Notch Signaling Pathway Regulates Ozone-Induced Lung Circadian Rhythm Disruption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Exposure
2.2. RNA Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.3. Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) Analysis
2.4. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Construction
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Reverse Transcription Quantitative PCR Validation
2.7. GEO Data Acquisition and Source
2.8. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
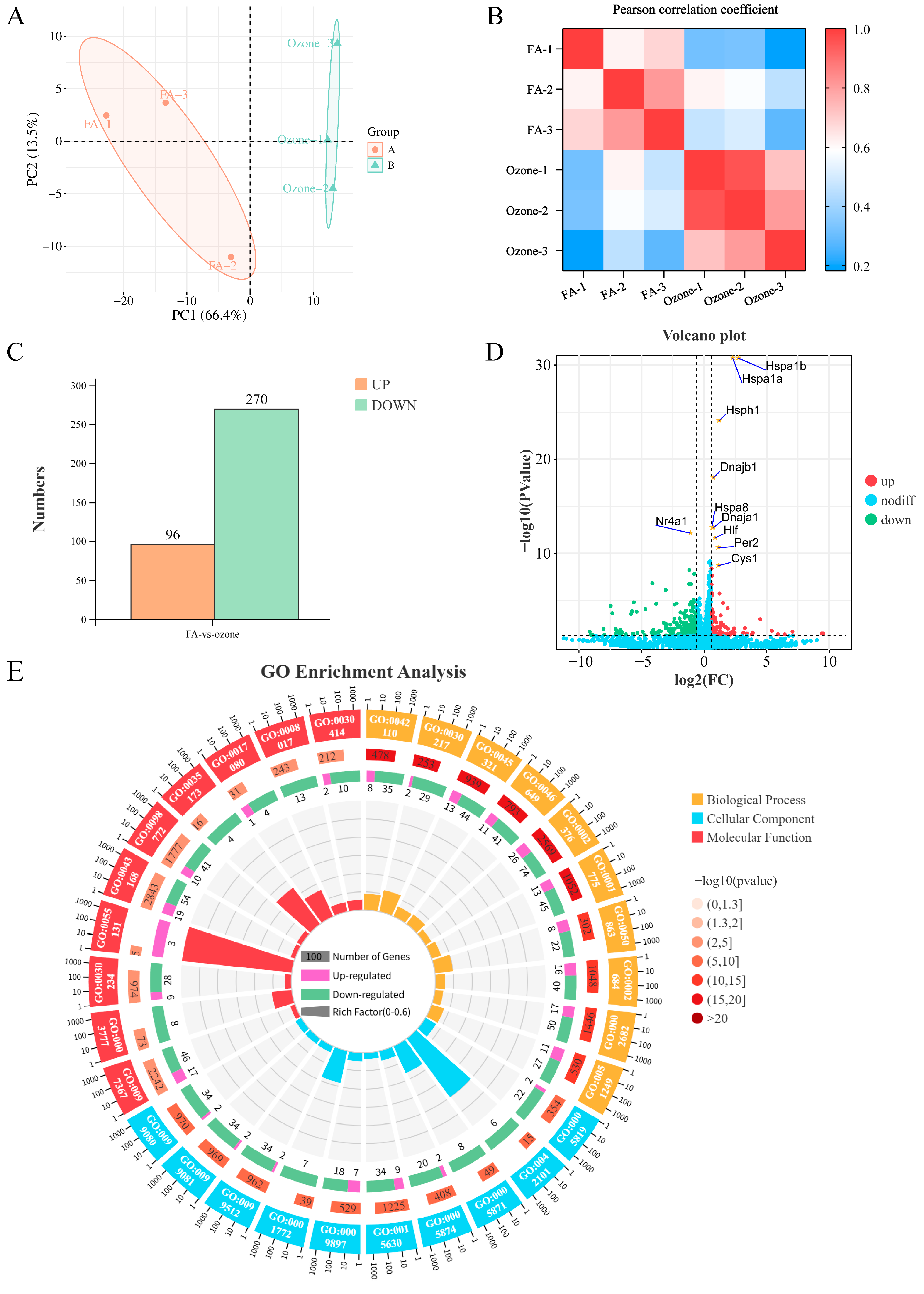
3.1. Transcriptomic Profiling Revealed Profound O3-Induced Alterations in Murine Lungs
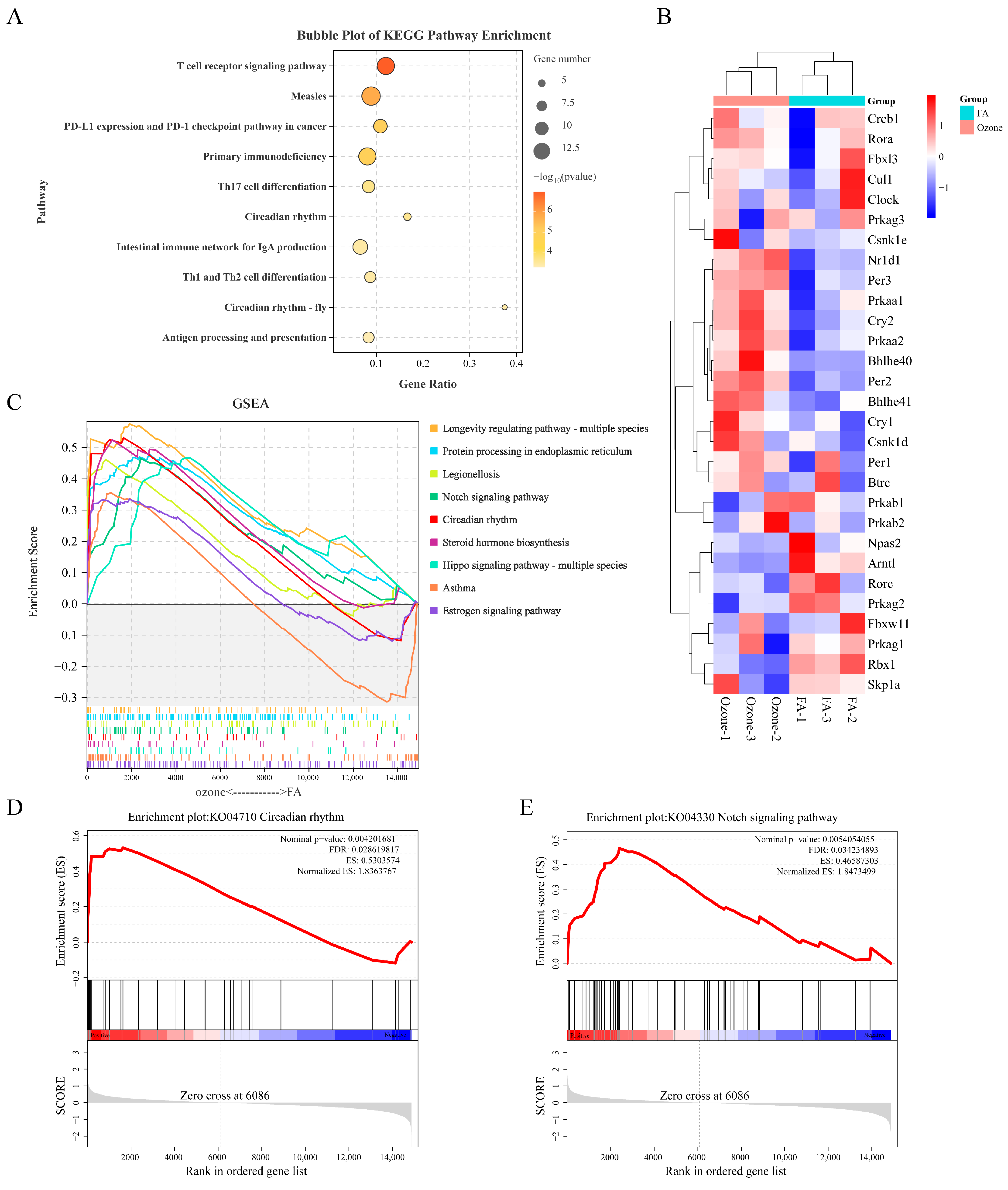
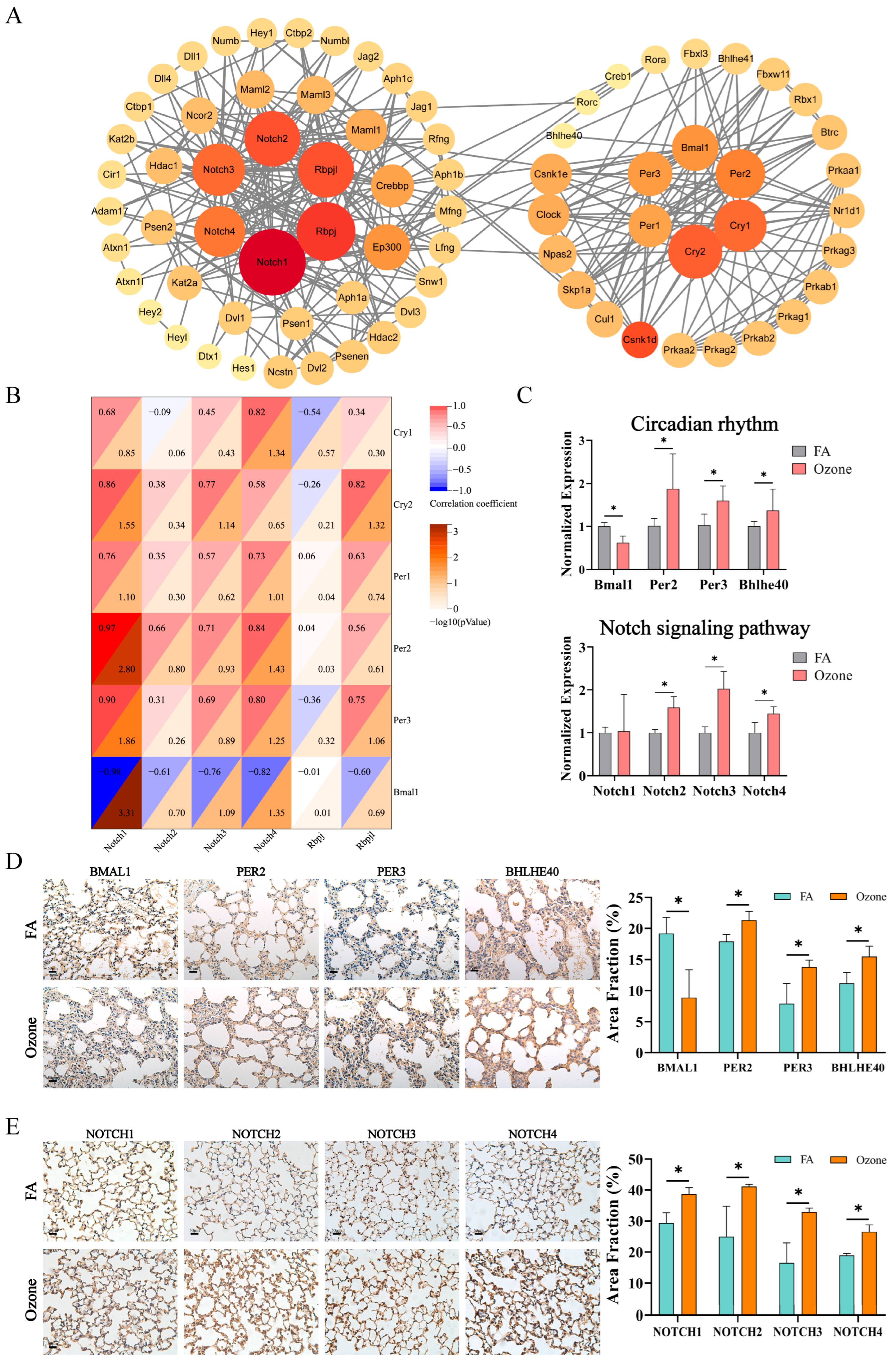
3.2. Notch Signaling Pathway and Circadian Rhythm Significantly Upregulated After O3 Exposure
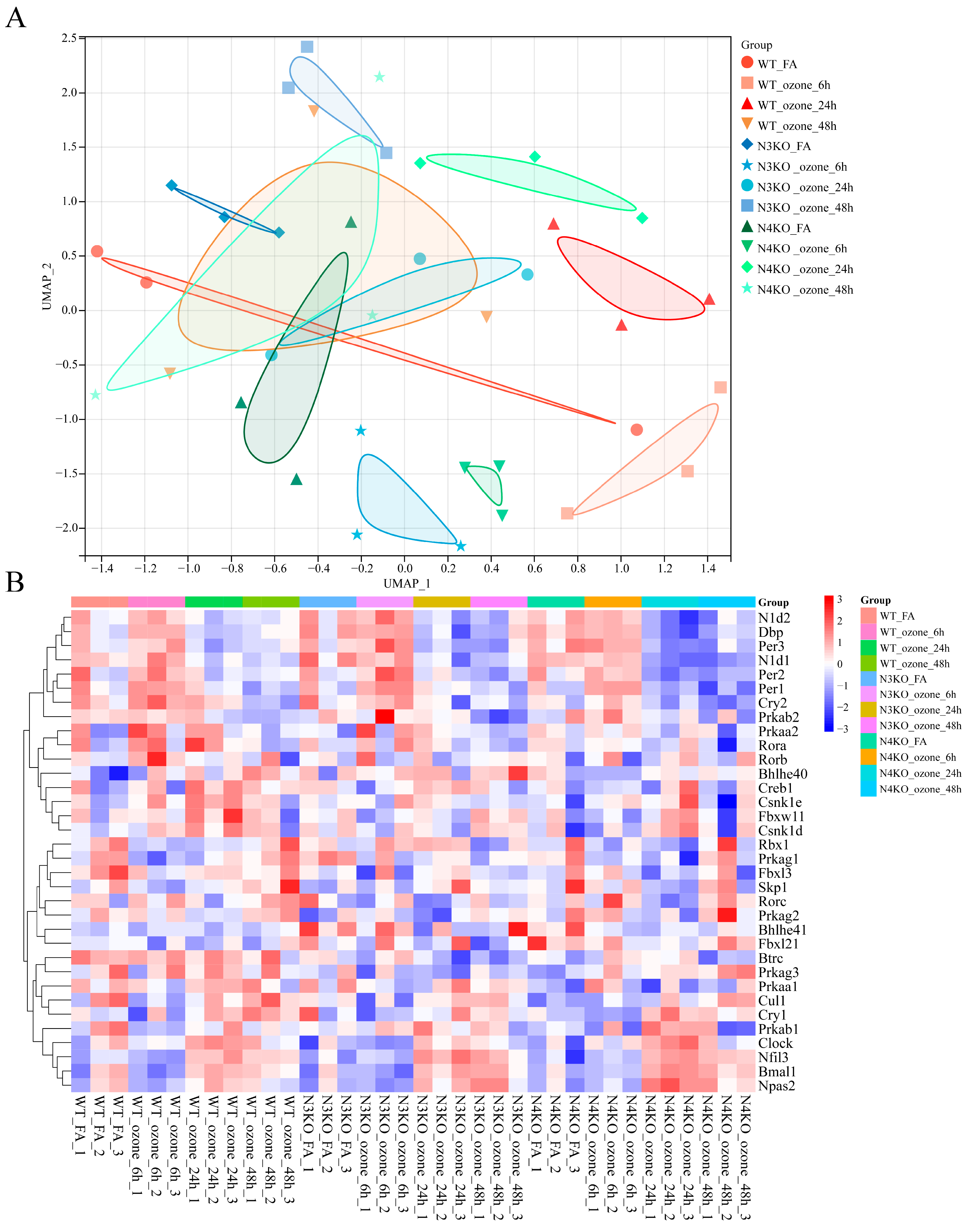
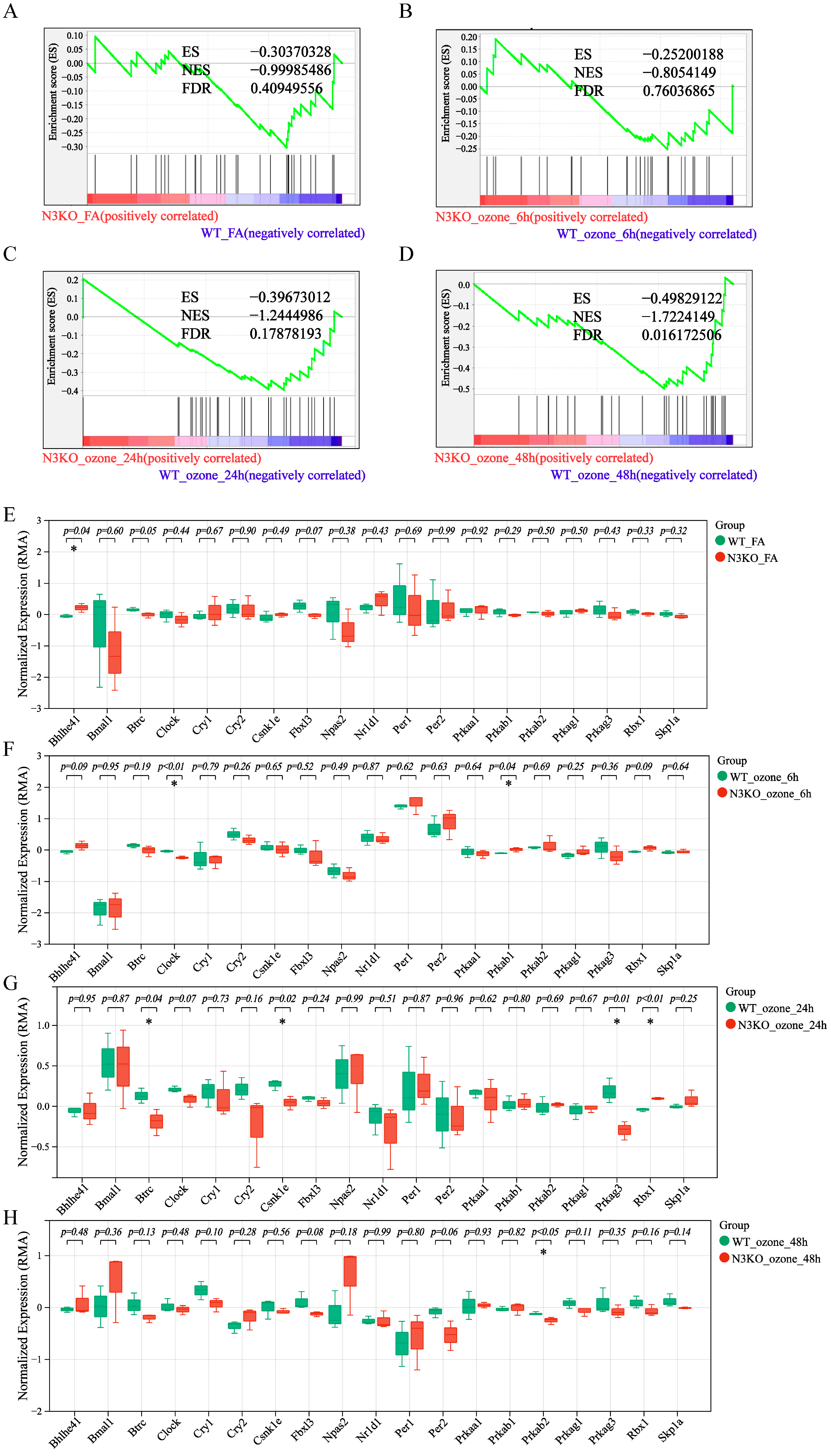
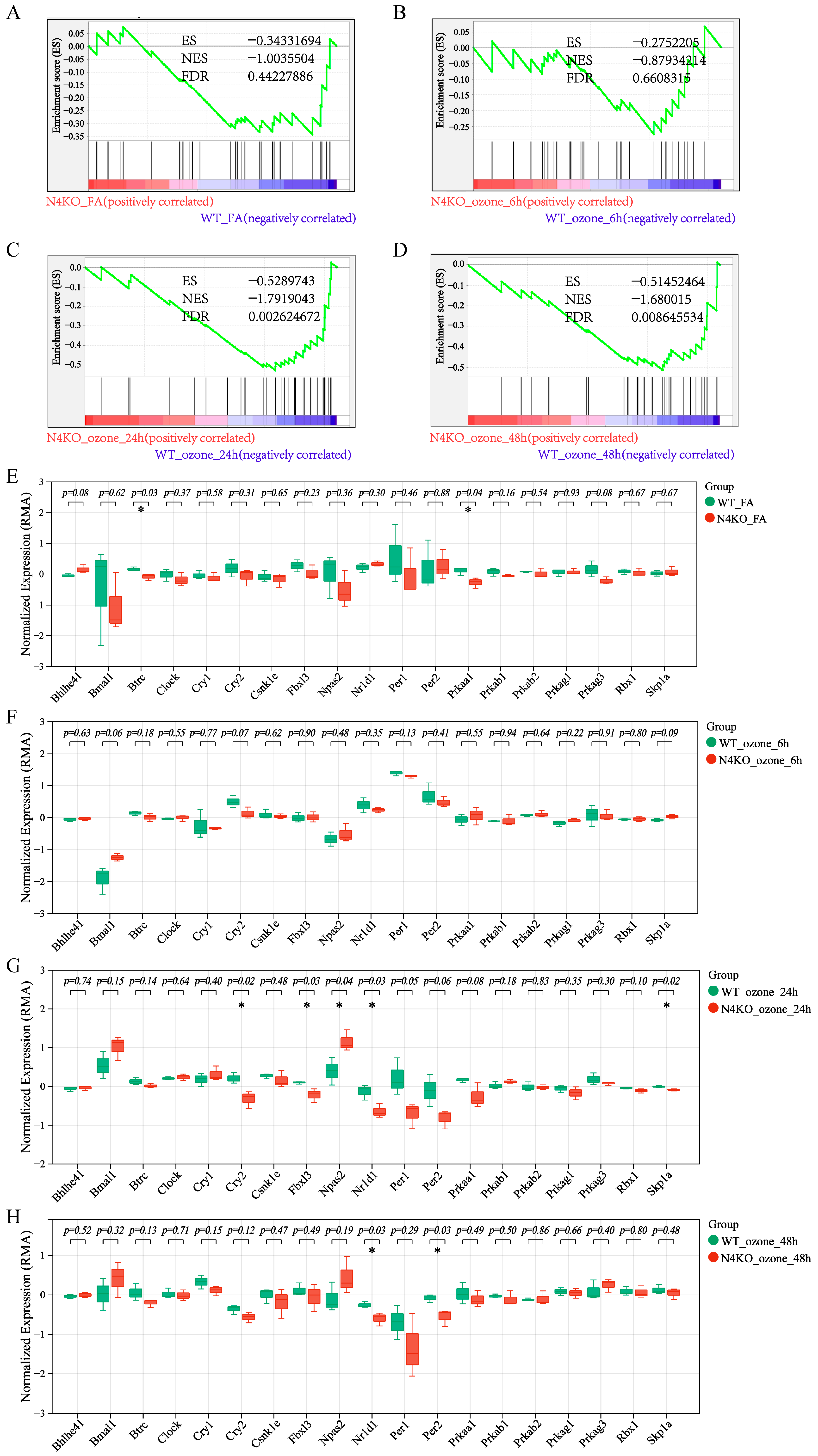
3.3. O3 Exposure Leads to Altered Circadian Rhythm Expression Patterns in the Lungs After Notch3/4 Knockout
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, B.; Zhen, L.; Wang, L.; Zhong, H.; Lin, C.; Yang, L.; Xu, W.; Huang, R.J. Revisiting the impact of temperature on ground-level ozone: A causal inference approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ou, X.; Sheng, D.; Yao, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, Q. Identification of response regulation governing ozone formation based on influential factors using a random forest approach. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, M.; Tang, G. Critical role of vertical exchange in the boundary layer on urban photochemical pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 987, 179779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assareh, N.; Beddows, A.; Stewart, G.; Holland, M.; Fecht, D.; Walton, H.; Evangelopoulos, D.; Wood, D.; Vu, T.; Dajnak, D.; et al. What Impact Does Net Zero Action on Road Transport and Building Heating Have on Exposure to UK Air Pollution? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 1274–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Yang, J. Effect of ambient ozone pollution on disease burden globally: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Li, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zong, L.; Wang, M.; Xie, Z.; Ho, H.C.; Gao, M.; et al. Substantially underestimated global health risks of current ozone pollution. