Converting Waste into Treasure: Efficient Adsorption of Cr(VI) Using Iron-Modified Rice Straw Biochar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experiment
2.1. Chemical Reagents and Materials
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of Adsorbent
2.3. Batch and Column Adsorption Experiments
3. Result and Discussion
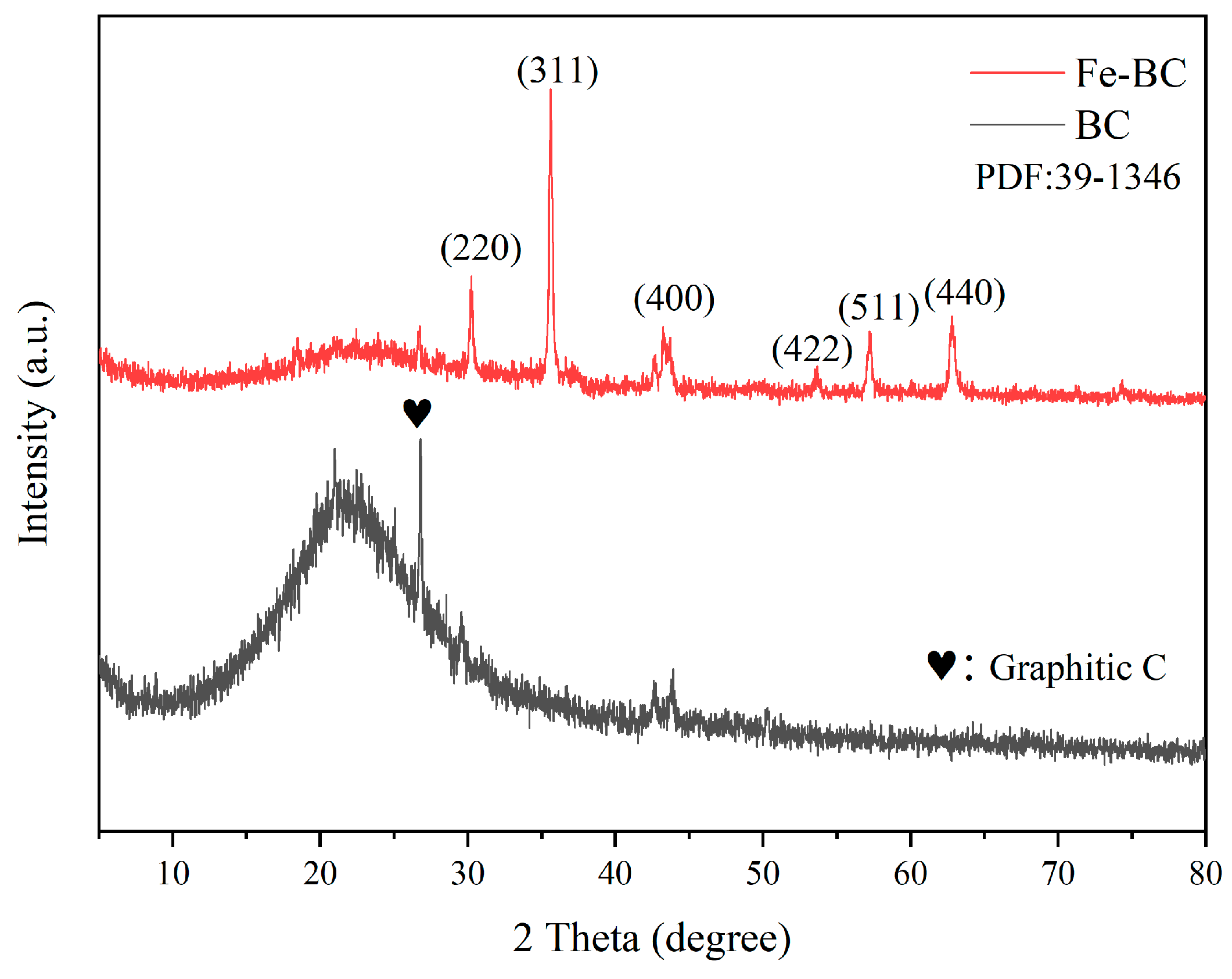
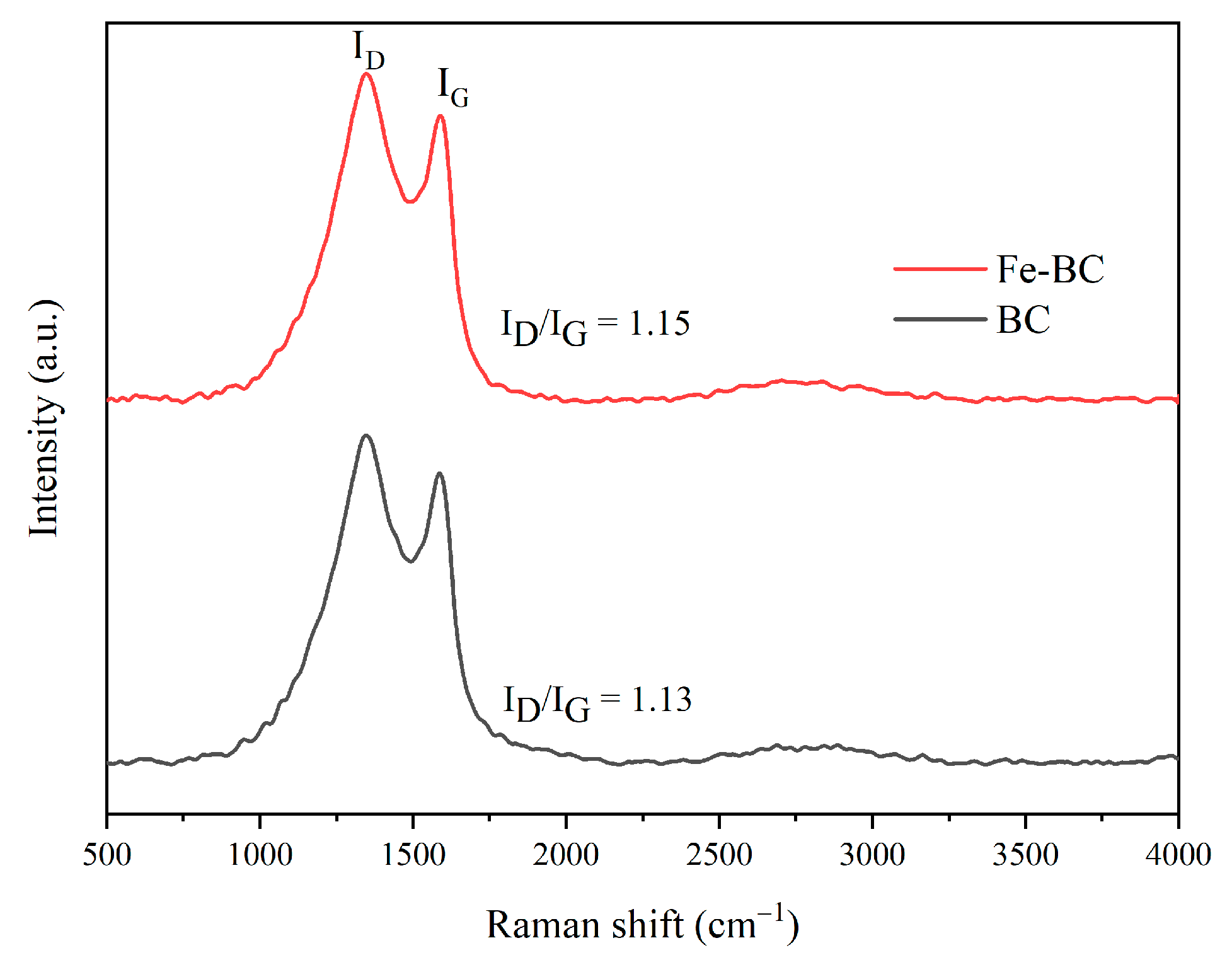
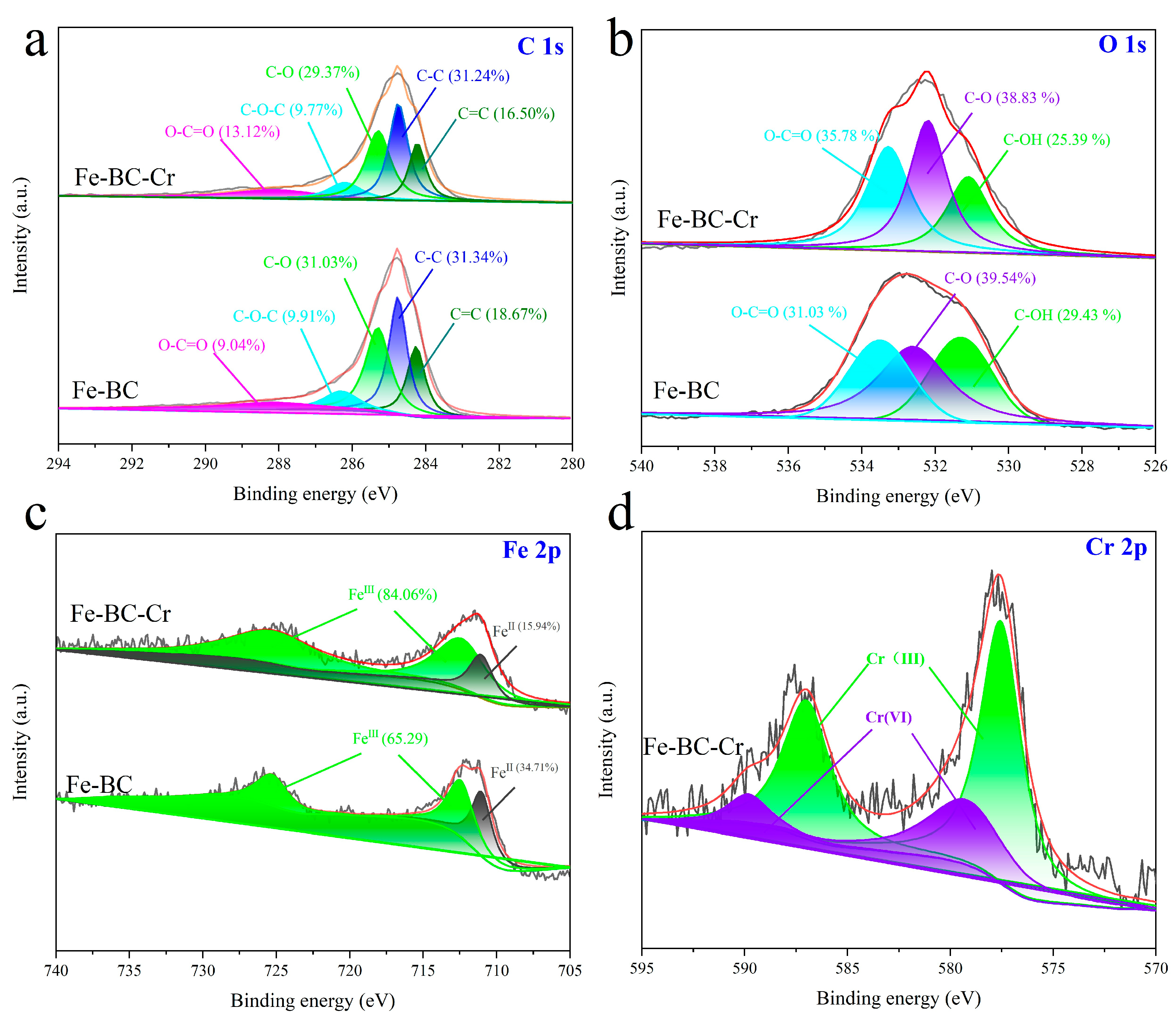
3.1. Characterization
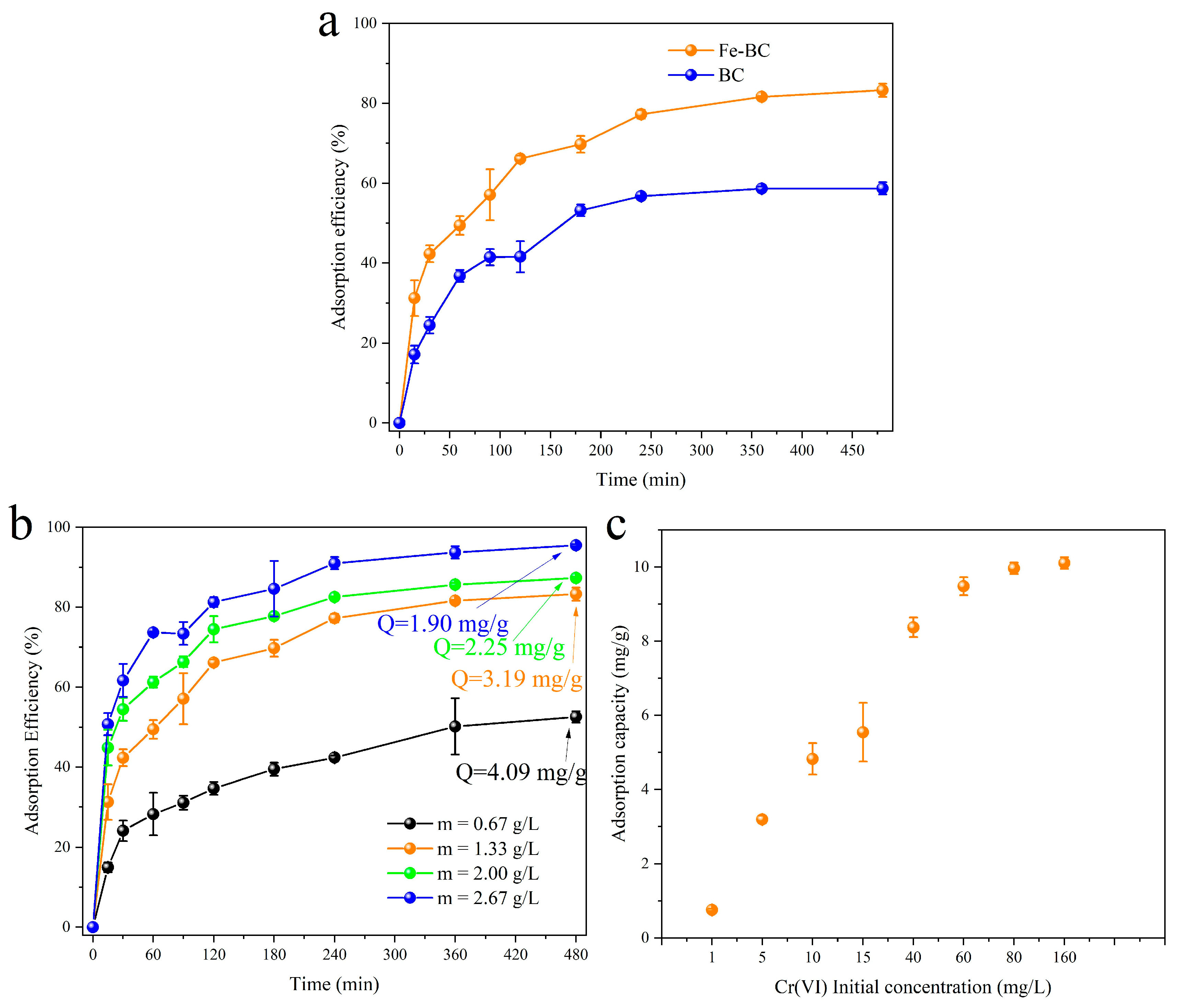
3.2. Adsorption Performance
3.3. Adsorption Isotherms
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics
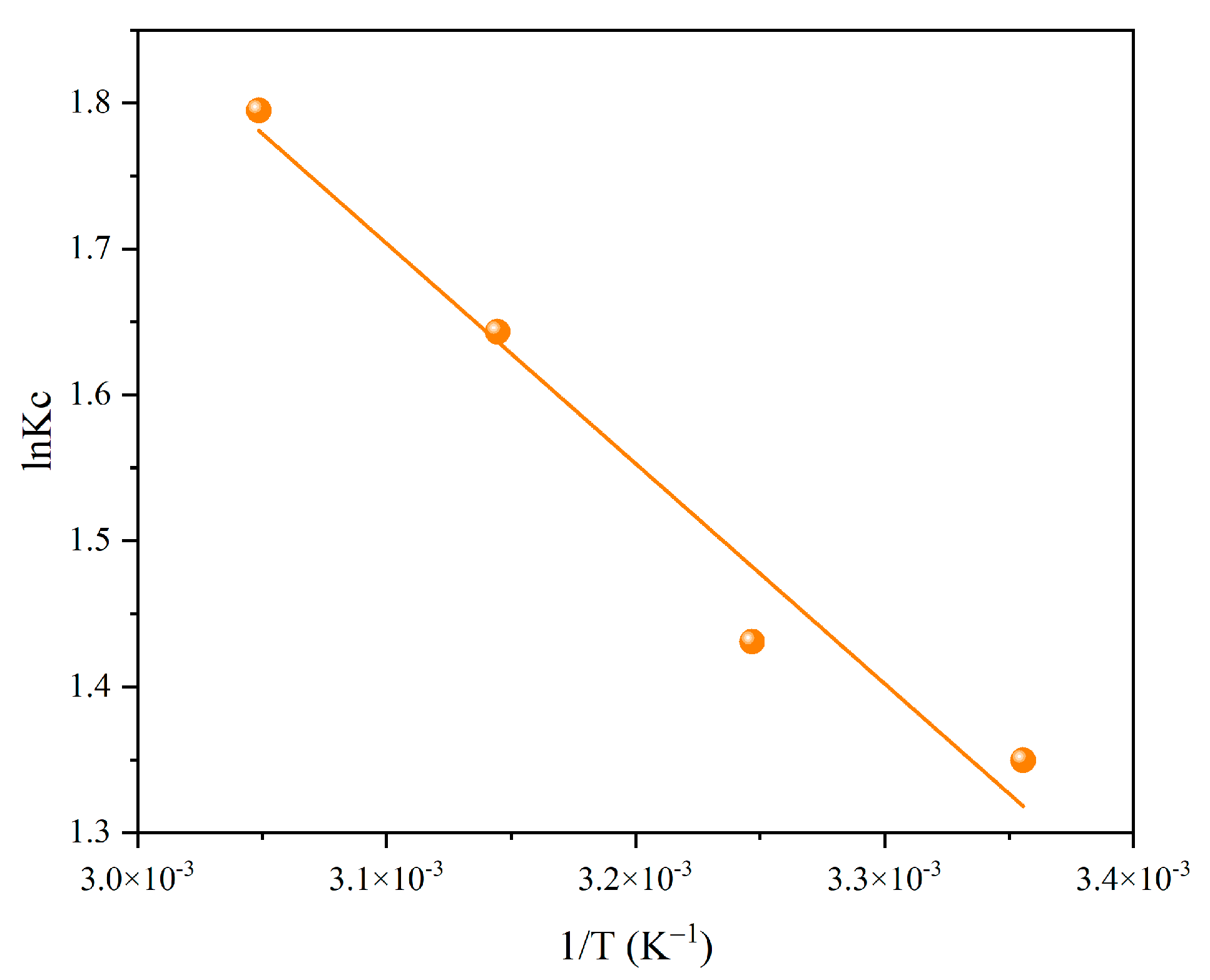
3.5. Adsorption Thermodynamics
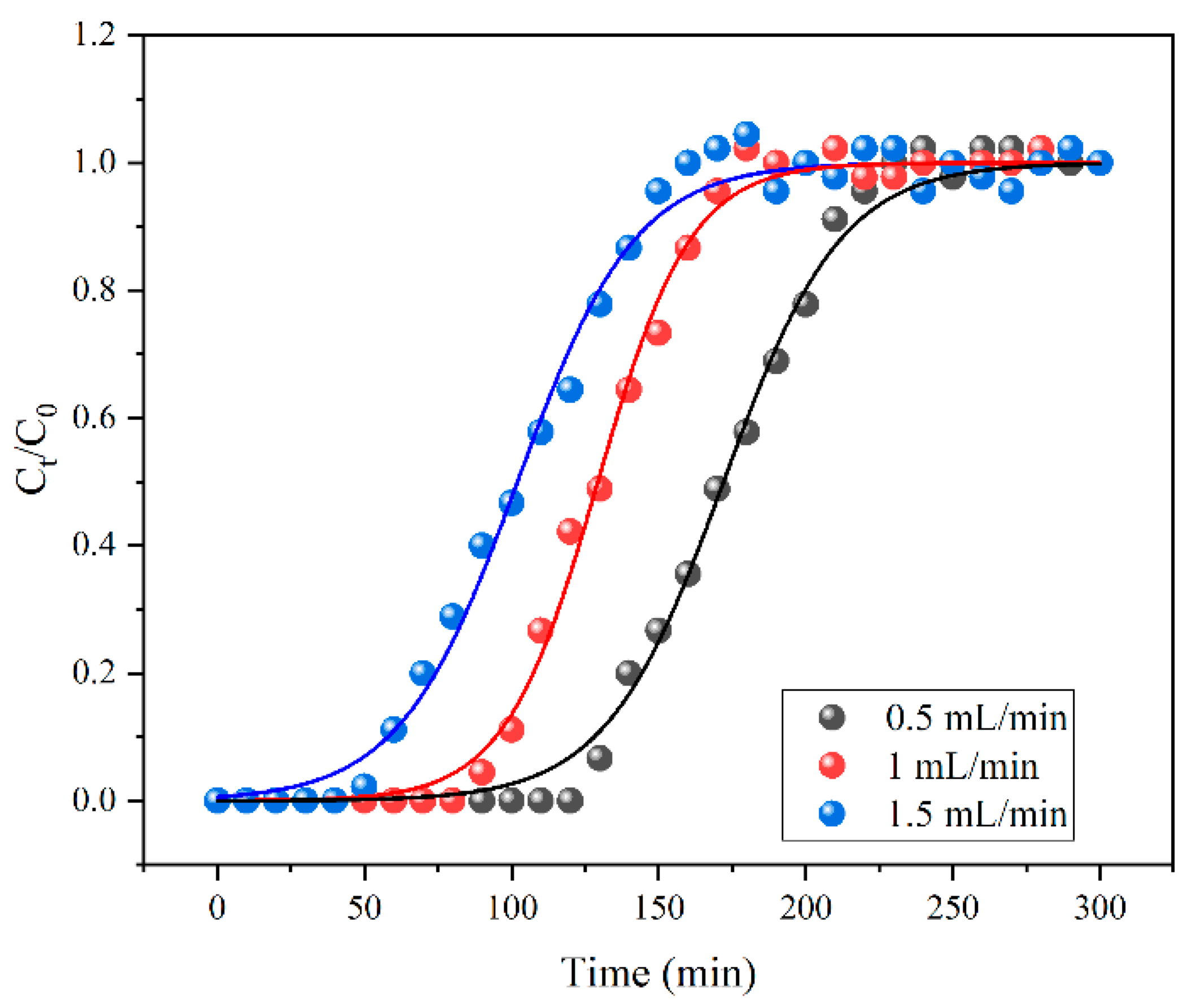
3.6. Dynamic Adsorption Experiment
3.7. Probable Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mo, W.; Yang, Y.; He, C.; Huang, Y.; Feng, J. Excellent adsorption properties of Mg/Al/Fe LDOs for Cr(VI) in water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, W.; Ilahi, N.; Kang, S.; Bahadur, A.; Banerjee, A.; Zada, S.; Ali, B.; Rafiq, M.; Zheng, G. Microbial diversity and community structure dynamics in acid mine drainage: Acidic fire with dissolved heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, S.; Che, W.; Li, Y. Removal of Cr(VI) from water using microalgae-based modified biochar: Adsorption performance, mechanisms, and life cycle assessment. Algal Res. 2025, 85, 103819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Liu, F.; Wang, G.; Liang, W.; Peng, C.; Zhang, W.; Lin, K.; Yang, J. Exploring different mechanisms of biochars in removing hexavalent chromium: Sorption, reduction and electron shuttle. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Wei, X.; Yin, H.; Zhu, M.; Luo, H.; Dang, Z. Synergistic removal of Cr(VI) by S-nZVI and organic acids: The enhanced electron selectivity and pH-dependent promotion mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, N.; Liu, P.; Liu, Y.; Lei, Y. Molecular-level investigation on removal mechanisms of aqueous hexavalent chromium by pine needle biochar. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Luo, H.; Cai, Y.; Dang, Z.; Yin, H. Selective removal of total Cr from a complex water matrix by chitosan and biochar modified-FeS: Kinetics and underlying mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 454, 131475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, G.; Zhou, J.; Jin, R. Interaction between hexavalent chromium and biologically formed iron mineral-biochar composites: Kinetics, products and mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Jiang, Y.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Zhao, Z.; Ren, S.; Liu, Z.; Crittenden, J.C. Mechanistic insights into adsorption and reduction of hexavalent chromium from water using magnetic biochar composite: Key roles of Fe3O4 and persistent free radicals. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Gao, F.; Lyu, H.; Ma, J.; Zhao, B.; Xu, S.; Ri, C.; Tang, J. Temperature-dependent carbothermally reduced iron and nitrogen doped biochar composites for removal of hexavalent chromium and nitrobenzene. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawed, A.; Golder, A.K.; Pandey, L.M. Bio-based iron oxide nanoparticles forming bi-functional chitosan composite adsorbent for Cr(VI) decontamination. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Yu, X.; Jia, Z.; Zhou, X. Cr(VI)-bioremediation mechanism of a novel strain Bacillus paramycoides Cr6 with the powerful ability to remove Cr(VI) from contaminated water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 455, 131519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Pan, R.; Xu, H.; Wu, S.; Liu, C.