Long-Term Exposure to 6-PPD Quinone Inhibits Glutamate Synthesis and Glutamate Receptor Function Associated with Its Toxicity Induction in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Maintenance
2.2. 6-PPDQ Exposure
2.3. Glutamate Content
2.4. Gene Expression
2.5. RNA Interference (RNAi)
2.6. Endpoints
2.7. Exogenous Glutamate Treatment
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. 6-PPDQ Decreased Glutamate Content
3.2. 6-PPDQ Decreased Expression of Genes Governing Glutamate Synthesis
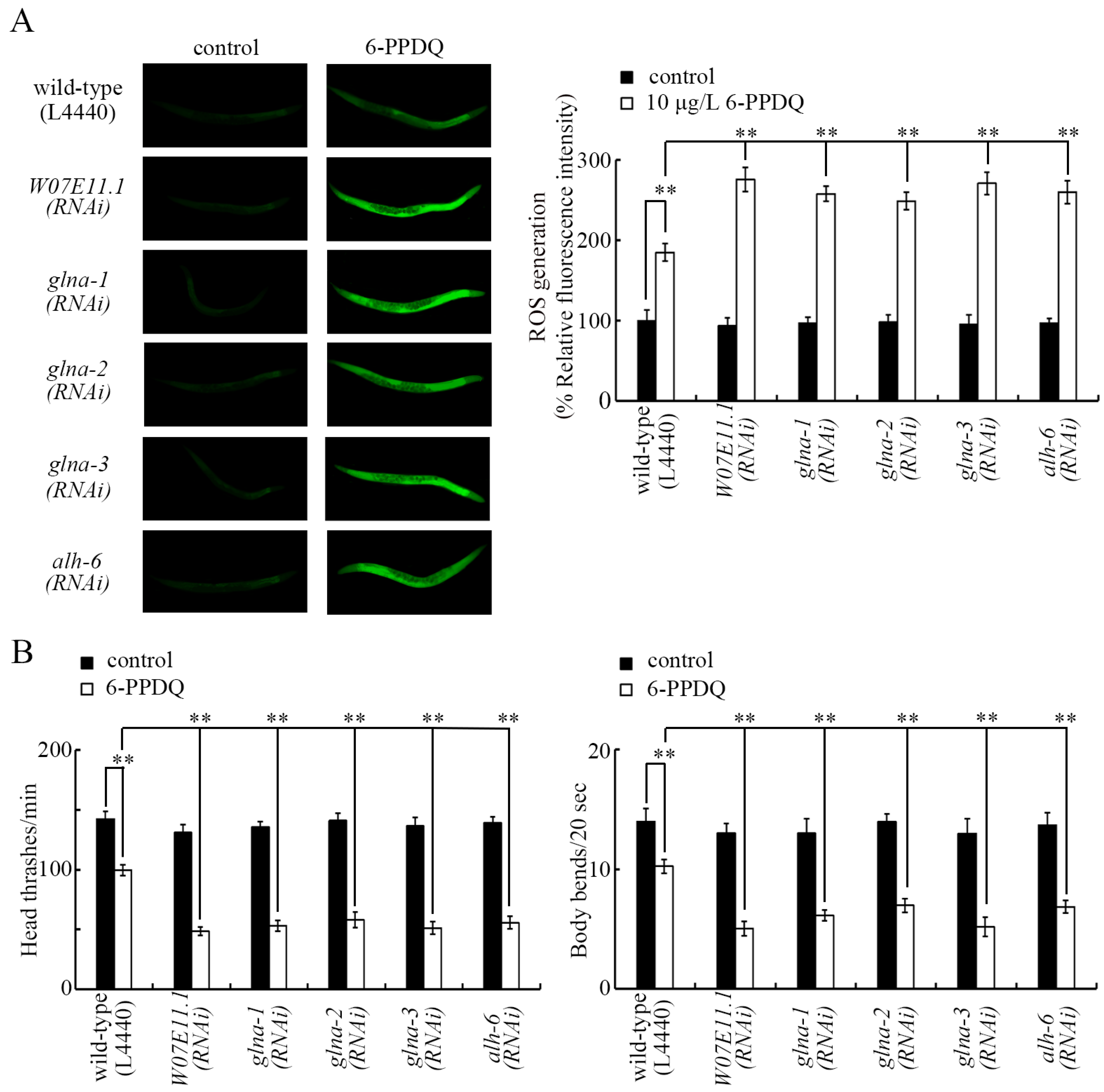
3.3. RNAI of W07E11.1, glna-1, glna-2, glna-3, and alh-6 Induced Susceptibility to 6-PPDQ Toxicity
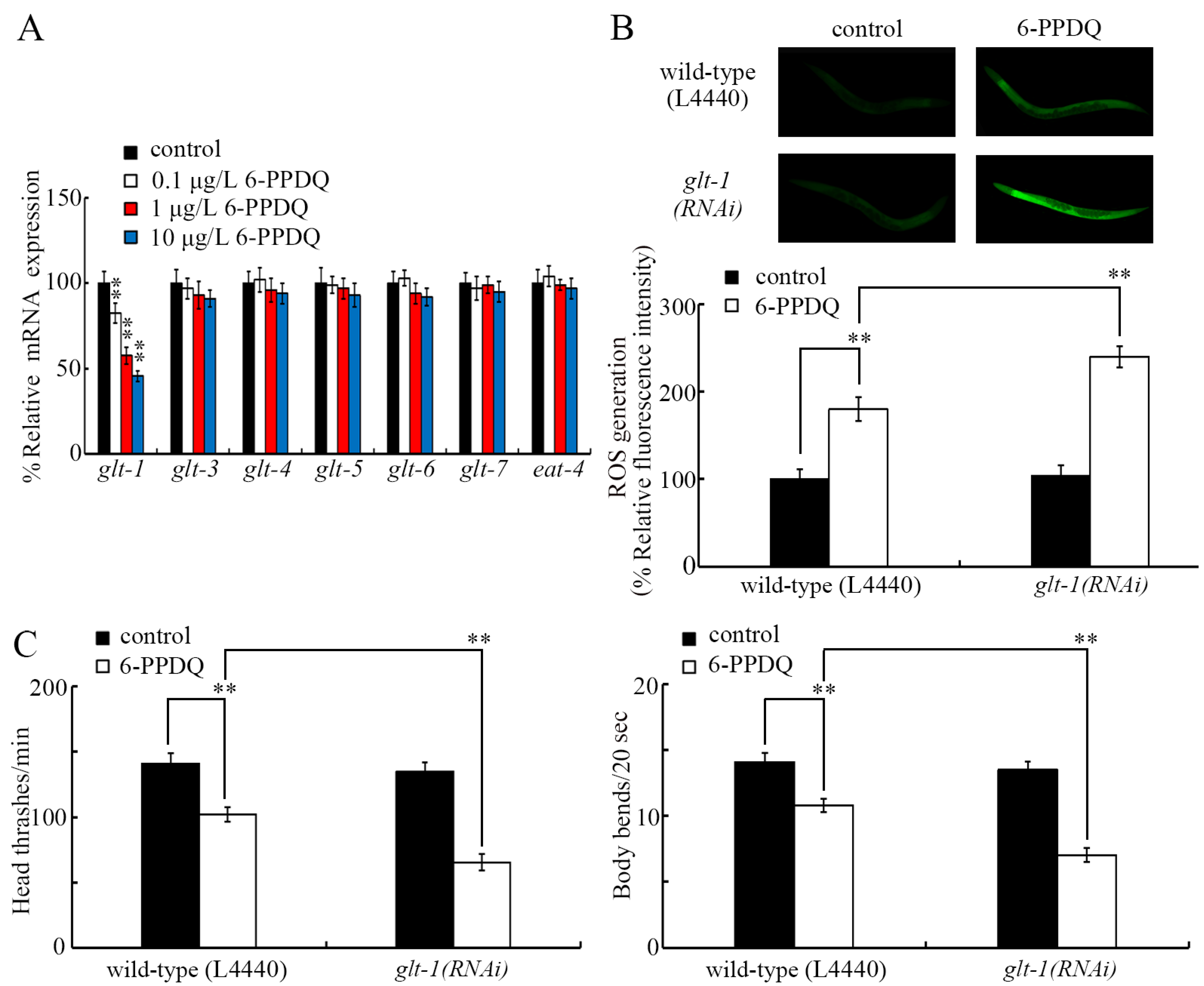
3.4. 6-PPDQ Decreased Expression of Glutamate Transporter Gene glt-1
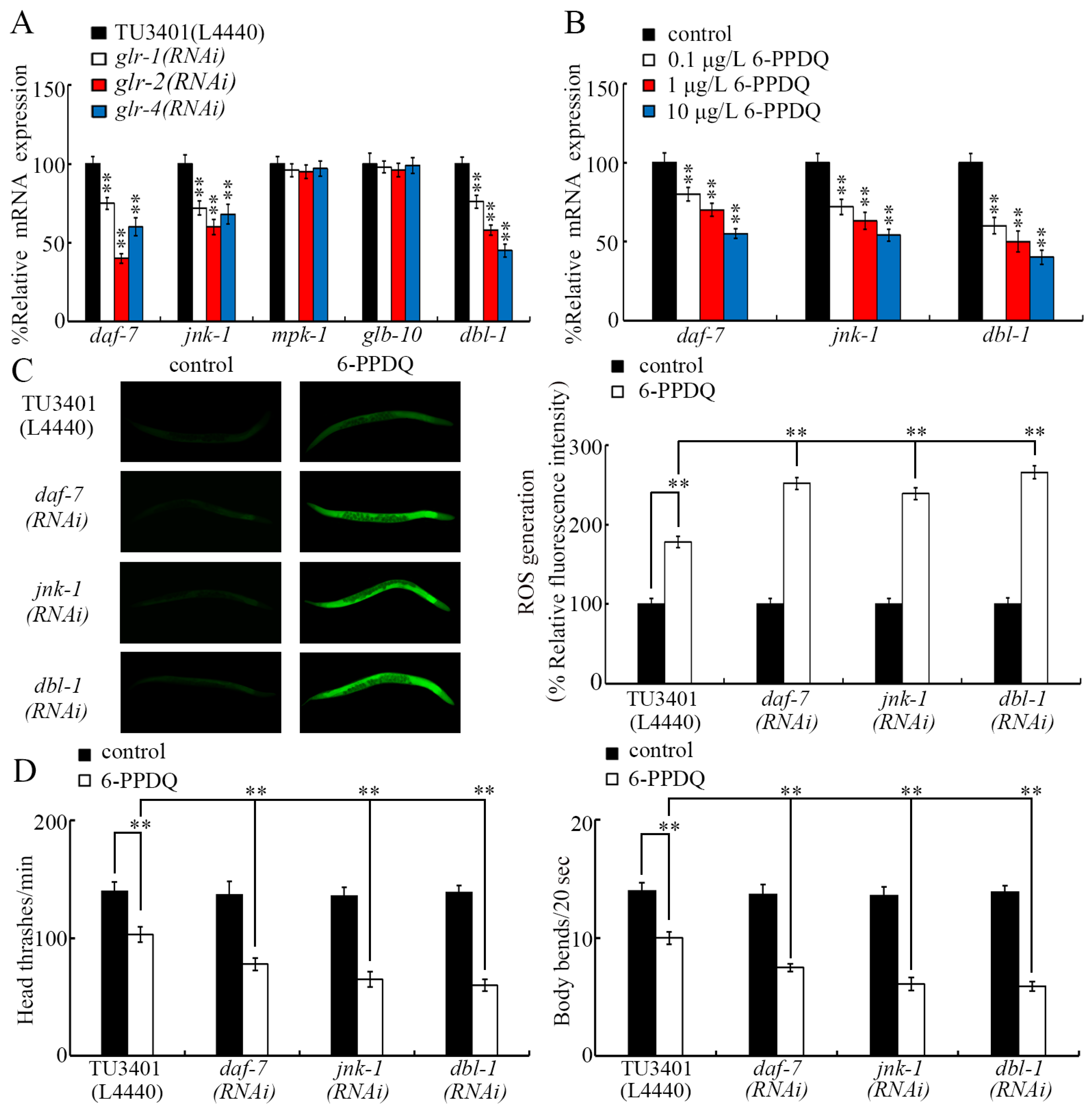
3.5. 6-PPDQ Decreased Expression of the Glutamate Receptor Genes glr-1, glr-2, and glr-4
3.6. GLR-1, GLR-2, and GLR-4 Regulated 6-PPDQ Toxicity by Affecting DAF-7, JNK-1, and DBL-1
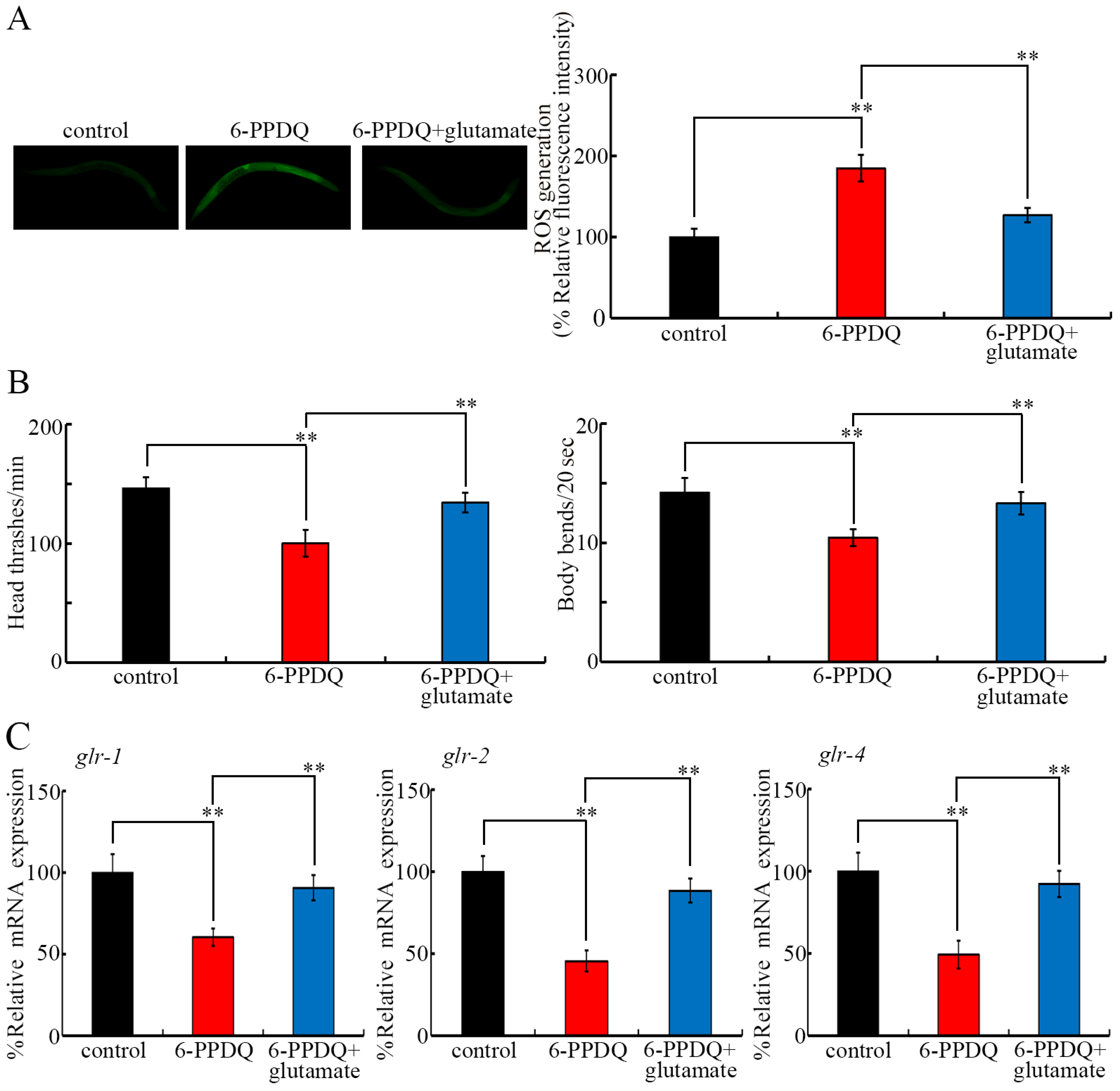
3.7. Pharmacological Effect of Glutamate Treatment on 6-PPDQ Toxicity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huntink, N.M.; Datta, R.N.; Noordermeer, J.W.M. Addressing durability of rubber compounds. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2004, 77, 476–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Wang, D.-Y. Tire-rubber related pollutant 6-PPD quinone: A review of its transformation, environmental distribution, bioavailability, and toxicity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; He, T.; Yang, X.; Gan, Y.; Qing, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y. Analysis, environmental occurrence, fate and potential toxicity of tire wear compounds 6PPD and 6PPD-quinone. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Liang, G.-Y.; Wang, D.-Y. Potential human health risk of the emerging environmental contaminant 6-PPD quinone. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 175057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Zhao, H.; Peter, K.T.; Gonzalez, M.; Wetzel, J.; Wu, C.; Hu, X.; Prat, J.; Mudrock, E.; Hettinger, R.; et al. A ubiquitous tire rubber–derived chemical induces acute mortality in coho salmon. Science 2021, 371, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Li, J.; Wan, X.; Ge, Y.; Liang, G.; Zhou, Y. P-phenylenediamine antioxidants and their quinone derivatives: A review of their environmental occurrence, accessibility, potential toxicity, and human exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, S.S.U.H.; Xu, Q.; Tayyab, M.; Pastorino, P.; Barcelò, D.