Direct and In-Utero Exposure to Quaternary Ammonium Disinfectants Alters Sperm Parameters and mRNA Expression of Epigenetic Enzymes in the Testes of Male CD-1 Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Husbandry for Mating Indices and Pregnancy Rates
2.2. Mating Indices and Pregnancy Rates
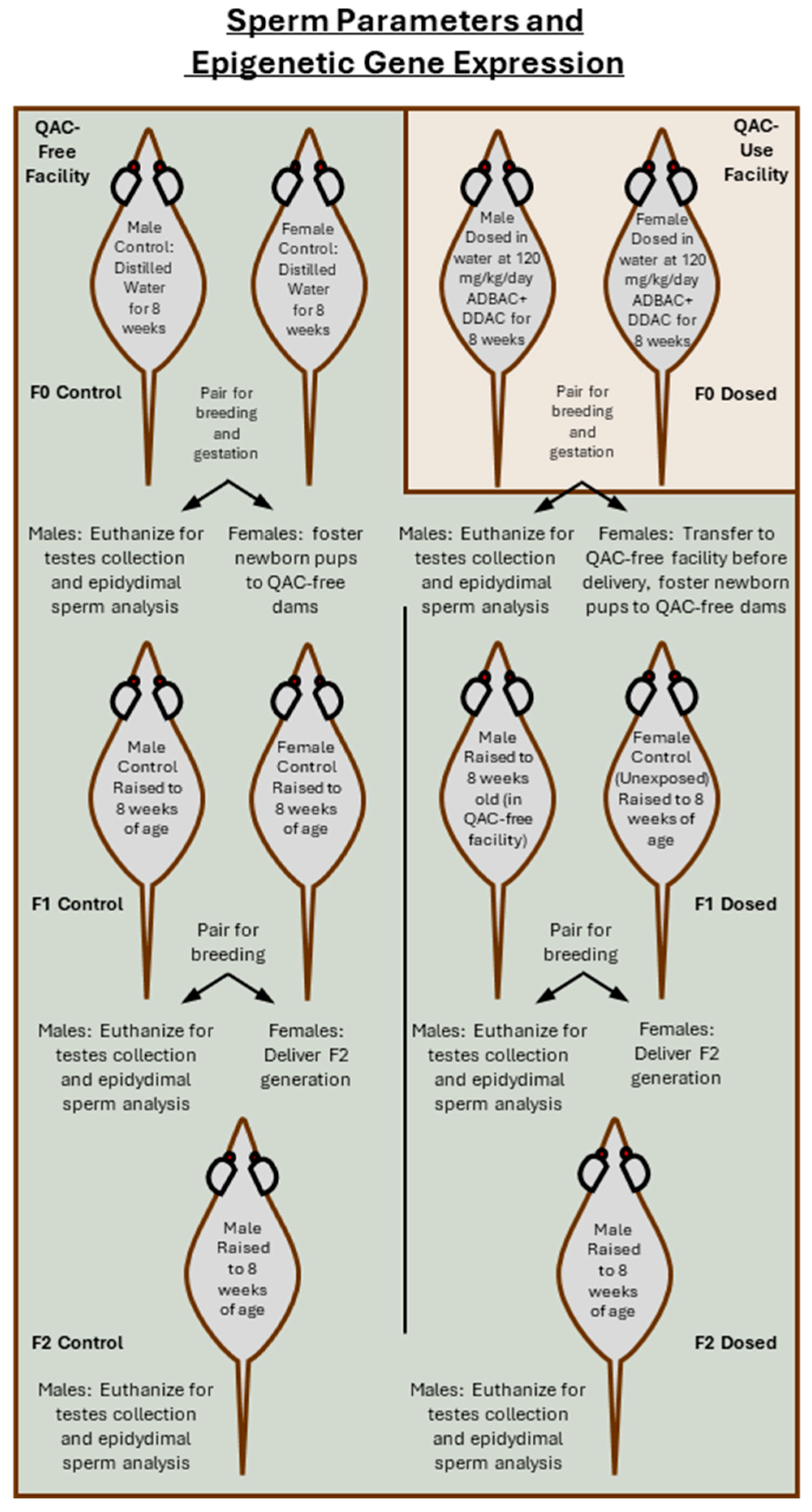
2.3. Husbandry for Generational Assessment of Sperm Parameters and Testis mRNA Expression
2.4. Sperm Collection and Computer-Automated Sperm Analysis (CASA)
2.5. mRNA Expression Determination
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Mating Indices and Pregnancy Rates
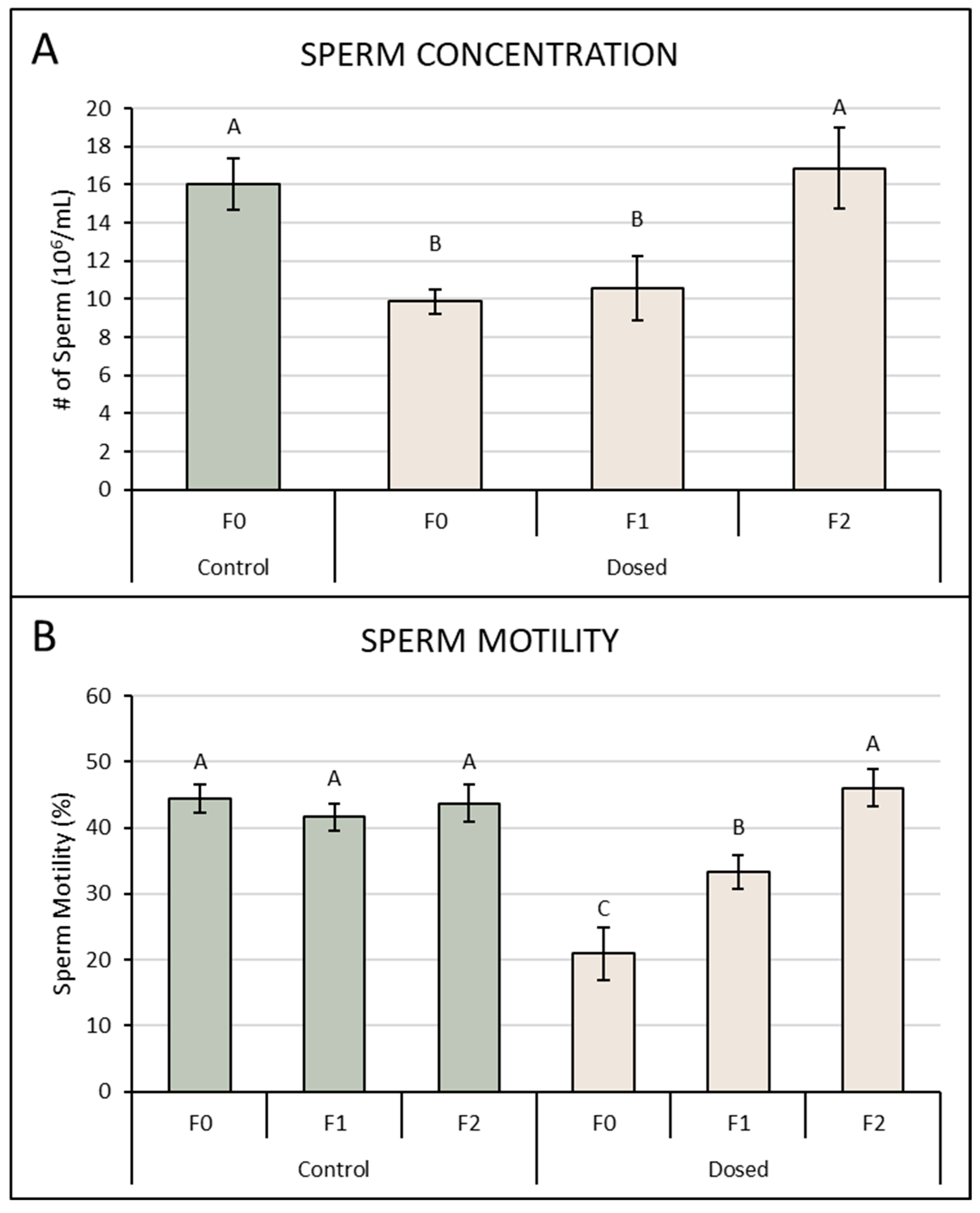
3.2. Sperm Concentration and Motility
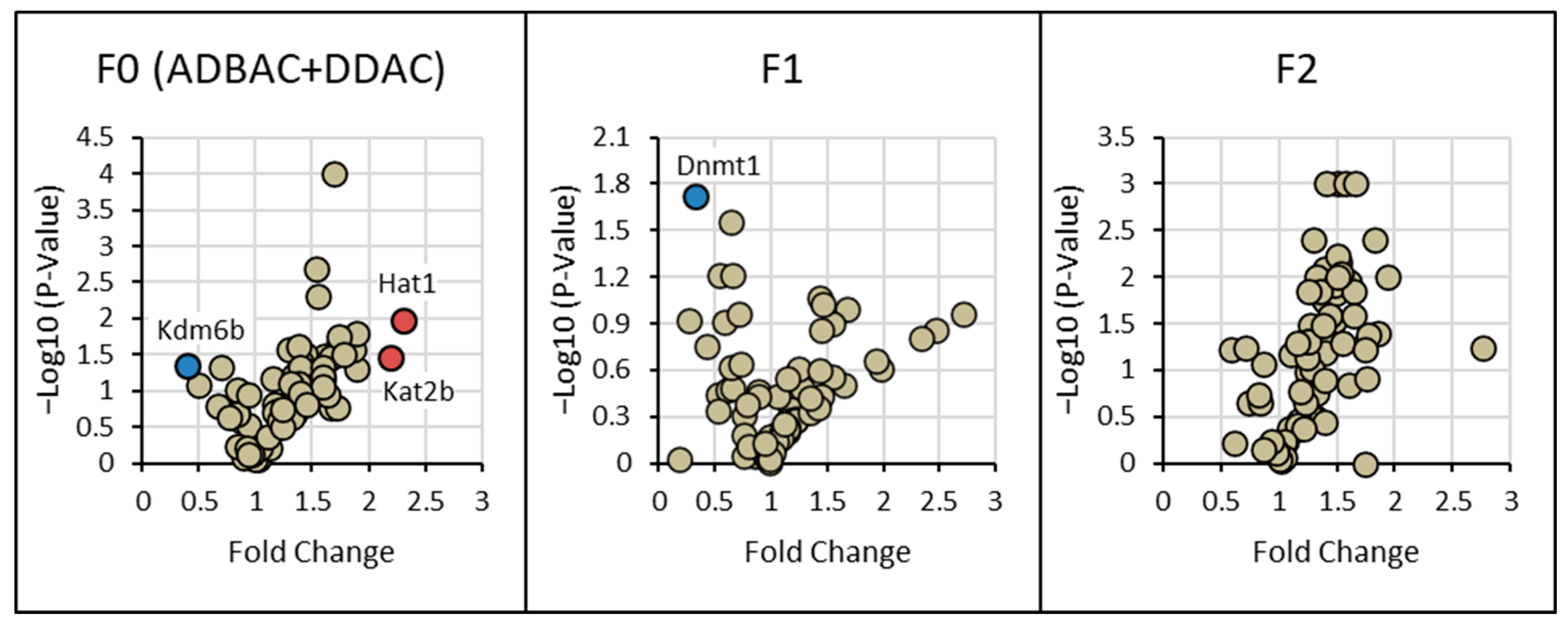
3.3. Gene Expression of Chromatin-Modifying Enzymes
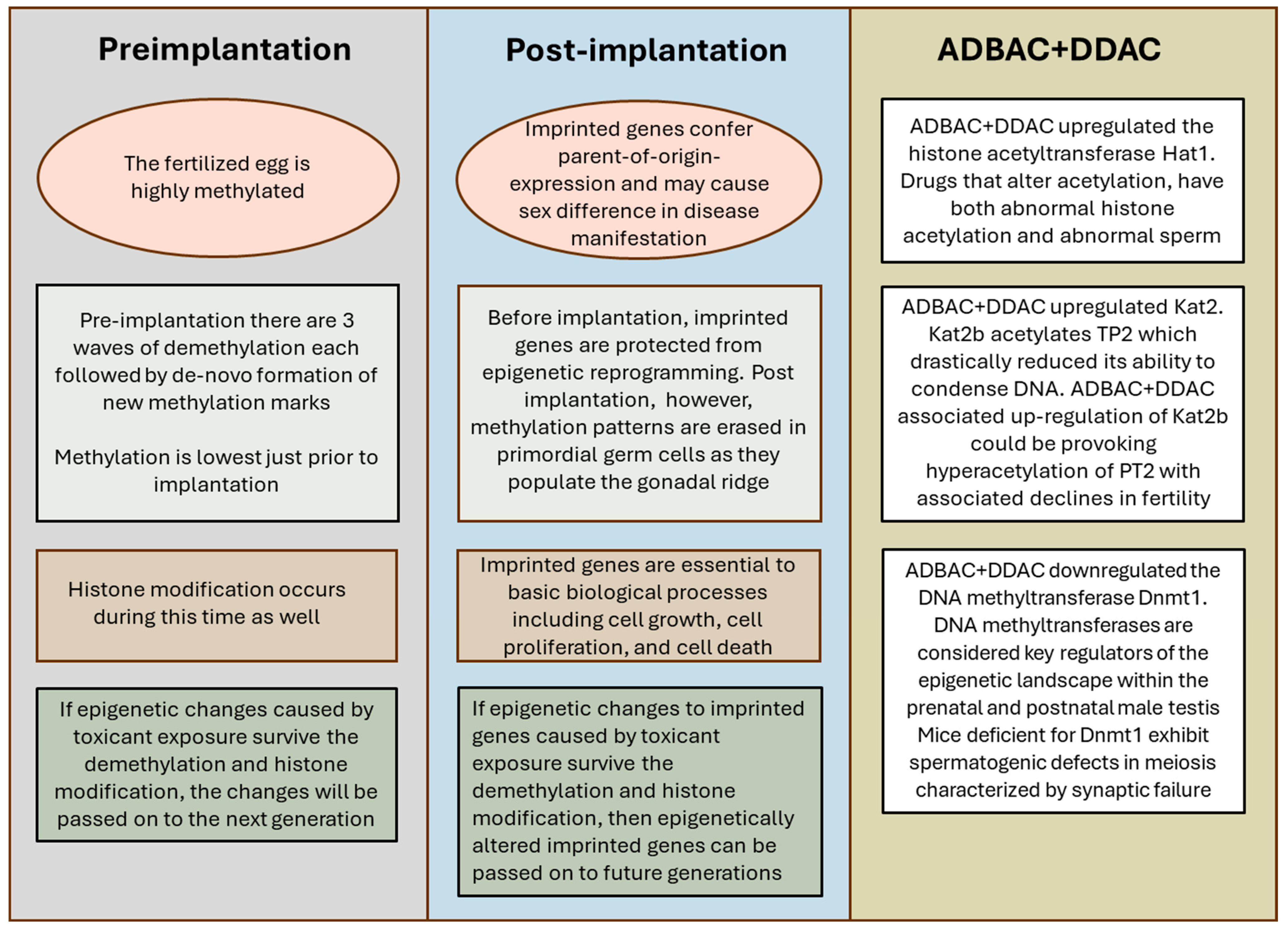
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| QACs | Quaternary Ammonium Compounds |
| ADBAC | Alkyl Dimethyl Benzyl Ammonium Chloride |
| DDAC | Didecyl Dimethyl Ammonium Chloride |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| CASA | Computer-automated Sperm Analysis |
| Hats | Histone Acetyltransferase |
| EDCs | Endocrine Disrupting Compounds |
References
- Ford, M.J.; Tetler, L.W.; White, J.; Rimmer, D. Determination of Alkyl Benzyl and Dialkyl Dimethyl Quaternary Ammonium Biocides in Occupational Hygiene and Environmental Media by Liquid Chromatography with Electrospray Ionisation Mass Spectrometry and Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 952, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrubec, T.C.; Seguin, R.P.; Xu, L.; Cortopassi, G.A.; Datta, S.; Hanlon, A.L.; Lozano, A.J.; McDonald, V.A.; Healy, C.A.; Anderson, T.C.; et al. Altered Toxicological Endpoints in Humans from Common Quaternary Ammonium Compound Disinfectant Exposure. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zheng, G.; Webster, T.F.; Salamova, A. Quaternary Ammonium Compounds: Bioaccumulation Potentials in Humans and Levels in Blood Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 14689–14698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melin, V.E.; Potineni, H.; Hunt, P.; Griswold, J.; Siems, B.; Werre, S.R.; Hrubec, T.C. Exposure to Common Quaternary Ammonium Disinfectants Decreases Fertility in Mice. Reprod. Toxicol. 