Effects of Dioxin Exposure on Brain Regional Volumes of Fathers from Birth Cohorts in Herbicide-Sprayed and Unsprayed Areas in Vietnam
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. MRI Data Acquisition and Analysis
2.3. Dioxin Exposure Assessment Using the DR-EcoScreen Bioassay
2.4. Social Anxiety Symptoms Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Dioxin Exposure on Frontal and Temporal Gray Matter Volumes
3.2. Effects of Dioxin Exposure on Gray Matter Volumes in the Gyri of the Temporal Lobes
3.2.1. Associations Between Residency in Bien Hoa and Gyrus Volumes of the Temporal Lobes
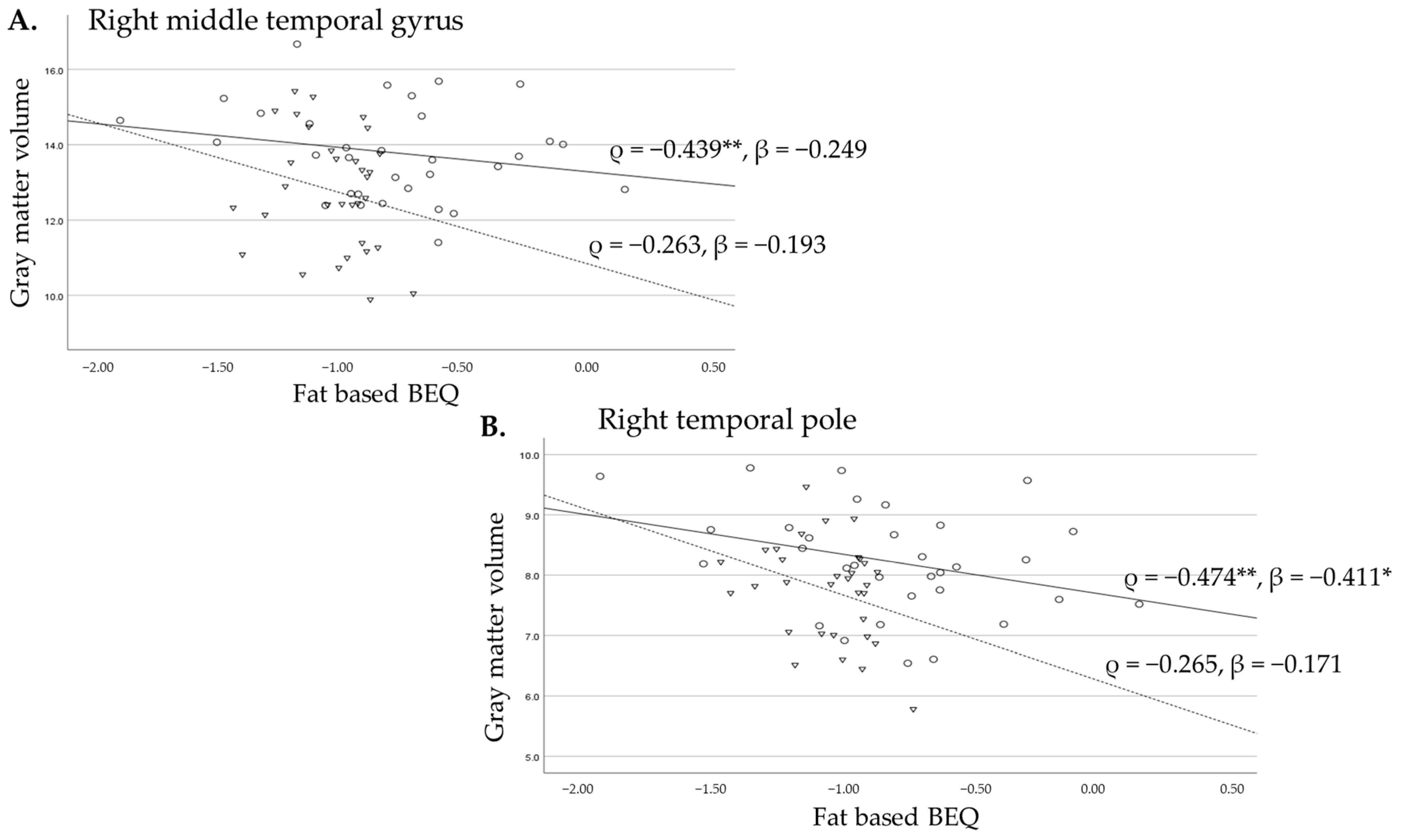
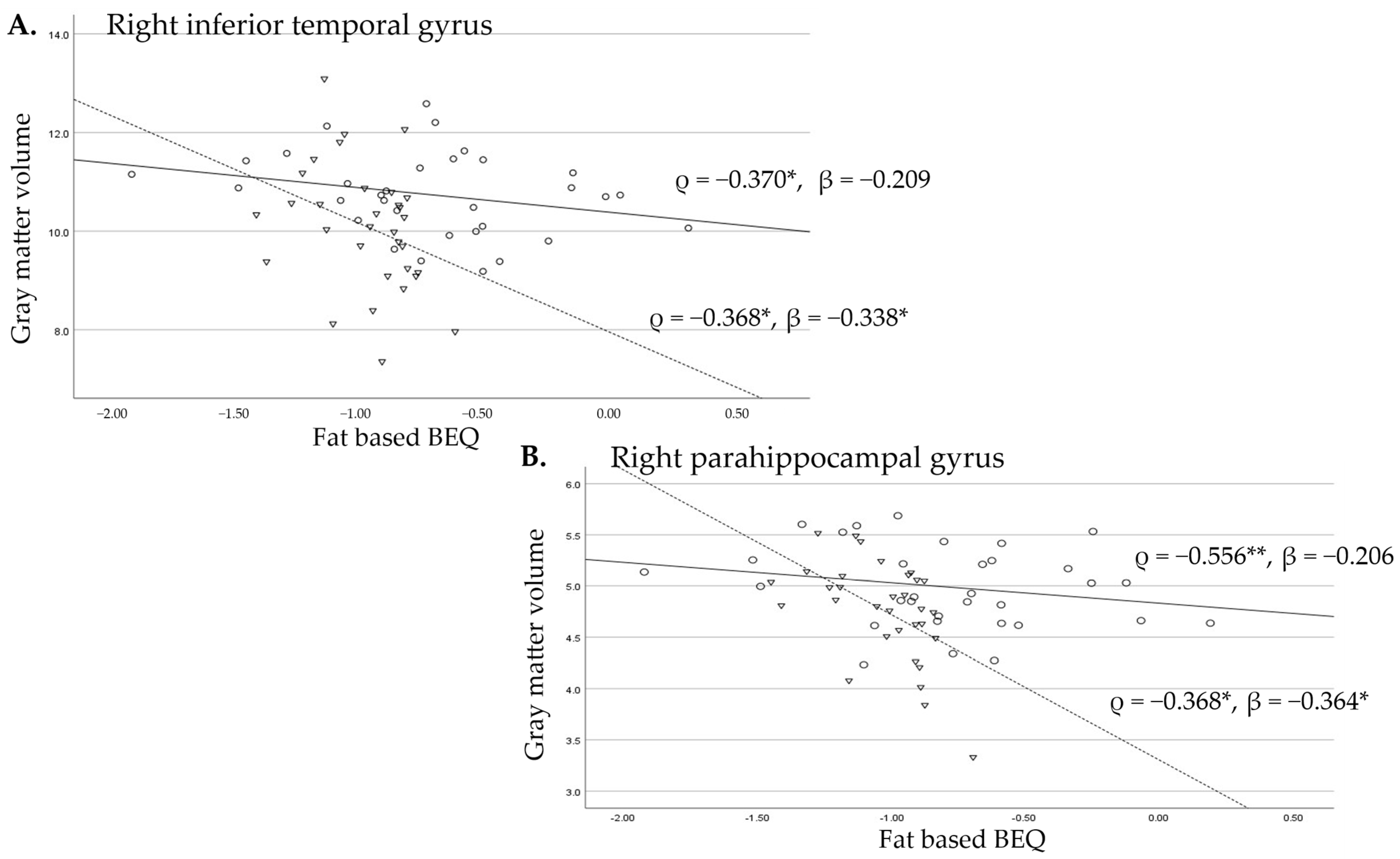
3.2.2. Associations Between Fat-Based BEQ Levels and Gyrus Volumes of the Temporal Lobes
3.3. Effects of Dioxin Exposure on SAD Symptoms
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Dioxin Exposure on Brain Gray Matter Volumes (Morphological Effects)
4.2. Effects of Dioxin Exposure on SAD Symptoms (Functional Effects)
4.3. Neurotoxic Effects of Dioxins on the Developing Brain
4.4. Neurotoxic Effects of Dioxins on the Adult Brain
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Schecter, A.; Dai, L.C.; Papke, O.; Prange, J.; Constable, J.D.; Matsuda, M.; Thao, V.D.; Piskac, A.L. Recent dioxin contamination from Agent Orange in residents of a southern Vietnam city. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2001, 43, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schecter, A.; Dai, L.C.; Thuy, L.; Quynh, H.T.; Minh, D.Q.; Cau, H.D.; Phiet, P.H.; Nguyen, N.; Constable, J.D.; Baughman, R. Agent Orange and the Vietnamese: The persistence of elevated dioxin levels in human tissues. Am. J. Public Health 1995, 85, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwernychuk, L.W. Dioxin hot spots in Vietnam. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 998–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Luong, H.; Tai, P.T.; Nishijo, M.; Trung, D.M.; Thao, P.N.; Van Son, P.; Van Long, N.; Linh, N.T.; Nishijo, H. Association of dioxin exposure and reproductive hormone levels in men living near the Bien Hoa airbase, Vietnam. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghi, T.N.; Nishijo, M.; Manh, H.D.; Tai, P.T.; Van Luong, H.; Anh, T.H.; Thao, P.N.; Trung, N.V.; Waseda, T.; Nakagawa, H.; et al. Dioxins and Nonortho PCBs in Breast Milk of Vietnamese Mothers Living in the Largest Hot Spot of Dioxin Contamination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5732–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghiem, G.T.; Nishijo, M.; Pham, T.N.; Ito, M.; Pham, T.T.; Tran, A.H.; Nishimaru, H.; Nishino, Y.; Nishijo, H. Adverse effects of maternal dioxin exposure on fetal brain development before birth assessed by neonatal electroencephalography (EEG) leading to poor neurodevelopment; a 2-year follow-up study. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, N.T.; Nishijo, M.; Nghiem, T.T.G.; Pham, T.T.; Tran, N.N.; Le, V.Q.; Vu, T.H.; Tran, H.A.; Phan, H.A.V.; Do, Q.; et al. Effects of perinatal dioxin exposure on neonatal electroencephalography (EEG) activity of the quiet sleep stage in the most contaminated area from Agent Orange in Vietnam. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 232, 113661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.T.; Pham, T.N.; Yokawa, T.; Nishijo, M.; The, T.P.; Do, Q.; Nishino, Y.; Nishijo, H. Alterations in regional brain regional volume associated with dioxin exposure in men living in the most dioxin-contaminated area in Vietnam: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) analysis using Voxel-Based Morphometry (VBM). Toxics 2021, 9, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.T.; Pham, T.N.; Nishijo, M.; Yokawa, T.; Pham The, T.; Takiguchi, T.; Nishino, Y.; Nishijo, H. Impact of dioxin exposure on brain morphometry and social anxiety in men living in the most dioxin-contaminated area in Vietnam. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2023, 166, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Matsuda, R.; Vu, H.T.; Pham-The, T.; Pham, T.N.; Takiguchi, T.; Nishino, Y.; Nishijo, H.; Nishijo, M. Bioassay using the DR-EcoScreen system to measure diox-in-related compounds in serum samples from individuals ex-posed to dioxins originating from Agent Orange in Vietnam. Toxics 2025, 13, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, J.; Friston, K.J. Unified segmentation. NeuroImage 2005, 26, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fix, J.D. Neuroanatomy, 2nd ed.; Williams & Wilkins, a Waverly Company: Ambler, PA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ribas, G.C. The cerebral sulci and gyri. Neurosurg. Focus 2010, 28, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, S.; Iida, M.; Yabushita, H.; Matsuda, T.; Kojima, H. In