Combined Effect of Metals, PFAS, Phthalates, and Plasticizers on Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Data Preprocessing
2.3. Bayesian Kernel Machine Regression
- measures the similarity between exposure profiles of individuals i and j.
- and represent the m-th pollutant exposure values for individuals i and j.
- M is the total number of pollutants in the mixture.
- ρ is a tuning parameter that controls the smoothness of the kernel function, where larger values result in smoother relationships, while smaller values capture more localized effects.
2.4. Implementation of BKMR Modeling
Evaluation and Interpretation of Results
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
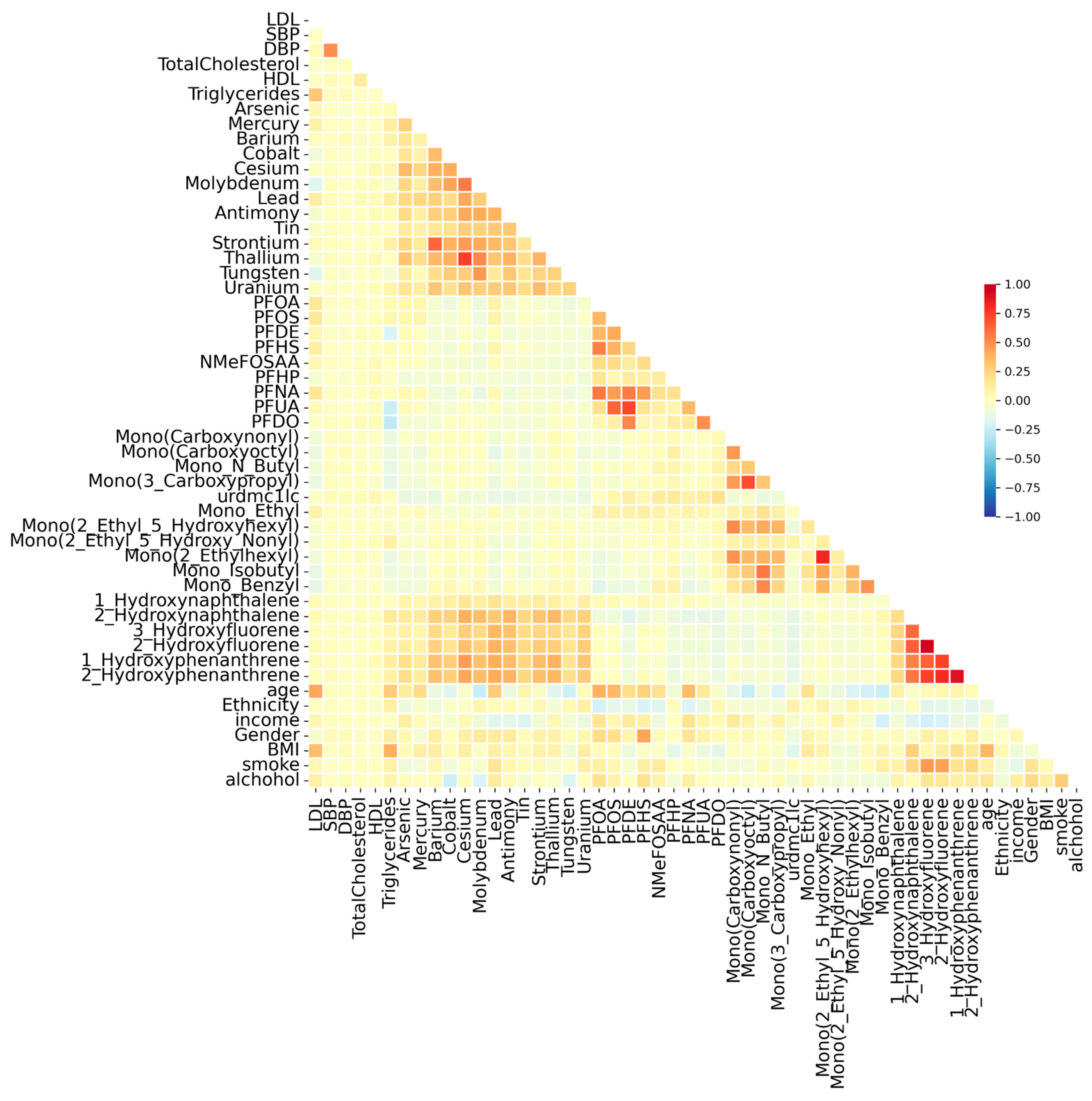
3.2. Correlation Analysis
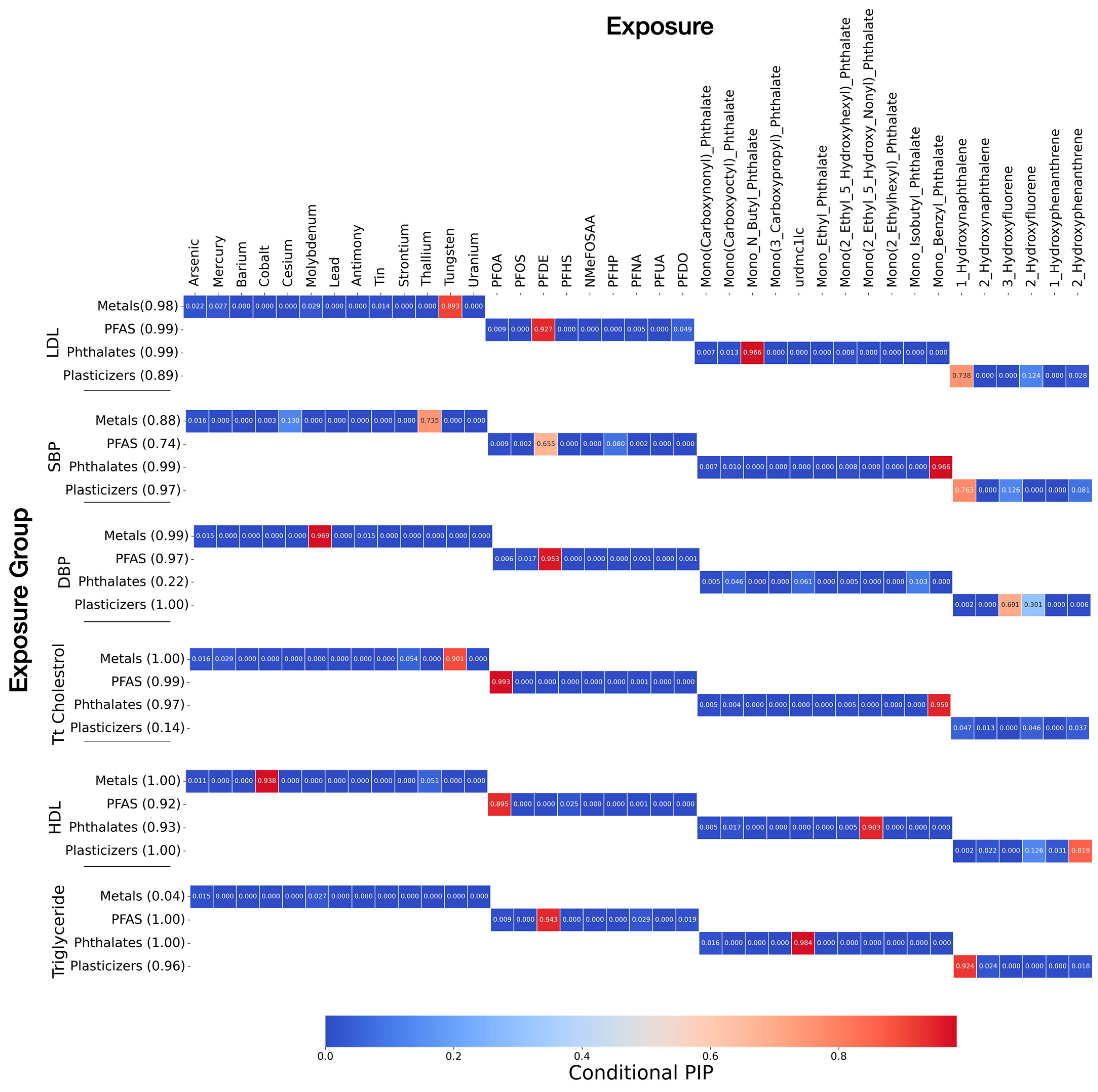
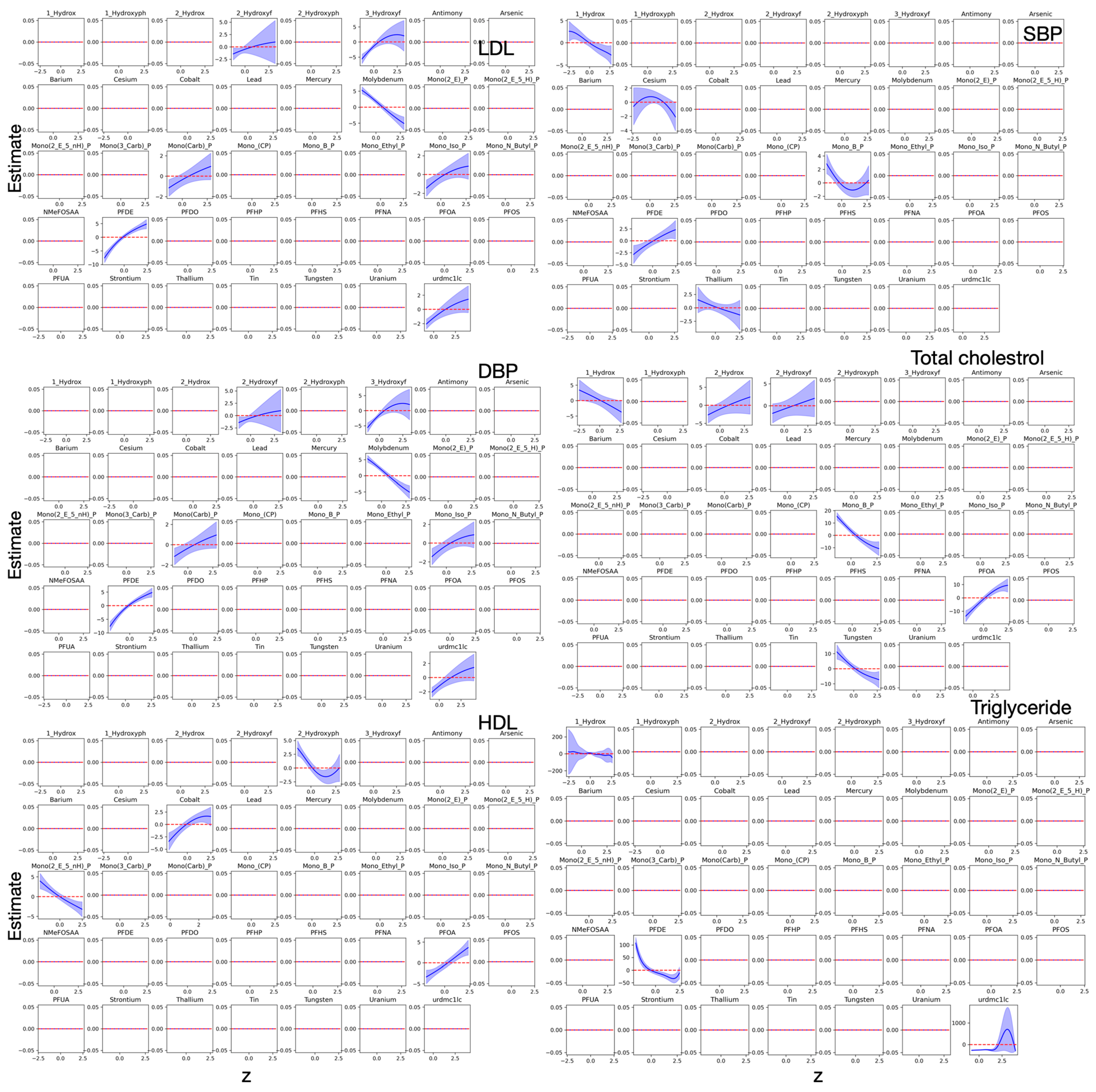
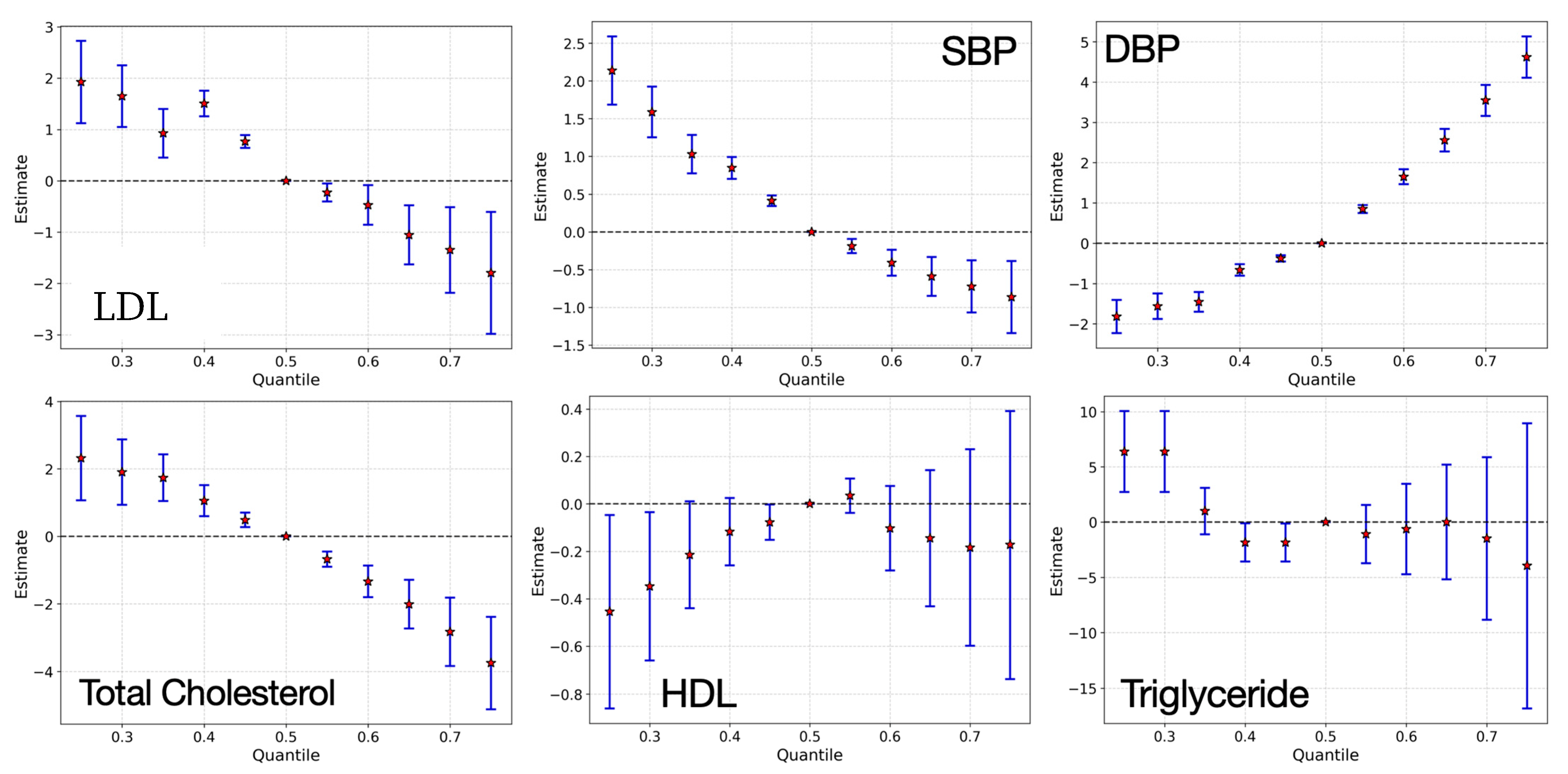
3.3. Bayesian Kernel Machine Regression
Posterior Inclusion Probabilities (PIPs)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, X.; Long, G.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Q.; Song, B.; Wu, K.H. Association of increased risk of cardiovascular diseases with higher levels of perfluoroalkylated substances in the serum of adults. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 89081–89092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, J.M.; Gennings, C.; Hauser, R.; Webster, T.F. What Can Epidemiological Studies Tell Us about the Impact of Chemical Mixtures on Human Health? Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, A6–A9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Relloso, A.; Grau-Perez, M.; Briongos-Figuero, L.; Gomez-Ariza, J.L.; Garcia-Barrera, T.; Duenas-Laita, A.; Bobb, J.F.; Chaves, F.J.; Kioumourtzoglou, M.A.; Navas-Acien, A.; et al. The association of urine metals and metal mixtures with cardiovascular incidence in an adult population from Spain: The Hortega Follow-Up Study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.W.; Joubert, B.R.; Braun, J.M.; Dilworth, C.; Gennings, C.; Hauser, R.; Heindel, J.J.; Rider, C.V.; Webster, T.F.; Carlin, D.J. Statistical Approaches for Assessing Health Effects of Environmental Chemical Mixtures in Epidemiology: Lessons from an Innovative Workshop. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, A227–A229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas-Acien, A.; Guallar, E.; Silbergeld, E.K.; Rothenberg, S.J. Lead exposure and cardiovascular disease—A systematic review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellez-Plaza, M.; Navas-Acien, A.; Menke, A.; Crainiceanu, C.M.; Pastor-Barriuso, R.; Guallar, E. Cadmium exposure and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in the U.S. general population. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenland, K.; Fletcher, T.; Savitz, D.A. Epidemiologic evidence on the health effects of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA). Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeker, J.D.; Sathyanarayana, S.; Swan, S.H. Phthalates and other additives in plastics: Human exposure and associated health outcomes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2097–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Dai, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, B. An association of elevated serum prolactin with phthalate exposure in adult men. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2011, 24, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, T.J.; Zota, A.R.; Schwartz, J.M. Environmental chemicals in pregnant women in the United States: NHANES 2003–2004. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; He, X. K-means clustering via principal component analysis. In Proceedings of the Twenty-First International Conference on Machine Learning, Banff, AB, Canada, 4–8 July 2004; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Heinze, G.; Wallisch, C.; Dunkler, D. Variable selection—A review and recommendations for the practicing statistician. Biom. J. 2018, 60, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billionnet, C.; Sherrill, D.; Annesi-Maesano, I. Estimating the health effects of exposure to multi-pollutant mixture. Ann. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobb, J.F.; Valeri, L.; Claus Henn, B.; Christiani, D.C.; Wright, R.O.; Mazumdar, M.; Godleski, J.J.; Coull, B.A. Bayesian kernel machine regression for estimating the health effects of multi-pollutant mixtures. Biostatistics 2015, 16, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, D.B.; Wilder, L.C.; Caudill, S.P.; Gonzalez, A.J.; Needham, L.L.; Pirkle, J.L. Urinary creatinine concentrations in the U.S. population: Implications for urinary biologic monitoring measurements. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Wong, L.Y.; Reidy, J.A.; Needham, L.L. Exposure of the U.S. population to bisphenol A and 4-tertiary-octylphenol: 2003–2004. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Wen, Y.; Cao, K.; He, S.; Wang, T. A review of common statistical methods for dealing with multiple pollutant mixtures and multiple exposures. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1377685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobb, J.F.; Claus Henn, B.; Valeri, L.; Coull, B.A. Statistical software for analyzing the health effects of multiple concurrent exposures via Bayesian kernel machine regression. Environ. Health 2018, 17, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers-for-Disease-Control-and-Prevention-(NHANES). MEC Laboratory Procedures Manual. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/public/2013/manuals/2013_MEC_Laboratory_Procedures_Manual.pdf (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Jerez, J.M.; Molina, I.; Garcia-Laencina, P.J.; Alba, E.; Ribelles, N.; Martin, M.; Franco, L. Missing data imputation using statistical and machine learning methods in a real breast cancer problem. Artif. Intell. Med. 2010, 50, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, P.D. Missing Data; CA Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2001; Volume 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, B.R.; Palmer, G.; Dunson, D.; Kioumourtzoglou, M.-A.; Coull, B.A. Environmental Mixtures Analysis (E-MIX) Workflow and Methods Repository. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasande, L.; Sathyanarayana, S.; Spanier, A.J.; Trachtman, H.; Attina, T.M.; Urbina, E.M. Urinary phthalates are associated with higher blood pressure in childhood. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 747–753.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Tang, S.Y.; Hwang, J.S.; Chan, C.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Su, T.C. Association between Levels of Urine Di-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate Metabolites and Heart Rate Variability in Young Adults. Toxics 2021, 9, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, D.O.; Arcaro, K.; Spink, D.C. Understanding the human health effects of chemical mixtures. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Oh, H.; Kim, M.-S. The effects of chemical mixtures on lipid profiles in the Korean adult population: Threshold and molecular mechanisms for dyslipidemia involved. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 39182–39208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoeller, R.T.; Vandenberg, L.N. Assessing dose–response relationships for endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs): A focus on non-monotonicity. Environ. Health 2015, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Magueresse-Battistoni, B.; Labaronne, E.; Vidal, H.; Naville, D. Endocrine disrupting chemicals in mixture and obesity, diabetes and related metabolic disorders. World J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, G.; Wang, Y.; Howe, C.G.; Romano, M.E. Exposure to metal mixtures in association with cardiovascular risk factors and outcomes: A scoping review. Toxics 2022, 10, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanobetti, A.; Austin, E.; Coull, B.A.; Schwartz, J.; Koutrakis, P. Health effects of multi-pollutant profiles. Environ. Int. 2014, 71, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, B.; Tan, S.-C.; Lee, C.M.; Yao, X.; Yan, H.; Shi, J. A study of air pollution of city clusters. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 3069–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.T.; Giovanoulis, G.; Cousins, A.P.; Magnér, J.; Cousins, I.T.; de Wit, C.A. Human exposure, hazard and risk of alternative plasticizers to phthalate esters. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, M.; Dunder, L.; Lind, P.M.; Lind, L.; Salihovic, S. Associations of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) with lipid and lipoprotein profiles. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2023, 33, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-H.; Shen, Y.-X.; Li, L.; Fan, T.-T.; Wang, Y.; Wei, N. Phthalate exposure and high blood pressure in adults: A cross-sectional study in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 15934–15942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, C.; Wan, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, B.; Wang, N.; Lu, Y. Exposure to phthalates and cardiovascular diseases in Chinese with type 2 diabetes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 58113–58122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, M.A.; Alatorre-Hinojosa, S.; Connors, L.T.; Singh, R.D.; Thompson, J.A. Plasticizers and cardiovascular health: Role of adipose tissue dysfunction. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 626448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhanam, S.D.; Ramamurthy, K.; Priya, P.S.; Sudhakaran, G.; Guru, A.; Arockiaraj, J. A combinational threat of micro-and nano-plastics (MNPs) as potential emerging vectors for per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) to human health. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gu, X.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, T. Di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and polystyrene microplastics co-exposure caused oxidative stress to activate NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway aggravated pyroptosis and inflammation in mouse kidney. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlin, D.J.; Rider, C.V.; Woychik, R.; Birnbaum, L.S. Unraveling the health effects of environmental mixtures: An NIEHS priority. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, A6–A8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, J.; Mazumdar, M.; Bellinger, D.; Christiani, D.; Wright, R.; Coull, B. Estimating the health effects of environmental mixtures using Bayesian semiparametric regression and sparsity inducing priors. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2020, 14, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrico, C.; Gennings, C.; Wheeler, D.C.; Factor-Litvak, P. Characterization of Weighted Quantile Sum Regression for Highly Correlated Data in a Risk Analysis Setting. J. Agric. Biol. Environ. Stat. 2015, 20, 100–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.C.; Rustom, S.; Carli, M.; Whitehead, T.P.; Ward, M.H.; Metayer, C. Assessment of Grouped Weighted Quantile Sum Regression for Modeling Chemical Mixtures and Cancer Risk. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillman, M.W.; Blaisdell, C.J. Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes, a Research Program of the National Institutes of Health. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2018, 30, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | n | Mean (SD) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 10,175 | 31 (24) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 9055 | 25.68 (7.96) |
| Percentage (%) | ||
| Alcohol (Had at least 12 alcohol drinks/1 yr?) | ||
| Yes | 3790 | 37.25 |
| No | 1623 | 15.95 |
| Don’t know | 8 | 0.08 |
| Smoke (Smoked at least 100 cigarettes in life) | ||
| Yes | 2579 | 25.35 |
| No | 3532 | 34.71 |
| Don’t know | 2 | 0.02 |
| Education (Education level—Adults 20+) | ||
| Less than 9th grade | 455 | 4.47 |
| 9–11th grades (Includes 12th grade with no diploma) | 791 | 7.77 |
| High school graduate/GED or equivalent | 1303 | 12.81 |
| Some college or AA degree | 1770 | 17.40 |
| College graduate or above | 1443 | 14.18 |
| Refused | 2 | 0.02 |
| Don’t know | 5 | 0.05 |
| Ethnicity (Race/Hispanic origin w/NH Asian) | ||