2014, 50, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Melin, V.E.; Melin, T.E.; Dessify, B.J.; Nguyen, C.T.; Shea, C.S.; Hrubec, T.C. Quaternary Ammonium Disinfectants Cause Subfertility in Mice by Targeting Both Male and Female Reproductive Processes. Reprod. Toxicol. 2016, 59, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, Z.A.; Melin, V.E.; Hrubec, T.C. Quaternary Ammonium Compound Exposure Causes Infertility by Altering Endocrine Signaling and Gametogenesis. Reprod. Toxicol. 2025, 132, 108817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2020 Assisted Reproductive Technology Fertility Clinic and National Summary Report. US Dept of Health and Human Services, 2022. Available online: https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/148215 (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Kumar, N.; Singh, A.K. Trends of Male Factor Infertility, an Important Cause of Infertility: A Review of Literature. J. Hum. Reprod. Sci. 2015, 8, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Giwercman, A.; Carlsen, E.; Keiding, N.; Skakkebaek, N.E. Evidence for Increasing Incidence of Abnormalities of the Human Testis: A Review. Environ. Health Perspect. 1993, 101 (Suppl. 2), 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sharpe, R.M. Sperm Counts and Fertility in Men: A Rocky Road Ahead. Science & Society Series on Sex and Science. EMBO Rep. 2012, 13, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gottardo, F.; Kliesch, S.; World Health Organization. Semen Analysis: Spermiogram According to WHO2010 Criteria. Urologe. Ausg. A 2011, 50, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, J.E.; Costa, M. Epigenetics and the Environment. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 983, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, D.N.; Krawczak, M.; Polychronakos, C.; Tyler-Smith, C.; Kehrer-Sawatzki, H. Where Genotype Is Not Predictive of Phenotype: Towards An Understanding of the Molecular Basis of Reduced Penetrance in Human Inherited Disease. Hum. Genet. 