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Meng, F. High-yield preparation of 1T-MoS2 with excellent piezo-catalytic activity via W6+ doping for antibiotics degradation and Cr(VI) reduction: Mechanistic insights from characterizations to DFT calculations. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2025, 361, 124688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Xiao, Y.; Tan, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Y.; Pi, K.; Qiu, G.; Yang, X. Influence of coexisting anions on the one-step electrochemical reduction and precipitation removal of Cr(VI): Implications for advanced wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Lafi, A.G.; Khuder, A. Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by activated carbon and its composite with P2W17O61: A spectroscopic study to reveal adsorption mechanism. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zhou, F.; Yang, C.; Lu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Tu, B.; Li, L. Adsorption and reduction of Cr(VI) by C-P-O groups in biochar: Performance and mechanisms. Solid State Sci. 2025, 160, 107815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.H.; Vu, H.P.N.; Do, P.V.; Kha, V.-P.; Van, N.T.; Phan, V.-T.; Huynh, D.-H.; Le, T.-S. Enhanced adsorption of Cr(VI) pollutants using CaFe2O4@rGO modified-biochar derived from mixture of black soldier flier exuviae and durian peel. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 66, 106017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-Z.; Li, R.; Ma, Z.-Q.-L.; Liu, C.-X.; Zhao, W.-T. Biochar-algae microspheres based on sodium alginate for the highly efficient adsorption of malachite green dye: Kinetics, isotherms, and mechanism of adsorption. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2025, 272, 104547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutabazi, E.; Qiu, X.; Song, Y.; Li, C.; Jia, X.; Hakizimana, I.; Niu, J.; Nuramkhaan, M.; Zhao, Y. Cr(VI) adsorption on activated carbon, sludge derived biochar, and peanut shells derived biochar: Performance, mechanisms during the reuse process and site energy distribution analysis. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 57, 104679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, Q.-M.; Nguyen, T.-B.; Chen, C.-W.; Chen, W.-H.; Bui, X.-T.; Dong, C.-D. KHCO3-activated high surface area biochar derived from brown algae: A case study for efficient adsorption of Cr(VI) in aqueous solution. Environ. Res. 2024, 247, 118227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militao, I.M.; Roddick, F.; Fan, L.; Zepeda, L.C.; Parthasarathy, R.; Bergamasco, R. PFAS removal from water by adsorption with alginate-encapsulated plant albumin and rice straw-derived biochar. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.-d.; Shen, L.; Cao, Y.-q. Animal or plant waste-derived biochar for Cd(II) immobilization: Effects of freeze-thaw-wet-dry cyclic aging on adsorption behavior in tea garden soils. Desalination Water Treat. 2020, 182, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, S.M.; Raj, R.; Chakraborty, I.; Dubey, B.K.; Ghangrekar, M.M. Sewage sludge biochar derived binder-free electrode for electrochemical advanced oxidation treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Sun, P.; Niu, S.; Shen, B.; Lyu, H. Atmosphere matters: The protection of wet ball milling instead of dry ball milling accelerates the electron transfer effect of sulfurized micron iron/biochar to Cr (VI). Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Gu, X.