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Khan, Z.H.; Li, G. Navigating the environmental dynamics, toxicity to aquatic organisms and human associated risks of an emerging tire wear contaminant 6PPD-quinone. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 356, 124313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Huang, J.W.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhang, J.N.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhao, J.L.; Ying, G.G. In vitro metabolism of the emerging contaminant 6PPD-quinone in human and rat liver microsomes: Kinetics, pathways, and mechanism. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 345, 123514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.-M.; Chao, J.; Gu, A.-H.; Wang, D.-Y. Evaluation of 6-PPD quinone toxicity on lung of male BALB/c mice by quantitative proteomics. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Kang, Q.; Liu, W.; Chen, D.; Wang, L.; Li, S. Chronic exposure to tire rubber-derived contaminant 6PPD-quinone impairs sperm quality and induces the damage of reproductive capacity in male mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 470, 134165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Wang, X.; Cao, G.; Wang, F.; Ru, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yan, J.; Xu, J.; et al. 6PPD-quinone exposure induces neuronal mitochondrial dysfunction to exacerbate Lewy neurites formation induced by alpha-synuclein preformed fibrils seeding. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, C.; Ma, L.; Gao, T.; Wang, Y. Environmental profiles, hazard identification, and toxicological hallmarks of emerging tire rubber-related contaminants 6PPD and 6PPD-quinone. Environ. Int. 2024, 187, 108677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Ji, X.; Peng, B.; Fang, M. In vitro and in vivo biotransformation profiling of 6PPD-quinone toward their detection in human urine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 9113–9124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.-Y. Exposure Toxicology in Caenorhabditis elegans; Springer Nature Pte Ltd.: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zeng, L.; Wang, C.; Shi, C.