Efficient Adsorption of Lead on Hydro-Pyrochar Synthesized by Two-Step Conversion of Corn Cob in Magnesium Chloride Medium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Synthesis
2.2. Metal Solution Preparation
2.3. Material Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
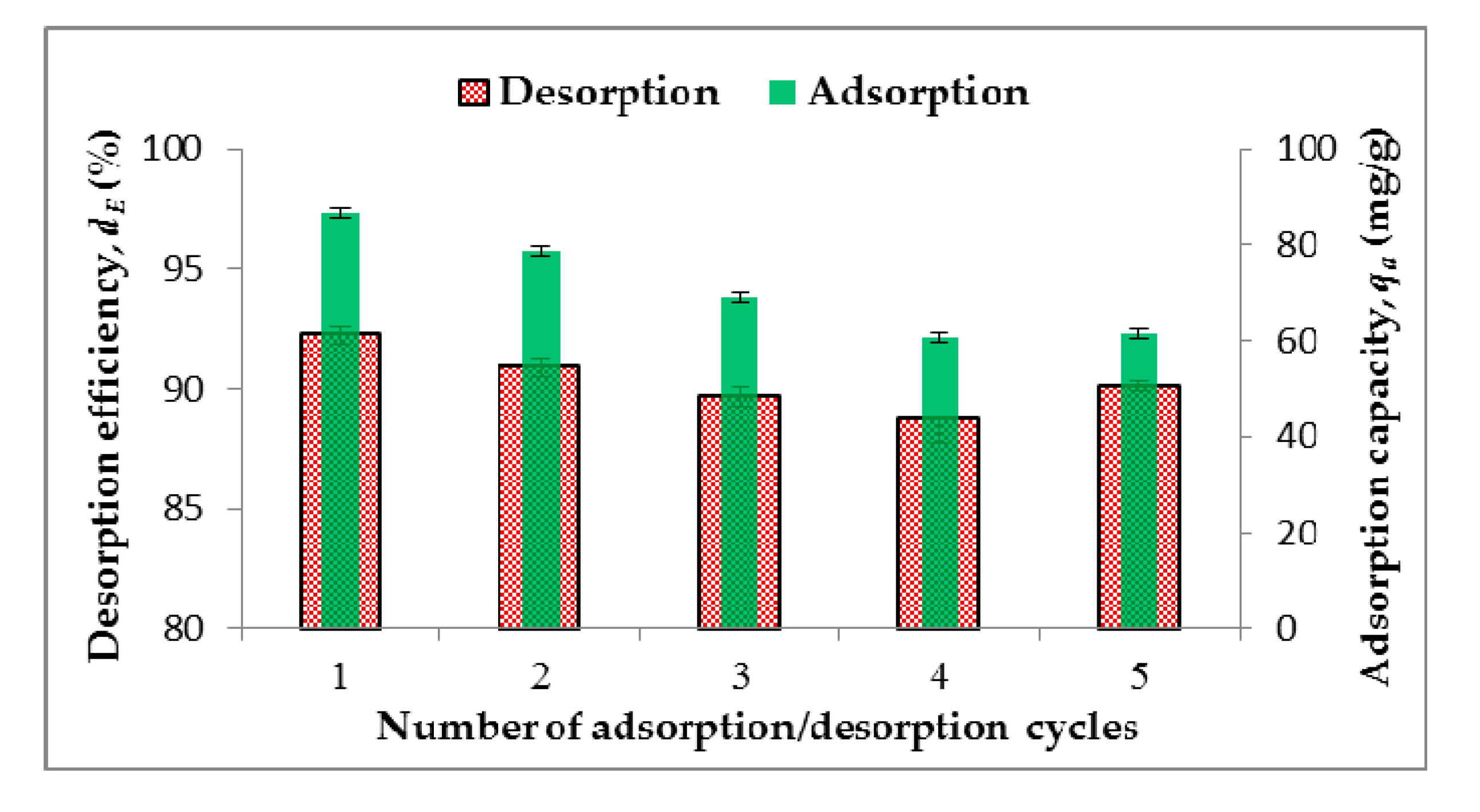
2.5. Recycling Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
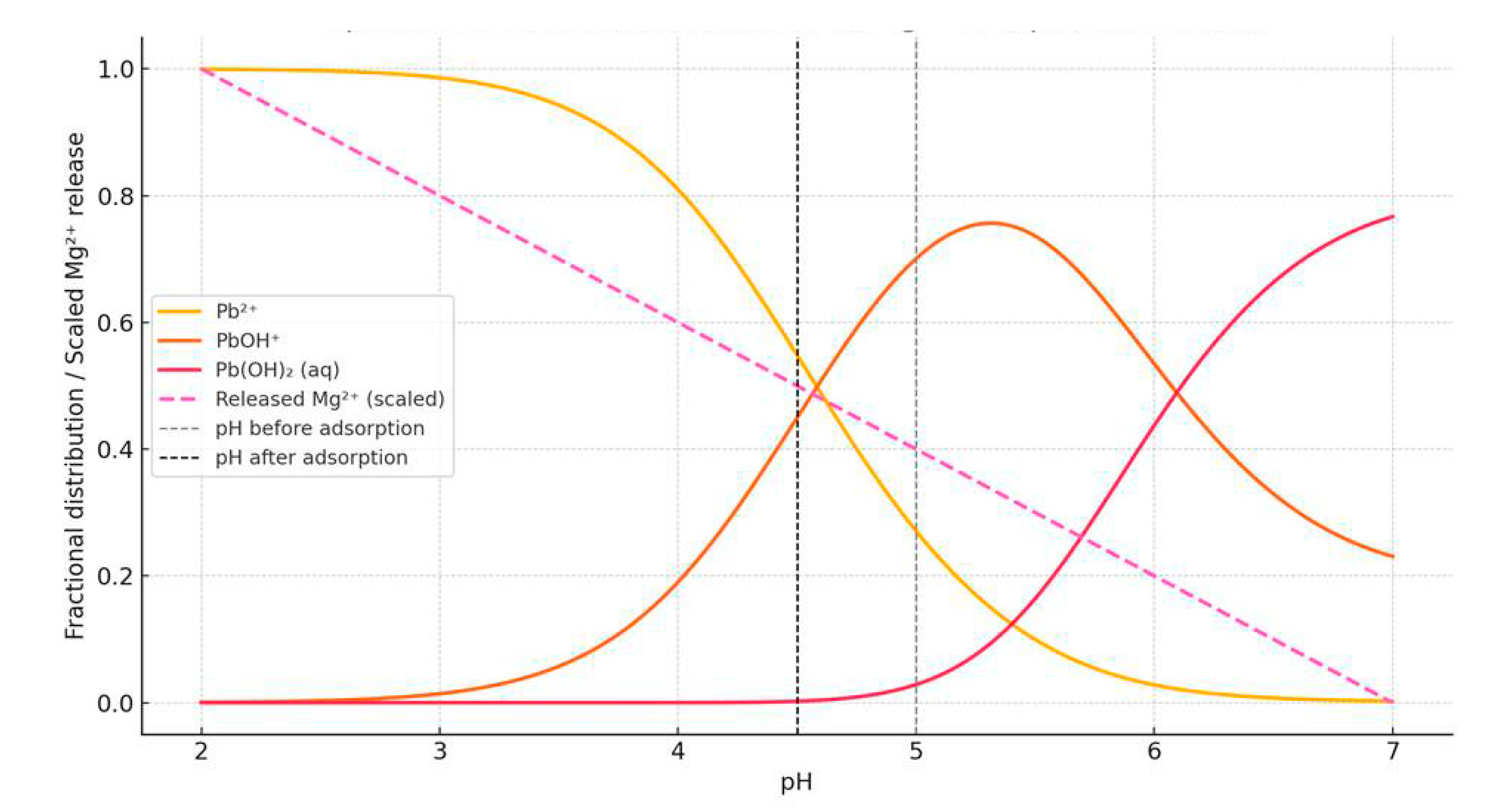
3.2. Impact of the pH on Pb Adsorption
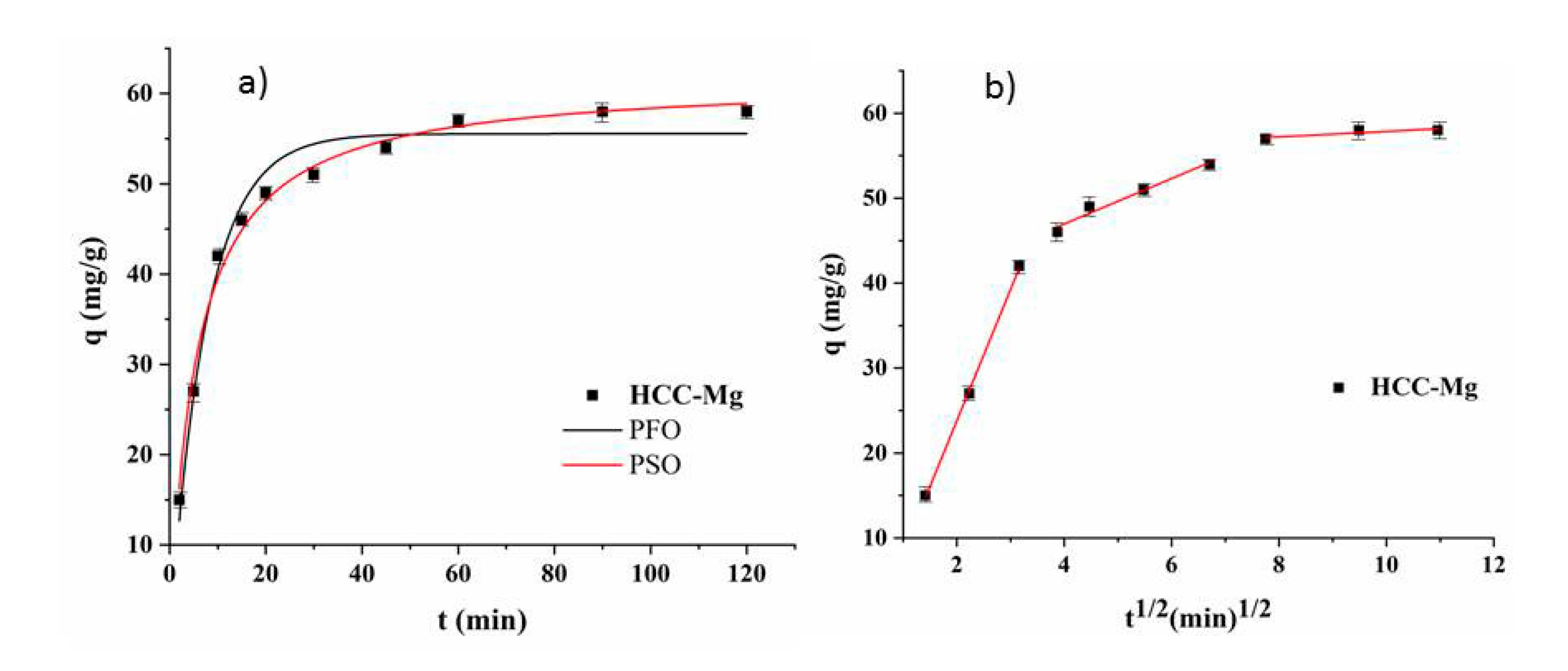
3.3. Kinetic Study
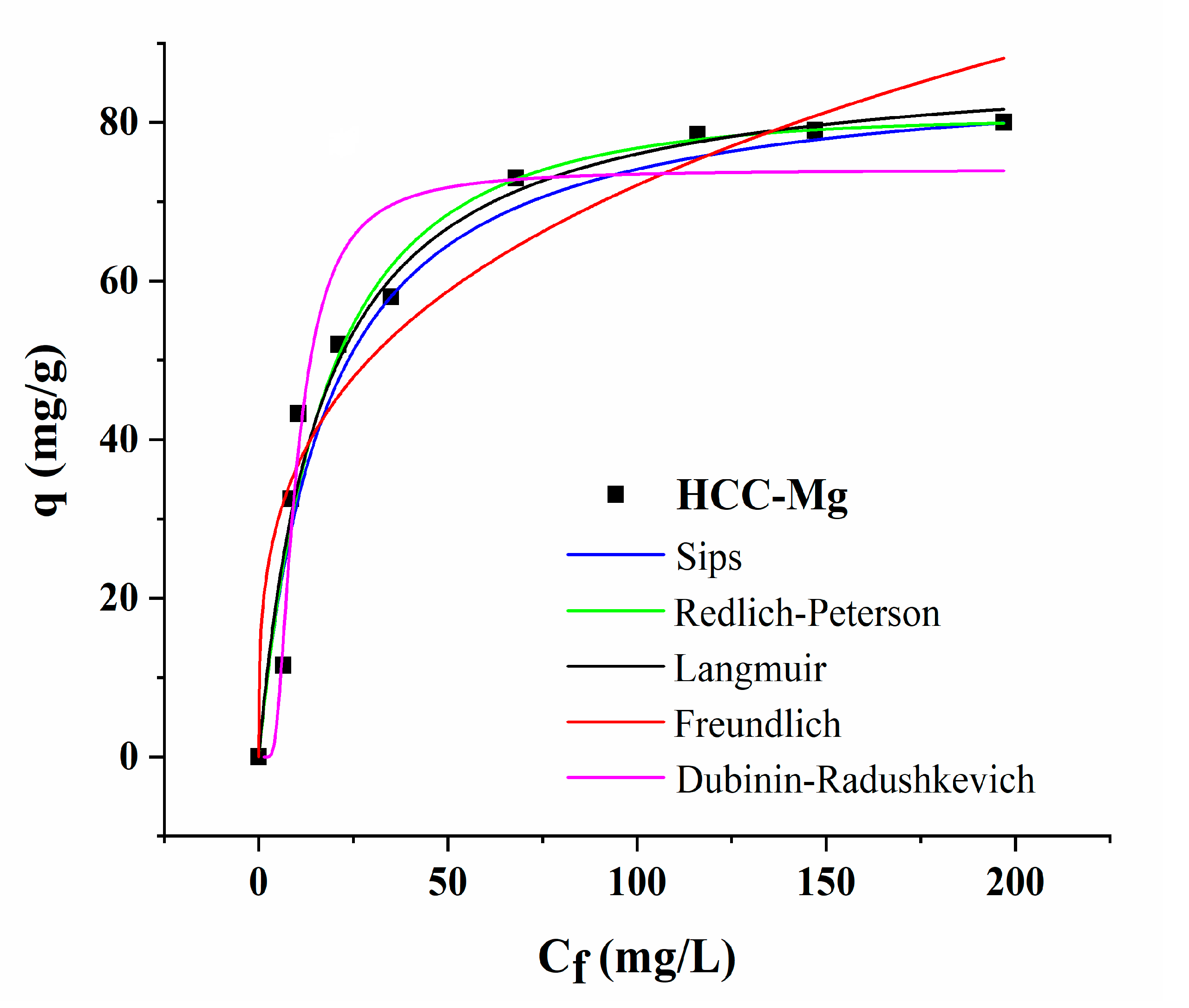
3.4. Isotherm Study
3.5. Desorption Study
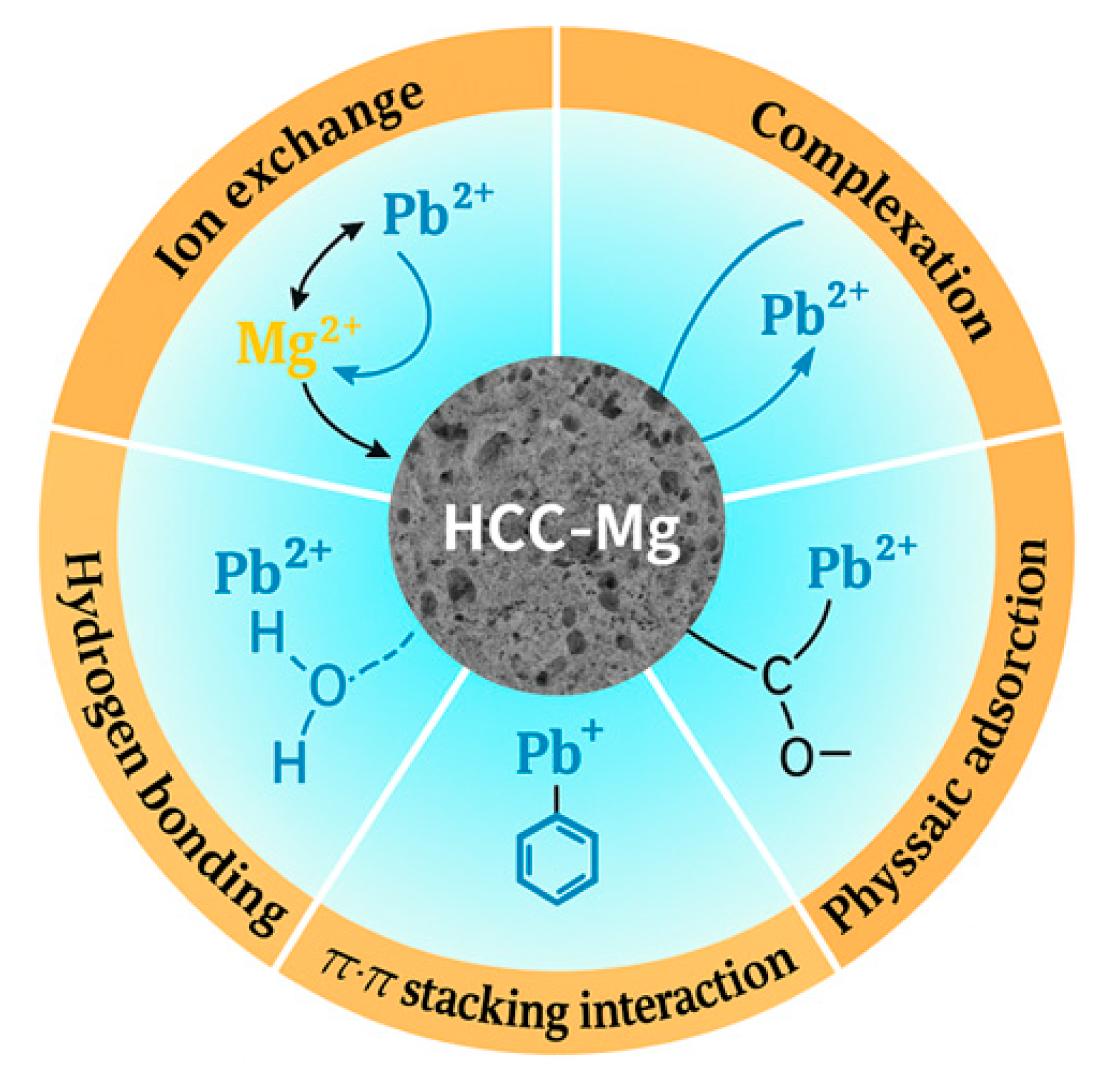
3.6. Proposed Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.-W.; Choi, H.; Hwng, U.-K.; Kang, J.-C.; Kang, Y.J.; Kim, K.I.; Kim, J.-H. Toxic effects of lead exposure on bioaccumulation, oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, and immune responses in fish: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 68, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Exposure to Lead: A Major Environmental Risk Factor for Children. 2010. Available online: https://www.who.int (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Petrović, J.; Ercegović, M.; Simić, M.; Koprivica, M.; Dimitrijević, J.; Jovanović, A.; Janković Pantić, J. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Waste Biomass: A Review of Hydrochar Preparation and Environmental Application. Processes 2024, 12, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanovic, D.; Dikić, J.; Štulović, M.; Anđić, Z.; Kamberović, Ž.; Jevtić, S. Sorption of Pb2+, Zn2+, Cu2+ and Ni2+ Ions on Na-enriched Natural Zeolite for Wastewater Treatment Process: A Kinetic Approach. Metall. Mater. Eng. 2023, 29, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrijević, J.; Jevtić, S.; Marinković, A.; Simić, M.; Koprivica, M.; Petrović, J. Ability of Deep Eutectic Solvent Modified Oat Straw for Cu(II), Zn(II), and Se(IV) Ions Removal. Processes 2023, 11, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milićević, S.; Milošević, V.; Povrenović, D.; Stojanović, J.; Martinović, S.; Babić, B. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution by using natural and Fe(III) oxyhydroxide clinoptilolite. Clays Clay Miner. 