vitro screening for aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonistic activity in 200 pesticides using a highly sensitive reporter cell line, DR-EcoScreen cells, and in vivo mouse liver cytochrome P450-1A induction by propanil, diuron and linuron. Chemosphere 2008, 74, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013; pp. 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Caballo, V.E.; Salazar, I.C.; Arias, B.; Irurtia, M.J.; Calderero, M.; Spain, C.-A.R.T. Validation of the Social Anxiety Questionnaire for Adults (SAQ-A30) with Spanish university students: Similarities and differences among degree subjects and regions. Behav. Psychol. 2010, 18, 5–34. [Google Scholar]
- Caballo, V.E.; Salazar, I.C.; Irurtia, M.J.; Arias, B.; Hofmann, S.G.; Team, C.-A.R. The multidimensional nature and multicultural validity of a new measure of social anxiety: The Social Anxiety Questionnaire for Adults. Behav. Ther. 2012, 43, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahn, R.; Moll, J.; Krueger, F.; Huey, E.D.; Garrido, G.; Grafman, J. Social concepts are represented in the superior anterior temporal cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6430–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grecucci, A.; Rubicondo, D.; Siugzdaite, R.; Surian, L.; Job, R. Uncovering the Social Deficits in the Autistic Brain. A Source-Based Morphometric Study. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajitani, K.; Tsuchimoto, R.; Omodaka, Y.; Matsushita, T.; Fukumori, H.; Sato, T.; Nagano, J. Neurodevelopmental disorder traits in taijin-kyofu-sho and social anxiety disorder: A cross-sectional study among university students. Psychiatry J. 2021, 2021, 1661617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.A.; Kyeong, S.; Kim, D.H. Long-term effects of defoliant exposure on brain atrophy progression in humans. NeuroToxicology 2022, 92, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Lee, S.; Kang, S.K.; Choi, W.J. Risk of dementia in Korean Vietnam War veterans. J. Prev. Alzheimers Dis. 2024, 11, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, S.; Yaffe, K.; Li, Y.; Byers, A.L.; Peltz, C.B.; Barnes, D.E. Agent Orange Exposure and Dementia Diagnosis in US Veterans of the Vietnam Era. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-García, N.A.; Orozco-Ibarra, M.; Estudillo, E.; Elizondo, G.; Gómez Apo, E.; Chávez Macías, L.G.; Sosa-Ortiz, A.L.; Torres-Ramos, M.A. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Post-Mortem Hippocampus and in Serum from Young, Elder, and Alzheimer’s Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, E.S.; Tischkau, S.A. The Role of AhR in the Hallmarks of Brain Aging: Friend and Foe. Cells 2021, 10, 2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, E.; Kubo, K.; Matsuyoshi, C.; Benner, S.; Hosokawa, M.; Endo, T.; Ling, W.; Kohda, M.; Yokoyama, K.; Nakajima, K.; et al. Developmental origin of abnormal dendritic growth in the mouse brain induced by in utero disruption of aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2015, 52, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latchney, S.E.; Majewska, A.K. Persistent organic pollutants at the synapse: Shared phenotypes and converging mechanisms of developmental neurotoxicity. Dev. Neurobiol. 2021, 81, 623–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, A. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) reveals evidence of antagonistic pleiotropy in the regulation of the aging process. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Residency Groups | Controls (n = 32) | Shorter BH Residency (n = 22) | Longer BH Residency (n = 10) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p-Value | Mean | SD | p-Value | |
| Age (years) | 39.3 | 4.2 | 34.1 | 5.7 | 0.001 | 38.3 | 5.4 | 0.795 |
| Education (years) | 13.4 | 3.2 | 12.2 | 3.3 | 0.298 | 11.5 | 3 | 0.184 |
| Height (cm) | 165.6 | 5.2 | 164.9 | 4.7 | 0.818 | 166.5 | 5.7 | 0.867 |
| Weight (Kg) | 64.4 | 8.6 | 65.2 | 9.4 | 0.930 | 68.9 | 8.7 | 0.295 |
| BMI | 23.4 | 2.4 | 24 | 3.1 | 0.713 | 24.8 | 2.7 | 0.274 |
| Fat-based BEQ (pg/g fat) | 53.1 | 1.8 | 148.8 | 2.5 | <0.001 | 106.5 | 2.1 | 0.020 |
| Residency Groups | N | Mean | SD | Adj Mean | 95%CI | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left frontal lobe | |||||||
| Control | 32 | 93.9 | 8.8 | 94.3 | 91.3 | 97.3 | ref |
| Shorter BH residency | 22 | 94.7 | 7.9 | 93.9 | 90.2 | 97.7 | ns |
| Longer BH residency | 10 | 99.3 | 5.1 | 99.6 | 94.9 | 104.2 | ns |
| Right frontal lobe | |||||||
| Control | 32 | 94.5 | 8.7 | 94.8 | 91.8 | 97.7 | ref |
| Shorter BH residency | 22 | 95.7 | 7.7 | 95.3 | 91.6 | 99.0 | ns |
| Longer BH residency | 10 | 100.7 | 5.2 | 100.8 | 96.3 | 105.4 | ns |
| Left temporal lobe | |||||||