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, B.; Chen, C.; et al. Review of the toxicity and potential molecular mechanisms of parental or successive exposure to environmental pollutants in the model organism Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Wang, D.-Y. Effect of disruption in intestinal barrier function during transgenerational process on nanoplastic toxicity induction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Sci. Nano 2025, 12, 2741–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.-T.; Li, Y.-H.; Wang, D.-Y. Polylactic acid microplastics cause transgenerational reproductive toxicity associated with activation of insulin and hedgehog ligands in C. elegans. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 942, 173746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-W.; Shao, Y.-T.; Hua, X.; Wang, Y.-X.; Wang, D.-Y. Nanoplastic at environmentally relevant concentrations induces toxicity across multiple generations associated with inhibition in germline G protein-coupled receptor CED-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Chemosphere 2024, 364, 143011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.-X.; Ruan, Q.-L.; Wang, D.-Y. Comparison of transgenerational toxicity on locomotion behavior and development of D-type motor neurons between pristine and amino modified nanoplastics at environmentally relevant doses in C. elegans. Toxics 2024, 12, 555. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.-Y.; Wang, Y.-X.; Bian, Q.; Wang, D.-Y. Transgenerational response of germline nuclear hormone receptor genes to nanoplastics at predicted environmental doses in Caenorhabditis elegans. Toxics 2024, 12, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Wang, D.-Y. Transgenerational intestinal toxicity of 6-PPD quinone in causing ROS production, enhancement in intestinal permeability and suppression in innate immunity in C. elegans. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.-X.; Ruan, Q.-L.; Wang, D.-Y. Paeoniflorin alleviates toxicity and accumulation of 6-PPD quinone by activating ACS-22 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 286, 117226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, X.; Wang, D.-Y. 6-PPD quinone at environmentally relevant concentrations induced damage on longevity in C. elegans: Mechanistic insight from inhibition in mitochondrial UPR response. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-W.; Shen, S.