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Cao, Y.; Yang, G.; Kuang, C.; Li, X.; Qing, Y.; Wu, Y. A novel almond shell biochar modified with FeS and chitosan as adsorbents for mitigation of heavy metals from water and soil. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 360, 130943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Deng, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Hou, K.; Zeng, G. Stabilization of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) with modified biochar for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 332, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Ning, P. Adsorption properties and mechanism of Cr(VI) by Fe2(SO4)3 modified biochar derived from Egeria najas. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 645, 128938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, K.; Tian, W.; Bai, J.; Zhao, J.; Du, Z.; Song, T.; Chu, M.; Wang, L.; Xie, W. Synthesis of floatable magnetic iron/biochar beads for the removal of chromium from aqueous solutions. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Bhattu, M.; Liew, R.K.; Verma, M.; Brar, S.K.; Bechelany, M.; Jadeja, R. Transforming rice straw waste into biochar for advanced water treatment and soil amendment applications. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 37, 103932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Han, J.; Mi, S.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Zuo, J.; Zhu, G. Creation of ultra-fine sulfide-modified nano zero-valent iron onto NH2-SiO2 surface for enhanced removal performance of Ni(II). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Xu, W.; Khan, S.B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Su, X.; Lin, Z. Preparation of sludge biochar rich in carboxyl/hydroxyl groups by quenching process and its excellent adsorption performance for Cr(VI). Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Shao, F.; Liao, Q.; Shang, J. Scavenging of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron supported by biochar. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 91, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Kumar, R.; Abhishek, K.; Shang, J.; Bhattacharya, S.; Sengupta, S.; Kumar, N.; Singh, R.K.; Mallick, J.; Kar, M.; et al. Single-step synthesis of activated magnetic biochar derived from rice husk for hexavalent chromium adsorption: Equilibrium mechanism, kinetics, and thermodynamics analysis. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 18, 100796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wan, Y.; Li, J.; Cai, Y.; Dang, Z.; Yin, H. MgxCu-biochar activated peroxydisulfate triggers reductive species for the reduction and enhanced electron-transfer degradation of electron-deficient aromatic pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Wang, J.J.; Li, R.; Park, J.; Meng, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pensky, S.; Zhang, Z. Enhanced sorption of hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] from aqueous solutions by diluted sulfuric acid-assisted MgO-coated biochar composite. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xiao, R.; Li, R.; Ali, A.; Chen, A.; Zhang, Z. Enhanced aqueous Cr(VI) removal using chitosan-modified magnetic biochars derived from bamboo residues. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.; Liu, M.; Chen, Z. Removal of metalloids and heavy metals from acid mine drainage using biosynthesized Fe/Cu NPs. Biochem. Eng. J. 2024, 201, 109158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.-K.; Ly-Tran, Q.-B.; Dinh, V.-P.; Duong, B.