| Control | 32 | 57.2 | 5.5 | 56.9 | 55.1 | 58.6 | ref |
| Shorter BH residency | 22 | 58.3 | 4.6 | 58.6 | 56.4 | 60.8 | ns |
| Longer BH residency | 10 | 61.6 | 2.8 | 61.8 | 59.1 | 64.5 | * |
| Right temporal lobe | |||||||
| Control | 32 | 56.8 | 5.3 | 56.4 | 54.8 | 58.0 | ref |
| Shorter BH residency | 22 | 58.6 | 4.2 | 59.1 | 57.1 | 61.1 | ns |
| Longer BH residency | 10 | 62.5 | 3.2 | 62.5 | 60.1 | 65.0 | ** |
| Left Hemisphere | Right Hemisphere | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residency Groups | N | Adj Mean | 95%CI | p | N | Adj Mean | 95%CI | p | ||
| Superior Temporal Gyrus | ||||||||||
| Control | 32 | 11.0 | 10.6 | 11.4 | ref | 32 | 10.9 | 10.5 | 11.3 | ref |
| Shorter BH residency | 22 | 11.3 | 10.8 | 11.8 | ns | 22 | 10.8 | 10.3 | 11.3 | ns |
| Longer BH residency | 10 | 11.9 | 11.3 | 12.5 | ns | 10 | 11.9 | 11.3 | 12.5 | ns |
| Fusiform Gyrus | ||||||||||
| Control | 32 | 7.3 | 7.1 | 7.6 | ref | 32 | 7.3 | 7.1 | 7.6 | ref |
| Shorter BH residency | 22 | 7.5 | 7.1 | 7.8 | ns | 22 | 7.5 | 7.2 | 7.8 | ns |
| Longer BH residency | 10 | 7.7 | 7.3 | 8.2 | ns | 10 | 8.0 | 7.6 | 8.3 | ns |
| Inferior Temporal Gyrus | ||||||||||
| Control | 32 | 9.6 | 9.3 | 10.0 | ref | 32 | 9.9 | 9.5 | 10.3 | ref |
| Shorter BH residency | 22 | 10.2 | 9.7 | 10.6 | ns | 22 | 10.8 | 10.3 | 11.4 | ns |
| Longer BH residency | 10 | 10.8 | 10.2 | 11.4 | * | 10 | 11.1 | 10.5 | 11.8 | ns |
| Middle Temporal Gyrus | ||||||||||
| Control | 32 | 13.2 | 12.6 | 13.7 | ref | 32 | 12.6 | 12.1 | 13.1 | ref |
| Shorter BH residency | 22 | 14.0 | 13.3 | 14.7 | ns | 22 | 13.8 | 13.2 | 14.5 | ns |
| Longer BH residency | 10 | 14.0 | 13.1 | 14.8 | ns | 10 | 14.4 | 13.6 | 15.2 | * |
| Parahippocampal Gyrus | ||||||||||
| Control | 32 | 4.8 | 4.6 | 4.9 | ref | 32 | 4.7 | 4.5 | 4.9 | ref |
| Shorter BH residency | 22 | 4.9 | 4.7 | 5.1 | ns | 22 | 5.0 | 4.8 | 5.2 | ns |
| Longer BH residency | 10 | 5.1 | 4.9 | 5.4 | ns | 10 | 5.1 | 4.9 | 5.4 | ns |
| Temporal Pole | ||||||||||
| Control | 32 | 7.8 | 7.4 | 8.2 | ref | 32 | 7.7 | 7.4 | 8.0 | ref |
| Shorter BH residency | 22 | 7.8 | 7.3 | 8.3 | ns | 22 | 8.1 | 7.7 | 8.4 | ns |
| Longer BH residency | 10 | 9.1 | 8.4 | 9.7 | * | 10 | 8.8 | 8.3 | 9.2 | ** |
| Social Anxiety Questionare (SAQ-A30) | Controls | Shorter BH Residency | Longer BH Residency | p | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Adj Mean | 95%CI | Mean | Adj Mean | 95%CI | Mean | Adj Mean | 95%CI | |||||