-H.; Wang, D.-Y. 6-PPD quinone at environmentally relevant concentrations induces immunosenescenece by causing immunosuppression during the aging process. Chemosphere 2024, 368, 143719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, X.; Liang, G.-Y.; Chao, J.; Wang, D.-Y. Exposure to 6-PPD quinone causes damage on mitochondrial complex I/II associated with lifespan reduction in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 472, 134598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Wang, D.-Y. 6-PPD quinone causes alteration in ubiquinone-mediated complex III associated with toxicity on mitochondrial function and longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, J.L.; Ristow, M. Lipid and carbohydrate metabolism in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 2017, 207, 413–446. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Wang, D.-Y. Exposure to 6-PPD quinone enhances glycogen accumulation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 359, 124600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-J.; Li, Y.-H.; Wang, D.-Y. Exposure to 6-PPD quinone disrupts glucose metabolism associated with lifespan reduction by affecting insulin and AMPK signals in Caenorhabditis elegans. Chemosphere 2024, 363, 142975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Wu, J.-W.; Wang, D.-Y. 6-PPD quinone causes lipid accumulation across multiple generations differentially affected by metabolic sensors and components of COMPASS complex in Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 366, 125539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-J.; Li, Y.-H.; Wang, D.-Y. Transgenerational response of glucose metabolism in Caenorhabditis elegans exposed to 6-PPD quinone. Chemosphere 2024, 367, 143653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monné, M.; Vozza, A.; Lasorsa, F.M.; Porcelli, V.; Palmieri, F. Mitochondrial carriers for aspartate, glutamate and other amino acids: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Zhuo, M. Glutamate acts as a key neurotransmitter for itch in the mammalian spinal cord. Mol. Pain 2023, 19, 17448069231152101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Jiang, J.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Tan, Y.; Song, S.; Shu, Q.; Huang, J. Glutamate alleviates cadmium toxicity in rice via suppressing cadmium uptake and translocation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Zhao, G. The effect of glna loss on the physiological and pathological phenotype of Parkinson‘s disease C. elegans. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2024, 38, e25129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Curran, S.P. Adaptive capacity to bacterial diet modulates aging in C. elegans. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, I.; Straud, S.; Driscoll, M. Caenorhabditis elegans glutamate transporters influence synaptic function and behavior at sites distant from the synapse. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 34412–34419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silveira, T.L.; Machado, M.L.; Arantes, L.P.; Zamberlan, D.C.; Cordeiro, L.M.; Obetine, F.B.B.; da Silva, A.F.; Tassi, C.L.; Soares, F.A.A. Guanosine prevents against glutamatergic excitotoxicity in C. elegans. Neuroscience 2019, 414, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronstone, G.J.; Harton, M.; Muldowney, M.; Reigle, J.; Funk, A.J.; O‘Donovan, S.M.; McCullumsmith, R.E.; Bauer, D.E. The C. elegans glutamate transporters GLT-4 and GLT-5 regulate protein expression, behavior, and lifespan. Neurochem. Int. 2025, 186, 105966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, S.; Wu, Q.; Tang, M.; Wang, D. Transmissions of serotonin, dopamine, and glutamate are required for the formation of neurotoxicity from Al2O3-NPs in nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Nanotoxicology 2013, 7, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 1974, 77, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.-Y. Procatechuic acid and protocatechuic aldehyde increase survival of Caenorhabditis elegans after fungal infection and inhibit fungal virulence. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1396733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-W.; Shao, Y.-T.; Hua, X.; Wang, D.-Y. Activated hedgehog and insulin ligands by decreased transcriptional factor DAF-16 mediate transgenerational nanoplastic toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.-Y. Nanoplastic at environmentally relevant concentrations activates germline mir-240-rab-5 signaling cascade to affect secreted ligands associated with transgenerational toxicity induction in C. elegans. Environ. Sci. Nano 2024, 11, 3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Wang, D.