2013, 61, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milojković, J.V.; Stojanović, M.D.; Mihajlović, M.L.; Lopičić, Z.R.; Petrović, M.S.; Šoštarić, T.D.; Ristić, M.Đ. Compost of aquatic weed Myriophyllum spicatum as low-cost biosorbent for selected heavy metal ions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, X.; Gao, F.; Wang, Z. Ferrocene-based metal-organic frameworks with dual synergistic active sites for selectively electrochemical removal of arsenic from contaminated water. Water Res. 2024, 260, 121915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, W.; Liu, J.; Tao, H.; Yang, J.; Qin, S.; Yamauchi, Y.; Yuliarto, B.; Asakura, Y.; Huang, L. Bipyridine covalent organic framework aerogel for highly selective recovery of palladium in wastewater. Chem. Sci. 2025, 16, 5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qui, B.; Tao, X.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Ding, X.; Chu, H. Biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal: A review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 155, 105081. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.; He, J.; Khan, M.A.; Chang, K.; Liu, Y.; Guo, G.; Li, X.; Jin, F.; Kuang, M.; Gouda, S.; et al. Potential Application Performance of Hydrochar from Kitchen Waste: Effects of Salt, Oil, Moisture, and pH. Toxics 2023, 11, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.-W.; Xu, H.; Guo, J.-Z.; Bai, L.-Q.; Li, B. Efficient adsorption of methylene blue on carboxylate-rich hydrochar prepared by one-step hydrothermal carbonization of bamboo and acrylic acid with ammonium persulphate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrović, J.T.; Stojanović, M.D.; Milojković, J.V.; Petrović, M.S.; Šoštarić, T.D.; Laušević, M.D.; Mihajlović, M.L. Alkali modified hydrochar of grape pomace as a perspective adsorbent of Pb2+ from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Huang, Y.; Cao, J.; Hu, H.; Dong, L.; Zha, J.; Su, Y.; Ruan, R.; Tao, S. Qualitative and relative distribution of Pb2+ adsorption mechanisms by biochars produced from a fluidized bed pyrolysis system under mild air oxidization conditions. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 323, 114600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Huang, S.; Laird, D.A.; Wang, X.; Meng, Z. Adsorption behaviour and mechanisms of cadmium and nickel on rice straw biochars in single-and binary-metal systems. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Lin, S.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, G.; Cai, C. Enhanced Adsorption of Cadmium by a Covalent Organic Framework-Modified Biochar in Aqueous Solution. Toxics 2024, 12, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthanna, A.J.; Mohammed, D.; Ioannis, A.; Kingsley, O.I. Recent progress on corn (Zea mays L.)-based materials as raw, chemically modified, carbonaceous, and composite adsorbents for aquatic pollutants: A review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2023, 172, 106004. [Google Scholar]
- Petrović, M.S.; Sostaric, T.D.; Pezo, L.L.; Stankovic, S.M.; Lacnjevac, C.M.; Milojkovic, J.V.; Stojanovic, M.D. Usefulness of ANN-based model for copper removal from aqueous solutions using agro industrial waste materials. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 2015, 21, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, M.; Šoštarić, T.; Stojanović, M.; Petrović, J.; Lačnjevac, Č.; Trivunac, K.; Stanković, S. Characterization and usefulness of corn cob as biosorbent for Pb2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ ions removal from aqueous solutions. Zas. Mat. 2016, 57, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, M.; Šoštarić, T.; Stojanović, M.; Petrović, J.; Mihajlović, M.; Ćosović, A.; Stanković, S. Mechanism of adsorption of Cu2+ and Zn2+ on the corn silk (Zea mays L.). Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, M.; Šoštarić, T.; Stojanović, M.; Milojković, J.; Mihajlović, M.; Stanojević, M.; Stanković, S. Removal of Pb2+ ions by raw corn silk (Zea mays L.) as a novel biosorbent. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 58, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gel ster stoffe. K. Sven. Vetenskapsakad. Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, W.; Morris, J. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, T.W.; Chakkravorti, R.K. Pore and solid diffusion models for fixed-bed adsorbers. AlChE J. 1974, 20, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Über die adsorption in lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57A, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinin, M.M.; Radushkevich, L.V. The equation of the characteristic curve of the activated charcoal. Proc. Acad. Sci. USSR Phys. Chem. Sect. 1947, 55, 331–337. [Google Scholar]