2013, 132, 1077–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Costa, E.; Dong, E.; Grayson, D.R.; Guidotti, A.; Ruzicka, W.; Veldic, M. Reviewing The Role of DNA (Cytosine-5) Methyltransferase Overexpression in the Cortical GABAergic Dysfunction Associated with Psychosis Vulnerability. Epigenetics. Epigenetics 2007, 2, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grayson, D.R.; Guidotti, A. The Dynamics of DNA Methylation in Schizophrenia and Related Psychiatric Disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 138–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Charlton, J.; Williams, R.D.; Sebire, N.J.; Popov, S.; Vujanic, G.; Chagtai, T.; Alcaide-German, M.; Morris, T.; Butcher, L.M.; Guilhamon, P.; et al. Comparative Methylome Analysis Identifies New Tumour Subtypes and Biomarkers for Transformation of Nephrogenic Rests into Wilms Tumour. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, Q.; Wei, W.; Jiang, Y.I.; Yang, H.; Liu, J. Promoter Methylation and Expression Changes of BRCA1 in Cancerous Tissues of Patients with Sporadic Breast Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 1807–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Marumo, T.; Yagi, S.; Kawarazaki, W.; Nishimoto, M.; Ayuzawa, N.; Watanabe, A.; Ueda, K.; Hirahashi, J.; Hishikawa, K.; Sakurai, H.; et al. Diabetes Induces Aberrant DNA Methylation in the Proximal Tubules of the Kidney. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2388–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Klibaner-Schiff, E.; Simonin, E.M.; Akdis, C.A.; Cheong, A.; Johnson, M.M.; Karagas, M.R.; Kirsh, S.; Kline, O.; Mazumdar, M.; Oken, E.; et al. Environmental Exposures Influence Multigenerational Epigenetic Transmission. Clin. Epigenetics 2024, 16, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rebuzzini, P.; Fabozzi, G.; Cimadomo, D.; Ubaldi, F.M.; Rienzi, L.; Zuccotti, M.; Garagna, S. Multi- and Transgenerational Effects of Environmental Toxicants on Mammalian Reproduction. Cells 2022, 11, 3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hrubec, T.C.; Melin, V.E.; Shea, C.S.; Ferguson, E.E.; Garofola, C.; Repine, C.M.; Chapman, T.W.; Patel, H.R.; Razvi, R.M.; Sugrue, J.E.; et