-N.; Nguyen, T.-P.-T.; Nguyen Kim Tuyen, P. Adsorption mechanism of aqueous Cr(vi) by Vietnamese corncob biochar: A spectroscopic study. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 39205–39218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, P.; Zhou, Z.; Huhetaoli; Wu, Y.; Lei, T. Characteristics and adsorption of Cr(VI) of biochar pyrolyzed from landfill leachate sludge. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 162, 105449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.; Bu, J.; Ren, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, K.; Ding, A. Mechanism of Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Aqueous Solution by Fe-Modified Biochar and Its Application. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X. Surface modified leaves with high efficiency for the removal of aqueous Cr (VI). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 484, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Gao, B.; Liu, Z.; Lin, P.; Liu, H.; Fu, H.; Zhang, H. Amine–functionalised magnetic graphene–oxide nanosheets for the adsorption and reduction of Cr(VI) in water. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2025, 152, 111891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yang, J.; Gao, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Xu, Z. Removal of chromium (VI) from water by porous carbon derived from corn straw: Influencing factors, regeneration and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Guo, C.; Guan, Q.; He, L.; Zhou, H.; Xin, H.; He, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, R. Efficient Anchoring of Cu(II)–Tetracycline Complex in Paper Mill Sludge Biochar-Limited Nanospace. ACS EST Water 2023, 4, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, M.; Ma, L.; Ren, J.; Ma, P.; Li, B.; Wu, N.; Song, Z.; Huang, L. Nitrogen