- Sips, R. On the structure of a catalyst surface. J. Chem. Phys. 1948, 16, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redlich, O.; Peterson, D. A useful adsorption isotherm. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 63, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, J.; Ercegović, M.; Simić, M.; Kalderis, D.; Koprivica, M.; Milojković, J.; Radulović, D. Novel Mg-doped pyro-hydrochars as methylene blue adsorbents: Adsorption behavior and mechanism. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 379, 121424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meili, L.; Lins, P.V.; Zanta, C.L.P.S.; Soletti, J.I.; Ribeiro, L.M.O.; Dornelas, C.B.; Silva, T.L.; Vieira, M.G.A. MgAl-LDH/Biochar composites for methylene blue removal by adsorption. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 168, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosavljević, N.B.; Ristić, M.Đ.; Perić-Grujić, A.A.; Filipović, J.M.; Štrbac, S.B.; Rakočević, Z.L.; Krušić, M.T.K. Removal of Cu2+ ions using hydrogels of chitosan, itaconic and methacrylic acid: FTIR, SEM/EDX, AFM, kinetic and equilibrium study. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 388, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, Q.; Fang, M.; Wu, D.; Cui, D.; Pan, S.; Bai, J.; Xu, F.; Wang, Z. Hydrothermal carbonization of food waste for sustainable biofuel production: Advancements, challenges, and future prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 165327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, Q.; Wu, D.; Cui, D.; Wu, C.; Bai, J.; Xu, F.; Liu, B.; Shan, Z.; Zhang, J. Influence of temperature and process water circulation on hydrothermal carbonization of food waste for sustainable fuel production. J. Energy Inst. 2024, 112, 101459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, Q.; Cui, D.; Wu, D.; Bai, J.; Qin, H.; Xu, F.; Wang, Z. Insights into the chemical structure evolution and carbonisation mechanism of biomass during hydrothermal treatment. J. Energy Inst. 2023, 108, 101257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Shi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zou, L.; Sun, J. Interaction between nano-biochar and Pb during migration in saturated porous media: Impact of ionic strength, pH and flow velocity. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 717, 136720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ding, L.; Yan, A.; Wei, J.; Liu, Y.; Niu, Y.; Qu, R. Facile fabrication of UiO-66-NH2 modified with dodecyl and polyethyleneimine by post-synthesis functionalization strategy and simultaneous adsorption removal of anionic and cationic dyes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 692, 134019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovici, I.C.; Dobrinas, S.; Soceanu, A.; Popescu, V.; Prodan, G.; Omer, I. New Approaches for Pb(II) Removal from Aqueous Media Using Nanopowder Sodium Titanosilicate: Kinetics Study Thermodynamic Behavior. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, M.; He, C.; Joya, M.B.; Kaka, A.Z.H.; Kollah, E.S.; Mwansa, B.K.; Tremblay, P.-L.; Zhang, T. A polyethyleneimine-coated thermally-oxidized graphitic-carbon nitride adsorbent for the removal of organic pollutants. Chemosphere 2025, 373, 144168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, M.; Petrović, J.; Šoštarić, T.; Ercegović, M.; Milojković, J.; Lopičić, Z.; Kojić, M. A Mechanism Assessment and Differences of Cadmium Adsorption on Raw and Alkali-Modified Agricultural Waste. Processes 2022, 10, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Dong, X.; Ime, I.M.; Gao, B.; Ma, L.Q. Pyrolytic temperatures impact lead sorption mechanisms by bagasse biochars. Chemosphere 2014, 105, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Wang, E. Adsorption and Recovery Studies of Cadmium and Lead Ions Using Biowaste Adsorbents from Aqueous Solution. Searations 2025, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Mosa, A.; Gao, B. Hydrochar Loaded with Nitrogen-Containing Functional Groups for Versatile Removal of Cationic and Anionic Dyes and Aqueous Heavy Metals. Water 2024, 16, 3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, S.; Qiu, R. Relative distribution of Pb2+ sorption mechanisms by sludge-derived biochar. Water Res. 2012, 46, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elaigwu, S.E.; Rocher, V.; Kyriakou, G.; Greenway, G.M. Removal of Pb2+ and Cd2+ from aqueous solution using chars from pyrolysis microwave-assisted hydrothermal carbonization of Prosopis africana shell. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 3467–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koprivica, M.; Simić, M.; Petrović, J.; Ercegović, M.; Dimitrijević, J. Evaluation of Adsorption Efficiency on Pb(II) Ions Removal Using Alkali-Modified Hydrochar from Paulownia Leaves. Processes 2023, 11, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madduri, S.; Elsayed, I.; Hassan, E.B. Novel oxone treated hydrochar for the removal of Pb(II) and methylene blue (MB) dye from aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Lu, C.; Liang, B.; Yin, C.; Lei, G.; Wang, B.; Zhou, X.; Zhen, J.; Quan, S.; Jing, Y. Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solution and Adsorption Kinetics of Corn Stalk Biochar. Separations 2023, 10, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.H.; Yang, Z.K.; Nagarajan, D.; Chang, J.S.; Ren, N.Q. High-efficiency removal of lead from wastewater by biochar derived from anaerobic digestion sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Yan, J.; Li, L.; Quan, G.; Ding, C.; Chen, T.; Yin, C.; Gao, J.; Hussain, Q. Does Biochar Alter the Speciation of Cd and Pb in Aqueous Solution. Bioresources 2014, 10, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Kuang, X.; Xu, Z.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Adsorption of Cadmium and Lead Capacity and Environmental Stability of Magnesium-Modified High-Sulfur Hydrochar: Greenly Utilizing Chicken Feather. Toxic 2024, 12, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Zheng, H.; Li, F.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Liu, C.; Chen, L.; Xing, B. Investigating the mechanisms of biochar’s removal of lead from solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 177, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhafez, A.A.; Li, J. Removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solution by using biochars derived from sugar cane bagasse orange peel. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 61, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Song, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Tao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z. Simultaneous scavenging of Cd(II) and Pb(II) from water by sulfide-modified magnetic pinecone-derived hydrochar. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 341, 130758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Guo, J.-Z.; Liu, J.-L.; Fang, L.; Lv, J.-Q.; Lv, K. Removal of aqueous-phase lead ions by dithiocarbamate modified hydrochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, B.; Zhao, L.; Sun, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, F. Biochar-supported reduced graphene oxide composite for adsorption and coadsorption of atrazine and lead ions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
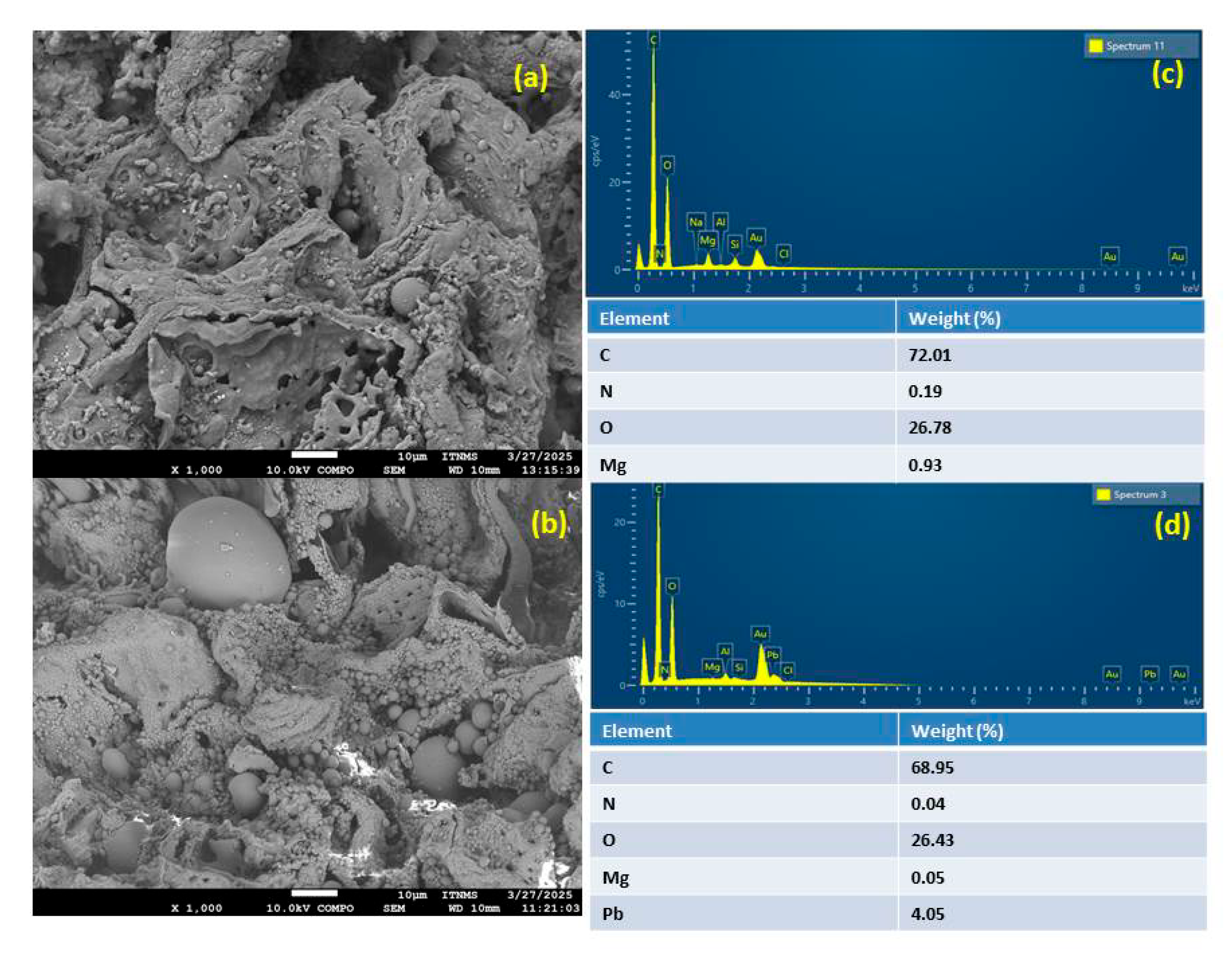
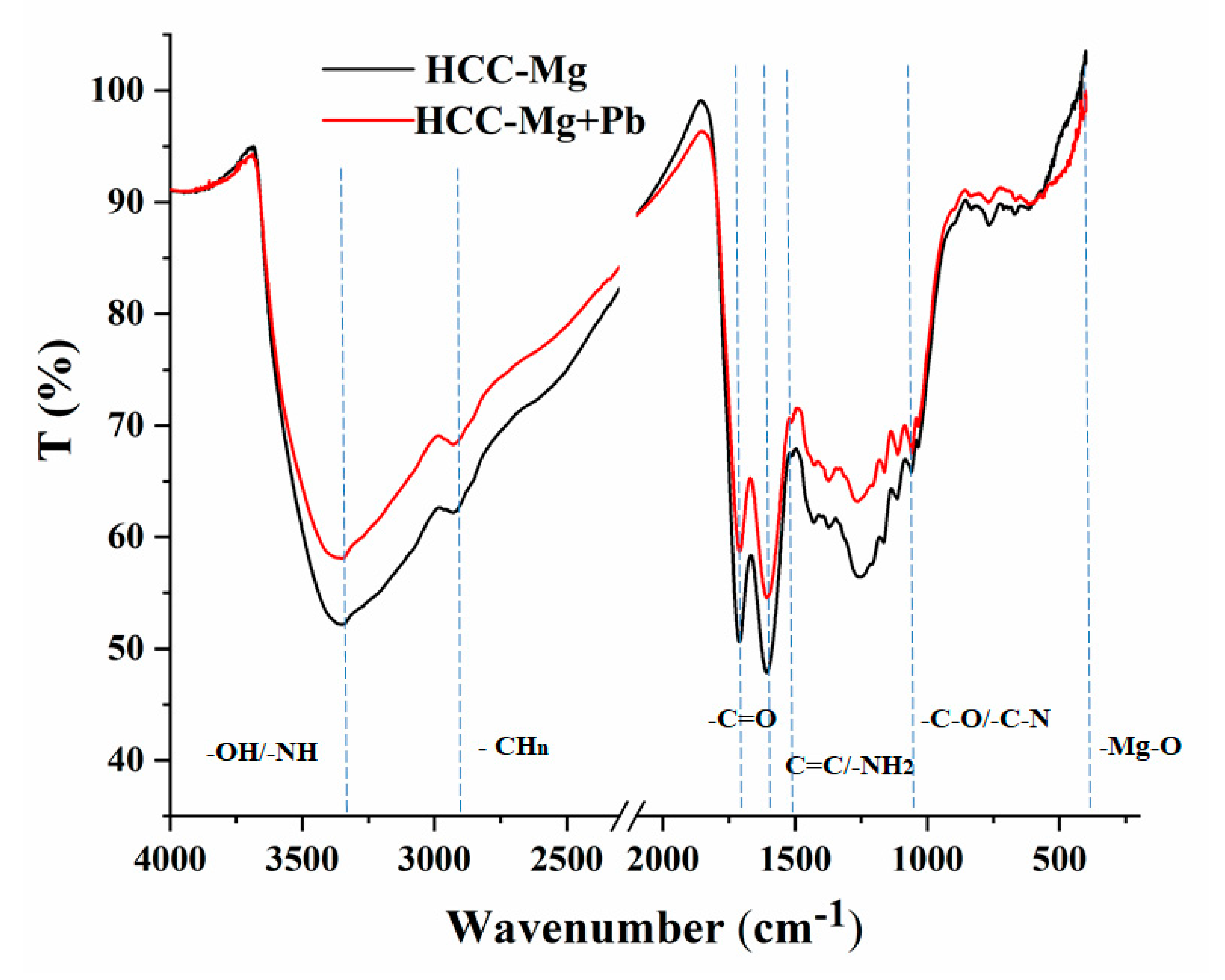
| Peak Position (cm−1) | Assigments | References |
|---|---|---|
| 3350 | –OH/–NH | [34] |
| 2930 | –CHn | [35] |
| Near 1710 | C=O | [36] |
| Near 1610 | C=O | [37] |
| Near 1526 | C=C/–NH2 | [34,37] |
| 1033 | –C-O/–C-N | [36] |
| 450 | –Mg-O | [32,33] |
| qe,exp | mg/g | 60.07 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFO | Intraparticle Diffusion | ||||
| qe,cal | mg/g | 55.54 | ki1 | mg g/min1/2 | 15.46 |
| k1 | 1/min | 0.13 | R2 | 0.999 | |
| R2 | 0.972 | ki2 | mg g/min1/2 | 2.66 | |
| PSE | R2 | 0.969 | |||
| qe,cal | mg/g | 61.63 | ki3 | mg g/min1/2 | 0.32 |
| k2 | g/mg min | 0.0029 | R2 | 0.791 | |
| R2 | 0.991 | ||||
| Two-Parameter Isotherm Models | Three-Parameter Isotherm Models | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | Sips | ||
| qmax (mg g−1) | 88.43 | qmax (mg g−1) | 87.08 |
| KL (L mg−1) | 0.061 | KS (mg L−1)−1/ns | 0.057 |
| R2 | 0.995 | nS | 1.01 |
| R2 | 0.997 | ||
| Freundlich | Redlich–Peterson | ||
| KF (mg g−1 (mg L−1)−1/nf) | 18.44 | KRP (L g−1) | 4.764 |
| nF | 3.38 | aRP (mg L−1)-g | 0.037 |
| R2 | 0.907 | g | 1.068 |
| R2 | 0.963 | ||
| Dubinin–Radushkevich | |||
| qDR (mg g−1) | 74.05 | ||
| KDR (mol2 J−1) | 67.76 | ||
| E (KJ mol−1) | 0.086 | ||
| R2 | 0.949 | ||
| Used Material | Preparation Method | pH | Temp (°C) | q (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn cob, raw | None | 5.0 | 25 | 5.95 | [19] |
| Sugarcane bagasse biochar | Pyrolysis | 5.0 | 25 | 21.0 | [43] |
| Luffa peels | HNO3/NaOH modification | 5.5 | 25 | 34.0 | [44] |