-Y. Transgenerational response of germline histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases to nanoplastics at predicted environmental doses in Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 952, 175903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.-S.; He, J.; Ye, Z.-J.; Xia, J.-Y.; Chen, M.; Chen, S.-Y.; Liu, K.-H.; Xing, P.-C.; Yang, J.-F.; Qian, Y.-J.; et al. Aged biodegradable nanoplastics enhance body accumulation associated with worse neuronal damage in Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 4352–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C.; Canfield, J.; Copes, N.; Brito, A.; Rehan, M.; Lipps, D.; Brunquell, J.; Westerheide, S.D.; Bradshaw, P.C. Mechanisms of amino acid-mediated lifespan extension in Caenorhabditis elegans. BMC Genet. 2015, 16, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-Y. Toxicology at Environmentally Relevant Concentrations in Caenorhabditis elegans; Springer Nature Pte Ltd.: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- An, L.; Fu, X.; Chen, J.; Ma, J. Application of Caenorhabditis elegans in lipid metabolism research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Hua, X.; Wang, D.-Y. Exposure to 6-PPD quinone enhances lipid accumulation through activating metabolic sensors of SBP-1 and MDT-15 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 121937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Wang, D.-Y. Disruption of dopamine metabolism by exposure to 6-PPD quinone in Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 337, 122649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.A.; Curran, S.P. Incomplete proline catabolism drives premature sperm aging. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, O.; Stuhr, N.L.; Yen, C.A.; Crimmins, E.M.; Arpawong, T.E.; Curran, S.P. Genetic variation in ALDH4A1 is associated with muscle health over the lifespan and across species. Elife 2022, 11, e74308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Qu, M.; Wang, D. Response of tyramine and glutamate related signals to nanoplastic exposure in Caenorhabditis elegans. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 217, 112239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Hua, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Han, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Xiang, M. Glutamatergic transmission associated with locomotion-related neurotoxicity to lindane over generations in Caenorhabditis elegans. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Lim, C.S.; Johnsen, R.; Albert, P.S.; Pilgrim, D.; Riddle, D.L. Control of C. elegans larval development by neuronal expression of a TGF-beta homolog. Science 1996, 274, 1389–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Yandell, M.D.; Roy, P.J.; Krishna, S.; Savage-Dunn, C.; Ross, R.M.; Padgett, R.W.; Wood, W.B. A BMP homolog acts as a dose-dependent regulator of body size and male tail patterning in Caenorhabditis elegans. Development 1999, 126, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, M.; Hisamoto, N.; Iino, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Ninomiya-Tsuji, J.; Matsumoto, K. A Caenorhabditis elegans JNK signal transduction pathway regulates coordinated movement via type-D GABAergic motor neurons. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 3604–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Liang, G.; Wang, D. Neurotoxicity and accumulation of CPPD quinone at environmentally relevant concentrations in Caenorhabditis elegans. Chemosphere 2024, 361, 142499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, D. Long-Term Exposure to 6-PPD Quinone Inhibits Glutamate Synthesis and Glutamate Receptor Function Associated with Its Toxicity Induction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Toxics 2025, 13, 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060434
Wang W, Li Y, Wang D. Long-Term Exposure to 6-PPD Quinone Inhibits Glutamate Synthesis and Glutamate Receptor Function Associated with Its Toxicity Induction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Toxics. 2025; 13(6):434. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060434
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wei, Yunhui Li, and Dayong Wang. 2025. "Long-Term Exposure to 6-PPD Quinone Inhibits Glutamate Synthesis and Glutamate Receptor Function Associated with Its Toxicity Induction in Caenorhabditis elegans" Toxics 13, no. 6: 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060434
APA StyleWang, W., Li, Y., & Wang, D. (2025). Long-Term Exposure to 6-PPD Quinone Inhibits Glutamate Synthesis and Glutamate Receptor Function Associated with Its Toxicity Induction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Toxics, 13(6), 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060434