and sulfur codoped micro-mesoporous carbon sheets derived from natural biomass for synergistic removal of chromium(VI): Adsorption behavior and computing mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 138930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sun, P.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zheng, X. Distinct chromium removal mechanisms by iron-modified biochar under varying pH: Role of iron and chromium speciation. Chemosphere 2023, 331, 138796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg/g) | kL (L/mg) | R2 | kF ((mg/g) (L/mg)1/n) | 1/n | R2 |
| 10.03 | 0.25 | 0.9309 | 3.34 | 0.25 | 0.9181 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Yao, R.; Yu, M.; Ye, Z.; Lu, Y.; Yu, X.; Tang, J.; Sun, J. Converting Waste into Treasure: Efficient Adsorption of Cr(VI) Using Iron-Modified Rice Straw Biochar. Toxics 2025, 13, 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060458
Liu H, Yao R, Yu M, Ye Z, Lu Y, Yu X, Tang J, Sun J. Converting Waste into Treasure: Efficient Adsorption of Cr(VI) Using Iron-Modified Rice Straw Biochar. Toxics. 2025; 13(6):458. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060458
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hang, Runlin Yao, Mingling Yu, Zongda Ye, Yingrui Lu, Xiaolong Yu, Jin Tang, and Jianteng Sun. 2025. "Converting Waste into Treasure: Efficient Adsorption of Cr(VI) Using Iron-Modified Rice Straw Biochar" Toxics 13, no. 6: 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060458
APA StyleLiu, H., Yao, R., Yu, M., Ye, Z., Lu, Y., Yu, X., Tang, J., & Sun, J. (2025). Converting Waste into Treasure: Efficient Adsorption of Cr(VI) Using Iron-Modified Rice Straw Biochar. Toxics, 13(6), 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060458