al. Ambient and Dosed Exposure to Quaternary Ammonium Disinfectants Causes Neural Tube Defects in Rodents. Birth Defects Res. 2017, 109, 1166–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Corazza, M.; Virgili, A. Airborne Allergic Contact Dermatitis from Benzalkonium Chloride. Contact Dermat. 1993, 28, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusano, F.; Luciano, S. Contact Allergy to Benzalkonium Chloride and Glutaraldehyde in a Dental Nurse. Contact Dermat. 1993, 28, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, O.H.; Henriksen, R.N.; Steinsvåg, S.K. The Effect of a Benzalkonium Chloride-Containing Nasal Spray on Human Respiratory Mucosa In Vitro as a Function of Concentration and Time of Action. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1995, 76, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirce, S.; Barranco, P. Cleaning Agents and Asthma. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 20, 542–550; quiz 2p following 550. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mezger, E.; Wendler, O.; Mayr, S.; Bozzato, A. Anaphylactic Reaction Following Administration of Nose Drops Containing Benzalkonium Chloride. Head Face Med. 2012, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huang, C.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z. Toxicity Research Status of Benzalkonium Chloride on Ocular Surface. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi 2014, 50, 303–306. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herron, J.; Reese, R.C.; Tallman, K.A.; Narayanaswamy, R.; Porter, N.A.; Xu, L. Identification of Environmental Quaternary Ammonium Compounds as Direct Inhibitors of Cholesterol Biosynthesis. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 151, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Herron, J.M.; Hines, K.M.; Tomita, H.; Seguin, R.P.; Cui, J.Y.; Xu, L. Multiomics Investigation Reveals Benzalkonium Chloride Disinfectants Alter Sterol and Lipid Homeostasis in the Mouse Neonatal Brain. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 171, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Datta, S.; He, G.; Tomilov, A.; Sahdeo, S.; Denison, M.S.; Cortopassi, G. In Vitro Evaluation of Mitochondrial Function and Estrogen Signaling in Cell Lines Exposed to the Antiseptic Cetylpyridinium Chloride. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 087015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Arnold, W.A.; Blum, A.; Branyan, J.; Bruton, T.A.; Carignan, C.C.; Cortopassi, G.; Datta, S.; DeWitt, J.; Doherty, A.C.; Halden, R.U.; et al. Quaternary Ammonium Compounds: A Chemical Class of Emerging Concern. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 7645–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Al Aboud, N.M.; Tupper, C.; Jialal, I. Genetics, Epigenetic Mechanism. In StatPearls [Internet]; Updated 14 August 2023; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532999/ (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Ou, X.; Yang, J.; Yang, L.; Zeng, H.; Shao, L. Histone Acetylation Regulated by Histone Deacetylases During Spermatogenesis. Andrology 2025, 13, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stouder, C.; Paoloni-Giacobino, A. Transgenerational Effects of the Endocrine Disruptor Vinclozolin on the Methylation Pattern of Imprinted Genes in the Mouse Sperm. Reproduction 2010, 139, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, H.; Chapin, R.E. Reproductive Toxicities of Methoxychlor Based on Estrogenic Properties of the Compound and Its Estrogenic Metabolite, Hydroxyphenyl Trichloroethane. Vitam. Horm. 2014, 94, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, J.R.; Susiarjo, M.; Bartolomei, M.S. Imprinting and Epigenetic Changes in the Early Embryo. Mamm. Genome 2009, 20, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.C.; Tavazoie, M.; Doetsch, F. Stem cells: From Epigenetics to MicoRNAs. Neuron 2005, 46, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, M.K.; Anway, M.D. Seminiferous Cord Formation and Germ-Cell Programming: Epigenetic Transgenerational Actions of Endocrine Disruptors. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1061, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubry, A.; Hoyo, C.; Jirtle, R.L.; Murphy, S.K. A Paternal Environmental Legacy: Evidence for Epigenetic Inheritance Through the Male Germ Line. Bioessays 2014, 36, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pradeepa, M.M.; Nikhil, G.; Hari Kishore, A.; Bharath, G.N.; Kundu, T.K.; Rao, M.R. Acetylation of Transition Protein 2 (TP2) by KAT3B (p300) Alters Its DNA Condensation Property and Interaction with Putative Histone Chaperone NPM3. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 29956–29967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kolthur-Seetharam, U.; Pradeepa, M.M.; Gupta, N.; Narayanaswamy, R.; Rao, M.R. Spatiotemporal Organization of AT- and GC-rich DNA and their Association with Transition Proteins TP1 and TP2 in Rat Condensing Spermatids. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2009, 57, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Iwamori, N.; Iwamori, T.; Matzuk, M.M. H3K27 demethylase, JMJD3, Regulates Fragmentation of Spermatogonial Cysts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yaman, R.; Grandjean, V. Timing of Entry of Meiosis Depends on a Mark Generated by DNA Methyltransferase 3a in Testis. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2006, 73, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saferali, A.; Moussette, S.; Chan, D.; Trasler, J.; Chen, T.; Rozen, R.; Naumova, A.K. DNA Methyltransferase 1 (Dnmt1) Mutation Affects Snrpn Imprinting in the Mouse Male Germ Line. Genome 2012, 55, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, J.; Muto, M.; Takebayashi, S.; Suetake, I.; Iwamatsu, A.; Endo, T.A.; Shinga, J.; Mizutani-Koseki, Y.; Toyoda, T.; Okamura, K.; et al. The SRA Protein Np95 Mediates Epigenetic Inheritance by Recruiting Dnmt1 to Methylated DNA. Nature 2007, 450, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, Y.; Yaman-Deveci, R.; Shirakawa, T.; Sharif, J.; Tomizawa, S.; Miura, F.; Ito, T.; Ono, M.; Nakajima, K.; Koseki, Y.; et al. Maintenance DNA Methylation in Pre-Meiotic Germ Cells Regulates Meiotic Prophase by Facilitating Homologous Chromosome Pairing. Development 2021, 148, dev194605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, R.; Proudhon, C.; Bestor, T.H.; Woodfine, K.; Lin, C.S.; Lin, S.P.; Prissette, M.; Oakey, R.J.; Bourc’his, D. The Parental Non-equivalence of Imprinting Control Regions During Mammalian Development and Evolution. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Smeester, L.; Yosim, A.E.; Nye, M.D.; Hoyo, C.; Murphy, S.K.; Fry, R.C. Imprinted Genes and the Environment: Links to the Toxic Metals Arsenic, Cadmium, Lead and Mercury. Genes 2014, 5, 477–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Drobná, Z.; Henriksen, A.D.; Wolstenholme, J.T.; Montiel, C.; Lambeth, P.S.; Shang, S.; Harris, E.P.; Zhou, C.; Flaws, J.A.; Adli, M.; et al. Transgenerational Effects of Bisphenol A on Gene Expression and DNA Methylation of Imprinted Genes in Brain. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wilkins, J.F.; Úbeda, F. Diseases Associated with Genomic Imprinting. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2011, 101, 401–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melin, V.E.; Hrubec, T.C. Direct and In-Utero Exposure to Quaternary Ammonium Disinfectants Alters Sperm Parameters and mRNA Expression of Epigenetic Enzymes in the Testes of Male CD-1 Mice. Toxics 2025, 13, 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090709
Melin VE, Hrubec TC. Direct and In-Utero Exposure to Quaternary Ammonium Disinfectants Alters Sperm Parameters and mRNA Expression of Epigenetic Enzymes in the Testes of Male CD-1 Mice. Toxics. 2025; 13(9):709. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090709
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelin, Vanessa E., and Terry C. Hrubec. 2025. "Direct and In-Utero Exposure to Quaternary Ammonium Disinfectants Alters Sperm Parameters and mRNA Expression of Epigenetic Enzymes in the Testes of Male CD-1 Mice" Toxics 13, no. 9: 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090709
APA StyleMelin, V. E., & Hrubec, T. C. (2025). Direct and In-Utero Exposure to Quaternary Ammonium Disinfectants Alters Sperm Parameters and mRNA Expression of Epigenetic Enzymes in the Testes of Male CD-1 Mice. Toxics, 13(9), 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090709