| Mexican American | 1730 | 17 |
| Other Hispanic | 960 | 9.43 |
| Non-Hispanic white | 3674 | 36.11 |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 2267 | 22.28 |
| Non-Hispanic Asian | 1074 | 10.56 |
| Other Race—Including multi-racial | 470 | 4.62 |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 5003 | 50.83 |
| Female | 5172 | 49.17 |
| Income (USD): Annual household income | ||
| USD 0 to USD 4999 | 273 | 2.46 |
| USD 5000 to USD 9999 | 407 | 4 |
| USD 10,000 to USD 14,999 | 639 | 6.28 |
| USD 15,000 to USD 19,999 | 658 | 6.47 |
| USD 20,000 to USD 24,999 | 880 | 8.65 |
| USD 25,000 to USD 34,999 | 1185 | 11.65 |
| USD 35,000 to USD 44,999 | 913 | 8.97 |
| USD 45,000 to USD 54,999 | 764 | 7.51 |
| USD 55,000 to USD 64,999 | 521 | 5.12 |
| USD 65,000 to USD 74,999 | 378 | 3.71 |
| USD 20,000 and over | 323 | 3.17 |
| Under USD 20,000 | 133 | 1.31 |
| USD 75,000 to USD 99,999 | 860 | 8.45 |
| USD 100,000 and over | 1781 | 17.50 |
| Refused | 252 | 2.48 |
| Don’t know | 75 | 0.74 |
| Metals | ||
| Lead (Pb, µg/dL) | 2664 | 0.46 (0.77) |
| Cadmium (Cd, µg/L) | 2664 | 0.24 (0.36) |
| Thallium (TI, µg/L) | 2664 | 0.19 (0.13) |
| Molybdenum (Mo, µg/L) | 2664 | 56.10 (56.12) |
| Arsenic (As, µg/L) | 2662 | 15.67 (46.74) |
| Mercury (Hg, µg/L) | 2666 | 0.51 (2.04) |
| Barium (Ba, µg/L) | 2664 | 1.77 (3.00) |
| Cobalt (Co, µg/L) | 2664 | 0.62 (1.78) |
| Cesium (Cs, µg/L) | 2664 | 4.97 (3.14) |
| Manganese (Mn, µg/L) | 2664 | 0.16 (0.49) |
| Antimony (Sb, µg/L) | 2664 | 0.08 (0.14) |
| Tin (Sn, µg/L) | 2664 | 1.44 (4.71) |
| Strontium (Sr, µg/L) | 2664 | 118.07 (182.79) |
| Tungsten (W, µg/L) | 2664 | 0.15 (0.58) |
| Uranium (U, µg/L) | 2664 | 0.01 (0.03) |
| PFAS | ||
| PFOA (ng/mL) | 1954 | 2.33 (3.01) |
| PFOS (ng/mL) | 1954 | 8.02 (32.70) |
| PFHS (ng/mL) | 2168 | 1.94 (2.21) |
| PFDE (ng/mL) | 2168 | 0.31 (1.21) |
| NMeFOSAA (ng/mL) | 2168 | 0.18 (0.29) |
| PFHP (ng/mL) | 2168 | 0.08(0.06) |
| PFNA (ng/mL) | 2168 | 0.87 (0.83) |
| PFUA (ng/mL) | 2168 | 0.23(1.93) |
| PFDO (ng/mL) | 2168 | 0.10 (0.16) |
| Phthalates and Plasticizers | ||