| Speaking in public (F1) | 14.5 | 14.5 | 12.4 | 16.6 | 14.6 | 14.5 | 11.9 | 17.1 | 14.0 | 14.1 | 10.9 | 17.3 | ns |
| Interaction with the opposite sex (F2) | 10.5 | 10.2 | 8.6 | 11.7 | 12.1 | 12.5 | 10.6 | 14.4 | 12.7 | 12.8 | 10.5 | 15.1 | ns |
| Assertive expression of annoyance, disgust or displeasure (F3) | 12.7 | 12.2 | 11.0 | 13.5 | 12.9 | 13.4 | 11.9 | 14.9 | 12.2 | 12.1 | 10.3 | 14.0 | ns |
| Criticism and embarrassment (F4) | 11.3 | 11.2 | 10.1 | 12.3 | 12.1 | 12.2 | 10.8 | 13.6 | 14.4 | 14.4 | 12.7 | 16.1 | * |
| Interaction with strangers (F5) | 14.0 | 14.0 | 12.8 | 15.3 | 15.1 | 15.2 | 13.6 | 16.8 | 14.6 | 14.4 | 12.4 | 16.3 | ns |
| Total | 63.0 | 62.0 | 56.8 | 67.2 | 67.0 | 68.2 | 61.8 | 74.6 | 68.5 | 68.5 | 60.6 | 76.4 | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, H.M.; Vu, H.T.; Pham, T.N.; Pham-The, T.; Yokawa, T.; Matsuda, R.; Nakamura, M.; Nishijo, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Nishino, Y.; et al. Effects of Dioxin Exposure on Brain Regional Volumes of Fathers from Birth Cohorts in Herbicide-Sprayed and Unsprayed Areas in Vietnam. Toxics 2025, 13, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090710
Nguyen HM, Vu HT, Pham TN, Pham-The T, Yokawa T, Matsuda R, Nakamura M, Nishijo M, Takahashi Y, Nishino Y, et al. Effects of Dioxin Exposure on Brain Regional Volumes of Fathers from Birth Cohorts in Herbicide-Sprayed and Unsprayed Areas in Vietnam. Toxics. 2025; 13(9):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090710
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Hai Minh, Hoa Thi Vu, Thao Ngoc Pham, Tai Pham-The, Takashi Yokawa, Ryo Matsuda, Masafumi Nakamura, Muneko Nishijo, Yutaro Takahashi, Yoshikazu Nishino, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Dioxin Exposure on Brain Regional Volumes of Fathers from Birth Cohorts in Herbicide-Sprayed and Unsprayed Areas in Vietnam" Toxics 13, no. 9: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090710
APA StyleNguyen, H. M., Vu, H. T., Pham, T. N., Pham-The, T., Yokawa, T., Matsuda, R., Nakamura, M., Nishijo, M., Takahashi, Y., Nishino, Y., Ngoc, N. T., & Nishijo, H. (2025). Effects of Dioxin Exposure on Brain Regional Volumes of Fathers from Birth Cohorts in Herbicide-Sprayed and Unsprayed Areas in Vietnam. Toxics, 13(9), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090710