| Corn straw biochar/rGO composite | HTC | 5.5 | 30 | 34.02 | [45] |
| Sludge-derived biochar | Pyrolysis | 5.0 | 25 | 30.88 | [46] |
| Prosopis africana shell biochar | Pyrolysis + HTC | 5.0 | 25 | 45.3 | [47] |
| Chamomile flowers | HNO3/NaOH modification | 5.0 | 25 | 49.5 | [44] |
| Paulownia leaf hydrochar | HTC | 5.0 | 25 | 49.62 | [48] |
| Pine wood hydrochar | Oxone-modified hydrochar | 5.0 | 25 | 46.7 | [49] |
| Corn stalk biochar | pyrolysis | 5.0 | 25 | 20.8 | [50] |
| Waste activated sludge biochar | Anaerobic digestion + pyrolysis | 5.0 | 25 | 53.96 | [51] |
| Peanut hull biochar | Pyrolysis | 5.5 | 25 | 63.09 | [52] |
| Modified chicken feather hydrochar | Mg-modified hydrochar | 5.0 | 25 | 70.41 | [53] |
| Peanut shell biochar | Pyrolysis | 5.0 | 25 | 82.5 | [54] |
| Orange peel biochar | Pyrolysis | 5.0 | 25 | 86.96 | [55] |
| HCC-Mg (this study) | HTC + MgCl2 pyrolysis | 5.0 | 25 | 87.05 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simić, M.; Petrović, J.; Koprivica, M.; Ercegović, M.; Dimitrijević, J.; Vuković, N.S.; Fiol, N. Efficient Adsorption of Lead on Hydro-Pyrochar Synthesized by Two-Step Conversion of Corn Cob in Magnesium Chloride Medium. Toxics 2025, 13, 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060459
Simić M, Petrović J, Koprivica M, Ercegović M, Dimitrijević J, Vuković NS, Fiol N. Efficient Adsorption of Lead on Hydro-Pyrochar Synthesized by Two-Step Conversion of Corn Cob in Magnesium Chloride Medium. Toxics. 2025; 13(6):459. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060459
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimić, Marija, Jelena Petrović, Marija Koprivica, Marija Ercegović, Jelena Dimitrijević, Nikola S. Vuković, and Núria Fiol. 2025. "Efficient Adsorption of Lead on Hydro-Pyrochar Synthesized by Two-Step Conversion of Corn Cob in Magnesium Chloride Medium" Toxics 13, no. 6: 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060459
APA StyleSimić, M., Petrović, J., Koprivica, M., Ercegović, M., Dimitrijević, J., Vuković, N. S., & Fiol, N. (2025). Efficient Adsorption of Lead on Hydro-Pyrochar Synthesized by Two-Step Conversion of Corn Cob in Magnesium Chloride Medium. Toxics, 13(6), 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060459