| Mono(carboxynonyl)_phthalate (ng/mL) | 2685 | 5.99 (25.40) |
| Mono(carboxyoctyl)_phthalate (ng/mL) | 2685 | 54.09 (115.83) |
| Mono(2-ethyl-5-carboxypentyl)_phthalate (ng/mL) | 2685 | 20.92(44.24) |
| Mono-n-butyl_phthalate (ng/mL) | 2685 | 17.93 (25.84) |
| Mono(3-carboxypropyl)_phthalate (ng/mL) | 2685 | 5.31 (15.45) |
| urdmc1lc (ng/mL) | 2685 | 0.10 (0.30) |
| Mono-ethyl_phthalate (ng/mL) | 2685 | 200.85(1067.64) |
| Mono(2-ethyl-5-hydroxyhexyl)_phthalate (ng/mL) | 2685 | 13.64 (32.82) |
| Mono(2-ethyl-5-hydroxy-nonyl)_phthalate (ng/mL) | 2685 | 0.72 (3.40) |
| Mono(2-ethylhexyl)_phthalate (ng/mL) | 2685 | 2.45 (5.33) |
| Mono-isobutyl_phthalate (ng/mL) | 2685 | 14.77 (23.48) |
| Monobenzyl phthalate (ng/mL) | 2685 | 11.24 (22.46) |
| 1-Hydroxynaphthalene (ng/L) | 2640 | 27,874.13 (724,051.50) |
| 2-Hydroxynaphthalene (ng/L) | 2641 | 8737.88 (13,875.15) |
| 3-Hydroxyfluorene (ng/L) | 2650 | 218.96 (462.62) |
| 2-Hydroxyfluorene (ng/L) | 2650 | 390.08 (713.54) |
| 1-Hydroxyphenanthrene (ng/L) | 2650 | 142.18 (223.26) |
| 2-Hydroxyphenanthrene (ng/L) | 2650 | 188.78 (293.77) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jehu-Appiah, D.; Obeng-Gyasi, E. Combined Effect of Metals, PFAS, Phthalates, and Plasticizers on Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Toxics 2025, 13, 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060476
Jehu-Appiah D, Obeng-Gyasi E. Combined Effect of Metals, PFAS, Phthalates, and Plasticizers on Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Toxics. 2025; 13(6):476. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060476
Chicago/Turabian StyleJehu-Appiah, Doreen, and Emmanuel Obeng-Gyasi. 2025. "Combined Effect of Metals, PFAS, Phthalates, and Plasticizers on Cardiovascular Disease Risk" Toxics 13, no. 6: 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060476
APA StyleJehu-Appiah, D., & Obeng-Gyasi, E. (2025). Combined Effect of Metals, PFAS, Phthalates, and Plasticizers on Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Toxics, 13(6), 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060476