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, R.C.; Togbe, D.; Couillin, I.; Segueni, N.; Han, L.; Quesniaux, V.F.J.; Stoeger, T.; Ryffel, B. Ozone-induced lung injury and inflammation: Pathways and therapeutic targets for pulmonary diseases caused by air pollutants. Environ. Int. 2025, 198, 109391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjomandi, M.; Balmes, J.R.; Frampton, M.W.; Bromberg, P.; Rich, D.Q.; Stark, P.; Alexis, N.E.; Costantini, M.; Hollenbeck-Pringle, D.; Dagincourt, N.; et al. Respiratory Responses to Ozone Exposure. MOSES (The Multicenter Ozone Study in Older Subjects). Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malig, B.J.; Pearson, D.L.; Chang, Y.B.; Broadwin, R.; Basu, R.; Green, R.S.; Ostro, B. A Time-Stratified Case-Crossover Study of Ambient Ozone Exposure and Emergency Department Visits for Specific Respiratory Diagnoses in California (2005–2008). Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, A.; Forrest, K.M.; Paul, O.; Issah, Y.; Valekunja, U.K.; Tang, S.Y.; Reddy, A.B.; Hennessy, E.J.; Brooks, T.G.; Chaudhry, F.; et al. Circadian regulation of lung repair and regeneration. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e164720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.; Wang, Q.; Rahman, I.; Sundar, I.K. Circadian molecular clock disruption in chronic pulmonary diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiermann, C.; Kunisaki, Y.; Frenette, P.S. Circadian control of the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomino-Segura, M.; Hidalgo, A. Circadian immune circuits. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20200798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Li, K.Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Wei, C.J.; Gao, Y.X.; Ren, Z.; Zhong, Y.B.; Yin, Z.J.; Ren, D.L. ROS regulates circadian rhythms by modulating Ezh2 interactions with clock proteins. Redox Biol. 2025, 81, 103526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, A.G.; Doherty, C.J.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Kay, S.A.; Schippers, J.H.; Dijkwel, P.P. CIRCADIAN CLOCK-ASSOCIATED 1 regulates ROS homeostasis and oxidative stress responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17129–17134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Pfrender, E.M.; Steffeck, A.W.T.; Reczek, C.R.; Zhou, Y.; Thakkar, A.V.; Gupta, N.R.; Kupai, A.; Willbanks, A.; Lieber, R.L.; et al. Immunomodulatory role of the stem cell circadian clock in muscle repair. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eadq8538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agusti, A.; Hedner, J.; Marin, J.M.; Barbé, F.; Cazzola, M.; Rennard, S. Night-time symptoms: A forgotten dimension of COPD. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2011, 20, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheer, F.A.J.L.; Hilton, M.F.; Evoniuk, H.L.; Shiels, S.A.; Malhotra, A.; Sugarbaker, R.; Ayers, R.T.; Israel, E.; Massaro, A.F.; Shea, S.A. The endogenous circadian system worsens asthma at night independent of sleep and other daily behavioral or environmental cycles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2018486118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incalzi, R.A.; Blasi, F.; Canonica, G.W.; Foschino, M.P.; Prediletto, R.; Simoni, L.; Ori, A.; Giovannetti, C.; Barsanti, S.; Scichilone, N. The Prescribing Practice for COPD: Relationship to Circadian Rhythm, Disease Severity, and Clinical Phenotype in the STORICO Observational Study. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 5582–5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannakopoulos, T.; Bauer, M.R.; Davidson, S.M.; Heimann, M.; Subbaraj, L.; Bhutkar, A.; Bartlebaugh, J.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Jacks, T. Circadian Rhythm Disruption Promotes Lung Tumorigenesis. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sundar, I.K.; Lucas, J.H.; Muthumalage, T.; Rahman, I. Molecular clock REV-ERBα regulates cigarette smoke–induced pulmonary inflammation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e145200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zasłona, Z.; Case, S.; Early, J.O.; Lalor, S.J.; McLoughlin, R.M.; Curtis, A.M.; O’Neill, L.A.J. The circadian protein BMAL1 in myeloid cells is a negative regulator of allergic asthma. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 312, L855–L860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Guo, Y.; Jian, X.; Miao, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Feng, F. Revealing the Molecular Mechanisms of Ozone-Induced Pulmonary Inflammatory Injury: Integrated Analysis of Metabolomics and Transcriptomics. Toxics 2025, 13, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, N.; Guo, C.; Lu, S.; Wei, Y. Transcriptome Profiling of the Lungs Reveals Molecular Clock Genes Expression Changes after Chronic Exposure to Ambient Air Particles. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2017, 14, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivel, R.; Vinayachandran, V.; Biswal, S.; Deiuliis, J.A.; Padmanabhan, R.; Park, B.; Gangwar, R.S.; Durieux, J.C.; Ebreo Cara, E.A.; Das, L.; et al. Exposure to Air Pollution Disrupts Circadian Rhythm through Alterations in Chromatin Dynamics. iScience 2020, 23, 101728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentner, N.J.; Weber, L.P. Intranasal benzo[a]pyrene alters circadian blood pressure patterns and causes lung inflammation in rats. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Glickman, J.; Subramaniam, M.; Shahsafaei, A.; Allamneni, K.P.; Aster, J.C.; Sklar, J.; Sunday, M.E. Functional diversity of notch family genes in fetal lung development. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2004, 286, L1075–L1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.T.; Nichol, K.S.; Chander Veerati, P.; Moheimani, F.; Kicic, A.; Stick, S.M.; Bartlett, N.W.; Grainge, C.L.; Wark, P.A.B.; Hansbro, P.M.; et al. Blocking Notch3 Signaling Abolishes MUC5AC Production in Airway Epithelial Cells from Individuals with Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 62, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, D.; Ouyang, R.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, P. Notch signaling in lung diseases: Focus on Notch1 and Notch3. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2016, 10, 468–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, A.; Gnemmi, I.; Rosani, U.; Maniscalco, M.; D’Anna, S.E.; Brun, P.; Carriero, V.; Bertolini, F.; Balbi, B.; Ricciardolo, F.L.M. Upregulation of Notch Signaling and Cell-Differentiation Inhibitory Transcription Factors in Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Tan, Q.; Tan, W.; Zhang, L.I. Cigarette smoke induces the expression of Notch3, not Notch1, protein in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, F.; Yin, Q.; Li, Z.; Shao, L.; Zhou, D.; Liu, L. The Circadian System Is Essential for the Crosstalk of VEGF-Notch-mediated Endothelial Angiogenesis in Ischemic Stroke. Neurosci. Bull. 2023, 39, 1375–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, S.; Ethel, M.; Bretegnier, V.; Goachet, C.; Wotawa, C.A.; Luka, M.; Coulpier, F.; Masson, C.; Ménager, M.; Colnot, C. Single-nucleus transcriptomics reveal the differentiation trajectories of periosteal skeletal/stem progenitor cells in bone regeneration. Elife 2024, 13, RP92519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpowicz, P.; Zhang, Y.; Hogenesch, J.B.; Emery, P.; Perrimon, N. The circadian clock gates the intestinal stem cell regenerative state. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskalev, A.; Shaposhnikov, M.; Snezhkina, A.; Kogan, V.; Plyusnina, E.; Peregudova, D.; Melnikova, N.; Uroshlev, L.; Mylnikov, S.; Dmitriev, A.; et al. Mining gene expression data for pollutants (dioxin, toluene, formaldehyde) and low dose of gamma-irradiation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhein, K.C.; McCaw, Z.; Gladwell, W.; Trivedi, S.; Bushel, P.R.; Kleeberger, S.R. Novel Roles for Notch3 and Notch4 Receptors in Gene Expression and Susceptibility to Ozone-Induced Lung Inflammation in Mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilburg-Basnyat, B.; Reece, S.W.; Crouch, M.J.; Luo, B.; Boone, A.D.; Yaeger, M.; Hodge, M.; Psaltis, C.; Hannan, J.L.; Manke, J.; et al. Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators Regulate Ozone-Induced Pulmonary and Systemic Inflammation. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 163, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Kong, X.; Jian, X.; Bo, Y.; Miao, X.; Chen, H.; Shang, P.; Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Fatty acids metabolism in ozone-induced pulmonary inflammatory injury: Evidence, mechanism and prevention. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 933, 173222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Xu, P.; Wu, X.; Gong, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Li, G.; Sang, N.; et al. Lung injuries induced by ozone exposure in female mice: Potential roles of the gut and lung microbes. Environ. Int. 2024, 183, 108422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Si, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Wu, J.; Chen, L.; Wei, C.; et al. The impact of ambient ozone pollution on pneumonia: A nationwide time-series analysis. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, S.M.; Balmes, J.R. Systematic Review of Ozone Effects on Human Lung Function, 2013 Through 2020. Chest 2022, 161, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundar, I.K.; Duraisamy, S.K.; Choudhary, I.; Saini, Y.; Silveyra, P. Acute and Repeated Ozone Exposures Differentially Affect Circadian Clock Gene Expression in Mice. Adv. Biol. (Weinh) 2023, 7, e2300045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, A.; Yang, H.; Ji, J.; Chen, Y.; Bao, W.; Li, F.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, X.; Li, Q.; Ben, S. Involvements of p38 MAPK and oxidative stress in the ozone-induced enhancement of AHR and pulmonary inflammation in an allergic asthma model. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, J.; Reick, M.; Wu, L.C.; McKnight, S.L. Regulation of clock and NPAS2 DNA binding by the redox state of NAD cofactors. Science 2001, 293, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.K.; Yamada, R.G.; Ukai, H.; Baggs, J.E.; Miraglia, L.J.; Kobayashi, T.J.; Welsh, D.K.; Kay, S.A.; Ueda, H.R.; Hogenesch, J.B. Feedback repression is required for mammalian circadian clock function. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, T.; Noshiro, M.; Sato, F.; Maemura, K.; Takeda, N.; Nagai, R.; Iwata, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Furukawa, M.; Miyazaki, K.; et al. A novel autofeedback loop of Dec1 transcription involved in circadian rhythm regulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 313, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, C.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, C.; Shi, M. Circadian clock gene Clock-Bmal1 regulates cellular senescence in Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, N.; Huang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, R. Role of NLRP3 in the exacerbation of ozone-induced allergic rhinitis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 265, 115506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Early, J.O.; Menon, D.; Wyse, C.A.; Cervantes-Silva, M.P.; Zaslona, Z.; Carroll, R.G.; Palsson-McDermott, E.M.; Angiari, S.; Ryan, D.G.; Corcoran, S.E.; et al. Circadian clock protein BMAL1 regulates IL-1β in macrophages via NRF2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8460–E8468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Meng, X.; Liu, Z.; Tang, M.; Lv, Z.; Huang, X.; Jin, H.; Han, X.; Liu, X.; Pu, W.; et al. Tracing the origin of alveolar stem cells in lung repair and regeneration. Cell 2024, 187, 2428–2445.e2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, D.; Li, J.; Cai, S.; He, S.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, J.; Chen, S.; Long, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, P.; et al. Notch1 regulates endothelial apoptosis via the ERK pathway in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2018, 315, C330–C340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Gong, D.; Wang, W. Soluble JAGGED1 inhibits pulmonary hypertension by attenuating notch signaling. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 2733–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.M.; Ye, Y.Z.; Qian, Z.D.; Zhang, Y.B. Notch signaling molecules as prognostic biomarkers for non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 3252–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ding, W.; Deng, X. PM(2.5), Fine Particulate Matter: A Novel Player in the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition? Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garriga-Canut, M.; Roopra, A.; Buckley, N.J. The basic helix-loop-helix protein, sharp-1, represses transcription by a histone deacetylase-dependent and histone deacetylase-independent mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 14821–14828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orian, A.; Gonen, H.; Bercovich, B.; Fajerman, I.; Eytan, E.; Israël, A.; Mercurio, F.; Iwai, K.; Schwartz, A.L.; Ciechanover, A. SCF(beta)(-TrCP) ubiquitin ligase-mediated processing of NF-kappaB p105 requires phosphorylation of its C-terminus by IkappaB kinase. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 2580–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaron, A.; Hatzubai, A.; Davis, M.; Lavon, I.; Amit, S.; Manning, A.M.; Andersen, J.S.; Mann, M.; Mercurio, F.; Ben-Neriah, Y. Identification of the receptor component of the IkappaBalpha-ubiquitin ligase. Nature 1998, 396, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, D.F.; Shackelford, D.B.; Mihaylova, M.M.; Gelino, S.; Kohnz, R.A.; Mair, W.; Vasquez, D.S.; Joshi, A.; Gwinn, D.M.; Taylor, R.; et al. Phosphorylation of ULK1 (hATG1) by AMP-activated protein kinase connects energy sensing to mitophagy. Science 2011, 331, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirogane, T.; Jin, J.; Ang, X.L.; Harper, J.W. SCFbeta-TRCP controls clock-dependent transcription via casein kinase 1-dependent degradation of the mammalian period-1 (Per1) protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 26863–26872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.W.; Hawley, S.A.; Green, K.A.; Anis, M.; Stewart, G.; Scullion, G.A.; Norman, D.G.; Hardie, D.G. CBS domains form energy-sensing modules whose binding of adenosine ligands is disrupted by disease mutations. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, E.-K. AMP-activated protein kinase as a key molecular link between metabolism and clockwork. Exp. Mol. Med. 2013, 45, e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liwocha, J.; Li, J.; Purser, N.; Rattanasopa, C.; Maiwald, S.; Krist, D.T.; Scott, D.C.; Steigenberger, B.; Prabu, J.R.; Schulman, B.A.; et al. Mechanism of millisecond Lys48-linked poly-ubiquitin chain formation by cullin-RING ligases. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2024, 31, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Leaderer, D.; Guss, C.; Brown, H.N.; Zhang, Y.; Boyle, P.; Stevens, R.G.; Hoffman, A.; Qin, Q.; Han, X.; et al. Ala394Thr polymorphism in the clock gene NPAS2: A circadian modifier for the risk of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Zhao, X.; Hatori, M.; Yu, R.T.; Barish, G.D.; Lam, M.T.; Chong, L.W.; DiTacchio, L.; Atkins, A.R.; Glass, C.K.; et al. Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by REV-ERB-α and REV-ERB-β. Nature 2012, 485, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killian, D.J.; Harvey, E.; Johnson, P.; Otori, M.; Mitani, S.; Xue, D. SKR-1, a homolog of Skp1 and a member of the SCF(SEL-10) complex, regulates sex-determination and LIN-12/Notch signaling in C. elegans. Dev. Biol. 2008, 322, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.C.; Rhee, D.Y.; Duda, D.M.; Kelsall, I.R.; Olszewski, J.L.; Paulo, J.A.; de Jong, A.; Ovaa, H.; Alpi, A.F.; Harper, J.W.; et al. Two Distinct Types of E3 Ligases Work in Unison to Regulate Substrate Ubiquitylation. Cell 2016, 166, 1198–1214.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Sequences 5′-3′ | |
|---|---|---|
| Bmal1 | Forward | CTCAACCATCAGCGACTTCA |
| Reverse | CCTTCCTTGGTGTTCTGCAT | |
| Per2 | Forward | AAAGCTGACGCACACAAAGAA |
| Reverse | ACTCCTCATTAGCCTTCACCT | |
| Per3 | Forward | AACACGAAGACCGAAACAGAAT |
| Reverse | CTCGGCTGGGAAATACTTTTTCA | |
| Bhlhe40 | Forward | CCGATTCTCCTCCATAGCCACT |
| Reverse | ACCTCCAGGAAGCCATCAGACC | |
| Notch1 | Forward | CAGGCAATCCGAGGACTATG |
| Reverse | CAGGCGTGTTGTTCTCACAG | |
| Notch2 | Forward | TGGTGGTCAGTGCATGGATAG |
| Reverse | ATCTGGGGACACACATCGAC | |
| Notch3 | Forward | TGGCGACCTCACTTAAGACT |
| Reverse | CACTGGCAGTTATAGGTGTTGAC | |
| Notch4 | Forward | CGAGGAAGATACGGAGTGGC |
| Reverse | CTGCTCTGGTGGGCATACAT | |
| β-actin | Forward | GGCCAACCGTGAAAAGATGA |
| Reverse | CAGCCTGGATGGCTACGTACA | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Jian, X.; Miao, X.; Jia, Y. Notch Signaling Pathway Regulates Ozone-Induced Lung Circadian Rhythm Disruption. Toxics 2025, 13, 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090733
Zhang X, Jian X, Miao X, Jia Y. Notch Signaling Pathway Regulates Ozone-Induced Lung Circadian Rhythm Disruption. Toxics. 2025; 13(9):733. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090733
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xinyu, Xiaotong Jian, Xinyi Miao, and Yangyang Jia. 2025. "Notch Signaling Pathway Regulates Ozone-Induced Lung Circadian Rhythm Disruption" Toxics 13, no. 9: 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090733
APA StyleZhang, X., Jian, X., Miao, X., & Jia, Y. (2025). Notch Signaling Pathway Regulates Ozone-Induced Lung Circadian Rhythm Disruption. Toxics, 13(9), 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090733







