M.K.; Jones, D.K.; Haskins, D.L.; Quinlin, K.A.; Wigren, M.A.; Hoverman, J.T.; Choi, Y.J.; et al. Chronic Toxicity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance–Free Firefighting Foams to Aquatic Organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2024, 43, 2436–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordner, A.; De la Rosa, V.Y.; Schaider, L.A.; Rudel, R.A.; Richter, L.; Brown, P. Guideline levels for PFOA and PFOS in drinking water: The role of scientific uncertainty, risk assessment decisions, and social factors. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Office of the Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition and Sustainment. Report on Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Active Sites Cleanup Costs; United States Department of Defense: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; p. 16. Available online: https://media.defense.gov/2022/Jul/21/2003039883/-1/-1/1/REPORT-ON-PER-AND-POLYFLUOROALKYL-SUBSTANCES-ACTIVE-SITES-CLEANUP-COSTS-June-2022.PDF (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Environmental Working Group. The Pentagon’s contamination time bomb: Cleanup backlog outpaces funding. News Insights, 15 May 2023. Available online: https://www.ewg.org/news-insights/news-release/2023/05/pentagons-contamination-time-bomb-cleanup-backlog-outpaces (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Wolohan, K.; Ling, A.; McCabe, A.; Vermace, B.; Richard, D.; Gantzer, C.; Nelson, S.; Muson, A.; Dursun, D.; Blate, M.; et al. Evluation of Current Alternatives and Estimateed Cost Curves for PFAS Removal and Destruction from Municipal Watewater, Biosolids, Landfill Leachate, and Compost Contact Water; Minnesota Pollution Control Agency: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- AutoinsuranceEZ. Gas vs. Electric Car Fires. Available online: https://www.autoinsuranceez.com/gas-vs-electric-car-fires/ (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Kalhoff, J.; Bresser, D.; Bolloli, M.; Alloin, F.; Sanchez, J.-Y.; Passerini, S. Enabling LiTFSI-based Electrolytes for Safer Lithium-Ion Batteries by Using Linear Fluorinated Carbonates as (Co)Solvent. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 2939–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, E.O.; Lizarraga, L.; Lambert, J.C.; Ahirke, A. ORD Human Health Toxicity Value for Lithium bis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]azanide (HQ-115) (CASRN 90076-65-6|DTXSID8044468); EPA IRIS Assessments; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, R.I.; Shokry, D.; Fazal, Z.; Rennels, B.C.; Freemantle, S.J.; La Frano, M.R.; Prins, G.S.; Erdogan, Z.M.; Irudayaraj, J.; Singh, R.; et al. Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid Alters Pro-Cancer Phenotypes and Metabolic and Transcriptional Signatures in Testicular Germ Cell Tumors. Toxics 2024, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sands, M.; Zhang, X.; Gal, A.; Laws, M.; Spinella, M.; Erdogan, Z.-M.; Irudayaraj, J. Comparative hepatotoxicity of novel lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (LiTFSI, ie. HQ-115) and legacy Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in male mice: Insights into epigenetic mechanisms and pathway-specific responses. Environ. Int. 2024, 185, 108556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sands, M.; Zhang, X.; Irudayaraj, J. Kidney toxicology of a novel compound Lithium Bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (LiTFSI, ie. HQ-115) used in energy applications: An epigenetic perspective. Sci. Environ. 2024, 955, 177019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewapriya, P.; Chadwick, L.; Gorji, S.G.; Schulze, B.; Valsecchi, S.; Samanipour, S.; Thomas, K.V.; Kaserzon, S.L. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in consumer products: Current knowledge and research gaps. J. Hazard. Mat Lett. 2023, 4, 100086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lendewig, M.; Marquez, R.; Franco, J.; Vera, R.E.; Vivas, K.A.; Forfora, N.; Venditti, R.A.; Gonzalez, R. PFAS regulations and economic impact: A review of U.S. pulp & paper and textiles industries. Chemosphere 2025, 377, 144301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BCLPemerging.com. PFAS Drinking Water Standards: STATE-by-State Regulations Updated: June 2025. Available online: https://www.bclplaw.com/en-US/events-insights-news/pfas-drinking-water-standards-state-by-state-regulations.html#:~:text=For%20example%2C%20Florida%2C%20Illinois%2C,(PWS)%20in%20various%20states (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Source Intelligence. PFAS Regulations by State for Consumer Products. Available online: https://blog.sourceintelligence.com/us-pfas-regulations-by-state#:~:text=PFAS%20are%20widely%20used%20in,gear%2C%20to%20enhance%20their%20durability (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Mavingui, P.; Boetsch, G.; Boissier, J.; Darriet, F.; Duboz, P.; Fritsch, C.; Giraudoux, P.; Le Roux, F.; Morand, S.; et al. The One Health Concept: 10 Years Old and a Long Road Ahead. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ankley, G.T.; Cureton, P.; Hoke, R.A.; Houde, M.; Kumar, A.; Kurias, J.; Lanno, R.; McCarthy, C.; Newsted, J.; Salice, C.J.; et al. Assessing the Ecological Risks of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Current State-of-the Science and a Proposed Path Forward. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 564–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).